India’s digital economy is on a meteoric rise, expected to reach USD 1 trillion by 2025. This surge in digital activity is fuelling the rapid expansion of its data centre market, positioning the country as a global player. With a projected market value of USD 4.5 billion by 2025, India’s data centre industry is set to surpass traditional regional hubs like Malaysia, Hong Kong, and Singapore.
This growth is driven by factors such as the proliferation of smartphones, internet connectivity, and digital services, generating massive amounts of data that need storage and processing. Government initiatives like Digital India and the National e-Governance Plan have promoted digitalisation, while favourable market conditions, including cost-effective infrastructure, skilled talent, and a large domestic market, make India an attractive destination for data centre investments.
As companies continue to invest, India is solidifying its role as a critical hub for Asia’s digital revolution, driving economic development and creating new opportunities for innovation and job creation.
What is Fuelling India’s Data Centre Growth?
India’s data centre industry is experiencing rapid growth in 2024, driven by a combination of strategic advantages and increasing demand. The country’s abundance of land and skilled workforce are key factors contributing to this boom.
- Digitisation push. The digital revolution is fueling the need for more sophisticated data centre infrastructure. The rise of social media, online gaming, and streaming apps has created a surge in demand for faster networks, better data storage options, and increased data centre services.
- Internet and mobile penetration. With 1.1 billion mobile phone subscribers, Indians use an average of 8.3 GB of data per month. As more people come online, businesses need to expand their data infrastructure to handle increased traffic, enhance service delivery, and support a growing digital economy.
- Increasing tech adoption. India’s AI market is projected to reach around USD 17 billion by 2027. As businesses integrate AI, IoT, cloud, and other technologies, data centres will become instrumental in supporting the vast computational and storage requirements.
- Government & regulatory measures. Apart from India being one of the world’s largest data consumption economies, government initiatives have also accelerated the ‘data based’ environment in the country. Additionally, states like Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu have implemented favourable real estate policies that reduce the costs of setting up data centres.
A Growing Network of Hubs
India’s data centre landscape is rapidly evolving, with major cities and emerging hotspots vying for a piece of the pie.
Mumbai-Navi Mumbai remains the undisputed leader, boasting a combined 39 data centres. Its strategic location with excellent submarine cable connectivity to Europe and Southeast Asia makes it a prime destination for global and domestic players.
Bangalore, India’s IT capital, is not far behind with 29 data centres. The city’s thriving tech ecosystem and skilled talent pool make it an attractive option for businesses looking to set up data centres.
Chennai, located on the east coast, has emerged as a crucial hub with 17 data centres. Its proximity to Southeast Asia and growing digital economy make it a strategic location. The Delhi-NCR region also plays a significant role, with 27 data centres serving the capital and surrounding areas.
Smaller cities like Pune, Jaipur, and Patna are rapidly emerging as data centre hotspots. As businesses seek to serve a growing but distributed user base across India, these cities offer more cost-effective options. Additionally, the rise of edge data centres in these smaller cities is further decentralising the data centre landscape.

A Competitive Market
India ranks 13th globally in the number of operational data centres, with 138 facilities in operation and an additional 45 expected to be completed by the end of 2025. Key initiatives include:
- AWS. AWS is investing USD 12.7 billion to establish four new data centres over the next two years.
- Meta. Meta is set to build a small data centre, potentially focused on cache with a 10-20 MW capacity.
- AdaniConnex. In partnership with EdgeConneX, AdaniConnex aims to develop a 1 GW network of hyperscale data centres over the next decade, all powered by 100% renewable energy.
- Google. Google is set to build an 80-storey data centre by 2025 and is in advanced talks to acquire a 22.5-acre land parcel for its first captive data centre.
- NTT. NTT is investing USD 241 million in a data campus, which will feature three data centres.
Data Centres: Driving Digital India’s Success
The Digital India initiative has transformed government services through improved online infrastructure and increased connectivity. Data centres play a pivotal role in supporting this vision by managing, storing, and processing the vast amounts of data that power essential services like Aadhaar and BharatNet.
Aadhaar, India’s biometric ID system, relies heavily on data centres to store and process biometric information, enabling seamless identification and authentication. BharatNet, the government’s ambitious project to connect rural areas with high-speed internet, also depends on data centres to provide the necessary infrastructure and support.
The impact of data centres on India’s digital transformation is far-reaching. Here are some key areas where data centres have made a significant contribution:
- Enabling Remote Work and Education. Data centres have been instrumental in supporting the surge in remote work and online learning during the pandemic. By providing the necessary infrastructure and connectivity, data centres have ensured business continuity and uninterrupted education.
- Fostering Start-Up Innovation. Data centres provide the essential infrastructure for start-ups to thrive. By offering reliable and scalable computing resources, data centres enable rapid growth and innovation, contributing to the expansion of India’s SaaS market.
- Supporting Government Services. Data centres underpin key government initiatives, including e-governance platforms and digital identity systems. They enhance the accessibility, transparency, and efficiency of government services, bridging the urban-rural divide and improving public service delivery.
Securing India’s Data Centre Future
Data centres are the backbone of India’s digital transformation, fuelling economic growth, government services, innovation, remote work, and technological progress. The Indian government’s ambitious plan to invest over USD 1 billion in hyperscale data centres over the next five years underscores the country’s commitment to building a robust digital infrastructure.
To secure the long-term success of India’s data centre industry, alignment with global standards and strategic investment are crucial. Prioritising reliability, efficiency, and sustainability will attract global providers and position India as a prime destination for digital infrastructure investments. Addressing challenges like legacy upgrades, modernisation, and cybersecurity risks will require collaboration across stakeholders, with government support and technological innovation playing key roles.
A unified effort from central and state governments is vital to enhance competitiveness. By fostering a favourable regulatory environment and offering incentives, the government can accelerate the development of world-class data centres. As India advances digitally, data centres will be instrumental in driving economic growth, improving quality of life, and solidifying India’s status as a global digital leader.

To mitigate the challenges of cloud vendor lock-in, 44% of organisations in Thailand will prioritise data centre consolidation and infrastructure modernisation in 2024.
Explore the key trends impacting Thailand’s technology adoption. Keep an eye out for more data-backed insights on tech markets across Southeast Asia.


ASEAN, poised to become the world’s 4th largest economy by 2030, is experiencing a digital boom. With an estimated 125,000 new internet users joining daily, it is the fastest-growing digital market globally. These users are not just browsing, but are actively engaged in data-intensive activities like gaming, eCommerce, and mobile business. As a result, monthly data usage is projected to soar from 9.2 GB per user in 2020 to 28.9 GB per user by 2025, according to the World Economic Forum. Businesses and governments are further fuelling this transformation by embracing Cloud, AI, and digitisation.
Investments in data centre capacity across Southeast Asia are estimated to grow at a staggering pace to meet this growing demand for data. While large hyperscale facilities are currently handling much of the data needs, edge computing – a distributed model placing data centres closer to users – is fast becoming crucial in supporting tomorrow’s low-latency applications and services.
The Big & the Small: The Evolving Data Centre Landscape
As technology pushes boundaries with applications like augmented reality, telesurgery, and autonomous vehicles, the demand for ultra-low latency response times is skyrocketing. Consider driverless cars, which generate a staggering 5 TB of data per hour and rely heavily on real-time processing for split-second decisions. This is where edge data centres come in. Unlike hyperscale data centres, edge data centres are strategically positioned closer to users and devices, minimising data travel distances and enabling near-instantaneous responses; and are typically smaller with a capacity ranging from 500 KW to 2 MW. In comparison, large data centres have a capacity of more than 80MW.
While edge data centres are gaining traction, cloud-based hyperscalers such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud remain a dominant force in the Southeast Asian data centre landscape. These facilities require substantial capital investment – for instance, it took almost USD 1 billion to build Meta’s 150 MW hyperscale facility in Singapore – but offer immense processing power and scalability. While hyperscalers have the resources to build their own data centres in edge locations or emerging markets, they often opt for colocation facilities to familiarise themselves with local markets, build out operations, and take a “wait and see” approach before committing significant investments in the new market.
The growth of data centres in Southeast Asia – whether edge, cloud, hyperscale, or colocation – can be attributed to a range of factors. The region’s rapidly expanding digital economy and increasing internet penetration are the prime reasons behind the demand for data storage and processing capabilities. Additionally, stringent data sovereignty regulations in many Southeast Asian countries require the presence of local data centres to ensure compliance with data protection laws. Indonesia’s Personal Data Protection Law, for instance, allows personal data to be transferred outside of the country only where certain stringent security measures are fulfilled. Finally, the rising adoption of cloud services is also fuelling the need for onshore data centres to support cloud infrastructure and services.
Notable Regional Data Centre Hubs
Singapore. Singapore imposed a moratorium on new data centre developments between 2019 to 2022 due to concerns over energy consumption and sustainability. However, the city-state has recently relaxed this ban and announced a pilot scheme allowing companies to bid for permission to develop new facilities.
In 2023, the Singapore Economic Development Board (EDB) and the Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) provisionally awarded around 80 MW of new capacity to four data centre operators: Equinix, GDS, Microsoft, and a consortium of AirTrunk and ByteDance (TikTok’s parent company). Singapore boasts a formidable digital infrastructure with 100 data centres, 1,195 cloud service providers, and 22 network fabrics. Its robust network, supported by 24 submarine cables, has made it a global cloud connectivity leader, hosting major players like AWS, Azure, IBM Softlayer, and Google Cloud.
Aware of the high energy consumption of data centres, Singapore has taken a proactive stance towards green data centre practices. A collaborative effort between the IMDA, government agencies, and industries led to the development of a “Green Data Centre Standard“. This framework guides organisations in improving data centre energy efficiency, leveraging the established ISO 50001 standard with customisations for Singapore’s context. The standard defines key performance metrics for tracking progress and includes best practices for design and operation. By prioritising green data centres, Singapore strives to reconcile its digital ambitions with environmental responsibility, solidifying its position as a leading Asian data centre hub.
Malaysia. Initiatives like MyGovCloud and the Digital Economy Blueprint are driving Malaysia’s public sector towards cloud-based solutions, aiming for 80% use of cloud storage. Tenaga Nasional Berhad also established a “green lane” for data centres, solidifying Malaysia’s commitment to environmentally responsible solutions and streamlined operations. Some of the big companies already operating include NTT Data Centers, Bridge Data Centers and Equinix.
The district of Kulai in Johor has emerged as a hotspot for data centre activity, attracting major players like Nvidia and AirTrunk. Conditional approvals have been granted to industry giants like AWS, Microsoft, Google, and Telekom Malaysia to build hyperscale data centres, aimed at making the country a leading hub for cloud services in the region. AWS also announced a new AWS Region in the country that will meet the high demand for cloud services in Malaysia.
Indonesia. With over 200 million internet users, Indonesia boasts one of the world’s largest online populations. This expanding internet economy is leading to a spike in the demand for data centre services. The Indonesian government has also implemented policies, including tax incentives and a national data centre roadmap, to stimulate growth in this sector.
Microsoft, for instance, is set to open its first regional data centre in Thailand and has also announced plans to invest USD 1.7 billion in cloud and AI infrastructure in Indonesia. The government also plans to operate 40 MW of national data centres across West Java, Batam, East Kalimantan, and East Nusa Tenggara by 2026.
Thailand. Remote work and increasing online services have led to a data centre boom, with major industry players racing to meet Thailand’s soaring data demands.
In 2021, Singapore’s ST Telemedia Global Data Centres launched its first 20 MW hyperscale facility in Bangkok. Soon after, AWS announced a USD 5 billion investment plan to bolster its cloud capacity in Thailand and the region over the next 15 years. Heavyweights like TCC Technology Group, CAT Telecom, and True Internet Data Centre are also fortifying their data centre footprints to capitalise on this explosive growth. Microsoft is also set to open its first regional data centre in the country.
Conclusion
Southeast Asia’s booming data centre market presents a goldmine of opportunity for tech investment and innovation. However, navigating this lucrative landscape requires careful consideration of legal hurdles. Data protection regulations, cross-border data transfer restrictions, and local policies all pose challenges for investors. Beyond legal complexities, infrastructure development needs and investment considerations must also be addressed. Despite these challenges, the potential rewards for companies that can navigate them are substantial.

For many organisations migrating to cloud, the opportunity to run workloads from energy-efficient cloud data centres is a significant advantage. However, carbon emissions can vary from one country to another and if left unmonitored, will gradually increase over time as cloud use grows. This issue will become increasingly important as we move into the era of compute-intensive AI and the burden of cloud on natural resources will shift further into the spotlight.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that data centres are responsible for up to 1.5% of global electricity use and 1% of GHG emissions. Cloud providers have recognised this and are committed to change. Between 2025 and 2030, all hyperscalers – AWS, Azure, Google, and Oracle included – expect to power their global cloud operations entirely with renewable sources.
Chasing the Sun
Cloud providers are shifting their sights from simply matching electricity use with renewable power purchase agreements (PPA) to the more ambitious goal of operating 24/7 on carbon-free sources. A defining characteristic of renewables though is intermittency, with production levels fluctuating based on the availability of sunlight and wind. Leading cloud providers are using AI to dynamically distribute compute workloads throughout the day to regions with lower carbon intensity. Workloads that are processed with solar power during daylight can be shifted to nearby regions with abundant wind energy at night.
Addressing Water Scarcity
Many of the largest cloud data centres are situated in sunny locations to take advantage of solar power and proximity to population centres. Unfortunately, this often means that they are also in areas where water is scarce. While liquid-cooled facilities are energy efficient, local communities are concerned on the strain on water sources. Data centre operators are now committing to reduce consumption and restore water supplies. Simple measures, such as expanding humidity (below 20% RH) and temperature tolerances (above 30°C) in server rooms have helped companies like Meta to cut wastage. Similarly, Google has increased their reliance on non-potable sources, such as grey water and sea water.
From Waste to Worth
Data centre operators have identified innovative ways to reuse the excess heat generated by their computing equipment. Some have used it to heat adjacent swimming pools while others have warmed rooms that house vertical farms. Although these initiatives currently have little impact on the environmental impact of cloud, they suggest a future where waste is significantly reduced.
Greening the Grid
The giant facilities that cloud providers use to house their computing infrastructure are also set to change. Building materials and construction account for an astonishing 11% of global carbon emissions. The use of recycled materials in concrete and investing in greener methods of manufacturing steel are approaches the construction industry are attempting to lessen their impact. Smaller data centres have been 3D printed to accelerate construction and use recyclable printing concrete. While this approach may not be suitable for hyperscale facilities, it holds potential for smaller edge locations.
Rethinking Hardware Management
Cloud providers rely on their scale to provide fast, resilient, and cost-effective computing. In many cases, simply replacing malfunctioning or obsolete equipment would achieve these goals better than performing maintenance. However, the relentless growth of e-waste is putting pressure on cloud providers to participate in the circular economy. Microsoft, for example, has launched three Circular Centres to repurpose cloud equipment. During the pilot of their Amsterdam centre, it achieved 83% reuse and 17% recycling of critical parts. The lifecycle of equipment in the cloud is largely hidden but environmentally conscious users will start demanding greater transparency.
Recommendations
Organisations should be aware of their cloud-derived scope 3 emissions and consider broader environmental issues around water use and recycling. Here are the steps that can be taken immediately:
- Monitor GreenOps. Cloud providers are adding GreenOps tools, such as the AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool, to help organisations measure the environmental impact of their cloud operations. Understanding the relationship between cloud use and emissions is the first step towards sustainable cloud operations.
- Adopt Cloud FinOps for Quick ROI. Eliminating wasted cloud resources not only cuts costs but also reduces electricity-related emissions. Tools such as CloudVerse provide visibility into cloud spend, identifies unused instances, and helps to optimise cloud operations.
- Take a Holistic View. Cloud providers are being forced to improve transparency and reduce their environmental impact by their biggest customers. Getting educated on the actions that cloud partners are taking to minimise emissions, water use, and waste to landfill is crucial. In most cases, dedicated cloud providers should reduce waste rather than offset it.
- Enable Remote Workforce. Cloud-enabled security and networking solutions, such as SASE, allow employees to work securely from remote locations and reduce their transportation emissions. With a SASE deployed in the cloud, routine management tasks can be performed by IT remotely rather than at the branch, further reducing transportation emissions.

2024 will be another crucial year for tech leaders – through the continuing economic uncertainties, they will have to embrace transformative technologies and keep an eye on market disruptors such as infrastructure providers and AI startups. Ecosystm analysts outline the key considerations for leaders shaping their organisations’ tech landscape in 2024.
Navigating Market Dynamics

Continuing Economic Uncertainties. Organisations will focus on ongoing projects and consider expanding initiatives in the latter part of the year.
Popularity of Generative AI. This will be the time to go beyond the novelty factor and assess practical business outcomes, allied costs, and change management.
Infrastructure Market Disruption. Keeping an eye out for advancements and disruptions in the market (likely to originate from the semiconductor sector) will define vendor conversations.
Need for New Tech Skills. Generative AI will influence multiple tech roles, including AIOps and IT Architecture. Retaining talent will depend on upskilling and reskilling.
Increased Focus on Governance. Tech vendors are guide tech leaders on how to implement safeguards for data usage, sharing, and cybersecurity.
5 Key Considerations for Tech Leaders
#1 Accelerate and Adapt: Streamline IT with a DevOps Culture
Over the next 12-18 months, advancements in AI, machine learning, automation, and cloud-native technologies will be vital in leveraging scalability and efficiency. Modernisation is imperative to boost responsiveness, efficiency, and competitiveness in today’s dynamic business landscape.
The continued pace of disruption demands that organisations modernise their applications portfolios with agility and purpose. Legacy systems constrained by technical debt drag down velocity, impairing the ability to deliver new innovative offerings and experiences customers have grown to expect.
Prioritising modernisation initiatives that align with key value drivers is critical. Technology leaders should empower development teams to move beyond outdated constraints and swiftly deploy enhanced applications, microservices, and platforms.

#2 Empowering Tomorrow: Spring Clean Your Tech Legacy for New Leaders
Modernising legacy systems is a strategic and inter-generational shift that goes beyond simple technical upgrades. It requires transformation through the process of decomposing and replatforming systems – developed by previous generations – into contemporary services and signifies a fundamental realignment of your business with the evolving digital landscape of the 21st century.
The essence of this modernisation effort is multifaceted. It not only facilitates the integration of advanced technologies but also significantly enhances business agility and drives innovation. It is an approach that prepares your organisation for impending skill gaps, particularly as the older workforce begins to retire over the next decade. Additionally, it provides a valuable opportunity to thoroughly document, reevaluate, and improve business processes. This ensures that operations are not only efficient but also aligned with current market demands, contemporary regulatory standards, and the changing expectations of customers.

#3 Employee Retention: Consider the Strategic Role of Skills Acquisition
The agile, resilient organisation needs to be able to respond at pace to any threat or opportunity it faces. Some of this ability to respond will be related to technology platforms and architectures, but it will be the skills of employees that will dictate the pace of reform. While employee attrition rates will continue to decline in 2024 – but it will be driven by skills acquisition, not location of work.
Organisations who offer ongoing staff training – recognising that their business needs new skills to become a 21st century organisation – are the ones who will see increasing rates of employee retention and happier employees. They will also be the ones who offer better customer experiences, driven by motivated employees who are committed to their personal success, knowing that the organisation values their performance and achievements.

#4 Next-Gen IT Operations: Explore Gen AI for Incident Avoidance and Predictive Analysis
The integration of Generative AI in IT Operations signifies a transformative shift from the automation of basic tasks, to advanced functions like incident avoidance and predictive analysis. Initially automating routine tasks, Generative AI has evolved to proactively avoiding incidents by analysing historical data and current metrics. This shift from proactive to reactive management will be crucial for maintaining uninterrupted business operations and enhancing application reliability.
Predictive analysis provides insight into system performance and user interaction patterns, empowering IT teams to optimise applications pre-emptively, enhancing efficiency and user experience. This also helps organisations meet sustainability goals through accurate capacity planning and resource allocation, also ensuring effective scaling of business applications to meet demands.

#5 Expanding Possibilities: Incorporate AI Startups into Your Portfolio
While many of the AI startups have been around for over five years, this will be the year they come into your consciousness and emerge as legitimate solutions providers to your organisation. And it comes at a difficult time for you!
Most tech leaders are looking to reduce technical debt – looking to consolidate their suppliers and simplify their tech architecture. Considering AI startups will mean a shift back to more rather than fewer tech suppliers; a different sourcing strategy; more focus on integration and ongoing management of the solutions; and a more complex tech architecture.
To meet business requirements will mean that business cases will need to be watertight – often the value will need to be delivered before a contract has been signed.


Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Juniper Networks for USD 40 per share, totaling an equity value of about USD 14 Billion. This strategic move is aimed to enhance HPE’s portfolio by focusing on higher-growth solutions and reinforcing their high-margin networking business. HPE expects to double their networking business, positioning the combined entity as a leader in networking solutions. With the growing demand for secure, unified technology driven by AI and hybrid cloud trends, HPE aims to offer comprehensive, disruptive solutions that connect, protect, and analyse data from edge to cloud.
This would also be the organisation’s largest deal since becoming an independent company in 2015. The acquisition is expected to be completed by late 2024 or early 2025.
Ecosystm analysts Darian Bird and Richard Wilkins provide their insights on the HPE acquisition and its implications for the tech market.

Converging Networking and Security
One of the big drawcards for HPE is Juniper’s Mist AI. The networking vendors have been racing to catch up – both in capabilities and in marketing. The acquisition though will give HPE a leadership position in network visibility and manageability. With GreenLake and soon Mist AI, HPE will have a solid AIOps story across the entire infrastructure.
HPE has been working steadily towards becoming a player in the converged networking-security space. They integrated Silver Peak well to make a name for themselves in SD-WAN and last year acquiring Axis Security gave them the Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), Secure Web Gateway (SWG), and Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) modules in the Secure Service Edge (SSE) stack. Bringing all of this to the market with Juniper’s networking prowess positions HPE as a formidable player, especially as the Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) market gains momentum.
As the market shifts towards converged SASE, there will only be more interest in the SD-WAN and SSE vendors. In just over one year, Cato Networks and Netskope have raised funds, Check Point acquired Perimeter 81, and Versa Networks has made noises about an IPO. The networking and security players are all figuring out how they can deliver a single-vendor SASE.
Although HPE’s strategic initiatives signal a robust market position, potential challenges arise from the overlap between Aruba and Juniper. However, the distinct focus on the edge and data center, respectively, may help alleviate these concerns. The acquisition also marks HPE’s foray into the telecom space, leveraging its earlier acquisition of Athonet and establishing a significant presence among service providers. This expansion enhances HPE’s overall market influence, posing a challenge to the long-standing dominance of Cisco.

The strategic acquisition of Juniper Networks by HPE can make a transformative leap in AIOps and Software-Defined Networking (SDN). There is a potential for this to establish a new benchmark in IT management.
AI in IT Operations Transformation
The integration of Mist’s AI-driven wireless solutions and HPE’s SDN is a paradigm shift in IT operations management and will help organisations transition from a reactive to a predictive and proactive model. Mist’s predictive analytics, coupled with HPE’s SDN capabilities, empower networks to dynamically adjust to user demands and environmental changes, ensuring optimal performance and user experience. Marvis, Mist’s Virtual Network Assistant (VNA), adds conversational troubleshooting capabilities, enhancing HPE’s network solutions. The integration envisions an IT ecosystem where Juniper’s AI augments HPE’s InfoSight, providing deeper insights into network behaviour, preemptive security measures, and more autonomous IT operations.
Transforming Cloud and Edge Computing
The incorporation of Juniper’s AI into HPE’s cloud and edge computing solutions promises a significant improvement in data processing and management. AI-driven load balancing and resource allocation mechanisms will significantly enhance multi-cloud environment efficiency, ensuring robust and seamless cloud services, particularly vital in IoT applications where real-time data processing is critical. This integration not only optimises cloud operations but also has the potential to align with HPE’s commitment to sustainability, showcasing how AI advancements can contribute to energy conservation.
In summary, HPE’s acquisition of Juniper Networks, and specifically the integration of the Mist AI platform, is a pivotal step towards an AI-driven, efficient, and predictive IT infrastructure. This can redefine the standards in AIOps and SDN, creating a future where IT systems are not only reactive but also intuitively adaptive to the evolving demands of the digital landscape.

The Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) industry, known for its cautious stance on technology, is swiftly undergoing a transformational modernisation journey. Areas such as digital customer experiences, automated fraud detection, and real-time risk assessment are all part of a technology-led roadmap. This shift is transforming the cybersecurity stance of BFSI organisations, which have conventionally favoured centralising everything within a data centre behind a firewall.
Ecosystm research finds that 75% of BFSI technology leaders believe that a data breach is inevitable. This requires taking a new cyber approach to detect threats early, reduce the impact of an attack, and avoid lateral movement across the network.
BFSI organisations will boost investments in two main areas over the next year: updating infrastructure and software, and exploring innovative domains like digital workplaces and automation. Cybersecurity investments are crucial in both of these areas.
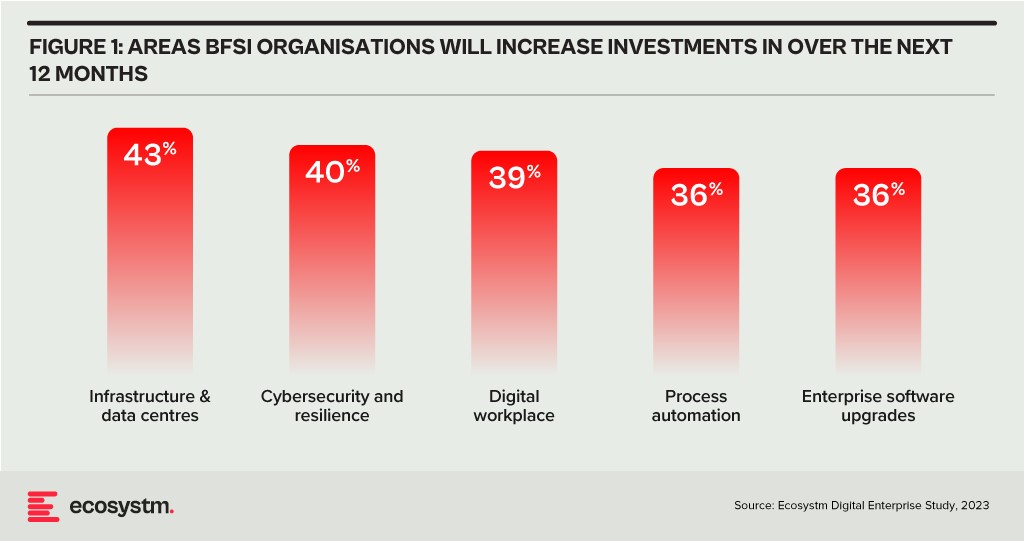
As a regulated industry, breaches come with significant cost implications, underscoring the need to prioritise cybersecurity. BFSI cybersecurity and risk teams need to constantly reassess their strategies for safeguarding data and fulfilling compliance obligations, as they explore ways to facilitate new services for customers, partners, and employees.
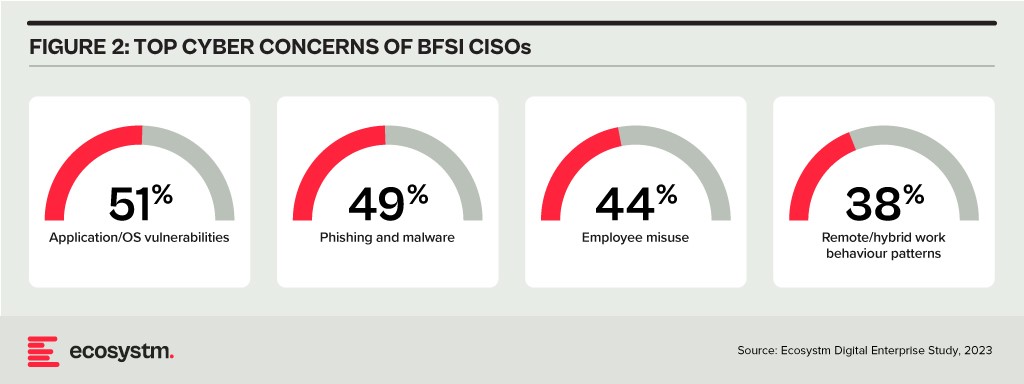
The primary concerns of BFSI CISOs can be categorised into two distinct groups:
- Expanding Technology Use. This includes the proliferation of applications and devices, as well as data access beyond the network perimeter.
- Employee-Related Vulnerabilities. This involves responses to phishing and malware attempts, as well as intentional and unintentional misuse of technology.
Vulnerabilities Arising from Employee Actions
Security vulnerabilities arising from employee actions and unawareness represent a significant and ongoing concern for businesses of all sizes and industries – the risks are just much bigger for BFSI. These vulnerabilities can lead to data breaches, financial losses, damage to reputation, and legal ramifications. A multi-pronged approach is needed that combines technology, training, policies, and a culture of security consciousness.
Training and Culture. BFSI organisations prioritise comprehensive training and awareness programs, educating employees about common threats like phishing and best practices for safeguarding sensitive data. While these programs are often ongoing and adaptable to new threats, they can sometimes become mere compliance checklists, raising questions about their true effectiveness. Conducting simulated phishing attacks and security quizzes to assess employee awareness and identify areas where further training is required, can be effective.
To truly educate employees on risks, it’s essential to move beyond compliance and build a cybersecurity culture throughout the organisation. This can involve setting organisation-wide security KPIs that cascade from the CEO down to every employee, promoting accountability and transparency. Creating an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting security concerns is critical for early threat detection and mitigation.
Policies. Clear security policies and enforcement are essential for ensuring that employees understand their roles within the broader security framework, including responsibilities on strong password use, secure data handling, and prompt incident reporting. Implementing the principle of least privilege, which restricts access based on specific roles, mitigates potential harm from insider threats and inadvertent data exposure. Policies should evolve through routine security audits, including technical assessments and evaluations of employee protocol adherence, which will help organisations with a swifter identification of vulnerabilities and to take the necessary corrective actions.
However, despite the best efforts, breaches do happen – and this is where a well-defined incident response plan, that is regularly tested and updated, is crucial to minimise the damage. This requires every employee to know their roles and responsibilities during a security incident.
Tech Expansion Leading to Cyber Complexity
Cloud. Initially hesitant to transition essential workloads to the cloud, the BFSI industry has experienced a shift in perspective due to the rise of inventive SaaS-based Fintech tools and hybrid cloud solutions, that have created new impetus for change. This new distributed architecture requires a fresh look at cyber measures. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) providers are integrating a range of cloud-delivered safeguards, such as FWaaS, CASB, and ZTNA with SD-WAN to ensure organisations can securely access the cloud without compromising on performance.
Data & AI. Data holds paramount importance in the BFSI industry for informed decision-making, personalised customer experiences, risk assessment, fraud prevention, and regulatory compliance. AI applications are being used to tailor products and services, optimise operational efficiency, and stay competitive in an evolving market. As part of their technology modernisation efforts, 47% of BFSI institutions are refining their data and AI strategies. They also acknowledge the challenges associated – and satisfying risk, regulatory, and compliance requirements is one of the biggest challenges facing BFSI organisations in the AI deployments.
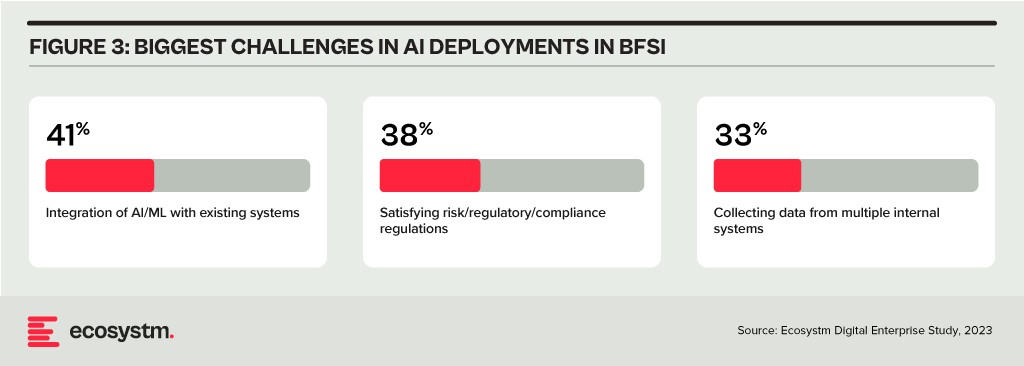
The rush to experiment with Generative AI and foundation models to assist customers and employees is only heightening these concerns. There is an urgent need for policies around the use of these emerging technologies. Initiatives such as the Monetary Authority of Singapore’s Veritas that aim to enable financial institutions to evaluate their AI and data analytics solutions against the principles of fairness, ethics, accountability, and transparency (FEAT) are expected to provide the much-needed guidance to the industry.
Digital Workplace. As with other industries with a high percentage of knowledge workers, BFSI organisations are grappling with granting remote access to staff. Cloud-based collaboration and Fintech tools, BYOD policies, and sensitive data traversing home networks are all creating new challenges for cyber teams. Modern approaches, such as zero trust network access, privilege management, and network segmentation are necessary to ensure workers can seamlessly but securely perform their roles remotely.

Looking Beyond Technology: Evaluating the Adequacy of Compliance-Centric Cyber Strategies
The BFSI industry stands among the most rigorously regulated industries, with scrutiny intensifying following every collapse or notable breach. Cyber and data protection teams shoulder the responsibility of understanding the implications of and adhering to emerging data protection regulations in areas such as GDPR, PCI-DSS, SOC 2, and PSD2. Automating compliance procedures emerges as a compelling solution to streamline processes, mitigate risks, and curtail expenses. Technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA), low-code development, and continuous compliance monitoring are gaining prominence.
The adoption of AI to enhance security is still emerging but will accelerate rapidly. Ecosystm research shows that within the next two years, nearly 70% of BFSI organisations will have invested in SecOps. AI can help Security Operations Centres (SOCs) prioritise alerts and respond to threats faster than could be performed manually. Additionally, the expanding variety of network endpoints, including customer devices, ATMs, and tools used by frontline employees, can embrace AI-enhanced protection without introducing additional onboarding friction.
However, there is a need for BFSI organisations to look beyond compliance checklists to a more holistic cyber approach that can prioritise cyber measures continually based on the risk to the organisations. And this is one of the biggest challenges that BFSI CISOs face. Ecosystm research finds that 72% of cyber and technology leaders in the industry feel that there is limited understanding of cyber risk and governance in their organisations.
In fact, BFSI organisations must look at the interconnectedness of an intelligence-led and risk-based strategy. Thorough risk assessments let organisations prioritise vulnerability mitigation effectively. This targeted approach optimises security initiatives by focusing on high-risk areas, reducing security debt. To adapt to evolving threats, intelligence should inform risk assessment. Intelligence-led strategies empower cybersecurity leaders with real-time threat insights for proactive measures, actively tackling emerging threats and vulnerabilities – and definitely moving beyond compliance-focused strategies.























