In this blog, our guest author Chandru Pingali talks about the potential benefits of the Blended working model and the impact it will have on FinTech and financial services organisations. “FinTech innovation and performance is here to stay and thrive. It needs to be backed by a well-oiled machine to support implementation of a blended workforce plan to institutionalise and scale.”

When under pressure to reduce costs and survive, we reimagine everything we do to build resilience and thrive. Never before have the buzzwords frugality, prudence and agility gained as much prominence – not just in one country or industry, but across global economies simultaneously (a phenomenon not seen since the Great Depression). And these words have sliced through the employment opportunities ruthlessly, leaving an abundance of talent to be gainfully employed differently.
So, is the freelance economy surging? Statistics appear to say yes. In 2018, freelancers had contributed almost USD 1.40 trillion to the US economy; 162 million freelancers work across US and EU-15. So, who are these people? Why is blended workforce new or relevant for the Asia Pacific? Why is it gaining more prominence now? How can enterprises create and implement a blended workforce strategy to reduce costs more permanently, while running and scaling businesses? What does the Future of Work and workforce mean? How can FinTech enterprises successfully implement a blended workforce strategy?
Let us take Singapore as an example. With 1000+ FinTech firms and increasing investments, the “smart financial centre” initiative of Singapore is a huge success story, recognised globally. To sustain this, apart from innovation and technology, the main ingredient is consistent availability of talent as the demand for expertise in technology and financial services increases, while the supply is inconsistent, uncurated and fragmented. Recent data from the Singapore government job portals reveal that there are several hundred jobs at any point in time posted by FinTech companies that are open for months! This invariably slows down the ability to build businesses, innovate or scale. Interestingly, while the local talent for technology and BFSI may be limited in Singapore, the crisis this year presented a significant opportunity to reimagine the Future of Work and workforce. While efforts should continue to upskill and reskill local talent, it is now possible to create dedicated local and cross-border talent hubs to work part-time, fulltime-short term with the option of working physically or remotely. We expect the plug and play of freelance management experts and expertise to cost 25-30% less to an enterprise, keeps costs flexible and dramatically shortens time to “hire and deploy” from an average of 120 days to 15 days.

Gigs and Generations – Conceptual Clarity of Who We Need
Culturally, the US and Europe are more accepting of freelancing as full-time careers compared to the Asia Pacific. It is predicted that by 2027 the majority of the workforce in the US will be freelancers overtaking traditional employment. The buzz in the Asia Pacific has just started with both employers and employable talent accepting a new reality – learning to run businesses with a blended workforce, starting at the top of the pyramid. Particularly, since the ratio of new jobs to lost jobs is skewed in the wrong direction.
Power of Blended Workforce
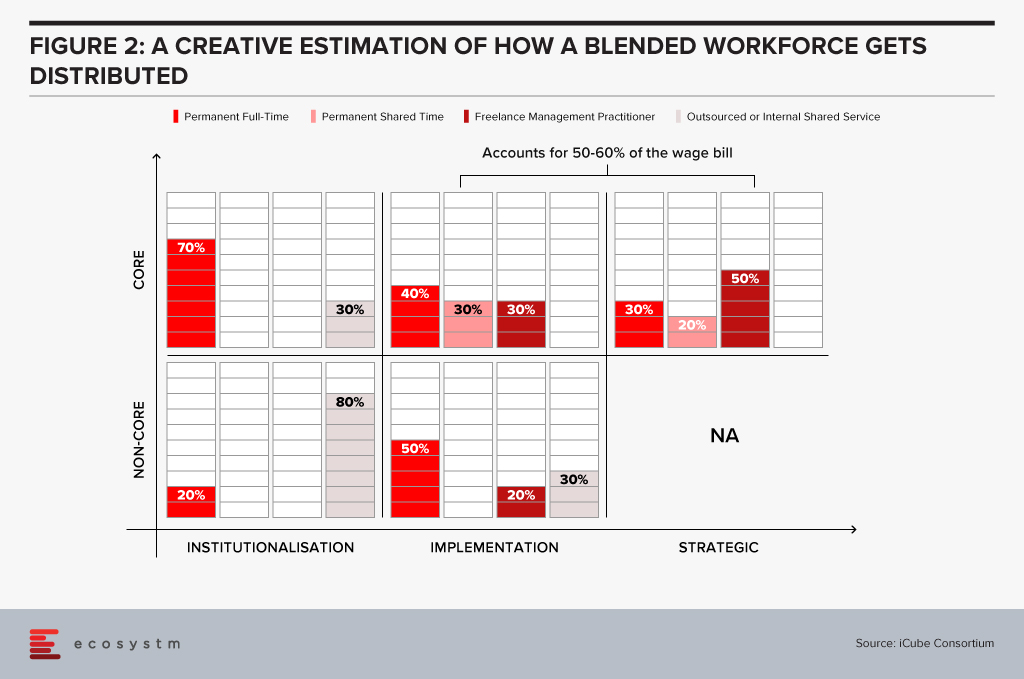
A blended workforce is a combination of permanent, part-time, full time-short term and turnkey practitioners, working as a single collaborative workforce. It is built around business activity clusters – Strategy, Implementation and Institutionalisation, applied to create a plan for core and non-core workforce to drive business.
A creative estimation of how a blended workforce gets distributed across the three business clusters is depicted below (Figure 2). What is important here is to recognise that the ratio of permanent to flexible workforce has to start at 10-15% across different levels. Enterprises will gain the most on cost optimisation when they focus on the management layer to go blended. Not an easy change to drive but then change is often driven by some tough calls and some low hanging fruits to build a sustainable cost model.
Developing & Implementing a Blended Workforce Strategy: What to Consider
Fix the core and flex the non-core should be the mantra
- Identify roles by each business and function
- Segregate core and non-core roles by job profiles
- Classify them into buckets of permanent full time, permanent part time, cyclical, and freelance on demand, based on:
- Time demand for the roles
- Importance to business goals
- Criticality to daily business output
- Criticality to daily or weekly business continuity
- Set up a process to engage and create a blended workforce strategy
- Implement the plan with a blend of a common self-service platform and a central client service team to source, engage and deploy workforces
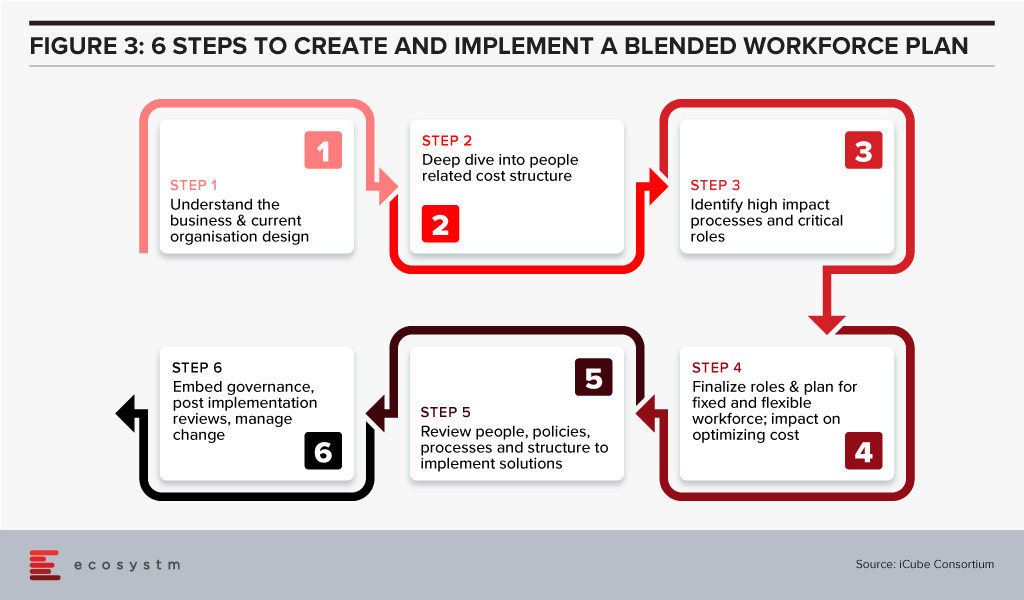
Once the process review is completed, the organisation structures will be finalised. Creation of a strategy and the process are the easier parts. A disciplined fulfilment of the plan is critical to success. So, is this the new normal? Pretty much yes, if organisations need to optimise costs and be agile to reduce or scale with freelance experts and shared talent pools.
The Potential Benefits of a Blended Workforce
A Blended Workforce will help reduce your talent scarcity gap, while providing thousands of work opportunities to locals who are freelance experts. So, what are these benefits that can make you sleep better at night better?
- Cost optimisation. Freelance experts do not need the fully loaded costs. They can work remotely or physically and do not need investment in regular training, insurance, or other related benefits.
- Targeted purpose-hire for short term. With deliverables specified upfront, measurable, results focused and tracked for closure.
- Job Sharing. Two or may be three, for the prize of one! Jobs can be dismantled to tasks or activity clusters to hire more than one expert in place of a full-time role. Enables razor sharp focus on sourcing for expertise, increases employment opportunities and accelerates productivity.
- Boundaryless with an opportunity to find cross-border talent pools to work on-demand, remotely. It cuts both ways- Singaporean talent finding work opportunities outside the country whilst the best talent from other countries made available to grow Singapore’s economy.
- Speed of hire is dramatically reduced (we have several client cases, with a reduction from an average of 120 days to 15 days, to clients’ delight!)
- Reduced infrastructure costs because the workforce works remotely or at best part-time physically. Easy to implement with hot desking, if needed but enables permanent cost reduction.
- Builds resilience by staying agile and nimble in the cost line, with an ability to scale up or down rapidly based on business needs.
How Open is the Financial Services Industry to Blended Workforce and Future of Work?
SolvecubeHR conducted a recent survey with CXOs across 22 countries, predominantly focused on the Asia Pacific region. Some key findings for the financial services industry are:
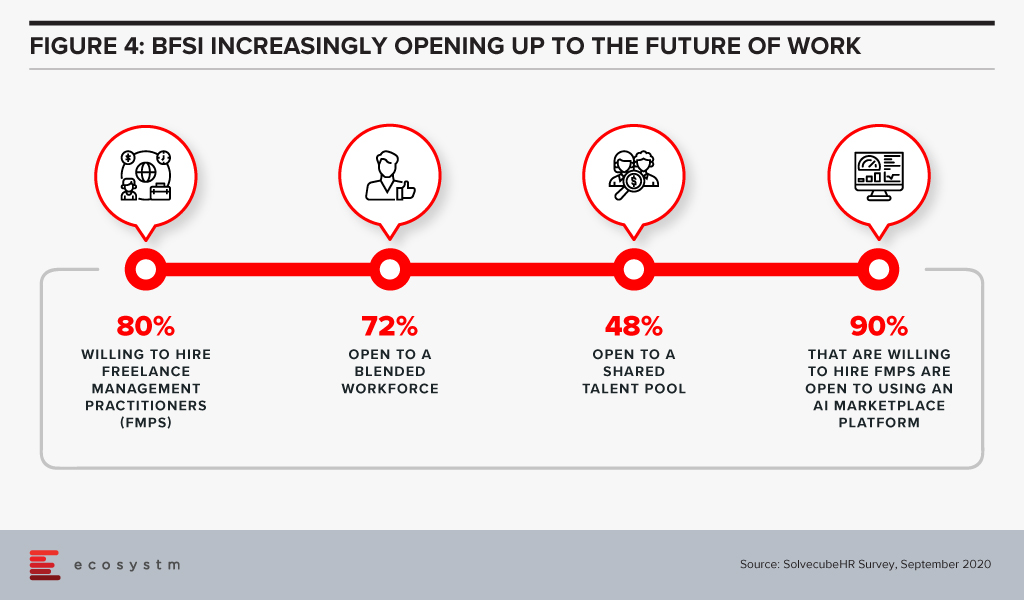
In summary, a blended workforce is the Future of Work. Asia Pacific will see a massive shift in its mindset from “jobs to work opportunities”. Employers and talent pools will embrace new ways of working to remain agile and prudent. The power of aggregation, curation, and collaboration by leveraging an AI matchmaking platform, backed by creation of shared talent pools, will be a game changer.
FinTech innovation and performance is here to stay and thrive. It needs to be backed by a well-oiled machine to support implementation of a blended workforce plan to institutionalise and scale.
We can build technologies to disintermediate people dependency, but we cannot take humans out of the human capital needed to build these technologies.
About iCube: iCube Consortium is a Singapore based, Human Capital Management (HCM) solutions firm, with an award-winning AI platform to source and manage freelance management experts and execute turnkey assignments in Asia and Middle East
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Talent Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit which will cover topics on Founders success and failure stories, pandemic impact on founders and talent development, upskilling and reskilling for the future of work.

Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) ratings towards investment criteria have become popular for potential investors to evaluate companies in which they might want to invest. As younger investors and others have shown an interest in investing based on their personal values, brokerage firms and mutual fund companies have begun to offer exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and other financial products that follow specifically stated ESG criteria. Passive investing with robo-advisors such as Betterment and Wealthfront have also used ESG criteria to appeal to this group.
The disruption caused by the pandemic has highlighted for many of us the importance of building sustainable and resilient business models based on multi-stakeholder considerations. It has also created growing investor interest in ESG.
ESG signalling for institutional investors
The increased interest in climate change, sustainable business investments and ESG metrics is partly a reaction of the society to assist in the global transition to a greener and more humane economy in the post-COVID era. Efforts for ESG standards for risk measurement will benefit and support that effort.
A recent study of asset managers by the investment arm of Institutional Shareholder Services (ISS) showed that more than 12% of respondents reported heightened importance of ESG considerations in their investment decisions or stewardship activities compared to before the pandemic.
In the area of hedge funds, there has been an increased demand for ESG-integrated investments since the start of COVID-19, according to 50% of all respondents of a hedge fund survey conducted by BNP Paribas Corporate and Institutional Banking of 53 firms with combined assets under management (AUM) of at least USD 500B.
ESG criteria may have a practical purpose beyond any ethical concerns, as these criteria may be able to help avoidance of companies whose practices could signal risk. As ESG gets more traction, investment firms such as JPMorgan Chase, Wells Fargo, and Goldman Sachs have published annual reports that highlight and review their ESG approaches and the bottom-line results.
But even with more options, the need for clarity and standards on ESG has never been so important. In my opinion, there must be an enhanced effort to standardise and harmonise ESG rating metrics.
How are ESG ratings made?
ESG ratings need both quantitative and qualitative/narrative disclosures by companies in order to be calculated. And if no data is disclosed or available, companies then move to estimations.
No global standard has been defined for what is included in a given company’s ESG rating. Attempts at standardising the list of ESG topics to consider include the materiality map developed by the Sustainable Accounting Standard Board (SASB) or the reporting standards created by the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI). But most ESG rating providers have been defining their own materiality matrices to calculate their scores.
Can ESG scoring be automatically integrated?
Just this month, Morningstar equity research analysts announced they will employ a globally consistent framework to capture ESG risk across over 1,500 stocks. Analysts will identify valuation-relevant risks for each company using Sustainalytics’ ESG Risk Ratings, which measure a company’s exposure to material ESG risks, then evaluate the probability those risks materialise and the associated valuation impact. ESG rating firms such as MSCI, Sustainalytics, RepRisk, and ISS use a rules-based methodology to identify industry leaders and laggards according to their exposure to ESG risks, as well as how well they manage those risks relative to peers.
Their ESG Risk Ratings measure a company’s exposure to industry-specific material ESG risks and how well a company is managing those risks. This approach to measuring ESG risk combines the concepts of management and exposure to arrive at an assessment of ESG risk – the ESG Risk Rating – which should be comparable across all industries. But some critics of this form of approach feel it is still too subjective and too industry-specific to be relevant. This criticism is relevant when you understand that the use of the ESG ratings and underlying scores may in future inform asset allocation. How might this better automated and controlled? Perhaps adding some AI might be useful to address this?
In one example, Deutsche Börse has recently led a USD 15 million funding round in Clarity AI, a Spanish FinTech firm that uses machine learning and big data to help investors understand the societal impact of their investment portfolios. Clarity AI’s proprietary tech platform performs sustainability assessments covering more than 30,000 companies,198 countries,187 local governments and over 200,000 funds. Where companies like Cooler Future are working on an impact investment app for everyday individual users, Clarity AI has attracted a client network representing over $3 trillion of assets and funding from investors such as Kibo Ventures, Founders Fund, Seaya Ventures and Matthew Freud.
What about ESG Indices? What do they tell us about risk?
Core ESG indexing is the use of indices designed to apply ESG screening and ESG scores to recognised indices such as the S&P 500®, S&P/ASX 200, or S&P/TSX Composite. SAM, part of S&P Global, annually conducts a Corporate Sustainability Assessment, an ESG analysis of over 7,300 companies. Core ESG indices can then become actionable components of asset allocation when a fund or separately managed accounts (SMAs) provider tracks the index.
Back in 2017, the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN) and the State Secretariat for International Finance (SIF) made it possible for all Swiss pension funds and insurance firms to measure the environmental impact of their stocks and portfolios for free. Currently, these federal bodies are testing use case with banks and asset managers. Its initial activities will be recorded in an action plan, which is due to be published in Spring 2021.
How can having a body of sustainable firms help create ESG metrics?
Creating ESG standard metrics and methodologies will be aided when there is a network of sustainable companies to analyse, which leads us to green fintech networks (GFN) of companies interested in exploring how their own technology investments can be supportive of ESG objectives. Switzerland is setting up a Green Fintech Network to help the country take advantage of the “great opportunity” presented by sustainable finance. The network has been launched by SIF alongside industry players, including green FinTech companies, universities, and consulting and law firms. Stockholm also has a Green Fintech Network that allows collaboration towards sustainability goals.
Concluding Thought
We should be curious about how ESG can provide decision-oriented information about intangible assets and non-financial risks and opportunities. More information and data from ESG data providers like SAM, combined with automation or AI tools can potentially provide a more complete picture of how to measure the long-term sustainable performance of equity and fixed income asset classes.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Investor Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Investor Summit which will cover topics tied to 2021 Investor Priorities, and Fundraising and exit strategies

In this blog, our guest author HE Jo Tyndall, delivers a message of hope for the future and talks about initiatives across all levels to combat climate change and biodiversity loss. “The pieces of the puzzle that will create a sustainable future are all there – it is time to start fitting them together.”

If, like me, you have watched Sir David Attenborough’s “witness statement” (A Life On Our Planet), it is easy to despair of the wanton, wilful destruction humanity has wreaked on the Earth, and to be horrified that so much of this has happened in one man’s (admittedly long) lifetime. The images he conjures – of distressed orangutans, starving polar bears, floods, fires and droughts, and of rampant deforestation – underscore how ubiquitous, urgent and overwhelming the climate change and biodiversity crises are.
But Sir David ends with a message of hope, and it is this I want to emphasise. Everywhere we look, there are green shoots of hope, many growing into sturdy saplings. They are coming thick and fast, and they are becoming mainstream – no longer relegated to the tick-box margins of policy or practice. The pieces of the puzzle that will create a sustainable future are all there – it is time to start fitting them together.
Political Signals Create a Ripple Effect
First, and foremost, in 2015 we got the Paris Agreement (and subsequently its rulebook). This was no mean feat. It set climate goals, gave us global rules for being transparent and accountable, and put governments on a path of continuous improvement to reach those collective goals. It is easy to dismiss global treaties as just words on paper, but this is to ignore the profound ripple effect those words have already had. (The Agreement held firm despite the US withdrawal – but the fillip when it re-joins will be welcome.)
The political signals set the first ripples off as governments needed climate policies to meet their Paris undertakings. The European Green Deal aims for a sustainable EU economy, with no net greenhouse gas emissions by 2050, decoupling economic growth from resource use. The UK will host next year’s UN Climate Change Conference of the Parties (COP26) – and has doubled its climate finance for the period 2021-2025.
In September this year, China – the world’s largest emitter of greenhouse gases – announced it would achieve carbon neutrality by 2060. Japan and Korea, too, have upped their mid-century targets to bring net emissions to zero.
The New Zealand Government has set a legislated goal for the country to be carbon neutral by 2050; has amended our Emissions Trading System (ETS) to ensure price signals encourage a move to low carbon; set up a green investment fund; invested heavily in research into reducing emissions from livestock production; and, most recently, made carbon-related financial disclosures mandatory for specified companies, banks, insurers and investment managers. We have also made it our mission to encourage governments to phase out fossil fuel subsidies (some US$400bn each year) that promote excessive consumption.
The Ripples Reach Cities and Businesses…
The political signals have flowed through to regional and local government. The C40 group (cities around the world working towards sustainability goals) now has 96 participating members – with many cities finding opportunities to collaborate with others in the network on joint projects.
It is becoming obvious that fossil fuel industries are at a disadvantage against increasingly cost-competitive renewable energy. Governments are working out how to manage a ‘just transition’ for the energy sector, while forward-leaning energy companies are re-shaping their business models in anticipation of a low carbon future.
Political signals encourage businesses to factor climate change into their planning and investment decisions. Businesses everywhere have read the political tea leaves and we see weekly announcements of pledges for carbon neutrality, ethical investing, green financing and so on. Whether it is Blackrock or NZ Super Fund making environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations integral to their investments, or Ikea’s IWAY (its ESG code of conduct for itself and its suppliers), business is showing a deeper commitment to sustainability than ever before.
Some industries will have to be more invested than others in emissions reduction, but this opens a world of opportunity and innovation. Energy & Utilities companies are implementing waste-to-energy solutions – Singapore’s Integrated Waste Management Facility (IWMF) is set to be the world’s largest energy recovery facility – and adoption of carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS) facilities is at last gathering momentum across energy systems. Industries like aviation and maritime, too, have to play a key role in a circular economy.
… And Individuals (the Last – and First – Pieces of the Puzzle)
The ripples have spread to individuals – people like you and me. I know there are still plenty of climate deniers around. But mindsets are changing – and when that happens, the ripples become a tidal wave of real change. If we each start thinking we can do it and we will do it, the change will happen. If we make it clear, in our preferences as consumers, and in our expectations of the businesses we buy from or invest in, the change will happen.
The numbers who recognise we must live within our planetary boundaries are growing, values are changing (especially in light of the pandemic), and our low-carbon future is a high-tech one – not hemp shirts and home-made candles (unless of course these are your thing). Digital is a critical part of the story. Blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) is being used to cater to a new generation of consumers, conscious of buying what is good for the world in the face of climate change and biodiversity loss. Food products are being branded using track-and-trace capabilities of Blockchain for ‘farm to fork’ visibility.
Who doesn’t want to breathe clean air, have lower energy bills, and eat safe and healthy food? Maybe we will see more initiatives like America’s Pledge, bringing together an entire ecosystem committed to fighting climate change, growing the economy, and protecting public health – an ecosystem of states, cities, businesses, universities, and citizens.
We now have the rules, the policy tools, the technologies, and – increasingly – we have the will to act. As we re-build our economies, our businesses, and our lives, let us re-build better. So, I would echo Sir David Attenborough’s optimism – it is just that we do not have his (95 years) lifetime left to put things right.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Impact Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Impact Summit which will cover topics tied to climate change and sustainability to build a better future

The ongoing global crisis is expected to drive more investments in FinTech. Blockchain adoption, in particular is expected to lead to a more open and interconnected economy that is borderless, transparent and does not need counter-party trust to operate. One particular area where Blockchain has been piloted is in smart contracts. Financial contracts involve legal work, document handling, sighting, signing, and sending them to the right people. All of this involves both time and people – and proves to be an expensive option eventually. Blockchain can speed this process up in a secure (with no failure points), interoperable and risk-free environment.
While smart contracts are expected to increase efficiency, there are questions being raised with respect to interpretation and technical capacity. The Law Commission in the UK is conducting a detailed study to analyse how current law applies to smart contracts and to highlight any uncertainties or gaps in relation to enforceability, interpretation and so on. The World Bank is looking at the role smart contracts could play in improving financial services in poorer nations – especially in insurance and short-term unsecured loans. Initiatives such as these are a positive step towards adoption.
However, smart contracts are not the only area that financial institutions and governments have in mind when they pilot and adopt Blockchain – and there are several recent instances.
Digital Currency
Many central banks have started identifying potential use cases for digital representation of fiat money that offers them unique advantages at various levels. According to Bank of International Settlements (BIS), 80% of the world’s central banks had already started to conceptualise and research the potential for central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), 40% are working on proofs-of-concept (POCs) and 10% are deploying pilot projects. The People’s Bank of China (PBOC) announced last month that it has processed more than three million digital yuan transactions since it began piloting its CBDC late last year. Transactions include bill payments, bar code scans, tap and go payments, and payments for transport and government services.
Singapore’s Project Ubin has successfully completed its fifth and final stage and is a step closer to greater adoption and live deployments of blockchain technology. The commercial applications of the payments network prototype include cross-border payments in multiple currencies, foreign currency exchange, settlement of foreign currency-denominated securities, as well as integration with other blockchain-based platforms to enable end-to-end digitalisation across many industries and use cases.
Crypto Exchange Ecosystems
A crypto exchange or digital currency exchange (DCE) makes it easier for buyers and sellers to securely store, buy, sell, or exchange crypto currencies. Various players across the financial industry have developed tools connecting the transactions, flow of funds, and financial instruments through crypto exchanges – including banks, digital payments and other FinTech providers.
In an effort to expand its retail presence, FTX acquired crypto app Blockfolio for USD 150 million in August 2020. Recently, FTX announced the launch of trade in the stocks of some of the largest global companies – Tesla, Apple, Amazon – by tokens against bitcoins, stablecoin and more.
In order to empower the emerging initiatives in the decentralised finance (DeFi) space, the world’s largest crypto exchange platform Binance announced the creation of a seed fund in September. Their USD 100 million accelerator fund added five new Blockchain projects – Bounce, DeFiStation, Gitcoin, JustLiquity and PARSIQ that will receive financial support from the fund.
PayPal has announced crypto buying and selling services through Paypal accounts. Paypal’s crypto service in partnership with Paxos is being rolled out in phases across the US. Outlining their plans for 2021, Paypal announced new crypto payments features including enhanced direct deposit, check cash, budgeting tools, bill pay, crypto support, subscription management, buy now/pay later functionalities and more with the integration of the capabilities offered by Honey – an internet browser extension and mobile app which PayPal bought for USD 4 billion in 2019.
It is expected that banks will join in as well – it has been reported that DBS Bank in Singapore is planning to launch a digital asset exchange platform to enable institutional and retail customers to trade cryptocurrencies.
Blockchain Enhancing Banking Features and Services
We are also witnessing several pilots and initiatives in banking industry functionalities such as settlements, identity management, security, transparency, and data management.
In theory, the bank reconciliation is simple, however, in practical aspects things may not work out so easily. The funding, lending, transfer, and transactions reconciliations is a complicated and time-consuming effort. in March 2020 the Spunta Banca DLT system promoted by the Italian Banking Association (ABI) and coordinated by ABI Lab was implemented across the Italian banking sector. Powered by R3’s Corda Enterprise blockchain, the solution streamlines and automates the reconciliation of transactions, provides real-time reconciliation process, handles technical elements with automated feedback and results in more transparent processes. Spunta has attracted broad interest from the Italian banking sector and since October, around 100 banks have been operating on Spunta to manage the interbank process and automate reconciliation of transactions.
Recently, in Spain, ten leading banks including Banco Santander, Bankia, BME, CaixaBank, Inetum, Liberbank, Línea Directa Aseguradora, Mapfre, Naturgy and Repsol, and the Alastria consortium have come together to build a self-managed digital identity (ID) solution dubbed as Dalion built on Blockchain technology. The project based on Alastria digital identity model (Alastria ID) aims to provide users with secure control on their digital information and personal data, making it easier for them to manage their digital identity. The project that was initiated in October 2019, has successfully completed the concept testing phase and is in its second phase, with the final solution expected to roll-out in mid-2021.
Grayscale, is the first digital currency investment vehicle to attain the status of a Securities and Exchange Commission reporting company. The digital assets management company is aggressively buying bitcoins and manages a total of USD 8.2 billion of cryptocurrency. Earlier this year, Singapore’s Matrixport, a financial services firm partnered with Simplex, an EU-licensed payments processing firm to enable buying of cryptocurrencies via VISA or Mastercard credit and debit cards with more than 20 supported fiat currencies.
As Blockchain matures we will see more large-scale adoption bringing collaborators together to form ecosystems that will give them a competitive edge. Solve some of their core challenges and empower their customers.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit
Get more insights into the evolution of blockchain and its applications at the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit. The world’s largest fintech event will explore different uses of blockchain technology, trials being conducted, and the vast opportunities in the financial services industries

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming embedded in financial services across consumer interactions and core business processes, including the use of chatbots and natural language processing (NLP) for KYC/AML risk assessment.
But what does AI mean for financial regulators? They are also consuming increasing amounts of data and are now using AI to gain new insights and inform policy decisions.
The efficiencies that AI offers can be harnessed in support of compliance within both financial regulation (RegTech) and financial supervision (SupTech). Authorities and regulated institutions have both turned to AI to help them manage the increased regulatory requirements that were put in place after the 2008 financial crisis. Ecosystm research finds that compliance is key to financial institutions (Figure 1).
SupTech is maturing with more robust safeguards and frameworks, enabling the necessary advancements in technology implementation for AI and Machine Learning (ML) to be used for regulatory supervision. The Bank of England and the UK Financial Conduct Authority surveyed the industry in March 2019 to understand how and where AI and ML are being used, and their results indicated 80% of survey respondents were using ML. The most common application of SupTech is ML techniques, and more specifically NLP to create more efficient and effective supervisory processes.
Let us focus on the use of NLP, specifically on how it has been used by banking authorities for policy decision making during the COVID-19 crisis. AI has the potential to read and comprehend significant details from text. NLP, which is an important subset of AI, can be seen to have supported operations to stay updated with the compliance and regulatory policy shifts during this challenging period.
Use of NLP in Policy Making During COVID-19
The Financial Stability Board (FSB) coordinates at the international level, the work of national financial authorities and international standard-setting bodies in order to develop and promote the implementation of effective regulatory, supervisory and other financial sector policies. A recent FSB report delivered to G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors for their virtual meeting in October 2020 highlighted a number of AI use cases in national institutions.
We illustrate several use cases from their October report to show how NLP has been deployed specifically for the COVID-19 situation. These cases demonstrate AI aiding supervisory team in banks and in automating information extraction from regulatory documents using NLP.
De Nederlandsche Bank (DNB)
The DNB is developing an interactive reporting dashboard to provide insight for supervisors on COVID-19 related risks. The dashboard that is in development, enables supervisors to have different data views as needed (e.g. over time, by bank). Planned SupTech improvements include incorporating public COVID-19 information and/or analysing comment fields with text analysis.
Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS)
MAS deployed automation tools using NLP to gather international news and stay abreast of COVID-19 related developments. MAS also used NLP to analyse consumer feedback on COVID-19 issues, and monitor vulnerabilities in the different customer and product segments. MAS also collected weekly data from regulated institutions to track the take-up of credit relief measures as the pandemic unfolded. Data aggregation and transformation were automated and visualised for monitoring.
US Federal Reserve Bank Board of Governors
One of the Federal Reserve Banks in the US is currently working on a project to develop an NLP tool used to analyse public websites of supervised regulated institutions to identify information on “work with your customer” programs, in response to the COVID-19 crisis.
Bank of England
The Bank developed a Policy Response Tracker using web scraping (targeted at the English versions of each authority/government website) and NLP for the extraction of key words, topics and actions taken in each jurisdiction. The tracker pulls information daily from the official COVID-19 response pages then runs it through specific criteria (e.g. user-defined keywords, metrics and risks) to sift and present a summary of the information to supervisors.
Market Implications
Even with its enhanced efficiencies, NLP in SupTech is still an aid to decision making and cannot replace the need for human judgement. NLP in policy decision is performing clearly defined information gathering tasks with greater efficiency and speed. But NLP cannot change the quality of the data provided, so data selection and choice are still critical to effective policy making.
For authorities, the use of SupTech could improve oversight, surveillance, and analytical capabilities. These efficiency gains and possible improvement in quality arising from automation of previously manual processes could be consideration for adoption.
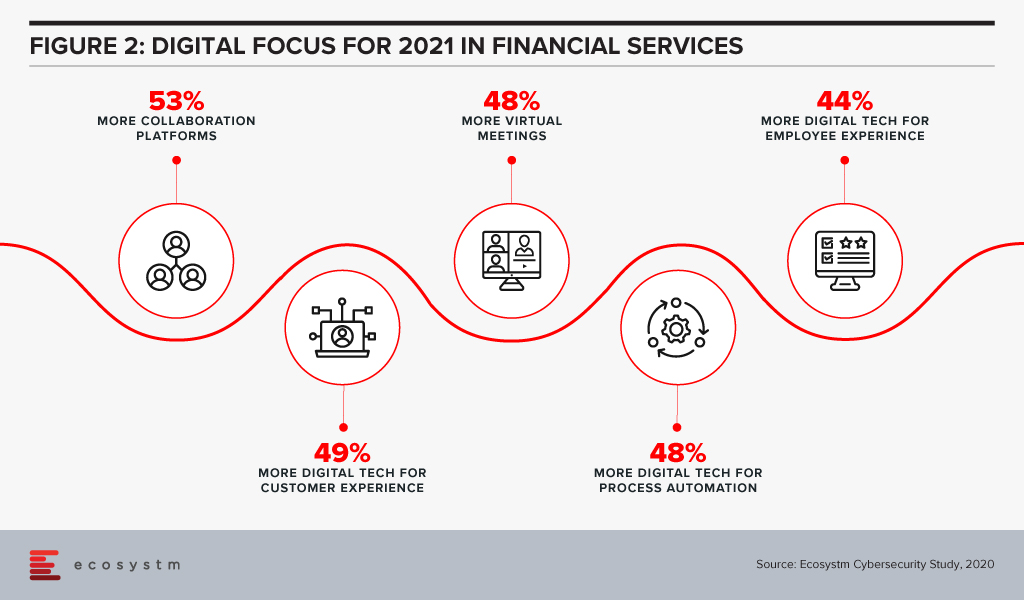
Attention will be paid in 2021 to focusing on automation of processes using AI (Figure 2).
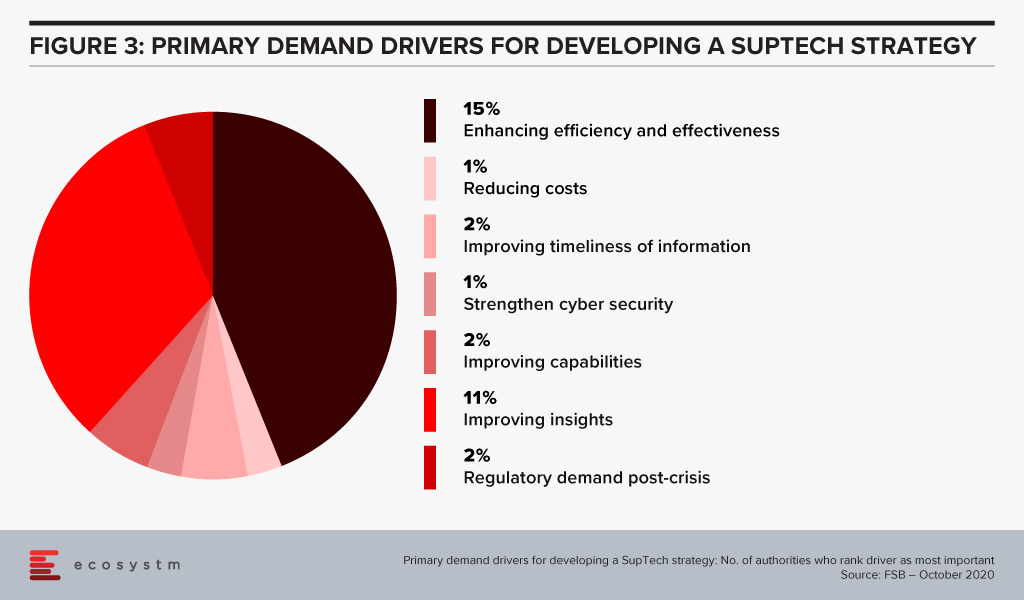
Based on a survey done by the FSB of its members (Figure 3), the majority of their respondents had a SupTech innovation or data strategy in place, with the use of such strategies growing significantly since 2016.
Summary
For more mainstream adoption, data standards and use of effective governance frameworks will be important. As seen from the FSB survey, SupTech applications are now used in reporting, data management and virtual assistance. But institutions still send the transaction data history in different reporting formats which results in a slower process of data analysing and data gathering. AI, using NLP, can help with this by streamlining data collection and data analytics. While time and cost savings are obvious benefits, the ability to identify key information (the proverbial needle in the haystack) can be a significant efficiency advantage.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit which will cover topics tied to creating infrastructure for a digital economy; and RegTech and SupTech policies to drive innovation and efficiencies in a co-Covid-19 world.

In the last few months, we have seen greater adoption of Fintech especially in the area of digital payments, as more organisations and consumers adopt eCommerce. However, Fintech also appears to grow in areas such as Regtech and blockchain for ease of reporting and enhanced transaction security. As we prepare for recovery, there will be a need for a more open and interconnected economy that is borderless and transparent and does not need counter-party trust to operate. Blockchain has a role to play in enabling that environment where transactions and processes are secure, interoperable and risk-free.
Australian Banking Leveraging Blockchain
Major Australian banks – ANZ Bank, the Commonwealth Bank of Australia (CBA) and Westpac – have joined hands with property management firm Scentre Group and IBM for the expansion and commercial launch of a Blockchain technology platform Lygon that manages end-to-end bank guarantees on retail property leases.
Financial guarantee is an essential part of retail property leases and involves a lot of paperwork such as payment assurances, financial guarantee, bank bonds, credit letters and other legal documents. Bank guarantees have primarily been issued through paper-based processes – digitalising the entire route will reduce the risks, manual errors and significantly speed up the complete procedure. The use of blockchain provides a trusted system of record for digitised documents, removes the risk of document loss and allows secure sharing of data. It also has a strong cryptography security aimed at eliminating fraud and enabling the sharing of key information across organisational boundaries.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Phil Hassey says, “This joint venture shows the value of applying new technology to bring legacy and overlooked business processes into the digital age. The ability to reduce the bank guarantee process time frame from one month to one hour, alongside a 15-minute onboarding highlights the speed and scale that can be gained from the technology.”
“It helps the landlord, retailer and bank alike. One of the key benefits for the retail tenant is that they can concentrate on running a business rather than the back-end administration required for the new lease. Furthermore, the blockchain technology will enable heightened security capabilities and reduce the risk to all parties of fraud and data loss.”
From this month, early adopters will be able to join the platform. The intention is to expand the services into New Zealand, with the view to creating a true cross-border solution. The platform will be open to the general public, along with new features, in early 2021.
A Successful Pilot
The platform was piloted in July 2019 and was proved successful later in the year. The outcomes reported to have been achieved include reduction of time to issue a bank guarantee from one month to one day; onboarding new applicants to the platform in less than 15 minutes; and supporting other common bank guarantee processes including amendments and cancellations. The pilot used live data and legal transactions from about 20 Australian businesses, with an aim to improve customer experience and process automation.
IBM, one of the 5 shareholders and the technology provider for the platform, is responsible for developing, operating, and maintaining the platform. The initial proof of concept (POC) was developed within the IBM Research division. The platform also runs on the IBM Blockchain Platform and IBM provides services such as the security.
Hassey says, “This initiative highlights that in a digital world – regardless of the platform – joint ventures can readily provide benefits to all stakeholders if digital enablement and technology is at the core of the execution.”
A decade ago, the axiom of a successful business model was to identify a need, find the market and then develop an idea or product that fits into that chain. It was a process of inserting a product in the customer’s already existing experience journey with the hope that the product/idea would deliver efficiency to the client. This efficiency could be financial, operational, marketing or cost savings – the uni-product, uni-feature approach.
There has been enough said about the many companies that failed to innovate beyond their existing product/feature and failed to stay ahead of the game. Nokia and Blackberry remain at the centre of any discussion about “lack of innovation”. There are others like Kodak, Canon, Napster, Palm, Blockbuster – that were devoured by innovative competitors.
The predators were ones with the vision to see the entire value chain and not just their own product. Netflix created content and distributed it, Apple touched the lives of their customers in multiple ways and AirBnb provided accommodation inventory, choice and booking all in one. The new secret sauce is to provide the customer with an ecosystem and not a product!
The Need to Transform
Cut to the COVID era – there are many businesses facing the downturn and experiencing the “moments of truth” giving rise to a desperate attempt to innovate, transform, survive, and come out as the rising stars. Ecosystm research finds that 98% of organisations have re-evaluated their Transformation roadmap (Figure 1), while 75% have started, accelerated or refocused their DX initiatives.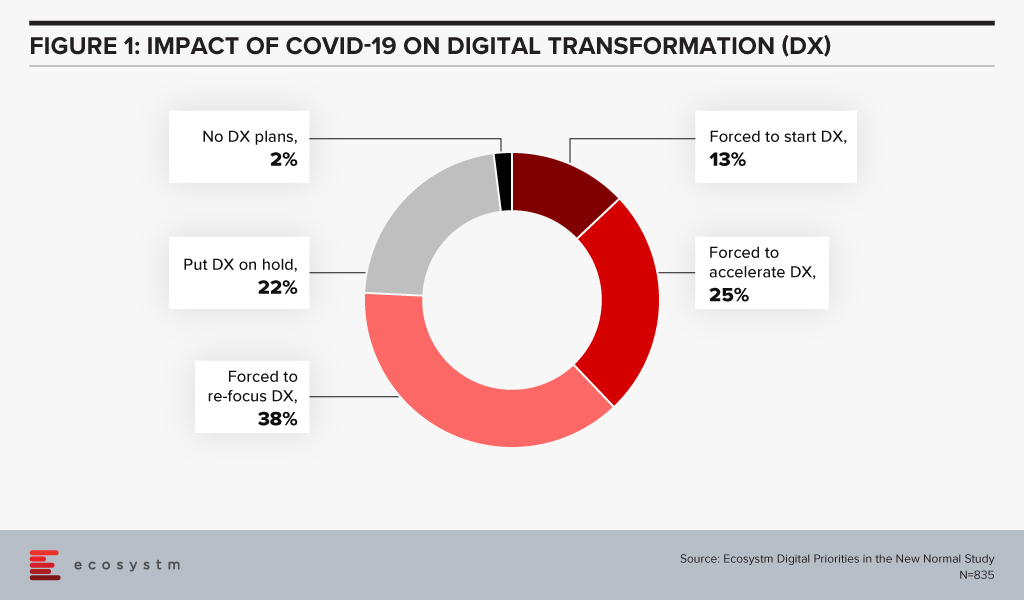
New business models are evolving, and accelerating digitalisation is the result. The digital movement, be it in food delivery or payments, is here to stay. This digital acceptance and absorption exaggerate the need for business models that capture holistic ecosystems and entire customer journeys, due to reasons that separate the hunter and the hunted.
- Margins will never be the same again as in the uni-product model. Using the F&B analogy; with the increasing number of customers wanting to dine in the comfort of their homes, restaurants cannot use ambiance as the price differentiator. Since most restaurants are available on food delivery services, customers are getting brand agnostic. This is the start of commoditisation of dining. Restaurants (or food caterers now!) will need to play the price card to remain competitive resulting in compressed margins. The food delivery market is expected to grow 4-fold to USD 8 billion by 2025 but with lower margins. This example of the food delivery model will be the same as experienced by retail, apparel and other industries.
- Customer experience will still be the differentiator and lever for loyalty and repeat purchase. Factors like proximity, parking, in-store experience, and store layout are fast getting replaced by the ease of navigation, user experience, seamless check out and finally efficient and timely delivery. The ease of transaction including multiple steps of search, assessment, evaluation, payment and delivery is of paramount importance. Customers do not want fractured journeys with multiple drop-offs. A unified seamless journey will win.
- Virtual, Digital and Automation are the three mantras that management consultants are betting on. However, this trilogy will not guarantee survival since the road to recovery is not a straight one. Different work schedules, observing various curves and on what point of the curve the business, its customer and the market are at, will add to the complexity of decision making and transformation.
Given the above, an obvious strategy to beat the existential crisis is to transform and seek out sustainable operating models. However, it may not be so simple since most businesses may not be able to change models as quickly as needed. There is an inherent cost to change since the existing processes and procedures have been well oiled and smoothed over time. The much-needed change requires the infusion of the 3Ts (time, technology, training) and associated costs. Most often, there is an inverse correlation noticed between the sturdiness of the business and its ability to be flexible to change. Businesses that are “rock-solid” and profitably sturdy and stable, have high inertia of transformation versus FinTech businesses, as an example, that pride themselves with nimble operations but are financially fragile and may not be able to absorb the cost of speedy transformation.
This Sturdy-Flexible continuum is the tight rope walk that businesses will need to walk in this need for transformation. Businesses that embark on this walk alone will find it extremely painful and lonely. Especially in the case of small business owners who are scared and low on all 3Ts.
The Rise of Ecosystems
The new world has manifested that businesses that use physical space or assets as their competitive advantage are more prone to be impacted. Retail, Education, Hospitality and Entertainment are some obvious examples that have been impacted by the physicality in their propositions. Digital businesses are more agile but have suffered in their inability to scale up in time to capture the increased demand.
Fashion retailer FJ Benjamin has decided to shut 300 physical stores and rely on online sales. This strategy also helps to utilise precious time to scale diversification. Other retailers too have been going down the FJ Benjamin path and ramping up eCommerce as this trend is expected to stick beyond COVID-19.
Zouk, the renowned nightclub with 30,000 square feet of space in Singapore uses this venue as a live streaming venue during the day to host bazaars for eCommerce vendors. From June 2020, it launched an online shop selling merchandise, bottled cocktails and food from its RedTail kitchen.
Transformation of businesses will require capabilities that were not created within their models. The instinct to survive in the short term will require businesses to create symbiotic partnerships. This will require some fresh thinking by business leaders.
- Change the “Build” obsession and not try to own every leg of the customer journey. That will not only take time but also distract capital and management.
- Rethink the customer needs – and this time think of the entire journey rather than an inward view of product-market fits. Customer needs are changing at breakneck speeds, so chasing and “building” these “fits” will always remain a common string amongst laggards.
- Connect with like-minded ecosystem players and complement strengths with a single-minded focus on solving customer problems.
- View technology stacks through the lens of your partners. There may be opportunities available from near open source technology solutions.
For example, FJ Benjamin will need the last-mile-delivery capability that will be provided by partners who have optimised in that field, Zouk has tied up with Lazada to host the bazaars and GrabFood is using underutilised taxi capacity to meet the increased demand for food delivery. There are many other examples in the O2O (Offline to Online) space.
This ecosystem approach is also relevant to other sectors like Financial Services. These firms also need to understand the changing consumer needs faster, with a mantra to deliver. Aspire, originally an alternate lending platform has gone through a metamorphosis and transformed into a Neobank. From a uni-product loan provider, it is now solving for a business account, card solution, integration with expense management solutions and continue to provide loans. Capabilities not necessarily built in-house.
The changing world will give rise to business models that will integrate and complement each other. Businesses with an ecosystem mindset will be winners while others might just be relegated to oblivion.

We are in the midst of an economic and social crisis. COVID-19 will have far-reaching effects on organisations and how they do business. It is expected to drive more investments in Fintech, especially in digital payments, as more organisations and consumers adopt eCommerce. Countries will also have to re-think the ways they trade with other countries, as travel restrictions continue. This is expected to boost the Fintech industry and July was witness to how Fintech organisations, financial institutions and governments are gearing up to leverage Fintech in their path to economic and social recovery.
Financial Industry Seeing More Open Banking Initiatives
The banking industry is fast moving towards collaboration and openness. July saw several initiatives that take the industry closer to open banking.
Late last year, South Korea piloted an open banking system with participation from local banks and lenders. The Financial Services Commission (FSC), South Korea’s top financial regulator reported in July that the initiative had participation from 72 companies including commercial banks and Fintech firms with 20 million subscribers using the open banking services.
Australia introduced an open banking initiative, monitored by the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC). From July, Australia’s banking customers can share their financial and banking data with accredited businesses under Consumer Data Right Act to access a better suite of financial applications.
There is global expansion as well. Railsbank, a global open banking platform with a presence in Southeast Asia introduced their services in the US market. The company will offer Banking-as-a Service, Cards-as-a Service and Credit Card-as-a-Service in the US market. Khaleeji Commercial Bank (KHCB), an Islamic bank in Bahrain, launched their open banking service enabling a customer to link their bank accounts with other banks and manage through the ‘Khaleeji 360’ platform. The portal allows clients to view all their bank accounts, automate operations and conduct banking through a unified platform.
Financial Institutions Increasing Partnerships with Fintech
Financial institutions no longer look at Fintech as competition. They appreciate that customers are at the centre of their entire operation – and Fintech services can and will provide them with the solutions they need. As financial institutions re-think their transformation journeys and face increasingly stringent regulations, they no longer have the option of ignoring Fintechs.
American Express, Visa, Mastercard and Discover came together to roll out a global standard. The big four’s advanced digital checkout solution Click to Pay is an online checkout system based on EMV Secure Remote Commerce (SRC) to make online payments across websites, mobile applications and connected devices, frictionless.
With an aim to unify payment solutions, a group of 16 major European banks launched the European Payment Initiative (EPI) to create a unified pan-European payment solution leveraging Instant Payments/SEPA Instant Credit Transfer (SCT Inst), including a card, e-wallet and P2P payments.
We also saw financial institutions strengthen their cross-border payment services in July. Deutsche Bank partnered with Airwallex to offer virtual account collections and API-enabled foreign exchange services in Japan and Hong Kong. The service will enable merchants and traders to transact through virtual accounts and APIs without opening bank accounts in foreign markets. Mastercard and Bank of China partnered to enhance cross-border business payments into China. This will enable global businesses to send payments to China while accessing real-time exchange rates, reduce the need for unnecessary documentation between merchants, and reduce transaction hassles and costs.
Fintechs Facilitating Cross-border Trade
Seamless cross-border financial transactions will be key to economic recovery, whether easy remittance or the ability to reach a larger market and be able to trade beyond borders.
July saw the formalisation of the Digital Economy Partnership Agreement (DEPA) between New Zealand, Chile and Singapore, to facilitate end-to-end digital trade, which includes establishing digital identities, paperless trade and the development of Fintech solutions to support it. The initiative also intends to allow cross-border data flow and give access to necessary government data to small and medium enterprises (SMEs) enabling them to be digital-ready to explore newer markets.
Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) signed an MoU with Jiaozi Fintech Dreamworks based in China opening new opportunities for innovation and trade. The agreement will enable Fintech companies based in both cities to access each other’s markets. Primarily established to facilitate the ‘Belt and Road’ initiative, it is a critical component of the DIFC’s 2024 strategy to strengthen relationships with the international financial community and increase access to the South-South corridor. Over the last few years, DIFC has been associated with over 200 Fintech organisations, and last month invested in four Fintech startups through their accelerator program. The agreement with Jiaozi will look at collaboration opportunities in Blockchain, AI and Cloud and will facilitate cross-border workshops and training programs.
Continuing Interests in Emerging Economies
Fintechs have been a means to bring about financial inclusion and are increasingly being used to target the unbanked and underbanked. Emerging economies continue to be attractive for Fintech organisations and global financial institutions.
With much of Malaysia’s economy dependent on foreign workers, Instapay, regulated by the Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM), announced a collaboration with Mastercard, to provide e-wallet accounts to the migrant workers. The widespread use of e-wallets by the migrant worker community will bring benefits to both workers, as well as their employers. Interestingly, Fintech providers in emerging economies are also looking to expand into other emerging markets. Malaysia’s GHL Group received approval from Philippines Securities and Exchange Commission to operate a lending business through their new unit, GHL Philippines Financing Services. GHL has been diversifying its business and has been operating its lending business in Malaysia and Thailand since 2019.
Crown Agent Bank, a wholesale foreign exchange and cross-border payment services based in the UK, partnered with South Africa’s biometric-based payment company, Paycode. Together the companies are aiming to reach 100 million unbanked customers where Crown Agents Bank will use their FX and payment services to bolster Paycode’s product offering and support financial inclusion across Sub-Saharan Africa.
India and Indonesia in the Asia Pacific continue to be popular markets because of the huge proportion of the unbanked population. Rapyd, a UK based global B2B Fintech-as-as-service provider partnered with major Indian e-payment providers – including Paytm, PhonePe, PayU, Citibank, DBS Bank, HDFC Bank, BharatPay, and Unimoni to launch an all-in-one payments solution that spans credit and debit cards, UPI, wallets, and cash. New registrations for digital banking in Indonesia are on the rise and Fintech startup Akulaku is capitalising on the potential digital banking overhaul to offer affordable and comprehensive financial services to consumers.
Fintechs benefiting other industries
The Fintech revolution has shown the path to several other industries – Healthcare and Agriculture are some of the industries that are hoping to benefit from Fintech organisations and their innovations. The MoU between Alibaba Cloud, Pfizer and Singapore’s Fintech Academy announced earlier in July, promises to give early and necessary guidance to Healthtech start-ups, and shows the deep connection between Healthtech and Fintech. In the Philippines, in an effort to improve financial services for farmers, AgriNurture acquired Fintech firm Pay8. By leveraging Pay8 e-wallet services, farmers will be able to access online payment services. This will enable the largely unbanked farmer community to become an active part of the economy.
The technology that these industries are looking to benefit from is Blockchain. South Korea brought Blockchain to their healthcare industry for better data management and storage. The 3 major telecommunications providers in the country – KT, SK Telecom and mobile carrier LG U+ – have also collaborated with KB Insurance to launch the blockchain-based mobile notification service (MNS) by matching customer data to their mobile subscription information. Oxfam Ireland – a charity organisation based in Ireland, received a sum of USD 1.18 million from the European Commission for a Blockchain-based pilot. The company is working on a project -The UnBlocked Cash – to help disaster-affected communities receive cash-based entitlements with more efficiency and traceability.
Fintech will continue to be a cornerstone of economic and social recovery in the future, and the financial industry will see more collaborations between Fintech organisations, financial institutions and governments. Other industries will continue to take learnings from Fintech.

Singapore is committed to empower its small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to make better financial decisions and avail of seamless trade and financial transactions across the larger global economy. In June, the Digital Economic Partnership Agreement (DEPA) was signed between New Zealand, Singapore and Chile. The initiative includes facilitating end-to-end digital trade – by creating digital identities, allowing paperless trade and developing Fintech solutions – and ensuring a trusted cross-border data flow. To learn more about the DEPA agreement, register for the “Re-image the Digital Economy” webinar on the 29th July at 10am SGT.
This follows the announcement that was made last year by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) and Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA); of the successful completion of phase 1 of the proof-of-concept (POC) for its Business sans Borders (BSB). BSB is meant to be a “meta-hub” connecting several SME-centric platforms (starting within the Philippines, India and Singapore) giving SMEs seamless access to a larger ecosystem of buyers, sellers, logistics service providers, financing, and digital solution providers; and allowing them to be part of the larger global marketplace. The PoC involved a collaboration with private sector partners such as GlobalLinker, Mastercard, PwC, SAP and Yellow Pages.
AMTD Aligns with the BSB Objective
Hongkong-based investment banking firm AMTD Group leads a consortium that includes Xiaomi Finance, Singapore’s SP Group, and Funding Societies, that is a contender for one of Singapore’s digital wholesale banking licenses. While announcing their bid, they had clearly stated that they aimed to focus on SMEs in the region and globally. They continue to focus on SMEs by strengthening their partner ecosystem.
Last week AMTD announced a partnership with GlobalLinker making them the preferred financial services partner on the GlobalLinker’s SME-focused platform. AMTD intends to make available their entire ecosystem to SMEs including their virtual bank in Hong Kong, Airstar and their potential digital wholesale bank consortium in Singapore (which is to be called Singa Bank). In line with Singapore’s BSB objective, the partnership will see GlobalLinker join AMTD’s network which includes Fintech companies, regional banks and enterprises – SpiderNet. SpiderNet is a cross-sector ecosystem which is continuously expanding to connect and collaborate with shareholders, government bodies, industry associations, and clients. GlobalLinker’s AI-powered SME networking platform fosters SME digitalisation and helps members and customers connect with each other and use digital solutions. AMTD will be part of this network and bring the breadth of their partner ecosystem onto GlobalLinker’s platform.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Dheeraj Chowdhry says, “This marks the deepening of the trend of convergence between the established industry players and the Fintechs. The inefficiency of the obsession to ‘build’ and the associated resource and cost effort has perhaps been recognised on both sides and hence the path of coexistence and synergy seems more pragmatic. Fintechs are not competing but, in fact, complementing industry players by accelerating customer adoption of new digital formats for the entire landscape.”
AMTD Continues to Strengthen Partner Ecosystem
Last week also saw AMTD announce a collaboration with Singapore’s CIMB Bank and Funding Societies, to explore opportunities to create a wide range of banking and capital market services to aid SMEs with a one-stop solution for cross-regional and financial products.
Such partnerships by AMTD provides a glimpse of the group’s strong focus on Singapore. In April this year, AFIN and AMTD partnered to establish the USD 36 million AMTD ASEAN-Solidarity Fund. In May, AMTD, MAS, and Singapore FinTech Association (SFA) announced the launch of a USD 4.3 million MAS-SFA-AMTD FinTech Solidarity Grant to support Singapore-based FinTech firms.
AMTD remains committed to evolving their capabilities and ecosystem to empower the SME market in Singapore and the region. AMTD Digital announced their intention of acquiring a controlling stake in PolicyPal, Singapore’s InsureTech pioneer, and CapBridge Financial, a leading private capital platform for investing in growth companies globally. They have also expressed their intentions to acquire a controlling stake in FOMO Pay, a Singapore-based QR code and digital payment solution provider.
“AMTD’s early cognizance of the need for a strong ecosystem has led the organisation to their foray into partnerships and stakes in PolicyPal, FOMO Pay and now GlobalLinker. This strengthens AMTD’s commitment to the Fintech space including stakes in AirStar Digital Bank in Hong Kong and the Digital Bank application in Singapore,” says Chowdhry. “The Fintechs in AMTD’s stable will be part of the ‘AMTD web’ associated companies cutting across geographies and accelerate the ‘Business sans Borders’ objective of MAS and IMDA.”











