Thailand has emerged as a key player in the 5G space in Southeast Asia. In February 2020, Thailand’s telecom regulator, NBTC auctioned 48 5G licenses to boost the development of Thailand’s digital economy. Later in the year, Thailand also announced the formation of the National 5G Committee to coordinate the 5G development roadmap with the digital economy vision.
The Future of 5G in Thailand
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Shamir Amanullah says, “The transformational nature of 5G, unlike its predecessors, is expected to boost adoption of IoT, smart manufacturing and broader Industry 4.0 initiatives to drive the economy. NBTC expects 5G technology to contribute over US$ 15 billion to the GDP in 2022. Key sectors expected to adopt are Healthcare, Manufacturing, Education and Agriculture.”
We are already seeing initial applications of 5G. “AIS and True have been launching 5G networks in hospitals across Thailand to support medical personnel in their fight against COVID-19. Telemedicine and robots using 5G are being used to prevent contact between affected patients and medical personnel. AIS has launched 5G networks in 158 hospitals in Bangkok and other major cities.”
Amanullah adds, “The changing landscape of remote working caused by COVID-19 has increased network traffic, especially a spike in the video, further amplifying the need for 5G infrastructure. The onboarding of many new digital users and increased adoption of digital solutions by businesses has whet the appetite for more speed, latency and more innovative services. 5G first-mover advantage is key especially for the major operators who can achieve significant scale in their new service offerings.”
The Thailand 5G Landscape
The major telecom providers bid for multiple licenses across different bands. While AIS and True bid for and won more licenses, other telecom providers such as DTAC are aiming more for a niche presence. They only bid for the high band 26 GHz auction, winning two out of the possible 26 licenses for 100 MHz blocks.
Amanullah discusses the benefits of different 5G bands. “The 700 MHz band covers large geographic areas while also being able to penetrate walls easily making it a highly valuable spectrum asset. The 2600 MHz band is attractive as most smartphones already have this radio.”
“The 26 GHz band provides for high-frequency spectrum, also known as mmWave spectrum. This band offers high-speed data and capacity but with a limited range. Applications expected to be used in the mmWave include virtual and augmented reality and remote health services. While DTAC has a smaller spectrum holding compared to AIS and True, they plan to complement with their coverage band to offer 5G services. The company is also believed to be keen in the 3500 MHz mid-range band when it becomes available. This band is currently occupied by satellite operator Thaicom.”
DTAC-NetFoundry Partnership
DTAC and NetFoundry recently announced a collaboration, to introduce a new network service dubbed as SmartConnect. SmartConnect is a network service which allows organisations to manage the network and cloud computing in a unified platform thus increasing efficiency, speed and security.
The partnership will enable both small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and large enterprises to leverage cloud-native networking capabilities to boost performance while increasing security when connecting to a cloud environment. SmartConnect service will replace traditional set-ups involving hardware, VPN devices by providing a new virtual network for organisations. This is expected to empower business users to access cloud-based data quicker – with eight to ten folds speed – than a conventional network in a highly secured environment at a fraction of a cost.
Amanullah says, “The Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) features in 5G – where a customised network service based on bandwidth speed or latency, specific to a variety of 5G use cases – brings an exciting new business and potentially lucrative opportunities. Network slicing allows for many virtual networks on a single physical network and NaaS theoretically allows for a customer to request for a tailored network service required. NaaS delivers virtual network services on a subscription basis which has the potential to be an exciting game-changer.”
DTAC is clearly gearing up for the changes in the industry. The SmartConnect service can become a true differentiator for them. It also gives an opportunity to DTAC to leverage NetFoundry’s integration with Azure, AWS and GCP to enhance cloud connectivity services and provide value to their enterprise users.
As the telecom industry transforms, it will see more such partnerships between telecom providers and technology vendors.
The 5G rollouts in Australia by Telstra, Optus and Vodafone will impact consumers and enterprises alike. It is expected that enterprises will see an uptick in IoT adoption, leveraging the lower latency to connect devices for real-time data transfer and insights. Industries, especially those that operate in remote and rural regions of the country such as Agriculture and Mining are expected to benefit immensely.
“However, there are challenges to leveraging digitalisation effectively, including a lack of awareness, knowledge and skills, and funding to support innovation and scale, in aligning with the growing pressure within sectors to meet increasing productivity and compliance requirements,” says Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Jannat Maqbool. “Adoption of IoT specifically is resulting in new data supply chains, that those operating in many industries cannot cater for with respect to infrastructure and also the skills necessary to process and extract valuable insights from the data.”
Ecosystm research shows that only 37% of organisations looking to adopt IoT in Australia have a strategic internal team to create the roadmap and manage the deployment. This indicates a lack of skills that organisations can utilise, depending on external resources such as consulting firms and ISVs instead. To cater to the expected growth in Australia’s IoT market, IoT Alliance Australia (IoTAA) – that represents more than 500 participating organisations and 1,000 individual participants – has come forward with the IoT Australia Skills Barometer survey.
The survey created in association with La Trobe University aims to gauge the IoT skills gap, to inform educators and adopters on the potential areas of focus for future skills development. It covers questions on IoT adoption, challenges expected, solutions being evaluated, and courses needed.
Addressing the Skills Gap
As the adoption of IoT increases, there will be added requirement for skills in data storage, infrastructure management and creating frameworks. The survey is expected to help the industry determine the skills gap, isolate training and re-skilling requirements and develop courses and hands-on sessions to address the end-to-end services requirements and better utilisation of data gathered from the devices.
There are some courses that are already available – mostly run in collaboration with industry. Last year, Rio Tinto, the Western Australia Government and South Metropolitan TAFE developed Australia’s first nationally-recognised remote operations course. Earlier this year, RMIT partnered with IBM to deliver the IoT and 5G business opportunity courses to equip business professionals with the right technology and business skills for IoT projects.
“Awareness of the potential of emerging technologies needs to target both non-technical and technical members of the organisation. This wider buy-in is needed to drive thinking around the ‘why’ from stakeholders across the business, enabling a more informed decision around the potential impact on existing resources, infrastructure, processes, products, required investment and business outcomes,” says Maqbool. “Any education and training program needs to allow for this focus on awareness, then provide opportunities to build on this for those that then want to gain the deeper knowledge and technical skills required to effectively leverage the IoT.”
“Education and training programs to support the uptake of digital technologies across the wider population and traditionally non-digital industries require a contextual learning and a flexible delivery approach.”
Government and Industry working together
“A digital divide exists in many countries – especially for those in rural communities. They are often not in a position to access the infrastructure necessary to support a real-world connection in a contextual learning environment, let alone having the digital literacy and scaffolding to get to a point where they can effectively consider leveraging emerging technologies,” says Maqbool.
This is where governments play a larger role. To accelerate innovation and make better use of technology the Australian Government is supporting clear communication and a better understanding of IoT, implementing standards and regulations, upgrading digital infrastructure, creating opportunities for economic and social benefits and collaborating with research and education institutes to deliver skills, innovation and growth in the IoT sector.
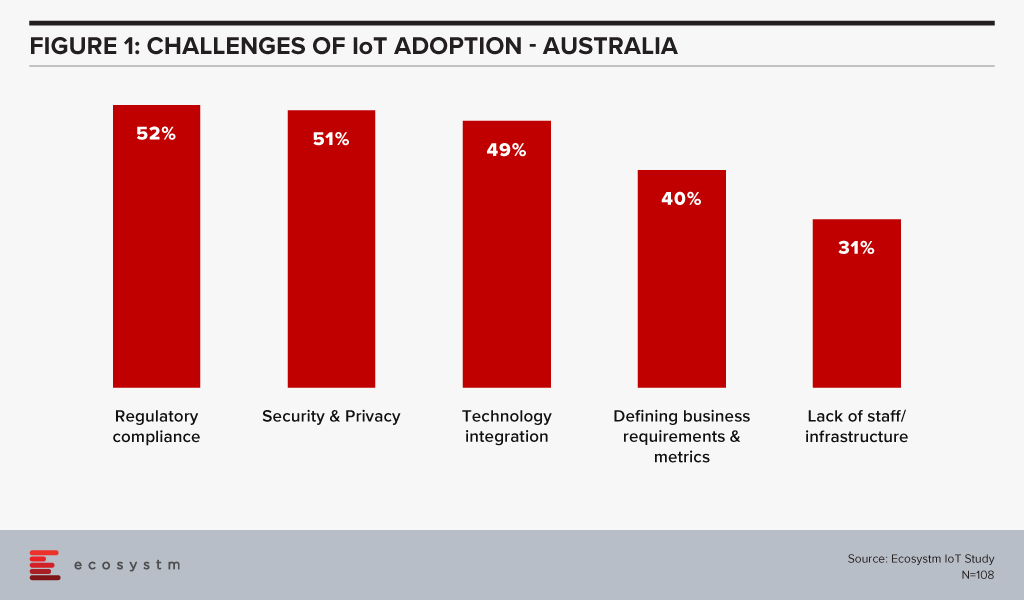
One of the key areas of focus will have to be cybersecurity. Regulatory compliance and security & privacy issues are the key barriers of IoT adoption in Australia (Figure 1).
Last year, the Australian government released a draft code of practice to enable businesses implementing IoT solutions to follow certain principles as a voluntary measure to defend against threats.
The Government is also seeing a larger potential for IoT in some industries. To support the Agriculture industry, the Australia Government has allocated USD 90 million to the Smart Farms program to support the development and uptake of best practices and technologies in farms, fisheries and forestry, with a special focus on regional communities. In its FY2019-20 federal budget, the Government announced plans to invest USD 1.4 million for a feasibility study and assess ways on improving digital on-farm connectivity. Similarly, Australia’s National Landcare Program (NLP) delivered by the Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment (DAWE) is receiving financial support until June 2023.

Australia’s data centre market has grown exponentially, to a large part due to the Government’s strong policies around cloud adoption. This is in line with the vision of creating a Digital Economy by 2025. Australia’s Tech Future talks about technological changes in 4 key areas including building infrastructure and providing secure access to high-quality data. Availability of local data centres is key to building better infrastructure to support the Digital Economy.
Cloud adoption, especially in the small and medium enterprise (SME) sector is expected to continue to rise. The Ecosystm Business Pulse Study shows that only 16% of Australian organisations had not increased their cloud investments after the COVID-19 crisis and its impact on the economy.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Tim Sheedy says, “The current pandemic has highlighted the digital ‘haves and have nots’ in Australia. The NBN has helped to narrow the gap, but too many in rural and regional Australia continue to suffer the tyranny of distance. Businesses and government departments have been reluctant to relocate outside of the major cities due to the lack of internet and data centre infrastructure. Investing in data centres in rural and regional locations will not only help to close the digital divide but also remove a significant barrier that stops businesses from investing in and relocating to locations out of cities.”
Growing Australia’s Data Centre Footprint
This week, Australia’s Leading Edge Data Centres and Schneider Electric announced a AU$30 million project where Schneider Electric will provide Tier-3-designed prefabricated data centre modules for Leading Edge’s six locations in Australia. Each site will host 75 racks with 5kW power density to support computing operations and minimise data exchange delays. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Darian Bird says, “The inaccessible nature of some sites makes them suitable for prefabricated data centres, which are plug-and-play containers that can be set up and maintained by a relatively small IT team. Standardisation in edge data centres and automation are key to remote management for anyone deploying distributed infrastructure.”
This announcement follows the news that Leading Edge has secured an investment of AU$20 million from Washington H. Soul Pattinson to construct 20 Tier-3 data centres across Australia. They have also received funding from the SparkLabs Cultiv8 2020 accelerator group. The funding will be used to build more than 20 Tier 3 data centres across regional Australia to provide faster internet speeds and direct cloud connectivity.
This will impact businesses that host mission-critical applications, and stricter uptime requirements, and is expected to benefit IoT, AgriTech and telecom industry applications.
Impact on Industry
Edge connectivity will create a seamless experience for the users to take advantage of faster computing with a local host, lower latency by taking connectivity to where operations reside, and data sovereignty by keeping data within the region, aiding in the development of Australia’s Digital Economy.
Sheedy sees this as an opportunity for primary industries. “One of the real challenges for farms and other agribusinesses investing in IoT and other tech-based solutions has been the lack of local or nearby computing infrastructure that will support applications that require low latency. Leading Edge’s investments in providing data centres in rural and regional Australia will mean these businesses can accelerate their digital transformations.”
With the simultaneous rollout of 5G, Smart City initiatives will also benefit from edge data centres. “Investment in edge infrastructure is likely to take off and follow the 5G coverage map across Australia. We will see operators take advantage of their vast network footprint and combine micro data centres with some 5G antenna locations,” says Bird. “Smart City initiatives will be made possible by 5G connected IoT devices but computing at the edge will be needed to keep, for example, public safety systems, operating in real-time. Many monitoring systems will require local data analysis to be effective.”
Bird also sees potential impacts on the Entertainment industry. “The COVID-19 restrictions and the launch of new services such as Disney+ and Binge in Australia will ensure streaming video continues its impressive growth trajectory. Even facilities such as sports stadiums are beginning to deliver in-person digital experiences to grab back attention from their online competitors. Positive user experience is crucial here and low latency is a must. We’ll see a shift towards edge computing delivered on-site as part of a distributed network. Regional data centres and local caching have always been vital for content delivery to ensure the quality of service and reduce bandwidth costs but the scale is unprecedented.”
Bird talks about potential retail opportunities in the future. “We may see anchor tenants at malls offering their excess capacity to smaller, nearby stores that need the benefits of edge but can’t justify the investment, similar to the way Amazon launched AWS.”
The opportunities that can be created by 5G continue to excite businesses and consumers alike. As 5G rollouts gather pace, new consumer experiences and business models emerge. For consumers, enhanced mobile broadband offers superior experience, driving the consumption of much more data-rich content and the more widespread application of emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR). For businesses, the low latency, higher bandwidth, and the ability to handle massive machine type communications promised by 5G create opportunities for a dizzying array of uses cases, usually linked to IoT technology.
As enterprise use cases like autonomous driving, remote surgery and software-defined factories are enabled by 5G, the impact of cybersecurity breaches becomes much greater. Breaches can potentially have a catastrophic impact – they could lead to serious damage to or the destruction of sensitive critical infrastructures, such as power stations and transportation systems.
Security vulnerabilities associated with 5G are underpinned by a change in network architecture. The latency benefits of 5G require a more distributed architecture to enable use cases which require real-time data processing. This leads to the virtualisation of higher-level network functions formerly performed by physical appliances. So 5G networks will necessarily create a greatly expanded attack surface. If an attacker gains control of the software managing the networks, they can also control the network and potentially cause chaos.
One of the major benefits of 5G is massively increased bandwidth. This is also a huge benefit for attackers. An increase in available bandwidth makes it much easier to generate attack traffic from compromised connected devices and vulnerable networks. As volumetric DDoS attacks grow in terms of frequency, magnitude, and sophistication, traditional defences such as out-of-band scrubbing centres and manual interventions become inadequate and expensive.
In a 5G World, Security Postures must be Agile and not Act as a Bottleneck to Performance
5G use cases require a radical shift in cybersecurity posture and a new set of security considerations. Networks managed by enterprises and service providers need to scale up to handle larger capacity requirements and scale out to accommodate the increased demands of edge computing and the growing volumes of IoT endpoints. Security infrastructure must change accordingly with upgrades to both physical and virtual components. Importantly, security postures must also be sufficiently agile to change with new requirements while ensuring that security does not act as a bottleneck to network performance.
A common response to the increasing complexity of distributed cloud and IoT environments – where existing tools cannot always detect new and emerging threats – is to deploy brand new security tools. This seems like a great solution but can lead to significant problems and compromise security. Over time, the deployment of multiple security tools creates an estate of siloed security products, sometimes reporting to their own dashboards. Although this management challenge is typically being addressed by service providers and large enterprises, most commonly with SIEM, they must continually ensure that there is provision for the centralisation of security alerts, so that cybersecurity staff do not face the challenge of monitoring multiple consoles and cross-referencing between disparate screens and information formats. Applying security policy changes is a laborious and time-consuming task in a multi-dashboard environment – representing a security threat in its own right.
In the case of large volumetric attacks, redirecting suspicious traffic to scrubbing centres adds latency and imposes a significant financial burden, since mitigation costs are directly tied to the volume of the data traffic. Large enterprises and service providers should consider adopting new DDoS protection approaches that incorporate AI, real-time analysis, and telemetry to automate a more intelligent and cost-effective detection and mitigation process.
Different Policies Required to Reflect Specific Needs of Each Use Case
5G allows mobile service providers to partition their network resources, to address a diverse set of use cases with differing performance and functional requirements. These varying service performance profiles have a direct impact on security protocol choices and policy implementation. For instance, the service in one use case, such as a Smart City application, may require extremely long device battery life, which constrains the security protocol in some other way (e.g., how often re-authentication is performed). In another example, the use case may be very privacy-sensitive, requiring unusually intensive security procedures (e.g., very frequent reallocation of temporary identities).
The complexity associated with securing highly distributed and virtualised networks powered by 5G, will grow enormously and be hampered by an ever-increasing skills shortage. The only way to address these challenges is to create an intelligent security infrastructure that is sufficiently agile to scale with the network and use AI to detect, contain and eliminate threats. Security managers will need a unified view of all assets – physical and virtual – so that multiple security policies can be enforced and managed.
Manufacturing is estimated to account for a fifth of Singapore’s GDP and is one of its growth pillars. Singapore has been talking about re-inventing the Manufacturing industry since 2017, when the Industry 4.0 initiatives to enable digitalisation and process automation of processes and to ensure global competitiveness were first launched. As part of the long-term strategy, the Government had spoken about investment into research and development (R&D) projects, developing transformation roadmaps and strengthening the skill sets of the workforce.
Singapore’s 5G Rollout
Last month, the Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) announced that Singtel and JVCo (formed by Starhub and M1) has won the 5G Call for Proposal. They will be required to provide coverage for at least half of Singapore by end-2022, scaling up to nationwide coverage by end 2025. While Singtel and JVCo will be allocated radio frequency spectrum to deploy nationwide 5G networks, other mobile operators, including MVNOs, can access these network services through a wholesale arrangement. The networks will also be supplemented by localised mmWave deployments that will provide high capacity 5G hotspots.
In October 2019, IMDA and the National Research Foundation had set aside $40 million to support 5G trials in strategic sectors such as maritime, aviation, smart estates, consumer applications, Industry 4.0 and government applications. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Jannat Maqbool says, “Reach, performance and robustness of connectivity and devices have long held back the ability to scale with the IoT as well as successful deployment of some solutions altogether. The integration of 5G with IoT has the potential to change that immensely. However, and possibly even more importantly, 5G will see the emergence of a true ‘Internet’, defined as ‘interconnected networks using standardised communication protocols’, made up of ‘things’ enabling never-before contemplated innovation – supporting economic development and community well-being.”
“While 5G offers enormous potential to produce economic and social benefits, to reach that potential we need to evaluate from a strategic perspective what it could mean for industries, employers and communities – then we need to invest in the infrastructure, innovation and associated development required to leverage the technology.”
Singapore’s Industry 4.0 Transformation
The Government is also focused on getting the industry ready for the transformation that 5G will bring. Last week, Singapore announced its first Industry 4.0 trial, where IMDA collaborates with IBM, M1 and Samsung to design, develop, test and benchmark 5G-enabled Industry 4.0 solutions that can be applied across various industries. The trials will begin at IBM’s facility in Singapore and involve open source infrastructure solutions from Red Hat to test Industry 4.0 use cases.
The project will test 5G-enabled use cases for Manufacturing, focusing on areas such as automated visual inspection using image recognition and video analytics, equipment monitoring and predictive maintenance, and the use of AR in increasing productivity and quality. The focus is also on leveraging 5G to reduce the cost of processing, by shifting the load from the edge device to centralised systems.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Kaushik Ghatak says, “For some time now, the Singapore Manufacturing industry has been in the quest for higher productivity in order to regain its foothold as a destination of choice for global manufacturing outsourcing. The 5G Industry 4.0 trial is a great initiative to fast-track identification and adoption of the right use cases in Manufacturing, in the areas of automation, visibility, analytics, as well as for opening new revenue streams through servitisation of smart products.”
5G will see increased collaboration in the Tech industry
With the advent of 5G, the market will see more collaboration between government agencies, telecom providers and cloud platform providers and network equipment providers. Governments globally have invested in 5G and so have the network and communications equipment providers. However, telecom providers are unsure of how to monetise 5G and cater to the shift in their customer profile from consumers to enterprises. IBM and Samsung had already announced the launch of a joint platform in late 2019. Collaborations such as these will be key to widespread 5G deployment and uptake.
Talking about the benefits of collaborative efforts such as this, Maqbool says, “Robustness and security built into 5G deployment from the outset is essential to enable the applications and innovation that many are promising the technology will deliver, including the ability to self-scale, automate fault management and support edge processing.”
It is interesting that the solutions developed will be featured at IBM’s Industry 4.0 Studio 5G Solutions Showcase, and that IBM and Samsung will evaluate successful solutions developed during the project for possible use in their operations in a broad range of markets and sectors. “Availability of proven use cases at IBM’s Solutions Showcase centre would benefit local manufactures greatly; in terms of easy access to right skills and proven technology architectures,” says Ghatak. “This initiative is a huge step towards realising the promise of the cyber physical world. The collaboration between the leaders in communications, equipment and software will ensure that the use case development is truly cutting edge.”

April saw the disruption of normal business operations due to the COVID-19 crisis. However, telecommunications companies continued initiatives to identify the best ways to serve customers and enterprises. The month saw a lot of activity in the 5G space across the globe, including partnerships, innovation in productisation and identifying 5G use cases.
Telecom providers building their 5G capabilities
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Shamir Amanullah noted in his blog that in the new normal telecom providers have fast evolved as the backbone of business and social interactions. Telecom operators are fervently working towards 5G network and services deployment in order to be an early mover in the market. In China, China Mobile has been one of the leaders in rolling out country-wide 5G. The tender to build around 250,000 fifth-generation wireless network base stations across 28 provincial regions was put out in March and in early April, Huawei emerged as the key winner with the contract to build nearly 60% of the base stations. ZTE also won nearly a third of the contract. Global network equipment providers will find entering the China market as challenge for a number of reasons, including the strength of their local players.
Huawei continues to be under scrutiny in the global market, however British telecom provider chose Ericsson to build the core of its 5G network. BT hopes to create and define a future roadmap of new services such as mobile edge computing, network slicing, enhanced mobile broadband and various enterprise services. The US market is another arena where the battle for 5G will be fought out. The T-Mobile – Sprint merger was finalised in early April. The New T-Mobile is committed to building the world’s best nationwide 5G network, which will bring lightning-fast speeds to urban areas and underserved rural communities alike. Other vendors are also vying for a larger share of the US market. Nex-Tech Wireless, a smaller rural telecom provider based in Kansas, is planning to transition from 4G to 5G by using Ericsson’s Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) to deploy 5G on existing bands. This will help Next-Tech wireless to leverage existing assets instead of building 5G capabilities from the ground-up – enabling them to seamlessly transfer from 4G to 5G.
The 5G developments are by no means limited mostly to the US and China. Korea’s telecom provider, KT and Far EasTone Taiwan (FET) signed an MOU to collaborate and jointly develop 5G services and digital content. With this deal, KT plans to boost its 5G powered content and services presence through FET.
Tech Vendors evolving their 5G offerings
Network and communications equipment providers have much to gain and more to lose as organisations look to leverage 5G for their IoT use cases. If 5G uptake does not take off, the bigger losers will be the network and communications equipment providers – the real investors in the technology. Also, as telecom providers look to monetise 5G they will find themselves dealing with a completely different customer base – they will take help from tech vendors that have more experience in the enterprise space, as well as industry expertise. Both network equipment vendors and other tech vendors are actively evolving their product offerings. There were numerous examples of this in April.
Microsoft’s decision to acquire Affirmed Networks is an example of how the major cloud providers are trying to be better embedded with 5G capabilities. This month also saw Microsoft announce Azure Edge Zones aimed at reducing latency for both public and private networks. AT&T is a good example of how public carriers will use the Azure Edge Zones. As part of the ongoing partnership with Microsoft, AT&T has already launched a Dallas Edge Zone, with another one planned for Los Angeles, later in the year. Microsoft also intends to offer the Azure Edge Zones, independent of carriers in denser areas. They also launched Azure Private Edge Zones for private enterprise networks suitable for delivering ultra-low latency performance for IoT devices.
The examples go beyond the cloud platform providers. Samsung and Xilinx, have joined forces to enable 5G deployments, with Samsung aiming to use the Xilinx Versal adaptive compute acceleration platform (ACAP) for worldwide 5G commercial deployments. Versal ACAP offers the compute density at low power consumption to perform the real-time, low-latency signal processing needed by 5G. Following the successful pilot of 450 MHz proof of concept 5G network, Nokia has partnered with PGE Systemy, a large energy sector company in Poland to deploy industrial grade 5G solutions and to support energy distribution for its next gen power grid. It is the band of choice for machine-to-machine communications in the energy sector, including smart meters. Nokia also released an AI-as-a-service offering – Nokia AVA 5G cognitive operations – to help telecom providers transform their services with AI-based solutions to support, network, business and operations.
Use cases for 5G adoption firming up
5G promises to revolutionise various industry solutions based on required data rates, low latency, reliability, and machine-type communications. Telecom providers and tech vendors alike are working on developing industry use cases to drive up adoption.
Vodafone Qatar and Dreama Orphan Care Centre and Protection Social Rehabilitation Centre (AMAN) have collaborated to support remote learning and education using 5G technology. This is aimed to enhance virtual education through e-learning, online schools, and connecting teachers and students through high-speed learning environment. In the post-COVID 19 era remote learning is expected to become a key sector and there is immense potential for uptake.
The Manufacturing industry remains a top focus area for 5G providers, with their early adoption of sensors and sensor data analytics. The Smart Internet Lab at the University of Bristol, UK has been awarded a 2 years project by UK’s Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport (DCMS) to enable 5G connectivity for the manufacturing sector. The project will primarily work on improving productivity and manufacturing, easy asset tracking and management with involvement of AR/VR technologies and industrial system management.
Gaming is another sector with huge potential for 5G adoption. With cloud gaming, gamers can access a library of popular high-quality games minus the need for expensive hardware which has been the case in the past. China Mobile Hong Kong and Ubitus teamed up to launch a 5G cloud gaming service – UGAME. The application is available for download from the Google Play store. While still at a beta phase, the telecom provider promises a revolutionary gaming experience, where the need for computers or consoles will be lessened by augmented smartphone capabilities.
In the midst of the uncertainties, telecom, network equipment providers and cloud platform providers appear to be gearing up for 5G in enabling a contactless and remote economy.
In The Top 5 Cloud trends for 2020, Ecosystm Principal Analyst, Claus Mortensen had predicted that in 2020, cloud and IoT will drive edge computing.
“Edge computing has been widely touted as a necessary component of a viable 5G setup, as it offers a more cost-effective and lower latency option than a traditional infrastructure. Also, with IoT being a major part of the business case behind 5G, the number of connected devices and endpoints is set to explode in the coming years, potentially overloading an infrastructure based fully on centralised data centres for processing the data,” says Mortensen.
Although some are positioning the Edge as the ultimate replacement of cloud, Mortensen believes it will be a complementary rather than a competing technology. “The more embedded major cloud providers like AWS and Microsoft can become with 5G providers, the better they can service customers, who want to access cloud resources via the mobile networks. This is especially compelling for customers who need very low latency access.”
Affirmed Networks Brings Microsoft to the 5G Infrastructure Table
Microsoft recently announced that they were in discussions to acquire Affirmed Networks, a provider of network functions virtualisation (NFV) software for telecom operators. The company’s existing enterprise customer base is impressive with over 100 major telecom customers including big names such as AT&T, Orange and Vodafone. Affirmed Networks’ recently appointed CEO, Anand Krishnamurthy says that their virtualised cloud-native network, Evolved Packet Core, allows for scale on demand with a range of automation capabilities, at 70% of the cost of traditional networks. The telecom industry has been steadily moving away from proprietary hardware-based infrastructure, opting for open, software-defined networking (SDN). This acquisition will potentially allow Microsoft to leverage their Azure platform for 5G infrastructure and for cloud-based edge computing applications.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Shamir Amanullah says, “The telecommunications industry is suffering from a decline in traditional services leading to a concerted effort in reducing costs and introducing new digital services. To do this in preparation for 5G, carriers are working towards transforming their operations and business support systems to a more virtualised and software-defined infrastructure. 5G will be dynamic, more than ever before, for a number of reasons. 5G will operate across a range of frequencies and bands, with significantly more devices and connections, highly software-defined with computing power at the Edge.”
Microsoft is by no means the only tech giant that is exploring this space. Google recently announced a new solution, Anthos for Telecom and a new service called the Global Mobile Edge Cloud (GMEC), aimed at giving telecom providers compute power on the Edge. At about the same time, HPE announced a new portfolio of as-a-service offering to help telecom companies build and deploy open 5G networks. Late last year, AWS had launched AWS Wavelength that promises to bring compute and storage services at the edge of telecom providers’ 5G networks. Microsoft’s acquisition of Affirmed Networks brings them to the 5G infrastructure table.
Microsoft Continues to Focus on 5G Offerings
The acquisition of Affirmed Networks is not the only Microsoft initiative to improve their 5G offerings. Last week also saw Microsoft announce Azure Edge Zones aimed at reducing latency for both public and private networks. AT&T is a good example of how public carriers will use the Azure Edge Zones. As part of the ongoing partnership with Microsoft, AT&T has already launched a Dallas Edge Zone, with another one planned for Los Angeles, later in the year. Microsoft also intends to offer the Azure Edge Zones, independent of carriers in denser areas. They also launched Azure Private Edge Zones for private enterprise networks suitable for delivering ultra low latency performance for IoT devices.
5G will remain a key area of focus for cloud and software giants. Amanullah sees this trend as a challenge to infrastructure providers such as Huawei, Ericsson and Nokia. “History has shown how these larger software providers can be fast, nimble, innovative, and extremely customer-centric. Current infrastructure providers should not take this challenge lightly.”
Telecom operators are fervently working towards 5G network and services deployment in order to be an early mover in the market. Operators are investing in Digital Transformation (DX) as well as inking partnerships with other players in the ecosystem to monetise on exciting new use cases in the enterprise segment and make market inroads.
The consumer market has become a retention play and on the whole many operators are experiencing declining margins and it appears unlikely that the consumer will pay more for higher speeds. Device affordability for mass-market remains a challenge though Chinese smartphone vendors are expected to release sub US$ 300 5G smartphones later this year. 5G can be expected to arrest the lengthening consumer upgrade cycle due to the attractions of not only faster speeds but improved streaming and cloud gaming. Data services revenues will continue to generate growth but this will be offset by losses in mobile voice services.
5G – An enterprise value proposition
Telecom operators have thus far been largely unsuccessful in penetrating the enterprise ICT market due to a variety of reasons including the slow pace of innovation, lack of a one-stop-shop offering, insufficient channel to market to especially small and medium enterprises (SMEs), and lack of skills in offering non-network services. 5G technology presents operators with another opportunity to address this long-standing challenge with the flexible features of enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC) and massive machine type communication (mMTC) enabling tailored network and services offerings. 5G promises to revolutionise various industry solutions based on required data rates, low latency, reliability, and machine-type communications.
Monetising 5G is a key topic among leading executives and new business models are being devised. Connectivity services will be offered with a mix and match of throughput, bandwidth volumes and latency requirements. Fixed Wireless in Southeast Asia will be very popular considering the low penetration of fibre to the home and will provide enterprises with a viable secondary connection to the internet. Popular applications including video streaming and gaming which are speed, latency and volume hungry will also be a target market for operators.
More speed, latency and number of connections
5G offers theoretical speeds of 20 times that of 4G, low latency of 1 millisecond (ms), a million connections per kilometre and is expected to power a new era of mobile Internet of Everything (IoE). Offering high speed is the initial offering to the market and operators are going to be offering minimum guaranteed speeds for the first time. A high definition movie could be downloaded in 10 seconds while low latency means better performance for live sports, gaming, mission-critical automation and driverless cars – among others.
Fixed Wireless Access is the new wireless fibre
5G will offer fixed wireless access (FWA) or “wireless fibre” to households as an alternative to fixed broadband. It can be ideal as a redundant second link offering when the primary link is down. FWA broadband services offer a serious alternative to fixed broadband services which is plagued by the high cost of civil works for fibre optic deployment and expansion of the network to reach the rural population. FWA is expected to make strong inroads into households in Southeast Asia with the exception of Singapore, as many nations lag in fixed broadband penetration. As a comparison, ITU reports that fixed broadband penetration in countries such as South Korea (41.6%) and Hong Kong (36.8%) lead their Southeast Asian counterparts – Singapore (28.0%), Vietnam (13.6%), Thailand (13.2%) and Malaysia (8.6%).
A boon for Video and Gaming industry
Gaming is huge in Southeast Asia, notably in Thailand and Indonesia, and operators can take advantage of this offering with partnerships and value-added services with cloud gaming, high bandwidth and low latency packages. With cloud gaming, gamers can access a library of popular high-quality games minus the need for expensive hardware which has been the case in the past. This platform allows content creators and publishers to access the huge Southeast Asian market and monetise.
B2B2x is not a new concept where operators partner with leading providers of video streaming services through direct billing and 5G will be able to offer low latency, for example for live events. This brings in not just a commission per subscriber but additional revenue for the additional network features such as low latency.
Video streaming providers such as Netflix, Viu, Hooq and Iflix are worthy partners for a subscription – so are ad-based video-on-demand services. Live sports streaming service also makes for a very lucrative opportunity with 5G features of high data throughput and low latency.
Readiness through digital transformation
Efforts for preparedness for this business shift means significant operational and technology platform improvements, operating on the cloud, ease of incorporating the partner ecosystem and supporting a multitude of pricing models. DX should run parallel to the build of 5G public and private networks for a telecom provider to be in a leadership position and for them to be able to fully monetise 5G. Operators will be making major changes to OSS and BSS to support 5G use cases with the ultimate goal of ensuring customer-centricity.
Ecosystm research finds that nearly two-thirds of telecom providers are looking to increase their cybersecurity spending in the year. It is also clear that the biggest driver of that spend are their DX projects (Figure 1).
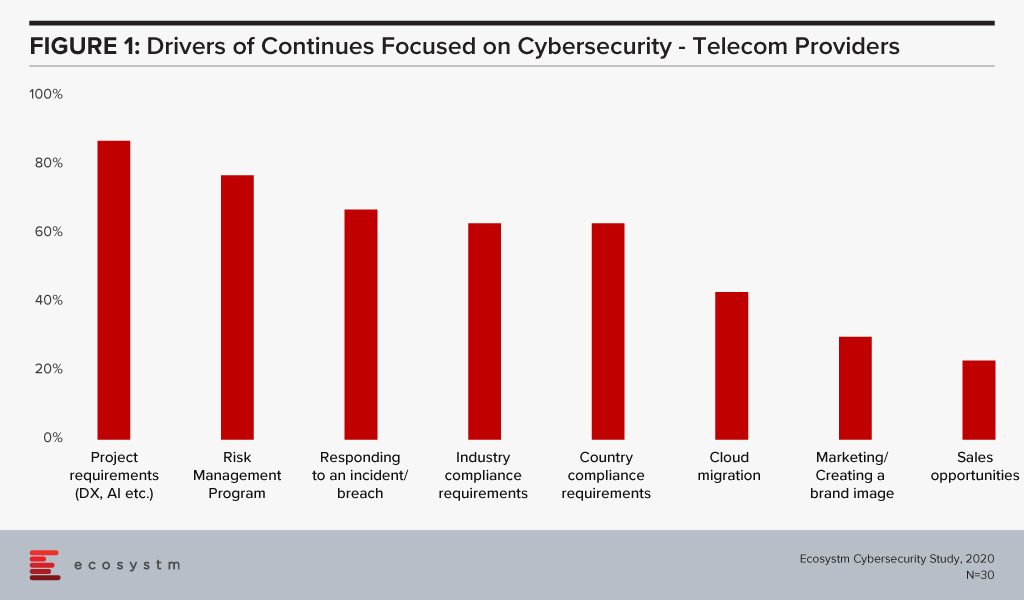
Cybersecurity is of paramount importance more than ever now with the increase in devices, software-based network services and edge computing. It is essential that a robust cybersecurity framework is in place as 5G will drive DX in enterprises, power the Digital Economy and provide the critical core infrastructure for Industry 4.0. Operators need to ramp up investment in cybersecurity technology, processes and people. A telecom operator’s compromised security can have country-wide, and even global consequences. As networks become more complex with numerous partnerships, there is a need for strategic planning and implementation of cybersecurity, with clear accountability defined for each party.
At the end of last year, Ecosystm published The Top 5 IoT Trends for 2020. Principal advisors, Kaushik Ghatak and Francisco Maroto predicted that in 2020 5G providers will be forced to operate outside their comfort zone. While the impact on network and communications equipment providers will be immense, 5G will also force telecom providers to re-think their existing business models. They may not be the best equipped to take 5G technology to market, they way the operate now.
Traditionally telecom providers have been focused on horizontal technologies and on connecting people. They have not had to have conversations around connecting machines – where every industry has their own unique use cases. This verticalisation, will force telecom providers to deal with newer stakeholders in their client organisations – not just IT infrastructure and Facilities. Several telecom providers have in the past become public cloud providers, as their markets becomes smaller and they face competition from global cloud storage providers. Now, telecom providers will increasingly look to partner with cloud providers and systems integrators with relevant industry experience, to translate the value proposition of what they are offering. “Strategic partnerships between leading technology and telecom operators are taking place especially in building various 5G use cases and applications centred on the cloud computing platform,” says Shamir Amanullah, Principal Advisor Ecosystm.
Maxis Strengthening their Market Position in Malaysia
The recently announced partnership between Maxis and Microsoft is an example of how these partnerships will pan out. Maxis does not want to be viewed only as a telecom provider and wants to be the leading Malaysia-based solutions provider. As telecom providers also start to tap the enterprise market, cloud and IoT will be key technology areas, that they should focus on.
“Maxis is leading the way as a converged solutions provider in Malaysia and following the appointment of Gökhan Ogut as the CEO in 2019, there has been a focus to grow the enterprise business which promises a lucrative opportunity,” says Amanullah.
“While the mobile connectivity market is effectively about customer retention in a saturated market, new opportunities lie in enterprise needs for fixed connectivity, managed services, cloud and IoT which is largely untapped. The expected deployment of the 5G network will spur new applications, business models and partnerships.”
Maxis’ move appears to be well-thought. Amanullah thinks that the strategic partnership with Microsoft will help Maxis accelerate its enterprise solutions offering combined IoT and 5G capabilities with Microsoft’s Azure IoT technology. It will also allow for hybrid environments, which is important given the rise of hybrid and multi-cloud adoption. Ecosystm research shows that hybrid cloud adoption in Malaysia is at a nascent 7%. But if they take a lesson from their neighbour, the rise in adoption will be steep. Our research finds that hybrid cloud adoption in Singapore is around 42%.
Telecom providers are also focusing on Digital Transformation (DX). In the Top 5 Telecommunications & Mobility Trends for 2020, Liam Gunson, Director Ecosystm says, “In 2020, operators will focus on transforming the core – remove unnecessary costs, improve customer experience, capture new opportunities – and on building telecom networks with scalability, flexibility, efficiency and agility.” Microsoft’s enterprise Modern Workplace solutions including Microsoft Teams will aid Maxis’ own DX efforts. Maxis will offer fixed line voice calls with the unified communications service.
Mutually Beneficial Partnership
Amanullah also sees this as a positive move for Microsoft. “Microsoft is poised to lead efforts in 5G network deployment which promises to enhance capabilities and drive new economic growth, especially with the focus on Industry 4.0. Maxis’ position as a leading enterprise communications provider and Microsoft’s enterprise technology experience and offerings promises a mutually beneficial partnership.”
Ecosystm research finds that Microsoft is the leading cloud provider in Malaysia when it comes to brand perception, and about a third of enterprise cloud deployments use Microsoft. Amanullah thinks that, “Microsoft’s leading position in cloud platforms is an attractive proposition for enterprises that are looking at speed, performance, reliability, global scale, security and lower costs.”
Talking about the 5G applications that the Malaysia market will see, Amanullah sees tremendous business opportunities in areas such as smart city, autonomous driving, smart traffic management, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), cloud gaming, and healthcare, to name a few.