2024 will be another crucial year for tech leaders – through the continuing economic uncertainties, they will have to embrace transformative technologies and keep an eye on market disruptors such as infrastructure providers and AI startups. Ecosystm analysts outline the key considerations for leaders shaping their organisations’ tech landscape in 2024.
Navigating Market Dynamics

Continuing Economic Uncertainties. Organisations will focus on ongoing projects and consider expanding initiatives in the latter part of the year.
Popularity of Generative AI. This will be the time to go beyond the novelty factor and assess practical business outcomes, allied costs, and change management.
Infrastructure Market Disruption. Keeping an eye out for advancements and disruptions in the market (likely to originate from the semiconductor sector) will define vendor conversations.
Need for New Tech Skills. Generative AI will influence multiple tech roles, including AIOps and IT Architecture. Retaining talent will depend on upskilling and reskilling.
Increased Focus on Governance. Tech vendors are guide tech leaders on how to implement safeguards for data usage, sharing, and cybersecurity.
5 Key Considerations for Tech Leaders
#1 Accelerate and Adapt: Streamline IT with a DevOps Culture
Over the next 12-18 months, advancements in AI, machine learning, automation, and cloud-native technologies will be vital in leveraging scalability and efficiency. Modernisation is imperative to boost responsiveness, efficiency, and competitiveness in today’s dynamic business landscape.
The continued pace of disruption demands that organisations modernise their applications portfolios with agility and purpose. Legacy systems constrained by technical debt drag down velocity, impairing the ability to deliver new innovative offerings and experiences customers have grown to expect.
Prioritising modernisation initiatives that align with key value drivers is critical. Technology leaders should empower development teams to move beyond outdated constraints and swiftly deploy enhanced applications, microservices, and platforms.

#2 Empowering Tomorrow: Spring Clean Your Tech Legacy for New Leaders
Modernising legacy systems is a strategic and inter-generational shift that goes beyond simple technical upgrades. It requires transformation through the process of decomposing and replatforming systems – developed by previous generations – into contemporary services and signifies a fundamental realignment of your business with the evolving digital landscape of the 21st century.
The essence of this modernisation effort is multifaceted. It not only facilitates the integration of advanced technologies but also significantly enhances business agility and drives innovation. It is an approach that prepares your organisation for impending skill gaps, particularly as the older workforce begins to retire over the next decade. Additionally, it provides a valuable opportunity to thoroughly document, reevaluate, and improve business processes. This ensures that operations are not only efficient but also aligned with current market demands, contemporary regulatory standards, and the changing expectations of customers.

#3 Employee Retention: Consider the Strategic Role of Skills Acquisition
The agile, resilient organisation needs to be able to respond at pace to any threat or opportunity it faces. Some of this ability to respond will be related to technology platforms and architectures, but it will be the skills of employees that will dictate the pace of reform. While employee attrition rates will continue to decline in 2024 – but it will be driven by skills acquisition, not location of work.
Organisations who offer ongoing staff training – recognising that their business needs new skills to become a 21st century organisation – are the ones who will see increasing rates of employee retention and happier employees. They will also be the ones who offer better customer experiences, driven by motivated employees who are committed to their personal success, knowing that the organisation values their performance and achievements.

#4 Next-Gen IT Operations: Explore Gen AI for Incident Avoidance and Predictive Analysis
The integration of Generative AI in IT Operations signifies a transformative shift from the automation of basic tasks, to advanced functions like incident avoidance and predictive analysis. Initially automating routine tasks, Generative AI has evolved to proactively avoiding incidents by analysing historical data and current metrics. This shift from proactive to reactive management will be crucial for maintaining uninterrupted business operations and enhancing application reliability.
Predictive analysis provides insight into system performance and user interaction patterns, empowering IT teams to optimise applications pre-emptively, enhancing efficiency and user experience. This also helps organisations meet sustainability goals through accurate capacity planning and resource allocation, also ensuring effective scaling of business applications to meet demands.

#5 Expanding Possibilities: Incorporate AI Startups into Your Portfolio
While many of the AI startups have been around for over five years, this will be the year they come into your consciousness and emerge as legitimate solutions providers to your organisation. And it comes at a difficult time for you!
Most tech leaders are looking to reduce technical debt – looking to consolidate their suppliers and simplify their tech architecture. Considering AI startups will mean a shift back to more rather than fewer tech suppliers; a different sourcing strategy; more focus on integration and ongoing management of the solutions; and a more complex tech architecture.
To meet business requirements will mean that business cases will need to be watertight – often the value will need to be delivered before a contract has been signed.


In 2024, business and technology leaders will leverage the opportunity presented by the attention being received by Generative AI engines to test and integrate AI comprehensively across the business. Many organisations will prioritise the alignment of their initial Generative AI initiatives with broader AI strategies, establishing distinct short-term and long-term goals for their AI investments.
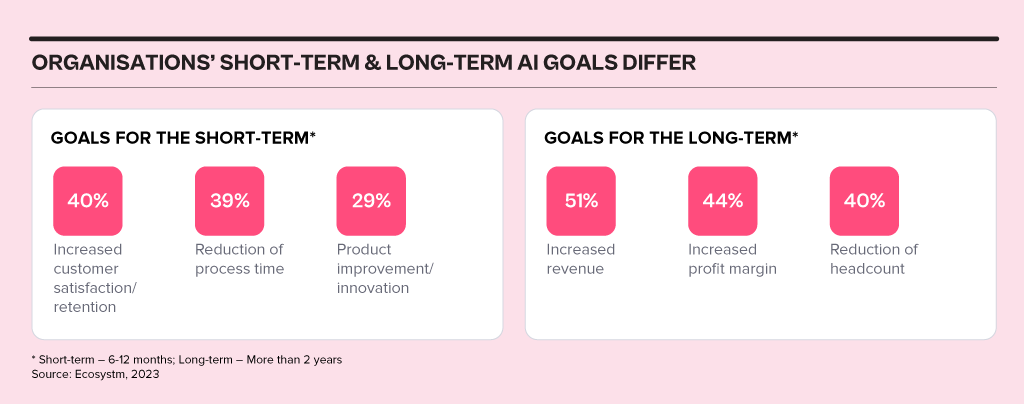
AI adoption will influence business processes, technology skills, and, in turn, reshape the product/service offerings of AI providers.
Ecosystm analysts Achim Granzen, Peter Carr, Richard Wilkins, Tim Sheedy, and Ullrich Loeffler present the top 5 AI trends in 2024.
Click here to download ‘Ecosystm Predicts: Top 5 AI Trends in 2024.
#1 By the End of 2024, Gen AI Will Become a ‘Hygiene Factor’ for Tech Providers
AI has widely been commended as the ‘game changer’ that will create and extend the divide between adopters and laggards and be the deciding factor for success and failure.
Cutting through the hype, strategic adoption of AI is still at a nascent stage and 2024 will be another year where companies identify use cases, experiment with POCs, and commit renewed efforts to get their data assets in order.
The biggest impact of AI will be derived from integrated AI capability in standard packaged software and products – and this will include Generative AI. We will see a plethora of product releases that seamlessly weave Generative AI into everyday tools generating new value through increased efficiency and user-friendliness.
Technology will be the first industry where AI becomes the deciding factor between success and failure; tech providers will be forced to deliver on their AI promises or be left behind.

#2 Gen AI Will Disrupt the Role of IT Architects
Traditionally, IT has relied on three-tier architectures for applications, that faced limitations in scalability and real-time responsiveness. The emergence of microservices, containerisation, and serverless computing has paved the way for event-driven designs, a paradigm shift that decouples components and use events like user actions or data updates as triggers for actions across distributed services. This approach enhances agility, scalability, and flexibility in the system.
The shift towards event-driven designs and advanced architectural patterns presents a compelling challenge for IT Architects, as traditionally their role revolved around designing, planning and overseeing complex systems.
Generative AI is progressively demonstrating capabilities in architectural design through pattern recognition, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making.
With the adoption of Generative AI, the role of an IT Architect will change into a symbiotic relationship where human expertise collaborates with AI insights.

#3 Gen AI Adoption Will be Confined to Specific Use Cases
A little over a year ago, a new era in AI began with the initial release of OpenAI’s ChatGPT. Since then, many organisations have launched Generative AI pilots.
In its second-year enterprises will start adoption – but in strictly defined and limited use cases. Examples such as Microsoft Copilot demonstrate an early adopter route. While productivity increases for individuals can be significant, its enterprise impact is unclear (at this time).
But there are impactful use cases in enterprise knowledge and document management. Organisations across industries have decades (or even a century) of information, including digitised documents and staff expertise. That treasure trove of information can be made accessible through cognitive search and semantic answering, driven by Generative AI.
Generative AI will provide organisations with a way to access, distill, and create value out of that data – a task that may well be impossible to achieve in any other way.

#4 Gen AI Will Get Press Inches; ‘Traditional’ AI Will Do the Hard Work
While the use cases for Generative AI will continue to expand, the deployment models and architectures for enterprise Generative AI do not add up – yet.
Running Generative AI in organisations’ data centres is costly and using public models for all but the most obvious use cases is too risky. Most organisations opt for a “small target” strategy, implementing Generative AI in isolated use cases within specific processes, teams, or functions. Justifying investment in hardware, software, and services for an internal AI platform is challenging when the payback for each AI initiative is not substantial.
“Traditional AI/ML” will remain the workhorse, with a significant rise in use cases and deployments. Organisations are used to investing for AI by individual use cases. Managing process change and training is also more straightforward with traditional AI, as the changes are implemented in a system or platform, eliminating the need to retrain multiple knowledge workers.

#5 AI Will Pioneer a 21st Century BPM Renaissance
As we near the 25-year milestone of the 21st century, it becomes clear that many businesses are still operating with 20th-century practices and philosophies.
AI, however, represents more than a technological breakthrough; it offers a new perspective on how businesses operate and is akin to a modern interpretation of Business Process Management (BPM). This development carries substantial consequences for digital transformation strategies. To fully exploit the potential of AI, organisations need to commit to an extensive and ongoing process spanning the collection, organisation, and expansion of data, to integrating these insights at an application and workflow level.
The role of AI will transcend technological innovation, becoming a driving force for substantial business transformation. Sectors that specialise in workflow, data management, and organisational transformation are poised to see the most growth in 2024 because of this shift.


While the discussions have centred around AI, particularly Generative AI in 2023, the influence of AI innovations is extensive. Organisations will urgently need to re-examine their risk strategies, particularly in cyber and resilience practices. They will also reassess their infrastructure needs, optimise applications for AI, and re-evaluate their skills requirements.
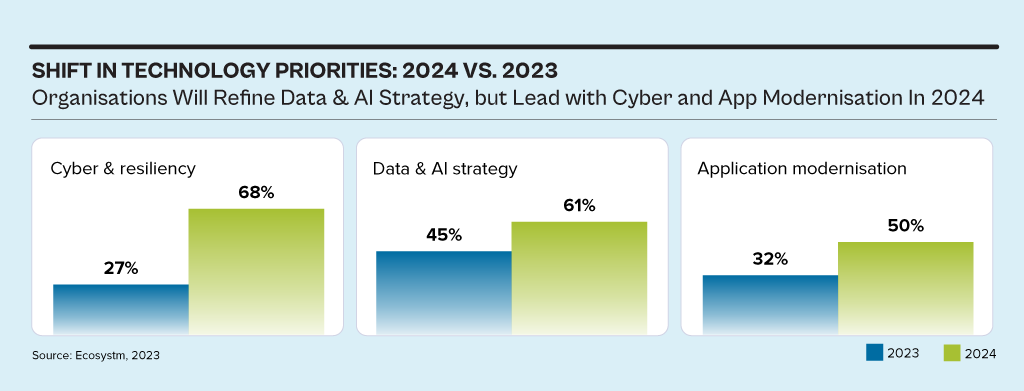
This impacts the entire tech market, including tech skills, market opportunities, and innovations.
Ecosystm analysts Alea Fairchild, Darian Bird, Richard Wilkins, and Tim Sheedy present the top 5 trends in building an Agile & Resilient Organisation in 2024.
Click here to download ‘Ecosystm Predicts: Top 5 Resilience Trends in 2024’ as a PDF.
#1 Gen AI Will See Spike in Infrastructure Innovation
Enterprises considering the adoption of Generative AI are evaluating cloud-based solutions versus on-premises solutions. Cloud-based options present an advantage in terms of simplified integration, but raise concerns over the management of training data, potentially resulting in AI-generated hallucinations. On-premises alternatives offer enhanced control and data security but encounter obstacles due to the unexpectedly high demands of GPU computing needed for inferencing, impeding widespread implementation. To overcome this, there’s a need for hardware innovation to meet Generative AI demands, ensuring scalable on-premises deployments.
The collaboration between hardware development and AI innovation is crucial to unleash the full potential of Generative AI and drive enterprise adoption in the AI ecosystem.
Striking the right balance between cloud-based flexibility and on-premises control is pivotal, with considerations like data control, privacy, scalability, compliance, and operational requirements.

#2 Cloud Migrations Will Make Way for Cloud Transformations
The steady move to the public cloud has slowed down. Organisations – particularly those in mature economies – now prioritise cloud efficiencies, having largely completed most of their application migration. The “easy” workloads have moved to the cloud – either through lift-and-shift, SaaS, or simple replatforming.
New skills will be needed as organisations adopt public and hybrid cloud for their entire application and workload portfolio.
- Cloud-native development frameworks like Spring Boot and ASP.NET Core make it easier to develop cloud-native applications
- Cloud-native databases like MongoDB and Cassandra are designed for the cloud and offer scalability, performance, and reliability
- Cloud-native storage like Snowflake, Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Storage provides secure and scalable storage
- Cloud-native messaging like Amazon SNS and Google Cloud Pub/Sub provide reliable and scalable communication between different parts of the cloud-native application

#3 2024 Will be a Good Year for Technology Services Providers
Several changes are set to fuel the growth of tech services providers (systems integrators, consultants, and managed services providers).
There will be a return of “big apps” projects in 2024.
Companies are embarking on significant updates for their SAP, Oracle, and other large ERP, CRM, SCM, and HRM platforms. Whether moving to the cloud or staying on-premises, these upgrades will generate substantial activity for tech services providers.
The migration of complex apps to the cloud involves significant refactoring and rearchitecting, presenting substantial opportunities for managed services providers to transform and modernise these applications beyond traditional “lift-and-shift” activities.
The dynamic tech landscape, marked by AI growth, evolving security threats, and constant releases of new cloud services, has led to a shortage of modern tech skills. Despite a more relaxed job market, organisations will increasingly turn to their tech services partners, whether onshore or offshore, to fill crucial skill gaps.

#4 Gen AI and Maturing Deepfakes Will Democratise Phishing
As with any emerging technology, malicious actors will be among the fastest to exploit Generative AI for their own purposes. The most immediate application will be employing widely available LLMs to generate convincing text and images for their phishing schemes. For many potential victims, misspellings and strangely worded appeals are the only hints that an email from their bank, courier, or colleague is not what it seems. The ability to create professional-sounding prose in any language and a variety of tones will unfortunately democratise phishing.
The emergence of Generative AI combined with the maturing of deepfake technology will make it possible for malicious agents to create personalised voice and video attacks. Digital channels for communication and entertainment will be stretched to differentiate between real and fake.
Security training that underscores the threat of more polished and personalised phishing is a must.

#5 A Holistic Approach to Risk and Operational Resilience Will Drive Adoption of VMaaS
Vulnerability management is a continuous, proactive approach to managing system security. It not only involves vulnerability assessments but also includes developing and implementing strategies to address these vulnerabilities. This is where Vulnerability Management Platforms (VMPs) become table stakes for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) as they are often perceived as “easier targets” by cybercriminals due to potentially lesser investments in security measures.
Vulnerability Management as a Service (VMaaS) – a third-party service that manages and controls threats to automate vulnerability response to remediate faster – can improve the asset cybersecurity management and let SMEs focus on their core activities.
In-house security teams will particularly value the flexibility and customisation of dashboards and reports that give them enhanced visibility over all assets and vulnerabilities.


In recent years, organisations have had to swiftly transition to providing digital experiences due to limitations on physical interactions; competed fiercely based on the customer experiences offered; and invested significantly in the latest CX technologies. However, in 2024, organisations will pivot their competitive efforts towards product innovation rather than solely focusing on enhancing the CX.

This does not mean that organisations will not focus on CX – they will just be smarter about it!
Ecosystm analysts Audrey William, Melanie Disse, and Tim Sheedy present the top 5 Customer Experience trends in 2024.
Click here to download ‘Ecosystm Predicts: Top 5 CX Trends in 2024’ as a PDF.
#1 Customer Experience is Due for a Reset
Organisations aiming to improve customer experience are seeing diminishing returns, moving away from the significant gains before and during the pandemic to incremental improvements. Many organisations experience stagnant or declining CX and NPS scores as they prioritise profit over customer growth and face a convergence of undifferentiated digital experiences. The evolving digital landscape has also heightened baseline customer expectations.
In 2024, CX programs will be focused and measurable – with greater involvement of Sales, Marketing, Brand, and Customer Service to ensure CX initiatives are unified across the entire customer journey.
Organisations will reassess CX strategies, choosing impactful initiatives and aligning with brand values. This recalibration, unique to each organisation, may include reinvesting in human channels, improving digital experiences, or reimagining customer ecosystems.

#2 Sentiment Analysis Will Fuel CX Improvement
Organisations strive to design seamless customer journeys – yet they often miss the mark in crafting truly memorable experiences that forge emotional connections and turn customers into brand advocates.
Customers want on-demand information and service; failure to meet these expectations often leads to discontent and frustration. This is further heightened when organisations fail to recognise and respond to these emotions.
Sentiment analysis will shape CX improvements – and technological advancements such as in neural network, promise higher accuracy in sentiment analysis by detecting intricate relationships between emotions, phrases, and words.
These models explore multiple permutations, delving deeper to interpret the meaning behind different sentiment clusters.

#3 AI Will Elevate VoC from Surveys to Experience Improvement
In 2024, AI technologies will transform Voice of Customer (VoC) programs from measurement practices into the engine room of the experience improvement function.
The focus will move from measurement to action – backed by AI. AI is already playing a pivotal role in analysing vast volumes of data, including unstructured and unsolicited feedback. In 2024, VoC programs will shift gear to focus on driving a customer centric culture and business change. AI will augment insight interpretation, recommend actions, and predict customer behaviour, sentiment, and churn to elevate customer experiences (CX).
Organisations that don’t embrace an AI-driven paradigm will get left behind as they fail to showcase and deliver ROI to the business.

#4 Generative AI Platforms Will Replace Knowledge Management Tools
Most organisations have more customer knowledge management tools and platforms than they should. They exist in the contact centre, on the website, the mobile app, in-store, at branches, and within customer service. There are two challenges that this creates:
- Inconsistent knowledge. The information in the different knowledge bases is different and sometimes conflicting.
- Difficult to extract answers. The knowledge contained in these platforms is often in PDFs and long form documents.
Generative AI tools will consolidate organisational knowledge, enhancing searchability.
Customers and contact centre agents will be able to get actual answers to questions and they will be consistent across touchpoints (assuming they are comprehensive, customer-journey and organisation-wide initiatives).

#5 Experience Orchestration Will
Accelerate
Despite the ongoing effort to streamline and simplify the CX, organisations often implement new technologies, such as conversational AI, digital and social channels, as independent projects. This fragmented approach, driven by the desire for quick wins using best-in-class point solutions results in a complex CX technology architecture.
With the proliferation of point solution vendors, it is becoming critical to eliminate the silos. The fragmentation hampers CX teams from achieving their goals, leading to increased costs, limited insights, a weak understanding of customer journeys, and inconsistent services.
Embracing CX unification through an orchestration platform enables organisations to enhance the CX rapidly, with reduced concerns about tech debt and legacy issues.


2023 has been an eventful year. In May, the WHO announced that the pandemic was no longer a global public health emergency. However, other influencers in 2023 will continue to impact the market, well into 2024 and beyond.
Global Conflicts. The Russian invasion of Ukraine persisted; the Israeli-Palestinian conflict escalated into war; African nations continued to see armed conflicts and political crises; there has been significant population displacement.
Banking Crisis. American regional banks collapsed – Silicon Valley Bank and First Republic Bank collapses ranking as the third and second-largest banking collapses in US history; Credit Suisse was acquired by UBS in Switzerland.
Climate Emergency. The UN’s synthesis report found that there’s still a chance to limit global temperature increases by 1.5°C; Loss and Damage conversations continued without a significant impact.
Power of AI. The interest in generative AI models heated up; tech vendors incorporated foundational models in their enterprise offerings – Microsoft Copilot was launched; awareness of AI risks strengthened calls for Ethical/Responsible AI.
Click below to find out what Ecosystm analysts Achim Granzen, Darian Bird, Peter Carr, Sash Mukherjee and Tim Sheedy consider the top 5 tech market forces that will impact organisations in 2024.
Click here to download ‘Ecosystm Predicts: Tech Market Dynamics 2024’ as a PDF
#1 State-sponsored Attacks Will Alter the Nature Of Security Threats
It is becoming clearer that the post-Cold-War era is over, and we are transitioning to a multi-polar world. In this new age, malevolent governments will become increasingly emboldened to carry out cyber and physical attacks without the concern of sanction.
Unlike most malicious actors driven by profit today, state adversaries will be motivated to maximise disruption.
Rather than encrypting valuable data with ransomware, wiper malware will be deployed. State-sponsored attacks against critical infrastructure, such as transportation, energy, and undersea cables will be designed to inflict irreversible damage. The recent 23andme breach is an example of how ethnically directed attacks could be designed to sow fear and distrust. Additionally, even the threat of spyware and phishing will cause some activists, journalists, and politicians to self-censor.

#2 AI Legislation Breaches Will Occur, But Will Go Unpunished
With US President Biden’s recently published “Executive order on Safe, Secure and Trustworthy AI” and the European Union’s “AI Act” set for adoption by the European Parliament in mid-2024, codified and enforceable AI legislation is on the verge of becoming reality. However, oversight structures with powers to enforce the rules are currently not in place for either initiative and will take time to build out.
In 2024, the first instances of AI legislation violations will surface – potentially revealed by whistleblowers or significant public AI failures – but no legal action will be taken yet.

#3 AI Will Increase Net-New Carbon Emissions
In an age focused on reducing carbon and greenhouse gas emissions, AI is contributing to the opposite. Organisations often fail to track these emissions under the broader “Scope 3” category. Researchers at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, found that training a single AI model can emit over 283T of carbon dioxide, equal to emissions from 62.6 gasoline-powered vehicles in a year.
Organisations rely on cloud providers for carbon emission reduction (Amazon targets net-zero by 2040, and Microsoft and Google aim for 2030, with the trajectory influencing global climate change); yet transparency on AI greenhouse gas emissions is limited. Diverse routes to net-zero will determine the level of greenhouse gas emissions.
Some argue that AI can help in better mapping a path to net-zero, but there is concern about whether the damage caused in the process will outweigh the benefits.

#4 ESG Will Transform into GSE to Become the Future of GRC
Previously viewed as a standalone concept, ESG will be increasingly recognised as integral to Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) practices. The ‘E’ in ESG, representing environmental concerns, is becoming synonymous with compliance due to growing environmental regulations. The ‘S’, or social aspect, is merging with risk management, addressing contemporary issues such as ethical supply chains, workplace equity, and modern slavery, which traditional GRC models often overlook. Governance continues to be a crucial component.
The key to organisational adoption and transformation will be understanding that ESG is not an isolated function but is intricately linked with existing GRC capabilities.
This will present opportunities for GRC and Risk Management providers to adapt their current solutions, already deployed within organisations, to enhance ESG effectiveness. This strategy promises mutual benefits, improving compliance and risk management while simultaneously advancing ESG initiatives.

#5 Productivity Will Dominate Workforce Conversations
The skills discussions have shifted significantly over 2023. At the start of the year, HR leaders were still dealing with the ‘productivity conundrum’ – balancing employee flexibility and productivity in a hybrid work setting. There were also concerns about skills shortage, particularly in IT, as organisations prioritised tech-driven transformation and innovation.
Now, the focus is on assessing the pros and cons (mainly ROI) of providing employees with advanced productivity tools. For example, early studies on Microsoft Copilot showed that 70% of users experienced increased productivity. Discussions, including Narayana Murthy’s remarks on 70-hour work weeks, have re-ignited conversations about employee well-being and the impact of technology in enabling employees to achieve more in less time.
Against the backdrop of skills shortages and the need for better employee experience to retain talent, organisations are increasingly adopting/upgrading their productivity tools – starting with their Sales & Marketing functions.


Earlier in the year, Microsoft unveiled its vision for Copilot, a digital companion that aims to provide a unified user experience across Bing, Edge, Microsoft 365, and Windows. This vision includes a consistent user experience. The rollout began with Windows in September and expanded to Microsoft 365 Copilot for enterprise customers this month.
Many organisations across Asia Pacific will soon face the question on whether to invest in Microsoft 365 Copilot – despite its current limitations in supporting all regional languages. Copilot is currently supported in English (US, GB, AU, CA, IN), Japanese, and Chinese Simplified. Microsoft plans to support more languages such as Arabic, Chinese Traditional, Korean and Thai over the first half of 2024. There are still several languages used across Asia Pacific that will not be supported until at least the second half of 2024 or later.
Access to Microsoft 365 Copilot comes with certain prerequisites. Organisations need to have either a Microsoft 365 E3 or E5 license and an Azure Active Directory account. F3 licenses do not currently have access to 365 Copilot. For E3 license holders the cost per user for adding Copilot would nearly double – so it is a significant extra spend and will need to deliver measurable and tangible benefits and a strong business case. It is doubtful whether most organisations will be able to justify this extra spend.
However, Copilot has the potential to significantly enhance the productivity of knowledge workers, saving them many hours each week, with hundreds of use cases already emerging for different industries and user profiles. Microsoft is offering a plethora of information on how to best adopt, deploy, and use Copilot. The key focus when building a business case should revolve around how knowledge workers will use this extra time.
Maximising Copilot Integration: Steps to Drive Adoption and Enhance Productivity
Identifying use cases, building the business proposal, and securing funding for Copilot is only half the battle. Driving the change and ensuring all relevant employees use the new processes will be significantly harder. Consider how employees currently use their productivity tools compared to 15 years ago, with many still relying on the same features and capabilities in their Office suites as they did in earlier versions. In cases where new features were embraced, it typically occurred because knowledge workers didn’t have to make any additional efforts to incorporate them, such as the auto-type ahead functions in email or the seamless integration of Teams calls.
The ability of your organisation to seamlessly integrate Copilot into daily workflows, optimising productivity and efficiency while harnessing AI-generated data and insights for decision-making will be of paramount importance. It will be equally important to be watchful to mitigate potential risks associated with an over-reliance on AI without sufficient oversight.
Implementing Copilot will require some essential steps:
- Training and onboarding. Provide comprehensive training to employees on how to use Copilot’s features within Microsoft 365 applications.
- Integration into daily tasks. Encourage employees to use Copilot for drafting emails, documents, and generating meeting notes to familiarise them with its capabilities.
- Customisation. Tailor Copilot’s settings and suggestions to align with company-specific needs and workflows.
- Automation. Create bots, templates, integrations, and other automation functions for multiple use cases. For example, when users first log onto their PC, they could get a summary of missed emails, chats – without the need to request it.
- Feedback loop. Implement a feedback mechanism to monitor how Copilot is used and to make adjustments based on user experiences.
- Evaluating effectiveness. Gauge how Copilot’s features are enhancing productivity regularly and adjust usage strategies accordingly. Focus on the increased productivity – what knowledge workers now achieve with the time made available by Copilot.
Changing the behaviours of knowledge workers can be challenging – particularly for basic processes that they have been using for years or even decades. Knowledge of use cases and opportunities for Copilot will not just filter across the organisation. Implementing formal training and educational programs and backing them up with refresher courses is important to ensure compliance and productivity gains.

The impact of AI on Customer Experience (CX) has been profound and continues to expand. AI allows a a range of advantages, including improved operational efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced experiences for both customers and employees.
AI-powered solutions have the capability to analyse vast volumes of customer data in real-time, providing organisations with invaluable insights into individual preferences and behaviour. When executed effectively, the ability to capture, analyse, and leverage customer data at scale gives organisations significant competitive edge. Most importantly, AI unlocks opportunities for innovation.
Read on to discover the transformative impact of AI on customer experiences.
Click here to download ‘Customer Experience Redefined: The Role of AI’ as a PDF

Generative AI has stolen the limelight in 2023 from nearly every other technology – and for good reason. The advances made by Generative AI providers have been incredible, with many human “thinking” processes now in line to be automated.
But before we had Generative AI, there was the run-of-the-mill “traditional AI”. However, despite the traditional tag, these capabilities have a long way to run within your organisation. In fact, they are often easier to implement, have less risk (and more predictability) and are easier to generate business cases for. Traditional AI systems are often already embedded in many applications, systems, and processes, and can easily be purchased as-a-service from many providers.
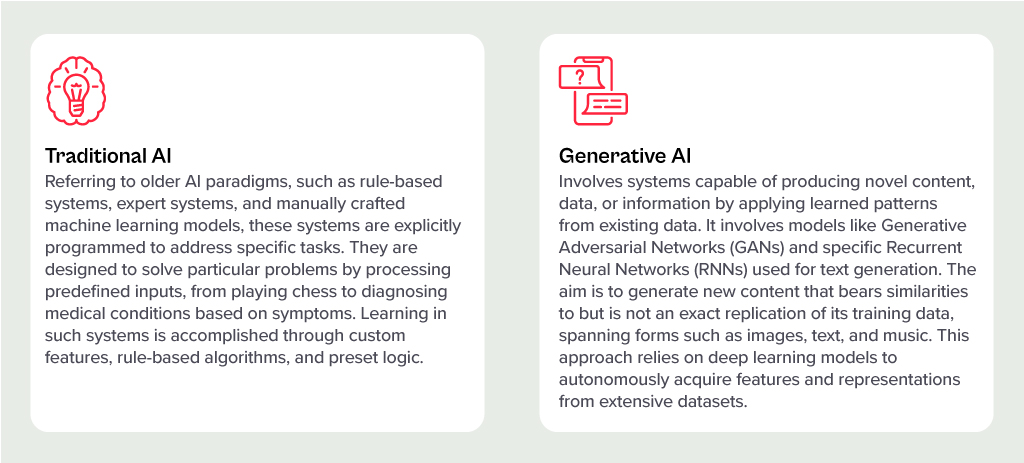
Unlocking the Potential of AI Across Industries
Many organisations around the world are exploring AI solutions today, and the opportunities for improvement are significant:
- Manufacturers are designing, developing and testing in digital environments, relying on AI to predict product responses to stress and environments. In the future, Generative AI will be called upon to suggest improvements.
- Retailers are using AI to monitor customer behaviours and predict next steps. Algorithms are being used to drive the best outcome for the customer and the retailer, based on previous behaviours and trained outcomes.
- Transport and logistics businesses are using AI to minimise fuel usage and driver expenses while maximising delivery loads. Smart route planning and scheduling is ensuring timely deliveries while reducing costs and saving on vehicle maintenance.
- Warehouses are enhancing the safety of their environments and efficiently moving goods with AI. Through a combination of video analytics, connected IoT devices, and logistical software, they are maximising the potential of their limited space.
- Public infrastructure providers (such as shopping centres, public transport providers etc) are using AI to monitor public safety. Video analytics and sensors is helping safety and security teams take public safety beyond traditional human monitoring.
AI Impacts Multiple Roles
Even within the organisation, different lines of business expect different outcomes for AI implementations.
- IT teams are monitoring infrastructure, applications, and transactions – to better understand root-cause analysis and predict upcoming failures – using AI. In fact, AIOps, one of the fastest-growing areas of AI, yields substantial productivity gains for tech teams and boosts reliability for both customers and employees.
- Finance teams are leveraging AI to understand customer payment patterns and automate the issuance of invoices and reminders, a capability increasingly being integrated into modern finance systems.
- Sales teams are using AI to discover the best prospects to target and what offers they are most likely to respond to.
- Contact centres are monitoring calls, automating suggestions, summarising records, and scheduling follow-up actions through conversational AI. This is allowing to get agents up to speed in a shorter period, ensuring greater customer satisfaction and increased brand loyalty.
Transitioning from Low-Risk to AI-Infused Growth
These are just a tiny selection of the opportunities for AI. And few of these need testing or business cases – many of these capabilities are available out-of-the-box or out of the cloud. They don’t need deep analysis by risk, legal, or cybersecurity teams. They just need a champion to make the call and switch them on.
One potential downside of Generative AI is that it is drawing unwarranted attention to well-established, low-risk AI applications. Many of these do not require much time from data scientists – and if they do, the challenge is often finding the data and creating the algorithm. Humans can typically understand the logic and rules that the models create – unlike Generative AI, where the outcome cannot be reverse-engineered.
The opportunity today is to take advantage of the attention that LLMs and other Generative AI engines are getting to incorporate AI into every conceivable aspect of a business. When organisations understand the opportunities for productivity improvements, speed enhancement, better customer outcomes and improved business performance, the spend on AI capabilities will skyrocket. Ecosystm estimates that for most organisations, AI spend will be less than 5% of their total tech spend in 2024 – but it is likely to grow to over 20% within the next 4-5 years.

It’s been barely one year since we entered the Generative AI Age. On November 30, 2022, OpenAI launched ChatGPT, with no fanfare or promotion. Since then, Generative AI has become arguably the most talked-about tech topic, both in terms of opportunities it may bring and risks that it may carry.
The landslide success of ChatGPT and other Generative AI applications with consumers and businesses has put a renewed and strengthened focus on the potential risks associated with the technology – and how best to regulate and manage these. Government bodies and agencies have created voluntary guidelines for the use of AI for a number of years now (the Singapore Framework, for example, was launched in 2019).
There is no active legislation on the development and use of AI yet. Crucially, however, a number of such initiatives are currently on their way through legislative processes globally.
EU’s Landmark AI Act: A Step Towards Global AI Regulation
The European Union’s “Artificial Intelligence Act” is a leading example. The European Commission (EC) started examining AI legislation in 2020 with a focus on
- Protecting consumers
- Safeguarding fundamental rights, and
- Avoiding unlawful discrimination or bias
The EC published an initial legislative proposal in 2021, and the European Parliament adopted a revised version as their official position on AI in June 2023, moving the legislation process to its final phase.
This proposed EU AI Act takes a risk management approach to regulating AI. Organisations looking to employ AI must take note: an internal risk management approach to deploying AI would essentially be mandated by the Act. It is likely that other legislative initiatives will follow a similar approach, making the AI Act a potential role model for global legislations (following the trail blazed by the General Data Protection Regulation). The “G7 Hiroshima AI Process”, established at the G7 summit in Japan in May 2023, is a key example of international discussion and collaboration on the topic (with a focus on Generative AI).
Risk Classification and Regulations in the EU AI Act
At the heart of the AI Act is a system to assess the risk level of AI technology, classify the technology (or its use case), and prescribe appropriate regulations to each risk class.
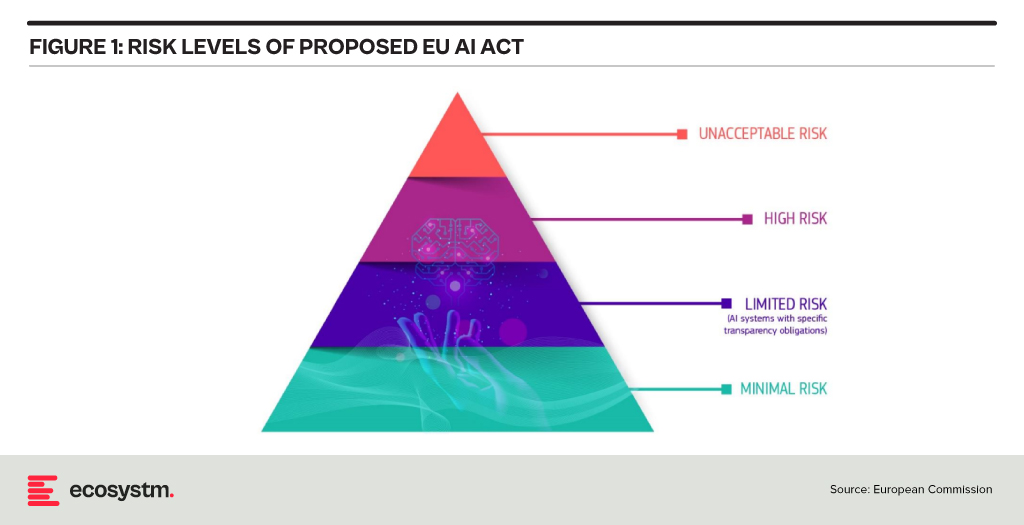
For each of these four risk levels, the AI Act proposes a set of rules and regulations. Evidently, the regulatory focus is on High-Risk AI systems.
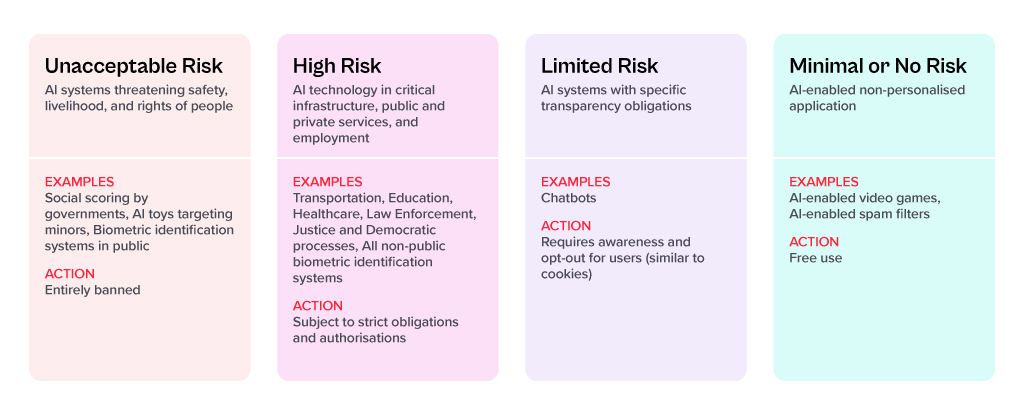
Contrasting Approaches: EU AI Act vs. UK’s Pro-Innovation Regulatory Approach
The AI Act has received its share of criticism, and somewhat different approaches are being considered, notably in the UK. One set of criticism revolves around the lack of clarity and vagueness of concepts (particularly around person-related data and systems). Another set of criticism revolves around the strong focus on the protection of rights and individuals and highlights the potential negative economic impact for EU organisations looking to leverage AI, and for EU tech companies developing AI systems.
A white paper by the UK government published in March 2023, perhaps tellingly, named “A pro-innovation approach to AI regulation” emphasises on a “pragmatic, proportionate regulatory approach … to provide a clear, pro-innovation regulatory environment”, The paper talks about an approach aiming to balance the protection of individuals with economic advancements for the UK on its way to become an “AI superpower”.
Further aspects of the EU AI Act are currently being critically discussed. For example, the current text exempts all open-source AI components not part of a medium or higher risk system from regulation but lacks definition and considerations for proliferation.
Adopting AI Risk Management in Organisations: The Singapore Approach
Regardless of how exactly AI regulations will turn out around the world, organisations must start today to adopt AI risk management practices. There is an added complexity: while the EU AI Act does clearly identify high-risk AI systems and example use cases, the realisation of regulatory practices must be tackled with an industry-focused approach.
The approach taken by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) is a primary example of an industry-focused approach to AI risk management. The Veritas Consortium, led by MAS, is a public-private-tech partnership consortium aiming to guide the financial services sector on the responsible use of AI. As there is no AI legislation in Singapore to date, the consortium currently builds on Singapore’s aforementioned “Model Artificial Intelligence Governance Framework”. Additional initiatives are already underway to focus specifically on Generative AI for financial services, and to build a globally aligned framework.
To Comply with Upcoming AI Regulations, Risk Management is the Path Forward
As AI regulation initiatives move from voluntary recommendation to legislation globally, a risk management approach is at the core of all of them. Adding risk management capabilities for AI is the path forward for organisations looking to deploy AI-enhanced solutions and applications. As that task can be daunting, an industry consortium approach can help circumnavigate challenges and align on implementation and realisation strategies for AI risk management across the industry. Until AI legislations are in place, such industry consortia can chart the way for their industry – organisations should seek to participate now to gain a head start with AI.






























































