2024 will be another crucial year for tech leaders – through the continuing economic uncertainties, they will have to embrace transformative technologies and keep an eye on market disruptors such as infrastructure providers and AI startups. Ecosystm analysts outline the key considerations for leaders shaping their organisations’ tech landscape in 2024.
Navigating Market Dynamics

Continuing Economic Uncertainties. Organisations will focus on ongoing projects and consider expanding initiatives in the latter part of the year.
Popularity of Generative AI. This will be the time to go beyond the novelty factor and assess practical business outcomes, allied costs, and change management.
Infrastructure Market Disruption. Keeping an eye out for advancements and disruptions in the market (likely to originate from the semiconductor sector) will define vendor conversations.
Need for New Tech Skills. Generative AI will influence multiple tech roles, including AIOps and IT Architecture. Retaining talent will depend on upskilling and reskilling.
Increased Focus on Governance. Tech vendors are guide tech leaders on how to implement safeguards for data usage, sharing, and cybersecurity.
5 Key Considerations for Tech Leaders
#1 Accelerate and Adapt: Streamline IT with a DevOps Culture
Over the next 12-18 months, advancements in AI, machine learning, automation, and cloud-native technologies will be vital in leveraging scalability and efficiency. Modernisation is imperative to boost responsiveness, efficiency, and competitiveness in today’s dynamic business landscape.
The continued pace of disruption demands that organisations modernise their applications portfolios with agility and purpose. Legacy systems constrained by technical debt drag down velocity, impairing the ability to deliver new innovative offerings and experiences customers have grown to expect.
Prioritising modernisation initiatives that align with key value drivers is critical. Technology leaders should empower development teams to move beyond outdated constraints and swiftly deploy enhanced applications, microservices, and platforms.

#2 Empowering Tomorrow: Spring Clean Your Tech Legacy for New Leaders
Modernising legacy systems is a strategic and inter-generational shift that goes beyond simple technical upgrades. It requires transformation through the process of decomposing and replatforming systems – developed by previous generations – into contemporary services and signifies a fundamental realignment of your business with the evolving digital landscape of the 21st century.
The essence of this modernisation effort is multifaceted. It not only facilitates the integration of advanced technologies but also significantly enhances business agility and drives innovation. It is an approach that prepares your organisation for impending skill gaps, particularly as the older workforce begins to retire over the next decade. Additionally, it provides a valuable opportunity to thoroughly document, reevaluate, and improve business processes. This ensures that operations are not only efficient but also aligned with current market demands, contemporary regulatory standards, and the changing expectations of customers.

#3 Employee Retention: Consider the Strategic Role of Skills Acquisition
The agile, resilient organisation needs to be able to respond at pace to any threat or opportunity it faces. Some of this ability to respond will be related to technology platforms and architectures, but it will be the skills of employees that will dictate the pace of reform. While employee attrition rates will continue to decline in 2024 – but it will be driven by skills acquisition, not location of work.
Organisations who offer ongoing staff training – recognising that their business needs new skills to become a 21st century organisation – are the ones who will see increasing rates of employee retention and happier employees. They will also be the ones who offer better customer experiences, driven by motivated employees who are committed to their personal success, knowing that the organisation values their performance and achievements.

#4 Next-Gen IT Operations: Explore Gen AI for Incident Avoidance and Predictive Analysis
The integration of Generative AI in IT Operations signifies a transformative shift from the automation of basic tasks, to advanced functions like incident avoidance and predictive analysis. Initially automating routine tasks, Generative AI has evolved to proactively avoiding incidents by analysing historical data and current metrics. This shift from proactive to reactive management will be crucial for maintaining uninterrupted business operations and enhancing application reliability.
Predictive analysis provides insight into system performance and user interaction patterns, empowering IT teams to optimise applications pre-emptively, enhancing efficiency and user experience. This also helps organisations meet sustainability goals through accurate capacity planning and resource allocation, also ensuring effective scaling of business applications to meet demands.

#5 Expanding Possibilities: Incorporate AI Startups into Your Portfolio
While many of the AI startups have been around for over five years, this will be the year they come into your consciousness and emerge as legitimate solutions providers to your organisation. And it comes at a difficult time for you!
Most tech leaders are looking to reduce technical debt – looking to consolidate their suppliers and simplify their tech architecture. Considering AI startups will mean a shift back to more rather than fewer tech suppliers; a different sourcing strategy; more focus on integration and ongoing management of the solutions; and a more complex tech architecture.
To meet business requirements will mean that business cases will need to be watertight – often the value will need to be delivered before a contract has been signed.


While the discussions have centred around AI, particularly Generative AI in 2023, the influence of AI innovations is extensive. Organisations will urgently need to re-examine their risk strategies, particularly in cyber and resilience practices. They will also reassess their infrastructure needs, optimise applications for AI, and re-evaluate their skills requirements.
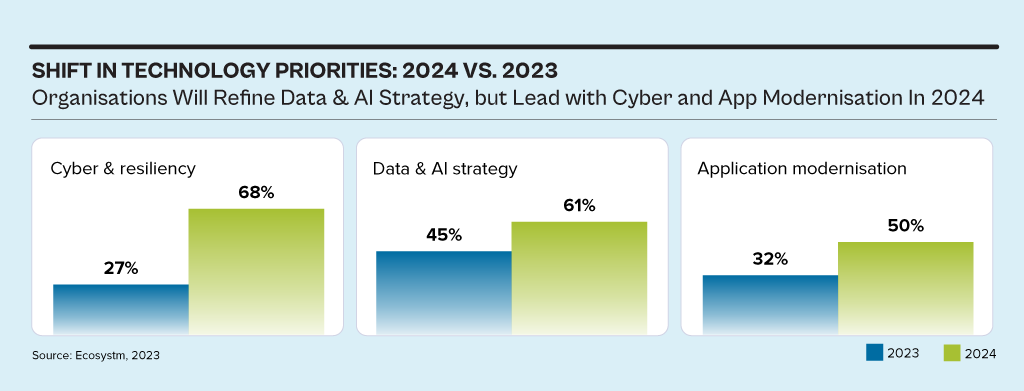
This impacts the entire tech market, including tech skills, market opportunities, and innovations.
Ecosystm analysts Alea Fairchild, Darian Bird, Richard Wilkins, and Tim Sheedy present the top 5 trends in building an Agile & Resilient Organisation in 2024.
Click here to download ‘Ecosystm Predicts: Top 5 Resilience Trends in 2024’ as a PDF.
#1 Gen AI Will See Spike in Infrastructure Innovation
Enterprises considering the adoption of Generative AI are evaluating cloud-based solutions versus on-premises solutions. Cloud-based options present an advantage in terms of simplified integration, but raise concerns over the management of training data, potentially resulting in AI-generated hallucinations. On-premises alternatives offer enhanced control and data security but encounter obstacles due to the unexpectedly high demands of GPU computing needed for inferencing, impeding widespread implementation. To overcome this, there’s a need for hardware innovation to meet Generative AI demands, ensuring scalable on-premises deployments.
The collaboration between hardware development and AI innovation is crucial to unleash the full potential of Generative AI and drive enterprise adoption in the AI ecosystem.
Striking the right balance between cloud-based flexibility and on-premises control is pivotal, with considerations like data control, privacy, scalability, compliance, and operational requirements.

#2 Cloud Migrations Will Make Way for Cloud Transformations
The steady move to the public cloud has slowed down. Organisations – particularly those in mature economies – now prioritise cloud efficiencies, having largely completed most of their application migration. The “easy” workloads have moved to the cloud – either through lift-and-shift, SaaS, or simple replatforming.
New skills will be needed as organisations adopt public and hybrid cloud for their entire application and workload portfolio.
- Cloud-native development frameworks like Spring Boot and ASP.NET Core make it easier to develop cloud-native applications
- Cloud-native databases like MongoDB and Cassandra are designed for the cloud and offer scalability, performance, and reliability
- Cloud-native storage like Snowflake, Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Storage provides secure and scalable storage
- Cloud-native messaging like Amazon SNS and Google Cloud Pub/Sub provide reliable and scalable communication between different parts of the cloud-native application

#3 2024 Will be a Good Year for Technology Services Providers
Several changes are set to fuel the growth of tech services providers (systems integrators, consultants, and managed services providers).
There will be a return of “big apps” projects in 2024.
Companies are embarking on significant updates for their SAP, Oracle, and other large ERP, CRM, SCM, and HRM platforms. Whether moving to the cloud or staying on-premises, these upgrades will generate substantial activity for tech services providers.
The migration of complex apps to the cloud involves significant refactoring and rearchitecting, presenting substantial opportunities for managed services providers to transform and modernise these applications beyond traditional “lift-and-shift” activities.
The dynamic tech landscape, marked by AI growth, evolving security threats, and constant releases of new cloud services, has led to a shortage of modern tech skills. Despite a more relaxed job market, organisations will increasingly turn to their tech services partners, whether onshore or offshore, to fill crucial skill gaps.

#4 Gen AI and Maturing Deepfakes Will Democratise Phishing
As with any emerging technology, malicious actors will be among the fastest to exploit Generative AI for their own purposes. The most immediate application will be employing widely available LLMs to generate convincing text and images for their phishing schemes. For many potential victims, misspellings and strangely worded appeals are the only hints that an email from their bank, courier, or colleague is not what it seems. The ability to create professional-sounding prose in any language and a variety of tones will unfortunately democratise phishing.
The emergence of Generative AI combined with the maturing of deepfake technology will make it possible for malicious agents to create personalised voice and video attacks. Digital channels for communication and entertainment will be stretched to differentiate between real and fake.
Security training that underscores the threat of more polished and personalised phishing is a must.

#5 A Holistic Approach to Risk and Operational Resilience Will Drive Adoption of VMaaS
Vulnerability management is a continuous, proactive approach to managing system security. It not only involves vulnerability assessments but also includes developing and implementing strategies to address these vulnerabilities. This is where Vulnerability Management Platforms (VMPs) become table stakes for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) as they are often perceived as “easier targets” by cybercriminals due to potentially lesser investments in security measures.
Vulnerability Management as a Service (VMaaS) – a third-party service that manages and controls threats to automate vulnerability response to remediate faster – can improve the asset cybersecurity management and let SMEs focus on their core activities.
In-house security teams will particularly value the flexibility and customisation of dashboards and reports that give them enhanced visibility over all assets and vulnerabilities.


The Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) industry, known for its cautious stance on technology, is swiftly undergoing a transformational modernisation journey. Areas such as digital customer experiences, automated fraud detection, and real-time risk assessment are all part of a technology-led roadmap. This shift is transforming the cybersecurity stance of BFSI organisations, which have conventionally favoured centralising everything within a data centre behind a firewall.
Ecosystm research finds that 75% of BFSI technology leaders believe that a data breach is inevitable. This requires taking a new cyber approach to detect threats early, reduce the impact of an attack, and avoid lateral movement across the network.
BFSI organisations will boost investments in two main areas over the next year: updating infrastructure and software, and exploring innovative domains like digital workplaces and automation. Cybersecurity investments are crucial in both of these areas.
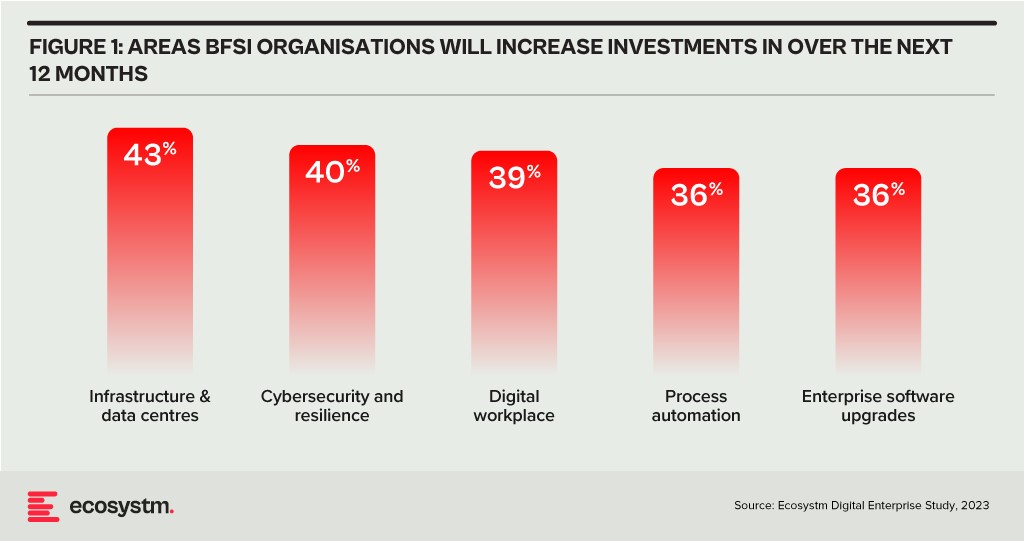
As a regulated industry, breaches come with significant cost implications, underscoring the need to prioritise cybersecurity. BFSI cybersecurity and risk teams need to constantly reassess their strategies for safeguarding data and fulfilling compliance obligations, as they explore ways to facilitate new services for customers, partners, and employees.
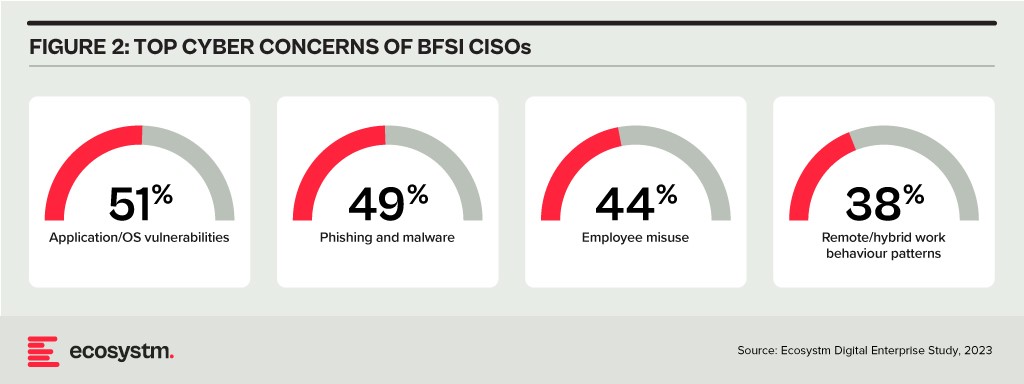
The primary concerns of BFSI CISOs can be categorised into two distinct groups:
- Expanding Technology Use. This includes the proliferation of applications and devices, as well as data access beyond the network perimeter.
- Employee-Related Vulnerabilities. This involves responses to phishing and malware attempts, as well as intentional and unintentional misuse of technology.
Vulnerabilities Arising from Employee Actions
Security vulnerabilities arising from employee actions and unawareness represent a significant and ongoing concern for businesses of all sizes and industries – the risks are just much bigger for BFSI. These vulnerabilities can lead to data breaches, financial losses, damage to reputation, and legal ramifications. A multi-pronged approach is needed that combines technology, training, policies, and a culture of security consciousness.
Training and Culture. BFSI organisations prioritise comprehensive training and awareness programs, educating employees about common threats like phishing and best practices for safeguarding sensitive data. While these programs are often ongoing and adaptable to new threats, they can sometimes become mere compliance checklists, raising questions about their true effectiveness. Conducting simulated phishing attacks and security quizzes to assess employee awareness and identify areas where further training is required, can be effective.
To truly educate employees on risks, it’s essential to move beyond compliance and build a cybersecurity culture throughout the organisation. This can involve setting organisation-wide security KPIs that cascade from the CEO down to every employee, promoting accountability and transparency. Creating an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting security concerns is critical for early threat detection and mitigation.
Policies. Clear security policies and enforcement are essential for ensuring that employees understand their roles within the broader security framework, including responsibilities on strong password use, secure data handling, and prompt incident reporting. Implementing the principle of least privilege, which restricts access based on specific roles, mitigates potential harm from insider threats and inadvertent data exposure. Policies should evolve through routine security audits, including technical assessments and evaluations of employee protocol adherence, which will help organisations with a swifter identification of vulnerabilities and to take the necessary corrective actions.
However, despite the best efforts, breaches do happen – and this is where a well-defined incident response plan, that is regularly tested and updated, is crucial to minimise the damage. This requires every employee to know their roles and responsibilities during a security incident.
Tech Expansion Leading to Cyber Complexity
Cloud. Initially hesitant to transition essential workloads to the cloud, the BFSI industry has experienced a shift in perspective due to the rise of inventive SaaS-based Fintech tools and hybrid cloud solutions, that have created new impetus for change. This new distributed architecture requires a fresh look at cyber measures. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) providers are integrating a range of cloud-delivered safeguards, such as FWaaS, CASB, and ZTNA with SD-WAN to ensure organisations can securely access the cloud without compromising on performance.
Data & AI. Data holds paramount importance in the BFSI industry for informed decision-making, personalised customer experiences, risk assessment, fraud prevention, and regulatory compliance. AI applications are being used to tailor products and services, optimise operational efficiency, and stay competitive in an evolving market. As part of their technology modernisation efforts, 47% of BFSI institutions are refining their data and AI strategies. They also acknowledge the challenges associated – and satisfying risk, regulatory, and compliance requirements is one of the biggest challenges facing BFSI organisations in the AI deployments.
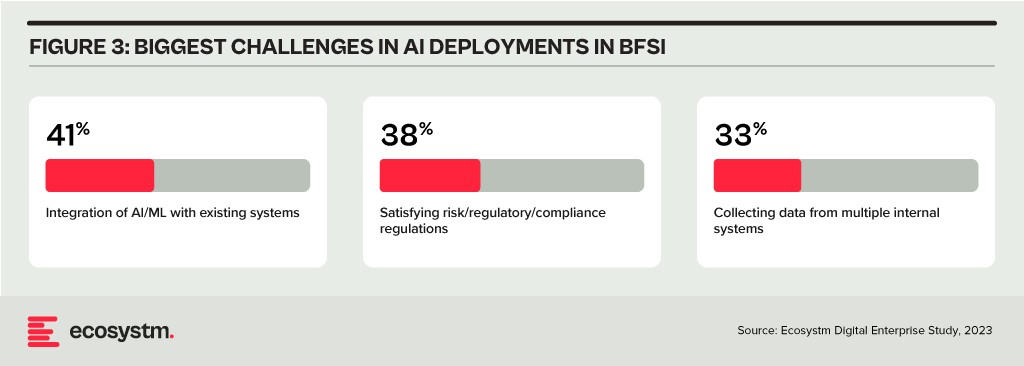
The rush to experiment with Generative AI and foundation models to assist customers and employees is only heightening these concerns. There is an urgent need for policies around the use of these emerging technologies. Initiatives such as the Monetary Authority of Singapore’s Veritas that aim to enable financial institutions to evaluate their AI and data analytics solutions against the principles of fairness, ethics, accountability, and transparency (FEAT) are expected to provide the much-needed guidance to the industry.
Digital Workplace. As with other industries with a high percentage of knowledge workers, BFSI organisations are grappling with granting remote access to staff. Cloud-based collaboration and Fintech tools, BYOD policies, and sensitive data traversing home networks are all creating new challenges for cyber teams. Modern approaches, such as zero trust network access, privilege management, and network segmentation are necessary to ensure workers can seamlessly but securely perform their roles remotely.

Looking Beyond Technology: Evaluating the Adequacy of Compliance-Centric Cyber Strategies
The BFSI industry stands among the most rigorously regulated industries, with scrutiny intensifying following every collapse or notable breach. Cyber and data protection teams shoulder the responsibility of understanding the implications of and adhering to emerging data protection regulations in areas such as GDPR, PCI-DSS, SOC 2, and PSD2. Automating compliance procedures emerges as a compelling solution to streamline processes, mitigate risks, and curtail expenses. Technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA), low-code development, and continuous compliance monitoring are gaining prominence.
The adoption of AI to enhance security is still emerging but will accelerate rapidly. Ecosystm research shows that within the next two years, nearly 70% of BFSI organisations will have invested in SecOps. AI can help Security Operations Centres (SOCs) prioritise alerts and respond to threats faster than could be performed manually. Additionally, the expanding variety of network endpoints, including customer devices, ATMs, and tools used by frontline employees, can embrace AI-enhanced protection without introducing additional onboarding friction.
However, there is a need for BFSI organisations to look beyond compliance checklists to a more holistic cyber approach that can prioritise cyber measures continually based on the risk to the organisations. And this is one of the biggest challenges that BFSI CISOs face. Ecosystm research finds that 72% of cyber and technology leaders in the industry feel that there is limited understanding of cyber risk and governance in their organisations.
In fact, BFSI organisations must look at the interconnectedness of an intelligence-led and risk-based strategy. Thorough risk assessments let organisations prioritise vulnerability mitigation effectively. This targeted approach optimises security initiatives by focusing on high-risk areas, reducing security debt. To adapt to evolving threats, intelligence should inform risk assessment. Intelligence-led strategies empower cybersecurity leaders with real-time threat insights for proactive measures, actively tackling emerging threats and vulnerabilities – and definitely moving beyond compliance-focused strategies.

Traditional network architectures are inherently fragile, often relying on a single transport type to connect branches, production facilities, and data centres. The imperative for networks to maintain resilience has grown significantly, particularly due to the delivery of customer-facing services at branches and the increasing reliance on interconnected machines in operational environments. The cost of network downtime can now be quantified in terms of both lost customers and reduced production.
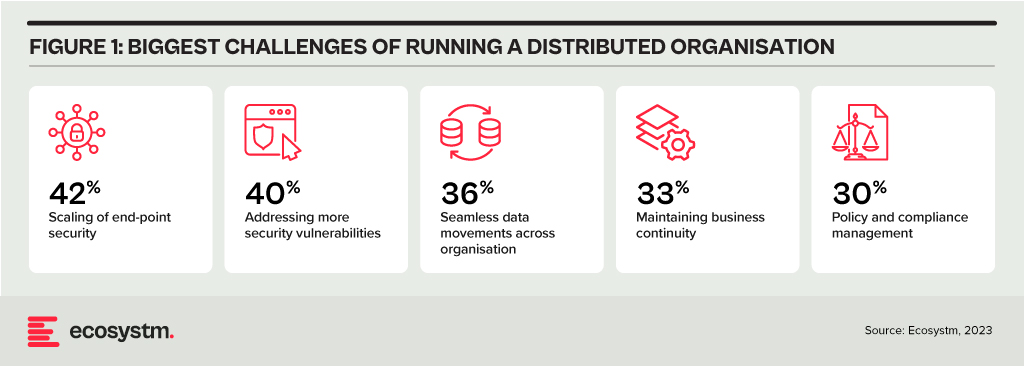
Distributed Enterprises Face New Challenges
As the importance of maintaining resiliency grows, so does the complexity of network management. Distributed enterprises must provide connectivity under challenging conditions, such as:
- Remote access for employees using video conferencing
- Local breakout for cloud services to avoid backhauling
- IoT devices left unattended in public places
- Customers accessing digital services at the branch or home
- Sites in remote areas requiring the same quality of service
Network managers require intelligent tools to remain in control without adding any unnecessary burden to end users. The number of endpoints and speed of change has made it impossible for human operators to manage without assistance from AI.
AI-Enhanced Network Management
Modern network operations centres are enhancing their visibility by aggregating data from diverse systems and consolidating them within a unified management platform. Machine learning (ML) and AI are employed to analyse data originating from enterprise networks, telecom Points of Presence (PoPs), IoT devices, cloud service providers, and user experience monitoring. These technologies enable the early identification of network issues before they reach critical levels. Intelligent networks can suggest strategies to enhance network resilience, forecast how modifications may impact performance, and are increasingly capable of autonomous responses to evolving conditions.
Here are some critical ways that AI/ML can help build resilient networks.
- Alert Noise Reduction. Network operations centres face thousands of alerts each day. As a result, operators battle with alert fatigue and are challenged to identify critical issues. Through the application of ML, contemporary monitoring tools can mitigate false positives, categorise interconnected alerts, and assist operators in prioritising the most pressing concerns. An operations team, augmented with AI capabilities could potentially de-prioritise up to 90% of alerts, allowing a concentrated focus on factors that impact network performance and resilience.
- Data Lakes. Networking vendors are building their own proprietary data lakes built upon telemetry data generated by the infrastructure they have deployed at customer sites. This vast volume of data allows them to use ML to create a tailored baseline for each customer and to recommend actions to optimise the environment.
- Root Cause Analysis. To assist network operators in diagnosing an issue, AIOps can sift through thousands of data points and correlate them to identify a root cause. Through the integration of alerts with change feeds, operators can understand the underlying causes of network problems or outages. By using ML to understand the customer’s unique environment, AIOps can progressively accelerate time to resolution.
- Proactive Response. As management layers become capable of recommending corrective action, proactive response also becomes possible, leading to self-healing networks. With early identification of sub-optimal conditions, intelligent systems can conduct load balancing, redirect traffic to higher performing SaaS regions, auto-scale cloud instances, or terminate selected connections.
- Device Profiling. In a BYOD environment, network managers require enhanced visibility to discover devices and enforce appropriate policies on them. Automated profiling against a validated database ensures guest access can be granted without adding friction to the onboarding process. With deep packet inspection, devices can be precisely classified based on behaviour patterns.
- Dynamic Bandwidth Aggregation. A key feature of an SD-WAN is that it can incorporate diverse transport types, such as fibre, 5G, and low earth orbit (LEO) satellite connectivity. Rather than using a simple primary and redundant architecture, bandwidth aggregation allows all circuits to be used simultaneously. By infusing intelligence into the SD-WAN layer, the process of path selection can dynamically prioritise traffic by directing it over higher quality or across multiple links. This approach guarantees optimal performance, even in the face of network degradation.
- Generative AI for Process Efficiency. Every tech company is trying to understand how they can leverage the power of Generative AI, and networking providers are no different. The most immediate use case will be to improve satisfaction and scalability for level 1 and level 2 support. A Generative AI-enabled service desk could provide uninterrupted support during high-volume periods, such as during network outages, or during off-peak hours.
Initiating an AI-Driven Network Management Journey
Network managers who take advantage of AI can build highly resilient networks that maximise uptime, deliver consistently high performance, and remain secure. Some important considerations when getting started include:
- Data Catalogue. Take stock of the data sources that are available to you, whether they come from network equipment telemetry, applications, or the data lake of a managed services provider. Understand how they can be integrated into an AIOps solution.
- Start Small. Begin with a pilot in an area where good data sources are available. This will help you assess the impact that AI could have on reducing alerts, improving mean time to repair (MTTR), increasing uptime, or addressing the skills gap.
- Develop an SD-WAN/SASE Roadmap. Many advanced AI benefits are built into an SD-WAN or SASE. Most organisations already have or will soon adopt SD-WAN but begin assessing the SASE framework to decide if it is suitable for your organisation.

Cyber threats are growing in volume, intensity, and complexity and are here to stay. Basic endpoint attacks are becoming intricate, multi-stage operations. Cybercriminals are launching highly coordinated and advanced attacks. This evolving threat landscape affects businesses of all sizes, jeopardising data, operations, and finances.
In the face of massive data leaks, costly ransomware payments, and an ever-expanding and complex threat landscape, the need to strengthen digital defences has driven significant advancements in cybersecurity.
Read on to find out how organisations, governments, industry associations and technology providers are evolving ways to combat cybercrime.
Download ‘Securing the Future: Cyber Resiliency in the Digital World’ as a PDF

Organisations in Asia Pacific are no longer only focused on employing a cloud-first strategy – they want to host the infrastructure and workloads where it makes the most sense; and expect a seamless integration across multiple cloud environments.
While cloud can provide the agile infrastructure that underpins application modernisation, innovative leaders recognise that it is only the first step on the path towards developing AI-powered organisations. The true value of cloud is in the data layer, unifying data around the network, making it securely available wherever it is needed, and infusing AI throughout the organisation.
Cloud provides a dynamic and powerful platform on which organisations can build AI. Pre-trained foundational models, pay-as-you-go graphics superclusters, and automated ML tools for citizen data scientists are now all accessible from the cloud even to start-ups.
Organisations should assess the data and AI capabilities of their cloud providers rather than just considering it an infrastructure replacement. Cloud providers should use native services or integrations to manage the data lifecycle from labelling to model development, and deployment.
In this Ecosystm Byte, sponsored by Oracle, Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Darian Bird presents the top 5 trends for Cloud in 2023 and beyond. Read on to find out more.
Download ‘The Top 5 Cloud Trends for 2023 & Beyond’ as a PDF


















































