Authored by Ullrich Loeffler and Kaushik Ghatak
Technology has been identified as a key enabler of innovation and transformation with great potential to disrupt and reshape entire industries. At the same time, the technology industry itself has been at the forefront of disruption with thousands of promising start-ups emerging in areas such as artificial intelligence (AI), Blockchain, cloud and cybersecurity to name a few.
In February 2020, Ecosystm had the opportunity to meet the executive team of Avanseus, an AI solution provider that promises to reshape traditional maintenance processes by leveraging AI-based algorithms for predictive maintenance and failure detection.
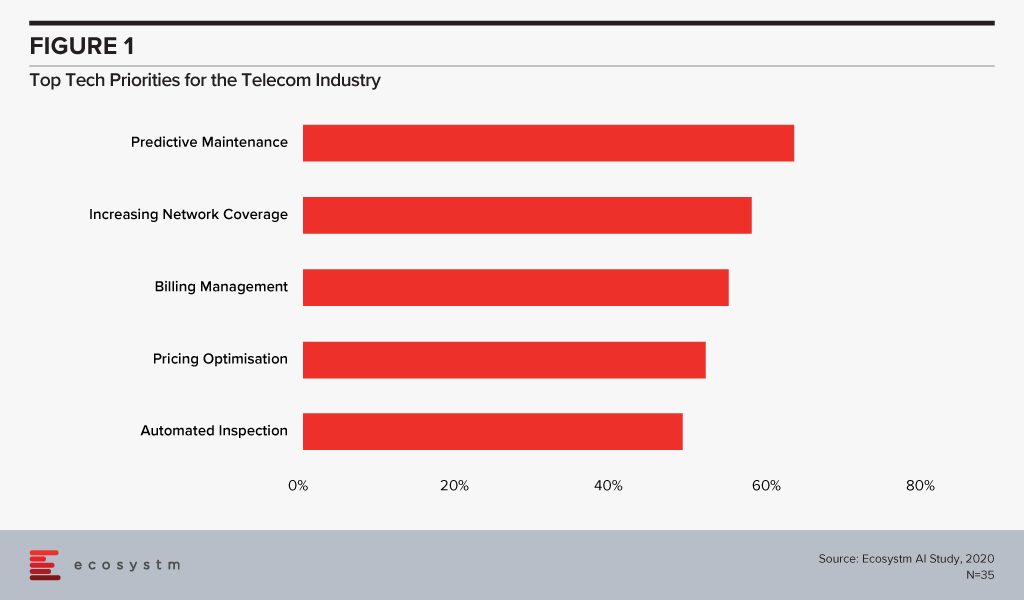
Avanseus is not the newest kid on the block having been launched in June 2015 with headquarters in Singapore. The founding team has extensive experience in the telecommunications sector from executive careers in both the operator and the network provider segments. The problem statement and value proposition that Avanseus was founded on is to support telecom companies to tackle the costly challenge of maintaining their increasingly complex networks and to ensure network performance and customer satisfaction. Ecosystm research finds that predictive maintenance is a key priority for telecom providers looking to invest in newer technologies (Figure 1).
The solution Avanseus offers aims to be simple in the way that its proprietary AI-enabled algorithms can assess and predict network performance and network failures with as little as 6 months of network data history to achieve a high degree of prediction accuracy across telecom networks. The simplicity of the solution further allows cost-effective proofs of concept (PoCs) which lets telecom prospects experience first-hand its potential to drive down maintenance cost and ensure network performance.
Avanseus had secured seed capital of US$2.5 million till the middle of 2017. At the end of 2018, Avanseus secured funding via convertible notes of US$1.3m – main noteholders being TNB Spring and SEEDS Capital (Enterprise Singapore). A global network equipment manufacturer and managed services provider became its first commercial customer in 2016. From there Avanseus has demonstrated steady growth achieving revenue of US$1 million in 2018 and US$2.3 million in 2019. 2020 is forecast to be a milestone year with predictions to become cash-flow positive and to achieve revenue growth of 150% over 2019.
As of February 2020, Avanseus employs 41 staff across multiple international locations including its headquarters in Singapore, its development centre in Bangalore and sales offices in Delhi, North and Latin America and Italy to grow its global presence. The team is complemented by 8 part-time consultants and a growing partner ecosystem which includes major consulting firms as well as technology partners such as Dell, Splunk and Siemens. Expanding its partnerships globally is a key part of its strategy in order to scale up on the opportunities it can contest.
Avanseus’ Potential Growth Path
Considering its young history, Avanseus has shown an impressive growth path which can be credited to staying true to its game plan and its original value proposition and solution design. A new fund-raising round had been kicked off at the end of 2019 with the aim to secure sufficient capital to accelerate growth over the coming years. Half of the anticipated funding will be invested into on-site consultants and sales teams while the other half will be invested in R&D to expand automation into APIs and other machine learning technologies. R&D has been a key focus from its early days which has led to the filing of 8 patents, 2 of which have been granted.
In order to accelerate growth further, Avanseus is also re-assessing the industries that could benefit from its predictive maintenance solutions. As with many startups and growth companies, innovation is often not a straight path and new opportunities and ideas arise as the market and customers are engaged. Several industries face similar challenges and benefit from reduced maintenance cost, reduced downtime, extended equipment lifecycles and improved services quality. To transfer the value proposition across use cases and industry applications Avanseus is looking to leverage approximately 80% of its existing solution and apply 20% of industry-specific domain expertise. This has opened up new growth opportunities in a number of areas such as Industrial IoT, Utilities, Manufacturing and supply chain. There are also opportunities in customer-focused industries such as Banking in niche areas such as maintenance of data centre operations.
Ecosystm Comments
As companies collect and manage an exploding amount of data assets within their operations or from their customers, there is an increasing opportunity for innovative technology vendors to support these companies in driving value from their data assets. Avanseus has demonstrated a clear vision and execution in addressing one of these opportunities by focusing on a clear problem statement and offering a ‘simple’ solution that presents a strong business case. As with every growth company, the challenge is to leverage this opportunity and secure the right funding and resources to scale up as quickly as possible.
Partnerships will be critical in its growth path but signing up partners alone may not translate to creating value. The challenge for Avanseus will be to achieve partner commitment and enablement across different geographies. This will require time and a dedicated channel strategy beyond opportunistic partnerships that are born out of specific client engagements.
Another opportunity that could turn into a challenge is the new range of solution applications that Avanseus has identified. Being a high growth company, the greater challenge is often to decide what not to do rather than what can be done. Avanseus is well advised to carefully select which industries it wants to expand into and focus on. Each new solution set will present a magnet for additional resources and funding and may well be a distraction.
The Oil and Gas industry has seen volatile times and is affected by its own set of unique challenges ranging from commodity price fluctuations, a potential supply crunch, geo-political events, and energy policies including energy transition. Moreover, the challenges and requirements are distinct at different stages of operations – upstream, midstream and downstream. The industry has been an early adopter of a few emerging technologies and is looking to leverage them to remain competitive and better employee management.
Drivers of Transformation in the Oil and Gas Industry
Remaining competitive in an evolving market
Oil and Gas companies are having to clean up old processes, as the market gets increasingly competitive. Ecosystm research finds that the top business priorities for Oil and Gas companies do not stop at cost reduction and revenue growth. The industry also has to focus on employee experience and safety, compliance, and increasingly even customer experience. And they must remain competitive through potential disruption in supply, demand and production; the rising costs of processes; and ongoing exploration costs. Oil and Gas companies are also focusing more on their downstream operations including retail in order to remain competitive.
Shortage of skilled workforce
The industry also faces the challenge of skills shortage. A survey conducted by the Global Energy Talent Index (GETI) found that nearly 70% of Oil and Gas professionals think the industry is already facing skills shortage or will be hit by it within the next 5 years. This is due to a number of reasons, including a reluctance of younger professionals to commit to a profession that has harsher conditions than many. Moreover, as energy transition becomes a topic of global discussion, many have a perception that the industry is not sustainable in the future. The industry also goes through cycles where they cut back on exploration and production, which results in the loss of skills and inadequate knowledge transfer. It has a long-term challenge around knowledge management.
Safety and environmental regulations
The industry has to contend with green energy movements and environmental regulations. There are several country-level regulations around air and water quality. Most Oil and Gas companies have cross-border operations and have to comply with a number of regulations on harmful emissions, greenhouse gases and offshore activities, in several countries. Increasingly, all leading Oil and Gas companies have to work in alignment with the Paris Agreement when developing solutions across functions – exploration, extraction and supply chain. There are also worker safety regulations and standards that they have to comply with.
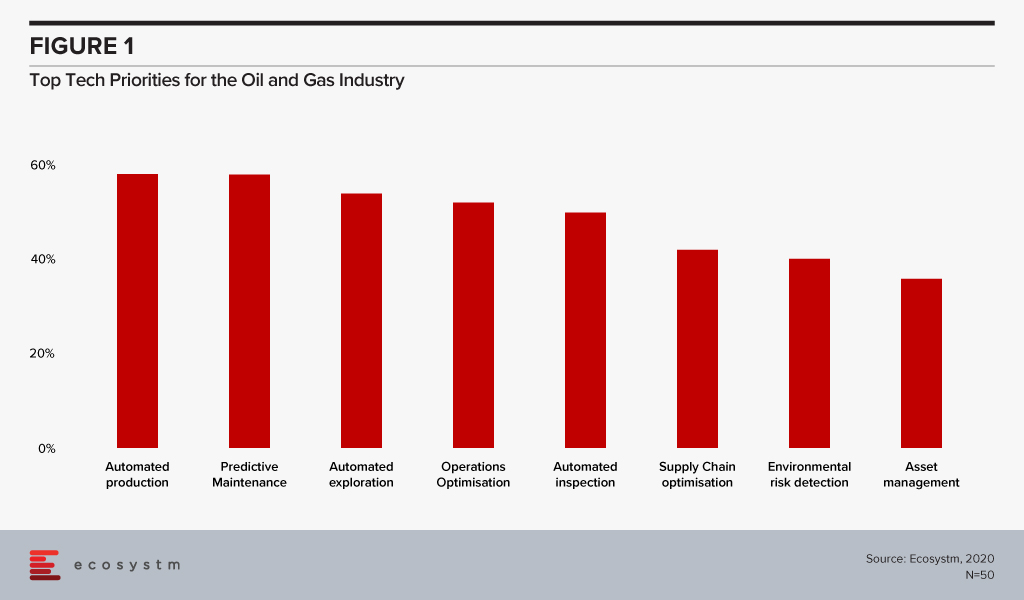
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for Oil and Gas companies that are focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). It is very clear that the key areas of focus are process automation, asset and supply chain management and compliance.
Technology as an Enabler of Oil and Gas Transformation
Several emerging technologies are being used by the Oil and Gas industry as they continue their struggle to remain competitive across the different stages of operations – upstream, midstream and downstream.
IIoT
As the costs of sensors go down, connectivity widens and computing power increases, the industry is seeing greater uptake of Industrial IoT (IIoT) solutions. From wearables (to monitor employee safety) to drones with smart cameras (for remote inspections, environmental monitoring), IoT solutions have an immense role to play in the Oil and Gas industry. The industry has had to be cautious about the choice of devices, however, due to pervasive inflammable hydrocarbons and the related regulations.
Not only are they implementing sensors, Ecosystm research finds that 30% of Oil and Gas companies are also leveraging the IoT sensor data for analytics and intelligence. A common application is in predictive maintenance. Two years ago, Chevron launched predictive maintenance solutions in its oil fields and refineries. While the pilot ran on heat exchangers, the company aims to connect all assets by 2024 and expects to save millions on asset management.
AI
AI and machine learning have applications across Oil and Gas operations, leveraging IoT sensor data. “Smart fields” where production is monitored centrally, has a high level of automated controls. AI/Analytics is allowing companies to run simulations, use predictive data models and identify patterns to gauge risks associated with new projects. This has an impact on production, exploration and making efficient use of existing infrastructure. Oilfield services company Baker Hughes has worked on an AI-based application that allows well operators to view real-time production data and predict future production with more accuracy.
AI is also helping organisations monitor environmental risk and has the potential to help Oil and Gas companies with their compliance requirements. Gazprom Neft, one of the largest suppliers of natural gas to Europe and Seismotech are exploring using AI for seismic data processing, for solutions that are specific to the needs of the industry.
While the applications of AI in the industry are often focused on upstream activities, AI has applications across all operations. In the midstream, transporting crude oil to refineries has always had its unique challenges. Since transport lead times are long and prices fluctuate based on the availability of products, organisations benefit from demand forecasting and price risk modelling. While the common perception of the industry does not include customer interactions, the truth is that the industry is increasingly focusing on the retail space. The need is enough for Shell to begin experimenting with virtual assistants as far back as in 2015, to interact with their retail customers. In fact, the company anticipates a higher adoption of AI in the industry and is collaborating with Udacity to bridge the skills gap.
Technologies empowering employees
As discussed earlier, one of the key challenges of the industry is the inability to manage a reliable knowledge management system that can help consistent knowledge and skills transfer. A single source of truth that can be accessed by all employees on processes, including safety requirements has an immense role to play to help with the skills shortage in the industry.
Enterprise mobility is another tech area that holds immense potential for the industry, with its huge proportion of mobile workers, many in remote locations. Mobility solutions can help in productivity, process optimisation and monitoring of health and safety of the employees and are increasingly incorporating wearables and location-based services. GIS and GPS systems are helping employees with accurate directions, easier access to drilling locations and more. Given the number of devices, platforms and OSs, the industry is seeing an increased interest in unified enterprise mobility (UEM) solutions. Ecosystm finds that more than a third of Oil and Gas companies have implemented or are evaluating UEM, while another 20% are expressing early interests.
Blockchain
The sheer quantity of documents, transaction records and contracts that a typical Oil and Gas company has to manage – including cross-border transactions – poses some difficulty for the industry. The companies have to reconcile and handle issues involving multiple contractors, sub-contractors, and suppliers. Supply chain and inventory management is also a challenge. With the adoption of Blockchain, the industry can automate the management of purchase orders, change orders, receipts, and other trade-related documentation, as well as inventory data with more efficiency and transparency. Blockchain is enabling a seamless supply chain, improved project management and simplifying contractual obligations at each point along the way. Gazprom Neft’s aviation refuelling business is an early adopter of Blockchain-based smart contracts. All refuelling operations are undertaken exclusively on the basis of digital contracts approved by both parties near real-time and eliminates the possibility of any breach of contract and makes the accounting process more transparent.
As the market continues to be volatile for Oil and Gas companies and uncertainties loom in the future, the industry will increasingly depend on technology to remain competitive.

In December 2019, the World Health Organisation (WHO) commemorated the 40th anniversary of smallpox eradication. Ironically, later that month the world was introduced to a new epidemic caused by the Novel Coronavirus. At the same time, the WHO’s fight against other epidemics such as the Ebola virus outbreaks in Congo is far from over. As the world becomes smaller in terms of access, the risks associated with a disease outbreak becomes greater.
Every disease outbreak puts our healthcare system in disarray. Not only does it affect the country where it originated, but it also has a far-reaching impact on healthcare systems in other countries. As of today, the coronavirus has reportedly spread beyond China to 16 countries. A visit to a public healthcare facility in Singapore in the last few days shows how the healthcare system is tracking everyone who visits a hospital or a polyclinic – not just patients. Clinicians are also conducting extra screenings. This has ramifications for healthcare systems, that are already strapped with staff shortage.
There are obvious economic ramifications – at least in the short term. Several companies are banning travel to China for their employees, while many manufacturing units in China have had to temporarily shut down. The impact is not restricted to China alone and has the potential to impact global trade and economy.
Every new disease that comes into the limelight also impacts the life sciences industry that has to divert their R&D resources into finding a cure and/or a vaccine for the disease. While winning the race for the first breakthrough can be a huge opportunity for the pharmaceutical company, it also impacts the regular research being conducted to protect us from other deadly diseases.
Unfortunately, we are always one step behind diseases, and we have to first think of cure and containment before we can consider prevention and eradication. As we wait and watch to see how fast the coronavirus epidemic is contained, we must acknowledge the role technology plays in managing epidemics and other disasters. Here are some initiatives:
Detection
One of the success stories to emerge from this disaster is the speed at which the risk of the outbreak was detected. 10 days before the WHO announcement, BlueDot, a healthcare monitoring platform had already detected the epidemic, from intelligence gathered from news reports, disease networks and official sources. The same platform – and a few others – are also predicting the global spread of the virus by mining global airlines ticketing data. This is a reassuring outcome of how technology and human analysis can effectively come together to improve health outcomes.
Research
While the current global concern is the speed of containment of the disease, eventually there will have to be more proactive measures to prevent another outbreak and to even eradicate the disease. To be able to understand the full nature of the pathogen and to come up with a vaccine, it is important that the virus is isolated. Scientists from the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity in Melbourne successfully grew the Wuhan coronavirus from a patient sample. While the Chinese authorities had released the genome sequence to help with the diagnosis, this ‘game-changer’ can be potentially used to detect the virus in patients who do not yet display the symptoms and eventually to develop a vaccine. Cutting-edge research in healthcare has always been conducted by such research and pharmaceutical organisations. They have consistently pushed the adoption of new technology in healthcare, especially in their R&D practices.
Management
As mentioned earlier, any outbreak taxes the front-line healthcare providers the most. They have very little time to change their triage and protocols to combat a disease that they have possibly never encountered. This is where clinical decision support systems that can incorporate these new protocols into the workflow comes in handy. Epic, the EHR provider has pushed a software update that does just that. According to Epic, this update was developed in collaboration with biocontainment experts, infectious disease physicians and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDCs). Collaborations such as this will be required if we have to devise a global protocol for epidemic management and containment.
There have been several other initiatives during this outbreak that show how different technologies can come together to benefit healthcare, especially to handle a crisis. Technology has always played a huge role in spreading the message in times of disaster, especially in emerging economies – with technologies such as AI, the potential of technology benefitting healthcare increases exponentially.

With the advancements in the technology landscape, the CIO’s role has become increasingly complex. One of the key challenges they face is in emerging and newer technology implementations, which require them to identify and partner with newer tech vendors. The common challenges that tech buyers face today include:
- The emergence of newer technologies that are catching the fancy of the C-suite and they are expected to adopt and deliver
- Getting management buy-in for IT investments (increasingly including discussions on ROI)
- Need to involve business stakeholders in tech decision-making
- Lack of sufficiently skilled internal IT
- Engagement with multiple tech vendors (including newer vendors that they have to establish a relationship with)
- Digital transformation projects that might require an overhaul (or at least a re-think) of IT systems
- Backdrop of compliance and risk management mandates
Many of these challenges will require the sourcing of new technology or a new tech partner and rethinking their vendor selection criteria. And selecting a tech vendor can be hard. The mere fact that there is an industry whose sole purpose is to help businesses select tech vendors goes to show the massive gap between what these providers sell and what businesses want. If there was easy alignment, the Tech Sourcing professionals and businesses would not have existed.
But over my time working with Tech Sourcing professionals, CIOs and business leaders, I have picked up on a few key factors that you should incorporate in your vendor selection process best practices. First and foremost, you are looking for a partner – someone who will be with you through the good and bad. Someone whose skills, products, services – and most importantly – culture, match your business and its needs.
I believe that the technology ecosystem is not really as competitive as we think. Yes, in practice Google competes with Microsoft in the office productivity space. But I often hear about companies moving from one to the other not for features, function or even price – but for a cultural match. Some traditional businesses were hoping Google can help them become more innovative, but in reality, their business culture smothered Google and meant they could not benefit from the difference in the ways of working. And I am not suggesting Microsoft is not innovative – more that Office represents the traditional ways of working – and perhaps can help a business take a more stepwise approach to change its own culture.
And I regularly hear about IT services deals (managed services, systems integration, consulting etc) going to the company that made the most sense from a cultural fit – where they were willing to take on the culture of their customer and embrace that way of working. In fact, I have been brought into many deals where a company hired a strategic consultant to create a new digital strategy or AI strategy, only to receive a document that is unworkable in their business and their culture.
So, I believe every strategic technology relationship should start and end with a cultural match. This company is a partner – not just a provider. How do you determine if they are a partner and measure cultural match? Well, that is the topic of an upcoming report of mine, so watch this space!
Questions You Should Ask Before Stepping in the Ring
There are also a number of questions that you should ask along with the partnership discussion:
- How will this solution change the organisation?
- What are the risks either way (of implementing or not implementing the solution)?
- Does the solution solve a key business problem?
- Is it likely to have more impact than the solution it is replacing?
- Where will the funding for the implementation come from?
- Have you calculated the ROI and the time to deployment?
- Have you baselined the current scenario so that you can measure improvement?
These can inform you of the business impact of the solution – and what you need to do to prepare for successful implementation (if you plan for success, you are more likely to be able to get faster benefits than if you do not plan for the change!)
Engagement Criteria for Your Shortlisting Process
In order to determine vendor selection process best practices, Ecosystm research tries to unearth the top criteria that organisations employ when shortlisting the vendors that they want to engage, across multiple technologies.
There is still a skills gap in internal IT and organisations want technical guidance from their Cloud and IoT vendors. With the plethora of options available in these tech areas, CIOs and IT teams also tend to look at the brand reputation when engaging with the vendor. Very often, organisations looking to migrate their on-prem solutions on the cloud engage with existing infrastructure providers or systems integrators for guidance, and existing relationships are significant. IoT solutions tend to be very industry-specific and a portfolio of specific industry use cases (actual deployments – not proofs of concept) can be impactful when selecting a vendor for planned deployments.
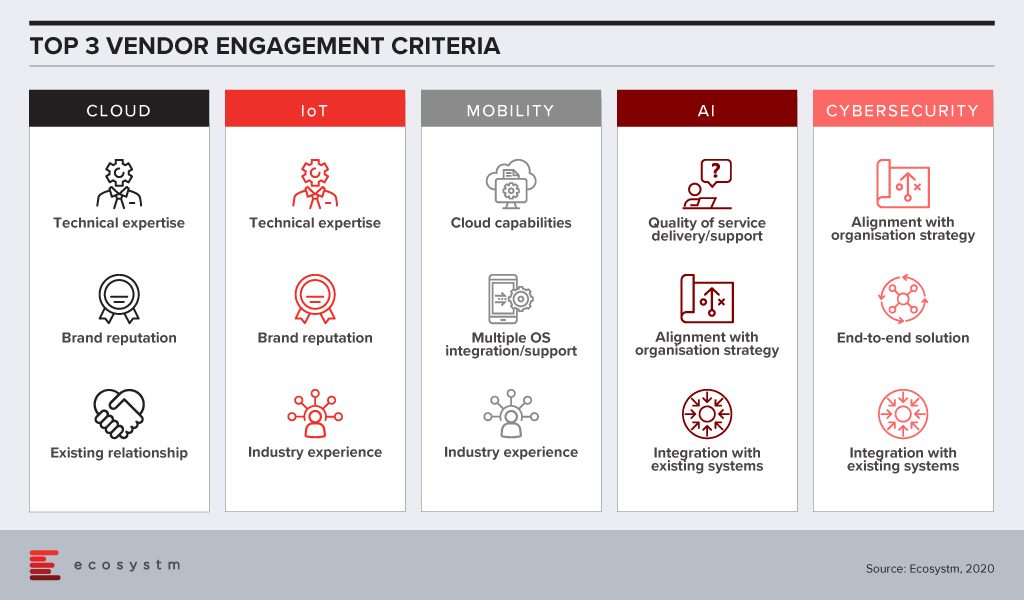
Artificial intelligence (AI) deployments are often linked with digital transformation (DX). Organisations look for a vendor that can understand the organisational strategy and customise the AI solutions to help the organisation achieve its goal. Adoption of AI is still at a nascent stage globally across all industries. Many organisations do not have the right skills, such as data scientists, yet. They appreciate that integration with internal systems will be key to reap the full benefits of the solutions, especially if the entire organisation has to benefit from the deployments. They also anticipate that they would have to have a continuous period of engagement with their vendors, right from identifying the right data set, data cleaning to the right algorithms that keep learning. Organisations will look at vendor partners who are known for delivering better customer experience.
This is true for cybersecurity solutions as well, as organisations are driven to continue their investments to adhere to the internal risk management requirements. Given how fragmented the cybersecurity landscape has become, organisations will also wish to engage with vendors that have an end-to-end offering, especially a managed security service provider (MSSP). Cybersecurity vendors are increasingly strengthening their partner ecosystem so that they can provide their client with the single-point-of-contact that they want.
Of the technologies mentioned in the figure, mobility is arguably the most mature. As organisations revisit their enterprise mobility solution as they go increasingly ‘Mobile First’, their requirements from their mobility vendors are more specific. They have decided over the years which OSs they want to support their enterprise applications and are looking for vendors with robust cloud offerings.
The vendor selection criteria will likely be different for each technology area. And as your knowledge and understanding of the technology increases, you should be able to drill the requirements down to the solution level, while making sure you engage with a vendor with the right culture.
Tim Sheedy’s upcoming report, ‘Best Practices for Vendor Evaluation and Selection’ is due to be published in February 2020.
The telecommunications industry has long been an enabler of Digital Transformation (DX) in other industries. Now it is time for the industry to transform in order to survive a challenging market, newer devices and networking capabilities, and evolving customer requirements. While the telecom industry market dynamics can be very local, we will see a widespread technology disruption in the industry as the world becomes globally connected.
Drivers of Transformation in the Telecom Industry
Remaining Competitive
Nokia Bell Labs expects global telecom operators to fall from 10 to 5 and local operators to fall from 800 to 100, between 2020 and 2025. Simultaneously, there are new players entering the market, many leveraging newer technologies and unconventional business models to gain a share of the pie. While previous DX initiatives happened mostly at the periphery (acquiring new companies, establishing disruptive business units), operators are now focusing on transforming the core – cost reduction, improving CX, capturing new opportunities, and creating new partner ecosystems – in order to remain competitive. There is a steady disaggregation in the retail space, driving consolidation in traditional network business models.
“The telecom industry is looking at gradual decline from traditional services and there has been a concerted effort in reducing costs and introducing new digital services,” says Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Shamir Amanullah. “Much of the telecom industry is unfortunately still associated with the “dumb pipe” tag as the over-the-top (OTT) players continue to rake in revenues and generate higher margins, using the telecom infrastructure to provide innovative services.”
Bringing Newer Products to Market
Industries and governments have shifted focus to areas such as smart energy, Industry 4.0, autonomous driving, smart buildings, and remote healthcare, to name a few. In the coming days, most initial commercial deployments will centre around network speed and latency. Technologies like GPON, 5G, Wifi 6, WiGig, Edge computing, and software-defined networking are bringing new capabilities and altering costs.
Ecosystm’s telecommunications and mobility predictions for 2020, discusses how 5G will transform the industry in multiple ways. For example, it will give enterprises the opportunity to incorporate fixed network capabilities natively to their mobility solutions, meaning less customisation of enterprise networking. Talking about the opportunity 5G gives to telecom service providers, Amanullah says, “With theoretical speeds of 20 times of 4G, low latency of 1 millisecond and a million connections per square kilometre, the era of mobile Internet of Everything (IoE) is expected to transform industries including Manufacturing, Healthcare and Transportation. Telecom operators can accelerate and realise their DX, as focus shifts to solutions for not just consumers but for enterprises and governments.”
Changing Customer Profile
Amanullah adds, “Telecom operators can no longer offer “basic” services – they must become customer-obsessed and customer experience (CX) must be at the forefront of their DX goals.” But the real challenge is that their traditional customer base has steadily diverged. On the one hand, their existent retail customers expect better CX – at par with other service providers, such as the banking sector. Building a customer-centric capability is not simple and involves a substantial operational and technological shift.
On the other hand, as they bring newer products to market and change their business models, they are being forced to shift focus away from horizontal technologies and connecting people – to industry solutions and connecting machines. As their business becomes more solution-based, they are being forced to address their offerings at new buying centres, beyond IT infrastructure and Facilities. Their new customer base within organisations wants to talk about a variety of managed services such as VoIP, IoT, Edge computing, AI and automation.
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for telecom service providers, focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). It is very clear that the top priorities are driving customer loyalty (through better coverage, smart billing and competitive pricing) and process optimisation (including asset maintenance).

Technology as an Enabler of Telecom Transformation
Several emerging technologies are being used internally by telecom service providers as they look towards DX to remain competitive. They are transforming both asset and customer management in the telecom industry.
IoT & AI
Telecom infrastructure includes expensive equipment, towers and data centres, and providers are embedding IoT devices to monitor and maintain the equipment while ensuring minimal downtime. The generators, meters, towers are being fitted with IoT sensors for remote asset management and predictive maintenance, which has cost as well as customer service benefits. AI is also unlocking advanced network traffic optimisation capabilities to extend network coverage intelligently, and dynamically distribute frequencies across users to improve network experience.
Chatbots and virtual assistants are used by operators to improve customer service and assist customers with equipment set-up, troubleshooting and maintenance. These AI investments see tremendous improvement in customer satisfaction. This also has an impact on employee experience (EX) as these automation tools free workforce from repetitive tasks and they be deployed to more advanced tasks.
Telecom providers have access to large volumes of customer data that can help them predict customer usage patterns. This helps them in price optimisation and last-minute deals, giving them a competitive edge. More data is being collected and used as several operators provide location-based services and offerings.
In the end, the IoT data and the AI/Analytics solutions are enabling telecom service providers to improve products and solutions and offer their customers the innovation that they want. For instance, Vodafone partnered with BMW to incorporate an in-built SIM that enables vehicle tracking and provides theft protection. In case of emergencies, alerts can also be sent to emergency services and contacts. AT&T designed a fraud detection application to look for patterns and detect suspected fraud, spam and robocalls. The system looks for multiple short-duration calls from a single source to numbers on the ‘Do Not Call’ registry. This enables them to block calls and prevent scammers, telemarketers and identity theft issues.
Cybersecurity
Talking about the significance of increasing investments in cybersecurity solutions by telecom service providers, Amanullah says, “Telecom operators have large customer databases and provide a range of services which gives criminals a great incentive to steal identity and payment information, damage websites and cause loss of reputation. They have to ramp up their investment in cybersecurity technology, processes and people. A telecom operator’s compromised security can have country-wide, and even global consequences. As networks become more complex with numerous partnerships, there is a need for strategic planning and implementation of security, with clear accountability defined for each party.”
One major threat to the users is the attack on infrastructure or network equipment, such as routers or DDoS attacks through communication lines. Once the equipment has been compromised, hackers can use it to steal data, launch other anonymous attacks, store exfiltrated data or access expensive services such as international phone calls. To avoid security breaches, telecom companies are enhancing cybersecurity in such devices. However, what has become even more important for the telecom providers is to actually let their consumers know the security features they have in place and incorporate it into their go-to-market messaging. Comcast introduced an advanced router to monitor connected devices, inform security threats and block online threats to provide automatic seamless protection to connected devices.
Blockchain
Blockchain can bring tremendous benefits to the telecom industry, according to Amanullah. “It will undeniably increase security, transparency and reduce fraud in areas including billing and roaming services, and in simply knowing your customer better. With possibilities of 5G, IoT and Edge computing, more and more devices are on the network – and identity and security are critical. Newer business models are expected, including those provided for by 5G network slicing, which involves articulation in the OSS and BSS.”
Blockchain will be increasingly used for supply chain and SLA management. Tencent and China Unicom launched an eSIM card which implements new identity authentication standards. The blockchain-based authentication system will be used in consumer electronics, vehicles, connected devices and smart city applications.
Adoption of emerging technologies for DX may well be the key to survival for many telecom operators, over the next few years.

Xiaomi Corporation – a Chinese electronics giant often dubbed the “Apple of China”, with specialisation in smartphones and smart devices – is now planning to focus on non-smartphone segments for growth. Last week the Beijing based company announced a planned investment of more than US$7 Billion in the areas of 5G, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Artificial Internet of Things (AIoT). The announcement builds on last year’s pledge to invest US$1.5 billion over five years in an “All in AIoT” (AI+IoT) strategy.
Setting the scene for AI, IoT and 5G
Facing stiff competition from the likes of Huawei (with 42% of China’s smartphone market share in Q3 2019), Xiaomi is aiming to sustain business growth in the face of a challenging smartphone market. Xiaomi Corp is well versed with 5G and not a newcomer in the AI space. They already make 5G devices, and AI has been embedded in Xiaomi’s technology ecosystem such as messaging, instore applications, smartphones, laptops, TVs, routers, speakers, and other smart devices. In fact, Xiaomi Corp claims to have the world’s largest consumer IoT platform with more than 213.2 million smart devices (excluding smartphones and laptops) connected to its IoT platform.
Commenting on the Xiaomi’s competitiveness amongst Chinese smartphone makers and market potential for AI, IoT and 5G globally, Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Tim Sheedy said “Xiaomi has had some recent successes as a smart device maker, with its robot vacuums and other devices quickly earning positive reviews and gaining market recognition. Xiaomi has been able to surpass many traditional players which demonstrates their capabilities of competing in the IoT/smart devices category.”
On the 5G capability aspect of Xiaomi Corp, Sheedy said, “it is early days for 5G – even in China – and the stated position of having many 5G devices in the market could put Xiaomi ahead of some of their competitors in relation to availability. Going forward, it will be interesting to look at the integration of AI, IoT and 5G by Xiaomi.”
Sheedy further added, “we can expect Xiaomi devices to get smarter and more interconnected. Xiaomi actually has the opportunity to take some of the home-centric device hubs out of the ecosystem as they connect straight to the 5G network, and are controlled by an intelligent cloud-based hub perhaps mostly accessed through Xiaomi mobile phones.”
Meeting the Cybersecurity standards
Cybersecurity concerns are common around Chinese device makers. Recently, Xiaomi wireless devices have been disabled from connecting to Google’s Nest devices due to security flaws. On top of this, there have been concerns over the last few years about how Chinese tech companies secure their products and who has access to the data.
“Privacy and security are concerns for consumers – but they are often trumped by convenience, features and off-course price. Xiaomi Corp is aiming to make some of the best devices in each category and as long as they respond quickly and openly to privacy issues, they are likely to continue to see success both inside and outside of China. Their focus on driving down costs in order to be a price leader will help them with this challenge too” said Sheedy. “Ultimately, the privacy and security issues will impact the entire market – not just Xiaomi or other Chinese vendors as the users will steer away from all “smart, connected devices” – not just those from specific suppliers.
Market Positioning Approach
Xiaomi Corporation’s philosophy is to do more business with smaller margins, which drove it to expand its smartphone market from China to other areas like India and Europe. The company is aiming to strengthen its positioning in the consumer electronics market with further tech investments.
Sheedy explains that “considering the fact that they are losing market share in handsets in China, I would imagine that they will double down their efforts to be better at what they do now – not enter entirely new markets. I expect that we will see them produce smarter, connected devices – getting into more of the home and consumer market rather than move into the enterprise market. The enterprise market requires different sales strategies and channels, different partners, different margins, different support mechanisms etc.”
Naturally, Xiaomi is not alone in investing heavily in next-generation technologies. For example, Huawei opened a dedicated IoT consumer lab at the end of 2018 and is continuing to commit resources to the development of this industry-changing technology.
“The 5G plus AIoT strategy is the right one for Xiaomi. They need to surround their competition and make their products better, smarter and more affordable. With the growth in 5G services, a product leadership in this space, beyond smartphones – in smart devices too – will set them up for continued success in what is a very competitive market” said Sheedy.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is perhaps the most electrifying and controversial of the so-called “disruptive” technologies. As AI becomes more sophisticated and the technology evolves, it will increasingly help to perform more complex tasks whether for personal or commercial use.
Today’s AI machines can replicate certain elements of intellectual ability and they are constantly striving to achieve more. This includes applications of autonomous vehicles, domestic and industrial robots, surveillance and security, automation, personal assistants, forecasting, data analysis and more.
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals top drivers of AI adoption. Organisations are trying to incorporate AI in their existing processes for better competitor analysis and insights, cost-effectiveness, deeper customer engagement to provide personalised service/product offerings, and for process redesign or automation.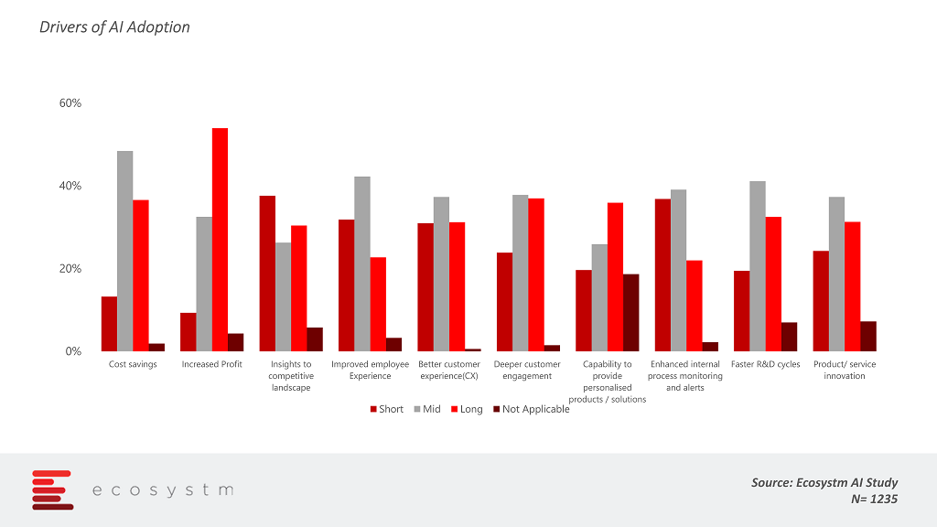
AI supporting technologies
AI is driving important technologies and processes and driving better, faster and more accurate decisions which help processes run more effectively and efficiently. With AI insights, business strategies will be more information-driven, efficient and consistent.
There are certainly many benefits that organisations are deriving from AI. Ecosystm AI study reveals that organisations implementing AI are using it to drive various business solutions including billing management, supply chain optimisation, predictive maintenance, enhancing operations and more.
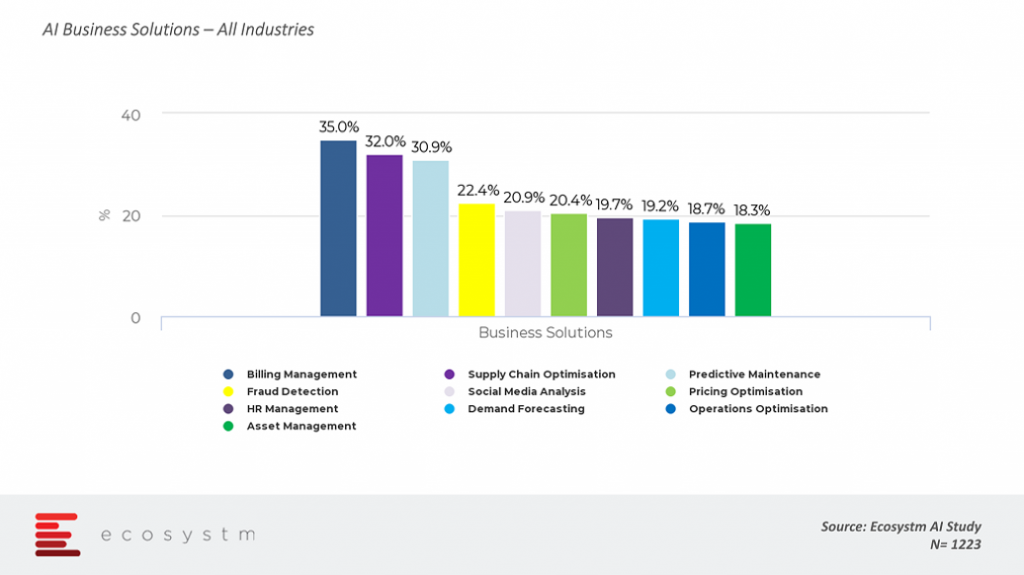
Below is a list of some hot technologies driven by AI.
Advanced Analytics
The proliferation of Big Data has led to the creation of massive data sets that can only be effectively analysed with AI tools and statistical models. AI can spot complex patterns in the data which is difficult for humans to understand. AI’s usefulness as an analytics tool is highly gaining importance in the use of predictive analytics and decision automation. Once sufficient data is available for use by AI, which is further filtered and processed thoroughly, the system can suggest actions or outcomes based on various parameters such as trends, patterns, historical information, frequency and more.
For example, the financial services industry is using advanced analytics to evaluate how customers earn, invest, spend and make financial decisions, which is useful for the organisations to customise their customers’ preference and offerings accordingly.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and speech recognition
NLP involves the learning of languages by machine through the means of interaction between computers and unstructured speech/text. NLP requires massive processing power and complex algorithms to reinforce learning mechanisms. To help in NLP, AI generates models, which are further improved to create NLP and speech simulations. Nowadays, Natural language is being implemented and used in various conversational interfaces, such as those with bots, artificial learning agents that can generalise to new environments, and autonomous vehicles.
Cognitive processing
Otherwise known as semantic computing, refers to a digital processing that attempts to mimic the operation of the human brain. In general, semantics means the meaning and interpretation of words and sentence structure and how words relate to other words. So, how is semantic related and what is the semantic analysis used for in AI? Semantic technology processes the logical structure of sentences to identify the most relevant elements in the text to understand the topic. It is especially suited to the analysis of large unstructured datasets with high efficiency.
Vantagepoint has an artificial intelligence tool to improve their trading results. It has a patented tool which can forecast stocks, futures, commodities, Forex and ETFs and claims an accuracy of up to 86%. The tool can predict changes in market trend direction up to three days in advance thus enabling traders to get in and out of trades at optimal times with confidence.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA has grown out of Business Process Automation (BPA) and refers to the use of AI to automate workflow and business processes. The advantages of RPA demonstrate it to be a solid tool in attaining higher quality output at lower costs which is much quicker than traditional methods. RPA can be used in IT support processes, back-office work, and workflow processes. The rules are programmed, and bots extract structured inputs from applications like Excel and enter them into other software such as CRM, SCM or accounting. A good example is the use of NLP to scan incoming emails and undertake the appropriate action, such as generating an invoice or flagging a complaint in an automated manner.
Machine Learning
Machine learning is an application of artificial intelligence (AI) which involves a combination of raw computing power and logic-based models to simulate the human learning process. Machine Learning is proving to be a successful approach to AI. When humans learn, they alter the way they relate information and the world, similarly when machines learn, they alter the data and form it into a piece of information.
An example, Image recognition is a popular application of machine learning in which images are fed into an algorithm, which attempts to recognise the contents of the image based on patterns. For instance, Yelp’s machine learning algorithms help the company’s human staff deal with tens of millions of photos to compile, categorise, and label the images more efficiently.
Chatbots and virtual assistants
Chatbots are robotic processes which simulate human conversation and automate functions. The technology is also used for so-called ‘virtual assistants’, which uses AI to interact with humans and aid with specific queries. They are increasingly being used to handle simple conversation and tasks in B2B and B2C environments. The addition of chatbots reduces human assistants and they can work throughout the clock. Chatbots and Virtual assistants improve with AI and can be trained to review conversations, past transactions and to draft a response based on context. If the user interacts with the bot through voice, then the chatbot requires a speech recognition engine.
Chatbots have been used in instant messaging (IM) applications and online interactive platforms. To exemplify, chatbots are deployed to assist online shoppers by answering noncomplex product questions, pricing, FAQ’s, order processing steps or forwarding information to human agents on complicated questions such as shipping delays or faults.
With AI technology evolving and improving so rapidly, many organisations are looking to use AI in their business, but there are still many questions to which adopters are seeking answers such as how to integrate AI into their existing systems, how to get access to data that will enable AI as well as the persistent technology concerns around cybersecurity and cost. The goal of many AI providers is to reach a stage where AI will support humans, control machines for us and automate repetitive tasks and processes.
Artificial Intelligence has come a long way and was one of the growing areas in 2019. Over the last few years, we have seen a growing number of AI based platforms, applications and tools that developers and scientists have worked to mimic a human brain. We believe that in 2020, AI will come out from the experimentation stage to the implementation and businesses will make deeper investments in AI to embed them in business applications.
This article presents the Top 5 Artificial Intelligence Trends for 2020 for the AI/Analytics market in 2020. It is based on the latest data from the global Ecosystm AI Study, and qualitative research by Ecosystm Principal Advisor Tim Sheedy.
The Top 5 Artificial Intelligence Trends for 2020
Here are the Top 5 Artificial Intelligence trends for 2020 that we believe will impact both businesses and consumers in 2020.
-
Digital Transformation puts Analytics Back on Top of the Tech Priority List
In an effort to help the business operate faster, IT teams are looking to better analytics to drive functions and decisions more accurately. While many business teams deploy their own technologies and systems – only the IT team is in a higher position to gather data from multiple systems of record in order to create the detailed insights that business users demand. Getting a view across the entire customer journey means analysing data across many systems – both front and back-end. Business teams struggle to get these types of insights on their own, which is why IT excels at providing great analytics to help make better and faster decisions.
Just like in previous generations of BI, the analytics market is starting to consolidate. While the ability to display data visually will always be important, it is the analytics that drives automated decisions that will often be of the most business value.
-
Automation will Lead Organisations to AI
RPA is increasingly moving beyond the usual task and process automation, to now being a business transformation lever. Additionally, there is an immense focus on incorporating AI/machine learning within RPA to make automation smart and intelligent. This allows software robots to mimic human behaviour and handle complex use cases, which was earlier not possible without human intervention.
Businesses will spend more money on their simple automation activities (RPA and analytics applications that do not learn) – but those that have already invested in automation are likely to want to take the next steps to AI.
-
AI will Start to be Embedded in Most Business Applications
To date AI has been an overlay to most applications – data is extracted from processes, learnings are made, and then the process is altered based on those learnings. In 2020 we will see mass availability of self-learning intelligent applications. The standard ERP, CRM, SCM, knowledge management solution and other business applications will have embedded intelligence. This will make it easier and faster for businesses to get the benefits of machine learning and AI without the need to hire expensive data scientists, or the requirement to learn the tools and platforms required for creating smart applications.
-
2020 will see the Democratisation of AI
Typically organisations required data scientists, AI coders, AI platforms and so on to do well in AI but with the increasing availability of AI in business applications, typical business users will begin to get a glimpse of what will be available at their fingertips in the next few years.
We expect templatised approaches to machine learning and associated technologies. Business users and data owners will be able to create algorithms that will improve business and customer outcomes. In some cases, we even expect AI to be available to consumers. We will start to see banking and finance applications that help better money management through learning – not just basic analytics, we will see more intelligent services in the market in 2020.
-
More Businesses Will Require AI on the Edge
In the next decade or two, it is estimated that there will be 100 billion IoT devices generating and exchanging data into the cloud, without any human intervention. With so many IoT devices generating a huge quantum of data, decisions will need to be made in real-time and the current cloud environments will be a bottleneck in data processing due to latency rates, network speed and traditional data architectures. To overcome this, Edge Computing solutions will be essential to work with a variety of sensor and data input devices, information processing and decisions driven by machine learning and AI, and additionally work with cloud for the next level of analytics, decisions and management.
Ecosystm in partnership with SGInnovate, the government-backed organisation that promotes Deep Tech in Singapore, released a series of four reports covering areas of mutual interest: Cybersecurity, Artificial Intelligence, Cities of the Future and Healthtech. ‘Ecosystm Predicts: The top 5 Artificial Intelligence trends for 2020’ report is a part of this collaboration and is available for download from Ecosystm and SGInnovate websites.
Download Report: The Top 5 Artificial Intelligence Trends for 2020
The full findings and implications of the report ‘Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Artificial Intelligence Trends for 2020’ are available for download from the Ecosystm website. Signup for Free to download the report and gain insight into ‘the Top 5 Artificial Intelligence Trends for 2020’, implications for tech buyers, implications for tech vendors, insights, and more resources. Download Link Below ?

++Update: A few days after we added this story, Australia released its AI roadmap focused on future investment in AI and machine learning, and Artificial Intelligence: Australia’s Ethics Framework.
Over the last few years, many countries have created plans to harness Artificial Intelligence (AI) for better citizen services. At this week’s SFFXSWITCH (Singapore FinTech Festival and Singapore Week of Innovation and TeCHnology), Singapore announced the next step in its Smart Nation initiative with the release of the “National AI Strategy”. The AI strategy will focus on social and economic benefits by providing modern infrastructure, intelligent services, and an excellent education system to citizens.
Commenting on Singapore’s AI adoption and implementation strategies, Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Tim Sheedy said “being a smaller country, Singapore is one of the few around the globe that can make investments into AI at a ‘country level’. Singapore has the luxury of having a progressive public sector that operates at the same speed as the private sector, and has the opportunity to become one of the leading economies in the world for both the deployment of AI in everyday services AND in ensuring the economy has the required skills.”
The key approach of the AI strategy
Singapore is aiming to position itself as a global hub for the development and implementation of AI solutions. National AI Office established under the Smart Nation and Digital Government Office (SNDGO) will be heading Singapore’s AI initiatives.
To begin with, the SNDGO will be initially working on key high-value sectors:
- Transport and Logistics: Intelligent Freight Planning
- Smart Cities and Municipal Services: Infra management and smart services
- Healthcare: Chronic Disease Prediction and Management
- Education: Personalised Education
- Safety and Security: Seamless border clearance operations
Speaking on AI strategies devised for transportation, smart cities, healthcare, education and safety and security in Singapore, Sheedy said “all of these investments are ones that you would make as an economy if you had the opportunity. They are all logical and will all benefit the lives of citizens and the success of the overall economy.”
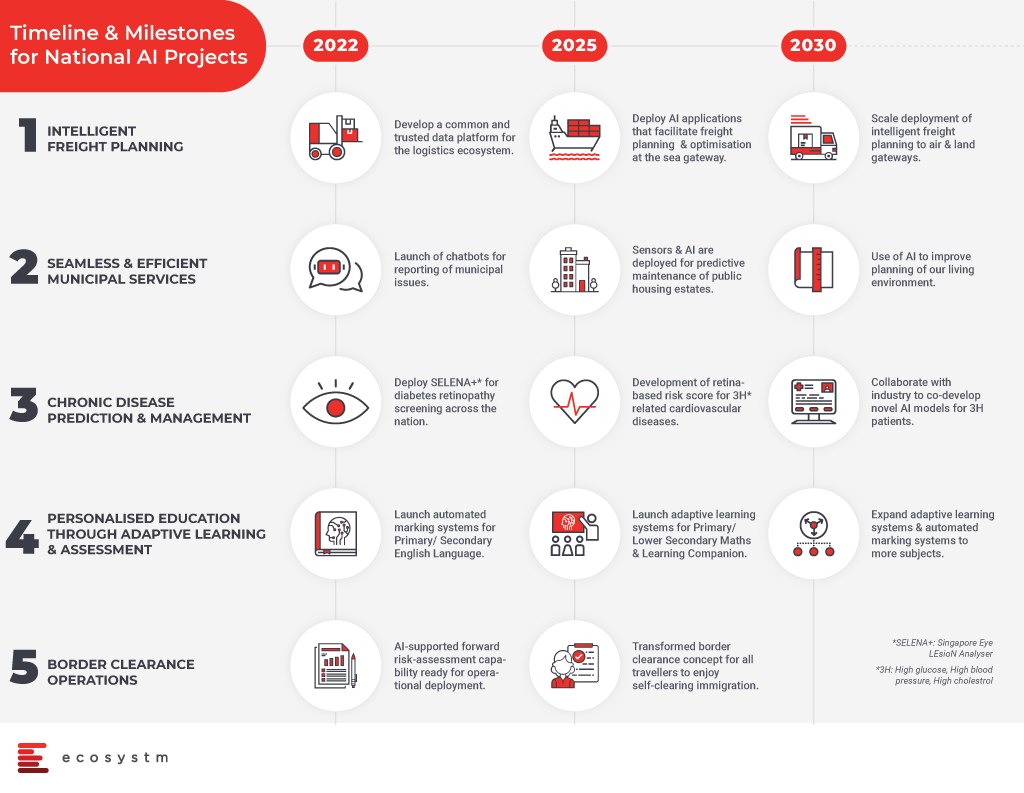
Transport and Logistics: To optimise the freight and delivery services, a common data platform will be built. The aim is to bring in efficient transportation and logistics with intelligent AI systems in place by 2022 and further AI developments will scale deployment, enable optimised delivery processes and routing of services for freight planning.
Smart Cities and Estates: The country aims to launch AI powered chatbots by 2022 to record municipal issues and allocate them to the responsible authorities. AI powered services will be introduced to better serve the residents. By 2025, efforts will be established to optimise estate maintenance through AI and sensors and by the year 2030, data driven insights will be used to improve the infrastructure and living environment in Singapore.
Healthcare: An all-new AI system known as SELENA+ will be in place to screen and detect diabetic eye disease. SELENA+ is a first artificial intelligence algorithm which performs automated retinal photo analysis to detect retinopathy and systemic complications in diabetics. In addition to this, AI capabilities will also be used to predict cardiovascular diseases and create personalised chronic risk scores. All of these will help to detect diseases and take early preventive measures by the healthcare teams for the welfare of country and betterment of the economy.
“This could detect chronic issues early, and reduce the impact of them on individuals, families and the economy. Being able to make investments at a macro level – like this happening in Singapore – will make sure everyone benefits” said Sheedy.
Education: AI in education will bring the benefits of automated marking systems for English language in primary and secondary education. Further, AI-enabled learning systems will help students on learning and mastery of topics. The government has planned to expand automated AI and adaptive learning systems to more subjects at a later stage.
Sheedy said, “with the government being able to influence and change the syllabus in schools and universities, as well as the skills in the public and private sector, Singapore is uniquely positioned to drive real economic benefit from their investment into AI.”
Safety and Security: AI systems will help in border security and clearance procedures. AI will enhance travel experience with automated immigration clearance systems involving face and iris scans. The immigration processes will develop into seamless self-clearance systems and become faster.
“A few countries have the ability to drive this level of planning – most countries have many levels of government which make this planning – or execution of plans – difficult.” said Sheedy. “Many are also leaving the investment to the private sector, which means it will happen eventually, but may see many competing initiatives or different capabilities emerge that only benefit a single company, not an entire economy.”
Smart Nation drive
Singapore’s government is highly active in transforming the country into a smart nation. Singapore was working with the World Economic Forum’s Centre for Fourth Industrial Revolution (WEF C4IR) in order to come out with a framework for ethical and responsible AI adoption and deployment by the Asian governments.
Singapore is also set to invest US$ 360 million on AI and other digital technologies through 2020 and has invited Chinese and American companies to be a part of this.
According to Sheedy, there are many benefits of having deep investments in AI and AI capabilities in an economy.
It will make Singapore a more attractive investment location. If access to government and other services are seamless, then the barriers to entry to starting a new business or creating a new business capability will be much lower. It will mean that it is easier to build a business case for businesses to move to Singapore or start in Singapore – attracting investment funds and employment into the island state.
It will boost export capabilities – both for the skills that will be in demand through technology and business service providers and for the intelligent products and services that will likely emerge from the early AI investments. If Singapore can make more of the products and services that they produce “smart” – then these products and services will see increased demand – both locally and outside of Singapore.
It will make Singapore a better place to live and visit. With seamless government services, easier travel into and out of the country, and a government that anticipates the needs of its citizens, the quality of life for residents will increase.
The country can get ahead of the challenges and downsides of AI – and legislate or plan for these challenges, to ensure these challenges are understood and managed before they become problems.
In the escalating initiatives to become an AI superpower, Singapore has clearly indicated they are fully committed to leveraging AI to drive growth and citizen services.
++Update
An AI roadmap report was published by the Australian Government in November 2019, co-developed by CSIRO’s Data61 and the Department of Industry, Innovation and Science. The report identifies the opportunities and benefits of AI that Australia could capture.
The report classifies the strategies to help develop AI capabilities to boost the productivity of industry, generate jobs, bring economic growth, and enhance the quality of citizens’ life. To drive this, Australia has identified 3 key areas where it has the best opportunity to create new value-
Health, Ageing, and Disability – To develop AI to improve healthcare, aged care, and disability services while reducing healthcare costs.
Cities, Towns, and Infrastructure – To develop an AI system for the cities and infrastructure to provide better services, safety efficiency in a smart and cost-effective way.
Natural resource and environment management – Develop AI for better natural resource management and improve the productivity of agriculture, mining, fisheries, forestry, and environmental management.