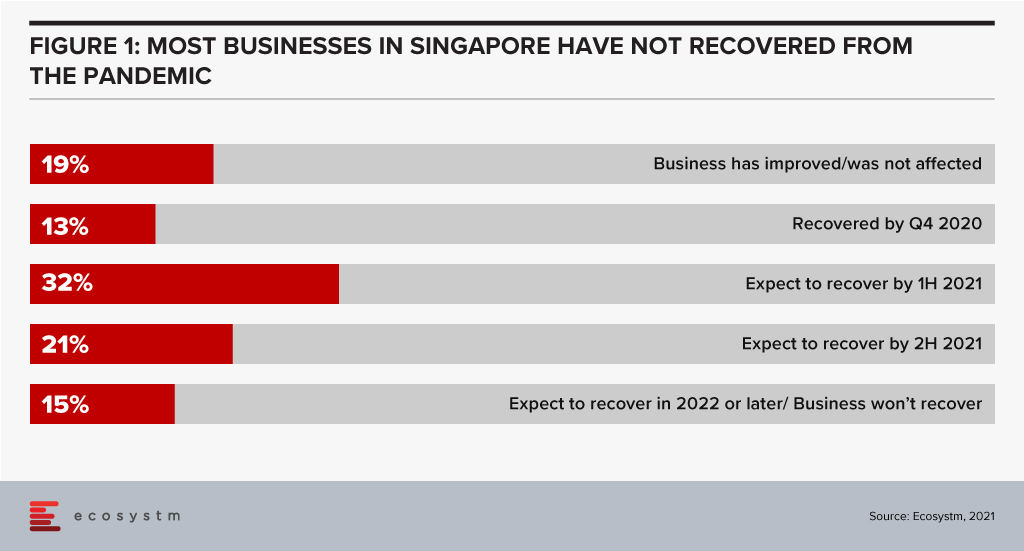
The past twelve months have been tough. Most businesses in Singapore (68%) still haven’t seen revenue recover to pre-pandemic levels. Many budgets are down and you are likely to have a long list of spending options that might help you grow revenue and pull your business out of the pandemic-induced slump. Even if your business is doing well, the pressure on budgets is real.
Increasing your CX Spend
Despite the pressure on budgets Ecosystm data makes a strong case to not cut your customer experience (CX) spend! Businesses in Singapore that are cutting their CX spend are less likely to return to growth, more likely to be competing on price (hence cutting margins), not focused on their digital and omnichannel customers, and have lower levels of innovation. Funnily enough, these are also the businesses with complex, legacy systems which need more focus to provide an improved CX! To be quite frank, businesses in Singapore who are cutting CX spend are setting themselves up for failure. With other businesses increasing CX spend, the gap between the customer experiences will grow to a point where customers will leave and it will be hard to catch up.
Prioritising your CX Spend
So now that you have secured your CX spend, where will you get the biggest bang for your buck? Let’s look at where businesses in Singapore are focusing their CX initiatives in 2021.
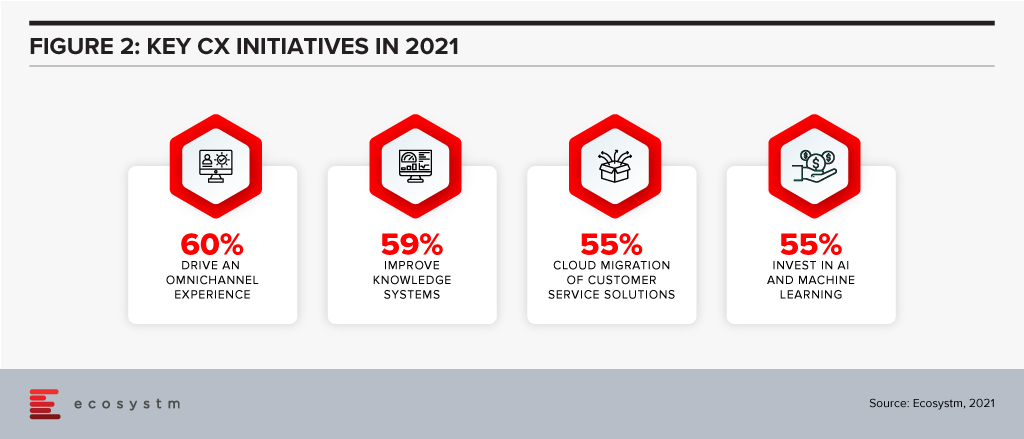
Offering an omnichannel experience. Your customers expect more than just a great digital experience – they want the right experience at the right touchpoint. The CX leaders in Singapore (who, unsurprisingly are often the market leaders) are already offering great omnichannel experiences, so this is quickly becoming about catching up – and not about getting ahead. Providing a consistent, personalised, and optimised experience across your digital touchpoints needs to be a top priority for your business today. If you are not offering conversational commerce solutions, start that strategy as soon as possible – you need to be where your customers are today. Extending this to physical channels and broader ecosystem partners should also be on your agenda.
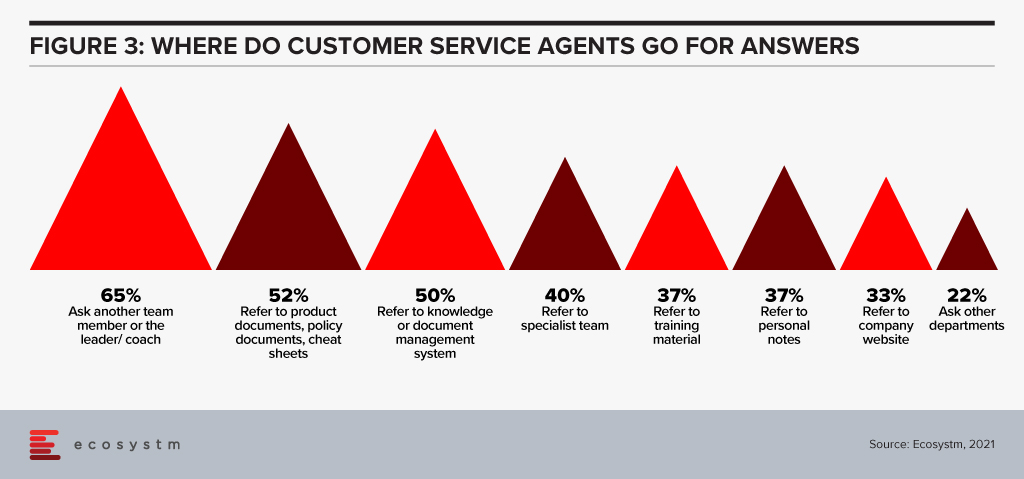
Improving knowledge systems. Your knowledge systems don’t do what they say on the box. They don’t provide answers to questions – for employees or customers. In fact, if your customer service agents get asked a question they don’t know the answer to, their number one source for answers is actually their colleagues or team leaders – NOT the knowledge management system! Start investing in systems – or ideally a single system – that help your employees get better, faster answers to questions. Make sure that the system is providing the same answers to both your employees and your customers across all touchpoints – physical and digital.
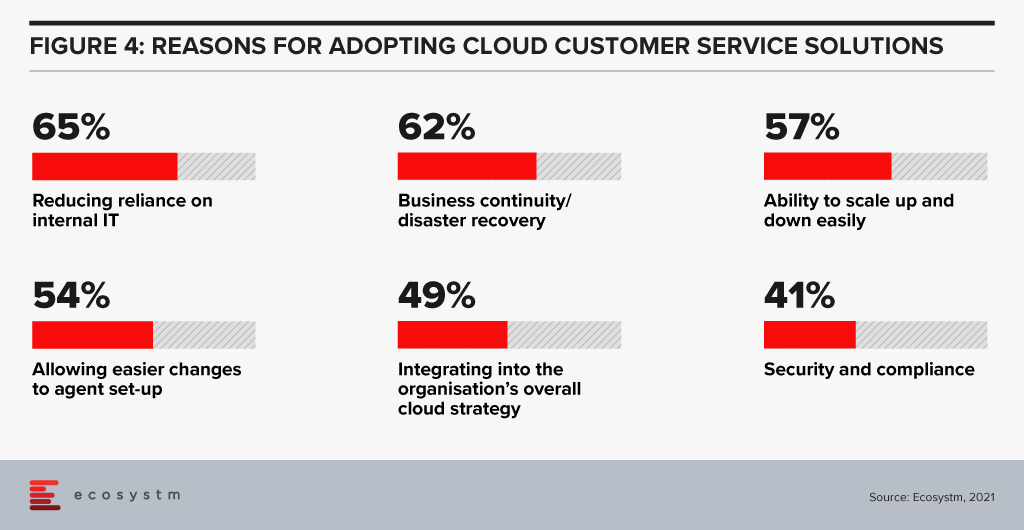
Migrating customer service platforms to the cloud. Over half the businesses in Singapore that we assessed have this as a top CX priority. Cloud solutions offer faster time to value, lower management costs, give access to more regular improvements and often provide the ability to easily integrate with partners who offer product extensions and customisations. This trend will continue in 2021 and 2022 as more businesses realise that their legacy customer service or contact centre platform is inhibiting their ability to innovate their customer experience. These systems also help businesses to stay compliant and reduce the reliance on internal IT – which has traditionally struggled to keep up with the fast-changing nature of the contact centre and customer service teams.
Investing in AI and machine learning. Many businesses are using AI to provide the personalised and optimised customer experiences they aspire to. AI and machine learning are allowing businesses to create personalised offers, offer a next-best action and automate services. Advanced banks in Singapore can create interest rate offers for each individual customer based on their credit profile and history. 46% of businesses in Singapore are already using AI to offer recommendations for customer service agents, 44% to optimise or test messaging and campaigns and 43% to provide faster, more accurate access to information and knowledge. 18 months ago, AI was a business differentiator – allowing your business to create a stand-out CX. Today AI is quickly becoming a standard practice – the battle now is around using AI to create personalised and optimised experiences.
A great customer experience will be the most important factor in lifting your business to pre-pandemic growth levels and helping your business remain competitive in today’s tough business conditions. When it comes to CX, there is no such thing as “saving your way to growth”.
Your opportunity to drive greater business success lies in your ability to better win, serve and retain your customers. Refresh your customer strategy and capability today to make 2021 an exceptional year for your business.

Authored by Alea Fairchild and Audrey William
There is a lot of hope on AI and automation to create intellectual wealth, efficiency, and support for some level of process stability. After all, can’t we just ask Siri or Alexa and get answers so we can make a decision and carry on?
Automation has been touted as the wonder formula for workplace process optimisation. In reality it’s not the quick fix that many business leaders desire. But we keep raising the bar on expectations from automation. Investments in voice technologies, intelligent assistants, augmented reality and touchscreens are changing customer experience (Figure 1). Chatbots are ubiquitous, and everything has the potential to be personalised. But will they solve our problems?
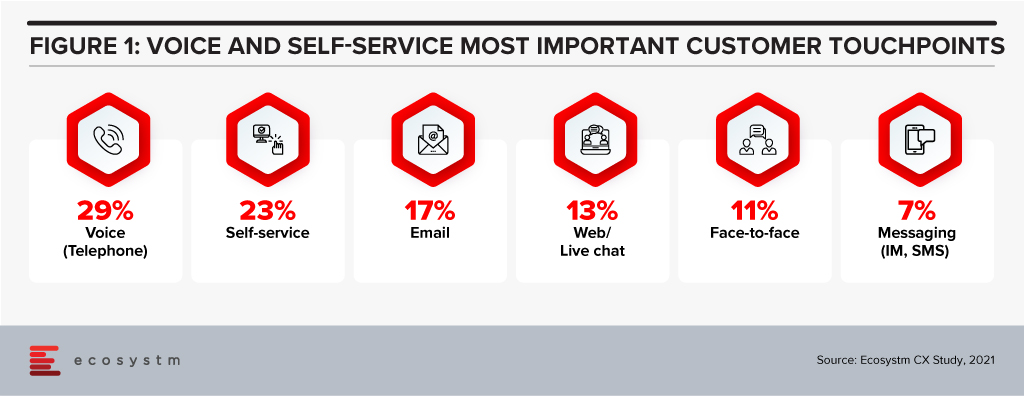
100 percent automation is not effective
Let’s first consider using automation to replace face-to-face interactions. There was a time when people were raving about the check-in experience at some of the hotels in Japan where robots and automated systems would take care of the check-in, in-stay and check-out processes. Sounds simple and good? Till 2019, if you checked into the Henn-na Hotel in Japan, you would be served and taken care of by 243 robots. It was viewed by many as a template for what a fully automated hotel could look like in the future.
The hotel had an in-room voice assistant called Churi. It could cope with basic commands, such as turning the lights on and off, but it was found to be deficient when guests started asking questions about places to visit or other more sophisticated queries. It was not surprising that the hotel decided to retire their robots. In the end it created more work for the hotel staff on-site.
People love the personal touch when they are in a hotel; and talking to someone at the front desk, requesting assistance from hotel staff, or even just a short chat over breakfast are some of the small nuances of why the emotional connection matters. Many quarantine hotels today use robots for food delivery, but the hotel staff is still widely available for questions. That automation is good, but you need the human intervention. So, getting the balance right is key.
Empathy plays a big role in delivering great Customer Experience
Similarly, there was a time when many industry observers and technology providers said that a contact centre will be fully automated, reducing the number of agents. While technologies such as Conversational AI have come along where you can now automate common or repetitive questions and with higher accuracy levels, the human agent still plays a critical role in answering the more complex queries. When the customer has a complicated question or request, then they will WANT to speak to an agent.
When it reaches a point where the conversation with the chatbot starts getting complicated and the customers need more help there should be the option – within the app, website or any other channel – to escalate the call seamlessly to a human agent. Sometimes, a chat is where the good experience happens – the emotional side of the conversation, the laughter, the detailed explanation. This human touch cannot be replaced by machines. Disgruntled customers are happier when an agent shows empathy. Front line staff and human agents act as the face of a company’s brand. Complete automation will not allow the individual to understand the culture of the company. These can be attained through conversations.
Humans as supervisors for AI – The New Workplace
Empathy, intuitiveness, and creativity are all human elements in the intelligence equation. Workers in the future will need to make their niche in a fluid and unpredictable environment; and translating data into action in a non-replicable way is one of the values of human input. The essence of engineering is the capacity to design around human limitations. This requires an understanding of how humans behave and what they want. We call that empathy. It is the difference between the engineer who designs a product, and the engineer who delivers a solution. We don’t teach our computer scientists and engineering students a formula for empathy. But we do try to teach them respect for both the people and the process.
For efficiency, we turn to automation of processes, such as RPA. This is designed to try to eradicate human error and assist us in doing our job better, faster and at a lower cost by automating routine processes. If we design it right, humans take the role of monitoring or supervisory controlling, rather than active participation.
At present, AI is not seen as a replacement for our ingenuity and knowledge, but as a support tool. The value in AI is in understanding and translating human preferences. Humans-in-the-loop AI system building puts humans in the decision loop. They also shift pressure away from building “perfect” algorithms. Having humans involved in the ethical norms of the decision allows the backstop of overly orchestrated algorithms.
That being said, the astute use of AI can deepen insights into what truly makes us human and can humanise experiences by setting a better tone and a more trusted engagement. Using things like sentiment analysis can de-escalate customer service encounters to regain customer loyalty.
The next transformational activity for renovating work is to advance interactions with customers by interpreting what they are asking for and humanising the experience of acquiring it which may include actually dealing with a human contact centre agent – decisions that are supported at the edge by automation, but at the core by a human being.
Implications
Ecosystm research shows that process automation will be a key priority for technology investments in 2021 (Figure 2).
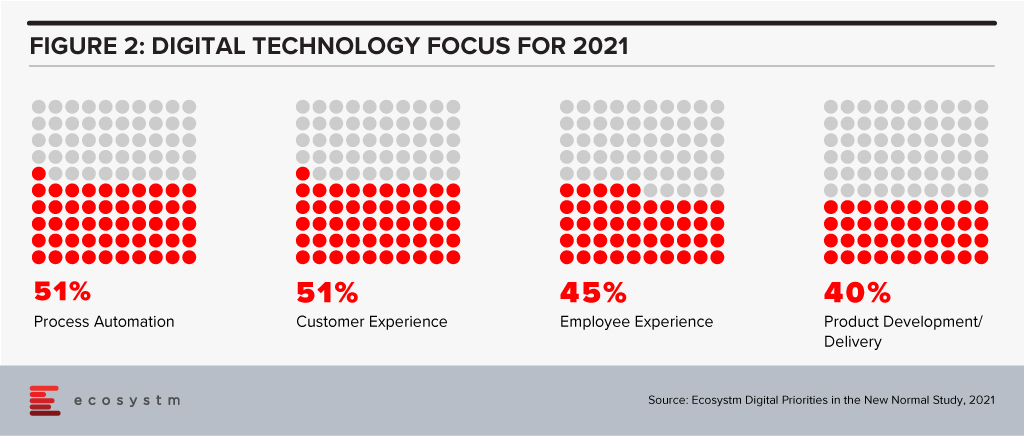
With AI and automation, a priority in 2021, it will be important to keep these considerations in mind:
- Making empathy and the human connection the core of customer experiences will bring success.
- Rigorous, outcome-based testing will be required when process automation solutions are being evaluated. In areas where there are unsatisfactory results, human interactions cannot – and should not – be replaced.
- It may be easy to achieve 90% automation for dealing with common, repetitive questions and processes. But there should always be room for human intervention in the event of an issue – and it should be immediate and not 24 hours later!
- Employees can drive greater value by working alongside the chatbot, robot or machine.
Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Customer Experience Trends for 2021
Download Ecosystm’s complimentary report detailing the top 5 customer experience trends for 2021 that your company should pay attention to along with tips on how to stay ahead of the curve.

In 2009 one of the foremost Financial Services industry experts was giving my team a deep dive into the Global Financial Crisis (GFS) and its ramifications. According to him, one of the key reasons why it happened was that most people in key positions in both industry and government had probably never seen a full downturn in their careers. There was a bit of a hiccup during the dot com bust but nothing that seriously interrupted the long boom that began somewhere in 1988. They had never experienced anything quite like 2008; so they never imagined that such a crisis could actually happen.
Similarly, 2020 was an unprecedented year – in our lives and certainly for the tech industry. The GFC (as the name suggests) was a financial crisis. A lot of people lost their jobs, but after the bailouts things went largely back to normal. COVID-19 is something different altogether – the impact will be felt for years and we don’t yet know the full implications of the crisis.
While we would like to start 2021 with a clean slate and never talk about the pandemic again, the reality is that COVID-19 will shape what we will see this year. In the first place it looks like the disease will still be around for a substantial part of the year. Secondly, all the changes it has brought in 2020 with entire workforces suddenly moving to operating from home will have profound implications for technology and customer experience this year.
As we ease into 2021, I look at some of the organisational and technology trends that are likely to impact customer experience (CX) in 2021.
#1 All Business is Now eBusiness
COVID-19 has ensured that the few businesses which did not have an online presence became acutely aware that they needed one. It created a need for many businesses to quickly initiate eCommerce. Forbes reported a 77% increase in eCommerce infrastructure spending YoY. This represents about 4 years of growth squeezed into the first 6 months of 2020!
From a CX point of view there is going to be far more interaction with brands and products through online channels. This is not just about eCommerce and buying from a portal. It is also about using tools like Instagram, Facebook and other social media platforms more widely. It is about learning to interact with the customer in multiple ways and touching their journeys at multiple points, all virtually using the web – mostly the mobile web.
Ecosystm research shows that almost three out of four companies have decided on accelerating or modifying the digitalisation they were undergoing (Figure 1). It is fair to expect that this gives a further boost to moving to the cloud. For the customer it will mean being able to access information in many new ways and connect with products, services, brands at multiple points on the web.
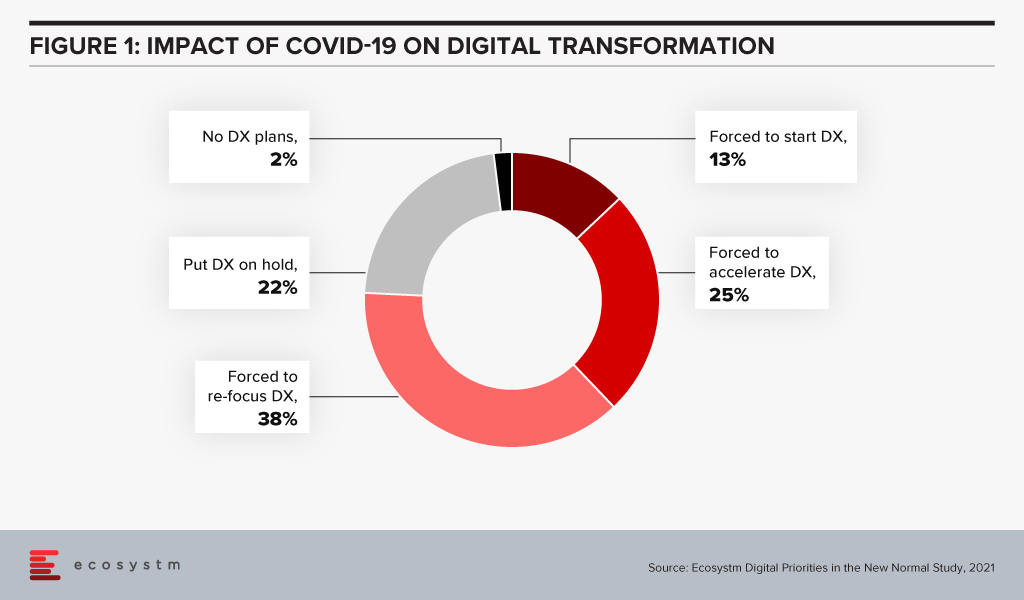
Since interacting with the customer at multiple points is new for most services, I foresee a lot of missed opportunities as companies learn to navigate a completely different landscape. Customers pampered by digitally native organisations often react harshly to even a small mistake. It will become critical for companies to not just become a bigger presence online but also to manage their customers well.
New solutions such as Customer Data Platforms (CDP), as opposed to CRM will become common. Players who are into Customer Experience management are likely to see huge business growth and new players will rapidly enter this space. They will promise to affordably manage CX across the globe, leveraging the cloud.
#2 Virtual Merges with Real
Virtual and Augmented Reality are not new. They have been around for a while. This will now cross the early adoption stage and is likely to proliferate in terms of use cases and importance.
AR/VR has so far been seen mainly in games where one wears an unwieldy – though ever-improving – headset to transport oneself into a 3D virtual world. Or in certain industrial applications e.g., using a mobile device to look at some machinery; the device captures what the eye can see while providing graphical overlays with information. In 2021 I expect to see almost all industrial applications adopting some form of this technology. This will have an impact on how products are serviced and repaired.
For the mainstream, 2020 was the year of videoconferencing – as iconic as the shift to virtual meetings has been, there is much more to come. Meetings, conferences, events, classrooms have all gone virtual. Video interaction with multiple people and sharing information via shared applications is commonplace. Virtual backgrounds which hide where you are actually speaking from are also widely used and getting more creative by the day.
Imagine then a future where you get on one of these calls wearing a headset and are transported into a room where your colleagues who are joining the call also are. You see them as full 3D people, you see the furniture, and the room decor. You speak and everyone sees your 3D avatar speak, gesture (as you gesture from the comfort of your home office) and move around. It will seem like you are really in the conference room together! If this feels futuristic or unreal try this or look at how the virtual office can look in the very near future.
While the solutions may not look very sophisticated, they will rapidly improve. AR/VR will start to really make its presence felt in the lives of consumers. From being able to virtually “try” on clothes from a boutique to product launches going virtual, these technologies will deeply impact customer experience in 2021 and beyond
In the immortal words of Captain Kirk, we will be going where no man has gone before – enabled by AR / VR.
#3 Digital CX will involve Multiple Technologies
AI, IoT and 5G will continue to support wider CX initiatives.
The advances that I have mentioned will gain impetus from 5G networking, which will enable unprecedented bandwidth availability. To deliver an AR experience over the cloud, riding on a 5G network, will literally be a game changer compared to the capabilities of older networks.
Similarly, IoT will lead to massive changes in terms of product availability, customisation and so on. 5G-enabled IoT will allow a lot more data to be carried a lot faster; and more processing at the edge. IoT will have some initial use cases in Retail, Services and other non-manufacturing sectors – but perhaps not as strongly as some commentators seem to indicate.
AI continues to drive change. While AI may not transform CX in 2021, this is a technology which will be a component of most other CX offerings, and so will impact customer experience in the next few years. In fact, thinking of businesses in 2025 I cannot believe that there will be a single business to customer (B2C) interaction which will not feature some form of AI technology.
I’d be interested to hear your thoughts on the technologies which will impact CX in 2021 – Connect with me on the Ecosystm platform.

In 2020, much of the focus for organisations were on business continuity, and on empowering their employees to work remotely. Their primary focus in managing customer experience was on re-inventing their product and service delivery to their customers as regular modes were disrupted. As they emerge from the crisis, organisations will realise that it is not only their customer experience delivery models that have changed – but customer expectations have also evolved in the last few months. They are more open to digital interactions and in many cases the concept of brand loyalty has been diluted. This will change everything for organisations’ customer strategies. And digital technology will play a significant role as they continue to pivot to succeed in 2021 – across regions, industries and organisations.
Ecosystm Advisors Audrey William, Niloy Mukherjee and Tim Sheedy present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for Customer Experience in 2021. This is a summary of the predictions – the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform.
The Top 5 Customer Experience Trends for 2021
- Customer Experience Will Go Truly Digital
COVID-19 made the few businesses that did not have an online presence acutely aware that they need one – yesterday! We have seen at least 4 years of digital growth squeezed into six months of 2020. And this is only the beginning. While in 2020, the focus was primarily on eCommerce and digital payments, there will now be a huge demand for new platforms to be able to interact digitally with the customer, not just to be able to sell something online.
Digital customer interactions with brands and products – through social media, online influencers, interactive AI-driven apps, online marketplaces and the like will accelerate dramatically in 2021. The organisations that will be successful will be the ones that are able to interact with their customers and connect with them at multiple touchpoints across the customer journey. Companies unable to do that will struggle.
- Digital Engagement Will Expand Beyond the Traditional Customer-focused Industries
One of the biggest changes in 2020 has been the increase in digital engagement by industries that have not traditionally had a strong eye on CX. This trend is likely to accelerate and be further enhanced in 2021.
Healthcare has traditionally been focused on improving clinical outcomes – and patient experience has been a byproduct of that focus. Many remote care initiatives have the core objective of keeping patients out of the already over-crowded healthcare provider organisations. These initiatives will now have a strong CX element to them. The need to disseminate information to citizens has also heightened expectations on how people want their healthcare organisations and Public Health to interact with them. The public sector will dramatically increase digital interactions with citizens, having been forced to look at digital solutions during the pandemic.
Other industries that have not had a traditional focus on CX will not be far behind. The Primary & Resources industries are showing an interest in Digital CX almost for the first time. Most of these businesses are looking to transform how they manage their supply chains from mine/farm to the end customer. Energy and Utilities and Manufacturing industries will also begin to benefit from a customer focus – primarily looking at technology – including 3D printing – to customise their products and services for better CX and a larger share of the market.
- Brands that Establish a Trusted Relationship Can Start Having Fun Again
Building trust was at the core of most businesses’ CX strategies in 2020 as they attempted to provide certainty in a world generally devoid of it. But in the struggle to build a trusted experience and brand, most businesses lost the “fun”. In fact, for many businesses, fun was off the agenda entirely. Soft drink brands, travel providers, clothing retailers and many other brands typically known for their fun or cheeky experiences moved the needle to “trust” and dialed it up to 11. But with a number of vaccines on the horizon, many CX professionals will look to return to pre-pandemic experiences, that look to delight and sometimes even surprise customers.
However, many companies will get this wrong. Customers will not be looking for just fun or just great experiences. Trust still needs to be at the core of the experience. Customers will not return to pre-pandemic thinking – not immediately anyway. You can create a fun experience only if you have earned their trust first. And trust is earned by not only providing easy and effective experiences, but by being authentic.
- Customer Data Platforms Will See Increased Adoption
Enterprises continue to struggle to have a single view of the customer. There is an immense interest in making better sense of data across every touchpoint – from mobile apps, websites, social media, in-store interactions and the calls to the contact centre – to be able to create deeper customer profiles. CRM systems have been the traditional repositories of customer data, helping build a sales pipeline, and providing Marketing teams with the information they need for lead generation and marketing campaigns. However, CRM systems have an incomplete view of the customer journey. They often collect and store the same data from limited touchpoints – getting richer insights and targeted action recommendations from the same datasets is not possible in today’s world. And organisations struggled to pivot their customer strategies during COVID-19. Data residing in silos was an obstacle to driving better customer experience.
We are living in an age where customer journeys and preferences are becoming complex to decipher. An API-based CDP can ingest data from any channel of interaction across multiple journeys and create unique and detailed customer profiles. A complete overhaul of how data can be segregated based on a more accurate and targeted profile of the customer from multiple sources will be the way forward in order to drive a more proactive CX engagement.
- Voice of the Customer Programs Will be Transformed
Designing surveys and Voice of Customer programs can be time-consuming and many organisations that have a routine of running these surveys use a fixed pattern for the data they collect and analyse. However, some organisations understand that just analysing results from a survey or CSAT score does not say much about what customers’ next plan of action will be. While it may give an idea of whether particular interactions were satisfactory, it gives no indication of whether they are likely to move to another brand; if they needed more assistance; if there was an opportunity to upsell or cross sell; or even what new products and services need to be introduced. Some customers will just tick the box as a way of closing off a feedback form or survey. Leading organisations realise that this may not be a good enough indication of a brand’s health.
Organisations will look beyond CSAT to other parameters and attributes. It is the time to pay greater attention to the Voice of the Customer – and old methods alone will not suffice. They want a 360-degree view of their customers’ opinions.

Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) ratings towards investment criteria have become popular for potential investors to evaluate companies in which they might want to invest. As younger investors and others have shown an interest in investing based on their personal values, brokerage firms and mutual fund companies have begun to offer exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and other financial products that follow specifically stated ESG criteria. Passive investing with robo-advisors such as Betterment and Wealthfront have also used ESG criteria to appeal to this group.
The disruption caused by the pandemic has highlighted for many of us the importance of building sustainable and resilient business models based on multi-stakeholder considerations. It has also created growing investor interest in ESG.
ESG signalling for institutional investors
The increased interest in climate change, sustainable business investments and ESG metrics is partly a reaction of the society to assist in the global transition to a greener and more humane economy in the post-COVID era. Efforts for ESG standards for risk measurement will benefit and support that effort.
A recent study of asset managers by the investment arm of Institutional Shareholder Services (ISS) showed that more than 12% of respondents reported heightened importance of ESG considerations in their investment decisions or stewardship activities compared to before the pandemic.
In the area of hedge funds, there has been an increased demand for ESG-integrated investments since the start of COVID-19, according to 50% of all respondents of a hedge fund survey conducted by BNP Paribas Corporate and Institutional Banking of 53 firms with combined assets under management (AUM) of at least USD 500B.
ESG criteria may have a practical purpose beyond any ethical concerns, as these criteria may be able to help avoidance of companies whose practices could signal risk. As ESG gets more traction, investment firms such as JPMorgan Chase, Wells Fargo, and Goldman Sachs have published annual reports that highlight and review their ESG approaches and the bottom-line results.
But even with more options, the need for clarity and standards on ESG has never been so important. In my opinion, there must be an enhanced effort to standardise and harmonise ESG rating metrics.
How are ESG ratings made?
ESG ratings need both quantitative and qualitative/narrative disclosures by companies in order to be calculated. And if no data is disclosed or available, companies then move to estimations.
No global standard has been defined for what is included in a given company’s ESG rating. Attempts at standardising the list of ESG topics to consider include the materiality map developed by the Sustainable Accounting Standard Board (SASB) or the reporting standards created by the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI). But most ESG rating providers have been defining their own materiality matrices to calculate their scores.
Can ESG scoring be automatically integrated?
Just this month, Morningstar equity research analysts announced they will employ a globally consistent framework to capture ESG risk across over 1,500 stocks. Analysts will identify valuation-relevant risks for each company using Sustainalytics’ ESG Risk Ratings, which measure a company’s exposure to material ESG risks, then evaluate the probability those risks materialise and the associated valuation impact. ESG rating firms such as MSCI, Sustainalytics, RepRisk, and ISS use a rules-based methodology to identify industry leaders and laggards according to their exposure to ESG risks, as well as how well they manage those risks relative to peers.
Their ESG Risk Ratings measure a company’s exposure to industry-specific material ESG risks and how well a company is managing those risks. This approach to measuring ESG risk combines the concepts of management and exposure to arrive at an assessment of ESG risk – the ESG Risk Rating – which should be comparable across all industries. But some critics of this form of approach feel it is still too subjective and too industry-specific to be relevant. This criticism is relevant when you understand that the use of the ESG ratings and underlying scores may in future inform asset allocation. How might this better automated and controlled? Perhaps adding some AI might be useful to address this?
In one example, Deutsche Börse has recently led a USD 15 million funding round in Clarity AI, a Spanish FinTech firm that uses machine learning and big data to help investors understand the societal impact of their investment portfolios. Clarity AI’s proprietary tech platform performs sustainability assessments covering more than 30,000 companies,198 countries,187 local governments and over 200,000 funds. Where companies like Cooler Future are working on an impact investment app for everyday individual users, Clarity AI has attracted a client network representing over $3 trillion of assets and funding from investors such as Kibo Ventures, Founders Fund, Seaya Ventures and Matthew Freud.
What about ESG Indices? What do they tell us about risk?
Core ESG indexing is the use of indices designed to apply ESG screening and ESG scores to recognised indices such as the S&P 500®, S&P/ASX 200, or S&P/TSX Composite. SAM, part of S&P Global, annually conducts a Corporate Sustainability Assessment, an ESG analysis of over 7,300 companies. Core ESG indices can then become actionable components of asset allocation when a fund or separately managed accounts (SMAs) provider tracks the index.
Back in 2017, the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN) and the State Secretariat for International Finance (SIF) made it possible for all Swiss pension funds and insurance firms to measure the environmental impact of their stocks and portfolios for free. Currently, these federal bodies are testing use case with banks and asset managers. Its initial activities will be recorded in an action plan, which is due to be published in Spring 2021.
How can having a body of sustainable firms help create ESG metrics?
Creating ESG standard metrics and methodologies will be aided when there is a network of sustainable companies to analyse, which leads us to green fintech networks (GFN) of companies interested in exploring how their own technology investments can be supportive of ESG objectives. Switzerland is setting up a Green Fintech Network to help the country take advantage of the “great opportunity” presented by sustainable finance. The network has been launched by SIF alongside industry players, including green FinTech companies, universities, and consulting and law firms. Stockholm also has a Green Fintech Network that allows collaboration towards sustainability goals.
Concluding Thought
We should be curious about how ESG can provide decision-oriented information about intangible assets and non-financial risks and opportunities. More information and data from ESG data providers like SAM, combined with automation or AI tools can potentially provide a more complete picture of how to measure the long-term sustainable performance of equity and fixed income asset classes.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Investor Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Investor Summit which will cover topics tied to 2021 Investor Priorities, and Fundraising and exit strategies

In this blog, our guest authors Randeep Sudan and Yamin Oo talk about the pervasiveness of the Digital Economy, and the key trends that will determine its future trajectory. “That the world in 2030 will be very different from today is obvious. We may, however, be surprised by the extent and sweep of the change ahead of us.”


The Digital Economy – a term first coined by Don Tapscott in 1994 – is not easy to define or measure. At one end, it is limited to the production and consumption of digital goods and services. On the other end, according to the European Parliament, “The digital economy is increasingly interwoven with the physical or offline economy making it more and more difficult to clearly delineate the digital economy“. We are, however, witnessing the Digital Economy transitioning to an economy that is digital.
Given the pervasiveness of the Digital Economy, its future will be determined by the complex interplay of several trends. Some of the trends that illustrate the future trajectory of the Digital Economy are:
Technology
We will see AI becoming ubiquitous as it is leveraged in every sector and sphere of activity. According to one estimate, AI is estimated to contribute USD 15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, which is more than the current GDP of China and India combined! We are also likely to see rapid progress in technologies related to Extended Reality (XR) in the coming years. COVID-19 is accelerating this trend, as we can see from the offerings of companies like Spatial and MeetinVR that facilitate virtual business meetings. The analog world’s rendering into its digital twin will see us moving towards a metaverse – a virtual shared space imagined in Neal Stephenson’s novel Snowcrash. Some of the biggest names in the tech industry – Apple (Apple glass), Facebook (Oculus), Sony (Playstation) – are assiduously working towards this direction.
Given the importance of telecom infrastructure to the Digital Economy, 5G networks are being rolled out in countries worldwide (Figure 1). However, even as 5G is being deployed, the buzz around 6G is getting louder. 6G may transmit data 100 times faster than 5G and may see deployment by 2030 given the decadal cycles for telecom: 1G in the 80s, 2G in the 90s, 3G in the decade following 2000, 4G in the decade starting 2010, and 5G beginning in the 2020s.
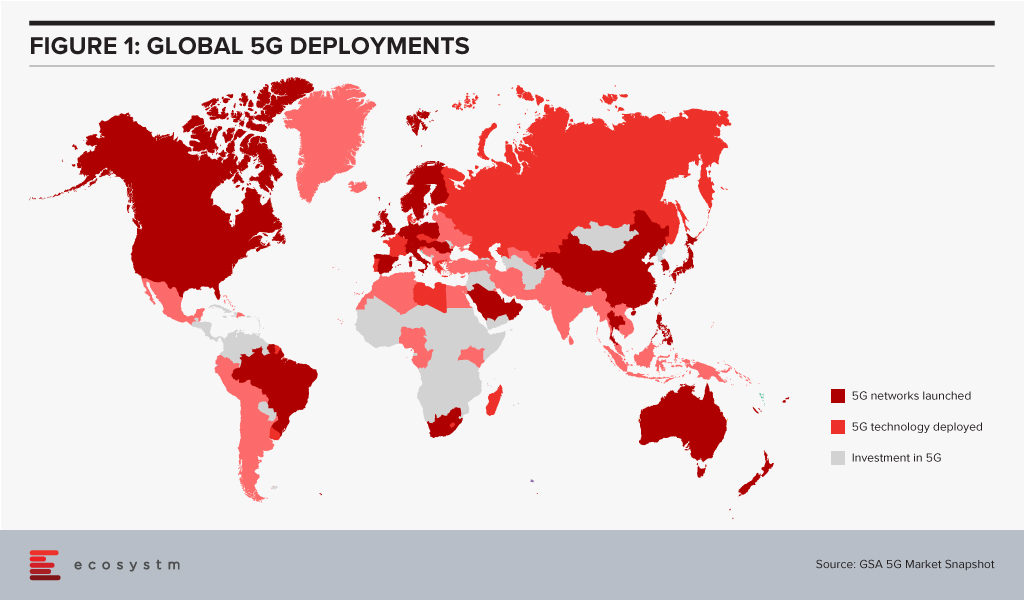
The availability of high bandwidth, low latency networks could lead to newer applications and further breakthroughs in innovative technologies.
The Future of Work
With the rapid growth in automation and AI, we are likely to see significant labour market disruptions. Moreover, COVID-19 has been a watershed for the global economy – its impacts will continue to be felt for many years to come. According to the International Labor Organization, 495 million full-time jobs were lost in the first two quarters of 2020 due to COVID-19. Lower and middle-income countries have suffered the most, with an estimated 23.3% drop in working hours – equivalent to 240 million jobs.
A recent report from the World Economic Forum estimates that by 2025, 85 million jobs may be displaced due to automation and AI, while 97 million new roles may emerge. We will see significant changes and turbulence in labour markets across multiple industries and geographies in the years ahead. If we look at how the top ten skills required by the top 10 US companies have been changing over time, we get an indication of the Future of Work. Companies are more focused on “soft” skills, that are not easily addressed by AI & Automation.
We are also likely to see a shift from humans adapting to technology to technologies adapting to humans. For example, the acceleration in digital twins combined with advancements in XR could allow unskilled workers to do skilled jobs. AR could guide a worker to repair a piece of mechanical equipment without long years of previous training. Similarly, the emergence of ‘Low Code No Code’ (LCNC) applications will allow ordinary individuals to do tasks that previously required specialised training.
Climate Change
Scientists have long focused our attention to limit the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere to 450 parts per million to avoid catastrophic climate change. In 2016, the World Meteorological Organization reported this concentration had crossed 400 parts per million, leaving us with a shorter runway to prevent calamitous climate change. We are, therefore, likely to see increased efforts to tackle climate change in the decade ahead.
Digital technologies can impact the global climate agenda in multiple ways: smart grids, smart buildings, smart appliances, intelligent transport systems, shared mobility, and 3D printing, to name a few. Digital technologies will also allow new sources of renewable energy to be tapped. For example, the molten core of the earth is over 6,000°C. “Just 0.1% of the heat content of Earth could supply humanity’s total energy needs for 2 million years,” according to AltaRock Energy. Advances in the use of digital technologies that allow for precise directional drilling will allow for advanced geothermal systems to be established as reliable power sources.
Splinternet
Tech bloggers like Doc Searls and Stephen Lewis had begun to theorise about a Splinternet as early as 2008. There was a danger of governments carving the world into geopolitical blocks and creating technology barriers. China’s Great Firewall and the US’s recent responses under the Trump administration are likely to hurtle us in the direction of a fractured internet. We may end up with the US dominating the western internet and China dominating a competing block of countries. The Digital Economy’s evolution would fracture into different camps, making it very different from what it is today.
Tech Regulation
The most valuable companies in the world today are in tech. Seven of the top ten companies in the world by market cap in 2020 are tech companies.
The recent investigation into competition in digital markets undertaken by the US House Judiciary Committee observed: “Over the past decade, the digital economy has become highly concentrated and prone to monopolisation. Several markets investigated by the Subcommittee – such as social networking, general online search, and online advertising – are dominated by just one or two firms. The companies investigated by the Subcommittee – Amazon, Apple, Facebook, and Google – have captured control over key channels of distribution and have come to function as gatekeepers. Just a decade into the future, 30% of the world’s gross economic output may lie with these firms, and just a handful of others.“
We have also witnessed the rapid diversification of data monopolies into other sectors. See, for example, the diversification of VC investments by Alibaba’s Ant Group over time. In 2015 they were investing in 5 areas, which has doubled in the last 5 years.
The call for the regulation of big tech will gain momentum in the coming years. The European Union is likely to lead here, just the way just it did in the case of its General Data Protection Regulation.
Governments will also require data monopolies to share data. China mandates its automakers to share data generated by electric vehicles with a government research institute. This data is essential for public safety and planning battery-recharging stations. The Australian Government promotes the concept of sharing “designated datasets” that could include data held by the private sector that has significant community benefits. Similarly, France’s Law for a Digital Republic requires the sharing data by certain categories of the private sector. Such blurring of boundaries between public and private data will become more important.
We will also see the growing importance of data trusts. These are structures where data is placed in the custody of a “Board of Trustees” who have a fiduciary responsibility to look after the interests of data owners. Such data trusts might give individuals better control over their data.
Every aspect of the economy is being digitalised today. In the next decade we are likely to witness foundational shifts in how the Digital or Data Economy is structured. It will also see increasing risks as cyber threats grow exponentially from cybercriminals and state actors. That the world in 2030 will be very different from today is obvious. We may, however, be surprised by the extent and sweep of the change ahead of us.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Economic Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Economic Summit which will cover topics tied to the state of the economy, path to recovery and re-framing the new financial services landscape

The Healthcare industry has had to pivot completely this year and 2021 will see it emerge a transformed industry. The impact will be seen on policies, how ecosystems evolve, and most obviously on healthcare provider organisations. COVID-19 has shifted the business priorities of healthcare providers and how these organisations invest and use technology. There will be another reset in 2021. However, given the immense impact of the pandemic, it would be near-impossible to restrict the prediction to only one year; and several of the trends will firmly define the industry way beyond 2021.
Ecosystm Advisors Aga Manhao, Arun Sethuraman, Krish Krishnan and Sash Mukherjee present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for Healthcare Trends in 2021. This is a summary of the Healthcare predictions – the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform.
The Top 5 Healthcare Trends for 2021
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Public Health Will Create New Opportunities Well Beyond 2021
The impact of COVID-19 will be on all levels. Increasing pressure from patients will challenge healthcare providers (from primary through to tertiary) throughout 2021. There will be larger global impacts as well – average nourishment is likely to go down in most countries, and there will be lower average (seasonal) immune health in many countries.
This is not all doom and gloom – there will be new business opportunities. Enterprises and innovators will find opportunities in:
- Supply Chain Arbitrage. Continued asymmetrical supply and demand will drive the movement of healthcare related goods and services across geographies.
- Investment. Investments in pharma/ vaccine/ diagnostics manufacturing and distribution will be driven more by short-term horizons, defensive capacity building, and supply security concerns. Technology and IP acquisition by pharma and medtech leaders will also accelerate.
- Innovation. COVID-linked gaps in health, immunity, nourishment, and lifestyles will lead to new products within foods, supplements, medications, and pharmaceuticals; and in tech-enabled personal devices and health monitoring apps or systems.
- New Businesses. We will see an upsurge in demand and supply of alternative medicines and devices as well, although these may still not be accepted in conventional medicine.
- Healthcare Policies Will Focus on Product & Manufacturing Security and Supply Chain Control
The COVID-19 crisis has exposed the need for better collaboration and visibility of external resources to handle unprecedented scenarios. Governments in countries that have done well to manage the crisis took the vital step of encouraging and being the hub for cross-agency collaboration. Having a siloed view of resources and the supply chain is not sufficient in combating larger challenges. Healthcare policy makers will work towards a more collaborative, AI-driven, supply chain.
Some of the world’s largest economies have already begun to take steps to reduce manufacturing and supply chain dependencies in pharma, vaccines, diagnostics and medical devices. What has shown up as opportunistic stockpiling or supply chain arbitrage will become more entrenched. Various governments will either incentivise or centralise the establishment of manufacturing and long-term supply contracts for their countries.
- 2021 Will be a Breakout Year for Community Health
COVID-19 has significantly disrupted current standards of care for chronic diseases world-wide. Frequency and necessity of patient visits to hospitals and clinics for routine checkups and minor interventions are being evaluated by healthcare planners and providers. There are concerns about the increasing cost of providing basic services, allocation of healthcare capacity to higher priority needs, and the need to reduce risk of exposure to the vulnerable population.
Telehealth and Digital Health technologies have seen a marked increase in adoption during the pandemic, but the real effectiveness of these solutions to solve a healthcare delivery problem is still emerging. We predict 2021 will be a breakout year for Community Health, powered by these two technologies. There will be an increased focus on building resilient communities and early warning systems. Number of visits to hospitals and clinics for routine observations will drop by 15-20% or even more. Privacy and Data security concerns will increase, and this will also lead to better policy and practices to address these concerns. 2021 promises to be a better year for coordinated community care.
- Healthcare Providers Will be More Tech-Dependent Than Ever
In 2020, healthcare providers’ technology investments took off on unexpected trajectories and they have digressed from their technology and transformation roadmap. Many solutions would have gone through an initial ‘proof-of-concept’ without the formal rigours and protocols. Many of these will be adopted for longer term applications.
Healthcare organisations had to pivot their technology spending when COVID-19 hit. There were several changes that were required to be made, including implementing operational measures to ensure staff safety and cutting down on non-essential expenses. When it comes to digital initiatives, the key focus areas were evolving service delivery and empowering employees with the right technology for care delivery – often remote. What providers did not have the time or resources for was to digitalise processes and retain focus on their entire patient demography – and not just those impacted by COVID-19. In 2021, we see a clear indication that not only will their priorities be different, healthcare providers will ramp up their technology investments in all areas.
- Medtech and Providers Will Find New Synergies
Medical devices which generate clinical data and/or are driven by clinical data will attract greater investment and higher R&D expenditure; and will either dominate or begin to set the direction for future consumer devices in the Healthcare space.
The popularity of telehealth and digital health will put pressure on healthcare providers to further draw data-driven insights from personal devices. They are likely to mandate the devices that they would be willing to use the data from They will have greater power to demand Interoperability and operating system convergences in the next few years from device developers and manufacturers.
2021 will see an increased use of devices such phones, bracelets and even anklets to track the spread of COVID-19. It will also see the transition of the smartphone to a medical device. The collection, sharing of data, running AI/machine learning will make our smartphones an integral part of remote patient management.

As organisations look to empower consumers with alternative channels of communication and engagement, there will be a greater adoption of Conversational AI. The biggest challenge lies in getting the deployment right from the start. There are many vendors that are promoting their offerings around Conversational AI, and some enterprises that have rushed to invest have been disappointed with the outcome – no improvement in CX but at a higher cost. Organisations need to evaluate the entire design framework, plan where AI fits into the enterprise’s overall CX vision and understand what constitutes Conversational AI.
This whitepaper outlines the definition of Conversational AI and what tech buyers need to consider before embarking on a Conversational AI deployment. The data used in this paper is from the global Ecosystm CX and AI studies, that are live and can be accessed on the Ecosystm platform.
Click Below to Download the Whitepaper

(Clicking on this link will take you to Nuance website where you can download the Whitepaper)

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming embedded in financial services across consumer interactions and core business processes, including the use of chatbots and natural language processing (NLP) for KYC/AML risk assessment.
But what does AI mean for financial regulators? They are also consuming increasing amounts of data and are now using AI to gain new insights and inform policy decisions.
The efficiencies that AI offers can be harnessed in support of compliance within both financial regulation (RegTech) and financial supervision (SupTech). Authorities and regulated institutions have both turned to AI to help them manage the increased regulatory requirements that were put in place after the 2008 financial crisis. Ecosystm research finds that compliance is key to financial institutions (Figure 1).
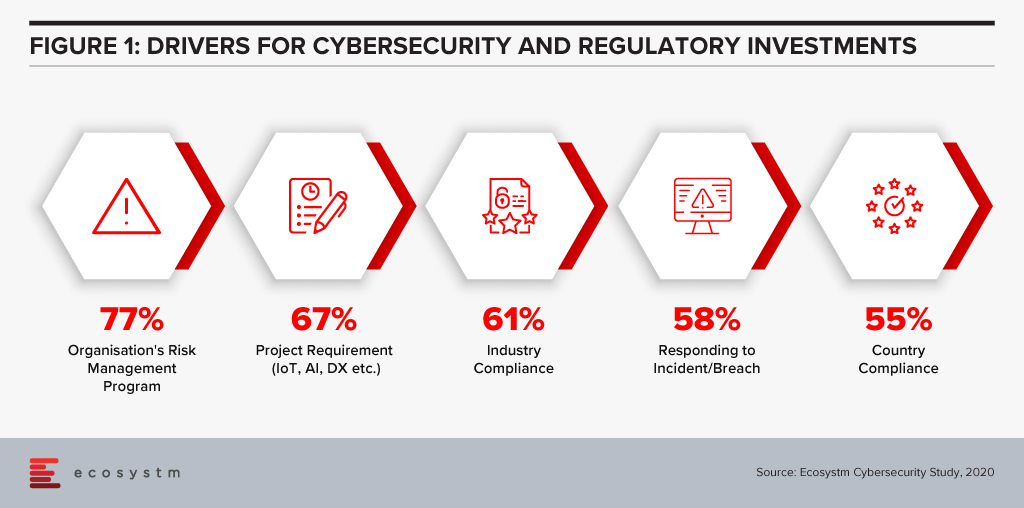
SupTech is maturing with more robust safeguards and frameworks, enabling the necessary advancements in technology implementation for AI and Machine Learning (ML) to be used for regulatory supervision. The Bank of England and the UK Financial Conduct Authority surveyed the industry in March 2019 to understand how and where AI and ML are being used, and their results indicated 80% of survey respondents were using ML. The most common application of SupTech is ML techniques, and more specifically NLP to create more efficient and effective supervisory processes.
Let us focus on the use of NLP, specifically on how it has been used by banking authorities for policy decision making during the COVID-19 crisis. AI has the potential to read and comprehend significant details from text. NLP, which is an important subset of AI, can be seen to have supported operations to stay updated with the compliance and regulatory policy shifts during this challenging period.
Use of NLP in Policy Making During COVID-19
The Financial Stability Board (FSB) coordinates at the international level, the work of national financial authorities and international standard-setting bodies in order to develop and promote the implementation of effective regulatory, supervisory and other financial sector policies. A recent FSB report delivered to G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors for their virtual meeting in October 2020 highlighted a number of AI use cases in national institutions.
We illustrate several use cases from their October report to show how NLP has been deployed specifically for the COVID-19 situation. These cases demonstrate AI aiding supervisory team in banks and in automating information extraction from regulatory documents using NLP.
De Nederlandsche Bank (DNB)
The DNB is developing an interactive reporting dashboard to provide insight for supervisors on COVID-19 related risks. The dashboard that is in development, enables supervisors to have different data views as needed (e.g. over time, by bank). Planned SupTech improvements include incorporating public COVID-19 information and/or analysing comment fields with text analysis.
Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS)
MAS deployed automation tools using NLP to gather international news and stay abreast of COVID-19 related developments. MAS also used NLP to analyse consumer feedback on COVID-19 issues, and monitor vulnerabilities in the different customer and product segments. MAS also collected weekly data from regulated institutions to track the take-up of credit relief measures as the pandemic unfolded. Data aggregation and transformation were automated and visualised for monitoring.
US Federal Reserve Bank Board of Governors
One of the Federal Reserve Banks in the US is currently working on a project to develop an NLP tool used to analyse public websites of supervised regulated institutions to identify information on “work with your customer” programs, in response to the COVID-19 crisis.
Bank of England
The Bank developed a Policy Response Tracker using web scraping (targeted at the English versions of each authority/government website) and NLP for the extraction of key words, topics and actions taken in each jurisdiction. The tracker pulls information daily from the official COVID-19 response pages then runs it through specific criteria (e.g. user-defined keywords, metrics and risks) to sift and present a summary of the information to supervisors.
Market Implications
Even with its enhanced efficiencies, NLP in SupTech is still an aid to decision making and cannot replace the need for human judgement. NLP in policy decision is performing clearly defined information gathering tasks with greater efficiency and speed. But NLP cannot change the quality of the data provided, so data selection and choice are still critical to effective policy making.
For authorities, the use of SupTech could improve oversight, surveillance, and analytical capabilities. These efficiency gains and possible improvement in quality arising from automation of previously manual processes could be consideration for adoption.
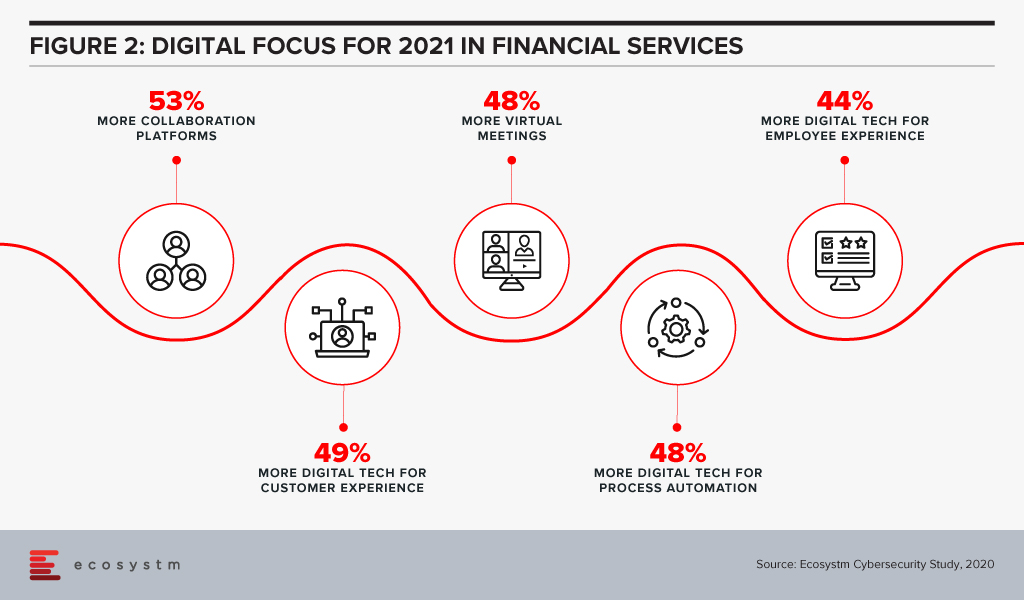
Attention will be paid in 2021 to focusing on automation of processes using AI (Figure 2).
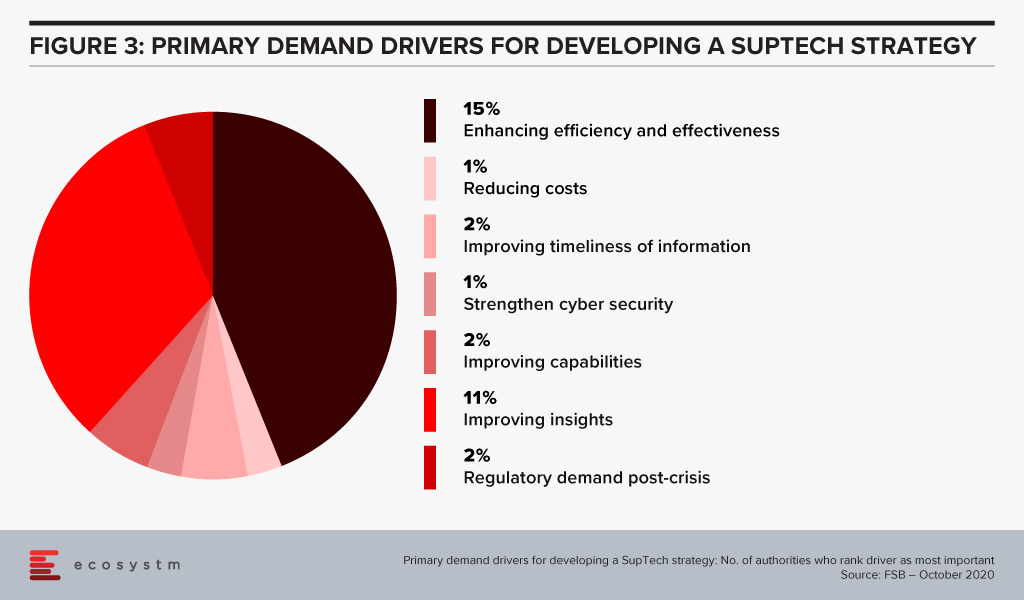
Based on a survey done by the FSB of its members (Figure 3), the majority of their respondents had a SupTech innovation or data strategy in place, with the use of such strategies growing significantly since 2016.
Summary
For more mainstream adoption, data standards and use of effective governance frameworks will be important. As seen from the FSB survey, SupTech applications are now used in reporting, data management and virtual assistance. But institutions still send the transaction data history in different reporting formats which results in a slower process of data analysing and data gathering. AI, using NLP, can help with this by streamlining data collection and data analytics. While time and cost savings are obvious benefits, the ability to identify key information (the proverbial needle in the haystack) can be a significant efficiency advantage.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit which will cover topics tied to creating infrastructure for a digital economy; and RegTech and SupTech policies to drive innovation and efficiencies in a co-Covid-19 world.











