Customer Experience teams are focused on creating a great omnichannel experience for their customers – allowing customers to choose their preferred channel or touchpoint. And many of these teams are aware of the challenges of omnichannel – often trying to prise the experience from one channel into another. Too often we create sub-optimal experiences, forcing customers to work harder for the outcome than if they were using other channels.
I know there have been times when I have found it easier to jump in the car and drive to a store or service centre, rather than filling in a convoluted online form or navigating a complex online buying process. I constantly crave larger screens as full web experiences are often better than mobile web experiences (although perhaps that is my ageing eyes!).
One of the factors that came out in a study conducted by Ecosystm and Sitecore is that customers don’t just want personalised experiences – they want optimised experiences. They want to have the right experience on the right device or touchpoint. It is not about the same experience everywhere – the focus should be on optimising experiences for each channel.
We call this “opti-channel”.
Use an Opti-Channel Strategy to Guide Investment and Effort
This is what you are probably doing already – but by accident. I suggest you formalise that strategy. Design customer experiences that are optimised for the right channel or touchpoint – and personalised for each customer. Stop forcing customers into sub-optimal experiences because you were told to make every customer experience an omnichannel one.
The move towards opti-channel accelerates your ability to provide the best experience for each customer, as you ask the important question “Does this channel suit this experience for this customer?” before the fact – not after the experience has been designed. It also eliminates the rework of existing experiences for new channels and provides clear guidance on the next-best action for each employee.

There Will be Conflict Between Opti-Channel and Personalisation
The challenge for opti-channel strategies will be to align them to your personalisation strategy. How will it work when you have analytics driving your personalisation strategy that say customer X wants a fully digital experience but your opti-channel strategy says part of the digital experience is sub-standard? And the answer to this lies in understanding the scope of your experience creation – are you trying to improve the existing experience or are you looking to create a new improved experience?
- If you are improving the existing experience, then you have less license to shift transactions and customer between channels – even if it is a better experience.
- If you are creating a new experience, you have the opportunity to start again with the overall experience and prove to customers that the new experience is actually a better one.
For example, when airlines moved away from in-person check-in to self-check-in kiosks, there was an initial uproar from customers who had not yet experienced it – claiming that it was less personal and less human. But the reality is that the airlines took the check-in screen that the agents were using and made it customer-facing. Travellers can now see the seats and configuration and select what is best for them.
This experience was reinvented again when the check-in moved to web and mobile. By turning the screen around to the customer, the experience actually felt more human and personal – not less. And by scattering agents around the screens and including a human check-in desk for the “exceptions”, the airlines could continue to optimise AND personalise the experience as required.
Opti-Channel Opens Many New Business Opportunities
Your end-state experience should consider what is the best channel or touchpoint for each step in a journey – then determine the logic or ability to shift channels. Pushing customers from a chatbot to web chat is easy. Moving from in-store to online might be harder, but there are currently some retailers looking to merge the in-store and digital experience – from endless aisle solutions to nearly 100% digital in-store. Some shoe and clothing stores offer digital foot and body scans in-store that help customers choose the right size when they shop online. And we are beginning to see the rollout of “magic mirrors” – such as one retailer who has installed them in fitting rooms and you can virtually try different colours of the same item without actually getting them off the shelf.
Businesses are trying to change customer behaviour – whether it is getting them into stores or mainly shopping online or encouraging them to call the contact centre or to even visit a service centre. Creating reasons for why that might be a better option, while also providing scaled-back omnichannel options is a great way to meet the needs of existing customers, create brand loyalty and attract new customers to your company or brand.

Organisations have found that it is not always desirable to send data to the cloud due to concerns about latency, connectivity, energy, privacy and security. So why not create learning processes at the Edge?
What challenges does IoT bring?
Sensors are now generating such an increasing volume of data that it is not practical that all of it be sent to the cloud for processing. From a data privacy perspective, some sensor data is sensitive and sending data and images to the cloud will be subject to privacy and security constraints.
Regardless of the speed of communications, there will always be a demand for more data from more sensors – along with more security checks and higher levels of encryption – causing the potential for communication bottlenecks.
As the network hardware itself consumes power, sending a constant stream of data to the cloud can be taxing for sensor devices. The lag caused by the roundtrip to the cloud can be prohibitive in applications that require real-time response inputs.
Machine learning (ML) at the Edge should be prioritised to leverage that constant flow of data and address the requirement for real-time responses based on that data. This should be aided by both new types of ML algorithms and by visual processing units (VPUs) being added to the network.
By leveraging ML on Edge networks in production facilities, for example, companies can look out for potential warning signs and do scheduled maintenance to avoid any nasty surprises. Remember many sensors are linked intrinsically to public safety concerns such as water processing, supply of gas or oil, and public transportation such as metros or trains.
Ecosystm research shows that deploying IoT has its set of challenges (Figure 1) – many of these challenges can be mitigated by processing data at the Edge.
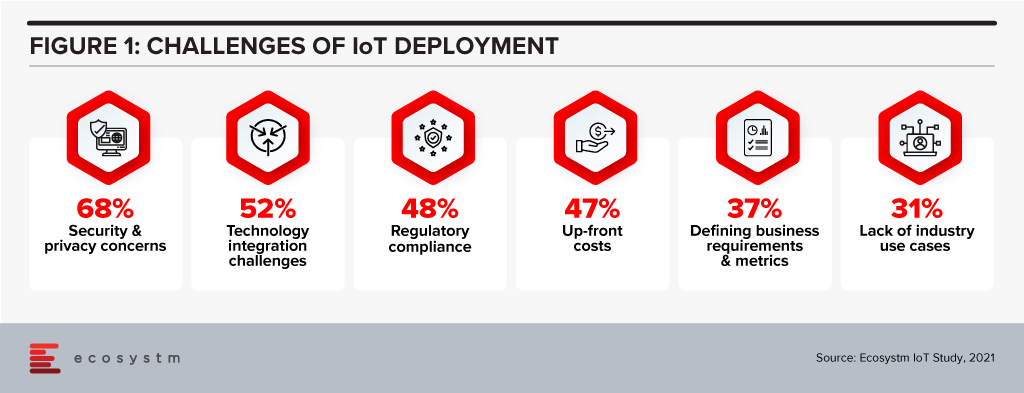
Predictive analytics is a fundamental value proposition for IoT, where responding faster to issues or taking action before issues occur, is key to a high return on investment. So, using edge computing for machine learning located within or close to the point of data gathering can in some cases be a more practical or socially beneficial approach.
In IoT the role of an edge computer is to pre-process data and act before the data is passed on to the main server. This allows a faster, low latency response and minimal traffic between the cloud server processing and the Edge. However, a better understanding of the benefits of edge computing is required if it has to be beneficial for a number of outcomes.
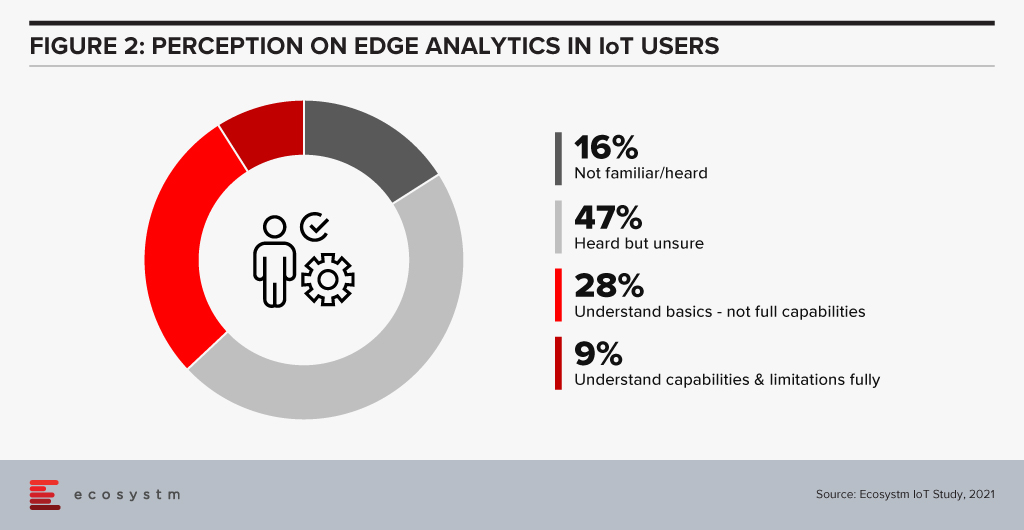

If we can get machine learning happening in the field, at the Edge, then we reduce the time lag and also create an extra trusted layer in unmanned production or automated utilities situations. This can create more trusted environments in terms of possible threats to public services.
What kind of examples of machine learning in the field can we see?
Healthcare
Health systems can improve hospital patient flow through machine learning (ML) at the Edge. ML offers predictive models to assist decision-makers with complex hospital patient flow information based on near real-time data.
For example, an academic medical centre created an ML pipeline that leveraged all its data – patient administration, EHR and clinical and claims data – to create learnings that could predict length of stay, emergency department (ED) arrival models, ED admissions, aggregate discharges, and total bed census. These predictive models proved effective as the medical centre reduced patient wait times and staff overtime and was able to demonstrate improved patient outcomes. And for a medical centre that use sensors to monitor patients and gather requests for medicine or assistance, Edge processing means keeping private healthcare data in-house rather than sending it off to cloud servers.
Retail
A retail store could use numerous cameras for self-checkout and inventory management and to monitor foot traffic. Such specific interaction details could slow down a network and can be replaced by an on-site Edge server with lower latency and a lower total cost. This is useful for standalone grocery pop-up sites such as in Sweden and Germany.
In Retail, k-nearest neighbours is often used in ML for abnormal activity analysis – this learning algorithm can also be used for visual pattern recognition used as part of retailers’ loss prevention tactics.
Summary
Working with the data locally on the Edge, creates reduced latency, reduced cloud usage and costs, independence from a network connection, more secure data, and increased data privacy.
Cloud and Edge computing that uses machine learning can together provide the best of both worlds: decentralised local storage, processing and reaction, and then uploading to the cloud, enabling additional insights, data backups (redundancy), and remote access.

Industries continue to innovate and disrupt to create and maintain a competitive edge – and their technology partners evolve their solution offerings to empower them.
We bring to you latest industry news from the Healthcare, Financial Services, Retail, Travel & Hospitality and Entertainment & Media industries to show you how organisations are leveraging technology. Find out more about organisations such as Services Australia, Paypal, Walmart, Zara and Amex – and how tech providers such as IBM, Oracle, Google and Uplift are supporting organisations across industries.
View the latest Ecosystm Bytes on Industries of the Future below, and reach out to our experts if you have questions.
For more ‘byte sized’ insights click on the link below

Last week Microsoft announced the acquisition of Nuance for an estimated USD 19.7 billion. This is Microsoft’s second largest acquisition ever, after they acquired LinkedIn in 2016. Nuance is an established name in the Healthcare industry and is said to have a presence in 10,000 healthcare organisations globally. Apart from Healthcare, Nuance has strong capabilities in Conversational AI and speech solutions to support other industries. This acquisition is in line with Microsoft’s go-to-market roadmap and strategies.
Microsoft’s Healthcare Focus
Microsoft announced their Healthcare Cloud last year and this acquisition will bolster their Healthcare offerings and market presence. Nuance’s product portfolio includes clinical speech recognition SaaS offerings – Dragon Ambient eXperience, Dragon Medical One and PowerScribe One for radiology reporting – on Microsoft Azure. The acquisition builds on already existing integrations and partnerships that were in place over the years.

“Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare offers its solution capabilities to healthcare providers using a ‘modular’ approach. Given how diverse healthcare providers are in their technology maturity and appetite for change, the more diverse the ‘modules’, the greater the opportunities for Microsoft. This partnership with Nuance also brings to the table established relationships with EHR vendors, which will be useful for Microsoft globally.
The Healthcare industry continues to struggle as the world negotiates the challenges of mass vaccination. But on the upside, the ongoing Healthcare crisis has given remote care a much-needed shot in the arm. Clinicians today will be more open to documentation and transcription services for process automation and compliance. The acquisition of Nuance’s Healthcare capabilities will definitely boost Microsoft’s market presence in provider organisations.
However, Healthcare is not the only industry that Microsoft and Nuance are focused on. The Microsoft Cloud for Retail that was launched earlier this year aims to offer integrated and intelligent capabilities to retailers and brands to improve their end-to-end customer journey. Nuance has omnichannel customer engagement solutions that can be leveraged in Retail and other industries. As Microsoft continues to verticalise their offerings, they will consider more acquisitions that will complement their value proposition.“
Microsoft’s Focus on Conversational AI
Microsoft already has several speech recognition offerings, speech to text services, and chatbots; and they continue to invest in the Conversational AI space. They have created an open-source template for creating virtual assistants to help Bot Framework developers. In February, Microsoft announced their industry specific cloud offerings for Financial services, Manufacturing, and Non-Profit, and also introduced a series of AI and natural language features in Microsoft Outlook, Microsoft Teams, Microsoft Office Lens and Microsoft Office mobile to deliver interactive, voice forward assistive experiences.

“There is no slowing down in this space and the acquisition clearly demonstrates the vision that Microsoft is building with Nuance – a vendor that has made speech recognition, text to speech, conversational AI the foundation of the company. This is a brilliant move by Microsoft in the Conversational AI space and a win-win for both companies.
This move could also mark further inroads for Microsoft into the contact centre space. With Teams now being integrated into contact centre technologies, working with large customers using speech and conversational AI, Dynamics 365 could herald the start of more acquisitions for Microsoft to bolster a wider customer engagement vision.
The Conversational AI war is heating up and various other cloud vendors such as Google and AWS are starting to get aggressive and have made investments in recent years to enhance their Conversational AI capabilities. Google Dialogflow has been seeing rapid uptake and they now have deep partnerships with Genesys, Avaya, Cisco and other contact centre players. Microsoft coming into the game and acquiring a company with years of history and IP in the speech space, demonstrates how the cloud battle and the war between Google, Microsoft and AWS is heating up in the Conversational AI. All of a sudden you have Microsoft as a powerhouse in this game.”

Ecosystm research finds that more than 80% of retail providers had to start or re-calibrate their digital transformation initiatives in 2020. While retailers will continue to focus on the shift in customer expectations, a mere focus on customer experience will not be enough. In this Ecosystm Bytes, we discuss what Retailers should prioritise in the years ahead and where technology will help.
View the latest Ecosystm Bytes below, and reach out to our experts if you have questions.
Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Retail & eCommerce Trends for 2021
Need more insight into 2021’s retail and eCommerce Industry trends? Ecosystm predictions explore how the industry is shaping and revamping the rules of retail in 2021. Learn more about our insights and trends on retail in 2021 below.

2020 was a strange year for retail. Businesses witnessed significant disruption to supply chains, significant swings in demand for products (toilet paper, puzzles, bikes etc!) and then sometimes incredible growth – as disposable income increased as many consumers are no longer taking expensive holidays. Overall, it was a mixed year, with many retailers closing down and others reporting record sales. The grocery sector boomed – with many restaurants and fast-food providers closed, sometimes the supermarkets were some of the few remaining open retailers.
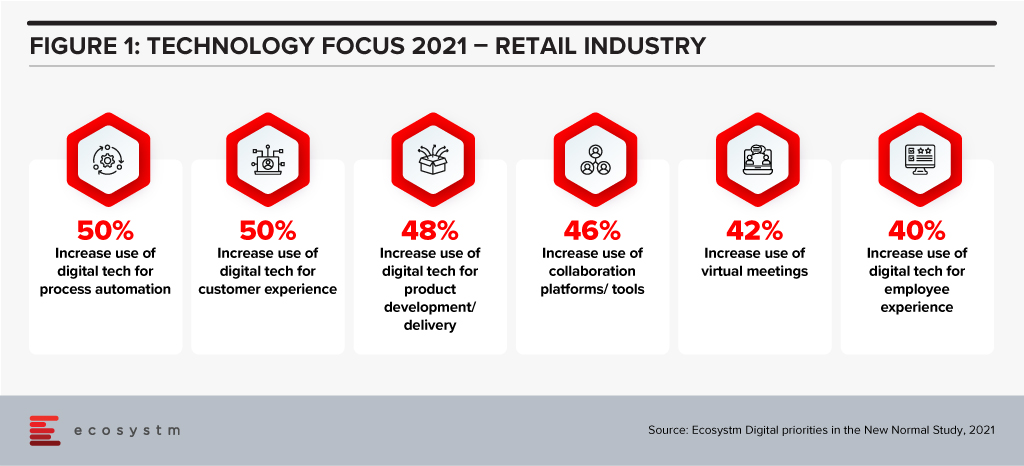
For many retailers, technology has become a key enabler to their transformation, survival and success (Figure 1).
Woolworths, Australia’s largest retailer, operates across the grocery, department store, drinks, and hospitality sectors. They hold a significant market share in most markets that they operate in. The company had a strong 2019/20 (financial year runs from July 2019 to June 2020) with sales up 8% – and in the first half of the 2020/21 financial year, sales were up nearly 11%. But the company is not resting on its laurels – one of its 6 key priorities is to “Accelerate Digital, eCom and convenience for our increasingly connected customers”. This requires more than just a deep technology investment, but a new culture, new skills, and new ways of working.
Woolworths’ Employee Focus
Woolworths has committed to invest AUD 50 million in upskilling and reskilling their employees in areas such as digital, data analytics, machine learning and robotics over the next three years. The move comes as a response to the way the Retail industry has been disrupted and the need to futureproof to stay relevant and successful. The training will be provided through online platforms and through collaborations with key learning institutions.
The supermarket giant is one of Australia’s largest private employers with more than 200,000 employees. Under Woolworths’ ‘Future of Work Fund’ their staff will be trained across supply chain, store operations, and support functions to enhance delivery and decision-making processes. The retailer will also create an online learning platform that will be accessible by Woolworths employees as well as by other retail and service companies to support the ecosystem. Woolworths has plans to upskill their staff in customer service abilities, leadership skills and agile ways of working.
Woolworths’ upskilling program will also support employees who were impacted by Woolworths planned closures of Minchinbury, Yennora, and Mulgrave distribution centres due in 2025.
Woolworths’ Tech Focus
Woolworths has been ramping up their technology investments and having tech-savvy employees will be key to their future success. In October 2020, Woolworths deployed micro automation technology to revamp their eCommerce facility in Melbourne to speed up the fulfilment of online grocery orders, and front and back-end operations. Woolworths also partnered with Dell Technologies in November 2020 to bring together their private and public cloud onto a single platform to improve mission-critical processes, applications and support inventory management operations across its retail stores.
Future of Work
For many years, Ecosystm has been advising our clients to invest more in the skills of the business. Every business will be using more cloud next year than they are this year; they will suffer more cybersecurity incidents; they will use more AI and machine learning; they will automate more processes than are automated today. More of their customer engagements will be digital, and more insight will be required to drive better outcomes for customers and employees. This all needs new skills – or more people trained on skills that some in the business already understand. But too many businesses don’t train in advance – instead waiting for the need and paying external consultants or expensive new hires for their skills. Empowered businesses – ones that are creating a future-ready, agile business – invest in their people, work environment, business processes and technology to create an environment where innovation, transformation and business change are accepted and encouraged (Figure 2).
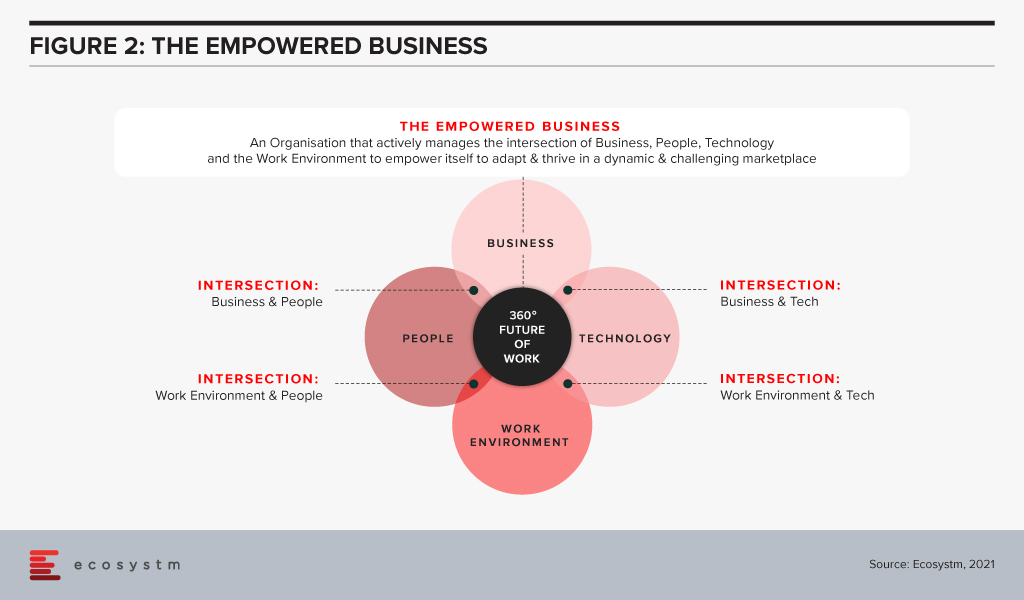
Empowered businesses can adapt to new challenges, new market conditions and respond to new competitive threats. By taking these steps to upskill and empower their employees, Woolworths is building towards empowering their own business for long term success.
Transform and be better prepared for future disruption, and the ever-changing competitive environment and customer, employee or partner demands in 2021. Download Ecosystm Predicts: The top 5 Future of Work Trends For 2021.

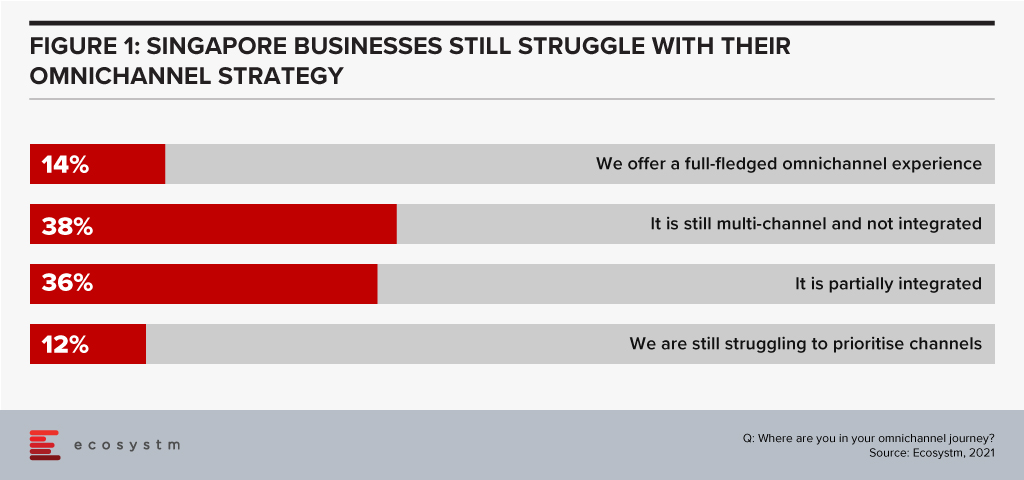
Customer needs are changing. Quickly. In 2020 having a great digital strategy went from being a nice-to-have to an absolute necessity. And in 2021, businesses that have great omnichannel experiences will go from a small minority to a majority as customers demand that they are served on their terms in their chosen platform. Only 14% of businesses in Singapore offer a complete omnichannel experience today – serving customers on their terms regardless of the location or platform (Figure 1). These businesses are setting the benchmark that the rest of the market needs to meet soon.
The Growing Importance of Social Media in Delivering Customer Experience
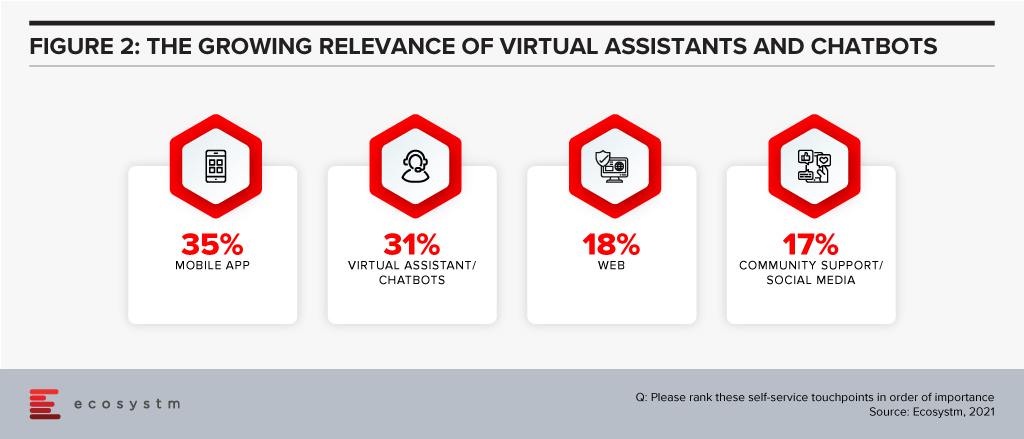
Chat and messaging are quickly becoming the normal way to interact with businesses – the view of a few years ago that “no one wants to chat with a bot” has quickly turned around. Now virtual assistants and chatbots are the second most important self-service channel for businesses in Singapore (Figure 2).
In fact, Zendesk’s global study shows that most customers (45%) use embedded messaging over social messaging apps (31%) and text/SMS (20%). That might be great for self-service, but for commerce, boundless opportunities exist to move to where the customer lives, communicates, and socialises today.
Smart businesses understand that customers spend their lives in other chat and social media platforms – such as Facebook Messenger, TikTok, Instagram, WeChat, Discord and WhatsApp. More customers expect to be served in these channels; they expect to be able to transact with their brands of choice. Why should they go to a mobile banking app to find their balance? Why can’t they get it in WhatsApp? They are often learning about the next Jordan or Yeezy shoe drop from their social network in Messenger – so why not transact with them there? Consider all your own personal WhatsApp, Messenger and other messaging platform groups discussing social activities, sporting teams, school activities or the latest fashion – these are ALL opportunities for commerce (Figure 3).

And there are use cases now. Airlines – such as KLM and Etihad Airways – are engaging customers on WeChat, Kakao Talk, and WhatsApp, helping them reschedule flights and answering customer service queries. Telecommunications providers are allowing customers to raise issues on messaging platforms – and are also using them to upsell and cross-sell new services. Transportation providers are making it easier to find a car or the the next scheduled bus right there in the messaging platforms. Retailers – such as 1-800 Flowers and Culture Kings – are not only serving customers but finding new customers on these messaging platforms.
Going beyond the messaging platforms, businesses are also looking to serve customers on their smart devices – such as Amazon Alexa/Echo and Google Nest/Home devices. Alerting customers to order updates, shipping details and product promotions is becoming standard practice for leading businesses. Digitally-savvy banks are allowing customers to not only track their balance but also make transfers and payments using these smart platforms.
Customers are more comfortable with these conversational commerce options – and they actually expect you to offer such services on your site, in your app, on their smart devices, and on their messaging platforms of choice. Your ability to provide outstanding customer experiences will not only be your ticket back to revenue growth but the recipe for long term business success. Meeting customer needs on their terms is a good place to start.
Delivering a Personalised Conversational Customer Experience
Customer experience (CX) decision-makers will have to rethink how they approach building richer CX capabilities to deliver personalised conversational interactions with customers.
Messaging should become part of a wider AI, Data, and Mobile strategy. Contact centre teams might feel that this is too ambitious a project and would prefer to continue to serve customers through the more traditional channels only. So, it is important to identify the key stakeholder/s who will drive the initiative. And the contact centre team should work with the Digital, Innovation and Marketing teams.
Designing the mobile experience and in app messaging for CX should have some of the following features:
- Ability to click a button to request for a service or escalate an issue that will, in turn, result in the company contacting the customer either by messaging or calling.
- Giving customers the option to contact through popular messaging platforms such as Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, LINE, WeChat, and others. Unifying these systems in a single interface that integrates with your customer service application is best practice.
- Having one single interface to manage and make payments – within the app itself or on the social messaging platform. Conversational commerce is about creating an ongoing relationship with customers throughout the entire customer journey. Don’t just focus on the sale or the post-sales experience – customers expect to be able to interact with your business from their platform of choice regardless of their need or stage in the customer journey.
- Embed deep analytics into the communication services to help the organisation better deliver a personalised CX.
- Ensure you have a solid, unified knowledge management interface at the backend so that all questions lead to the same answers regardless of channel, platform or touchpoint.
Your opportunity to drive greater business success lies in your ability to better win, serve and retain your customers. Refresh your customer strategy and capability today to make 2021 an exceptional year for your business.

Authored by Alea Fairchild and Mike Zamora
There have been a few articles recently about investment companies looking to buy large national US retail companies, for example, JC Penney and Dillards. Their historical approach was to purchase the land and develop the sites as a retail centre and operate their stores. They then lease the remaining retail space to other retailers. It is a business model which has been in use for many decades.
Historically a long and deep negative economic cycle has caused some retail operators/developers to sell part of their operations. This happened in the US in 1995 with Sears. The real estate development and investment companies’ interest is in exploring if there is a higher and better use for the properties. That is the essence of land economics, going from a lower economic use to a higher income/value use.
A key difference this time is the use of advanced technology. We see this in many dimensions: building systems and operations; retail management, social media, entertainment and food and beverage (F&B) operations.
The Smart Building revolution in Retail is about changing the management philosophy of buildings and using technology to aid in the process. The defining characteristic of building smarter is not the application of technology or a function of outcomes on energy use or maintenance. Instead, it is a commitment to leveraging the overall footprint to achieve the goals that perhaps inspired the building in the first place.
Evolution of Space for Retail Activities
The old axiom of real estate is location, location, location. This means that every retail centre will have to be assessed for its best purpose for its locations and surrounding environment. Retail has been morphing in the past few years from a traditional purpose of picking something up to an intersection of shopping and entertainment. This combines on-premise activities with a buying transaction which can be handled either onsite or online. Technology infrastructure investment opportunities are driven by optimising the customer retail experience.
Retail centres are seeking new functionality, including the adaptation of both design and use. Below are four approaches we believe can be used to assess each retail centre.
Reuse: Retail Lifecycle – Consumption to Redemption
There is a shift from consumers discovering and experiencing products in a physical retail space to retailers delivering on-demand. Many smaller retailers have capitalised on this by becoming pick-up points for online orders. They hope to increase footfall by drawing the customer into their own premises when retrieving their online delivery.
Retail centres need to expand on this trend to become a fulfilment location rather than a retail shopping space. Consumers could pick up online orders, recycle used goods, get products maintained and repaired, have appointments for personal services (dental, eye, hair, dry cleaning, etc.), try and test goods in mini-showrooms and collect points and benefits from gamification activities. By having a centralised exchange facility with multiple functionalities, consumer data can be leveraged to create marketing pull activities such as exclusive shopping events, and personalised customer service based on preferences and purchase history.
The current square meterage can be reallocated for distribution including the use of dark stores, green recycling centres for 3D printed product disposal and retail pick-up and exchange points. Staff will not be salespeople, but customer delivery service managers. The technology opportunities in this area would be re-allocation of network resources; focus on efficiency in delivery and customer satisfaction; and automation tools for customer service staff.
Redesign: Blended – Community Environment and Retail Experience
An alternative and more involved development approach would be to redesign the retail centre with deeper use cases to get more customers to come and stay longer. If a consumer stays onsite longer, there is a higher probability they will spend more at the retail centre. The future retail centre (Figure 1) would include additional space usages for a community space, a distribution centre for pick-ups, expanded F&B and remote working.
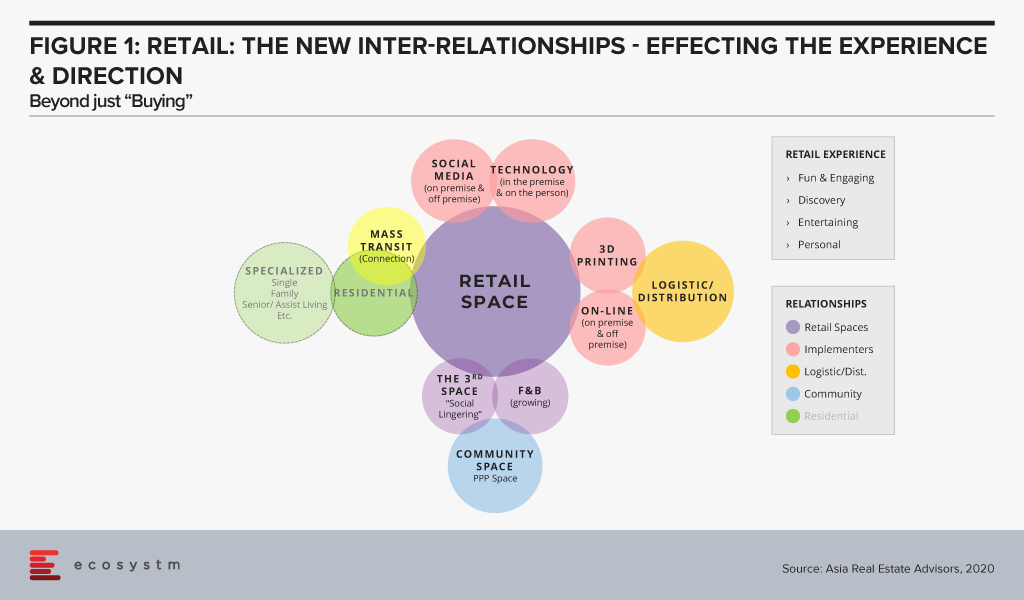
The technology opportunities are in two areas: customer experience and building operations. From a customer perspective, some technology examples would include entertainment and gaming in the F&B area, digital signage and mobile device technology to further engage people. For building operations examples could include technologies to control climate, lighting, security, energy management and building management.
Redevelop – Living Space for a Quality of Life
In some locations, the retail environment could have an oversupply of newly development retail centres. This means the optimal use for the centre would be to change it to a ‘Village Community’ – a community where people can live, work, learn and play. It would encompass multiple uses – multi-family residential units, a community centre, learning centres for younger children and a co-working area. The technology opportunies would be identical to a connected Smart City – at a lesser scale. Smart residential solutions would make the living environmental more user friendly. Retail could include digital media, mobile push features, enhanced and operational technology, energy management, climate control and security. Schools could include interactive and collaborative tools. Parks would have Wi-Fi and enhanced security. Connected Services (eg utilities, fire life safety, security and communications) could include operational technology systems for utilities, audio and video security systems and communication.
Repurpose: Knowledge & Learning Environment
For some retail centres a redevelopment may not be required, but would instead need a major repurposing of the space. The repurpose could be as a learning or healthcare centre. Learning environments require large open spaces with high ceilings for auditoriums or class rooms; common areas for gathering in between classes; onsite housing for students; food courts; and adequate parking for commuters. A healthcare environment would require patient reception, examination rooms, inpatient rooms, surgical units, and administrative offices. It could also include a medical learning centre.
The technology opportunities would be to develop a 24×7 site, with technologies to support the key purpose of the centre. The learning environment could include collaborative audio/video tools for Smart Classrooms. The social areas could including advanced food ordering and delivery systems and multiple player gaming centres for entertainment. The living areas would include systems and technology for smart living. The parking area could include enhanced security and surveillance systems, and smart parking systems. Behind the scenes, the building operations would need to upgrade energy management, building maintenance and management, digital food court operations, and a wellness air quality system.
The Future of Sustainable Retail Space
The decline of a retail centre is not necessarily a bad thing for a community. It is just the “Circle of Life” as an area evolves. Locations morph over the long-term. This has been seen in all the large cities around the world which have stood the test of time, eg. London, Paris, Amsterdam, New York, Tokyo and Beijing. The transformation also breathes fresh air into the surrounding environment. There are multiple layers of technology available to provide for an incredible Sustainable and Smart Community. It is large opportunity, not only for real estate developers, but also for technology vendors who understand the transformation process into the multiple variations of smart environments. Large real estate players and REITs will buy these retail portfolios and begin to transform older, low revenue, semi-vacant shopping centres into vibrant destination centres. Technology vendors should bring their ideas and systems to the attention of retail real estate owners early on in the the process. This will increase their chances of having their systems incorporated into the overall design concept and operational approach. It is a physical and digital transformation which improves neighborhoods, businesses and the city. It is a win for all.

The Retail industry has had to pivot fast this year – having faced early supply chain disruptions, social distancing restrictions due to COVID-19, uncertain demand and falling margins. But the biggest challenge faced was the evolved consumer buying behaviour. Customers were forced to go online, and eCommerce platforms thrived even through the difficult times. Retailers have to continue to cater to this shift in buyer behaviour.
As retailers continue to evolve their capabilities, Woolworths, the Australian chain of grocery stores, recently announced that it has launched new micro automation technology for one of its eCommerce facilities located in Melbourne to speed up the fulfilment of online grocery orders. In 2019 Woolworths had partnered with a US based eGrocery startup, Takeoff Technologies.
Woolworths Automates Dark Store
Woolworths eCommerce floor space spanning across 2,400 sqm is equipped with micro automation technology that allows it to segregate and move groceries from automated storage units that can hold an inventory of 10,000 products and bring them directly to those you pick the orders. The innovative model is designed to make the inventory storage space compact and move high-volume online grocery products to consumers with greater speed, efficiency and accuracy. While grocery products will be picked from automated units, perishables such as fruits, vegetables and meat will continue to be picked up by shop floor workers. Woolworths has employed 50 new employees to fulfil online orders and is expected to fill 100 more vacancies.
“It appears that Woolworths is continuing to use New Zealand to test new technology before introducing it into their much larger Australian market. They are extending the introduction of the technology they first announced for use in their New Zealand online fulfilment centres – the Auckland dark store in November 2019 with a second in Christchurch announced in January 2020,” says Ecosystm Principal Advisor Alan Hesketh. “The Carrum Downs, Melbourne, store will be the first implementation of automation in Australia. Woolworths has announced a third dark store for Wellington in late September 2020 – it would be surprising it was not automated as well.”
Talking about the increase in the use of dark stores, Hesketh sayss, “The challenge with the current model of online stores is the use of expensive retail floor space for picking orders that cannot be used to serve physical customers. With the increase in online sales, accelerated by COVID-19, the volumes are now sufficient in urban areas to make these dark stores profitable. This allows the use of lower-cost, centralised, distribution central space for the dark stores.”
An Example of how Retailers are Pivoting Successfully
Woolworths has been constantly developing their capabilities to improve customer experience and process efficiency. The demand for online products and groceries skyrocketed during COVID-19 which resulted in a temporary shortage of online products and Woolworths had to temporarily stop online ‘Pick up’ and ‘Delivery Now’ orders nationally. To ensure smoother delivery services, they partnered with Sherpa, Drive Yellow, and Uber. Earlier this month, Woolworths announced that six stores in Australia would go completely cashless. Woolworths has around 1,050 stores in Australia which operates on a mix of cash and e-payments.
To keep pace with the online growth, Woolworths automated dark stores will be a potential game changer as they are expected to be able to dispatch online orders five times faster, compared to a standard Woolworths store.
“This increased capacity also means Woolworths’ online offer is less likely to be overwhelmed in the event of another COVID-19 lockdown. This improved access to groceries will be an important benefit to vulnerable members of communities, as well as those customers wary of visiting physical stores,” says Hesketh.
“For their physical stores that support home delivery, Woolworths will now be able to repurpose or release the space used by the pick-and-pack operations. In-store customers will get a better experience without the Woolworths personnel picking orders in the aisles.”




























