In the report, Ecosystm Predicts: The Top Healthcare Trends for 2020, we had noted the similarities between the healthcare and the financial services industries and that Healthtech will take lessons from the Fintech industry.
In the report, Ecosystm Principal Analyst, Sash Mukherjee said, “Fintech plays a significant role in driving greater inclusion, especially to drive the induction of the unbanked into the mainstream economy, give the underbanked more options to leverage the broader financial services available, and reduce disparity in the adoption of financial services by bridging the gender gap and differences based on ethnicity and socio-economic status. It is not hard to imagine a similar fate for Healthtech. As the industry focuses on value-based outcomes, governments put in more regulations around accountability and transparency in the industry, and people expect the customer experience that they get out of their retail interactions, Healthtech start-ups will become as mainstream as Fintech start-ups.”
However, Mukherjee notes that there might be some pitfalls in this journey, especially when organisations focus more on the technology and less on the actual application and benefits of the technology. “Innovators and start-ups need to align themselves early, with corporates and technology providers to gain a better understanding of the market and regulatory landscape.”
Singapore bringing key industry stakeholders together
The MoU between Alibaba Cloud, Pfizer and Singapore’s Fintech Academy announced yesterday, is a move in the right direction that promises to give early and necessary guidance to Healthtech start-ups. Under the newly formed Healthcare Fintech Alliance (HFA), Alibaba will provide infrastructural support and technological mentorship to the Healthtech and Fintech start-ups to help them leverage cloud, AI and other technologies for their future requirements. The Fintech Academy will guide these start-ups through talent management and venture building programs. Pfizer will provide thought leadership through its network of healthcare experts and opinion leaders, including guidance on commercialisation of the products and services. The Healthcare Fintech Alliance initiative will begin with a pilot in Singapore, Indonesia, and Vietnam before expanding to other regions – Malaysia and the Philippines.
Mukherjee says, “The healthcare industry, for all the cutting-edge research, that it represents, has been remarkably slow to transform. But the COVID-19 crisis has forced the industry to transform, without the luxury or time to think about it. While the implications on the life sciences and provider organisations is clearer, there has simultaneously emerged a need for transformation in the healthcare payer industry. There will be greater demand from consumers for micro-financing to tide over sudden healthcare crises and greater transparency in how these funds are managed. Again, there is an immense potential here for the industry to learn from Fintech.”
Healthcare Fintech Alliance Focus Areas
The focus areas for Healthcare Fintech Alliance shows the deep connection between Healthtech and Fintech.
- Healthcare Affordability. Micro-financing and other financial models involving patients, family members, payers, and other healthcare stakeholders
- Value Based Healthcare. Linking payment schemes to a drug’s effectiveness, health outcomes or utilisation
- Outcome Monitoring. Tracking and reporting of outcomes derived from patients, wearables, healthcare providers, R&D databases and real-world evidence.
- Personalised Healthcare. Using digital technology to tailor healthcare to individual needs
- Innovative Healthtech Devices. Driving adoption in digital tools, such as diagnostic tools linked to medicine access and reimbursement
- Population Health Management. Leveraging patient and associated data in a compliant way to better understand population health characteristics, for effective wellness programs, treatment protocols and cost management.
“Alliances such as these have potential benefits for the industry stakeholders such as Alibaba and Pfizer. Alibaba has been focusing on the Southeast Asia market – earlier in the month the Alibaba Cloud Philippines Ecosystem Alliance was formed to support digital transformation in start-ups and small and medium enterprises. Initiatives such as this is an effective way to associate themselves with the evolving start-up community in the region,” says Mukherjee. “Life sciences companies operate in an extremely competitive global market where they have to work on new products against a backdrop of competition from generics and global concern over rising healthcare expenditure. Against that backdrop, this alliance is the right go-to-market messaging for Pfizer as well.”
“However, the deepest positive impact of alliances such as these will be on the Healthcare industry as a whole. It makes concepts such as value-based healthcare, remote care and personalised healthcare achievable in the near future.”
As organisations stride towards digitalisation, re-evaluate their business continuity plans and define what the Future of Work will look for them, Cloud adoption is expected to surge. In June, there were several announcements that indicate the market is responding to this increased interest.
Cloud Providers Gearing up to Enable Economic Recovery
Global economies are slowly gearing up for a technology-led recovery phase and several organisations are taking advantage of the disruption to start or accelerate their digital transformation plans. Many are looking at this as a good opportunity to replace their legacy systems. Cloud providers are expected to lead from the front when it comes to helping the economy recover.
Government agencies have been immensely impacted by the COVID-19 crisis and will need to shift fast into the recovery mode. Salesforce launched a multi-tenant dedicated Cloud infrastructure for their US Federal, state and local government customers, government contractors, and federally funded research and development centres. Hosted on AWS GovCloud and FedRAMP compliant, it provides customers with a compliant and secure environment to deploy Salesforce’s CRM platform and industry solutions. The launch is expected to empower government agencies with the ability to deliver better services, scale to unprecedented demands and connect to citizens on their channel of choice.
Initiatives such as the UK Crown Commercial Service (CCS) and Google Cloud agreement will also help in the recovery phase. This allows qualified public sector agencies to avail of a discounted price for their Google Cloud deployments. Earlier in the year CCS entered into a price arrangement with Microsoft as well. If Cloud has to be the vehicle for economic recovery, such arrangements will benefit cash-strapped public sector organisations.
The recovery will also require the entire technology ecosystem to engage not only with large enterprises but also small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Alibaba Cloud announced an investment of US$ 283 million to revamp its global partner program. They plan to introduce new partner-customer communication processes to enhance response time and bring more opportunities to independent software vendors (ISVs) managed service providers (MSPs) and system integrators (SIs) as partners.
Europe Emerging as a Cloud Hub
As a fallout of the current political scenario, Europe is pushing for more cloud independence and to become an innovation hub as a vendor-neutral network for cloud computing providers and their customers.
GAIA-X Foundation is a federated data infrastructure project initiated to build a unified system of cloud and data services to be protected by EU Laws – including GDPR, the free flow of non-personal data regulation and the Cybersecurity Act. France and Germany kicked off the GAIA-X cloud project last year and the system is open for participation to national and European initiatives for exchange of data across industries and services such as AI, IoT and data analytics. GAIA-X took another step towards becoming a real option for European organisations with the establishment as a legal entity in June. Various organisations – including Dassault, Orange, Siemens, SAP, Atos, Scaleway and Deutsche Telekom are a part of this non-profit platform, working together on Cloud applications, high-performance computing as well as edge systems. The project is expecting to release a working model by early 2021 and will be further enhanced in phases.
Global Cloud leaders are also focusing on expanding their presence in Europe. In February, Microsoft announced a new data centre in Spain leveraging Telefónica infrastructure. In a similar move, Google Cloud announced its plans to expand in the region in partnership with Telefónica. Telefonica and Google are expected to jointly work on Spain’s digitalisation through edge infrastructure and 5G for consumers and telecom infrastructure.
Cloud Providers Bolstering their Cybersecurity Capabilities
2020 has witnessed a host of cybersecurity threats and data breaches. While Cloud providers have always evolved their cybersecurity capabilities, it has become important for them to become vocal about these measures to build trust in the industry.
To complement the Microsoft Azure IoT security, Microsoft acquired IoT security specialist CyberX, last month. The acquisition will enable greater security for the IoT devices connected to the Microsoft network and will help their customers to gain visibility through a map of devices thus allowing them to gather information on security risks associated with thousands of sensors and connected devices. This will enhance smart grid, smart manufacturing and digital assets and profiles and reduce vulnerabilities across production and supply chain.
In another move which will benefit the ISV and SI ecosystem, NetFoundry’s zero trust networking API is now available on RapidAPI. RapidAPI’s marketplace enables developers to easily find, connect to, and manage the APIs they need to build a range of applications. Now the ISV and developer community can access NetFoundry’s software-only, zero trust models on RapidAPI.
More Partnerships between Software/Industry Solutions Providers and Cloud Providers
The COVID-19 crisis has had a far-reaching impact on several industries. The technologies that are expected to see the most uptake are IoT and Future of Work technologies.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Kaushik Ghatak says, “COVID-19 has brought to the fore the need for managing risks better. And the key to managing risks is to have better visibility and drive data-driven decisions; the sweet spot for IoT technologies.”
Last week, Microsoft and Hitachi announced a strategic alliance to accelerate the digital transformation of the Manufacturing and Logistics industries across Southeast Asia, Japan and North America. The first solutions are expected to be made available in Thailand as early as this month. Hitachi brings to the table their industry solutions, such as Lumada, and their IoT-ready industrial controllers HX Series. These solutions will be fully integrated with the Microsoft cloud platform, leveraging Azure, Dynamics 365 and Microsoft 365.
Another sector that has seen significant disruption is Real Estate. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Andrew Milroy in his blog Proptech: Driving Digital Transformation in the Wake of COVID-19 sees a real opportunity for the sector to transform. “Many activities within the property ecosystem have remained unchanged for decades. There are several opportunities for digital engagement and automation in this sector, ranging from the use of robots in construction to the ‘uberisation’ of the residential property customer journey.”
June saw Honeywell and SAP partner to create a joint cloud-based solution based on Honeywell Forge and SAP cloud. The cloud solution is aimed at real estate operators and customers providing aggregated financial and operational insights in real-time. The solution leverages the Honeywell Forge autonomous buildings solution and the SAP Cloud for Real Estate solution, enabling facility managers and building owners to reposition their real estate portfolios through parameters such as cost savings and energy efficiency and help improve the tenant experience.
As organisations struggle to maintain operations during the ongoing crisis, there has been an exponential increase in employees working from home and relying on the Future of Work technologies. Ecosystm principal Advisor, Audrey William says, “During the COVID-19 pandemic, people have become reliant on voice, video and collaboration tools and even when things go back to normal in the coming months, the blended way of work will be the norm. There has been a surge of video and collaboration technologies. The need to have good communication and collaboration tools whether at home or in the office has become a basic expectation especially when working from home. It has become non-negotiable.”
AWS and Slack announced a multi-year partnership to collaborate on solutions to enable the Workplace of the Future. This will give Slack users the ability to manage their AWS resources within Slack, as well as replace Slack’s voice and video call features with AWS’s Amazon Chime. And AWS will be using Slack for their internal communication and collaboration.
Delivering excellent customer experience in the midst of the crisis has proved to be difficult for organisations. Customer care centres have been especially impacted by high volumes of customer interactions – through voice and non-voice channels. This will see a major rise in adoption of cloud contact centre solutions. Contact centre providers are ramping up their capabilities in anticipation. Genesys selected AWS as their preferred cloud partner to deliver new features to customers and build a global and secure infrastructure.
The industry can expect more news from Cloud providers in the next few months as they ramp up their capabilities and channel their go-to-market messaging.
Gain access to more insights from the Ecosystm Cloud Study

Microsoft announced in 2018 that they were investing US$ 5 billion globally in IoT innovation and research for the next 4 years – the focus being on secure IoT, creating development tools and intelligent services for IoT and the edge, and on growing their partner ecosystem.
Last year Microsoft’s industry updates showcased several IoT implementations across industries and their edge-based solutions portfolio, customers and partner ecosystem. The tech giant revealed nearly 150% YoY growth with customers such as Starbucks, Chevron, Walmart, Walgreens, BMW and Volkswagen added to the Azure platform, leveraging IoT services to accelerate their digital transformation journey. Microsoft also announced more than 70 partnerships with some of the big names in the IoT ecosystem, such as Universal Electronics, SAP, and Cradlepoint to extend solutions and support for the Microsoft IoT business.
Extending IoT Capabilities with Strategic Partnerships
There were several recent announcements which indicate that Microsoft is focused on strengthening their IoT and industry capabilities – and this is a timely move. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Kaushik Ghatak says, “COVID-19 has brought to the fore the need for managing risks better. And the key to managing risks is to have better visibility and drive data-driven decisions; the sweet spot for IoT technologies. IoT is at the core of the Industry 4.0 story where deep domain expertise in industry verticals is a pre-requisite to success. It is heartening to see that Microsoft is taking the lead in building a powerful ecosystem by developing key partnerships with leading providers of Industry solutions.”
Last week, Microsoft and Hitachi announced a strategic alliance to accelerate the digital transformation of the Manufacturing and Logistics industries across Southeast Asia, Japan and North America. The first solutions are expected to be made available in Thailand as early as this month. Hitachi brings to the table their industry solutions, such as Lumada, and their IoT-ready industrial controllers HX Series. These solutions will be fully integrated with the Microsoft cloud platform, leveraging Azure, Dynamics 365 and Microsoft 365.
The three areas where the Hitachi solution is expected to bring strength to Microsoft’s industry offering are:
- Process optimisation and increased manufacturing productivity. Hitachi Digital Supply Chain and Azure IoT leveraged to analyse 4M data collected from manufacturing sites for visualisation/ analysis of production processes
- Logistics optimisation. Digital technologies such as Azure Maps and Hitachi Digital Solution for Logistics/Delivery Optimisation Service to analyse data on parameters such as traffic congestion, storage locations and delivery locations, to enabling smart routing
- Predictive maintenance and remote assist. HoloLens 2, Dynamics 365 Remote Assist and other smart devices, to empower first-line workers
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Niloy Mukherjee feels that with projections of 43 – 100 billion IoT connected devices in the next few years, IoT is obviously a hot space. “We can think of IoT as a stack with four layers – the devices/sensors, the connection layer, the cloud and computing layer and the business apps layer. With Azure, Microsoft is very well positioned in the cloud and compute layer and can grab a large chunk of this fast-growing market. Tying with players like Hitachi allows Microsoft to integrate with the business apps layer and perhaps also some devices. It is absolutely the right strategy and I would expect them to go for many more such alliances. With Microsoft’s strength in the enterprise market, IoT gives them a great opportunity to increase their share of cloud workloads with customers.”
Addressing the Challenges of IoT Adoption
Ecosystm research shows that the biggest challenges in IoT adoption are security and integration concerns (Figure 1).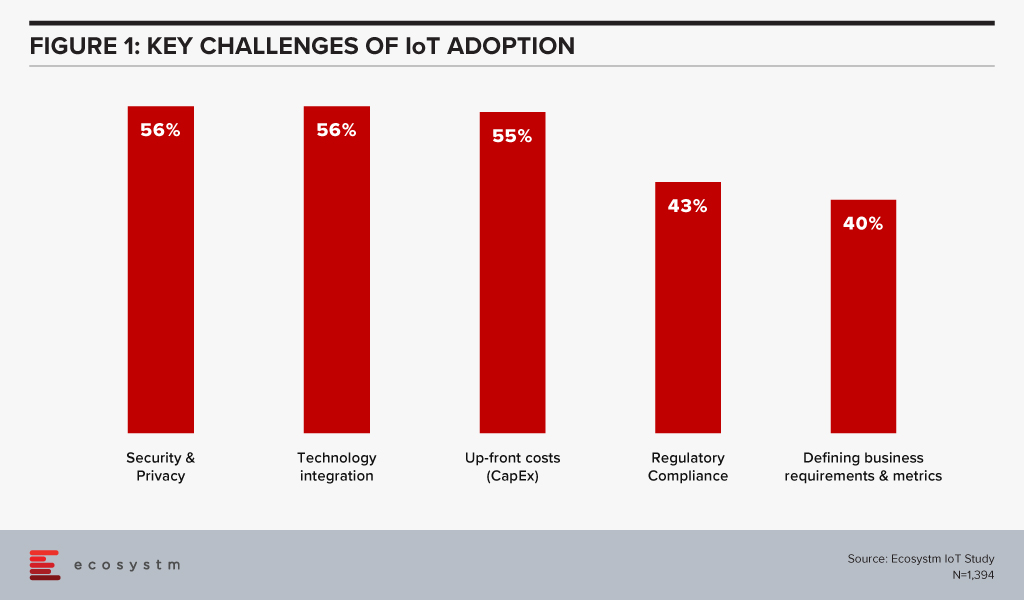
In 2018, when Microsoft started actively focusing on IoT, they also launched the Azure Certified for IoT program to maintain consistency and enhanced interoperability across their device partner ecosystem. This addresses the integration challenges that organisations face when deploying IoT. Microsoft continues to grow their IoT ecosystem, ensuring faster IoT deployments, with hardware and software that has been pre-tested and verified to work with Microsoft Azure IoT services. Last week also saw Cyient joining Microsoft Azure as a certified partner for IoT. Cyient IoT Edge Gateway 5400, their flagship IoT gateway product is now Microsoft Azure Certified for IoT. This is expected to accelerate IoT deployment for Cyient customers and enable a seamless integration of edge devices to the cloud.
Ghatak says, “To scale up their IoT business, Microsoft would need to develop a substantially large ecosystem, beyond few key players such as Hitachi, who dominate at the large enterprise segment of the market. That is where partnerships with smaller and niche industry solutions providers such as Cyient fits in. More niche providers such as Cyient will increase Microsoft’s reach into medium and smaller segments of the enterprise market.”
Addressing the Increasing Threat Landscape
Recent cyber-attack trends and security breach statistics reveal a huge increase in cybercrime activities, in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. As the number of IoT sensors, devices and gateways increase, so does the risk of security breaches. As shown in figure 1, cybersecurity concerns are real and can act as a barrier to IoT adoption, despite the benefits that the technology brings. Automated vulnerability management capabilities, that allow risk assessment and patch installation where necessary will see an increase in IoT adoption.
To complement Microsoft Azure IoT security, Microsoft acquired IoT security specialist CyberX, last month. The acquisition will enable greater security for the IoT devices connected to the Microsoft network and will help their customers to gain visibility through a map of devices thus allowing them to gather information on security risks associated with thousands of sensors and connected devices. This will enhance smart grid, smart manufacturing and digital assets and profiles and reduce vulnerabilities across production and supply chain.
Mukherjee says, “The key concern for the expansion of IoT into more and more use cases in the next few years is really going to be security. New areas like VR and AR are emerging from futuristic fantasy to real-world reality. These will tempt many enterprises – but security will be the key concern to address. And so, Microsoft’s simultaneous push on security completely aligns with this. As the Ecosystm MSSP VendorScope results show Microsoft’s strategy on cybersecurity seems to be working.”
Talking about Microsoft’s go-to-market strategy, Mukherjee adds, “Microsoft is obviously spreading its net far and wide for all cloud applications including IoT, to go-to-market with partners. One of the key focus area here is the SME segment, which is forecast to be one of the hot growing segments for IoT in the next few years. The more offerings from the business apps layer that Microsoft integrates, the more they enable their partners to sell to their customers.”

If the post go-live adoption of technology implementation is not done well, an organisation will not be able to realise the full potential of the promised ‘value’ from their digital investments. Sash Mukherjee, Principal Analyst, Ecosystm speaks with Dr. Kaushik Ghatik, Principal Advisor, Ecosystm about the importance of change management.
Podcast: Play in new window | Download (6.1MB)
Subscribe Spotify | Amazon Music | JioSaavn | Podchaser | RSS | More
Last week, the Australia government joined other countries in the Asia Pacific region in highlighting the growth of attack surface in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In our recently launched study Digital Priorities in the New Normal, we find that 87% of organisations in the Asia Pacific have increased investments in one or more cybersecurity solutions. However, this has to be backed by a reassessment of organisations’ risk positions and a re-evaluation of data protection and compliance policies.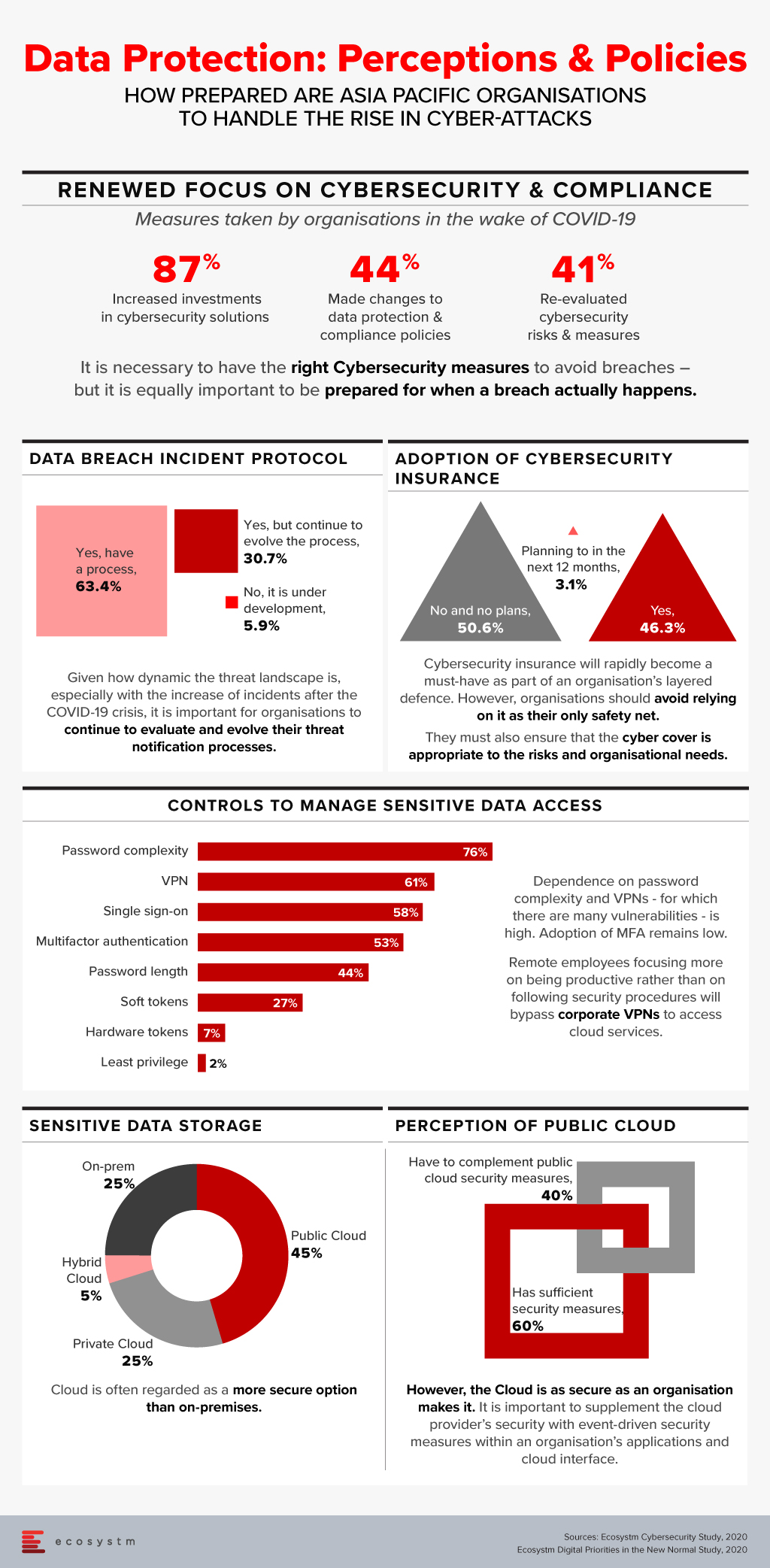

Thailand has emerged as a key player in the 5G space in Southeast Asia. In February 2020, Thailand’s telecom regulator, NBTC auctioned 48 5G licenses to boost the development of Thailand’s digital economy. Later in the year, Thailand also announced the formation of the National 5G Committee to coordinate the 5G development roadmap with the digital economy vision.
The Future of 5G in Thailand
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Shamir Amanullah says, “The transformational nature of 5G, unlike its predecessors, is expected to boost adoption of IoT, smart manufacturing and broader Industry 4.0 initiatives to drive the economy. NBTC expects 5G technology to contribute over US$ 15 billion to the GDP in 2022. Key sectors expected to adopt are Healthcare, Manufacturing, Education and Agriculture.”
We are already seeing initial applications of 5G. “AIS and True have been launching 5G networks in hospitals across Thailand to support medical personnel in their fight against COVID-19. Telemedicine and robots using 5G are being used to prevent contact between affected patients and medical personnel. AIS has launched 5G networks in 158 hospitals in Bangkok and other major cities.”
Amanullah adds, “The changing landscape of remote working caused by COVID-19 has increased network traffic, especially a spike in the video, further amplifying the need for 5G infrastructure. The onboarding of many new digital users and increased adoption of digital solutions by businesses has whet the appetite for more speed, latency and more innovative services. 5G first-mover advantage is key especially for the major operators who can achieve significant scale in their new service offerings.”
The Thailand 5G Landscape
The major telecom providers bid for multiple licenses across different bands. While AIS and True bid for and won more licenses, other telecom providers such as DTAC are aiming more for a niche presence. They only bid for the high band 26 GHz auction, winning two out of the possible 26 licenses for 100 MHz blocks.
Amanullah discusses the benefits of different 5G bands. “The 700 MHz band covers large geographic areas while also being able to penetrate walls easily making it a highly valuable spectrum asset. The 2600 MHz band is attractive as most smartphones already have this radio.”
“The 26 GHz band provides for high-frequency spectrum, also known as mmWave spectrum. This band offers high-speed data and capacity but with a limited range. Applications expected to be used in the mmWave include virtual and augmented reality and remote health services. While DTAC has a smaller spectrum holding compared to AIS and True, they plan to complement with their coverage band to offer 5G services. The company is also believed to be keen in the 3500 MHz mid-range band when it becomes available. This band is currently occupied by satellite operator Thaicom.”
DTAC-NetFoundry Partnership
DTAC and NetFoundry recently announced a collaboration, to introduce a new network service dubbed as SmartConnect. SmartConnect is a network service which allows organisations to manage the network and cloud computing in a unified platform thus increasing efficiency, speed and security.
The partnership will enable both small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and large enterprises to leverage cloud-native networking capabilities to boost performance while increasing security when connecting to a cloud environment. SmartConnect service will replace traditional set-ups involving hardware, VPN devices by providing a new virtual network for organisations. This is expected to empower business users to access cloud-based data quicker – with eight to ten folds speed – than a conventional network in a highly secured environment at a fraction of a cost.
Amanullah says, “The Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) features in 5G – where a customised network service based on bandwidth speed or latency, specific to a variety of 5G use cases – brings an exciting new business and potentially lucrative opportunities. Network slicing allows for many virtual networks on a single physical network and NaaS theoretically allows for a customer to request for a tailored network service required. NaaS delivers virtual network services on a subscription basis which has the potential to be an exciting game-changer.”
DTAC is clearly gearing up for the changes in the industry. The SmartConnect service can become a true differentiator for them. It also gives an opportunity to DTAC to leverage NetFoundry’s integration with Azure, AWS and GCP to enhance cloud connectivity services and provide value to their enterprise users.
As the telecom industry transforms, it will see more such partnerships between telecom providers and technology vendors.
The 5G rollouts in Australia by Telstra, Optus and Vodafone will impact consumers and enterprises alike. It is expected that enterprises will see an uptick in IoT adoption, leveraging the lower latency to connect devices for real-time data transfer and insights. Industries, especially those that operate in remote and rural regions of the country such as Agriculture and Mining are expected to benefit immensely.
“However, there are challenges to leveraging digitalisation effectively, including a lack of awareness, knowledge and skills, and funding to support innovation and scale, in aligning with the growing pressure within sectors to meet increasing productivity and compliance requirements,” says Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Jannat Maqbool. “Adoption of IoT specifically is resulting in new data supply chains, that those operating in many industries cannot cater for with respect to infrastructure and also the skills necessary to process and extract valuable insights from the data.”
Ecosystm research shows that only 37% of organisations looking to adopt IoT in Australia have a strategic internal team to create the roadmap and manage the deployment. This indicates a lack of skills that organisations can utilise, depending on external resources such as consulting firms and ISVs instead. To cater to the expected growth in Australia’s IoT market, IoT Alliance Australia (IoTAA) – that represents more than 500 participating organisations and 1,000 individual participants – has come forward with the IoT Australia Skills Barometer survey.
The survey created in association with La Trobe University aims to gauge the IoT skills gap, to inform educators and adopters on the potential areas of focus for future skills development. It covers questions on IoT adoption, challenges expected, solutions being evaluated, and courses needed.
Addressing the Skills Gap
As the adoption of IoT increases, there will be added requirement for skills in data storage, infrastructure management and creating frameworks. The survey is expected to help the industry determine the skills gap, isolate training and re-skilling requirements and develop courses and hands-on sessions to address the end-to-end services requirements and better utilisation of data gathered from the devices.
There are some courses that are already available – mostly run in collaboration with industry. Last year, Rio Tinto, the Western Australia Government and South Metropolitan TAFE developed Australia’s first nationally-recognised remote operations course. Earlier this year, RMIT partnered with IBM to deliver the IoT and 5G business opportunity courses to equip business professionals with the right technology and business skills for IoT projects.
“Awareness of the potential of emerging technologies needs to target both non-technical and technical members of the organisation. This wider buy-in is needed to drive thinking around the ‘why’ from stakeholders across the business, enabling a more informed decision around the potential impact on existing resources, infrastructure, processes, products, required investment and business outcomes,” says Maqbool. “Any education and training program needs to allow for this focus on awareness, then provide opportunities to build on this for those that then want to gain the deeper knowledge and technical skills required to effectively leverage the IoT.”
“Education and training programs to support the uptake of digital technologies across the wider population and traditionally non-digital industries require a contextual learning and a flexible delivery approach.”
Government and Industry working together
“A digital divide exists in many countries – especially for those in rural communities. They are often not in a position to access the infrastructure necessary to support a real-world connection in a contextual learning environment, let alone having the digital literacy and scaffolding to get to a point where they can effectively consider leveraging emerging technologies,” says Maqbool.
This is where governments play a larger role. To accelerate innovation and make better use of technology the Australian Government is supporting clear communication and a better understanding of IoT, implementing standards and regulations, upgrading digital infrastructure, creating opportunities for economic and social benefits and collaborating with research and education institutes to deliver skills, innovation and growth in the IoT sector.
One of the key areas of focus will have to be cybersecurity. Regulatory compliance and security & privacy issues are the key barriers of IoT adoption in Australia (Figure 1).
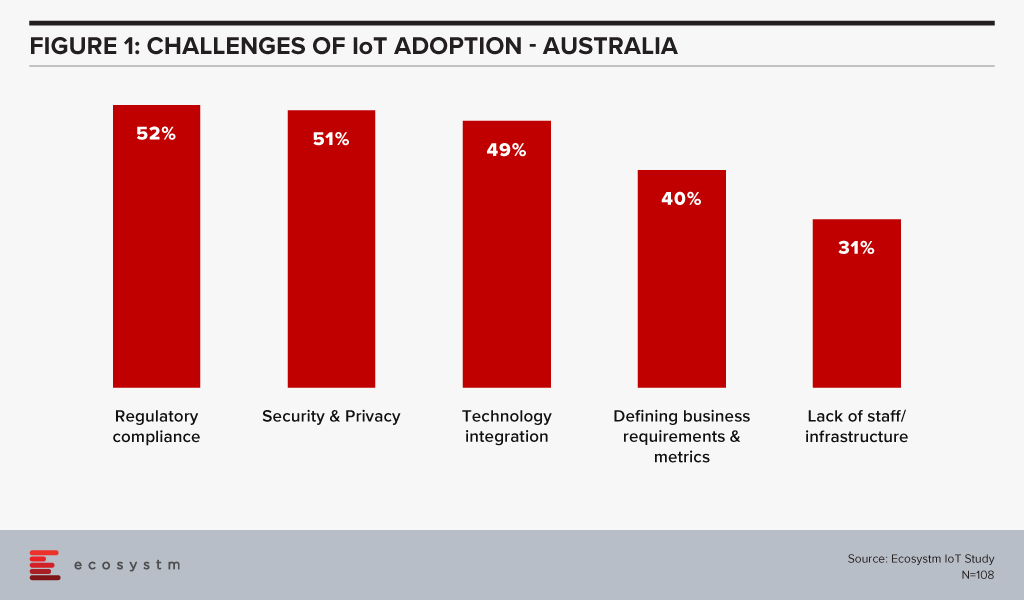
Last year, the Australian government released a draft code of practice to enable businesses implementing IoT solutions to follow certain principles as a voluntary measure to defend against threats.
The Government is also seeing a larger potential for IoT in some industries. To support the Agriculture industry, the Australia Government has allocated USD 90 million to the Smart Farms program to support the development and uptake of best practices and technologies in farms, fisheries and forestry, with a special focus on regional communities. In its FY2019-20 federal budget, the Government announced plans to invest USD 1.4 million for a feasibility study and assess ways on improving digital on-farm connectivity. Similarly, Australia’s National Landcare Program (NLP) delivered by the Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment (DAWE) is receiving financial support until June 2023.

This week saw SAS and Microsoft announce a strategic partnership both in their technology offerings and go-to-market strategy. SAS analytical products and industry solutions will be migrated onto Microsoft Azure as the preferred cloud provider for the SAS Cloud. Microsoft hopes to leverage SAS’ industry expertise, especially in healthcare and financial services. This partnership builds on SAS integrations across Microsoft cloud solutions for Azure, Dynamics 365, Microsoft 365 and Power Platform.
Here is what our Analysts say:
“To date, the focus of cloud computing has been around providing customers with levels of agility, speed, and scalability that cannot be provided by on-premises solutions. Customers have benefitted from this cloud functionality by being able to provision new services rapidly, pivot swiftly when they need to change their business models and build resilience and flexibility into the ways in which they do business. Today, customers are asking for more. Microsoft has responded to this demand by forming or enhancing cloud partnerships with leading cloud vendors including Salesforce, SAP, Oracle, Workday, ServiceNow and Adobe, as part of an overall strategy to make it easier for customers to choose Azure as their key enterprise foundation, and to offer more functionality.
Across industries, from healthcare to financial services, businesses finally realise the potential value of data. They recognise that the most competitive businesses are those that fully leverage the data that they can access. Businesses want cloud services to offer AI and machine learning capabilities. They want to use these capabilities to become more innovative and more competitive. To do this, these cloud services need to be integrated more tightly with capabilities which Microsoft does not have.
SAS is the leader in data analytics and AI software for enterprises, so it makes perfect sense for Microsoft to partner with the company. Integrating SAS models with Microsoft’s cloud estate, in particular Azure will enable Microsoft to offer its customers more than the typical benefits of cloud services. They can offer their customers intelligent cloud services.
SAS can offer its customers a more comprehensive solution by integrating its AI and machine learning capabilities into the Microsoft cloud estate. SAS and Microsoft will combine their engineering resources to ensure that SAS’ analytics products work well on Azure. A key priority is building an Azure-optimised version of Viya, the cloud version of SAS’ core analytics toolkit. SAS will also look at ways in which it can integrate its software with the native analytics services provided in Azure.
Importantly, companies will create joint solutions across multiple verticals. An example of a joint solution is SAS’ IoT analytics and the Azure IoT platform being used to increase situational awareness of rising stream levels, to predict where flooding might occur, thus improving emergency response.
SAS software will continue to be cloud-agnostic. But, SAS itself will migrate its internal operation and its global cloud business to Azure. The expanded partnership with Microsoft does not impact SAS customers who run on AWS or GCP. But, Azure customers can expect to see benefits over time as SAS and Microsoft work closely on joint solutions.”
“The SAS and Microsoft relationship goes well beyond ‘Azure is our cloud hosting platform of choice’. It brings together Microsoft’s leading suite of AI tools and cloud infrastructure and platform capabilities and the leading analytics and intelligent applications provider. Through the combined toolset, every-day applications have the opportunity to become even more intelligent – and the industry-specific intelligent business processes that SAS is known for will be able to be hosted on the cloud, and more deeply integrated into existing solutions and PaaS services. The ability to embed SAS workloads into containers means that a broader user set can access and learn from the analytics that they provide – and automate an even greater number of business and customer processes using the AI and Analytics toolsets from both providers.
It also simplifies the management of SAS software and gives a clear and easy path to the public cloud for SAS customers who have not yet made that transition.
The partnership has the opportunity to further accelerate Microsoft’s transition towards even smarter applications. Microsoft has already been recognised in the market as having one of the better AI capabilities – mostly because of embedding intelligence into existing applications and processes. But Microsoft was never going to be able to provide the intelligence for every process in every industry. This partnership will accelerate Microsoft towards the automation of more processes that are used by customers across the spectrum of sectors and industries – and it obviously extends SAS’ reach beyond their traditional customer base.”
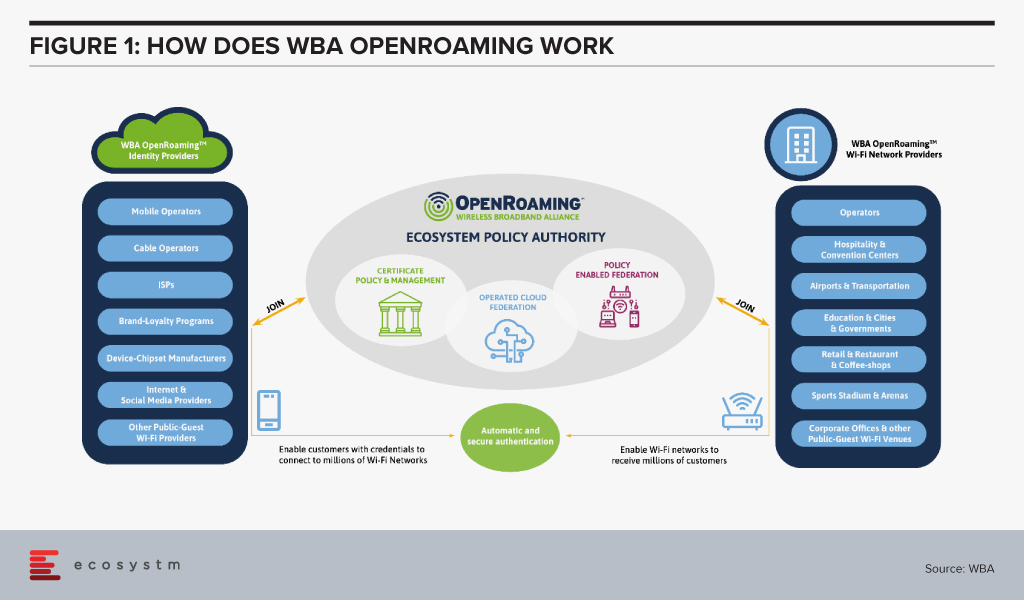
The Wireless Broadband Alliance (WBA) was formed in 2003 to enable a seamless and interoperable Wi-Fi experience across the global wireless ecosystem. The key objective of the alliance was to bring together multiple stakeholders – such as telecom providers, technology vendors and enterprises – to work on areas such as industry guidelines, pilot projects, standards to promote end-to-end services and drive adoption in Wi-Fi, 5G, IoT and others.
WBA OpenRoaming™
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Ashok Kumar says, “Wi-Fi has gained increasing popularity worldwide over the last two decades and has now become an essential network technology with ubiquitous service that it is utilitarian. However, it has been viewed as a collection of islands of heterogenous networks, requiring re-authentication each time a mobile user transits from one network and re-connects with another Wi-Fi network, with the associated hurdles of logging back in, making it cumbersome.”
“The lack of interoperability between Wi-Fi networks has been a drawback for service providers, compared to the ease of use associated with global mobile networks, such as 4G, LTE, 5G, and so on, which offer seamless roaming connectivity.”
The WBA OpenRoaming™ initiative was announced last month, to create a globally available Wi-Fi ecosystem that offers a federation of automatic and secure connections for billions of devices to millions of Wi-Fi networks. It provides a new global standards-led approach, removing public-guest Wi-Fi connectivity barriers and brings greater convenience and security to the wireless ecosystem. WBA OpenRoaming™ removes the need to search for Wi-Fi networks, to repeatedly enter or create login credentials, or to constantly reconnect or re-register to public Wi-Fi networks.
Several leading technology companies and telecom service providers have extended support to WBA OpenRoaming™ standards – Samsung, Google, Cisco, Intel, Aptilo, AT&T, Boingo Wireless, Broadcom, Comcast, Deutsche Telekom and Orange to name a few.
“Wi-Fi is arguably the most ground-breaking wireless technology of our time. From the first public Wi-Fi hotspots in the early 2000s which enabled radically increased productivity on the move, through to the role Wi-Fi has in today’s pandemic environment. With WBA OpenRoaming™ we want to revolutionise how individual users as well as businesses engage with Wi-Fi, removing the need to repeatedly log in, re-connect, share passwords or re-register for Wi-Fi networks as we travel locally, nationally or internationally”, said Tiago Rodrigues, CEO of the WBA, “Instead, no matter where we are, the new framework automates how users connect to Wi-Fi while seamlessly aligning to cellular network connectivity. It does so by bringing together a federation of trusted identity providers so that individual users are allowed to automatically join any network managed by a federation member.”
WBA OpenRoaming™ can simplify Wi-Fi, much like the cellular roaming experience. Kumar says, “ The WBA OpenRoaming™, with support from major global service providers, network solution vendors, and authentication & security firms, has the potential to address the issue of seamless interoperability in the Wi-Fi networks ecosystem with ease-of-use and security.”
WBA OpenRoaming™ Framework
The framework and standards are based on cloud federation, consisting of a global database of networks and identities, dynamic discovery and the Wireless Roaming Intermediary Exchange (WRIX); cybersecurity consisting of Public Key Infrastructure a RadSec providing the certificate policy, management and brokerage services; and network automation facilitated by an automated roaming consortium framework and policy and Wi-Fi CERTIFIED Passpoint®*.
The Impact of WBA OpenRoaming™
“Enterprises are expected to benefit enormously from the opportunity to create new commercial business models and innovative services with speed and simplicity,” says Kumar.
Maturing mobile technologies such as 5G and Wi-Fi 6 along with next generation wireless devices, could make OpenRoaming™ more seamless and extend its applications further.
Cisco in particular has been leading the charge with several pilots that showcase the benefits of OpenRoaming™. Earlier this year, it partnered with Oxbotica, an autonomous vehicle software provider, to demonstrate how OpenRoaming™ can unlock the potential of autonomous vehicle fleets, allowing a seamless and secure sharing of high-volume data while on the move.
Last year, Cisco also showcased the benefits of OpenRoaming™ in a pilot at the Mobile World Congress in Barcelona with Samsung as the identity provider. Attendees were connected to the network throughout the venue, with connectivity extended to even local train stations and the airport. This unified experience was possible despite the fact that at least three network providers were involved. Pilots such as these gives the industry a glimpse of what benefits lie ahead.
Kumar sees the impact being extended across industries. “The impact of WBA OpenRoaming™ will be in the introduction of innovative services for consumers and enterprise users in public Wi-Fi networks in industries such as Hospitality, Transportation (airport and rail), Retail outlets, Smart City solutions, and local community networks.”
Learn more about WBA OpenRoaming™, visit www.openroaming.org
*Wi-Fi CERTIFIED Passpoint® is a registered trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance












