Over the past year, Ecosystm has conducted extensive research, including surveys and in-depth conversations with industry leaders, to uncover the most pressing topics and trends. And unsurprisingly, AI emerged as the dominant theme. Here are some insights from our research on the Manufacturing industry.
Click here to download “AI in Manufacturing: Success Stories & Insights” as a PDF
AI is revolutionising production lines, supply chains, and product development in the manufacturing sector. Yet, many manufacturers find themselves stuck between ambition and execution. Those who bridge this gap will gain a competitive edge, driving innovation and leading the industry forward.
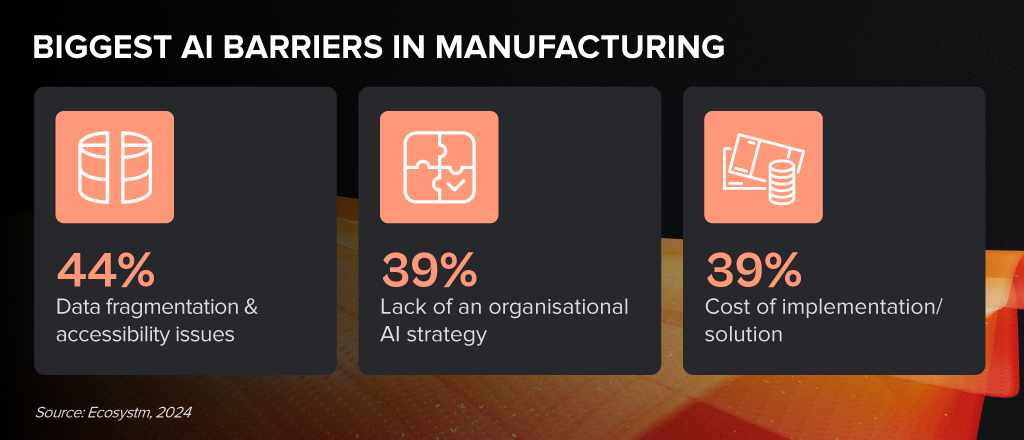
Despite the challenges, Manufacturing organisations are witnessing early AI success in these 3 areas:
- 1. Quality Control & Assurance
- 2. Supply Chain Management & Optimisation
- 3. Process Automation & Efficiency
Quality Control & Assurance
- Defect Detection. Identifying defects in products and improving quality
- Product Inspection. Implementing AI-powered vision systems to inspect products and ensure they meet quality standards
- Data Analysis. Analysing operational data and customer feedback to identify operations and product issues
“AI is the future of design. It streamlines the design process, leading to faster time-to-market and superior products.” – OPERATIONS LEADER
Supply Chain Management & Optimisation
- Inventory Management. Optimising inventory levels and reducing costs
- Supply Chain Visibility. Gaining real-time visibility into supply chain operations
- Demand Forecasting. Predicting demand for products to improve production planning and inventory management
“By leveraging AI, we’re not just optimising our supply chain; we’re pioneering sustainable practices to reduce our carbon footprint.” – CIO
Process Automation and Efficiency
- Process Optimisation. Identifying areas for improvement and potential operational bottlenecks
- Predictive Maintenance. Predicting equipment failures and preventing downtime
- Customer Feedback Analysis. Analysing customer feedback to improve design processes, products, and services
“Our goal is to build intelligent manufacturing plants. By proactively monitoring equipment health, we minimise downtime and maximise productivity – we have set a new internal standard for operational efficiency in the last two years.” – HEAD OF PRODUCTION

Despite an increase in energy efficiency investment, the construction sector’s energy consumption and CO₂ emissions have rebounded to an all-time high. Buildings currently contribute 39% of global energy-related carbon emissions – 28% from operational needs like heating and cooling, and 11% from construction materials.
In the next three decades, with the global population expected to reach 9.7 billion, the construction industry will face the pressure to meet growing infrastructure and housing demands while adapting to stricter environmental regulations.
The urgency of climate action demands that governments mandate low-carbon practices in urban development.
Increase Use of Low-Carbon Materials
Traditional building materials like concrete, steel, and brick are strong and durable but environmentally costly. This high embodied carbon footprint is prompting a shift towards low-carbon alternatives. Indonesia is using ‘green cement’ – made using environmentally friendly materials – in the development of its new futuristic capital Nusantara. This has led to an estimated reduction in carbon emissions of up to 38% per tonne of cement so far.
Nordic countries are setting ambitious targets for low-carbon materials. Starting in 2025, Finland will require life cycle assessments and material declarations in construction to reduce emissions, detailing building components and material origins. Denmark is also prioritising low-carbon materials through energy-efficient designs, sustainable materials, and stringent building codes.
Mandate Whole-Life Carbon Emission Assessments
Whole Life-Cycle Carbon (WLC) emissions encompass all the carbon a building generates throughout its lifespan, from material extraction to demolition and disposal. Assessing WLC gives a comprehensive understanding of a building’s total environmental impact.
The London Plan is a roadmap for future development and achieving the goal of a zero-carbon city. The plan includes provisions for WLC analysis, specific energy hierarchies, and strategies to reduce London’s carbon footprint.
With a bold vision of a fully circular city by 2050, the Amsterdam Circular Strategy 2020-2025 lays out a comprehensive roadmap to achieve this goal. Key elements include mapping material flows to reduce reliance on virgin resources and mandating WLC assessments.
Enforce Clean Construction Standards
From green building codes to tax incentives, governments around the world are implementing innovative strategies to encourage sustainable building practices.
The Philippines’ National Building Code requires green building standards and energy efficiency measures for new buildings.
Seattle offers expedited permits for projects meeting embodied carbon standards, speeding up eco-friendly construction, and reinforcing the city’s environmental goals.
New Jersey offers businesses a tax credit of up to 5% for using low-carbon concrete and an additional 3% for concrete made with carbon capture technology.
Promote Large-Scale Adaptive Reuse
Large-scale adaptive reuse includes reducing carbon emissions by making existing buildings and infrastructure a larger part of the climate solution.
London’s Battersea Power Station restored its iconic chimneys and Art Deco façade, transforming it into a vibrant hub with residential, commercial, and leisure spaces.
The High Line in New York has been transformed into a public park with innovative landscaping, smart irrigation, and interactive art installations, enhancing visitor experience and sustainability.
Singapore using adaptive reuse to rejuvenate urban and industrial spaces sustainably. The Jurong Town Corporation is repurposing a terrace factory for sustainable redevelopment and preserving industrial heritage. In Queenstown, historical buildings in Tanglin Halt are being reused to maintain historical significance and add senior-friendly amenities.
Establish Circular Economy
As cities worldwide start exploring ways to go circular, some are already looking into different ways to leverage innovative practices to implement circular initiatives.
Toronto is embedding circular criteria into procurement by requiring circular economy profiles, vendor action plans, and encouraging circular design for parklets. The city also recommends actions for transitioning to a circular economy and is developing e-learning on circular procurement for staff.
Japan uses Building Information Modeling to optimise resource consumption and reduce waste during construction, with a focus on using recycled materials to promote sustainability in building projects.
Adopt Electric Vehicles
The share of EVs increased from 4% in 2020 to 18% in 2023 and is expected to grow in 2024. This trend reflects a global shift toward cleaner transportation, driven by technological advancements and rising environmental awareness.
The Delhi EV Policy aims to expand charging infrastructure and incentives, targeting 18,000 charging points by 2024, with 25% EV registrations and one charging outlet per 15 EVs citywide.
Singapore is adopting EVs to reduce land transport emissions as part of its net-zero goal, aiming to cut emissions by 1.5 to 2 million tonnes. The EV Roadmap targets cost parity with internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and 60,000 charging points by 2030.
Australia has set new rules to limit vehicle pollution, encouraging car makers to sell more electric vehicles and reduce transportation pollution.
Promote Circular Economy Marketplaces
Circular marketplaces play an important role in the new economy, changing the way we use, manufacture, and purpose materials and products.
The UK’s Material Reuse Portal aggregates surplus construction materials post-deconstruction, offering guidance and connections to service providers. It integrates with various data sources, can be customised for different locations, and provides free access to sustainable materials. Future plans include expanding marketplace partnerships to enhance material reuse.
Build Reuse is a US-based online marketplace specialising in salvaged and surplus building materials. It connects buyers and sellers for reclaimed items like wood, bricks, fixtures, and architectural elements, promoting resource efficiency and reducing construction waste.
Setting and achieving Sustainability goals is complex in BFSI. To be truly sustainable, organisations need to:
- Reduce internal energy consumption and carbon footprint
- Fund the transition to decarbonisation in high emission industries
- Introduce “green” customer products and services
- Monitor carbon data for financed emissions
Data and AI have the potential to assist in achieving these objectives, provided they are used effectively. Here is how.
Download ‘Driving Sustainability with Data and AI in Financial Services’ as a PDF

In our previous Ecosystm Insights, Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Gerald Mackenzie, highlighted the key drivers for boosting ESG maturity and the need to transition from standalone ESG projects to integrating ESG goals into organisational strategy and operations.
This shift can be difficult, requiring an alignment of ESG objectives with broader strategic aims and using organisational capabilities effectively. The solution involves prioritising essential goals, knitting them into overall business strategy, quantifying success metrics, and establishing incentives and governance for effective execution.
The benefits are proven and significant. Stronger Customer and Employee Value Propositions, better bottom line, improved risk profile, and more attractive enterprise valuations for investors and lenders.
According to Gerald, here are 5 things to keep in mind when starting on an ESG journey.
Download ‘Embedding Sustainability in Corporate Strategy and Operations’ as a PDF

As an industry, the tech sector tends to jump on keywords and terms – and sometimes reshapes their meaning and intention. “Sustainable” is one of those terms. Technology vendors are selling (allegedly!) “sustainable software/hardware/services/solutions” – in fact, the focus on “green” or “zero carbon” or “recycled” or “circular economy” is increasing exponentially at the moment. And that is good news – as I mentioned in my previous post, we need to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions if we want a future for our kids. But there is a significant disconnect between the way tech vendors use the word “sustainable” and the way it is used in boardrooms and senior management teams of their clients.
Defining Sustainability
For organisations, Sustainability is a broad business goal – in fact for many, it is the over-arching goal. A sustainable organisation operates in a way that balances economic, social, and environmental (ESG) considerations. Rather than focusing solely on profits, a sustainable organisation aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
This is what building a “Sustainable Organisation” typically involves:
Economic Sustainability. The organisation must be financially stable and operate in a manner that ensures long-term economic viability. It doesn’t just focus on short-term profits but invests in long-term growth and resilience.
Social Sustainability. This involves the organisation’s responsibility to its employees, stakeholders, and the wider community. A sustainable organisation will promote fair labour practices, invest in employee well-being, foster diversity and inclusion, and engage in ethical decision-making. It often involves community engagement and initiatives that support societal growth and well-being.
Environmental Sustainability. This facet includes the responsible use of natural resources and minimising negative impacts on the environment. A sustainable organisation seeks to reduce its carbon footprint, minimise waste, enhance energy efficiency, and often supports or initiates activities that promote environmental conservation.
Governance and Ethical Considerations. Sustainable organisations tend to have transparent and responsible governance. They follow ethical business practices, comply with laws and regulations, and foster a culture of integrity and accountability.
Security and Resilience. Sustainable organisations have the ability to thwart bad actors – and in the situation that they are breached, to recover from these breaches quickly and safely. Sustainable organisations can survive cybersecurity incidents and continue to operate when breaches occur, with the least impact.
Long-Term Focus. Sustainability often requires a long-term perspective. By looking beyond immediate gains and considering the long-term impact of decisions, a sustainable organisation can better align its strategies with broader societal goals.
Stakeholder Engagement. Understanding and addressing the needs and concerns of different stakeholders (including employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and shareholders) is key to sustainability. This includes open communication and collaboration with these groups to foster relationships based on trust and mutual benefit.
Adaptation and Innovation. The organisation is not static and recognises the need for continual improvement and adaptation. This might include innovation in products, services, or processes to meet evolving sustainability standards and societal expectations.
Alignment with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs). Many sustainable organisations align their strategies and operations with the UNSDGs which provide a global framework for addressing sustainability challenges.
Organisations Appreciate Precise Messaging
A sustainable organisation is one that integrates economic, social, and environmental considerations into all aspects of its operations. It goes beyond mere compliance with laws to actively pursue positive impacts on people and the planet, maintaining a balance that ensures long-term success and resilience.
These factors are all top of mind when business leaders, boards and government agencies use the word “sustainable”. Helping organisations meet their emission reduction targets is a good starting point – but it is a long way from all businesses need to become sustainable organisations.
Tech providers need to reconsider their use of the term “sustainable” – unless their solution or service is helping organisations meet all of the features outlined above. Using specific language would be favoured by most customers – telling them how the solution will help them reduce greenhouse gas emissions, meet compliance requirements for CO2 and/or waste reduction, and save money on electricity and/or management costs – these are all likely to get the sale over the line faster than a broad “sustainability” messaging will.











































