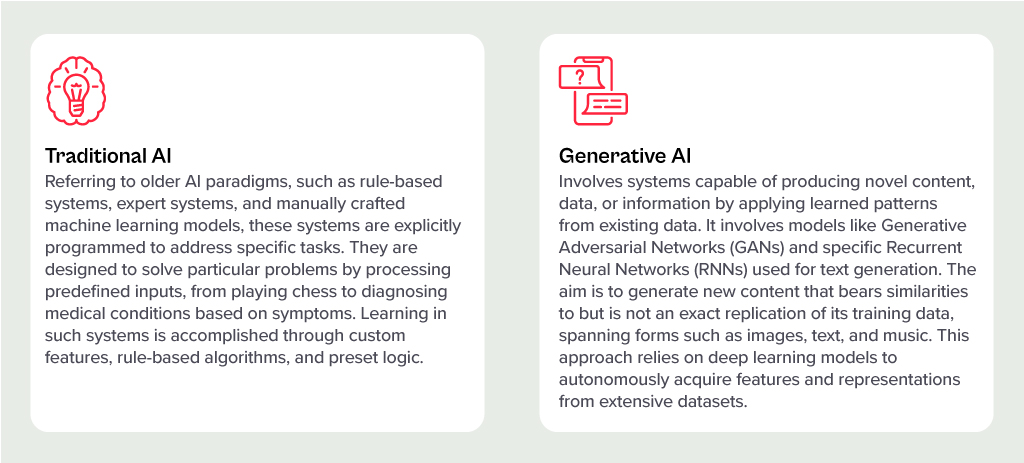
Generative AI has stolen the limelight in 2023 from nearly every other technology – and for good reason. The advances made by Generative AI providers have been incredible, with many human “thinking” processes now in line to be automated.
But before we had Generative AI, there was the run-of-the-mill “traditional AI”. However, despite the traditional tag, these capabilities have a long way to run within your organisation. In fact, they are often easier to implement, have less risk (and more predictability) and are easier to generate business cases for. Traditional AI systems are often already embedded in many applications, systems, and processes, and can easily be purchased as-a-service from many providers.
Unlocking the Potential of AI Across Industries
Many organisations around the world are exploring AI solutions today, and the opportunities for improvement are significant:
- Manufacturers are designing, developing and testing in digital environments, relying on AI to predict product responses to stress and environments. In the future, Generative AI will be called upon to suggest improvements.
- Retailers are using AI to monitor customer behaviours and predict next steps. Algorithms are being used to drive the best outcome for the customer and the retailer, based on previous behaviours and trained outcomes.
- Transport and logistics businesses are using AI to minimise fuel usage and driver expenses while maximising delivery loads. Smart route planning and scheduling is ensuring timely deliveries while reducing costs and saving on vehicle maintenance.
- Warehouses are enhancing the safety of their environments and efficiently moving goods with AI. Through a combination of video analytics, connected IoT devices, and logistical software, they are maximising the potential of their limited space.
- Public infrastructure providers (such as shopping centres, public transport providers etc) are using AI to monitor public safety. Video analytics and sensors is helping safety and security teams take public safety beyond traditional human monitoring.
AI Impacts Multiple Roles
Even within the organisation, different lines of business expect different outcomes for AI implementations.
- IT teams are monitoring infrastructure, applications, and transactions – to better understand root-cause analysis and predict upcoming failures – using AI. In fact, AIOps, one of the fastest-growing areas of AI, yields substantial productivity gains for tech teams and boosts reliability for both customers and employees.
- Finance teams are leveraging AI to understand customer payment patterns and automate the issuance of invoices and reminders, a capability increasingly being integrated into modern finance systems.
- Sales teams are using AI to discover the best prospects to target and what offers they are most likely to respond to.
- Contact centres are monitoring calls, automating suggestions, summarising records, and scheduling follow-up actions through conversational AI. This is allowing to get agents up to speed in a shorter period, ensuring greater customer satisfaction and increased brand loyalty.
Transitioning from Low-Risk to AI-Infused Growth
These are just a tiny selection of the opportunities for AI. And few of these need testing or business cases – many of these capabilities are available out-of-the-box or out of the cloud. They don’t need deep analysis by risk, legal, or cybersecurity teams. They just need a champion to make the call and switch them on.
One potential downside of Generative AI is that it is drawing unwarranted attention to well-established, low-risk AI applications. Many of these do not require much time from data scientists – and if they do, the challenge is often finding the data and creating the algorithm. Humans can typically understand the logic and rules that the models create – unlike Generative AI, where the outcome cannot be reverse-engineered.
The opportunity today is to take advantage of the attention that LLMs and other Generative AI engines are getting to incorporate AI into every conceivable aspect of a business. When organisations understand the opportunities for productivity improvements, speed enhancement, better customer outcomes and improved business performance, the spend on AI capabilities will skyrocket. Ecosystm estimates that for most organisations, AI spend will be less than 5% of their total tech spend in 2024 – but it is likely to grow to over 20% within the next 4-5 years.

It’s been barely one year since we entered the Generative AI Age. On November 30, 2022, OpenAI launched ChatGPT, with no fanfare or promotion. Since then, Generative AI has become arguably the most talked-about tech topic, both in terms of opportunities it may bring and risks that it may carry.
The landslide success of ChatGPT and other Generative AI applications with consumers and businesses has put a renewed and strengthened focus on the potential risks associated with the technology – and how best to regulate and manage these. Government bodies and agencies have created voluntary guidelines for the use of AI for a number of years now (the Singapore Framework, for example, was launched in 2019).
There is no active legislation on the development and use of AI yet. Crucially, however, a number of such initiatives are currently on their way through legislative processes globally.
EU’s Landmark AI Act: A Step Towards Global AI Regulation
The European Union’s “Artificial Intelligence Act” is a leading example. The European Commission (EC) started examining AI legislation in 2020 with a focus on
- Protecting consumers
- Safeguarding fundamental rights, and
- Avoiding unlawful discrimination or bias
The EC published an initial legislative proposal in 2021, and the European Parliament adopted a revised version as their official position on AI in June 2023, moving the legislation process to its final phase.
This proposed EU AI Act takes a risk management approach to regulating AI. Organisations looking to employ AI must take note: an internal risk management approach to deploying AI would essentially be mandated by the Act. It is likely that other legislative initiatives will follow a similar approach, making the AI Act a potential role model for global legislations (following the trail blazed by the General Data Protection Regulation). The “G7 Hiroshima AI Process”, established at the G7 summit in Japan in May 2023, is a key example of international discussion and collaboration on the topic (with a focus on Generative AI).
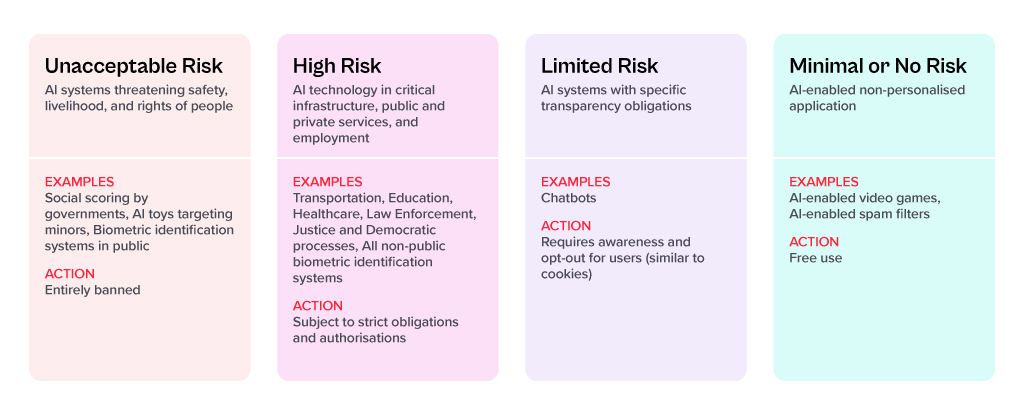
Risk Classification and Regulations in the EU AI Act
At the heart of the AI Act is a system to assess the risk level of AI technology, classify the technology (or its use case), and prescribe appropriate regulations to each risk class.
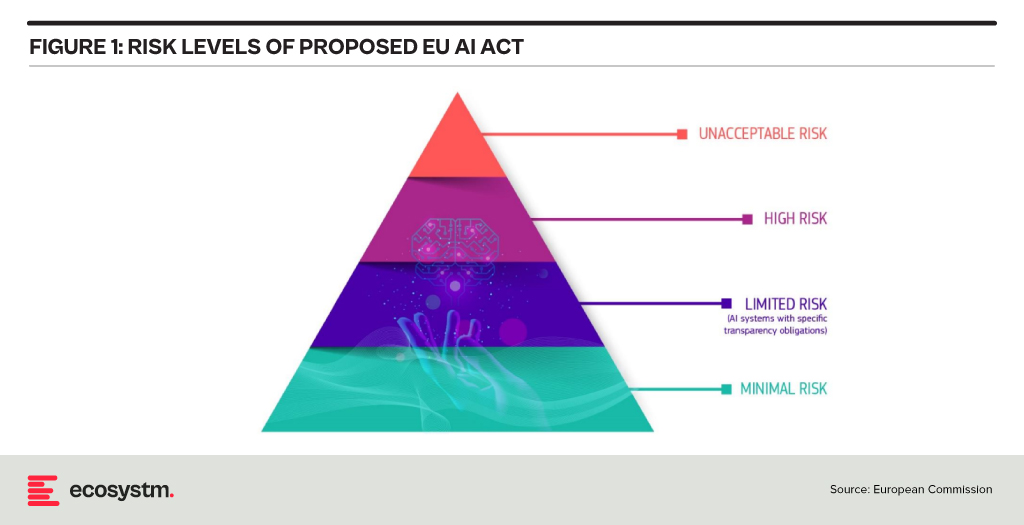
For each of these four risk levels, the AI Act proposes a set of rules and regulations. Evidently, the regulatory focus is on High-Risk AI systems.
Contrasting Approaches: EU AI Act vs. UK’s Pro-Innovation Regulatory Approach
The AI Act has received its share of criticism, and somewhat different approaches are being considered, notably in the UK. One set of criticism revolves around the lack of clarity and vagueness of concepts (particularly around person-related data and systems). Another set of criticism revolves around the strong focus on the protection of rights and individuals and highlights the potential negative economic impact for EU organisations looking to leverage AI, and for EU tech companies developing AI systems.
A white paper by the UK government published in March 2023, perhaps tellingly, named “A pro-innovation approach to AI regulation” emphasises on a “pragmatic, proportionate regulatory approach … to provide a clear, pro-innovation regulatory environment”, The paper talks about an approach aiming to balance the protection of individuals with economic advancements for the UK on its way to become an “AI superpower”.
Further aspects of the EU AI Act are currently being critically discussed. For example, the current text exempts all open-source AI components not part of a medium or higher risk system from regulation but lacks definition and considerations for proliferation.
Adopting AI Risk Management in Organisations: The Singapore Approach
Regardless of how exactly AI regulations will turn out around the world, organisations must start today to adopt AI risk management practices. There is an added complexity: while the EU AI Act does clearly identify high-risk AI systems and example use cases, the realisation of regulatory practices must be tackled with an industry-focused approach.
The approach taken by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) is a primary example of an industry-focused approach to AI risk management. The Veritas Consortium, led by MAS, is a public-private-tech partnership consortium aiming to guide the financial services sector on the responsible use of AI. As there is no AI legislation in Singapore to date, the consortium currently builds on Singapore’s aforementioned “Model Artificial Intelligence Governance Framework”. Additional initiatives are already underway to focus specifically on Generative AI for financial services, and to build a globally aligned framework.
To Comply with Upcoming AI Regulations, Risk Management is the Path Forward
As AI regulation initiatives move from voluntary recommendation to legislation globally, a risk management approach is at the core of all of them. Adding risk management capabilities for AI is the path forward for organisations looking to deploy AI-enhanced solutions and applications. As that task can be daunting, an industry consortium approach can help circumnavigate challenges and align on implementation and realisation strategies for AI risk management across the industry. Until AI legislations are in place, such industry consortia can chart the way for their industry – organisations should seek to participate now to gain a head start with AI.

Zurich will be the centre of attention for the Financial and Regulatory industries from June 26th to 28th as it hosts the second edition of the Point Zero Forum. Organised by Elevandi and the Swiss State Secretariat for International Finance, this event serves as a platform to encourage dialogue on policy and technology in Financial Services, with a particular emphasis on adopting transformative technologies and establishing the necessary governance and risk frameworks.
As a knowledge partner, Ecosystm is deeply involved in the Point Zero Forum. Throughout the event, we will actively engage in discussions and closely monitor three key areas: ESG, digital assets, and Responsible AI.
Read on to find out what our leaders — Amit Gupta (CEO, Ecosystm Group), Ullrich Loeffler (CEO and Co-Founder, Ecosystm), and Anubhav Nayyar (Chief Growth Advisor, Ecosystm) — say about why this will be core to building a sustainable and innovative future.
Download ‘Building Synergy Between Policy & Technology’ as a PDF















