Xiaomi Corporation – a Chinese electronics giant often dubbed the “Apple of China”, with specialisation in smartphones and smart devices – is now planning to focus on non-smartphone segments for growth. Last week the Beijing based company announced a planned investment of more than US$7 Billion in the areas of 5G, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Artificial Internet of Things (AIoT). The announcement builds on last year’s pledge to invest US$1.5 billion over five years in an “All in AIoT” (AI+IoT) strategy.
Setting the scene for AI, IoT and 5G
Facing stiff competition from the likes of Huawei (with 42% of China’s smartphone market share in Q3 2019), Xiaomi is aiming to sustain business growth in the face of a challenging smartphone market. Xiaomi Corp is well versed with 5G and not a newcomer in the AI space. They already make 5G devices, and AI has been embedded in Xiaomi’s technology ecosystem such as messaging, instore applications, smartphones, laptops, TVs, routers, speakers, and other smart devices. In fact, Xiaomi Corp claims to have the world’s largest consumer IoT platform with more than 213.2 million smart devices (excluding smartphones and laptops) connected to its IoT platform.
Commenting on the Xiaomi’s competitiveness amongst Chinese smartphone makers and market potential for AI, IoT and 5G globally, Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Tim Sheedy said “Xiaomi has had some recent successes as a smart device maker, with its robot vacuums and other devices quickly earning positive reviews and gaining market recognition. Xiaomi has been able to surpass many traditional players which demonstrates their capabilities of competing in the IoT/smart devices category.”
On the 5G capability aspect of Xiaomi Corp, Sheedy said, “it is early days for 5G – even in China – and the stated position of having many 5G devices in the market could put Xiaomi ahead of some of their competitors in relation to availability. Going forward, it will be interesting to look at the integration of AI, IoT and 5G by Xiaomi.”
Sheedy further added, “we can expect Xiaomi devices to get smarter and more interconnected. Xiaomi actually has the opportunity to take some of the home-centric device hubs out of the ecosystem as they connect straight to the 5G network, and are controlled by an intelligent cloud-based hub perhaps mostly accessed through Xiaomi mobile phones.”
Meeting the Cybersecurity standards
Cybersecurity concerns are common around Chinese device makers. Recently, Xiaomi wireless devices have been disabled from connecting to Google’s Nest devices due to security flaws. On top of this, there have been concerns over the last few years about how Chinese tech companies secure their products and who has access to the data.
“Privacy and security are concerns for consumers – but they are often trumped by convenience, features and off-course price. Xiaomi Corp is aiming to make some of the best devices in each category and as long as they respond quickly and openly to privacy issues, they are likely to continue to see success both inside and outside of China. Their focus on driving down costs in order to be a price leader will help them with this challenge too” said Sheedy. “Ultimately, the privacy and security issues will impact the entire market – not just Xiaomi or other Chinese vendors as the users will steer away from all “smart, connected devices” – not just those from specific suppliers.
Market Positioning Approach
Xiaomi Corporation’s philosophy is to do more business with smaller margins, which drove it to expand its smartphone market from China to other areas like India and Europe. The company is aiming to strengthen its positioning in the consumer electronics market with further tech investments.
Sheedy explains that “considering the fact that they are losing market share in handsets in China, I would imagine that they will double down their efforts to be better at what they do now – not enter entirely new markets. I expect that we will see them produce smarter, connected devices – getting into more of the home and consumer market rather than move into the enterprise market. The enterprise market requires different sales strategies and channels, different partners, different margins, different support mechanisms etc.”
Naturally, Xiaomi is not alone in investing heavily in next-generation technologies. For example, Huawei opened a dedicated IoT consumer lab at the end of 2018 and is continuing to commit resources to the development of this industry-changing technology.
“The 5G plus AIoT strategy is the right one for Xiaomi. They need to surround their competition and make their products better, smarter and more affordable. With the growth in 5G services, a product leadership in this space, beyond smartphones – in smart devices too – will set them up for continued success in what is a very competitive market” said Sheedy.
We can safely bet that in the decade taking us to 2030, technology will continue to impact and shape our world. Ecosystm has already predicted the top technology trends for 2020 (AI, Cloud, Cybersecurity, IoT). It is time to look beyond the year and see what 2030 has in store for us. There is a distinct possibility that there will be newer technologies in future that we are yet to hear of, waiting at the threshold to disrupt the existing tech space. Also by 2030, there will be many technologies that are considered futuristic today that will have become mainstream. Let us explore some of them.
Computing Technology
Quantum computing has been promising to take computing beyond current limits – going beyond bits to qubits. Qubits represent atoms, ions, photons or electrons and their respective control devices that are working together to act as computer memory and processor. It has the potential to process exponentially more data than current computers.
Even with various technology providers such as Google, IBM, AWS and Microsoft having announced their quantum computing innovations, it does not appear to be nearly enough to disrupt computing yet. The race to demonstrate the first usable quantum computer is on and start-ups such as Rigetti are challenging the established players. Whether or not the vision we have of quantum computers is fully realised, it will definitely bring in a new breed of computers with advanced processors capable of handling data, million times faster than today’s supercomputers.
Technology providers and government research organisations will continue the R&D initiatives to meet quantum’s real-world potential. Over the next decade, quantum computing applications are set to impact scientific research and exploration, including space exploration and materials science. Quantum computing will also impact us in our everyday lives enabling better weather forecasting and personalised healthcare.
Storage Technologies
Cloud storage has dominated most of the previous decade, enabling real-time access to data for both consumers and enterprises. The current storage technologies are reaching the verge of their theoretical storage capacity, given the amount of data we generate. Researchers continue to push the envelope when it comes to capacity, performance, and the reduction of the physical size of storage media. Some storage technologies of the future that have the potential to become mainstream are:
DNA Data storage
DNA stores the ‘data’ for every living organism and one day it could be the ultimate hard drive! DNA data storage consists of long chains of the nucleotides A, T, C and G – which are the building blocks of our DNA chains. DNA storage and computing systems use liquids to move molecules around, unlike electrons in silicon-based systems. This enables the stored data to be more secure and potentially allows an almost infinite storage lifespan. Researchers from Microsoft and the University of Washington have demonstrated the first fully automated system to store and retrieve data in manufactured DNA – a key step in taking the technology out of the realms of theory and into reality. The technology is still too expensive and requires new engineering solutions for it to be viable in the near future. However, there are several research organisations and start-ups out there working on creating synthetic DNA – data storage is seen as one of the many applications of the technology.
Glass Data storage
5D Glass Discs are being researched and experts say that they could store 3000x more data than CDs with a span of 13.8 billion years. The discs are made out of nanostructured glass, and the data is stored and retrieved using femtosecond laser writing. The discs are made by a laser that makes microscopic etchings in nano glass. The University of Southampton has developed the highest storage efficiency in a data storage device to date. Microsoft’s Project Silica has developed a proof of concept for its quartz glass storage in partnership with Warner Bros, storing the 1978 classic movie, Superman on a palm-size glass disc.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the science of understanding and manipulating materials on a nanometre scale. It has the potential to create the ultimate IoT sensors. Nanotechnology is already being used in the production of some microprocessors, batteries, computer displays, paints and cosmetics. But this really is just the beginning of a nano revolution.
The most researched nanotechnology applications are probably in medical science. By injecting or implanting tiny sensors, detailed information can be gathered about the human body. Innovations in implantable nanotechnology will grow and we will see more applications and innovations such as Smart Dust – a string of smart computers each smaller than a grain of sand. They can arrange themselves in nests in specified body locations for diagnostics or cure. The focus is not only on early detection but also on storing encrypted patient information. MIT is working on a nanotechnology application which involves nanoparticles or tiny robots powered by magnetic fields for targeted drug delivery.
Healthcare is not the only industry where nanotechnology will become mainstream. Materials science will see huge adoption and development of nanotechnology applications, this will drive innovation even in wearable devices and smart clothing. Nanomaterials will be used for monitoring in manufacturing, power plants, aircrafts and so on.
Printing Technologies
Astonishingly, it has been nearly 40 years since 3D printing technology was conceptualised. In the last few years, there has been rapid adoption in prototyping using 3D printers in manufacturing and construction. There has also been considerable research applications such as printing food and replacement organs. For example, companies have already demonstrated that they can create 3D prototypes of human liver tissue patches and implant them in mice.
4D printing will be the next step. With 4D printing, we can change shapes of 3D-printed objects upon stimuli from specific environmental conditions, such as temperature, light or humidity. Although the 4D printing technology is still in the R&D phase, this technology of the future has huge implications in the applications of engineering, manufacturing and construction. For instance, 4D printed bricks could change shape and size when placed alongside other bricks on the wall giving us better insights on how to protect property from natural disasters.
Connectivity Technologies
The world is becoming increasingly connected. Access to fast and reliable Internet is one of the many reasons for economic and social progress. There is constant R&D on a more seamless connectivity option. Industry giants are coming up with solutions to connect people in remote areas – such as providing emergency connectivity through helium balloons. Facebook’s Internet.org intends to provide universal connectivity using drones, low-Earth orbit and geosynchronous satellites. It is easy to predict that in 2030 everyone will have connectivity. While we are discussing the full impact of 5G, China’s Ministry of Science and Technology has already announced that they are embarking on R&D on 6G – more suited to a world where IoT becomes mainstream.
Li-Fi Technology
Li-Fi technology (Light Fidelity) works on visible light communications which sends data at a much higher speed. As we look for lower latency and higher speed, Li-Fi may very well be the technology that becomes mainstream in 2030. It is a wireless optical networking technology that uses LEDs for data transmission. In the lab, Li-Fi applications have reached transfer speeds of 10 Gbps, faster than the Wi-Fi 6 router. Li-Fi is being pegged as the network technology that will finally enable the true Edge. The recent Aircraft Interiors Expo (AIX) showcased a Li-Fi application that supported 40 Mbps transmissions and streamed HD content from a visible passenger service unit (PSU).
Ecosystm will continue to scan the horizon for newer technologies that can potentially disrupt the already disruptive tech world.
What do you think are the technologies of the future that will shape our lives in this decade? Tell us in your comments.
As we move into a new decade, the Telecommunications industry is ripe for disruption, as it gets reshaped by bountiful bandwidth and software enabled flexibility. Several countries have spent the last decade building fibre access networks. 5G is expected to lower latency and provide greater flexibility. As virtualisation, AI and automation combine to make networks even more cost effective it will broaden use cases to include widespread adoption of IoT.
The Top 5 Telecommunications and Mobility Trends for 2020
Below are the top 5 Telecommunications and Mobility Trends for 2020. It is based on the latest data from the global Ecosystm Mobility Study and is based on qualitative research by Liam Gunson, Director, Product and Solutions at Ecosystm.
-
50 Shades of 5G
In 2020, 5G will be a major step change in what a mobile network can do – in terms of capacity, efficiency, stability, and latency. The amount of money and investment associated with it will also keep it in the spotlight. The year will see 5G move beyond trials to actual commercial rollouts – but that will also mean more regulations and a competitive landscape. There will be multiple deployment models:
- In fixed vs mobile markets, the most obvious choice will be to take a share of the home broadband space first
- Markets with strong growth in data usage and higher ARPUs will evolve 4G to provide higher bandwidth while looking to 5G for their economic benefits in efficiently managing spectrum
- In other areas, operators will be forced to explore spectrum or infrastructure sharing to spread costs across lower ARPUs or align with regulators’ desire to limit licenses. This is likely to be more common in emerging markets and low-density areas.
-
Enterprise Mobility Will Witness a Renaissance
Enterprise mobility will be back on IT teams’ agenda after having taken a backseat for a few years. Ecosystm research shows that over 72% of organisations have a Mobile First strategy. This is set to accelerate for a number of reasons:
- Companies are increasingly adopting agile or new ways of working to speed up innovation and delivery – and this includes working in new teams and activity-based working
- As more millennials and the Gen Z enter the workforce, there will be a steady rise of the ‘gig economy’ and a high percentage of contract, part-time and freelance workers
- As organisations become more agile and the workforce increasingly mobile there will be a bigger drive towards space optimisation, seeing a higher adoption of shared offices and co-working spaces
-
The Future of the LAN is Cloudy
The next few years will see a re-think of the traditional LAN/WAN set-up, as user needs change with Digital Transformation (DX) initiatives, and new technologies such as GPON, 5G, Wifi 6, WiGig, and software-defined networking bring new capabilities and alter costs. Enterprise network will change in the following ways:
- Wireless connectivity will move beyond BYOD and guest access and become the primary connection type – the connection points will be sensors and access points, and not PCs
- AI, virtualisation and software-defined networking will bring more flexibility as they lessen the need for specialised hardware, centralise control, and speed up configuration changes
- Enterprises will stop thinking of their network as a physical space and start seeing it as a set of capabilities. Equipment will be increasingly centralised in data centres (possibly on the Edge) to allow workers to work from virtually anywhere.
-
Intelligence at the Edge – from Connected Things to Conscious Things
We have moved past step 1 of IoT, where the focus was on making sensors and chipsets cheap enough to be incorporated in millions of different devices, as well as a to find cost-effective ways to handle the data requirements. 2020 will see IoT move to step 2 – from sensing to responding. AI will become easier to develop and use, while edge compute, high-bandwidth, and low latency networks will make it possible to be embedded into an expanding number of use cases where devices and processes need to make real-time adjustments.
This will become most obvious as we see an increased use of cameras as sensors. With their ability to capture details, they are the most effective sensors we can have. The challenge has been that high definition video is incredibly data heavy, creating issues when trying to transport and analyse it. Edge compute will help to bring the analytics closer to the source lowering the transport costs, while also lowering latency and increasing security.
-
Expansion Drives Consolidation
Telecommunications operators have been evolving for a while now using measures such as acquiring new companies, establishing disruptive business units and so on. In 2020, these operators will focus on transforming the core – remove unnecessary costs, improve customer experience, capture new opportunities – and on building telecom networks with scalability, flexibility, efficiency and agility.
As providers become more flexible, they will not only be easier to integrate with, but will also be able to manage more products and niche requirements. Traditionally 80-90% of their revenues have come from consumers and Telecommunications providers own these relationships. Now they will have to start working on their B2B relationships.
Ultimately the network game will be one of scale, and this will force operators to consolidate to survive. Nokia Bell Labs expects global operators to fall from 10 to 5 between 2020 and 2025, and local operators to fall from 800 to 100 – this looks completely plausible at the moment.
Download Report: The top 5 Telecommunications & Mobility Trends For 2020
The full findings and implications of the report ‘Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Telecommunications & Mobility Trends For 2020’ are available for download from the Ecosystm platform. Signup for Free to download the report and gain insight into ‘the top 5 Telecommunications & Mobility Trends For 2020’, implications for tech buyers, implications for tech vendors, insights, and more resources. Download Link Below ?

Financial institutions are being challenged by and collaborating with Fintech organisations in equal measures. As their focus on customers increase, they will collaborate and partner with these disruptors. Fintech is also getting attention from governments in both emerging and mature countries as a means to achieve their financial inclusion and digital economy goals. Fintech investments will continue to surge through 2020 across the solution areas.
The Top 5 Fintech Trends For 2020
The Top 5 Fintech Trends are based on the latest data from the global Ecosystm AI and Cybersecurity studies and is also based on qualitative research by Ecosystm CEO Amit Gupta and Principal Advisor Paul Gestro.
-
One for All and All for One
Fintech will have a much greater impact than we realise, and we will continue to see it drive the induction of the unbanked into the mainstream economy. The growth in mobile phone penetration, however, continues to grow at a faster pace than banking accessibility across emerging economies. We will continue to see Fintech play a significant role in driving greater inclusion, especially to bring in the underserved in the emerging economies and reducing the gender gap when it comes to adoption of financial services – creating greater inclusion overall.
The democratisation and accessibility of financial services will also result in far greater uptake of the sharing economy and we will continue to see non-traditional companies enter the payments and financial services markets. Fintechs that have environmental and social impact, beyond financial impact, will also find it easier to secure funds from Impact Investors.
-
The Year of the Banks
2020 is the year banks will need to embrace Fintech – fully. They know full well that customers are at the centre of their entire operation – and Fintech services can and will provide them with the solutions they need. They have been skeptical about adopting Fintech but as they begin their transformation journeys and face increasingly stringent regulations, they might no longer have the option of ignoring Fintechs.
Banks are already adopting, evaluating and developing strategies for AI, RPA, and Cybersecurity adoption – but they will feel the need for more innovation and speed in 2020.
-
Asia Becomes Middle Earth
Asia has fast become the centre for both innovation and investment. Asia’s fast pace of urbanisation and the increasing prosperity of the middle class is attracting investments. Venture capital-backed Fintech companies raised more than USD 40B in 2018 – with the bulk coming out of China. Investments in Asia is expected to grow, and will benefit later stage Fintech startups.
These investments, a lack of strict policies (yet!) and the large number of unbanked and underbanked are also fuelling innovation in Asia. Several large financial institutions in Asia have already made public announcements of the Fintech investments and this will cause a ripple effect.
-
Nothing Artificial About AI
AI sits at the heart of most Fintech solutions. And AI has slowly made its way in decision-making and process automation. The first step to AI is automation and robotic process automation (RPA) will transform customer experience and will allow integration of legacy systems in financial institutions. As IoT and Blockchain mature they will be increasingly integrated within AI solutions.
Another area which will see AI adoption in financial institutions is Cybersecurity – machine learning can predict the patterns of criminals (or rogue/irresponsible employees) to stop events before they start. Fintech solutions such as Regtech and Suptech has a definite play in this space.
-
Regtech Will Take Centre Stage
In 2020, Regtech will take the centre stage as the emerging Fintech solution. Together with AI, a better ability to use data and predict trends, Regtech will be used to fight financial crime and reduce costly compliance-related mistakes.
The old way of just employing more people to run the compliance tasks is not sustainable. routine tasks such as KYC, AML and compliance verification are ripe for automation. Moreover, Regtech ROI is relatively easier to set and measure.
Download Report: The top 5 Fintech trends for 2020
The full findings and implications of the report ‘Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Fintech Trends for 2020’ are available for download from the Ecosystm platform. Signup for Free to download the report and gain insight into ‘the top 5 Fintech trends for 2020’, implications for tech buyers, implications for tech vendors, insights, and more resources. Download Link Below ?

As the ‘Experience Economy’ becomes a reality, organisations will look beyond improving customer experience (CX) to enhancing employee experience (EX). It is estimated that people spend a third of their life at their workplaces. This realisation will drive organisations to focus on EX over priorities such as growing revenue or reducing costs. Retaining employees is important in today’s war for talent – and organisations have started appointing Chief Experience Officers. Ultimately, workplace technology should drive employee productivity – and there is a proven link between happy and productive employees.
The Top 5 Workplace Of The Future Trends For 2020
The Top 5 Workplace of the Future trends are drawn from the findings of the global Ecosystm CX Study and are also based on qualitative research by Ecosystm Principal Advisors, Tim Sheedy and Audrey William.
-
Employee Experience as a Business Focus Will Drive Faster Adoption of Consumer Collaboration Tools
Organisations in mature economies already have employee experience (EX) and CX as their top business priorities. This comes with an understanding that offering a great customer and employee experience will lead to revenue growth, profit growth and lower costs.
For communication and collaboration solutions, if the experience is not right, employees will move on to the next best app for the right experience. The competition between the vendors across voice, video and collaboration is heightening. It may sound simple but that is where the innovation needs to happen in the industry. If employees do not like what IT has provided for them, they will download the application of their choice for work. This will be a huge challenge especially in industries that are heavily regulated such as Financial Services and Healthcare.
-
HR KPIs Will Drive IT Teams to Invest in Workplace Analytics
HR teams are ultimately responsible for driving improved EX. And a happy employee is a productive employee – so an employee’s environment (managed by the Operations or Facilities team) and their technology (managed by the IT team) will have the biggest impact on driving employee satisfaction. To drive these outcomes, we will see these three teams work closer than they ever have – and not just on a project basis, but as a permanent arrangement.
Investments in Workplace Analytics will increase, and there will be more collaboration between IT, HR and Facilities Management to drive best practices for employees. Right now, there is very little collaboration between the three departments in driving better workplace practices. Workplace Analytics will help solve problems related to poor office practices around email overload, long work hours, absenteeism, usage of rooms and other facilities, employee discontent, as well as understand the overall trends on communications and collaboration solutions usage.
-
5G Services will Push Organisations to Rethink their Network
Today 5G is not available in many countries – and where it is available coverage is generally spotty. But this will change in 2020 as more operators launch or expand their 5G coverage. The unique capabilities of 5G to offer software-defined networks (SDNs) – designed specifically for organisations’ needs – will help businesses rethink the way they operate. They can stop thinking of their network as a physical place and start thinking of it as a set of capabilities and this takes work beyond designated physical addresses. Retailers will be able to offer complete retail environments from wherever they choose. Banks will be able to offer complete in-branch services from anywhere. Employees will be able to get access to all sorts of data and systems regardless of location. 5G is about much more than a faster network – the potential to transform enterprise networks will see a huge rethink of the network and the way IT teams provide technology services to their employees.
-
Organisations Will Wake Up to the Need for the Right Knowledge Management Solution
IT has been guilty of dictating the knowledge management (KM) requirements and platforms to the business. Many customer teams are using tools that are inherently wrong for the job. Management is using tools that do not support their needs, and information workers are given generic platforms when they have specific needs. 2020 will see a fragmentation of the KM market as businesses start to buy based on customer and employee needs – not based on what the IT team dictates.
-
2020 Will See a Rise in CPaaS Adoption
Cloud-based platforms that enable developers to add real-time communications features within the workflow of their own business applications will be the next big area of innovation in the unified communications space. Through the use of APIs, developers can embed communication capabilities into their existing business applications, without extra hardware or software costs. Developers can embed it directly into the cloud platform so the time to market is fast. Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) will see greater adoption as more organisations look to build code and apply agile and DevOps methodologies.
Download Report: The top 5 Workplace of the future trends for 2020
The full findings and implications of the report ‘Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Workplace of the future Trends for 2020’ are available for download from the Ecosystm platform. Signup for Free to download the report and gain insight into ‘the top 5 Workplace of the future trends for 2020’, implications for tech buyers, implications for tech vendors, insights, and more resources. Download Link Below ?

Increasingly organisations are looking to improve customer and employee experience over other traditional metrics such as growing revenue or reducing costs. Organisations are transitioning from business metrics to customer experience (CX) ones, and employing CX leaders. 2020 will see many businesses make significant breakthroughs in improving the CX.
The top 5 Customer Experience trends for 2020
Here are the top 5 CX trends and the related technology markets in 2020. It draws on the latest data from the global Ecosystm CX Study that is live and ongoing on the Ecosystm platform and based on qualitative analyses by Ecosystm Principal Advisors Tim Sheedy and Audrey William.
-
Asia will Catch up with North America and ANZ in Customer Obsession
Many Asian economies – particularly those in Southeast Asia – have not needed to focus too much on CX. The proportion of businesses starting to map customer journeys is accelerating, and there is a growing focus on making those journeys easier, more effective and more enjoyable. We are seeing this play out in the levels of interest in – and deployment of – cloud contact centres. Australia and New Zealand have been leading the deployments in the last two years. Deploying cloud and using machine learning and AI at the core to understand how to deliver personalised CX is part of a wider CX strategy for several organisations.
In 2020 we expect large organisations in Southeast Asia and North Asia to transform their CX and contact centre capabilities and make the move to cloud-based contact centre environments.
-
CX Initiatives will Dovetail with Broader Digital Ones
Many businesses have taken a bimodal IT approach to their technology platforms – driving customer-centric changes at pace while keeping their back-end systems slow. In the drive to make the entire business fast and innovative, these back-end systems are being modernised. But over 90% of businesses have not yet seen a customer or business benefit from this digital agenda.
This will change in 2020 as more businesses get some competitive advantage from the digital initiatives they are driving inside of their business. This will be driven by the linking of the customer-centric technology initiatives with the back-end ones. This means that customer applications will be infused with data and analytics from other systems, making them smarter and increasing the potential for automation and AI to drive down costs and increase personalisation and customisation.
-
Hyper-personalisation will Move from Concept to Reality – Powered by Customer Journey Analytics
The idea of creating unique experiences for each customer has been discussed for years – but few businesses are really doing it today. 2020 will see businesses outside of the top 5% experiment and deploy hyper-personalised CX. It will move from the top web brands to mass market as more companies invest in automation, predictive analytics and AI.
But hyper-personalisation is not possible without Customer Journey Analytics. Businesses need to understand the end-to-end journey of each customer to understand how to personalise it. Therefore, Customer Journey Analytics will take centre-stage in 2020. The challenge for years has been that customer teams have focused on the traditional inbound and outbound interaction with the customer. Brands now need to understand and personalise the experience before the customer interacts with the brand and after they are done interacting with the brand. The ability to apply machine learning and AI to offer insights to predict the movement and journey of the customer will be a significant focus – and challenge – for customer teams. Customer Journey Analytics will allow brands to deliver that “frictionless” service.
-
There will be a Renewed Focus on Compliance and Security in CX
With the recent banking royal commission hearings in Australia to GDPR and other global regulations around privacy and customer data handling, customer teams will now have to make sure that all forms of voice and non-voice interactions are monitored close to 100% of the time. Very few customer teams do that today and are at risk of non-compliance. As monitoring can be labour intensive, there will be a need for organisations to invest in analytics and AI applications around compliance and monitoring.
The recording of customer calls means that highly sensitive information could be stored for years and the risk of the contact centre breaching regulatory compliance requirements enhances. Solutions today have various ways to block the recording of key phrases or sections and some solutions apply APIs to the flow of the recording. As soon as the agent enters sensitive information such as credit card details, the recording stops to resume after the sensitive data is blocked or deleted. That way the sensitive conversation is not recorded or heard by anyone monitoring the call. Contact centres must adhere to this strictly, but few do. Businesses also need to know real time if an agent is misinforming the customer. Contact Centre Outsourcers will also have to re-look at how compliant they are and how much they have invested in securing customer data. There will be greater pressure on them to take on greater risks and share the risk burden with their clients.
-
Businesses will Use AI and Analytics to Measure CX
The drive to improve CX has every business and government department measuring the experience at every opportunity. A one-minute transaction in a store can prompt a five-minute survey asking for feedback. As a consequence, customers are experiencing survey fatigue. Surveys are also not the best way to measure how customers feel after they have interacted with a brand. Already, many will not participate unless there is a discount or incentive, which eats into future margins. Smart businesses will begin to use AI to detect emotions and mood, and analytics to measure experiences.
Download Report: The top 5 Customer Experience trends for 2020
The full findings and implications of the report ‘Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Workplace of the future Trends for 2020’ are available for download from the Ecosystm platform. Signup for Free to download the report and gain insight into ‘the top 5 Workplace of the future trends for 2020’, implications for tech buyers, implications for tech vendors, insights, and more resources. Download Link Below ?

Authored by attending Ecosystm analysts, Ullrich Loeffler (Chief Operating Officer), Kaushik Ghatak (Principal Advisor, Digital Transformation and Supply Chain) and Liam Gunson (Director, Product and Solutions)
Bosch Software Innovation (Bosch SI) hosted its annual analyst briefing in Singapore on 6th December 2019 to provide an update on its business, strategy and solution portfolio in the APAC region.
Bosch has expanded its capability and reshaped its go-to-market approach in a bid to not only position itself as a world leading IoT company, but also help move the IoT market forward.
A number of new solutions were demonstrated through the day. From tenants asking their building management if the gym was busy, to smartphones detecting a manufacturing fingerprint so you could avoid buying a counterfeit.
At the heart of the business updates though was a new organisational approach to prove markets and integrate user perspectives into solution development. Bosch is looking to achieve this by setting up dedicated, cross-divisional entities which can focus on user needs to drive growth while collating requirements for the Bosch SI centres.
Bosch SI essentially will perform a role of an IoT business incubator within Bosch Group, and once a vertical within Bosch SI has reached a certain level of business, it is spun off into a separate company focusing on that area. There are three business units that have met the threshold and have spun off so far.
Broader challenges still remain for IoT adoption. Patchy connectivity, varied regulation, and a lack of standardisation will continue to hamper the IoT market. However, from a user perspective the timing is right. Ecosystm research shows that while IoT uptake is limited, intention is strong. Enterprises will be looking for partners with a willingness to understand their needs and design around them, in order to help get initial projects off the ground.
Bosch Business Update – From Innovation to Commercialisation
Bosch SI was created to build Internet of Things (IoT) solutions, leveraging Bosch’s 133-year experience in developing and manufacturing products for the automotive, industrial and consumer segments. Founded in 2008, by 2019 Bosch SI has established 10 global offices, of which some have solution development capabilities, employing over 700 IoT experts. Four of the Bosch SI offices are located in Asia Pacific – Singapore, Nanjing, Shanghai and Tokyo.
Figure 1: Bosch Software Innovations in Numbers
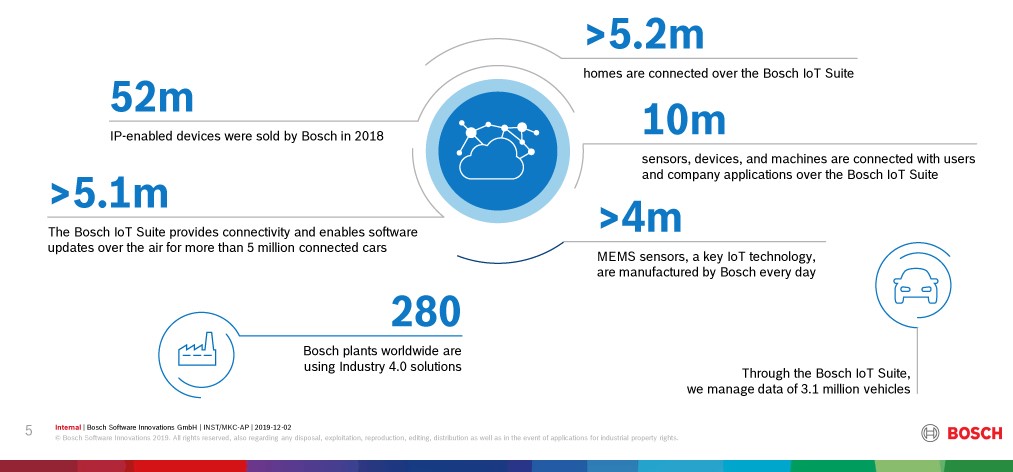
The Bosch IoT Vision and Strategy is not limited to Bosch SI’s but spans across the full Bosch Group. An indication of the dedication to the IoT story is that Bosch is committed to enabling connectivity for all existing product portfolios ranging across its industrial, automotive, manufacturing and consumer product lines by 2021.
Another indication of Bosch’s IoT business maturing is that in 2018 Bosch it formed 3 new subsidiaries, each being a dedicated entity to take targeted IoT Industry solutions to market. The new business entities focus on
- Connected Industry
- Connected Mobility
- Residential IoT
with other areas such as Agriculture, Retail, Energy, Mobility, Manufacturing and Home & Building as potential future spin-offs. The announcement is significant as it separates the innovation and commercialisation functions. Bosch SI becomes the dedicated R&D and incubation engine to take new industry solutions to a defined threshold before a dedicated entity is formed to achieve commercial scale.
Despite the fact that IoT has been greatly overhyped since the term was coined by Kevin Ashton in 1999, Ecosystm research shows evidence that adoption is accelerating across the region. Figure 2 outlines the current and planned adoption of ‘sensor-based analytics’ within organisations. The research strongly supports Bosch’s timing for investments in scaling the commercialisation of its solutions.
Figure 2: Industry Adoption of Sensor-Based Analytics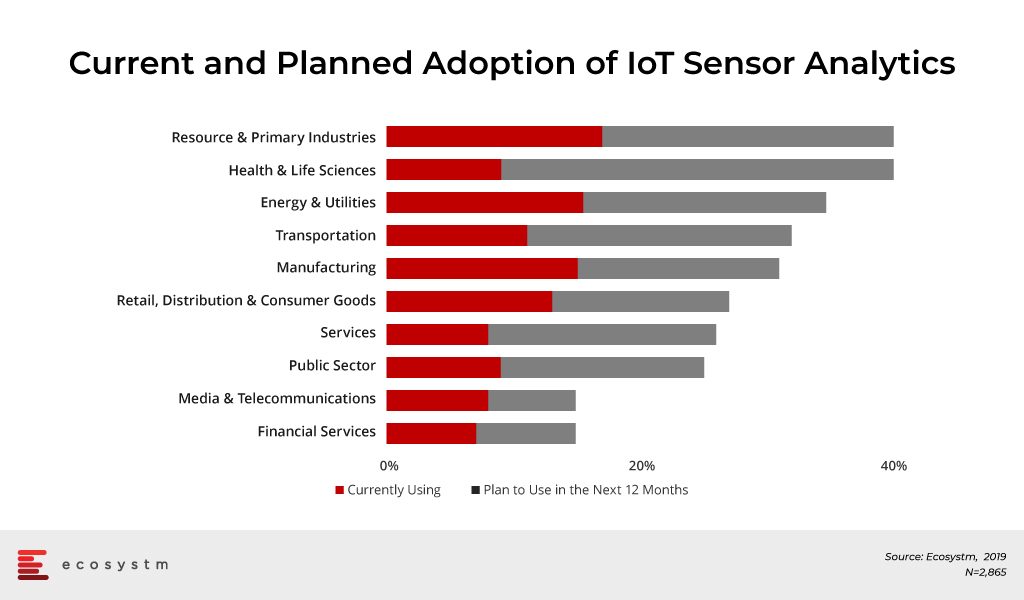
Market Pull over Technology Push is creating proven Industry Use Cases
The locations and specialisations of Bosch’s Innovation Centres across Asia are no accident and result directly from engagements with local clients. Each innovation centre specialises in certain solutions that have arisen from the productisation of solutions developed for customers. This ‘market pull’ strategy is a clear differentiation to the commonly practiced ‘technology push’ approach which has seen many vendors struggle to gain traction for their IoT solutions. Key industry solutions developed by Bosch SI are:
- Agriculture – Bosch Plantect: (Japan). Plantect is a sensor-based monitoring system for early detection and prevention of plant diseases in greenhouses. The current solution targets greenhouse farmers for tomatoes, cucumber and strawberries.
- Smart Building – Bosch Lift Manager (Singapore). Lift Manager is an AI-supported solution that can be retrofitted in existing lifts with set algorithms to monitor and predict lift malfunctions and enable predictive maintenance.
- Smart Building – Connected Buildings (Singapore). Bosch Connected Building leverages cameras and sensors to optimise business operations such as Air Quality, Light Monitoring & Control, Lift Monitoring, Occupancy Tracking, Asset Tracking, Carpark Monitoring, and Object Tracking.
- Manufacturing – Secure Product Fingerprint Solutions (China). Secure Product Fingerprint captures a unique fingerprint for products to combat counterfeits and connect manufacturers with their users.
The Bosch IoT Ecosystem – Open Source and API enabled Platform
Bosch has realised that IoT is a concept that cannot be owned and delivered by a single entity. As such Bosch aims to establish its Bosch IoT Suite as the platform to connect any Bosch or third party “things” to deliver targeted industry services and solutions.
Bosch IoT Suite can be deployed on Bosch’s own IoT Cloud or through Cloud partners such as AWS, Microsoft or Huawei (for China only). It is a PaaS offering that packages unified device APIs to connect things with device management, software updates over the air, data management and security capabilities. An inbuilt analytics engine assists with business logic tools to drive business value out of the data collected. The open source and open standards architecture promote the development of in-house or third-party industry applications as platform add-ons and use cases.
Bosch and Market Outlook
IoT has been one of the most hyped ‘buzz words’ for the last few years but true market adoption is yet to follow suit. Ecosystm research shows that market intention is positive with more industry-focused uses cases and simpler ‘plug and play’ style solutions available that require less CapEx and shorter time to value.
Bosch is well positioned to capitalise on this trend. Its focus on developing proven use cases for targeted industry sectors and then working with anchor customers and testing the solutions internally within Bosch, is a clear differentiator in the market. Commercially scaling these solutions will remain the key challenge as decision stakeholders may not be the key beneficiary of the solution. In the connected building example, tenants will be the key beneficiary of finding quiet gym slots or having better air quality but it remains questionable whether this will convince the building owner or operator to put pen to paper and sign-off on relevant IoT investments. An area that Bosch needs to focus on, is the articulation of its business proposition and more importantly connect this to the business value to prospects and customers. As solutions scale in the market, broader sales and partner teams will need to be enabled to bring this message to the relevant stakeholders. The fact that these stakeholders may sit outside Bosch’s traditional comfort zone will not make this endeavor easier.
Bosch will also face varying market regulations that could create road bumps in scaling its solutions. The Bosch Lift Manager solution as an example provides sensor diagnostics for predictive maintenance scheduling. Many existing lift maintenance contracts however follow local regulations that require ongoing scheduled servicing of elevators which reduces the cost savings potential.
The decision to establish standalone IoT entities is seen as a strong commitment and the right move to take advantage of the presented IoT opportunity. The high degree of customer advocacy and industry experience further makes Bosch a strong contender of the Industry 4.0 revolution.
The future of cities is critical to the future of the global economy, given that they now account for more than half of the world’s population and more than 80% of global GDP. Cities around the world have very similar struggles and objectives: ensuring a competitive economy, a sustainable environment, and a high quality of life for their citizens. We look at the trends for cities in 2020 from the lens of data, mobility, energy, public safety, and jobs.
This article presents the top 5 Cities of the Future trends for 2020 and the related technology markets. It draws on the latest data from the global Ecosystm IoT Study that is live and ongoing on the Ecosystm platform and based on qualitative analysis by Ecosystm Board Advisor Randeep Sudan and Ecosystm Principal Analyst Sash Mukherjee.
The top 5 Cities of the Future trends for 2020
Here are the top 5 Cities of the Future trends for 2020 that we believe will impact governments, businesses and citizens in 2020:
- The Emergence of Data Smart Cities
The global economy is fast becoming digital, and data is at the very heart of a growing digital economy. Cities are increasingly adopting Data Smart strategies, a trend that will dominate the market in 2020.
Data Smart strategies focus on addressing data silos and making data available across organisational boundaries for better decision making. They expand the availability of data through real-time capture with the help of IoT devices and leverage the power and promise of data by using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data analytics. Singapore is an excellent example of how Data Smart cities are designing their data strategies. Singapore‘s data governance framework includes the concept of Single Sources of Truth (SSOT) – where all government stakeholders have access to the same data. To make access easier, there are data aggregators, the Trusted Centers (TCs). Not only has the Government thought out the data aggregation and management angle, but also of digital enablers for the use of AI, including a code repository for AI and platform for the rapid development of AI-based solutions.
-
Intelligent Infrastructure for Smart Mobility
Traffic congestion and pollution have become an inevitable by-product of urbanisation, especially with the rise of individually owned cars. Several cities across the world have tried wide-ranging initiatives such as road space rationing and congestion pricing. However, the success of these initiatives will lie with intelligent infrastructure and smart enforcement.
2020 will see several cities making investments in demand-responsive services, where public transportation systems can respond in real-time to the changing traffic needs of the city rather than run on predetermined routes and schedules. There will also be a rise in the number of transport options, including mass transit, car-sharing, bike-sharing, ride-sharing, and personal mobility devices.
-
Smart Energy Ecosystem
Urbanisation will see higher energy costs, and a fierce competition for resources. Smart Cities are actively focusing on smarter energy options that focus on reducing energy consumption, lowering emissions, and providing better service and support to consumers.
The Energy & Utilities industry has been the first adopters of Smart Energy solutions and as they introduce smart meters for the consumers, they open the market up. The initiatives range from promoting a greener environment, expanding the use of renewable energy, and introducing ‘smart’ solutions to utility providers, enterprises, and homes.They can also help Energy and Utilities companies to comply with government regulations and meet sustainability and carbon emission goals. On the consumer side, going forward, the Construction industry is expected to be the frontrunner in promoting energy efficiency, with increasing uptake of Smart Building solutions.
-
The Rise of the Gig Economy
All Cities of the Future need to prepare for the workforce of the future. The gig economy will have a huge number of part-time, contract workers and freelance workers. This trend will only go up as more millennials and the Gen Z enter the workforce. They will force organisations to innovate and make employee experience a key business priority.
Simultaneously, there has been a steep rise in the sharing economy, seeing peer-to-peer (P2P) economic activities, based primarily on providing a service or sharing access to goods and services. Community-based online platforms are on the rise, and several industries – such as financial services, hospitality, and retail – are being disrupted in both mature and emerging economies.
-
Increased Use of AI in Public Safety
In this world of hyper-surveillance, cities use CCTV cameras for multiple reasons ranging from traffic monitoring, remote asset tracking, and crime prevention. Airports and police departments have been actively using facial recognition. They have also been experimenting with advanced video analytics that can identify persons of interest through other parameters such as gait.
Surveillance is not the only use of AI in governments. Predictive analytics is being used by police departments and the judiciary, for risk assessment and crime reduction. AI for process optimisation also impacts public safety. While discussions and debates on ethics will be rampant, most governments will invest in AI for public safety.
Ecosystm in partnership with SGInnovate, the government-backed organisation that promotes Deep Tech in Singapore, released a series of four reports covering areas of mutual interest: Cybersecurity, Artificial Intelligence, Cities of the Future and Healthtech.
‘Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Cities of the Future Trends for 2020’ report is a part of this collaboration and is available for download from Ecosystm and SGInnovate websites.
Download Report: The Top 5 Cities of the Future trends for 2020
The full findings and implications of the report ‘Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Cities of the Future trends for 2020’ are available for download from the Ecosystm platform. Signup for Free to download the report and gain insight into ‘Top 5 Cities of the Future trends for 2020’, implications for tech buyers, implications for tech vendors, insights, and more resources. Download Link Below ?

As the Healthcare industry becomes more consumer-focused, and consumers more tech savvy, even the most traditional healthcare organisations will have to innovate. The industry will see several instances of innovation whether new clinical research-backed, scientific solutions, technology disruptors such as IoT, Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning and Blockchain or business model and process changes.
This article presents the Top 5 Healthtech Trends for 2020 for the Healthcare market in 2020. The trends are drawn from the findings of the global Ecosystm Customer Experience (CX) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) studies and is based on qualitative research by Ecosystm Principal Analyst Principal Analyst Sash Mukherjee.
The Top 5 Trends for Healthtech for 2020
Here are the top 5 healthtech trends for 2020 that we believe will impact healthcare organisations (provider, payer and life sciences), patients and consumers in 2020.
-
The Shift from Patients to Customers Will Become Real
As more devices (consumer and enterprise) and applications enter the market, people will take ownership and interest in their own health outcomes. This will see a continued growth in online communities and comparison sites (on physicians, hospitals, and pharmaceutical products). Increasingly, insurance providers will use data from wearable devices for a more personalised approach, promoting and rewarding good health practices.
Beyond the use of wearables and health and wellness apps, we will also see an exponential increase in uptake of home-based healthcare products and services, whether for primary care and chronic disease management, or long-term and palliative care. The desire for real-time access to healthcare has led to a rapid consumerisation of the industry and has forced healthcare providers to actively focus on customer experience (CX), which according to the global Ecosystm CX study is the top business priority for healthcare organisations today.
-
Healthtech Will Take Lessons from Fintech
Healthcare organisations will take lessons from other customer-focused industries such as hospitality, retail and financial services. A focus on CX will also require an omni-channel strategy.
Given the similarities between the financial and healthcare industries (stringent regulations, process-based legacy systems and so on) Fintech organisations will teach Healthtech organisations how to disrupt the industry. Like Fintech, Healthtech play a greater role in inclusion – ensuring health and wellness for all, including universal health coverage. As the industry focuses on value-based outcomes, governments introduce more regulations around accountability and transparency, and people expect the CX that they get out of their retail interactions, Healthtech start-ups will become as mainstream as Fintech start-ups.
-
Healthcare Providers Will Jump on the Innovation Bandwagon
Traditionally, healthcare providers have lagged behind payer and life sciences organisations when it comes to innovation. However, that is changing fast as several provider organisations now have innovation centres, where ideas on how to improve operational parameters and clinical outcomes are incubated. They are also being creative when it comes to getting funds for these programs.
Incorporating the newest scientific advances into care protocol is largely driven by finances. But technology disrupters such as IoT, AI and machine learning are being incorporated with Operations as the key area of focus. As provider organisations increase their customer-focus, CX initiatives such as access to records, reducing waiting periods, streamlining billing and so on, will be addressed in several organisations. Innovative payment solutions (involving both patients and insurance providers) may well be the low-hanging fruit for innovators as they have the potential to significantly improve both revenue cycle management and CX.
-
Data Will Cause the Next Healthcare Divide
There has always been a divide in healthcare – based on economic and geographic parameters. A new divide will open up based on how organisations are able to leverage the huge amount of data that they are sitting on. How they leverage the data will impact an organisation’s ability to improve patient loyalty and to gain an edge over their competition.
On the one hand, governments are encouraging the three main branches of the healthcare industry that have depended on each other but worked in silos, to be more collaborative and share data. On the other hand, if we ask healthcare organisations about their biggest challenge in implementing emerging technologies such as AI, they will cite lack of data access. Organisations must also bear in mind that introducing tech innovations will be largely useless without changes in business processes that allow for these innovations, and without education and involvement of the entire organisation.
-
Life Sciences and Medical Devices Organisations Will be Forced to Rethink their R&D
The responsibility of cutting-edge research in Healthcare has always been on life sciences and medical devices organisations. Life sciences companies operate in an extremely competitive global market where they have to work on new products against a backdrop of competition from generics and a global concern over rising healthcare expenditure. Apart from regulatory challenges, medical devices manufacturers also face immense competition from local manufacturers as they enter each new market.
Sales and distribution for these organisations have been traditional – using agents, distributors, clinicians and healthcare providers. But now they need to change their go-to-market strategies, target patients and consumers directly and package their product offerings into value-added services. This will require them to incorporate CX enhancers in their R&D, going beyond drug discovery and product innovation.
Ecosystm in partnership with SGInnovate, the government-backed organisation that promotes Deep Tech in Singapore, released a series of four reports covering areas of mutual interest: Cybersecurity, Artificial Intelligence, Cities of the Future and Healthtech. ‘Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Cities of the Future Trends for 2020’ report is a part of this collaboration and is available for download from Ecosystm and SGInnovate websites.