The Education sector is currently facing immense challenges with enabling a remote learning environment and ensuring the safety of staff, employees, and students. This is on top of the usual challenges of resource optimisation, student retention, student recruitment, and so on. Moreover, today’s students are millennials and post-millennials, who are digital natives – pushing educational institutions to adopt technology to attract the right cohort and provide an education that equips the students for the workplace of the future. The industry is being driven to transform, to keep up with student expectations on delivery, access to the resource, and how they choose to communicate with their educators and peers.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Dr Alea Fairchild says, “Education administration budgets are not increasing, but the pressure for quick response and more personalised interaction for students, means that administrators need to focus on interaction as the core competency. This requires institutions to automate as much of the volume back-office activity as feasible. The challenge is that individualised course structures mean more complex billing configurations.”
Dr Fairchild, who is active in international education in Belgium, says, “Individual study paths, including Erasmus exchanges, create a need for an audit trail on transfers, exemptions and completions.”
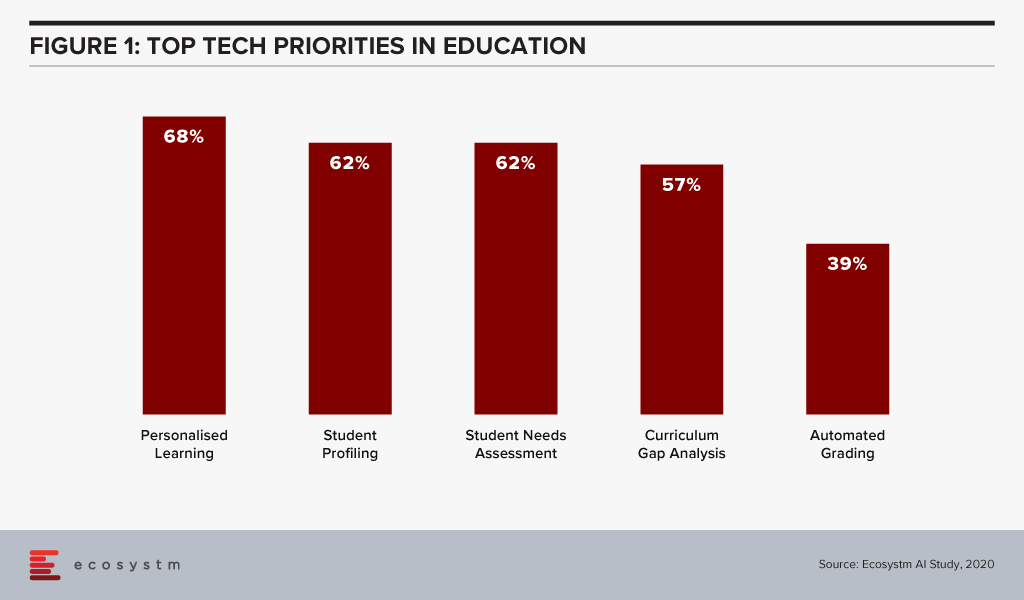
Ecosystm research finds that educational institutions are focused on adopting emerging technologies mainly to improve student services (Figure 1). The processes are being automated to reduce risks, errors and turnaround times for results and application processing, while also removing repetitive tasks so administration can focus on more value-add student-facing activities.
University of Staffordshire Embraces Digital Transformation
The University of Staffordshire is a “connected university” with an emphasis on industry connections and graduate employability. At the heart of Stoke-on-Trent and a regional hub for healthcare education, the university has six schools as well as a well-known degree in computer games design.
The UK-based University has over the years built a reputation for being keen on embracing digital as a way of better management, offering better student services, and serving the larger community. In 2018, Staffordshire University announced plans to build a multi-million-pound apprenticeship hub at its Stoke-on-Trent campus supported by tech giants including Microsoft to equip students with digital skills and to deliver more than 6,500 new apprenticeships over the next decade.
Last year, the University implemented a digital assistant, called Beacon, hosted on Microsoft Azure Cloud that provides support to their students on their learning and on-campus activities, including monitoring their emotional well-being and providing recommendations on groups and societies that they might be interested in. Beacon aims to ease the life of a university student, acting as a digital coach, and to minimise drop-outs due to stress and uncertainty.
Like its peer organisations, in the wake of the pandemic, the university was able to implement a blended learning program – offering courses through digital and remote learning systems from this semester for the entire 2020-21 session.
Focusing on Transformation through Automation
The University of Staffordshire, recently implemented robotic process automation (RPA) as part of its digital transformation plan. Talking about the role of RPA in Education, Dr Fairchild says, “This is a recent trend in higher education, with other new initiatives seen at the University of Auckland and University of Melbourne. RPA as a tool is used in Education to achieve the service levels required to meet both students’ and potential students’ expectations. This includes downloading student applications, processing language waiver requests, and entering academic results. These are all rule-based, high volume applications where automation increases speed and reduces errors.”
The University is using Blue Prism Cloud to access the RPA software and has plans for a automation-led digital transformation roadmap. Dr Fairchild says, “Blue Prism is based on Java and uses a Top-Down approach. It offers a visual designer with no recorders, scripts, or any intervention. Blue Prism is based on process diagrams that utilise core programming concepts and create the operational process flows to analyse, modify and scale business capability.”
The Staffordshire Digital team initially implemented RPA in the Finance department, as it involves a lot of administrative and back-office operations such as management of finance, records, tuition fees details and more. The University’s emphasis is to free up personnel and make them focus on more productive areas. This is beneficial for both the administrative staff’s feeling of personal contribution as well as student service satisfaction levels. “Using RPA gives the opportunity to universities to revisit, redesign, and improve their existing processes in line with expectations from digital native students. For prospective students, the next wave of RPA integration is intelligent machine learning algorithms to help route emails and integrate chatbots to address questions on course selection,” says Dr Fairchild.

In this session, Ecosystm Principal Analyst, Sash Mukherjee, and Ecosystm CEO, Amit Gupta discuss the foundational shifts in industries due to socio-economical factors that have been simmering for a while and more immediately COVID-19; and the role of technology in planning ahead.
Podcast: Play in new window | Download (7.4MB)
Subscribe Spotify | Amazon Music | JioSaavn | Podchaser | RSS | More
Last week, trading on the New Zealand Exchange (NZX) was disrupted on four consecutive days as a result of a sustained cyber-attack on to push market updates to the public as their website crashed and as a precautionary measure, NZX halted the trading sessions. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Andrew Milroy says, “The recent NZX attack overwhelmed its public-facing NZX.com website and its Market Announcement Platform (MAP). This meant that investors could not see company announcements in real-time, preventing NZX from complying with regulatory requirements for continuous disclosure.”
The attacks which began on Tuesday came from overseas and made NZX struggle in recovering connectivity, over a five-day period. The cyber-attackers targeted NZX through distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks which is a common way to overwhelm the network with sheer amount of traffic until it disrupts the services.
Milroy says, “It is not clear yet clear who launched the attack, but it is likely to be either an extortion attempt by a large cyber gang or a nation state attack. The attack was a very large, persistent, and sophisticated volumetric DDoS attack. A typical response to such an attack is to increase network bandwidth. However, additional bandwidth is becoming less effective at preventing DDoS attacks. DDoS attacks are getting larger and no amount of bandwidth can address the largest attacks, some of which exceed 1Tbps. DDoS attackers are increasingly focusing on the harder to protect application layer, rather than the network layers.”
The Government Communications Security Bureau (GCSB), network provider Spark, and international bodies provided assistance to NZX to mitigate the attack. Milroy adds, “NZX has also turned to Akamai for additional DDoS protection. Akamai’s Kona Site Defender is understood to be the solution being used. The product is designed to deflect network-layer DDoS traffic and absorb application-layer DDoS traffic at the edge. Mitigation capabilities aim to protect against attacks in the cloud.”
Growing Importance of Government Advisories and Investments
In November 2019, CERT NZ warned financial organisations of several global attacks including ransomware. The attacks were reportedly from Russia-based hacking groups. In an advisory, CERT NZ suggested businesses should implement DDoS protection services, and check network ports connected to avoid vulnerabilities and not pay any ransom to cybercriminals.
Following the CERT NZ warning last year, and considering the recent cyberattacks, GCSB has issued a security advisory to all businesses in New Zealand to be cautious on cyber incidents such as DDoS and ransomware attacks. The advisory comes from the GCSB’s National Cyber Security Centre. This is particularly aimed at small businesses that might have limited cybersecurity resources. The agency has asked them to report such incidents to Cert NZ. Advice includes:
- Approaching cybersecurity services providers to immediately implement any responsive actions (warning that organisations might incur additional fees)
- Temporarily transferring online services to a cloud-based hosting service
- Avoiding the disclosure of the IP address of the origin web server, and using a firewall, if using a content delivery network
- Using a DDOS mitigation service for the duration of attacks, in case they face attacks
- Disabling functionality or removing content from vulnerable online services
As a part of the New Zealand government’s cybersecurity strategy, last year the Government announced the allocation of USD 5.38 million to focus on security over the next four years, on top of USD 6.26 million funding for CERT NZ. The attack landscape and frequency has since increased in the aftermath of COVID-19.
Milroy says, “It will become increasingly important for governments the world over to make a concerted effort to protect their critical infrastructure, data assets and especially empower their SME communities with the right cybersecurity measures and timely guidance.”

Ecosystm Principal Analyst Sash Mukherjee in conversation with Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Telecommunications & Media, Shamir Amanullah. In this session, they discuss the state of the telecom market in Southeast Asia; and the impact of COVID-19 and the growth of the Digital Economy on the market.
Podcast: Play in new window | Download (6.5MB)
Subscribe Spotify | Amazon Music | JioSaavn | Podchaser | RSS | More
Organisations are on a fast track to digitalisation. The Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal study finds that 60% of organisations anticipate increased use of digital technologies for process automation, even after the COVID-19 restrictions are lifted. One of the key challenges that these organisations will face is the lack of internal digital skills – especially in emerging technologies. One of the success metrics of any technology adoption is employee uptake. Without the necessary skills or understanding of the benefits of emerging technology, employees will largely shy away from digital offerings, even the ones that will make their work more efficient and their lives easier.
Organisations are realising the value of making their workforce future ready.
DBS Instilling Company-Wide Digital Culture
Far-sighted companies are collaborating with technology vendors and professional training providers to promote tech awareness and education to futureproof their workforce. DBS Bank in Singapore has collaborated with AWS to train and upskill 3,000 employees – including the leadership team – with AI and machine learning skills through gamification in a DBS x AWS DeepRacer League.
The AWS DeepRacer Leagues have been previously organised in several parts of the world, but the DBS x AWS DeepRacer will be the first to be organised at this scale. The league will enable DBS employees to get their hands-on AI and machine learning tutorials online. They will then have the opportunity to test out their new skills in programming a 3D racing simulator and iteratively fine-tune their models and compete with each other. The learning program is entirely cloud-based and aims to ingrain digital skills in the workforce.
DBS has won several accolades for their digital transformation and innovation initiatives, and they continue to experiment with emerging technologies. In 2019, DBS digitalised and simplified end-to-end credit processing, setting the foundation for advanced credit risk management using data analytics and machine learning. They have also deployed an AI-powered engine for self-service digital options to its retail banking customers. Taking their employees along with them on this journey is a wise move.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Ravi Bhogaraju says, “With the increasing use of automation, AI and machine learning, the nature of work and businesses is transforming rapidly. This is creating opportunities for processes to be automated and increasing the use of AI and Deep Learning into the business processes of the organisation. Industry value chains are transforming – AI and machine learning is adding automation, analytics and predictive intelligence to the portfolio. The recent news of DBS and AWS partnering to upskill the bank’s workforce underscores the value of creating a future ready workforce.”
“Such upskilling efforts add industry-specific context to make them more effective. BCG refers to this as ‘Human + AI’. A recent study from BCG and MIT shows that 18% of companies in the world that are pioneering AI are making money with it. Those companies focus 80% of their AI initiatives on effectiveness and growth, taking better decisions – not replacing humans with AI to save costs.”
Government Focus on Digital Skills Upgrade
This week, Singapore also saw another initiative to bridge digital skills gaps – this time from the public sector. In 2018, the Government launched its Smart Nation Scholarship program to attract and nurture talent, and later involve them in various departments to drive Singapore’s Smart Nation initiatives. The most recent Smart Nation Scholarship program 2020 attracted 723 applicants (17% more than the previous year). This is a slightly different approach, aimed at attracting digital native employees and mentoring them for digital leadership. After completing their studies, the 15 scholarship recipients are set to join public sector agencies such as Cyber Security Agency of Singapore (CSA), Government Technology Agency (GovTech), and Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA), to give the younger generation an opportunity to co-create the country’s Smart Nation vision.
Bhagaraju says, “Both private and government institutions are working to enhance workforce skills, improve marketability and making the workforce future ready. Industry 4.0 and the digital revolution have created the need to address the skill gaps that have arisen. Government programs such as the Skills Future program in Singapore, Malaysia’s HRD upskilling program, and the EU-28 European Digital initiative are all making a sustained effort to promote lifelong learning and acquisition/upgrading of skills for their respective citizens with quite successful results, that will have long-term impacts.”

As the search for a COVID-19 vaccine intensifies, there is a global focus on the Life Sciences industry. The industry has been hit hard this year – having to deliver overtime through a disrupted supply chain, unexpected demand spikes, and reduction of revenues from their regular streams. Life sciences organisations are already challenged by the breadth of their focus – across R&D and clinical discovery; Manufacturing & Distribution; and Sales & Marketing. Increasingly, many pharmaceutical and medtech organisations choose to outsource some of these functions, which brings to fore the need for a robust compliance framework. In the Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal Study, two-thirds of life sciences organisations mention that they have either been forced to start, accelerate or refocus their Digital Transformation initiatives – the remaining one-third have put their Digital Transformation on hold. The industry is clearly at an inflection point.
Challenges of the Life Sciences Industry
Continued Focus on R&D. Life sciences companies operate in an extremely competitive global market where they have to work on new products against a backdrop of competition from generics and a global concern over rising healthcare expenditure. Apart from regulatory challenges, they also face immense competition from local manufacturers as they enter each new market.
Re-thinking their Distribution Strategy. Sales and distribution for many pharma and medtech organisations have been traditional – using agents, distributors, clinicians, and healthcare providers. But now they need to change their go-to-market strategies, target patients and consumers directly and package their product offerings into value-added services. This will require them to incorporate customer experience enhancers in their R&D, going beyond drug discovery and product innovation.
Tracking Global Regulations. Governments across the world are trying to manage their healthcare budgets. They are also more focused on chronic disease management. The focus has shifted to value-based medicine in general, but pharma and medtech products are being increasingly held accountable by health outcomes. Governments are increasingly implementing drug reforms around what clinicians can prescribe. Global Life Sciences organisations have to constantly monitor the regulations in the multiple countries where they operate and sell. They are also accountable for their entire supply chain, especially ensuring a high product quality and fraud prevention.
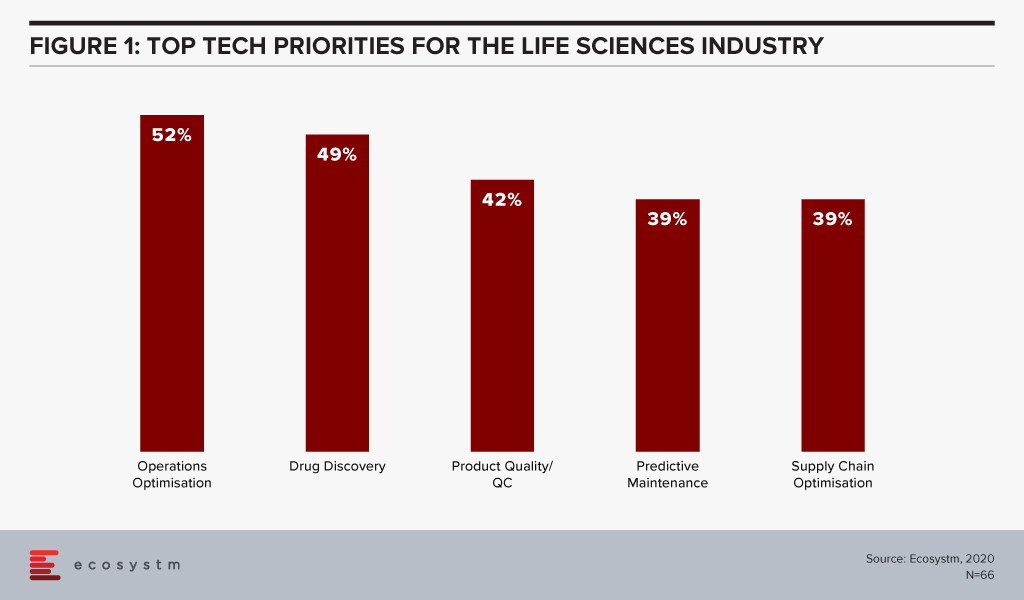
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for Life Sciences organisations, focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). They appear to be investing in emerging technology especially in their R&D and clinical discovery and Manufacturing functions.
Technology as an Enabler of Life Sciences Transformation
Discovery and Development
With the evolution of technology, Life Sciences organisations are able to automate much of the mundane tasks around drug discovery and apply AI and machine learning to transform their drug discovery and development process. They are increasingly leveraging their ecosystem of smaller pharma and medtech companies, research laboratories, academic institutions, and technology providers to make the process more time and cost efficient.
Using an AI algorithm, the researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have discovered an antibiotic compound that can kill many species of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. MIT’s algorithm screens millions of chemical compounds and chooses the antibiotics which have the potential to eliminate bacteria resistant to existing drugs. Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering is manufacturing 3D printed organ-on-a-chip to give insights on cell, tissue, and organ biology to help the pharma sector with drug development, disease modelling and finally in the development of personalised medicine.
Life Sciences are also engaging more with technology partners – whether emerging start-ups or established players. Pfizer and Saama are working together on AI clinical data mining. The companies are developing and deploying an AI-based analytical tool where Pfizer provides clinical data and domain knowledge to train models on the Saama Life Science Analytics Cloud (LSAC). Saama was identified as a partner at a hackathon. Sanofi and Google have established a new virtual Innovation Lab to develop scientific and commercial solutions, using multiple Google capabilities from cloud computing to AI.
Tech providers also keep evolving their capabilities in the Life Sciences industry for more efficient drug discovery and better treatment protocols. Microsoft’s Project Hanover uses machine learning to develop a personalised drug protocol to manage acute myeloid leukaemia. Similarly, Apple’s ResearchKit – an open-source framework is meant to help researchers and developers create iOS-based applications in the field of medical research.
Manufacturing and Logistics
The industry also faces the challenges faced by any Manufacturing organisation and has the need to deploy manufacturing analytics, and advanced supply chain technology for better process and optimisation and agility. There is also the need for complete visibility over their supply chain and inventory for traceability, safety, and fraud prevention. Emerging technologies such as Blockchain will become increasingly relevant for real-time track and trace capability.
The MediLedger Network was established as an open network to the entire pharma supply chain. The project brings a consortium of some of the world’s largest pharmaceutical companies, and logistics providers to improve drug supply chain management.
Since the data on the distributed ledger is encrypted, it creates a secure system without any vulnerabilities. This eliminates counterfeit products and ultimately ensures the quality of the pharma products and promotes increased patient safety. To foster security and improve the supply chain, the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) successfully completed a pilot with a group including IBM, KPMG, Merck and Walmart to support U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) to trace vaccines and prescription medicines throughout the country.
Diagnostics and Personalised Healthcare
As more devices (consumer and enterprise) and applications enter the market, people will take ownership and interest in their own health outcomes. This is seeing a continued growth in online communities and comparison sites (on physicians, hospitals, and pharmaceutical products). Increasingly, insurance providers will use data from wearable devices for a more personalised approach; promoting and rewarding good health practices.
Beyond the use of wearables and health and wellness apps, we will also see an exponential increase of home-based healthcare products and services – whether for primary care and chronic disease management, or long-term and palliative care. As patients become more engaged with their care, the life sciences industry is beginning to serve them through personalised approach, medicines, right diagnosis and through advanced medical devices and products.
An online tool developed by the University of Virginia Health Systems helps identify patients that have a high risk of getting a stroke and helps them reduce that risk. This tool calculates the patient’s probability of suffering a stroke by measuring the severity of their metabolic syndrome – taking into account a number of conditions that include high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels and excess body fat. Life Sciences organisations are increasingly having to invest in customer-focused solutions such as these.
Wearables with special smart software to monitor health parameters, gauge drug compatibility and monitor complications are being implemented by Life Sciences organisations. The US FDA approved a pill called Abilify MyCite fitted with a tiny ingestible sensor that communicates with a patch worn by the patient to transmit data on a smartphone. Medtech companies continue to develop FDA approved health devices that can monitor chronic conditions. Smart continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and insulin pens send blood glucose level data to smartphone applications allowing the wearer to easily check their information and detect trends.
Technologies such as AR/VR are also enabling Life Sciences companies with their diagnostics. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals has created an AR/VR app called “In My Eyes” to better diagnose vision impairment in patients.
What is interesting about these personalised products is that not only do they improve clinical outcomes, they also give Life Sciences companies access to rich data that can be used for further product development and improvement.
The Life Sciences industry will continue to operate in an unpredictable and competitive market. This is evident by the several mergers and acquisitions that we witness in the industry. As they continue to use cutting-edge technology for their R&D practices, they will leverage technology to transform other functions as well.

We continue to receive responses from the tech buyer community on the impact of COVID-19 on Digital Transformation initiatives, and the early business and technology measures that were implemented to combat the crisis. As the months go by, it is becoming apparent that organisations have implemented the early measures and are now looking ahead to their journey to recovery.
IT Teams realised that even if they had the right technology solutions, they were unprepared for the scale or capacity to extend these technology offerings to handle the sudden and enormous changes required to manage the crisis. Their cloud business applications, cybersecurity and collaboration solutions were simply not sufficient to meet the needs of the remote workforce. As organisations become more conscious of business continuity planning (BCP) for future eventualities, they will boost their technology capabilities, over the next 12 months.
Another area the study aims to explore is how optimistic is the business outlook, when it comes to expecting a return to normalcy. Only 3% of organisations are expecting a New Normal that is very different from where things were at the beginning of the year. About a third of organisations are expecting a return to normalcy by the end of the year, while the majority expect to recover by the middle of 2021. Also, some industries are more optimistic of a recovery than others. As an example, 35% of healthcare organisations expect a return to normalcy by the end of the year. This is a positive indicator, given that the industry has been in the forefront of the crisis, for nearly 6 months now.
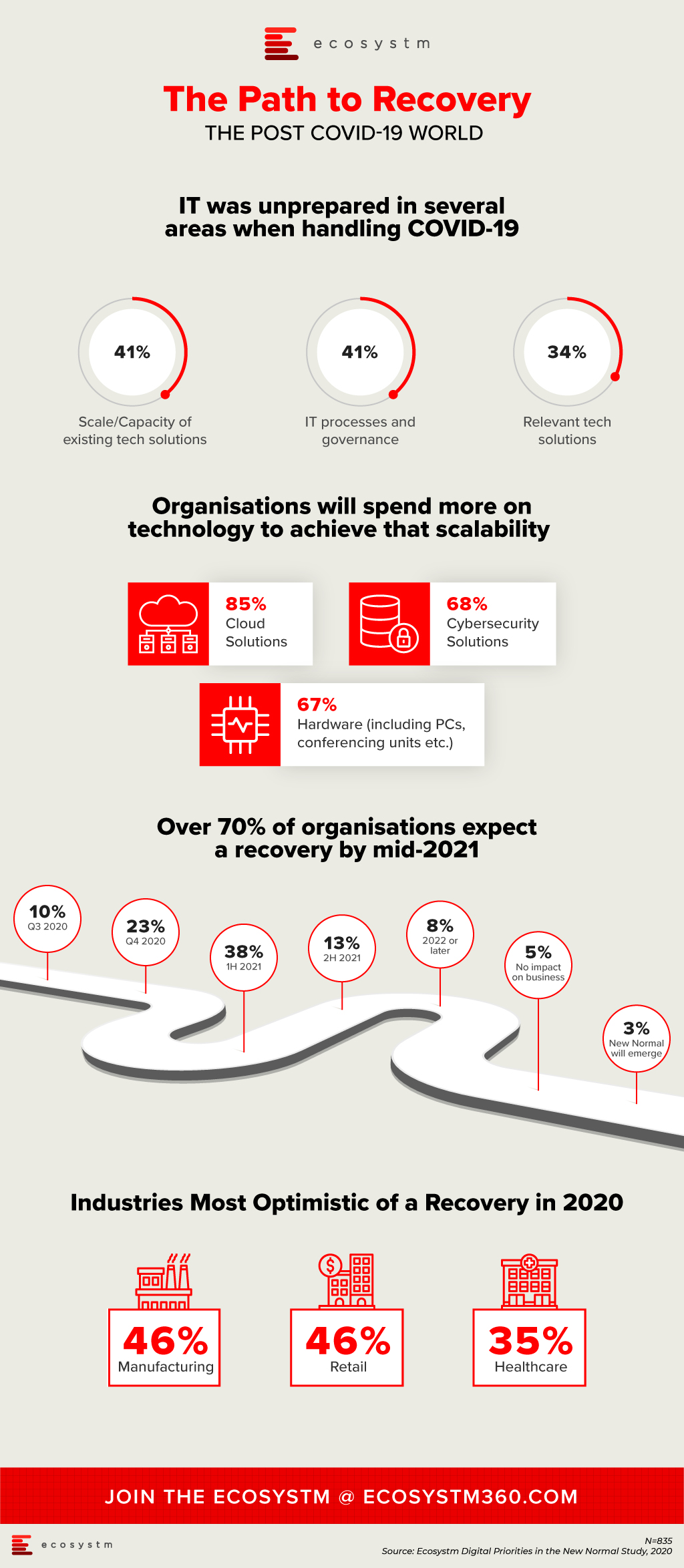
More insights on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and technology areas that will see continued investments, as organisations get into the recovery phase, can be found in the Digital Priorities in the New Normal Study.
Global supply chains were impacted early and badly by the COVID-19 pandemic. The fact that the pandemic started in China – the leader in the Manufacturing industry – meant that many enterprises globally had to re-evaluate their supply chain and logistics. This was compounded by the impact on demand – for some sectors the demand went down significantly, while in others, especially for items required to fight the crisis, there was an unexpected spike in demand. There was also the need for many manufacturers and retailers to shift to eCommerce, to directly access the market and sustain their businesses. These sudden shifts that were required of the industry, opened up the need for a global supply chain that is more integrated, agile and responsive.
Last week, global heavyweights with a stake in the global supply chain, joined a consortium to work on creating that agility. This includes PepsiCo, BMW, Shopify, DHL, and the United States Postal Service and some emerging tech companies. The alliance will actively work on solutions to embed automation and digitalisation in the logistics and supply chain systems. While this consortium was formed last year, recent events have accelerated the need to fix a global problem.
Co-Creation and Innovation
LINK is a collaborative ecosystem, co-founded by Innovation Endeavors and Sidewalk Infrastructure Partners (SIP) to bring together emerging tech start-ups, institutions and global organisations to innovate and make supply chains resilient. The tech start-ups involved include the likes of Fabric, that has large automated micro-fulfillment centres for faster deliveries, and Third Wave Automation, that has developed automated forklifts with enhanced safety measures.
LINK aims to transform global supply chains, with the use of technologies such as automation, IoT, AI, and Robotics. The solutions developed by the start-ups will be tested in real-life situations, often in large organisations with complex operations. On the other hand, the start-ups will have access to the internal systems of these large organisations to understand the data and their organisational needs.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Kaushik Ghatak says, “COVID-19 has brought the need for supply chain agility and resilience to a completely new level of criticality. Companies in the ‘New Normal’ will need higher levels of nimbleness and flexibility to be able to recover from this crisis quickly and sustain in an increasing disruptive world. Increased ability to sense and respond to disruptions will be key to success. It will require better visibility of their entire supply chain, increasing efficiencies, building necessary redundancies (in form of inventory and capacity) where they are required the most – redundancy comes at a cost – and being flexible and innovative to cater to the rapid market and supply-side changes. Rapid digitalisation to build such capabilities will be a key to success.”
“Managing such rapid changes is usually a struggle for organisations with large and complex supply chains, because of the years of past practices, systems and culture. For them Innovation is a must, but the path to innovation is difficult. The LINK collaboration model is the right step towards addressing that challenge. Collaborating with start-ups can infuse new ideas, more innovative ways of solving a problem and rapid testing of use cases in the areas of IoT, AI and automation.”
Involving Start-ups for Innovation
This initiative is a great example of how larger enterprises are looking to leverage innovations by the start-up community. The Financial Services industry has been an early beneficiary, when it stopped competing with Fintech organisations, partnering with them instead. Other industries have started to recognise the benefits of fast pivots and the role start-ups can play.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Ravi Bhogaraju says, “Bringing together companies that have complementary and unique capabilities to solve industry issues is a great way to speed up experimentation and innovation.”
However, he recognises that forming alliances such as this, comes with its own set of challenges. “One of the key things to recognise in such a construct is that the team members from different possessions bring with them their unique belief systems, organisational and country cultural constructs. Expectations on how things should work, can become quite tricky to navigate. The talent and expertise in such an environment need to be facilitated be able to deliver high quality outcomes.”
Talking about how these constructs can work successfully, delivering what started out to deliver, Bhogaraju says, “An agile team setup can help tremendously as it uses two key principles – People and Interactions over processes; as well as Working models over documentation.”
“A clear expectation setting through contracting at the beginning of the project cycle can help establish the ways of working and rules of engagement. Increased regular feedback and problem solving should continuously fine tune the ways of working. This way teams can get through the norming process at pace and scale and eventually focus on outcomes, rather than fumble over each other and/or have ego flareups.”
“The key is to get to creative problem-solving working cohesively – the intent being to challenge the status quo – stepping outside the box and using all capabilities within the team. Blending the subcultures together using agile way of working and principles, can be a fantastic way to make that happen – failing which you have the challenge of trying to somehow bring together different work products, people and preferences.”
2020 is a significant year for Singapore’s Smart Nation vision, as the Government takes stock of what they have achieved and shape their journey forward till 2025 (or 2030, in some instances). Singapore Digital (SG:D) has introduced several initiatives to empower small and medium enterprises (SMEs) with cloud-native solutions and digital payments. Cybersecurity remains a concern and the Cyber Security Agency (CSA) was established in 2015 with the express purpose of making cybersecurity a foundation for digital adoption in enterprises and citizens. Late last year the CSA and TNB Ventures announced the 2019 Cybersecurity Industry Call for Innovation in collaboration with 10 participating organisations, including the Integrated Health Information Systems (IHiS), Jurong Town Corporation (JTC), Keppel Data Centres, Ministry of Defence (MINDEF), and Ministry of Health (MOH). The aim is to build capability in areas such as:
- Cyber Readiness. To support cyber self-assessment and ensure overall cyber preparedness
- Industrial Protection. To defend Operational Technology (OT) systems against potential cyber threats
- Secure Access. To help users manage authentication and ensure safe systems access
- Smart Detection. To identify anomalies and intrusions and provide intelligent threat analysis.
CSA recently announced that 9 cybersecurity organisations have been selected to receive USD 0.70 million to build security capabilities to boost Singapore’s defences in critical industries such as Healthcare, Energy & Utilities, Smart City and Public Sector, under the Co-innovation and Development Proof-of-Concept Funding Scheme.
The organisations selected – Group-IB; Secure IC; Acronis; Amaris AI; Scantist; SecureAge; Insider security; EY Advisory; and Emerson – bring a range of cybersecurity capabilities product and service capabilities, to address critical cybersecurity challenges in analysing and predicting attacks from various sources, threat actors and cybercriminal identities.
Singapore’s Continued Focus on Cybersecurity
Singapore has witnessed various threats and breaches at industrial and Government level. Ecosystm Principal Advisor Andrew Milroy says, “The Singapore Government faces an increasing risk for malicious cyber activity. The SingHealth breach of 2018 highlighted the importance of up-to-date cybersecurity within Singapore government agencies. Of particular concern is the growing threat from nation state actors – this is particularly difficult to guard against. These advanced and persistent threats are common and often difficult to detect.”
“Of particular importance is taking a zero-trust approach to cybersecurity – once someone gets into your network, their access to resources must be restricted. Tight control of privilege is also often overlooked so Privileged Access Management (PAM) is critical. CSA is working with these 9 local cybersecurity companies to provide ‘best-of-breed’ customised cybersecurity solutions that will strengthen the cybersecurity posture of government agencies and minimise operational, reputational and legal risk.”
In October last year, CSA announced it’s Operational Technology (OT) masterplan to secure systems in the OT environment, develop OT cybersecurity training programs, strengthen OT policies and mitigate emerging OT cyber threats. One of the key challenges that organisations face in implementing cybersecurity measures is the lack of cyber skills. CSA’s Cybersecurity Career Mentoring Programme provides career guidance to young aspiring professionals and tertiary students who are keen to pursue their career in cybersecurity. In June CSA partnered with SCS to organise the program.
Through such programs and initiatives, Singapore aims to strengthen its cyber resilience and make cyber capability a foundation for its Smart Nation vision.











