
Governments face multiple challenges which are further getting highlighted by the ongoing global crisis. They have to manage the countries’ financial performances, reducing fiscal deficits. Every economy – whether emerging or mature – face challenges in bridging economic and social divides and ensuring equal access to infrastructure across the population. Most governments have challenges associated with the changes in demographics – whether because of rapid urbanisation, a fast ageing population or those associated with immigration policies.
Government agencies have the task of ensuring reliable public service, keeping their citizens safe, and striving for cost optimisation. In this constantly evolving world, agencies need to rely on technology to manage ever-growing citizen expectations and rising costs. Several government agencies have started their digital transformation (DX) journey replacing their legacy systems to transform the way they deliver services to their citizens.
Drivers of Transformation in Public Sector
Creating cross-agency synergies
Government agencies have access to enormous quantities of citizen data. But much of that data resides with individual agencies, often with no real synergies between them. For improved cost management and better utilisation of the data, it is imperative for governments to think of cross-agency collaboration systems and tools which give the larger entity a better visibility of their resources, contracts and citizen information. This involves, developing procedures, frameworks and working beyond their limited boundaries, leveraging technology to share information, applications, platform and processes. While this has been in discussion for nearly a decade now, most government agencies still work in departmental siloes and find it hard to work as a networked entity. The Ecosystm AI study finds that nearly three-quarters of public sector organisations find data access a challenge for their AI projects.
Improving citizen engagement
Increasingly, citizens are becoming tech-savvy and are expecting digital services from their government agencies. Not only that, but they are also ready to have conversations with agencies and provide feedback on matters of convenience and public safety. With the popularity of social media, citizens now have the capability to take their feedback to a wider open forum, if the agency fails to engage with them. Public sector organisations have to streamline and automate the services they provide, including payments, and provide real-time services that require collaborative feedback and increased participation from citizens. Smart governments are successfully able to leverage their citizen engagement to use open data platforms – Data.gov and data.gov.uk, are allowing communities to target and solve problems for which governments do not have the bandwidth. With citizen centricity and open government policies, there is also an ever-increasing need for greater accountability and transparency.
Managing project performance and costs
Most government projects involve several stakeholders and are complex in terms of the data, infrastructure and investments required. To take better decisions in terms of project complexity, risks and investments, public sector agencies need to have a structured project management framework, using an optimum mix of physical. technical, financial and human resources. In an environment where citizens expect more accountability and transparency, and where projects are often funded by citizens’ taxes, running these projects become even more complicated. Government agencies struggle to get funding, optimise costs (especially in projects that run over multiple years and political environments), and demonstrate some form of ROI. There is also an overwhelming requirement to detect and prevent frauds.
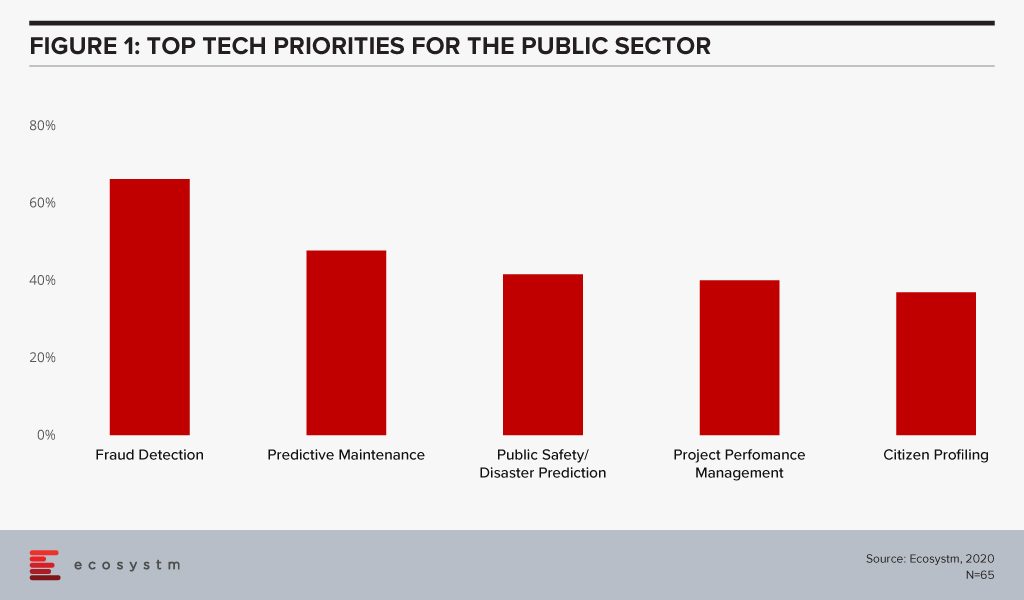
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for public sector, that are focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). It is very clear that the key areas of focus are cost optimisation (including fraud detection and project performance management) and having access to better data to provide improved citizen services (such as public safety and predicting citizen behaviour).
Technology as an Enabler of Public Sector transformation
Several emerging technologies are being used by government agencies as they look towards DX in the public sector.
The Push to Adopt Cloud
To prepare for the data surge that governments are facing and will continue to face, there is a push towards replacing legacy systems and obsolete infrastructure. The adoption of cloud services for data processing and storage is helping governments to provide efficient services, improve productivity, and reduce maintenance costs. Moreover, cloud infrastructure and services help governments provide open citizen services. The Government of India has built MeghRaj, India’s national cloud initiative to host government services and applications including local government services to promote eGovernance and better citizen services. The New Zealand Government has sent a clear directive to public sector organisations that public cloud services are preferred over traditional IT systems, in order to enhance customer experiences, streamline operations and create new delivery models. The objective is to use public cloud services for Blockchain, IoT, AI and data analytics.
Transparency through Communication & Collaboration technologies
Since the 1990s, the concept of eGovernment has required agencies to not only digitise citizen services but also work on how they communicate better with their citizens. While earlier modes of communication with citizens were restricted to print, radio or television, digital government initiatives have introduced more active communication using mobile applications, discussion forums, online feedback forms, eLearning, social media, and so on. Australia’s Just Ask Once allows citizens to access information on various government services at one place for better accessibility. More and more government agencies are implementing an omnichannel communication platform, which allows them to disseminate information across channels such as web, mobile apps, social media and so on. In the blog The Use of Technology in Singapore’s COVID-19 Response, Ecosystm analysts spoke about the daily updates shared by the Government through mobile phones. Demonstrating cross-agency collaboration, the information disseminated comes from multiple government agencies – the same channel is also used to drip-feed hygiene guidelines and the evolving government policies on travel, trade and so on.
AI & Automation for Process Efficiency and Actionable Intelligence
Governments are focusing on leveraging centralised resources and making processes smarter through the adoption of AI platforms. Initiatives such as the Singapore Government’s concept of Single Sources of Truth (SSOT), where all decision-making agencies have access to the same data, is the first step in efficient AI adoption. Singapore’s government agencies also have three data aggregators – Trusted Centers (TCs). This enables initiatives such as Vault-Gov.SG which allows government officials to browse a metadata catalogue and download sample data to run exploratory analytics. To push the adoption of AI, several governments are focusing on roadmaps and strategies such as Singapore’s National AI Strategies to transform the country by 2030, and the Government of Australia’s AI Roadmap and framework to help in the field of industry, science, energy, and education.
The first step of AI adoption is often through automation tools, such as virtual assistants and chatbots. The US Citizen and Immigration Service (USCIS) introduced an AI powered chatbot Emma to better support citizens through self-service options and reduce the workload of their customer service agents. The department of Human Services in Australia rolled out various chatbots named Roxy, Sam, Oliver, Charles and the most latest in progress PIPA (Platform Independent Personal Assistant) to provide information on various services and assist on queries.
Real-time data access with IoT
Governments have the responsibility of enforcing law and order, infrastructure management and disaster management. Real-time information data access is key to these initiatives. IoT sensors are being used in various government applications in object detection, and risk assessment in cities as well as remote areas. For example, IoT-enabled traffic monitoring and surveillance systems are embedded to provide real-time updates and continuous monitoring that can be used to solve issues, as well as provide real-time information to citizens. In a futuristic step, the US Department of Transportation (USDOT) is working with auto manufacturers on embedding vehicle to vehicle communication capabilities in all vehicles to avoid collision with emergency braking and vehicle speed monitoring. In an effort to promoting smart city initiatives and for infrastructure maintenance, New Zealand has installed smart cameras with automated processing capabilities, and IoT based street lighting system. IoT has tremendously benefited the supply chain and logistics sector. The US Army’s Logistics Support Activity (LOGSA) is using IoT for one of the Government’s biggest logistics systems. and military hardware with on-board sensors to analyse data directly from the vehicles for better asset maintenance. Again like in AI, there is a need for a clear roadmap for government adoption of emerging technologies, especially considering the safety and ethics angle. The Government of UK has introduced IoTUK, a program to help the public sector and private enterprises to come together and develop IoT technologies considering aspects such as privacy, security, and reliability.
Blockchain enabled Traceability & Transparency
Moving paper-based systems to digitised systems makes processes efficient to a degree. However, more is required for full traceability and transparency. Managing the data flow and safeguarding the information is vital for government organisations, especially as there is an increase in cross-agency collaboration. Government agencies and departments across the globe are increasingly collaborating using Blockchain technology, while at the same time maintaining the security of the data. For instance, in Georgia, the government department of Land, Property and Housing Management is using Blockchain to maintain land and property records. The blockchain-based land registry allows speedier approvals with no involvement of paperwork or multi-party signatures on physical documents. This is enhancing service quality while offering better security measures as the data is digitally stored in the National Agency of Public Registry’s land title database. Estonia is using Blockchain to protect their digital services such as electronic health records, legal records, police records, banking information, covering data and devices from attacks, misuse, and corruption.
Technology-led digital transformation has become the norm for public sector organisations across both emerging and mature economies. However, agencies need to create clear roadmaps and frameworks, including RoI considerations (which may not only be financial but should include citizen experience) and avoid ad-hoc implementations. The key consideration that government agencies should keep in mind is citizen security and ethics when adopting emerging technologies.







