Southeast Asia has evolved into an innovation hub with Singapore at the centre. The entrepreneurial and startup ecosystem has grown significantly across the region – for example, Indonesia now has the 5th largest number of startups in the world.
Organisations in the region are demonstrating a strong desire for tech-led innovation, innovation in experience delivery, and in evolving their business models to bring innovative products and services to market.
Here are 5 insights on the patterns of technology adoption in Southeast Asia, based on the findings of the Ecosystm Digital Enterprise Study, 2022.
- Data and AI investments are closely linked to business outcomes. There is a clear alignment between technology and business.
- Technology teams want better control of their infrastructure. Technology modernisation also focuses on data centre consolidation and cloud strategy
- Organisations are opting for a hybrid multicloud approach. They are not necessarily doing away with a ‘cloud first’ approach – but they have become more agnostic to where data is hosted.
- Cybersecurity underpins tech investments. Many organisations in the region do not have the maturity to handle the evolving threat landscape – and they are aware of it.
- Sustainability is an emerging focus area. While more effort needs to go in to formalise these initiatives, organisations are responding to market drivers.
More insights into the Southeast Asia tech market below.
Click here to download The Future of the Digital Enterprise – Southeast Asia as a PDF

The semiconductor industry is 70-years old and has a prominent – and sometimes inconspicuous – presence in our daily lives. Many of us, however, have become more aware of the industry and the ramifications of its disruption, because of recent events. The pandemic, natural disasters, power outages, geo-political conflicts, and accelerated digital transformation have all combined to disrupt the semiconductor sector, leaving no organisation immune to the impacts of the continuing global chip crisis.
It is estimated that 200 downstream industries have failed to fulfill customer demands owing to the silicon scarcity, ranging from automotive, consumer electronics, utilities and even the supply of light fixtures.
This Ecosystm Bytes discusses the impact of the crisis and highlights major initiatives that chip manufacturers and governments are taking to combat it, including:
- The factors leading to the shortage in the semiconductor industry
- The impact on industry sectors such as Automotive, Consumer Electronics and MedTech
- How leading chip makers such as TSMC, Intel and Samsung are increasing their manufacturing capabilities
- The importance of Asia to the semiconductor industry
- How countries such as Malaysia and India are aiming to build self-sufficiency in the industry
Read on to find out more.

Never before has the world experienced a shutdown in both supply and demand which has effectively slammed the brakes on economic activities and forced a complete rethink on how to continue doing business and maintain social interactions. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated digitalisation of consumers and enterprises and the telecommunications industry has been the pillar which has kept the world ticking over.
It is unthinkable just how the human race would have coped with such massive disruption, two decades ago in the absence of broadband internet. The technology and telecom sector has seen a rise in their visible importance in recent months. Various findings show that peak level traffic was about 20-30% higher than the levels before the pandemic. The rise in traffic coupled with the fervent growth of the digital economy augurs well for the technology and telecom sector in Southeast Asia.
Revenues Hit Despite Rise in Traffic
Unfortunately, the rise in network traffic has not translated to an increase in revenue for many operators in the region. The winners, that enjoyed YoY growth in Q1 2020 despite challenging circumstances were: Maxis (4.9%) and DiGi (3.4%) in Malaysia; dtac (3.3%) and True (5.7%) in Thailand; PDLT (7.5%) and Globe (1.4%) in the Philippines; and Indosat Ooredoo (7.9%) and XL Axiata (8.8%) in Indonesia. The telecom operators that struggled include: Celcom (-6.1%) and TM (-8.0%) in Malaysia; Singapore’s trio of Singtel (-6.5%), StarHub (-15.2%) and M1 (-10.3%); and AIS (-1.0%) in Thailand.
Key market trends include a dip in prepaid subscribers due to fall in tourist numbers, roaming income losses due to travel restrictions, and a general decline in average revenue per user (ARPU) due to weaker customer spend. The postpaid customer segment was resilient while the fixed broadband revenue stream was stable due to the increase in work from home (WFH) practices. With fixed tariffs, there are no incremental gains with an increase in usage. Voice revenue has been hit with the increase in collaboration-based communication applications such as Zoom and Microsoft Teams.
Equipment sales fell as global supply chains were severely disrupted and impacted new sign-ups of the more premium customers. Most markets in Southeast Asia depend on retail outlets as a key channel to the market, which has been hampered.
With the job losses across the world, bad debts and weakened customer spend is inevitable and it is imperative that the operators provide for reflective pricing strategies, listen to new customer requirements to ensure customer retention and strengthening of their market position. In May, Verizon’s CEO Hans Vestberg said nearly 800,000 of their subscribers were unable to pay their monthly bills. Discussions with operators in Southeast Asia also highlighted this as a current concern.
Enterprise Segment Target for New Growth
Ecosystm research shows that enterprises in Southeast Asia are increasingly considering telecom operators as go-to-market partners (Figure 1). Enterprises are demanding more than just devices and connectivity and with the fervent digital transformation (DX) efforts underway, services such as managed services, business application services, cybersecurity and network services are in demand. Technology vendors have an opportunity to partner with the right telecom operator in each market to enhance their IT market offerings, ahead of the 5G rollouts.
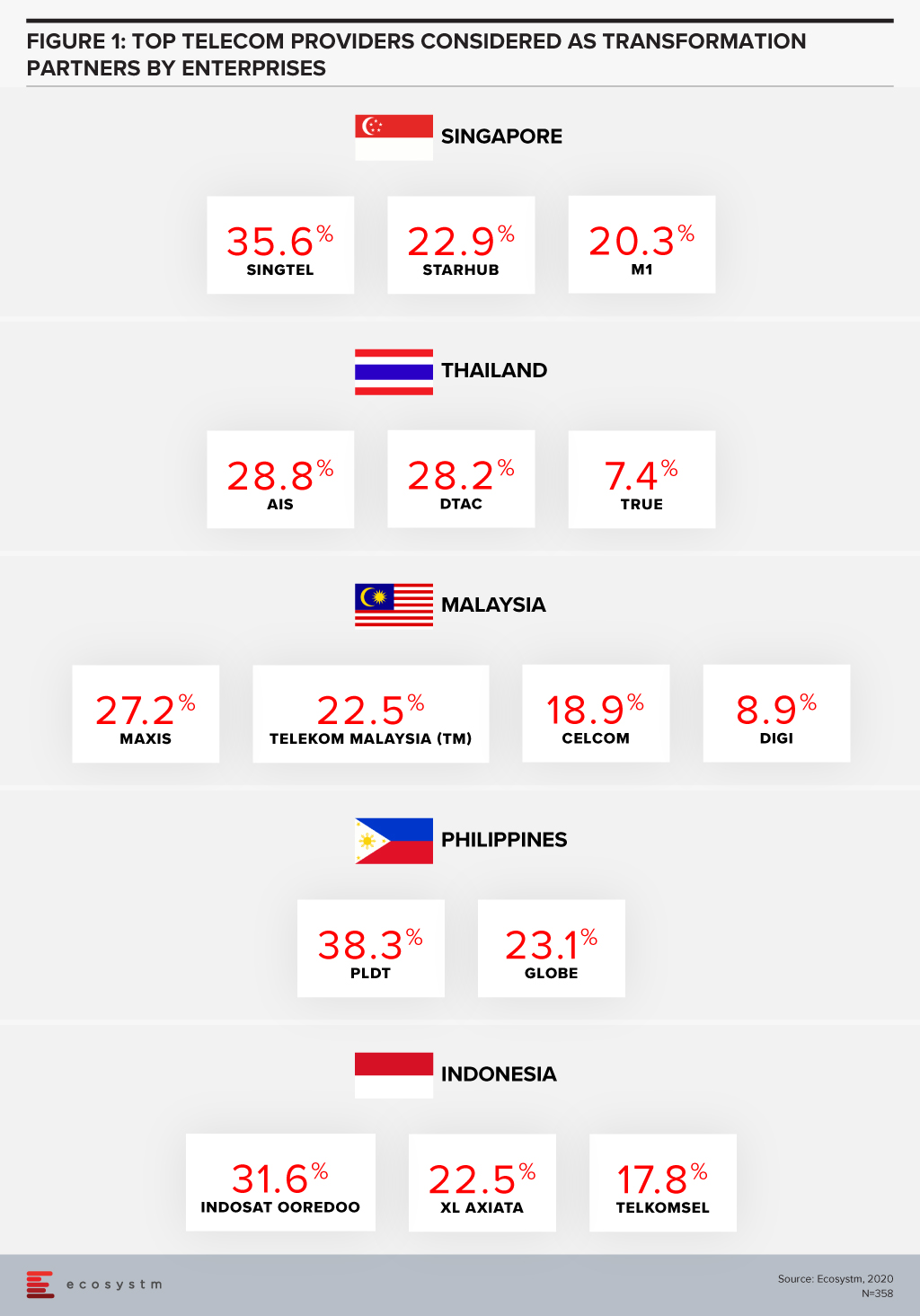
The broad 5G ecosystem inculcates cross-sector innovation and greater collaboration leading to new business models and exciting new opportunities. Singtel is the leading operator in the region and has the enterprise segment contributing approximately 65% to its revenue in its domestic market. In the World Communications Award 2019, Singtel won both “Best Enterprise Service” and “The Broadband Pioneer” awards. This places Singtel in a fine position to capitalise on the 5G enterprise services.
5G Needed Now More Than Ever
The pandemic has seen a rise in network traffic, onboarding of the digital customer and rapid DX of businesses which has whetted the appetite for faster broadband speeds and new services. Southeast Asia countries stand to profit from the trade war between the US and China and 5G features of low latency and higher security can boost adoption of IoT, Smart Manufacturing and broader Industry 4.0 goals to drive the economy.
Fixed Wireless in Southeast Asia is expected to be very popular considering the low penetration of fibre to the home (with the exception of Singapore) and will provide enterprises with a viable secondary connection to the internet. Popular applications – including video streaming and gaming – which are speed, latency and volume hungry will also be a target market for operators. Mobile operators that do not have a fixed broadband offering can enter this space and provide a serious “wireless fibre” alternative to homes and businesses.
Governments and telecom regulators ought to make spectrum available to the major telecom operators as soon as possible in order to ensure that the cutting edge 5G communications services are made available to consumers and businesses. Many experts believe 5G can raise the competitiveness of a nation.
Recent research from World Economic Forum (WEF) has found that significant economic and social value can be gained from the widespread deployment of 5G networks, with 5G facilitating industrial advances, productivity and improving the bottom line while enabling sustainable cities and communities. GSMA notes that mobile technologies and services in the wider Asia Pacific region generated USD 1.6 trillion of economic value while the mobile ecosystem supported 18 million jobs as well as contributing USD 180 billion of funding to the public sector through taxation.
US-China Trade War Threatens to Change Equipment Supplier Landscape
Despite severe pressures caused by the US-China trade war, Huawei posted an impressive 13.1% YoY growth in 1H 2020 registering revenue of USD 64.88 billion. Both Huawei and ZTE generate approximately 60% of their business from their domestic markets which is critical with the current unfavourable global sentiments. Huawei has diversified its business and built its consumer devices business which should withstand the disruptions caused by the political challenges.
Ericsson and Nokia stand to benefit from Huawei’s current global position and this was evident with the wins for the 5G contracts by Singtel and JVCo (Singtel and M1). The JVCo announced it selected Nokia to build the Radio Access Network (RAN) for the 5G standalone (SA) mmWave network infrastructure in the 3.5GHz radio frequency band. Singtel selected Ericsson to provide for the RAN on the same mmWave network.
However, while there is an opportunity for NEC and Samsung to join the party, Huawei is expected to do well in most other countries in Southeast Asia.
The Rise of the Digital Economy in Southeast Asia
A recent Google report valued the internet economy in Southeast Asia at USD 100 billion in 2019, more than tripling since 2015, and the sector is expected to hit USD 300 billion in 2025. With a population of approximately 570 million people, the region has some of the fastest-growing internet economies in the world.
The Indonesia market is the largest in the region and is expected to hit USD 133 billion from USD 40 billion in 2025. Indonesia’s lack of a world-class telecom infrastructure coupled with their slowness in 5G adoption has not impeded the country’s attractiveness for global technology investors who see the 270 million population as an immense opportunity. US tech giants, Facebook, Google, and PayPal have invested in Indonesia to reap the benefits from the growing digital economy powered by unicorns such as Gojek, Bukalapak, Tokopedia. In June 2020, Google Cloud launched in Jakarta, only the second in the region after Singapore with the four big unicorns being anchor customers.
In 2025, Google predicts Thailand to be the second-largest internet economy worth USD 50 billion. The internet economy for Singapore, Malaysia and the Philippines are estimated to be over USD 27 billion each. Shopee and Lazada are the top eCommerce apps in the region and have seen an increase in sales due to the disruption in the Retail industry. In-store shopping contributes to more than 50% of Retail in Singapore and Malaysia – this provides a tremendous opportunity for eCommerce players.
While movement restrictions are gradually being lifted, some things may never return where they were before COVID-19. Public debts have risen with numerous aids and handouts impacting economic growth forecast and rising unemployment is impacting customer spending power. On the plus side, DX of businesses and sharp onboarding of customers have redefined interactions, and sectors such as Education, are going online which will boost the digital economy. While the challenges are evident, exciting times are ahead for the technology and telecom sector in Southeast Asia.

In the blog, The Top 5 Fintech Trends for 2020, we had spoken about the impact of Fintech on financial inclusion. “Fintech will have a much greater impact than we realise, and we will continue to see it drive the induction of the unbanked into the mainstream economy. The growth in mobile phone penetration, however, continues to grow at a faster pace than banking accessibility across emerging economies. We will continue to see Fintech play a significant role in driving greater inclusion, especially to bring in the underserved in the emerging economies and reducing the gender gap when it comes to adoption of financial services – creating greater inclusion overall.”
Fintech Driving Financial Inclusion in Malaysia
Much of Malaysia’s economy is dependent on foreign workers with an estimate of 3-4 million migrants that roughly contribute to about 30% of the country’s labour force. Instapay, regulated by the Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM), caters to the underbanked community of foreign migrant workers, and recently announced a collaboration with Mastercard, to provide e-wallet accounts to Malaysian migrant workers. The app supports 9 languages and aims to have 100,000 users in the first year.
The widespread use of e-wallets by the migrant worker community is meant to bring benefits to both them, as well as their employers. It enables employers to use digital technologies for payroll management, reducing their dependence on cash handling, reducing costs and eliminating downtime as their employees no longer need to queue up on paydays.
The Instapay e-wallet also gives a largely underbanked segment of the society access to affordable financial products and services. The partnership with Mastercard gives Instapay’s customers access to the global network of merchants and ATMs, allowing easier access to financial services.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Dheeraj Chowdhry says, “Instapay’s foray into e-wallets furthers and supports the country’s objective of democratising banking and moving to a cashless economy. Collaboration with an international player like Mastercard helps a domestic Fintech to deliver a product that is country agnostic. The migrant worker can not only use the Instapay wallet within Malaysia but also in their home country.”
Malaysia’s Focus on Fintech
The Malaysia Government aims to create a cashless society, lower transaction costs and provide access to the underserved customers. There are two kinds of financial inclusion – for the lower income group as well as for the small and medium enterprises (SMEs) – and Malaysia is committed to both. Digital payments and e-wallets aimed at the lower income group receives an estimated 36% of Fintech funding. The stumbling block is that about a third of the country’s population does not have smartphones, so funds transfer using mobile phone messages is still relevant in the country. Development of the SME sector and eCommerce are twin focus areas for the Digital Economy vision. This provides a ready market for digital payments. Also, while the SME community will still have access to traditional funding, there is expected to be a greater push towards crowdfunding and peer-to-peer financing. It is expected that the share of Fintech funding for alternative funding will grow beyond the estimated 6% that it receives now.
According to a Mastercard Impact Study 2020, Malaysia has the highest e-wallet usage in Southeast Asia. As the country moves towards creating a cashless society, the Government is hoping e-wallet adoption increases. Several initiatives and schemes have been rolled out to promote e-wallets adoption. Last month, Malaysia announced the intention to spend an estimated USD 176 million in 2020 to encourage e-wallet adoption. Earlier this year, the Government announced the e-Tunai Rakyat program to boost the adoption of e-wallets, supported by Grab, Boost and Touch ‘n Go. Chowdhry says, “Instapay e-wallet is yet another manifestation of the amplified focus on e-wallets in Malaysia. BNM has set aside an estimated USD 108 million and has introduced a scheme to give USD $7.25 in credit for every adoption of any of the top 3 e-wallets. This scheme has accelerated e-wallets in the country that has set an adoption target of 15 million i.e. half of its population.”
“This push is backed by a structured approach of increasing the number of small merchants accepting card payments. With BNM’s focus, there are as many as half a million POS terminals out there for both credit cards and QR codes.”
“Malaysia’s regulators have to be applauded for having a well-coordinated, holistic and converging strategy on creating a cashless economy. The issuance, acceptance and regulatory policies have been completely synergised to deliver.”
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of the telecommunications industry which has now become the backbone of the new normal, both in a social and business sense. The last few months have seen a number of changes including more video usage, location of traffic and time of traffic. Network usage is on the rise and telecom carriers are prioritising on the resilience of their networks and the quality of services offered to their customers.
What goes up must come down
According to Speedtest, global mobile and broadband speeds have suffered as a result of the increase in traffic with speeds dropping in March 2020 for mobile to 30.47 Mbps (from 31.62 Mbps in February) and fixed broadband to 74.64 Mbps (from 75.41 Mbps in February). In Southeast Asia, only Singapore and Vietnam averaged mobile speeds of 54.37 Mbps and 33.97 Mbps respectively, exceeding the global average speeds. As for fixed broadband, Singapore ranked highest globally achieving 197.26 Mbps while Thailand and Malaysia clocked 149.95 Mbps and 79.86 Mbps respectively, trumping the global average speeds.
Southeast Asian carriers increase network efficiency and quality
Singapore. The country’s ICT regulator, Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA), reported an increase in internet usage and its intentions to support telecom carriers in boosting network capacity to ensure essential services run smoothly. Priority will be given to high traffic and residential areas where a larger proportion of the population are working from home. The Ministry of Communications and Information (MCI) reported that Singapore has at least 30 percent buffer in network capacity even during peak periods. Major TV operators Mediacorp, Singtel and Starhub have made more content available for free during this period. This may further impact network speeds as customers are consuming more content over wifi (on mobile apps) or over the fibre networks.
Thailand. Part of the country’s public assistance measures during the pandemic, include offering about 30 million mobile subscribers 10GB free data. The National Broadcasting and Telecommunications Commission (NBTC) will also upgrade the speeds of fixed broadband to at least 100 Mbps which is expected to benefit 1.2 million household subscribers. Leading operator Advanced Info Service (AIS) recently announced that it has deployed 5G networks at hospitals to boost network capacity and speeds, and is deploying robots for telemedicine to empower the healthcare system to fight COVID-19.
Malaysia. Maxis and Telekom Malaysia (TM) reported a surge in traffic since the movement control order (MCO) was implemented by the Government on the 18th March 2020. The MCO is expected to run at least until 28th April 2020. TM cited a 30 percent increase in usage attributed to the increase in traffic for streaming, online games and teleconferencing. Leading operators Maxis, Digi, Celcom and U Mobile have offered 1GB free data during the MCO period as part of the Government’s stimulus package. Maxis, TM, Digi and Celcom have also committed significant manpower to ensure that the networks are operating efficiently and to ensure customer support. Leading TV operator Astro has made all movie, news and cartoon networks available to all its customers until the 28th April 2020.
Social distancing fillip for video conferencing
The rise of social distancing has made us all seek new ways to connect, mainly through video chat. Video conferencing traffic is on the rise as it is the next best thing to face-to-face meetings. Microsoft Teams and Zoom have been big benefactors. The American Economic Institute (AEI) notes that Zoom hit some 200 million users daily from a daily average 10 million. Microsoft Teams added some 12 million registrations to a total of 44 million.
Many predict that the home working trend will continue in the recovery stage and beyond, due to improvements in the telecommunications infrastructure and impending rollout of 5G. It is also predicted that the commercial property sector is likely to suffer due to this trend. This period also highlights the critical importance of cybersecurity with increasing occurrences of hacking and fraud. Zoom is being forced to reinforce their privacy and security measures, as an example.
COVID-19 has changed the way we web
On the social front, many are also using video conferencing to communicate with friends and family. Operators relaxing and offering additional data has undoubtedly contributed to the increase in this usage too. Now that many are homebound, network traffic in residential areas are higher than ever. In the past, peak hours of traffic at homes were at night – this has changed with adults and children homebound. Adults are using video conferencing and more voice calls; while children are using elearning, playing games or streaming videos. The European Commission had asked Netflix and other streaming platforms to reduce streaming quality to standard definition (SD). Netflix has assured that it has the capability to manage levels of streaming quality in accordance with the networks quality requirement of individual countries.
Online gaming and video streaming have emerged as winners and have seen an increase in consumption in these times as they provide for entertainment for millions stuck at home. There is tremendous opportunity for both telecom operators and content providers to increase their number of services in this area. Netflix, YouTube, Microsoft Xbox and PlayStation are among the winners in this sector. YouTube provides for a primary news source and commentary on the epidemic for many. Netflix’s stocks are near an all-time high at present.
eCommerce boost for essentials goods and services
The eCommerce sector should see a major improvement in Southeast Asia as physical channels to market have reduced. Emerging economies such as Malaysia and Thailand should see an improvement in services and embrace eCommerce like their mature counterparts. Statista reports that the average Malaysian eCommerce shopper spent just US$159 and Thailand just US$100 on online consumer goods purchases in 2018, considerably lower than the global average of US$634. There is huge opportunity to provide for basic necessities such as online grocery, food and delivery of goods. As a consequence, contactless payment and the transport and logistics sector will be forced to adapt their business operations to ride this wave successfully. As eCommerce transactions diversify and increase in emerging markets, it will give telecom providers an opportunity to keep engaging with platform players.
Telecom carriers are likely to suffer financial losses due to the scale of the disruption COVID-19 has brought about. However, there are some positives takeaways from this period. The increase of network traffic and the changing patterns have driven carriers to better understand network traffic management. The sharp consumer and business onboarding as far as applications and digital services are concerned, has given the digital economy and 5G use cases a shot in the arm. This is likely to spur innovation in services including communications, eCommerce, payments, logistics and healthcare among others.

The Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC) has estimated that the country’s Digital Economy is worth USD3 trillion. Several initiatives have been introduced to promote the vision of a Digital Economy including: creating the Malaysia Tech Entrepreneur Programme (MTEP) aimed at tech founders who want to make Malaysia their base; the Malaysia Innovation Policy Council for industry collaboration on digital technology initiatives and streamlining policy/regulatory issues to support innovation; and the National eCommerce Roadmap aimed at small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to promote cross-border eCommerce.
Data Protection Laws for a Digital Economy
However, any country that aspires to be a Digital Economy, must have robust data protection laws that safeguards its citizens’ data. Malaysia’s Personal Data Protection Act 2010 (PDPA), was passed by the Malaysian Parliament in 2010 and came into force in late 2013. While the PDPA does provide guidelines for personal data protection to some extent, in light of technological advances, newer laws such as GDPR that are shaping the industry, and to keep up with the aspirations of creating a Digital Economy, there is a need for more comprehensive privacy laws.
“Growing the Digital Economy is a key agenda for Malaysia and a revised PDPA is a key component in ensuring trust and transparency,” says Shamir Amanullah, Principal Advisor Ecosystm. “The increasing and complex use of data and the proliferation of devices pose serious challenges which the data protection laws have to address. The recent US Federal Trade Commission’s hefty fines on Facebook and Equifax highlight the need to protect data of consumers and businesses alike.”
The PDPA is clearly a work in progress where while fast-growing areas such as electronic marketing and online privacy are mentioned in the act, there are no specific provisions to deal with breaches in these areas.
Updating the PDPA
In the last few years, Malaysia has realised that the PDPA fails to cover some areas. As an example, it does not take into consideration the proliferation of biometric data. The national ID card (MyKad) stores data using biometrics (thumbprints) and there is a clear rise in use of facial recognition technology in the country. Grab partnered with the Ministry of Transport last year, to use facial recognition technology to protect their drivers.
Malaysia is committed to their Digital Economy vision and is looking to update the PDPA, to make it more appropriate for contemporary needs and technology. The Government is consulting its citizens on possible ways to improve the PDPA. Between 14-28 February, the public can provide feedback on their thoughts and requirements on data privacy, through the Ministry of Communications and Multimedia’s web portal.
Some of the areas that have been found lacking and where feedback is being sought are expanding applications of the PDPA to data processors, making it compulsory to notify data breaches and simplifying cross-border personal data transfer.
Speaking about the areas that are likely to be addressed, Amanullah notes, “The review of the PDPA and the ongoing public consultation will deliberate extending the PDPA to non-commercial transactions. The existing PDPA does not cover non-commercial transactions involving charities, religious activities and even social media. The EU, Japan and – closer home – the Philippines have data protection acts which regulate both commercial and non-commercial transactions.”
Malaysia’s Communications & Multimedia Minister, Gobind Singh Deo, has from the start spoken about the need to update and bring the PDPA up to speed. “The goal of the Digital Economy is to take Malaysian enterprises beyond the country to Southeast Asian and global markets,” says Amanullah. “The EU GDPR is recognised as a leading global framework for data protection and is set to play a big role in the revised PDPA, to ensure that Malaysian companies adhere to the same data protection standards as global organisations.”
“The appointment of Data Protection Officers will be a major move to ensure that companies that hold sensitive private data have the necessary skills, processes and technology in place to comply with data protection laws.”




























