Ecosystm Principal Analyst Sash Mukherjee in conversation with Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Telecommunications & Media, Shamir Amanullah. In this session, they discuss the state of the telecom market in Southeast Asia; and the impact of COVID-19 and the growth of the Digital Economy on the market.
Podcast: Play in new window | Download (6.5MB)
Subscribe Spotify | Amazon Music | JioSaavn | Podchaser | RSS | More
Organisations are on a fast track to digitalisation. The Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal study finds that 60% of organisations anticipate increased use of digital technologies for process automation, even after the COVID-19 restrictions are lifted. One of the key challenges that these organisations will face is the lack of internal digital skills – especially in emerging technologies. One of the success metrics of any technology adoption is employee uptake. Without the necessary skills or understanding of the benefits of emerging technology, employees will largely shy away from digital offerings, even the ones that will make their work more efficient and their lives easier.
Organisations are realising the value of making their workforce future ready.
DBS Instilling Company-Wide Digital Culture
Far-sighted companies are collaborating with technology vendors and professional training providers to promote tech awareness and education to futureproof their workforce. DBS Bank in Singapore has collaborated with AWS to train and upskill 3,000 employees – including the leadership team – with AI and machine learning skills through gamification in a DBS x AWS DeepRacer League.
The AWS DeepRacer Leagues have been previously organised in several parts of the world, but the DBS x AWS DeepRacer will be the first to be organised at this scale. The league will enable DBS employees to get their hands-on AI and machine learning tutorials online. They will then have the opportunity to test out their new skills in programming a 3D racing simulator and iteratively fine-tune their models and compete with each other. The learning program is entirely cloud-based and aims to ingrain digital skills in the workforce.
DBS has won several accolades for their digital transformation and innovation initiatives, and they continue to experiment with emerging technologies. In 2019, DBS digitalised and simplified end-to-end credit processing, setting the foundation for advanced credit risk management using data analytics and machine learning. They have also deployed an AI-powered engine for self-service digital options to its retail banking customers. Taking their employees along with them on this journey is a wise move.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Ravi Bhogaraju says, “With the increasing use of automation, AI and machine learning, the nature of work and businesses is transforming rapidly. This is creating opportunities for processes to be automated and increasing the use of AI and Deep Learning into the business processes of the organisation. Industry value chains are transforming – AI and machine learning is adding automation, analytics and predictive intelligence to the portfolio. The recent news of DBS and AWS partnering to upskill the bank’s workforce underscores the value of creating a future ready workforce.”
“Such upskilling efforts add industry-specific context to make them more effective. BCG refers to this as ‘Human + AI’. A recent study from BCG and MIT shows that 18% of companies in the world that are pioneering AI are making money with it. Those companies focus 80% of their AI initiatives on effectiveness and growth, taking better decisions – not replacing humans with AI to save costs.”
Government Focus on Digital Skills Upgrade
This week, Singapore also saw another initiative to bridge digital skills gaps – this time from the public sector. In 2018, the Government launched its Smart Nation Scholarship program to attract and nurture talent, and later involve them in various departments to drive Singapore’s Smart Nation initiatives. The most recent Smart Nation Scholarship program 2020 attracted 723 applicants (17% more than the previous year). This is a slightly different approach, aimed at attracting digital native employees and mentoring them for digital leadership. After completing their studies, the 15 scholarship recipients are set to join public sector agencies such as Cyber Security Agency of Singapore (CSA), Government Technology Agency (GovTech), and Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA), to give the younger generation an opportunity to co-create the country’s Smart Nation vision.
Bhagaraju says, “Both private and government institutions are working to enhance workforce skills, improve marketability and making the workforce future ready. Industry 4.0 and the digital revolution have created the need to address the skill gaps that have arisen. Government programs such as the Skills Future program in Singapore, Malaysia’s HRD upskilling program, and the EU-28 European Digital initiative are all making a sustained effort to promote lifelong learning and acquisition/upgrading of skills for their respective citizens with quite successful results, that will have long-term impacts.”

As the search for a COVID-19 vaccine intensifies, there is a global focus on the Life Sciences industry. The industry has been hit hard this year – having to deliver overtime through a disrupted supply chain, unexpected demand spikes, and reduction of revenues from their regular streams. Life sciences organisations are already challenged by the breadth of their focus – across R&D and clinical discovery; Manufacturing & Distribution; and Sales & Marketing. Increasingly, many pharmaceutical and medtech organisations choose to outsource some of these functions, which brings to fore the need for a robust compliance framework. In the Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal Study, two-thirds of life sciences organisations mention that they have either been forced to start, accelerate or refocus their Digital Transformation initiatives – the remaining one-third have put their Digital Transformation on hold. The industry is clearly at an inflection point.
Challenges of the Life Sciences Industry
Continued Focus on R&D. Life sciences companies operate in an extremely competitive global market where they have to work on new products against a backdrop of competition from generics and a global concern over rising healthcare expenditure. Apart from regulatory challenges, they also face immense competition from local manufacturers as they enter each new market.
Re-thinking their Distribution Strategy. Sales and distribution for many pharma and medtech organisations have been traditional – using agents, distributors, clinicians, and healthcare providers. But now they need to change their go-to-market strategies, target patients and consumers directly and package their product offerings into value-added services. This will require them to incorporate customer experience enhancers in their R&D, going beyond drug discovery and product innovation.
Tracking Global Regulations. Governments across the world are trying to manage their healthcare budgets. They are also more focused on chronic disease management. The focus has shifted to value-based medicine in general, but pharma and medtech products are being increasingly held accountable by health outcomes. Governments are increasingly implementing drug reforms around what clinicians can prescribe. Global Life Sciences organisations have to constantly monitor the regulations in the multiple countries where they operate and sell. They are also accountable for their entire supply chain, especially ensuring a high product quality and fraud prevention.
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for Life Sciences organisations, focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). They appear to be investing in emerging technology especially in their R&D and clinical discovery and Manufacturing functions.
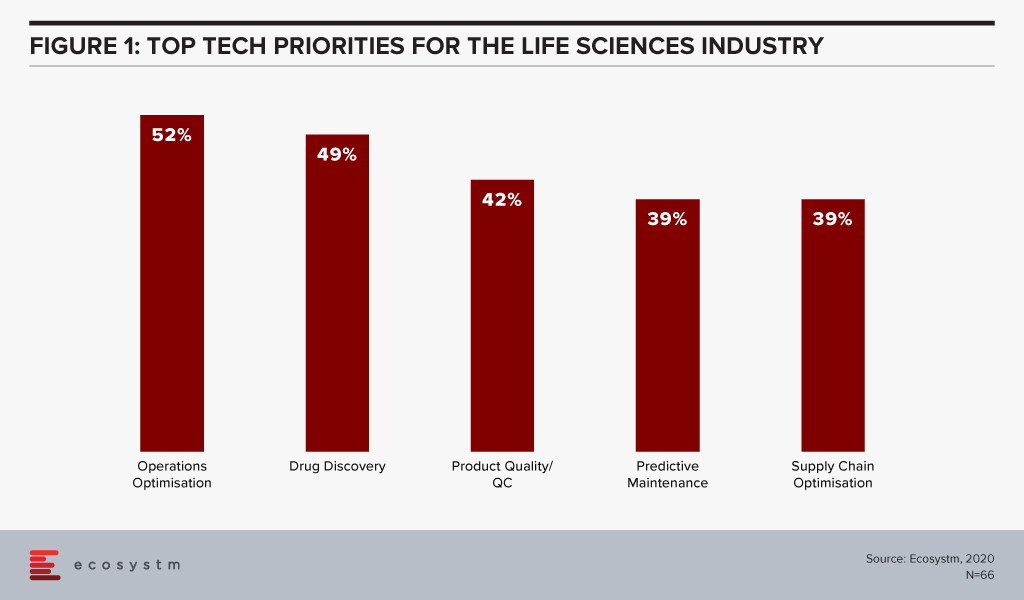
Technology as an Enabler of Life Sciences Transformation
Discovery and Development
With the evolution of technology, Life Sciences organisations are able to automate much of the mundane tasks around drug discovery and apply AI and machine learning to transform their drug discovery and development process. They are increasingly leveraging their ecosystem of smaller pharma and medtech companies, research laboratories, academic institutions, and technology providers to make the process more time and cost efficient.
Using an AI algorithm, the researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have discovered an antibiotic compound that can kill many species of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. MIT’s algorithm screens millions of chemical compounds and chooses the antibiotics which have the potential to eliminate bacteria resistant to existing drugs. Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering is manufacturing 3D printed organ-on-a-chip to give insights on cell, tissue, and organ biology to help the pharma sector with drug development, disease modelling and finally in the development of personalised medicine.
Life Sciences are also engaging more with technology partners – whether emerging start-ups or established players. Pfizer and Saama are working together on AI clinical data mining. The companies are developing and deploying an AI-based analytical tool where Pfizer provides clinical data and domain knowledge to train models on the Saama Life Science Analytics Cloud (LSAC). Saama was identified as a partner at a hackathon. Sanofi and Google have established a new virtual Innovation Lab to develop scientific and commercial solutions, using multiple Google capabilities from cloud computing to AI.
Tech providers also keep evolving their capabilities in the Life Sciences industry for more efficient drug discovery and better treatment protocols. Microsoft’s Project Hanover uses machine learning to develop a personalised drug protocol to manage acute myeloid leukaemia. Similarly, Apple’s ResearchKit – an open-source framework is meant to help researchers and developers create iOS-based applications in the field of medical research.
Manufacturing and Logistics
The industry also faces the challenges faced by any Manufacturing organisation and has the need to deploy manufacturing analytics, and advanced supply chain technology for better process and optimisation and agility. There is also the need for complete visibility over their supply chain and inventory for traceability, safety, and fraud prevention. Emerging technologies such as Blockchain will become increasingly relevant for real-time track and trace capability.
The MediLedger Network was established as an open network to the entire pharma supply chain. The project brings a consortium of some of the world’s largest pharmaceutical companies, and logistics providers to improve drug supply chain management.
Since the data on the distributed ledger is encrypted, it creates a secure system without any vulnerabilities. This eliminates counterfeit products and ultimately ensures the quality of the pharma products and promotes increased patient safety. To foster security and improve the supply chain, the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) successfully completed a pilot with a group including IBM, KPMG, Merck and Walmart to support U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) to trace vaccines and prescription medicines throughout the country.
Diagnostics and Personalised Healthcare
As more devices (consumer and enterprise) and applications enter the market, people will take ownership and interest in their own health outcomes. This is seeing a continued growth in online communities and comparison sites (on physicians, hospitals, and pharmaceutical products). Increasingly, insurance providers will use data from wearable devices for a more personalised approach; promoting and rewarding good health practices.
Beyond the use of wearables and health and wellness apps, we will also see an exponential increase of home-based healthcare products and services – whether for primary care and chronic disease management, or long-term and palliative care. As patients become more engaged with their care, the life sciences industry is beginning to serve them through personalised approach, medicines, right diagnosis and through advanced medical devices and products.
An online tool developed by the University of Virginia Health Systems helps identify patients that have a high risk of getting a stroke and helps them reduce that risk. This tool calculates the patient’s probability of suffering a stroke by measuring the severity of their metabolic syndrome – taking into account a number of conditions that include high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels and excess body fat. Life Sciences organisations are increasingly having to invest in customer-focused solutions such as these.
Wearables with special smart software to monitor health parameters, gauge drug compatibility and monitor complications are being implemented by Life Sciences organisations. The US FDA approved a pill called Abilify MyCite fitted with a tiny ingestible sensor that communicates with a patch worn by the patient to transmit data on a smartphone. Medtech companies continue to develop FDA approved health devices that can monitor chronic conditions. Smart continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and insulin pens send blood glucose level data to smartphone applications allowing the wearer to easily check their information and detect trends.
Technologies such as AR/VR are also enabling Life Sciences companies with their diagnostics. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals has created an AR/VR app called “In My Eyes” to better diagnose vision impairment in patients.
What is interesting about these personalised products is that not only do they improve clinical outcomes, they also give Life Sciences companies access to rich data that can be used for further product development and improvement.
The Life Sciences industry will continue to operate in an unpredictable and competitive market. This is evident by the several mergers and acquisitions that we witness in the industry. As they continue to use cutting-edge technology for their R&D practices, they will leverage technology to transform other functions as well.

We continue to receive responses from the tech buyer community on the impact of COVID-19 on Digital Transformation initiatives, and the early business and technology measures that were implemented to combat the crisis. As the months go by, it is becoming apparent that organisations have implemented the early measures and are now looking ahead to their journey to recovery.
IT Teams realised that even if they had the right technology solutions, they were unprepared for the scale or capacity to extend these technology offerings to handle the sudden and enormous changes required to manage the crisis. Their cloud business applications, cybersecurity and collaboration solutions were simply not sufficient to meet the needs of the remote workforce. As organisations become more conscious of business continuity planning (BCP) for future eventualities, they will boost their technology capabilities, over the next 12 months.
Another area the study aims to explore is how optimistic is the business outlook, when it comes to expecting a return to normalcy. Only 3% of organisations are expecting a New Normal that is very different from where things were at the beginning of the year. About a third of organisations are expecting a return to normalcy by the end of the year, while the majority expect to recover by the middle of 2021. Also, some industries are more optimistic of a recovery than others. As an example, 35% of healthcare organisations expect a return to normalcy by the end of the year. This is a positive indicator, given that the industry has been in the forefront of the crisis, for nearly 6 months now.
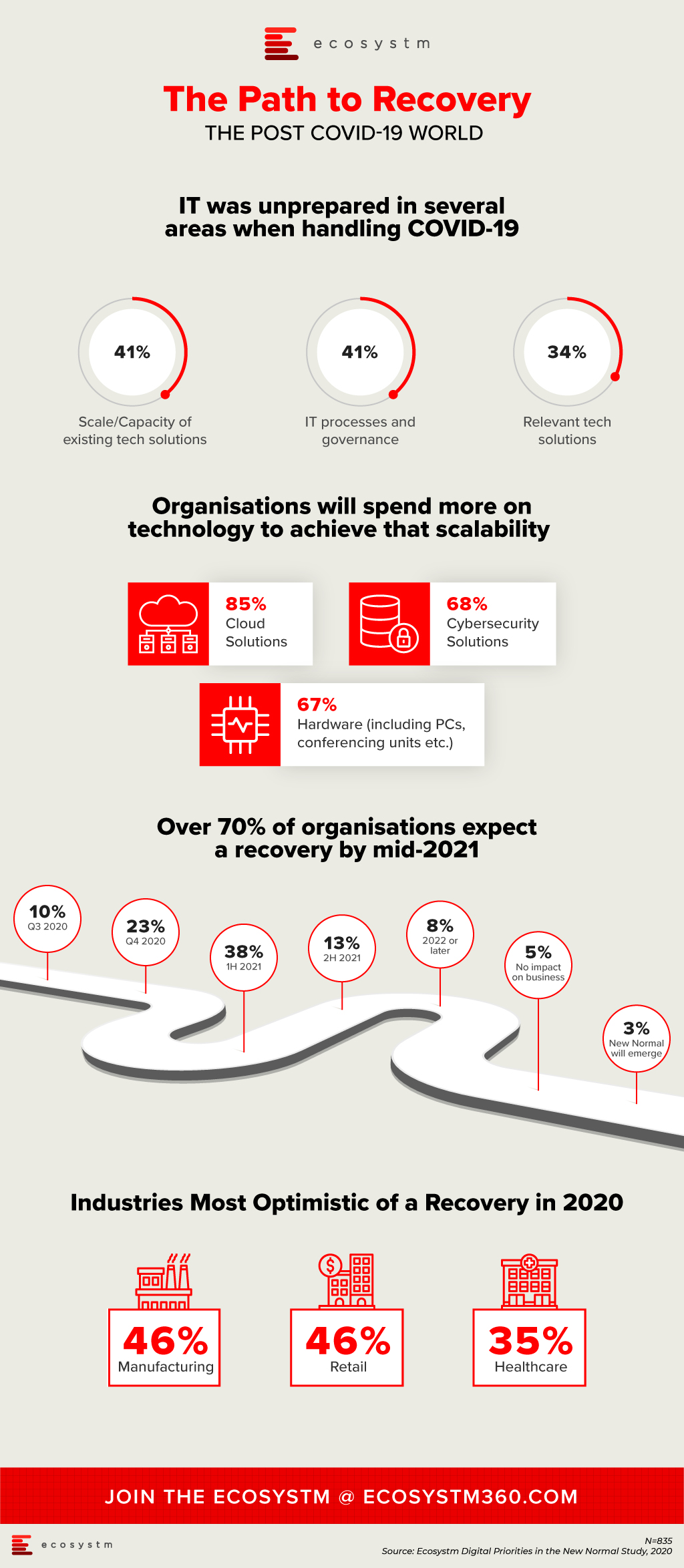
More insights on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and technology areas that will see continued investments, as organisations get into the recovery phase, can be found in the Digital Priorities in the New Normal Study.
Global supply chains were impacted early and badly by the COVID-19 pandemic. The fact that the pandemic started in China – the leader in the Manufacturing industry – meant that many enterprises globally had to re-evaluate their supply chain and logistics. This was compounded by the impact on demand – for some sectors the demand went down significantly, while in others, especially for items required to fight the crisis, there was an unexpected spike in demand. There was also the need for many manufacturers and retailers to shift to eCommerce, to directly access the market and sustain their businesses. These sudden shifts that were required of the industry, opened up the need for a global supply chain that is more integrated, agile and responsive.
Last week, global heavyweights with a stake in the global supply chain, joined a consortium to work on creating that agility. This includes PepsiCo, BMW, Shopify, DHL, and the United States Postal Service and some emerging tech companies. The alliance will actively work on solutions to embed automation and digitalisation in the logistics and supply chain systems. While this consortium was formed last year, recent events have accelerated the need to fix a global problem.
Co-Creation and Innovation
LINK is a collaborative ecosystem, co-founded by Innovation Endeavors and Sidewalk Infrastructure Partners (SIP) to bring together emerging tech start-ups, institutions and global organisations to innovate and make supply chains resilient. The tech start-ups involved include the likes of Fabric, that has large automated micro-fulfillment centres for faster deliveries, and Third Wave Automation, that has developed automated forklifts with enhanced safety measures.
LINK aims to transform global supply chains, with the use of technologies such as automation, IoT, AI, and Robotics. The solutions developed by the start-ups will be tested in real-life situations, often in large organisations with complex operations. On the other hand, the start-ups will have access to the internal systems of these large organisations to understand the data and their organisational needs.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Kaushik Ghatak says, “COVID-19 has brought the need for supply chain agility and resilience to a completely new level of criticality. Companies in the ‘New Normal’ will need higher levels of nimbleness and flexibility to be able to recover from this crisis quickly and sustain in an increasing disruptive world. Increased ability to sense and respond to disruptions will be key to success. It will require better visibility of their entire supply chain, increasing efficiencies, building necessary redundancies (in form of inventory and capacity) where they are required the most – redundancy comes at a cost – and being flexible and innovative to cater to the rapid market and supply-side changes. Rapid digitalisation to build such capabilities will be a key to success.”
“Managing such rapid changes is usually a struggle for organisations with large and complex supply chains, because of the years of past practices, systems and culture. For them Innovation is a must, but the path to innovation is difficult. The LINK collaboration model is the right step towards addressing that challenge. Collaborating with start-ups can infuse new ideas, more innovative ways of solving a problem and rapid testing of use cases in the areas of IoT, AI and automation.”
Involving Start-ups for Innovation
This initiative is a great example of how larger enterprises are looking to leverage innovations by the start-up community. The Financial Services industry has been an early beneficiary, when it stopped competing with Fintech organisations, partnering with them instead. Other industries have started to recognise the benefits of fast pivots and the role start-ups can play.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Ravi Bhogaraju says, “Bringing together companies that have complementary and unique capabilities to solve industry issues is a great way to speed up experimentation and innovation.”
However, he recognises that forming alliances such as this, comes with its own set of challenges. “One of the key things to recognise in such a construct is that the team members from different possessions bring with them their unique belief systems, organisational and country cultural constructs. Expectations on how things should work, can become quite tricky to navigate. The talent and expertise in such an environment need to be facilitated be able to deliver high quality outcomes.”
Talking about how these constructs can work successfully, delivering what started out to deliver, Bhogaraju says, “An agile team setup can help tremendously as it uses two key principles – People and Interactions over processes; as well as Working models over documentation.”
“A clear expectation setting through contracting at the beginning of the project cycle can help establish the ways of working and rules of engagement. Increased regular feedback and problem solving should continuously fine tune the ways of working. This way teams can get through the norming process at pace and scale and eventually focus on outcomes, rather than fumble over each other and/or have ego flareups.”
“The key is to get to creative problem-solving working cohesively – the intent being to challenge the status quo – stepping outside the box and using all capabilities within the team. Blending the subcultures together using agile way of working and principles, can be a fantastic way to make that happen – failing which you have the challenge of trying to somehow bring together different work products, people and preferences.”
2020 is a significant year for Singapore’s Smart Nation vision, as the Government takes stock of what they have achieved and shape their journey forward till 2025 (or 2030, in some instances). Singapore Digital (SG:D) has introduced several initiatives to empower small and medium enterprises (SMEs) with cloud-native solutions and digital payments. Cybersecurity remains a concern and the Cyber Security Agency (CSA) was established in 2015 with the express purpose of making cybersecurity a foundation for digital adoption in enterprises and citizens. Late last year the CSA and TNB Ventures announced the 2019 Cybersecurity Industry Call for Innovation in collaboration with 10 participating organisations, including the Integrated Health Information Systems (IHiS), Jurong Town Corporation (JTC), Keppel Data Centres, Ministry of Defence (MINDEF), and Ministry of Health (MOH). The aim is to build capability in areas such as:
- Cyber Readiness. To support cyber self-assessment and ensure overall cyber preparedness
- Industrial Protection. To defend Operational Technology (OT) systems against potential cyber threats
- Secure Access. To help users manage authentication and ensure safe systems access
- Smart Detection. To identify anomalies and intrusions and provide intelligent threat analysis.
CSA recently announced that 9 cybersecurity organisations have been selected to receive USD 0.70 million to build security capabilities to boost Singapore’s defences in critical industries such as Healthcare, Energy & Utilities, Smart City and Public Sector, under the Co-innovation and Development Proof-of-Concept Funding Scheme.
The organisations selected – Group-IB; Secure IC; Acronis; Amaris AI; Scantist; SecureAge; Insider security; EY Advisory; and Emerson – bring a range of cybersecurity capabilities product and service capabilities, to address critical cybersecurity challenges in analysing and predicting attacks from various sources, threat actors and cybercriminal identities.
Singapore’s Continued Focus on Cybersecurity
Singapore has witnessed various threats and breaches at industrial and Government level. Ecosystm Principal Advisor Andrew Milroy says, “The Singapore Government faces an increasing risk for malicious cyber activity. The SingHealth breach of 2018 highlighted the importance of up-to-date cybersecurity within Singapore government agencies. Of particular concern is the growing threat from nation state actors – this is particularly difficult to guard against. These advanced and persistent threats are common and often difficult to detect.”
“Of particular importance is taking a zero-trust approach to cybersecurity – once someone gets into your network, their access to resources must be restricted. Tight control of privilege is also often overlooked so Privileged Access Management (PAM) is critical. CSA is working with these 9 local cybersecurity companies to provide ‘best-of-breed’ customised cybersecurity solutions that will strengthen the cybersecurity posture of government agencies and minimise operational, reputational and legal risk.”
In October last year, CSA announced it’s Operational Technology (OT) masterplan to secure systems in the OT environment, develop OT cybersecurity training programs, strengthen OT policies and mitigate emerging OT cyber threats. One of the key challenges that organisations face in implementing cybersecurity measures is the lack of cyber skills. CSA’s Cybersecurity Career Mentoring Programme provides career guidance to young aspiring professionals and tertiary students who are keen to pursue their career in cybersecurity. In June CSA partnered with SCS to organise the program.
Through such programs and initiatives, Singapore aims to strengthen its cyber resilience and make cyber capability a foundation for its Smart Nation vision.

As organisations come to terms with the “new normal”, technology companies are presenting unique offerings to help them tide over the situation and lead them towards economic and social recovery. These companies are also leading from the front and demonstrating how to transform with agility and pace – evolving their business and delivery models.
Organisations are dependent on digital technologies more than ever before. In 2020, we have already seen unprecedented and rapid adoption of technologies such as audio and video conferencing, collaboration tools to engage with employees and clients, contactless services, and AI/automation. This will have a wider impact on the technology industry, community, and redefining the workplace of the future.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Tim Sheedy hosted a virtual roundtable with business leaders from some of the world’s largest technology service providers to discuss how they managed the challenges during the pandemic; and the measures they implemented to support not only their business operations and working environment, but also to help their customers negotiate these difficult times.
The Role of Technology During the COVID-19 Crisis
When the COVID-19 crisis hit, IT teams found themselves largely unprepared. Ecosystm research finds that only 9% of organisations considered their IT fully prepared for the changes that had to be implemented (Figure 1). More than a third did not have the right technology solutions and 41% were unprepared for the scale of the changes required and the capacity to extend the existing technology to meet client and employee needs. 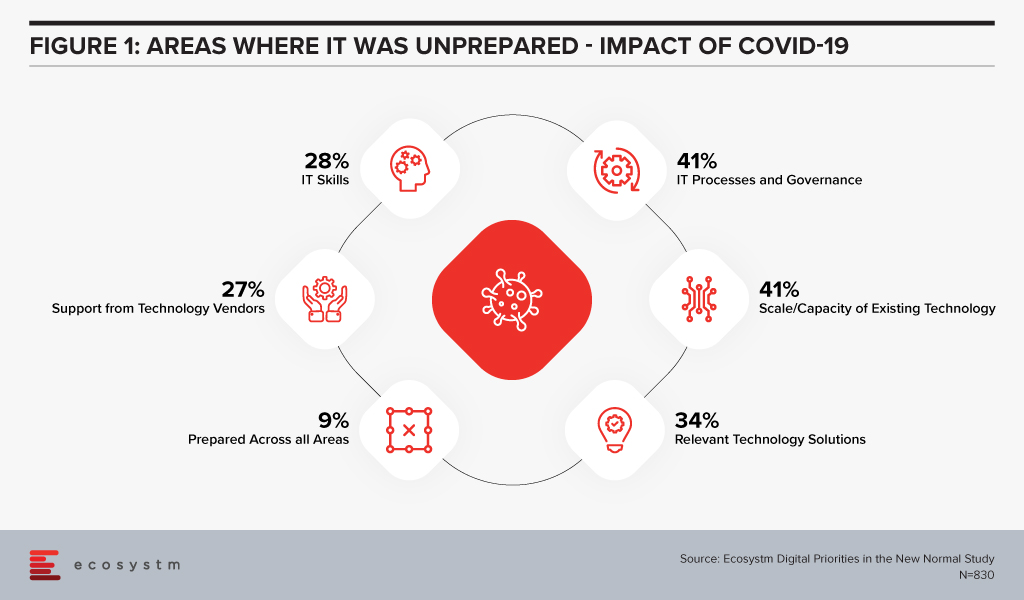
While 27% of organisations felt that they needed more support from their IT provider, further questioning reveals that only 4% switched technology providers for better support during these difficult times. Organisations are looking to their technology partners for guidance, as they negotiate the new normal.
Here are some of the discussion points that emerged in the conversation with the technology providers.
Business Continuity Planning is Still Evolving
One of the early impacts on businesses was due to their dependence on outsourced services and offshore models. Several concerns emerged – how could their provider continue to operate offsite; would they be able to access the network remotely; how should fully remote teams be managed and so on. In addition to this, there were other challenges such as supply chain disruptions and a sudden change in business. Even technology providers felt that they were navigating uncharted territory.
“Remote project delivery is not new, it’s been going on for a few years; but I think that there’s been a lot of non-believers out there. This experience has moved a lot of those non-believers to the believer category. A lot of our delivery can be done from home – think of the savings of time and money that can be realised through this.” – Andrew Campbell, Partner Asia Pacific for Talent and Transformation, IBM
Moreover, the rising workload and client expectation has led businesses to move towards exploring automation and AI.
“The thing that is changing now is, when we approach a new opportunity or an existing customer with a new requirement, we look at using automation. Typically, when you go in to design a solution you always think of the human aspect. We’re working very hard to move our thinking to automation first and then supplementing it with the human side as a backup.” – Michael Horton, Executive VP, ANZ, HCL Technologies
Data has become paramount in this time of crisis. The right use of data is helping organisations fulfil customer requirements, enhance their experience, and optimise services and products.
“Those organisations that have a good understanding of the data within their business, and how that data can be used to understand the impact on their business, are starting to have much better clarity on future requirements.” – Peter Lawther, Oceania Regional Technology Officer, Fujitsu
Organisations should take the learnings from managing this situation to keep evolving their business continuity plans – keeping in mind individual business needs and growth and business strategies.
Having the Right Infrastructure Means Employees are Productive
The lockdown and social distancing measures forced organisations to focus on the infrastructure that can support their remote and hybrid work environment.
“Before the pandemic around 20-30% of our staff logged on to a VPN, but with remote working, all of a sudden, we were at 90%.” – Lawther
The adoption of digital tools and online infrastructure led businesses to re-think how they were delivering their services. While some organisations had the tools, governance and the protocols in place, there is still a long way to go for organisations to solve their infrastructure and networking challenges.
“It gets down to the quality of the equipment that the staff use – which ranges from decent laptops, phones, and network connections. If you don’t have that now, people cannot work effectively.” – Horton
Several of these organisations, focused on ergonomics as well, when evaluating their employees’ infrastructural needs when working from home. This extra focus on infrastructural needs – with the employees firmly on their mind – ensured that there was minimal impact on delivery.
Caring for Your People is More Important than Ever
The pandemic has changed the way people work, socialise, and interact. While this appears to have become the new norm, adjusting to it can create emotional stress. Simultaneously, as organisations focus on survival and recovery, workloads have increased. Employees are working extended hours, without taking adequate hours. There is an immediate need to involve organisations’ HR practices in evaluating the emotional well-being of employees and finding better ways to engage with remote staff, to reduce stress.
“A key aspect of handling the crisis has been empathy, transparency and engagement with employees. In a business environment, we have all sorts of teams, cultures, clients, and so on. The common thread in this model is that everyone’s just become a lot friendlier, more empathic, more transparent.” – Sumit Nurpuri, COO, SE Asia Hong Kong and Taiwan, Capgemini
Organisations will have to be innovative in the way they manage these people challenges. For example, a common problem that has emerged is employees attending meetings, with interruptions from family, especially children.
“One of the things that we did as a part of our team meetings is that we assigned tasks to children at the beginning of the call and in the last few minutes, the children presented back to the teams on what they’ve been up to. It was a mechanism for us to make sure that we were involving our staff and understanding their current situation – and trying to make it as easy for them to work, as possible.” – Lawther
Taking the Opportunity to Drive Positive Outcomes
The other aspect businesses are trying to overcome is meeting the rising expectations of clients. This has led them to focus on skills training, mostly delivered through e-learning platforms. Organisations find that this has translated into increased employee performance and a future-ready workforce.
The crisis disrupted economies and societies across the globe, with business and industry coming to a standstill in most countries. Unexpected business benefits emerged from the necessity to comply with country regulations. By and large, employees have been more productive. Also, many organisations re-evaluated their commercial property requirements and many were able to reduce expenses on office rentals (for many this will not be immediate, but there is a future potentiality). Similarly, there were other areas where businesses saw reduced expenses – operational costs such as equipment maintenance and travel expenses.
“When you start global projects and global implementations, you typically do some kind of global design work and maybe fly in people from all over the world, typically to a centralised location. This has changed to virtual meetings and collaborative interactions on online global design. The amount of time and money that was saved – that would typically be spent on people traveling to manage these global design workshops – was great” – Campbell
Most organisations, across industries, will have to make considerable changes to their IT environment. The Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal study finds that 70% expect considerable to significant changes to their IT environment, going forward. Technology providers will remain a significant partner in organisations’ journey to transformation, recovery and success.

We are in the midst of an economic and social crisis. COVID-19 will have far-reaching effects on organisations and how they do business. It is expected to drive more investments in Fintech, especially in digital payments, as more organisations and consumers adopt eCommerce. Countries will also have to re-think the ways they trade with other countries, as travel restrictions continue. This is expected to boost the Fintech industry and July was witness to how Fintech organisations, financial institutions and governments are gearing up to leverage Fintech in their path to economic and social recovery.
Financial Industry Seeing More Open Banking Initiatives
The banking industry is fast moving towards collaboration and openness. July saw several initiatives that take the industry closer to open banking.
Late last year, South Korea piloted an open banking system with participation from local banks and lenders. The Financial Services Commission (FSC), South Korea’s top financial regulator reported in July that the initiative had participation from 72 companies including commercial banks and Fintech firms with 20 million subscribers using the open banking services.
Australia introduced an open banking initiative, monitored by the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC). From July, Australia’s banking customers can share their financial and banking data with accredited businesses under Consumer Data Right Act to access a better suite of financial applications.
There is global expansion as well. Railsbank, a global open banking platform with a presence in Southeast Asia introduced their services in the US market. The company will offer Banking-as-a Service, Cards-as-a Service and Credit Card-as-a-Service in the US market. Khaleeji Commercial Bank (KHCB), an Islamic bank in Bahrain, launched their open banking service enabling a customer to link their bank accounts with other banks and manage through the ‘Khaleeji 360’ platform. The portal allows clients to view all their bank accounts, automate operations and conduct banking through a unified platform.
Financial Institutions Increasing Partnerships with Fintech
Financial institutions no longer look at Fintech as competition. They appreciate that customers are at the centre of their entire operation – and Fintech services can and will provide them with the solutions they need. As financial institutions re-think their transformation journeys and face increasingly stringent regulations, they no longer have the option of ignoring Fintechs.
American Express, Visa, Mastercard and Discover came together to roll out a global standard. The big four’s advanced digital checkout solution Click to Pay is an online checkout system based on EMV Secure Remote Commerce (SRC) to make online payments across websites, mobile applications and connected devices, frictionless.
With an aim to unify payment solutions, a group of 16 major European banks launched the European Payment Initiative (EPI) to create a unified pan-European payment solution leveraging Instant Payments/SEPA Instant Credit Transfer (SCT Inst), including a card, e-wallet and P2P payments.
We also saw financial institutions strengthen their cross-border payment services in July. Deutsche Bank partnered with Airwallex to offer virtual account collections and API-enabled foreign exchange services in Japan and Hong Kong. The service will enable merchants and traders to transact through virtual accounts and APIs without opening bank accounts in foreign markets. Mastercard and Bank of China partnered to enhance cross-border business payments into China. This will enable global businesses to send payments to China while accessing real-time exchange rates, reduce the need for unnecessary documentation between merchants, and reduce transaction hassles and costs.
Fintechs Facilitating Cross-border Trade
Seamless cross-border financial transactions will be key to economic recovery, whether easy remittance or the ability to reach a larger market and be able to trade beyond borders.
July saw the formalisation of the Digital Economy Partnership Agreement (DEPA) between New Zealand, Chile and Singapore, to facilitate end-to-end digital trade, which includes establishing digital identities, paperless trade and the development of Fintech solutions to support it. The initiative also intends to allow cross-border data flow and give access to necessary government data to small and medium enterprises (SMEs) enabling them to be digital-ready to explore newer markets.
Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) signed an MoU with Jiaozi Fintech Dreamworks based in China opening new opportunities for innovation and trade. The agreement will enable Fintech companies based in both cities to access each other’s markets. Primarily established to facilitate the ‘Belt and Road’ initiative, it is a critical component of the DIFC’s 2024 strategy to strengthen relationships with the international financial community and increase access to the South-South corridor. Over the last few years, DIFC has been associated with over 200 Fintech organisations, and last month invested in four Fintech startups through their accelerator program. The agreement with Jiaozi will look at collaboration opportunities in Blockchain, AI and Cloud and will facilitate cross-border workshops and training programs.
Continuing Interests in Emerging Economies
Fintechs have been a means to bring about financial inclusion and are increasingly being used to target the unbanked and underbanked. Emerging economies continue to be attractive for Fintech organisations and global financial institutions.
With much of Malaysia’s economy dependent on foreign workers, Instapay, regulated by the Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM), announced a collaboration with Mastercard, to provide e-wallet accounts to the migrant workers. The widespread use of e-wallets by the migrant worker community will bring benefits to both workers, as well as their employers. Interestingly, Fintech providers in emerging economies are also looking to expand into other emerging markets. Malaysia’s GHL Group received approval from Philippines Securities and Exchange Commission to operate a lending business through their new unit, GHL Philippines Financing Services. GHL has been diversifying its business and has been operating its lending business in Malaysia and Thailand since 2019.
Crown Agent Bank, a wholesale foreign exchange and cross-border payment services based in the UK, partnered with South Africa’s biometric-based payment company, Paycode. Together the companies are aiming to reach 100 million unbanked customers where Crown Agents Bank will use their FX and payment services to bolster Paycode’s product offering and support financial inclusion across Sub-Saharan Africa.
India and Indonesia in the Asia Pacific continue to be popular markets because of the huge proportion of the unbanked population. Rapyd, a UK based global B2B Fintech-as-as-service provider partnered with major Indian e-payment providers – including Paytm, PhonePe, PayU, Citibank, DBS Bank, HDFC Bank, BharatPay, and Unimoni to launch an all-in-one payments solution that spans credit and debit cards, UPI, wallets, and cash. New registrations for digital banking in Indonesia are on the rise and Fintech startup Akulaku is capitalising on the potential digital banking overhaul to offer affordable and comprehensive financial services to consumers.
Fintechs benefiting other industries
The Fintech revolution has shown the path to several other industries – Healthcare and Agriculture are some of the industries that are hoping to benefit from Fintech organisations and their innovations. The MoU between Alibaba Cloud, Pfizer and Singapore’s Fintech Academy announced earlier in July, promises to give early and necessary guidance to Healthtech start-ups, and shows the deep connection between Healthtech and Fintech. In the Philippines, in an effort to improve financial services for farmers, AgriNurture acquired Fintech firm Pay8. By leveraging Pay8 e-wallet services, farmers will be able to access online payment services. This will enable the largely unbanked farmer community to become an active part of the economy.
The technology that these industries are looking to benefit from is Blockchain. South Korea brought Blockchain to their healthcare industry for better data management and storage. The 3 major telecommunications providers in the country – KT, SK Telecom and mobile carrier LG U+ – have also collaborated with KB Insurance to launch the blockchain-based mobile notification service (MNS) by matching customer data to their mobile subscription information. Oxfam Ireland – a charity organisation based in Ireland, received a sum of USD 1.18 million from the European Commission for a Blockchain-based pilot. The company is working on a project -The UnBlocked Cash – to help disaster-affected communities receive cash-based entitlements with more efficiency and traceability.
Fintech will continue to be a cornerstone of economic and social recovery in the future, and the financial industry will see more collaborations between Fintech organisations, financial institutions and governments. Other industries will continue to take learnings from Fintech.

Agriculture is significant to New Zealand’s economy and the Government aims to create more efficient land usage, better environmental outcomes, and to drive sustainability for food and supply chain across domestic and international markets.
In an effort to grow the agritech sector into an even stronger economic contributor, increase agritech exports and advance sustainable production in New Zealand and globally, the Government of New Zealand has committed to spend USD 7.6 million on the implementation of an Agritech Industry Transformation Plan as part of a strategy for the food and fibre industry. The plan is the culmination of views and insights representing a cross-section of more than 130 members of New Zealand’s agritech ecosystem – the Government, industry, and the Māori and wider community – providing their collective vision to focus attention on the sector for a competitive edge.
Roadmap to Accelerate New Zealand’s Agritech
To further boost the innovation in agritech and upscale the Sustainable Food & Fibre Futures (SFF Futures), an additional USD 56 million has been earmarked for smaller grassroots community projects to large-scale industry development. This will support the Government’s Fit for a better world Roadmap – a 10-year roadmap for the primary industry; and add value across the agriculture, horticulture, fisheries and marine, and forestry sectors.
The Roadmap includes objectives such as:
- Adding USD 29 billion in export earnings over the next decade (2020 to 2030) through a focus on creating value
- Reducing the biogenic methane emissions to below 10% by 2030 and restoring New Zealand’s freshwater environments
- Employing 10% more New Zealanders in the food and fibres sector by 2030, and 10,000 more by 2024
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Jannat Maqbool says, “In addition to the current environment with COVID-19, a new generation of consumers across the globe is becoming considerate that they buy what is good for the world in the face of climate change, biodiversity loss and the degradation of waterways. The ability to manage and assure quality and safety from ‘farm to fork’ is now more important than ever, leveraging technology for traceability, risk management, and rapid response capability to meet consumer demands and relevant legislative requirements.”
Through this Industry Transformation Plan (ITP), the Government seeks to attract investments in New Zealand’s agritech intellectual property (IP), develop the necessary infrastructure, focus on export opportunities, address current concerns related to connectivity and data, and ensure a skilled workforce that is able to both develop and effectively leverage agritech.
Maqbool says, “The success of the plan will depend on how well relevant stakeholders engage and ongoing support from government to help create the conditions required for the sector to realise its potential.”
Key Milestones
The Government of New Zealand is working to retain competitiveness in global agriculture. Some key initiatives include:
Farm 2050 Country Partnership. New Zealand became the first country partner of Farm2050- a global agritech initiative that brings together farmers, researchers, the market and investors to collaborate effectively.
Western Growers partnership. Western Growers and New Zealand signed a partnership agreement to develop agritech. It also opened doors for New Zealand’s agritech researchers and companies working in the robotics and automation space to enter the US Market.
The Australia New Zealand Agritech Council. The Australia New Zealand Agritech Council was launched to help the countries work closely on agricultural practices and to cooperate on agritech.
New Zealand is fast becoming an example of how technology providers and food producers can collaborate on improving yields, optimising production methods and reducing waste, predicting demand, and safeguarding supply chains.











