The telecommunications industry has long been an enabler of Digital Transformation (DX) in other industries. Now it is time for the industry to transform in order to survive a challenging market, newer devices and networking capabilities, and evolving customer requirements. While the telecom industry market dynamics can be very local, we will see a widespread technology disruption in the industry as the world becomes globally connected.
Drivers of Transformation in the Telecom Industry
Remaining Competitive
Nokia Bell Labs expects global telecom operators to fall from 10 to 5 and local operators to fall from 800 to 100, between 2020 and 2025. Simultaneously, there are new players entering the market, many leveraging newer technologies and unconventional business models to gain a share of the pie. While previous DX initiatives happened mostly at the periphery (acquiring new companies, establishing disruptive business units), operators are now focusing on transforming the core – cost reduction, improving CX, capturing new opportunities, and creating new partner ecosystems – in order to remain competitive. There is a steady disaggregation in the retail space, driving consolidation in traditional network business models.
“The telecom industry is looking at gradual decline from traditional services and there has been a concerted effort in reducing costs and introducing new digital services,” says Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Shamir Amanullah. “Much of the telecom industry is unfortunately still associated with the “dumb pipe” tag as the over-the-top (OTT) players continue to rake in revenues and generate higher margins, using the telecom infrastructure to provide innovative services.”
Bringing Newer Products to Market
Industries and governments have shifted focus to areas such as smart energy, Industry 4.0, autonomous driving, smart buildings, and remote healthcare, to name a few. In the coming days, most initial commercial deployments will centre around network speed and latency. Technologies like GPON, 5G, Wifi 6, WiGig, Edge computing, and software-defined networking are bringing new capabilities and altering costs.
Ecosystm’s telecommunications and mobility predictions for 2020, discusses how 5G will transform the industry in multiple ways. For example, it will give enterprises the opportunity to incorporate fixed network capabilities natively to their mobility solutions, meaning less customisation of enterprise networking. Talking about the opportunity 5G gives to telecom service providers, Amanullah says, “With theoretical speeds of 20 times of 4G, low latency of 1 millisecond and a million connections per square kilometre, the era of mobile Internet of Everything (IoE) is expected to transform industries including Manufacturing, Healthcare and Transportation. Telecom operators can accelerate and realise their DX, as focus shifts to solutions for not just consumers but for enterprises and governments.”
Changing Customer Profile
Amanullah adds, “Telecom operators can no longer offer “basic” services – they must become customer-obsessed and customer experience (CX) must be at the forefront of their DX goals.” But the real challenge is that their traditional customer base has steadily diverged. On the one hand, their existent retail customers expect better CX – at par with other service providers, such as the banking sector. Building a customer-centric capability is not simple and involves a substantial operational and technological shift.
On the other hand, as they bring newer products to market and change their business models, they are being forced to shift focus away from horizontal technologies and connecting people – to industry solutions and connecting machines. As their business becomes more solution-based, they are being forced to address their offerings at new buying centres, beyond IT infrastructure and Facilities. Their new customer base within organisations wants to talk about a variety of managed services such as VoIP, IoT, Edge computing, AI and automation.
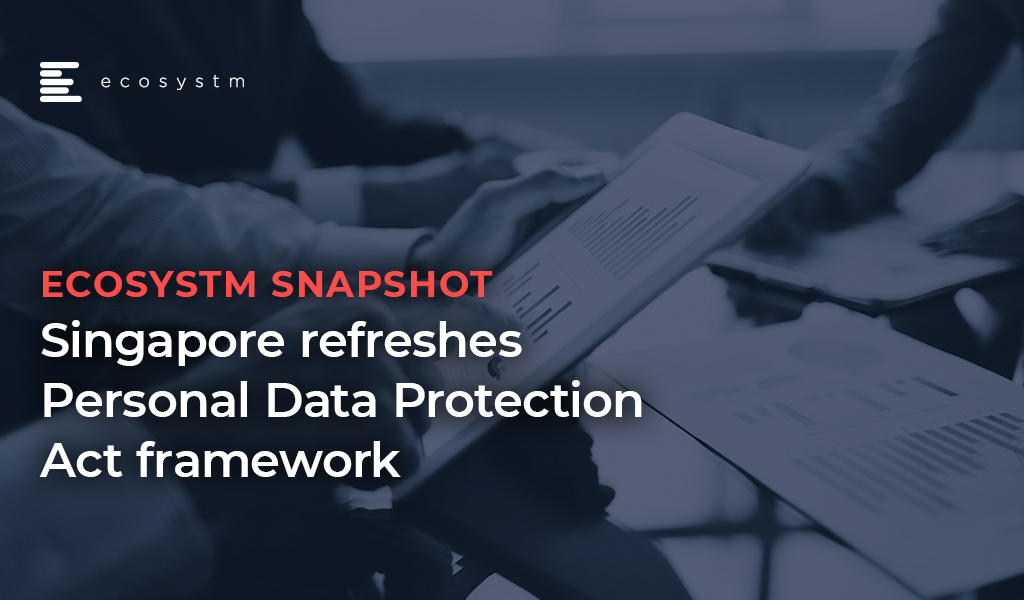
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for telecom service providers, focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). It is very clear that the top priorities are driving customer loyalty (through better coverage, smart billing and competitive pricing) and process optimisation (including asset maintenance).
Technology as an Enabler of Telecom Transformation
Several emerging technologies are being used internally by telecom service providers as they look towards DX to remain competitive. They are transforming both asset and customer management in the telecom industry.
IoT & AI
Telecom infrastructure includes expensive equipment, towers and data centres, and providers are embedding IoT devices to monitor and maintain the equipment while ensuring minimal downtime. The generators, meters, towers are being fitted with IoT sensors for remote asset management and predictive maintenance, which has cost as well as customer service benefits. AI is also unlocking advanced network traffic optimisation capabilities to extend network coverage intelligently, and dynamically distribute frequencies across users to improve network experience.
Chatbots and virtual assistants are used by operators to improve customer service and assist customers with equipment set-up, troubleshooting and maintenance. These AI investments see tremendous improvement in customer satisfaction. This also has an impact on employee experience (EX) as these automation tools free workforce from repetitive tasks and they be deployed to more advanced tasks.
Telecom providers have access to large volumes of customer data that can help them predict customer usage patterns. This helps them in price optimisation and last-minute deals, giving them a competitive edge. More data is being collected and used as several operators provide location-based services and offerings.
In the end, the IoT data and the AI/Analytics solutions are enabling telecom service providers to improve products and solutions and offer their customers the innovation that they want. For instance, Vodafone partnered with BMW to incorporate an in-built SIM that enables vehicle tracking and provides theft protection. In case of emergencies, alerts can also be sent to emergency services and contacts. AT&T designed a fraud detection application to look for patterns and detect suspected fraud, spam and robocalls. The system looks for multiple short-duration calls from a single source to numbers on the ‘Do Not Call’ registry. This enables them to block calls and prevent scammers, telemarketers and identity theft issues.
Cybersecurity
Talking about the significance of increasing investments in cybersecurity solutions by telecom service providers, Amanullah says, “Telecom operators have large customer databases and provide a range of services which gives criminals a great incentive to steal identity and payment information, damage websites and cause loss of reputation. They have to ramp up their investment in cybersecurity technology, processes and people. A telecom operator’s compromised security can have country-wide, and even global consequences. As networks become more complex with numerous partnerships, there is a need for strategic planning and implementation of security, with clear accountability defined for each party.”
One major threat to the users is the attack on infrastructure or network equipment, such as routers or DDoS attacks through communication lines. Once the equipment has been compromised, hackers can use it to steal data, launch other anonymous attacks, store exfiltrated data or access expensive services such as international phone calls. To avoid security breaches, telecom companies are enhancing cybersecurity in such devices. However, what has become even more important for the telecom providers is to actually let their consumers know the security features they have in place and incorporate it into their go-to-market messaging. Comcast introduced an advanced router to monitor connected devices, inform security threats and block online threats to provide automatic seamless protection to connected devices.
Blockchain
Blockchain can bring tremendous benefits to the telecom industry, according to Amanullah. “It will undeniably increase security, transparency and reduce fraud in areas including billing and roaming services, and in simply knowing your customer better. With possibilities of 5G, IoT and Edge computing, more and more devices are on the network – and identity and security are critical. Newer business models are expected, including those provided for by 5G network slicing, which involves articulation in the OSS and BSS.”
Blockchain will be increasingly used for supply chain and SLA management. Tencent and China Unicom launched an eSIM card which implements new identity authentication standards. The blockchain-based authentication system will be used in consumer electronics, vehicles, connected devices and smart city applications.
Adoption of emerging technologies for DX may well be the key to survival for many telecom operators, over the next few years.

What used to be commonly known by names such as computer security or IT security is now most commonly referred to as cybersecurity. The techniques of securing computers, applications, networks, programs and data have evolved and so has the terminology. The change in the jargon reflects the progression from discrete to interconnected devices and networks. It is only when the computers and devices became connected with each other – and with the Internet – that the issues and attempts of unauthorised access became prominent.
Simply put, cybersecurity is the protection of computer systems from cyber-attacks. This is made possible with multiple layers of security across the system, individual devices, enterprises and even nations against unauthorised access and exploitation.
Cybersecurity is a constant battle
Preventing cyberattacks is a challenging task for security professionals and to accomplish that, cybersecurity experts should stay ahead of cyber attackers and cybercriminals. A range of effective methods and technologies have been devised to strengthen cybersecurity. One important aspect of cybersecurity is identity and access management (IDAM). IDAM allows various defined levels of access on the basis of individual roles, administrator levels and even at a system level. The common IDAM methods include single sign-on systems, multi-factor authentication, privileged access management (PAM), biometrics, voice or facial recognition, and other distinctive physical attributes to verify and identify individuals. IDAM procedures are being implemented at all levels of businesses, enterprises and even for national-level security with the growth of eGovernment systems.
Another common security measure is Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) software and services. The term combines security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM) and is provided by vendors as software or appliance. SIEM works by collecting log data and delivering real-time insights and generates security alerts using a range of techniques. SIEM is used by enterprises where compliance to a set, or sets, of rules is a strong factor. In addition, it also prevents interferences from individual attackers, organised crime groups, or other actors.
SIEM systems comprise three major components:
- Data collection. SIEM system collects logs and data from system activity, access, firewalls, application monitors, operating system layers and network traffic and generates an event every time activity happens.
- Data analysis. The SIEM system is tasked with correlating and analysing data in a format. The analysis is performed in various ways: log management and retention, event correlation, user activity monitoring, and predictive and forensic analysis.
- Another major step is reporting in the form of real-time alerts, dashboards, email and SMS notifications of events, analytical reporting, auditing and governance, and compliance.
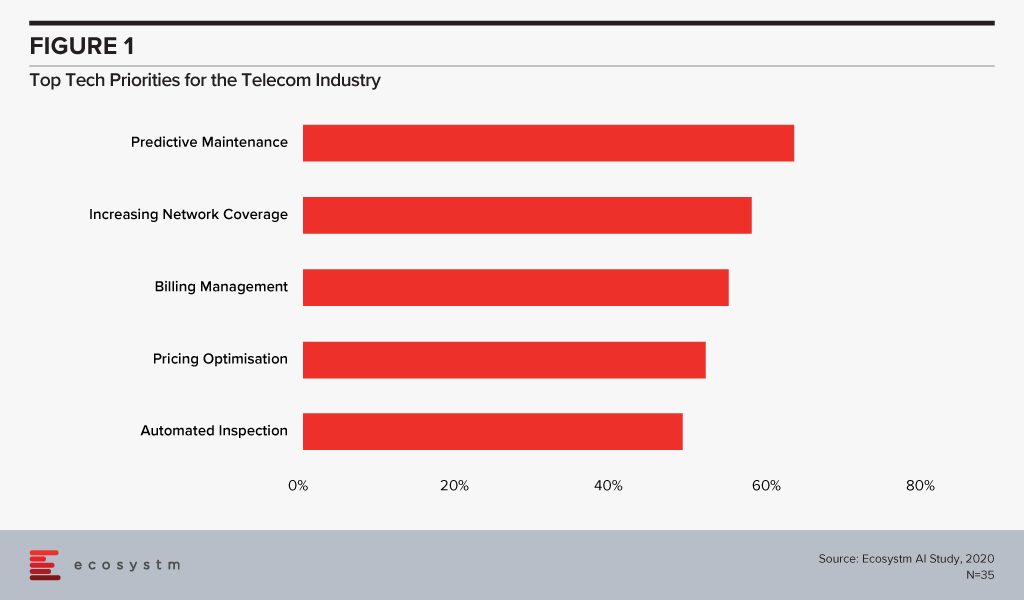
The global Ecosystm Cybersecurity Study covers various cybersecurity solutions such as Crisis Communication solutions; Security Operations & Incident Response, IDAM and more. The study shows that organisations are primarily focusing more on Application, Data and Network level security, whereas, the other cybersecurity fields such as Crisis communication, Fraud transaction, IDAM, Threat Analysis and Reporting are looked down.
National Cybersecurity and Safety
Countries across the globe are accelerating their cybersecurity efforts to address risks, enhance public safety, protect communications, safeguard mission-critical applications and prevent threats. Cybersecurity is important to governments, where it is increasingly seen as an area of international conflict. Most countries have now setup their dedicated national cybersecurity centres, drawing on the capabilities of private industry, government and academic specialists in the area.
As cybersecurity threats have proliferated and computer technology has advanced, government data security compliance has become increasingly complex. The governments of various nations have set up compliances with a wave of new privacy regulations.
Security is an ongoing and constant effort which should be adopted at an individual, business, organisation, enterprise and national level. To strengthen cybersecurity there are many excellent solutions, a range of comprehensive suites and products. However, malicious parties and criminals are constantly employing new techniques and technologies. It is a new arms race, and there is no one size fits all solution.
Cybersecurity will remain an important topic of discussion on the world forum. 2020 is predicted to see an increasing number of state-sponsored cyber-attacks especially on utilities and public infrastructure. In addition, the number of AI based devices will increase which will receive specific attention from regulators for data and cybersecurity. Finally, there will be opportunities for mergers and acquisitions and investments in established cybersecurity providers to remain innovative and growing.
Here are the Top 5 Cybersecurity Trends for 2020, that we believe, will impact both businesses and consumers in 2020.
The Top 5 Cybersecurity Trends for 2020
The Top 5 Cybersecurity Trends for 2020 are drawn from the findings of the global Ecosystm Cybersecurity Study and is also based on qualitative research by Ecosystm Principal Advisors Alex Woerndle, Carl Woerndle and Claus Mortensen.
-
API Vulnerabilities will Become a Main Hacker Target
APIs grant access and provide transparency for developers – providing access and insights from both internal and external data. But they are inherently insecure. We have already seen several high-profile API breaches and announced API bugs. For example, in October 2018, Google had to shut down Google+ after an API bug exposed details for over 500,000 users.
We believe the problem will get significantly worse in 2020, with API attacks quickly becoming one of – if not the most – frequent target for hackers.
-
Operational Technology Security will Continue to Lag in 2020
Operational Technology (OT) refers to the hardware and software used to monitor and manage how devices that run on an organisation’s infrastructure perform. These devices have become smarter, remotely accessible and increasingly connected to networks. However, they were never designed with this in mind.
With organisations continuing to focus on data breaches – the investment in OT security will continue to lag. This will create a ‘security debt’ over coming years for those that do not invest in preventative controls now.
-
AI Training will Receive Attention from Regulators and the Public as a Possible Infringement of Privacy
News that Amazon’s Alexa was eavesdropping on its users, and that Apple’s Siri and Google’s Assistant, also kept recordings to help train their AI raised many concerns about how data to train AI is collected and stored. Apart from the initial consternation in the press and on social media, nothing much seems to have happened from a regulatory perspective.
2020 will be the year when AI training relying on consumer data will start to become regulated.
-
Major GDPR Fines in 2020 will Force MNCs to Invest in Security Compliance
GDPR came into effect in May 2018, but we still have not seen huge amounts of fines being issued in the EU. Only two fines were issued in 2018, while at least 17 were known to be issued in the first half of 2019, totalling about EUR 52 million. In the third quarter of 2019, at least 12 fines were issued totalling about EUR 328 million.
The trend is clear: Expect to see a magnitude of companies across EU be penalised in 2020. We also expect several fines above EUR 100 million and GDPR impacting countries outside the EU.
-
Mergers & Acquisitions will Ratchet up Significantly in 2020
The fragmented global security market consists of thousands of vendors and consultancies. Every day a swathe of new start-ups announces their ground-breaking new technology. Coupled with significant investments in tertiary education and industry certifications for a growing workforce, the next generation of cybersecurity entrepreneurs are entering with force.
We believe that this creates both threats and opportunities for established cybersecurity providers that need to remain innovative and growing. Similarly, this presents smaller or more niche cybersecurity start-ups with an avenue for funding or acquisition.
Ecosystm in partnership with SGInnovate, the government-backed organisation that promotes Deep Tech in Singapore, released a series of four reports covering areas of mutual interest: Cybersecurity, Artificial Intelligence, Cities of the Future and Healthtech. ‘Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Cybersecurity Trends for 2020’ report is a part of this collaboration and is available for download from Ecosystm and SGInnovate websites.
Download Report: The top 5 Cybersecurity trends for 2020
The full findings and implications of the report ‘Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Cybersecurity Trends for 2020’ are available for download from the Ecosystm platform. Signup for Free to download the report and gain insight into ‘the top 5 Cybersecurity trends for 2020’, implications for tech buyers, implications for tech vendors, insights, and more resources. Download Link Below ?

In June 2019, Ecosystm conducted Roundtables in Sydney and Melbourne supported by our partner Delphix. IT and business executives from data-intensive industries in Australia came together to discuss how to overcome data-driven constraints and enable innovation by effectively managing and distributing data in a secure environment within organisations. These are the salient points that emerged from the sessions.
In the course of my facilitation, I realised that the key focus of the discussions was on how organisations today handle their biggest asset – data – and manage all the moving parts in large and diverse settings and in very traditional enterprises that are transitioning into data-driven “New Age” businesses.
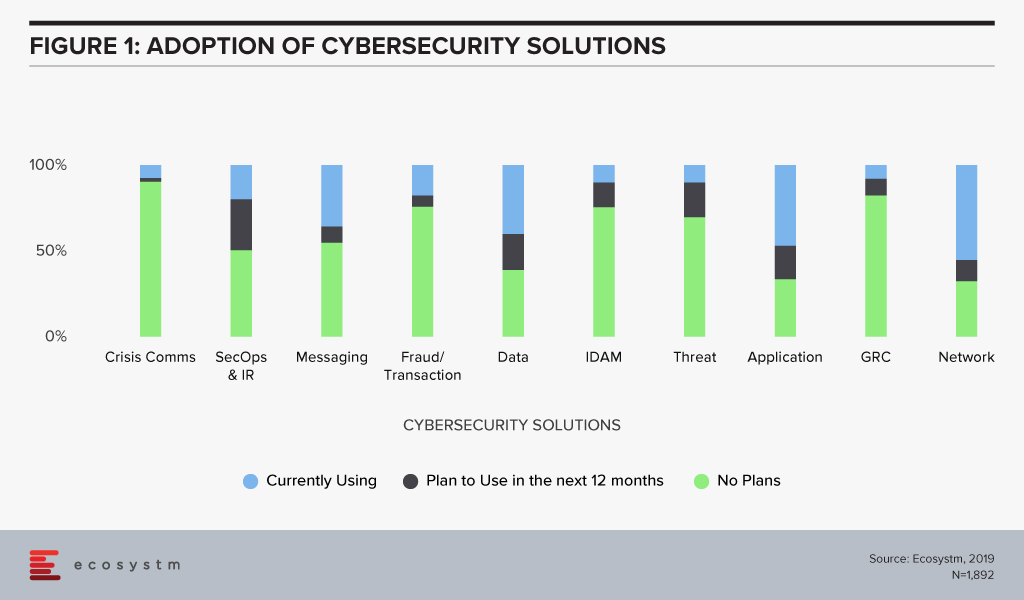
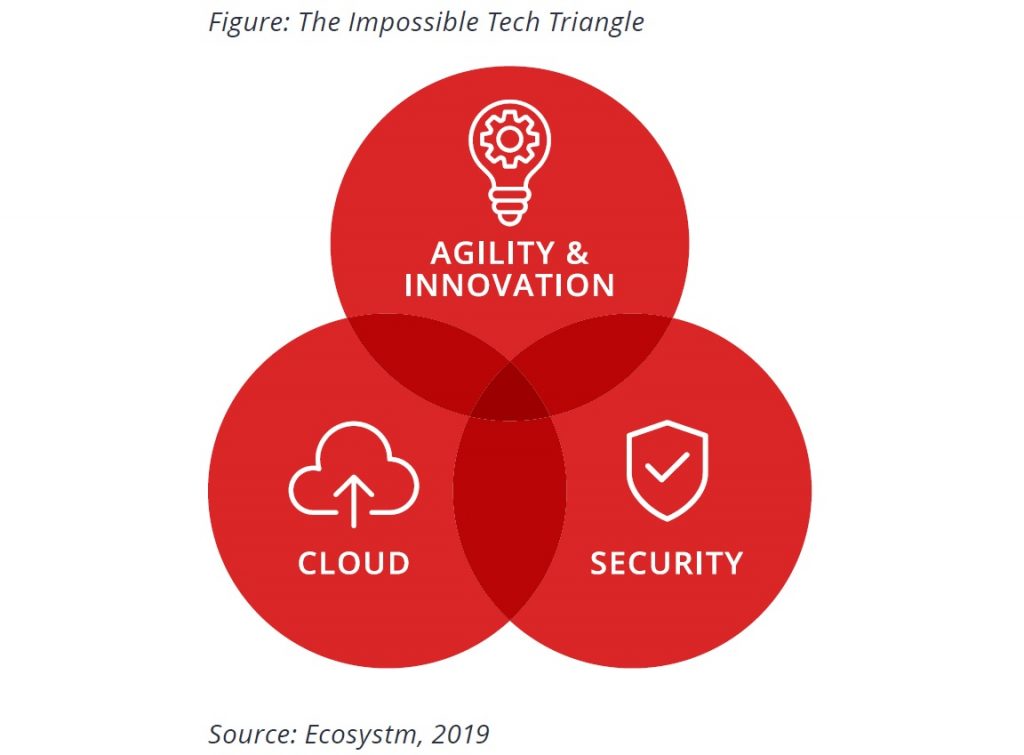
The Impossible Tech Triangle
Data has never been so prolific or strategic as it is today. Multiple sources of data generation and technologically savvy customers have seen a data explosion. Simultaneously, personalised services and data insights have seen a drive toward using the data for increased intelligence in most industries. The biggest risk organisations face and what CSOs and business leaders spend sleepless nights on, is significant disruption due to compromise. Moreover, the complexity of the technology platforms means that no organisation is 100% certain that they have it right and that they are managing the risk effectively.
Does this give rise to a similar situation as in Marketing and Advertising where the triangle of price, quality and speed appear to be unattainable by many organisations?
Key takeaways from the sessions
#1 Drivers & Challenges of Cloud adoption
The fact that discussions around agility and innovation can happen with the intensity it does today, is because organisations have embraced Cloud infrastructure and application development platforms and SaaS solutions.Every organisation’s Cloud journey is unique, driven by its discrete set of requirements. Organisations choosing cloud may not have the resources to build in-house systems – or may choose to migrate to the cloud for various reasons such as cost, productivity, cross-border collaboration or for compliance.
When embarking on a Cloud journey it is important to have a clear roadmap that involves instilling a Cloud-First culture and training the IT organisation in the right skills for the environment. Concerns around costs, security, and data ownership are still synonymous with Cloud, therefore, organisations can distill the workload from a cost angle before jumping on Cloud. It is important for organisations to appreciate when a Cloud option will not work out from a cost angle and to have the right cost considerations in place, because organisations that do a straight resource swapover on Cloud are likely to end up paying more.
Data ownership and data residency can also be challenging, especially from a compliance standpoint. For some, the biggest challenge is to know the status of their data residency. The challenges are not just around legacy systems but also in terms of defining a data strategy that can deliver the desired outcomes and managing risk effectively without ruining the opportunities and rewards that data utilisation can bring. Cloud transformation projects bring in data from multiple and disparate sources. A clear data strategy should manage the data through its entire lifecycle and consider aspects such as how the data is captured, stored, shared, and governed.
#2 Perception on Public Cloud Security
While security remains a key concern when it comes to Cloud adoption, Cloud is often regarded as a more secure option than on-premise. Cloud providers have dedicated security focus, constantly upgrade their security capabilities in response to newer threats and evolve their partner ecosystem. There is also better traceability with Cloud as every virtual activity can be tracked, monitored, and is loggable.
However, the Cloud is as secure as an organisation makes it. The Cloud infrastructure may be secure, but the responsibility of securing applications lies with the organisation. The perception that there is no need to supplement public Cloud security features can have disastrous outcomes. It is important to supplement the Cloud provider’s security with event-driven security measures within an organisation’s applications and cloud infrastructure. As developers increasingly leverage APIs, this need to focus on security, along with functionality and agility should be emphasised on. Organisations should be aware that security is a shared responsibility between the Cloud provider and the organisation.
#3 Viewing Security as a Business Risk – not IT Risk
The Executive Management and the Board may be involved in the Security strategy and GRC policies of an organisation. But a consistent challenge Security teams face is convincing the Board and Senior Management on the need for ongoing focus and investments on cybersecurity measures. Often, these investments are isolated from the organisation’s KPIs and are harder to quantify. But Security breaches do have financial and reputational impact on organisations. Mature organisations are beginning to view Security as a business risk requirement and not a matter of IT risk alone. One of the reasons why Senior Management and Boards do not understand the full potential of data breaches is because CISOs do not translate the implications in business terms. It is their responsibility to find ways to procure senior management buy-in, so that Security becomes part of the Strategy and the costs associated gets written into the cost of doing business.
Training sessions that educate the stakeholders on the basics of the risks associated with using knowledge systems can help. Simulation of actual cybersecurity events and scenario testing can bring home the operational issues around recovery, assessment and containment and it is important to involve senior stakeholders in these exercises. However, eventually the role of the CSO will evolve. It will become a business role and traverse Security across the entire organisation – physical as well as cybersecurity. This is when organisations will truly recognise investment in Security as a business requirement.
#4 Moving away from Compliance-driven Security Practices
Several organisations look at Security as part of their compliance exercise, and compliance is built into their organisational risk management programmes. Often, security practices are portrayed as a product differentiator and used as a marketing tool. An organisation’s Security strategy should be more robust than that and should not only be focused on ticking the right compliance boxes.
A focus on compliance often means that Security teams continually create policies and call out non-compliance rather than proactively contribute to a secure environment. Applications teams do not always have the right skills to manage Security. The focus of the Security team should not be on telling Applications teams what they are doing wrong and writing copious policies, procedures and standards, expecting others to execute on the recommendations. There should be a focus on automated policy-driven remediation that does not restrict the Applications team per se but focuses on unsafe practices, when they are detected. Their role is to work on the implementation and set up Security practices to help the Applications team do what they do best.
#5 Formulating the Right Incident Response Policy
In the Ecosystm Cybersecurity study, 73% of global organisations think that a data breach is inevitable – so organisations largely believe that “it is not about if, but when”. About 50% of global organisations have a cyber insurance policy or are evaluating one. This trend will only rise. Policy-driven incident response measures are an absolute requirement in all enterprises today. However, to a large extent even their incident response policies are compliance driven. 65% of the organisations appear to be satisfied with their current breach handling processes. It is important to keep evolving the process in the face of new threats.
Organisations should also be aware of the need for people management during an incident. Policies might be clear and adhered to, but it is substantially harder to train the stakeholders involved on how they will handle the breach emotionally. It extends to how an organisation manages their welfare both during an incident and long after the incident response has been closed off.
Over the two sessions, we explored how to achieve the ‘unattainable triangle’ of Cloud, Agility and Security. What I found interesting – yet unsurprising – is that discussions were heavily focussed on the role of Security. On the one hand, there is the challenge of the current threat landscape. On the other hand, Security teams are required to deliver a Cloud and an agile development strategy in tandem. This disconnect ultimately highlights the need for Security and data management to be embedded and managed from the very start, and not as an afterthought.
Here are some of the moments from the session –
At the 7th Personal Data Protection Seminar, Minister for Communications and Information S. Iswaran announced a framework to bolster Singapore’s digital economy and to drive Singapore’s vision of turning the country into a regional data protection hub.
The Personal Data Protection Commission (PDPC), which oversees the country’s Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA), has developed a new framework to better support organisations in the hiring and training requirements of Data Protection Officers.
Why the Need?
PDPA has been around for a while and the new framework is brought into practice to enable a greater focus of government and organisations on data privacy. According to Ecosystm’s expert on GDPR and Data Privacy, Claus Mortensen, “the initiative reflects the difference between ‘theory’ and ‘practice’ when it comes to data security. PDPA is not making changes to the present regulatory framework, but they are putting together a program and guidelines for how companies can apply and abide by the present regulatory framework.”
Ensuring PDPA framework compliance
The PDPC plans to collaborate with the National Trades Union Congress (NTUC), Employment and Employability Institute (e2i) and NTUC LearningHub to create a year-long pilot training program to train at least 500 data protection officers in its first intake. The Data Protection Officers would help to manage the complex and highly sensitive task of data flows.
To ensure the data flow mechanisms and to ensure security, Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) has been appointed as Singapore’s Accountability Agent (AA) for the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Cross Border Privacy Rules (CBPR) and Privacy Recognition for Processors (PRP) Systems certifications. IMDA will allow Singaporean organisations to be certified in APEC CBPR and PRP Systems for accountable data transfers.
“The PDPA requires a data protection officer to be appointed in every organisation. This framework is focused on educating and certifying these officers. However, it mostly makes it easier for slightly larger companies who can afford to send employees on longer training programs or who are able to hire people, who have taken the certificates. Smaller organisations – such as start-ups – would benefit more from detailed guidelines and from on-premises guidance. Establishing a framework for such services could be the next area of focus for the PDPC.” said Mortensen.
Legislature for the data handling and exchange practices
The private data has become an increased target of hackers as well as an international commodity. Attackers always mine the cyberspace for any leaks or financial information that they can exploit to their advantage.
“Managing sensitive data is notoriously complicated – especially for ‘legacy’ companies that still have or rely on non-digitised data. Even when all data is digital, employees may have copies on their PCs, they may have partial backups on removable media, some data may need to be shared with sub-contractors, moved around between cloud providers, etc. This can make it very difficult to map out PDPA relevant data in the organisation. Even when the data has been mapped, it can be difficult to ensure that all business and data processes are compliant. This is where on-premises guidance can make a difference,” said Mortensen. “While the government clearly aim the new framework initiatives at helping SMEs, it will help further protect consumer’s sensitive data.”
Importance of Cyber Security
A business harnessing digital technology can’t afford to gamble with sensitive data and rising cyber-attacks. The government is taking initiatives by forming guidelines and regulations to prevent cyber-attacks, but it is the responsibility of businesses to have a cybersecurity strategy in place to prevent a breach. If a business becomes a victim of hacking, it is perceived as a failure to the company.
The government passed the PDPA law and compliance to ensure that businesses understand the importance of cybersecurity. Therefore, every business, organisation or academic institution must ensure compliance with the data protection act and must have security best practices to safeguard the data of its customers.
It can often be difficult to keep track of assets and transactions in a business, and that is where Blockchain is unleashing its potential. It is revolutionising enterprises with its shared ledger technology. There are numerous, and specialised, use cases of Blockchain but the adoption is nascent in most industries. There are a few early adoption use cases of Blockchain, however, which have the potential to replace traditional systems and processes.
In the global Ecosystm Mobility study, organisations are asked about the adoption of Blockchain as a means of authentication. Industries that appear most open to Blockchain adoption are those that have also embraced IoT for tracking and traceability.
Adoption of Blockchain for Authentication – An Industry Comparison
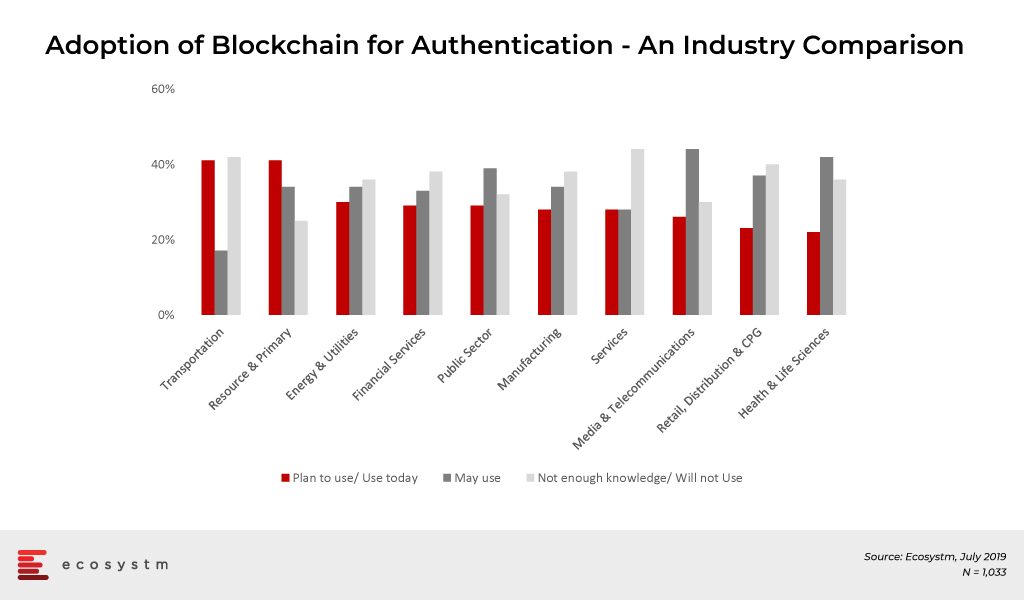
Across industries Blockchain technology is being used primarily for these use cases:
Supply Chain Traceability
Supply chain traceability allows producers, retailers, and consumers to track products from source to consumer. It connects all points in the supply chain, creating transparency and trust in the product. When a business comprises complex processes, a large and dispersed workforce, multiple locations and different operations, a lot of administrative and regulatory frameworks are required to manage and control the supply chain. Functions such as order management, procurement, import, delivery, tracking, and invoicing have their own unique set of requirements and processes. In several cases, especially across primary and retail industries, business complexity has been reduced with the use of Blockchain. The technology allows for improving digital assets and inventory tracking for better services and processes.
Blockchain is ensuring food safety by providing a complete view of the supply chain and creating a real-time trail of products – allowing a ‘farm to fork’ view. Walmart is a good example of how retailers can use Blockchain technology to ensure that they sell fresh produce. Fresh produce shipments can be tracked as they change hands from the farmers to the middlemen, to the distributor and finally to the store. This can have an enormous impact on containing food-borne diseases and food contamination. Not only does Blockchain increase food safety, it ensures fresher food since it secures production and packing dates.
Intellectual Property Intermediary (IPI), an organisation established under Singapore’s Ministry of Trade and Industry, is an affiliate of Enterprise Singapore and focuses on technology innovations in the industry that can empower enterprises to develop new processes, products, and services. IPI has identified Blockchain Technology for Food as an area where the industry can benefit from innovation. The ecosystem will also benefit from the information gathered, with the potential to further improve the production chain.
Fraud Prevention
Taking supply chain visibility a step further, Blockchain technology is being used for fraud prevention – especially payment fraud. Financial transactions are complex and involve multi-step processes and human intervention – involving collaterals, settlement, currency denominations, third-party mediation, and so on. It is often the prime target for fraudsters. The most common instances of fraud involve bank to bank transactions, mobile payments, and digital identity fraud, essentially by tampering with ID or using it an unsanctioned way – providing unauthorised access to digital systems and falsifying information.
Blockchain helps automate preventive measures enabling real-time information sharing which is transmitted on a chain of connected devices where all the nodes in a system verify the transaction. Since it stores the data on several nodes and every other user on the network has a copy of the entire data on the Blockchain, it is virtually impossible to hack or destroy it completely.
Earlier this year, Standard Chartered Singapore showcased their cross-border trade finance transaction which digitalises trade processes and financing documentation. Blockchain enabled the transaction between parties by digitally streamlining the documentation process while providing security and transparency between the partners. Not only does it support the clients’ entire supply chain, but it also creates a transparent way to provide same-day trade financing.
Non-profit organisation BitGive Foundation uses Blockchain technology to provide greater visibility to their donors into the receipt of funds and how they are used by sharing financial information and project results in real-time. The GiveTrack project is built on Bitcoin and Blockchain and is a user-friendly, data-centered and comprehensive user interface. People making donations can precisely track the donations and how the funds were used.
Legal & Compliance
In industries that have higher Compliance & Regulatory requirements, Blockchain can enable safe, secure, and scalable data-sharing. The industry is seeing instances of self-executing contracts, smart registries, secure and time-stamped documents with Blockchain. Blockchain is introducing abilities to record events for a long duration which might include indisputable claims, criminal records, case procedures to support the potential legal work.
Dubai launched a city wide blockchain strategy. Dubai Land Department is implementing blockchain to make property transactions secure, transparent and immutable, thereby reducing fraud and eliminating reams of physical documents. This impacts the entire ecosystem – customers, developers, the land department, utility providers, payment channels, and municipalities – to work in collaboration.
Shipping companies that need to enforce global contracts daily are also benefitting from Blockchain. However, the biggest use cases will eventually come from the Public Sector – across citizen services and criminal justice systems. For instance, National Stock Exchange of India (NSE) is testing Blockchain e-voting facilities. The project is still at the pilot stage and aims to tokenised voting which makes it easy to conduct test and audit for the votes. This allows the regulating authorities to access real-time data, and at the same time, provides means to audit the regulators.
Cybersecurity
73% of global organisations believe that a data breach is inevitable, according to the Ecosystem Cybersecurity Study, and only 18% of them use some form of tokenisation and other cryptographic tools. Blockchain technology offers several capabilities in mitigating cybersecurity risks and detecting and combating cyber attacks. For example, Blockchain can be used to prevent DDoS attacks, and crypto secured biometric keys can replace passwords providing robust ID authentication systems, more secure DNS and decentralised storage. Blockchain implementation can also prevent man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks by encrypting the data in transit so it is not manipulated during the transmission or accessed by unauthorised parties – thus maintaining data integrity and confidentiality.
Lockheed Martin, a US security company, is implementing Blockchain into their protocol. The company is enhancing Blockchain cybersecurity protocol measures in engineering systems, supply chain risk management, and software development. This includes researching on expanding on Blockchain capabilities protect their weapons development unit and make it incorruptible.
eGovernment initiatives will also benefit from Blockchain. The biggest stumbling block for providing eservices has always been cybersecurity, where the Government cannot be sure that the citizens are able to access their own records in a secure manner. It has always been a question of responsibility and liability – is the Government liable for a data breach that happens because of a citizen’s fault? Estonia is using Blockchain to protect their digital services such as electronic health records, legal records, police records, banking information, covering data and devices from attacks, misuse, and corruption.
Customer Experience
The ultimate benefit of Blockchain will be realised when it is used to enhance Customer Experience (CX). It brings transparency in doing business, gives on-demand data visibility and fosters trust in customers. A company that shows all transactions between the company and the customer, and in a secure manner, can create a better relationship, increase overall customer satisfaction and retain their customers in a competitive market. For example, Blockchain technology can allow more secure and transparent loyalty programmes, through token creation that can be redeemed on-demand, without customer service intervention. Singapore Airlines’ KrisFlyer structures their payments and loyalty programme with Blockchain. Their digital wallet enables members to convert KrisFlyer miles into KrisPay miles instantly to pay for their purchases at partner merchants. The users can pay through an application by scanning a QR code at a merchant’s location .
Customers will increasingly look for ease of use and security in their transactions. Bank of America has filed a patent for Blockchain powered ATM, for securing records and authenticating business and personal data. This will boost the transaction rate and facilitate various transaction experience with full encryption and security. Blockchain-enabled transactions can be registered and completed with greater easy while lowering the transaction costs for customers and keeping the network safe.
While Blockchain technology is continuing to evolve for a range of applications and industries, it comes with its own share of risks. Adoption should not be based on the hype around the technology but should be evaluated carefully. The starting point should obviously be a real business needs analysis.
Speak with an expert today to evaluate whether your organisation can benefit from Blockchain.
The 5th VeeamON event held in Miami Beach recently, attracted around 2,000 customers and partners. The 2-day conference is the annual Veeam gathering of mainly IT admins to learn about and get certification for Veeam’s latest product releases. Veeam Co-Founder and EVP, Sales and Marketing, Ratmir Timashev provided Veeam’s update on business affairs and strategy.
Business Updates
What Timashev describes as Veeam’s ‘Act I’ has seen them emerge as a leader in backup and availability solutions for virtual environments over the last 10 years. ‘Act I’ further helped Veeam reach the milestone of US$1 billion in sales – over the current 12 months period – which elevates Veeam into an exclusive club of only 34 software companies that have achieved this milestone (and very few privately owned software companies have achieved this globally). Going forward, Veeam will continue to focus on their Hybrid Cloud strategy and what they describe as ‘Act II’ of their growth journey.
In line with the market moving from on-premises to cloud to hybrid environments, the next phase of growth will focus on adding hybrid cloud functionality to their existing hypervisor- and physical agent-centred software portfolio. By continuing their strategy on partnering and channels, the solutions are designed to make it easy for service providers to deliver Veeam as managed services to the market.
Ecosystm Comment. Ecosystm’s ongoing Cloud research shows that almost 100% of companies have shifted at least one workload onto the cloud which makes cloud undoubtedly mainstream. Despite that broad adoption we see cloud maturity still at an early stage as the number of SaaS workloads and the complexity of on-premises and cloud integration will increase over time. Our research shows that companies currently use an average of 3 separate SaaS applications which is expected to double over the next 12 months.
Stages of Cloud Management
Organisations’ requirements to manage their data assets in the hybrid world will mature in tandem with their expanded cloud footprint. Veeam describes this path as the ‘5 Stages of Cloud Management’.
Figure 1: Veeam’s Stages of Cloud Management
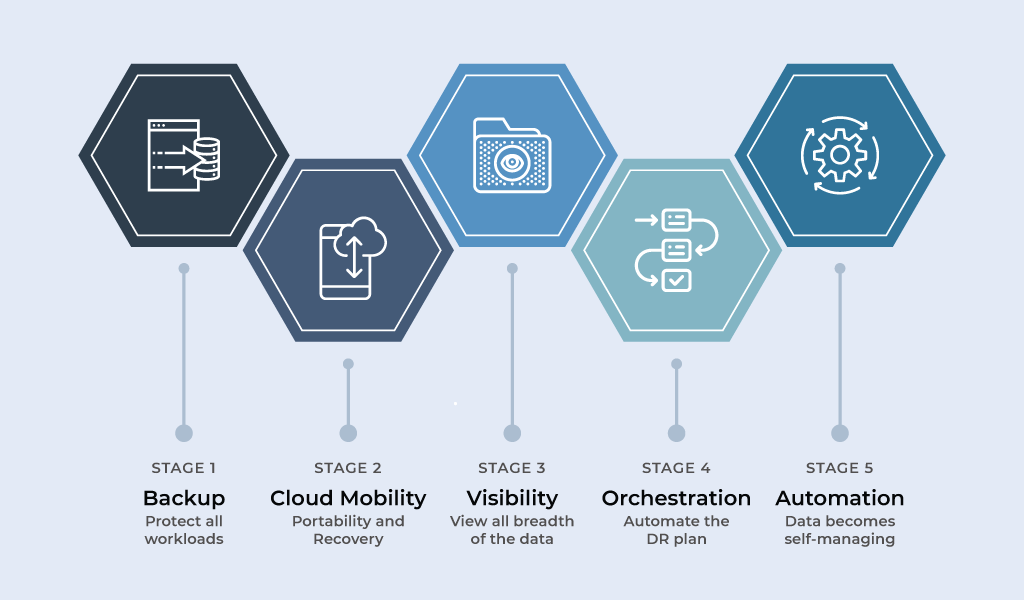
Veeam sees the majority of the market currently sitting at stage 1 or 2 providing a strong pipeline and growth path in taking customers along their ‘Act II’ journey.
Ecosystm Comment. We would raise some caution as the execution of this strategy may play out as more challenging than anticipated. Our research shows that a majority of companies – especially in emerging markets – see cloud as a means to shift the responsibility of data protection and availability, onto their cloud providers. The ongoing global Ecosystm Cybersecurity research reveals that nearly half the organisations rely solely on their public cloud provider to secure even their most sensitive data.
Figure 2: Perception on Public Cloud Security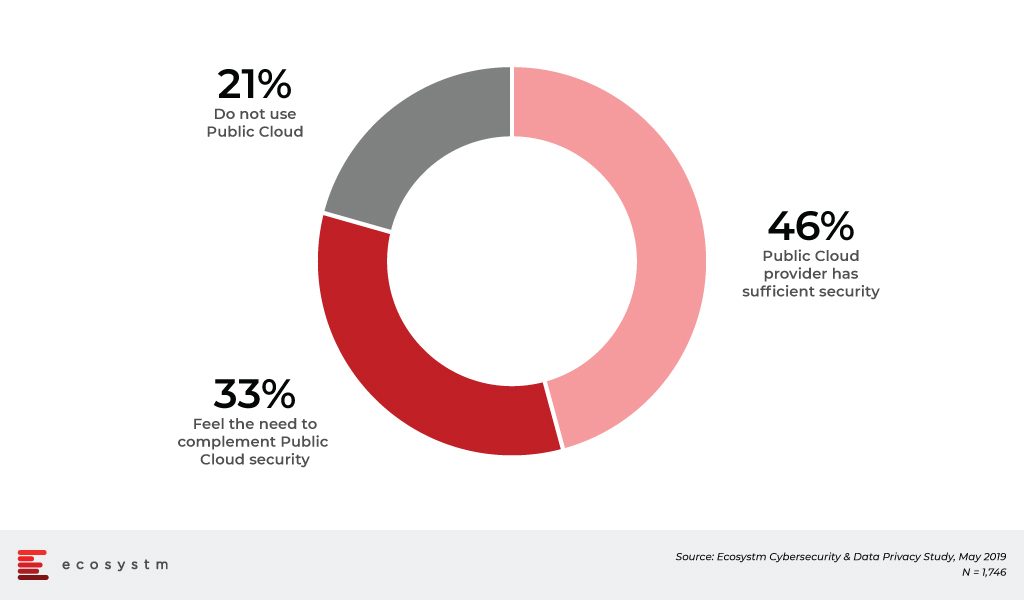
This finding is concerning when competitiveness has increasingly moved away from the traditional measures such as cost, quality and time to a company’s data and IP assets. So Veeam is urged to equip their partners and sales team with a strong educational message that the responsibility of data protection and availability cannot be shifted solely onto the cloud provider. The responsibility and accountability remains with the organisation and has to be managed across the increasingly hybrid environments.
Product Announcements
Keeping with the tradition, Veeam leveraged VeeamON 2019 as the platform for a number of product releases and announcements. In alignment with the business strategy, most of the new features support data management in hybrid cloud environments as well as new integrations and features for SaaS and Cloud platforms.
The most anticipated release of version 10 of Veeam’s flagship Availability Suite has not yet happened. Announced at VeeamON 2017, Version 10 will be released towards the second half of 2019. While the delay may be of concern, we would give Veeam credit for adopting a true SaaS model for their product development process. They have constantly released newer features and functionality to the current suite, opting to release some features faster to market to answer to specific customer demands at the time, such as centralised agent management support and Universal Storage API support. The key new features of Availability Suite 9.5 Update 4 include easy management of cloud migration and cloud mobility, cloud-native backup, cost-effective data retention, and portable cloud-ready licensing, increased security and data governance.
Veeam Availability Orchestrator v2 is the second generation of Veeam’s DR orchestration platform reducing the manual processes to achieve auditable DR, operational recovery and platform migrations. With increasing industry regulations this capability could give organisations of all sizes and resources the tools to prove and proactively remediate service level agreement (SLA) attainment for internal and external compliance regulations and audits with extensive reporting and compliance capabilities.
Nutanix Mine with Veeam is another product which received a lot of interest at VeeamON. With availability announced for late 2019, Mine is a partnership with Nutanix to provide more comprehensive and affordable solutions for secondary storage layers. Similar joint offerings have also been announced with ExaGrid. Mine provides Nutanix hyper-converged infrastructure with highly integrated Veeam Backup & Replication solutions to provide easy deployment and scaling, faster time to value and standardised IT operations management.
Ecosystm Comment. Ecosystm’s research shows that regulatory requirements are key to organisations’ propensity to invest in data protection and availability solutions. They are often built into the organisations’ risk management programmes as well.
Figure 3: Drivers of Continued Focus on Cybersecurity

Availability Orchestrator v2 presents a strong entry point for Veeam to start the discussions for a more holistic data management solution. Providing the automation of the DR orchestration, scenario planning and auditable DR documentation strengthens Veeam’s claim to be the rightful owner of the Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC) discussion. Furthermore, although it may be from leftfield, Ecosystm sees a great opportunity for some partnerships with Cybersecurity insurance companies to make Veeam Availability Orchestrator an accepted standard for Cybersecurity premium assessments and rebates. Ecosystm has seen a rapid rise of Cybersecurity insurance adoption with nearly 50% of global organisations already signed on to different policies. With adoption expected to accelerate over the coming years, Cybersecurity insurers could present a new route to market that is not in competition to its existing network of more than 60,000 partners.
Looking Ahead
Veeam has announced ‘Act II’ as the second stage of growth to carry on from their initial virtual machine-centred availability solution. The strategy follows the natural evolution and path of the market and will not require a major rethink or restructure of the Veeam business.
What is changing is the scale of business in geographical coverage, product portfolio and most importantly the Veeam partner ecosystem. In the same way that Veeam expanded their breadth in ‘Act I’ from the original VMware hypervisor backup to the broader hypervisor market and core infrastructure integrations, ‘Act II’ will require expansion across the key cloud platforms, exponentially growing SaaS landscape and the different tiered infrastructure providers.
Veeam’s product development teams have been one of the main beneficiaries of Veeam’s $500 million fund raising exercise earlier in 2019 (investors include Insight Venture Partners & Canada Pension Plan Investment Board) as they invested further in organic internal development instead of acquiring and integrating third party capabilities.
Geographical expansion is another area where the $500 million has been invested in. Veeam currently sits at 350,000 customers with 4,000 being added on a monthly basis. Emerging markets such as Asia Pacific are the engines of the growth but there are still markets and partnerships to be explored and developed. Across Asia Pacific alone Veeam opened 4 new offices in the first 5 months of 2019 and further expansions are planned for the months to come. The race for scale is essential to execute on ‘Act II’ but it brings operational challenges to scale in tandem with their operations while maintaining the culture that made Veeam what they are.
Ecosystm Comment. There is no doubt that there is a lot of work ahead of Veeam in executing on ‘Act II’. We have seen early proof that execution is following strategy, with new partnerships in the tiered storage space (such as Nutanix and ExaGrid), new products focussed across mainstream SaaS applications such as Office365 and tighter cloud integrations with Azure and AWS. There is currently lesser compatibility with Alibaba Cloud and no integration with Google which would be essential to accelerate their growth especially in Asia Pacific which has been highlighted as Veeam’s growth engine. The SaaS landscape presents an even tougher challenge for Veeam. Veeam Backup for Office365 has demonstrated the strong opportunity of workload-based availability solutions but developing the same capability across hundreds or thousands of diverse SaaS applications will present challenges. At the same time, we agree with Veeam’s focus on going deep into their solutions integration with the key partners and workloads that present the greatest opportunity today rather than spreading resources to put breadth over depths at this stage.
In 2013 Ratmir Timashev predicted to reach $1 billion within 6 years which was achieved just in time for VeeamON 2019. There were no new predictions made for ‘Act II’ but we see Veeam on the right path to announce tangible progress on their ‘Act II’ execution at VeeamON 2020 in Las Vegas.
On 17 May 2019, the New Zealand Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern and the Singapore Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong signed a formal arrangement, to step up collaboration in the areas of trade, defence, cybersecurity, science and technology, and arts and culture.
To strengthen cybersecurity, the Cyber Security Agency of Singapore (CSA) and the National Cyber Policy Office (NCPO) of New Zealand inked an agreement on information sharing, cybersecurity and capacity building in the region. A new Cyber Security Arrangement will support greater information exchange, including through an annual cybersecurity dialogue between the two countries. The aim of the agreement is to increase information exchange, prevent incidents and threats and follow best practices on data, infrastructure, and systems protection.
Commenting on the announcement Ecosystm Principal Advisor, New Zealand-based Jannat Maqbool, said, “Engaging internationally on cybersecurity research and initiatives is fundamental given the trans-boundary nature of the cyberspace. As both nations become more digitised and connected, a collaboration will enable each to leverage strengths in key areas to develop a multi-pronged approach to cybersecurity. Both countries will also be in a better position to weigh in on the development of rules-based international order for cyberspace.”
Echoing these comments, Ecosystm Board Advisor, and former Global Head, Digital Development Unit at the World Bank, Randeep Sudan explains how cybersecurity is critical to the growth and development of the digital economy. “Mitigating cyber risks will require coordinated action by multiple stakeholders, including governments, the private sector, academia, and non-governmental organisations,” Sudan says. These bilateral and multilateral G2G partnerships are, therefore, an essential piece in tackling cyber threats. “Given that Singapore and New Zealand are leading players in cyberspace, a G2G collaboration between them will offer learnings of immense value to other governments,” Sudan continues.
Due to Ecosystm’s own close ties with New Zealand, and considering that we are headquartered in Singapore, we are ourselves actively engaged in promoting the dialogue between New Zealand and Singapore. Ecosystm CEO Amit Gupta and Chief Operating Officer, Ullrich Loeffler are in New Zealand this week to participate in Techweek New Zealand (an annual initiative to promote and build awareness for new technologies and innovation in New Zealand) to meet key stakeholders and attend industry events.
 |
 |
Commenting on the sidelines of Techweek, Amit Gupta gave his thoughts on the agreement, “Both New Zealand and Singapore are in hyper-innovation mode at the moment. With the advent of Blockchain and AI especially spurring the growth of the Fintech ecosystem in New Zealand, there is strong potential gains in engaging with the already thriving Singapore Fintech ecosystem.”
New Zealand and Singapore are not only model free markets, but also have been key proponents of data privacy over the years, an area that requires a serious look, as we start to apply new emerging technologies such as AI. “There is an opportunity for these two forward-looking nations to take it a step further to build an actionable Data Privacy Corridor to streamline the Fintech collaboration between them,” Gupta added. “With New Zealand being an export economy and Singapore, a strong services economy, this would enable a much more seamless collaboration between these two countries.”
The collaboration does not end at cybersecurity and Fintech. As part of the partnership, a joint work programme is being negotiated, starting with two flagship collaborations – an advanced data science research platform to build New Zealand’s data science capability; and a food and nutrition cooperative science programme with a focus on ‘future foods’. Both countries have different areas of expertise, and collaborative measures such as these, give them an opportunity to share best practices that will prove mutually beneficial.
AT&T became the first North American operator to join the ranks of the Global Telco Security Alliance formed by Singtel, Etisalat, Softbank, and Telefónica. The alliance which was formed last year in April 2018 in a pact to amalgamate the capabilities of telecommunications operators on security aspects and fight collectively against cyber attacks.
AT&T joined as an equal member with other founding members of the group. Over the past few years, AT&T has been building its cybersecurity capabilities and has recently acquired AlienVault– a commercial and open source developer – to offer a platform that integrates and automates point security products to manage cyber attacks. AlienVault has been rebranded as AT&T Cybersecurity, and includes consulting and managed security services. Similarly, at the end of 2018, Singtel revealed the brand ‘Trustwave’ that combines the capabilities of partners such as Optus and NCS, to provide a comprehensive security suite and services to help organisations fight cybercrime.
With the rising risks of cyber-attacks, these initiatives are providing a synergistic front and helping organisations to analyse and act faster against cyber threats. The alliance plans to expand its global footprint and span across APAC, Europe, MEA and America.
Speaking about the alliance, Alex Woerndle, Principal Analyst Cybersecurity, Ecosystm says that, “Similar collaborations exists within other industries already – most commonly they use regular information-sharing sessions with the collective security teams to discuss what each is experiencing, what strategies and tactics have worked or failed, and provide details on the type and nature of attacks. The telcos – at a minimum – should be collaborating at that level. But given the global nature of this alliance, they will need to consider how they can aggregate threat information and share it in a more agile way on a day to day, hour to hour and minute to minute basis.”
The alliance accounts for a significant percentage of the overall traffic and is a tangible example of companies taking steps to fight cyber attacks. “As the threat landscape continues to expand there is an opportunity to broaden the intelligence – sharing what they collectively gather and analyse, to strengthen the defences of the broader market not just in their local geographies, and to impact globally”, says Woerndle. “Think of the immense opportunities to share intelligence gathered collectively by all the major telcos, to proactively prevent attacks on their clients – from other enterprises down to small/medium businesses and consumers. Law enforcement could benefit from the global telco collaboration, also”