In the Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Healthcare Trends in 2022 we have said that 2022 will be the year when we start seeing the second-order impacts of the pandemic and we will see healthcare providers address these impacts. This means an increase in tech adoption and a greater (and in some cases, renewed) interest in tech providers to focus on the Healthcare industry.
Last month, we saw announcements of Francisco Partners acquiring the healthcare data and analytics assets from the IBM Watson Health business unit. This was neither unexpected nor an isolated news – it follows a series of significant Healthcare tech news from last year.
Here are some announcements from 2021 that I feel give us an indication of where the Healthcare tech market is headed.
- Oracle’s acquisition of Cerner
- Microsoft’s continued focus on Healthcare with the Nuance acquisition
- The acquisition of athenahealth by private equity firms
- Examples of the focus on mental health such as the creation of Headspace Health
- The interest of consumer apps in Healthcare as witnessed by Peloton’s corporate wellness programme.
Read on to find out more about these announcements. And let me know what you think is the most interesting Healthcare tech announcement in the last year.
Download “Where is Healthcare Tech Headed?” slides as a PDF.

Cities worldwide have been facing unexpected challenges since 2020 – and 2022 will see them continue to struggle with the after-effects of COVID-19. However, there is one thing that governments have learnt during this ongoing crisis – technology is not the only aspect of a Cities of the Future initiative. Besides technology, Cities of the Future will start revisiting organisational and institutional structures, prioritise goals, and design and deploy an architecture with data as its foundation.
Cities of the Future will focus on being:
- Safe. Driven by the ongoing healthcare crisis
- Secure. Driven by the multiple cyber attacks on critical infrastructure
- Sustainable. Driven by citizen consciousness and global efforts such as the COP26
- Smart. Driven by the need to be agile to face future uncertainties
Read on to find out what Ecosystm Advisors, Peter Carr, Randeep Sudan, Sash Mukherjee and Tim Sheedy think will be the leading Cities of the Future trends for 2022.
Click here to download Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Trends for Cities of the Future in 2022

As we return to the office, there is a growing reliance on devices to tell us how safe and secure the environment is for our return. And in specific application areas, such as Healthcare and Manufacturing, IoT data is critical for decision-making. In some sectors such as Health and Wellness, IoT devices collect personally identifiable information (PII). IoT technology is so critical to our current infrastructures that the physical wellbeing of both individuals and organisations can be at risk.
Trust & Data
IoT are also vulnerable to breaches if not properly secured. And with a significant increase in cybersecurity events over the last year, the reliance on data from IoT is driving the need for better data integrity. Security features such as data integrity and device authentication can be accomplished through the use of digital certificates and these features need to be designed as part of the device prior to manufacturing. Because if you cannot trust either the IoT devices and their data, there is no point in collecting, running analytics, and executing decisions based on the information collected.
We discuss the role of embedding digital certificates into the IoT device at manufacture to enable better security and ongoing management of the device.
Securing IoT Data from the Edge
So much of what is happening on networks in terms of real-time data collection happens at the Edge. But because of the vast array of IoT devices connecting at the Edge, there has not been a way of baking trust into the manufacture of the devices. With a push to get the devices to market, many manufacturers historically have bypassed efforts on security. Devices have been added on the network at different times from different sources.
There is a need to verify the IoT devices and secure them, making sure to have an audit trail on what you are connecting to and communicating with.
So from a product design perspective, this leads us to several questions:
- How do we ensure the integrity of data from devices if we cannot authenticate them?
- How do we ensure that the operational systems being automated are controlled as intended?
- How do we authenticate the device on the network making the data request?
Using a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) approach maintains assurance, integrity and confidentiality of data streams. PKI has become an important way to secure IoT device applications, and this needs to be built into the design of the device. Device authentication is also an important component, in addition to securing data streams. With good design and a PKI management that is up to the task you should be able to proceed with confidence in the data created at the Edge.
Johnson Controls/DigiCert have designed a new way of managing PKI certification for IoT devices through their partnership and integration of the DigiCert ONE™ PKI management platform and the Johnson Controls OpenBlue IoT device platform. Based on an advanced, container-based design, DigiCert ONE allows organisations to implement robust PKI deployment and management in any environment, roll out new services and manage users and devices across your organisation at any scale no matter the stage of their lifecycle. This creates an operational synergy within the Operational Technology (OT) and IoT spaces to ensure that hardware, software and communication remains trusted throughout the lifecycle.

Rationale on the Role of Certification in IoT Management
Digital certificates ensure the integrity of data and device communications through encryption and authentication, ensuring that transmitted data are genuine and have not been altered or tampered with. With government regulations worldwide mandating secure transit (and storage) of PII data, PKI can help ensure compliance with the regulations by securing the communication channel between the device and the gateway.
Connected IoT devices interact with each other through machine to machine (M2M) communication. Each of these billions of interactions will require authentication of device credentials for the endpoints to prove the device’s digital identity. In such scenarios, an identity management approach based on passwords or passcodes is not practical, and PKI digital certificates are by far the best option for IoT credential management today.
Creating lifecycle management for connected devices, including revocation of expired certificates, is another example where PKI can help to secure IoT devices. Having a robust management platform that enables device management, revocation and renewal of certificates is a critical component of a successful PKI. IoT devices will also need regular patches and upgrades to their firmware, with code signing being critical to ensure the integrity of the downloaded firmware – another example of the close linkage between the IoT world and the PKI world.
Summary
PKI certification benefits both people and processes. PKI enables identity assurance while digital certificates validate the identity of the connected device. Use of PKI for IoT is a necessary trend for sense of trust in the network and for quality control of device management.
Identifying the IoT device is critical in managing its lifespan and recognizing its legitimacy in the network. Building in the ability for PKI at the device’s manufacture is critical to enable the device for its lifetime. By recognizing a device, information on it can be maintained in an inventory and its lifecycle and replacement can be better managed. Once a certificate has been distributed and certified, having the control of PKI systems creates life-cycle management.

Organisations have found that it is not always desirable to send data to the cloud due to concerns about latency, connectivity, energy, privacy and security. So why not create learning processes at the Edge?
What challenges does IoT bring?
Sensors are now generating such an increasing volume of data that it is not practical that all of it be sent to the cloud for processing. From a data privacy perspective, some sensor data is sensitive and sending data and images to the cloud will be subject to privacy and security constraints.
Regardless of the speed of communications, there will always be a demand for more data from more sensors – along with more security checks and higher levels of encryption – causing the potential for communication bottlenecks.
As the network hardware itself consumes power, sending a constant stream of data to the cloud can be taxing for sensor devices. The lag caused by the roundtrip to the cloud can be prohibitive in applications that require real-time response inputs.
Machine learning (ML) at the Edge should be prioritised to leverage that constant flow of data and address the requirement for real-time responses based on that data. This should be aided by both new types of ML algorithms and by visual processing units (VPUs) being added to the network.
By leveraging ML on Edge networks in production facilities, for example, companies can look out for potential warning signs and do scheduled maintenance to avoid any nasty surprises. Remember many sensors are linked intrinsically to public safety concerns such as water processing, supply of gas or oil, and public transportation such as metros or trains.
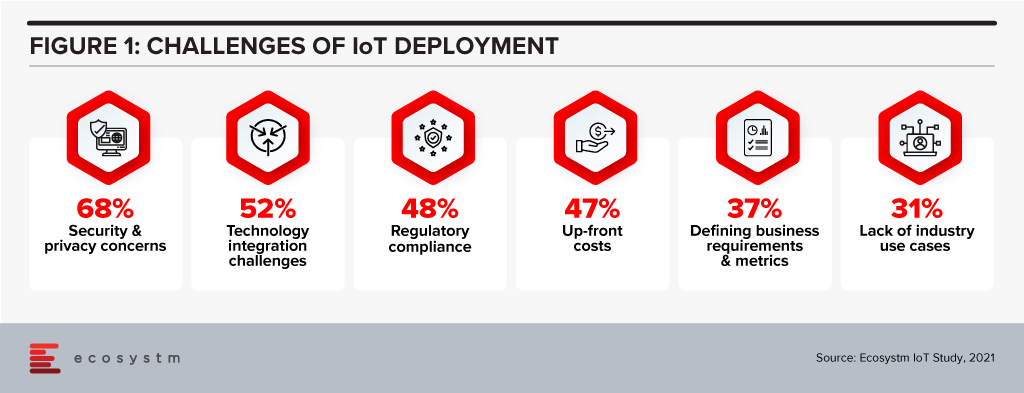
Ecosystm research shows that deploying IoT has its set of challenges (Figure 1) – many of these challenges can be mitigated by processing data at the Edge.
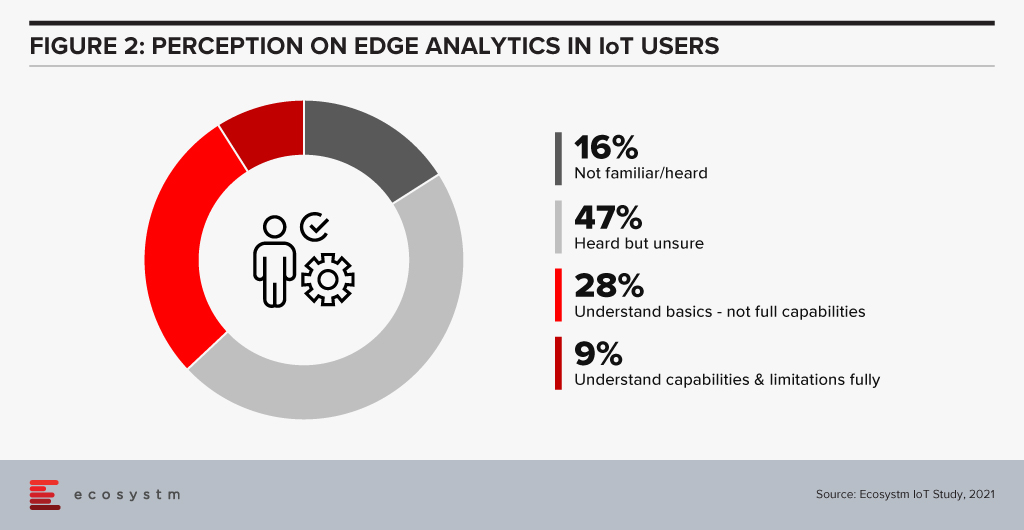
Predictive analytics is a fundamental value proposition for IoT, where responding faster to issues or taking action before issues occur, is key to a high return on investment. So, using edge computing for machine learning located within or close to the point of data gathering can in some cases be a more practical or socially beneficial approach.
In IoT the role of an edge computer is to pre-process data and act before the data is passed on to the main server. This allows a faster, low latency response and minimal traffic between the cloud server processing and the Edge. However, a better understanding of the benefits of edge computing is required if it has to be beneficial for a number of outcomes.

If we can get machine learning happening in the field, at the Edge, then we reduce the time lag and also create an extra trusted layer in unmanned production or automated utilities situations. This can create more trusted environments in terms of possible threats to public services.
What kind of examples of machine learning in the field can we see?
Healthcare
Health systems can improve hospital patient flow through machine learning (ML) at the Edge. ML offers predictive models to assist decision-makers with complex hospital patient flow information based on near real-time data.
For example, an academic medical centre created an ML pipeline that leveraged all its data – patient administration, EHR and clinical and claims data – to create learnings that could predict length of stay, emergency department (ED) arrival models, ED admissions, aggregate discharges, and total bed census. These predictive models proved effective as the medical centre reduced patient wait times and staff overtime and was able to demonstrate improved patient outcomes. And for a medical centre that use sensors to monitor patients and gather requests for medicine or assistance, Edge processing means keeping private healthcare data in-house rather than sending it off to cloud servers.
Retail
A retail store could use numerous cameras for self-checkout and inventory management and to monitor foot traffic. Such specific interaction details could slow down a network and can be replaced by an on-site Edge server with lower latency and a lower total cost. This is useful for standalone grocery pop-up sites such as in Sweden and Germany.
In Retail, k-nearest neighbours is often used in ML for abnormal activity analysis – this learning algorithm can also be used for visual pattern recognition used as part of retailers’ loss prevention tactics.
Summary
Working with the data locally on the Edge, creates reduced latency, reduced cloud usage and costs, independence from a network connection, more secure data, and increased data privacy.
Cloud and Edge computing that uses machine learning can together provide the best of both worlds: decentralised local storage, processing and reaction, and then uploading to the cloud, enabling additional insights, data backups (redundancy), and remote access.

Industries continue to innovate and disrupt to create and maintain a competitive edge – and their technology partners evolve their solution offerings to empower them.
We bring to you latest industry news from the Healthcare, Financial Services, Retail, Travel & Hospitality and Entertainment & Media industries to show you how organisations are leveraging technology. Find out more about organisations such as Services Australia, Paypal, Walmart, Zara and Amex – and how tech providers such as IBM, Oracle, Google and Uplift are supporting organisations across industries.
View the latest Ecosystm Bytes on Industries of the Future below, and reach out to our experts if you have questions.
For more ‘byte sized’ insights click on the link below

Since the start of this millennium, no region has transformed as much as Asia. There has been significant paradigm shifts in the region and the perception that innovation starts in the US or in Europe and percolates through to Asia after a time lag, has been shattered. Asia is constantly demonstrating how dynamic, and technology-focused it is. This is getting fueled by the impact of the growing middle class on consumerism and the spirit of innovation across the region. The region has also seen a surge in new and upcoming business leaders who are embracing change and looking beyond success to creating impact.
What is Driving Innovation in Asia?
The “If you ain’t got it, build it” attitude. One of the key drivers of this shift is the age of the average population in Asia. According to the UN the Asia Pacific region has nearly 60% of the world’s youth population (between the age of 17-24). With youth comes dynamism, a desire to change the world, and innovation. As this age group enters the workforce, they will transform their lives and the companies they work in. They are already showing a spirit of agility when it comes to solving challenges – they will build what they do not have.
The Need to enable Foundational Shifts. The younger generation is more aware of environmental, social and governance issues that the world continues to face. Many of the countries in the region are emerging economies, where these issues become more apparent. COVID-19 has also inculcated an empathy in people and they are thinking of future success in terms of impact. The desire to enable foundational shifts is giving direction to the transformation journey in the region. The wonderful new paradigm that is the Digital Economy allows us to cut across all segments; and technology and its advancements has immense potential to create a more sustainable and inclusive future for the world.
Realising the Power of Momentum. The pandemic has caused major disruptions in the region. But every crisis also presents an opportunity to perhaps re-imagine a brighter world through a digital lens. The other thing that the pandemic has done is made people and organisations realise that to succeed they need to be open to change – and that momentum is important. As organisations had to pivot fast, they realised what I have been saying for years – we shouldn’t “let perfect get in the way of better”. This adaptability and the readiness to fail fast and learn from the mistakes early for eventual success, is leading to faster and more agile transformation journeys.
Where are we seeing the most impact?
Industries are Transforming. There are industries such as Healthcare and Education that had to transform out of a necessity and urgency brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic. This has led to a greater impetus for change and optimism in these industries. These industries will continue to transform as governments focus significantly on creating “Social Safety Nets” and technology plays a key role in enabling critical services across Health, Education and Food Security. Then there are industries, such as the Financial Services and Retail, that had a strong customer focus and were well on their digital journeys before the pandemic. The pandemic boosted these efforts.
But these are not the only industries that are transforming. There are industries that have been impacted more than others. There are several instances of how organisations in these industries are demonstrating not only resilience but innovation. The Travel & Hospitality industry has had several such instances. As business models evolve the industry will see significant changes in digital channels to market, booking engines, corporate service offerings and others, as the overall Digital Strategy is overhauled.
Technologies are Evolving. Organisations depended on their tech partners to help them make the fast pivot required to survive and succeed in the last year – and tech companies have not disappointed. They have evolved their capabilities and continue to offer innovative solutions that can solve many of the ongoing business challenges that organisations face in their innovation journey. More and more technologies such as AI, machine learning, robotics, and digital twins are getting enmeshed together to offer better options for business growth, process efficiency and customer engagement. And the 5G rollouts will only accelerate that. The initial benefits being realized from early adoption of 5G has been for consumers. But there is a much bigger impact that is waiting to be realised as 5G empowers governments and businesses to make critical decisions at the edge.
Tech Start-ups are Flourishing. There are immense opportunities for technology start-ups to grow their market presence through innovative products and services. To succeed these companies need to have a strong investment roadmap; maintain a strong focus on customer engagement; and offer technology solutions that can fulfil the global needs of their customers. Technologies that promote efficiency and eliminate mundane tasks for humans are the need of the hour. However, as the reliance on technology-led transformation increases, tech vendors are becoming acutely aware that they cannot be best-in-class across the different technologies that an organisation will require to transform. Here is where having a robust partner ecosystem helps. Partnerships are bringing innovation to scale in Asia.
We can expect Asia to emerge as a powerhouse as businesses continue to innovate, embed technology in their product and service offerings – and as tech start-ups continue to support their innovation journeys.
Ecosystm CEO Amit Gupta gets face to face with Garrett Ilg, President Asia Pacific & Japan, Oracle to discuss the rise of the Asia Digital economies, the impact of the growing middle class on consumerism and the spirit of innovation across the region.

Last week Microsoft announced the acquisition of Nuance for an estimated USD 19.7 billion. This is Microsoft’s second largest acquisition ever, after they acquired LinkedIn in 2016. Nuance is an established name in the Healthcare industry and is said to have a presence in 10,000 healthcare organisations globally. Apart from Healthcare, Nuance has strong capabilities in Conversational AI and speech solutions to support other industries. This acquisition is in line with Microsoft’s go-to-market roadmap and strategies.
Microsoft’s Healthcare Focus
Microsoft announced their Healthcare Cloud last year and this acquisition will bolster their Healthcare offerings and market presence. Nuance’s product portfolio includes clinical speech recognition SaaS offerings – Dragon Ambient eXperience, Dragon Medical One and PowerScribe One for radiology reporting – on Microsoft Azure. The acquisition builds on already existing integrations and partnerships that were in place over the years.

“Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare offers its solution capabilities to healthcare providers using a ‘modular’ approach. Given how diverse healthcare providers are in their technology maturity and appetite for change, the more diverse the ‘modules’, the greater the opportunities for Microsoft. This partnership with Nuance also brings to the table established relationships with EHR vendors, which will be useful for Microsoft globally.
The Healthcare industry continues to struggle as the world negotiates the challenges of mass vaccination. But on the upside, the ongoing Healthcare crisis has given remote care a much-needed shot in the arm. Clinicians today will be more open to documentation and transcription services for process automation and compliance. The acquisition of Nuance’s Healthcare capabilities will definitely boost Microsoft’s market presence in provider organisations.
However, Healthcare is not the only industry that Microsoft and Nuance are focused on. The Microsoft Cloud for Retail that was launched earlier this year aims to offer integrated and intelligent capabilities to retailers and brands to improve their end-to-end customer journey. Nuance has omnichannel customer engagement solutions that can be leveraged in Retail and other industries. As Microsoft continues to verticalise their offerings, they will consider more acquisitions that will complement their value proposition.“
Microsoft’s Focus on Conversational AI
Microsoft already has several speech recognition offerings, speech to text services, and chatbots; and they continue to invest in the Conversational AI space. They have created an open-source template for creating virtual assistants to help Bot Framework developers. In February, Microsoft announced their industry specific cloud offerings for Financial services, Manufacturing, and Non-Profit, and also introduced a series of AI and natural language features in Microsoft Outlook, Microsoft Teams, Microsoft Office Lens and Microsoft Office mobile to deliver interactive, voice forward assistive experiences.

“There is no slowing down in this space and the acquisition clearly demonstrates the vision that Microsoft is building with Nuance – a vendor that has made speech recognition, text to speech, conversational AI the foundation of the company. This is a brilliant move by Microsoft in the Conversational AI space and a win-win for both companies.
This move could also mark further inroads for Microsoft into the contact centre space. With Teams now being integrated into contact centre technologies, working with large customers using speech and conversational AI, Dynamics 365 could herald the start of more acquisitions for Microsoft to bolster a wider customer engagement vision.
The Conversational AI war is heating up and various other cloud vendors such as Google and AWS are starting to get aggressive and have made investments in recent years to enhance their Conversational AI capabilities. Google Dialogflow has been seeing rapid uptake and they now have deep partnerships with Genesys, Avaya, Cisco and other contact centre players. Microsoft coming into the game and acquiring a company with years of history and IP in the speech space, demonstrates how the cloud battle and the war between Google, Microsoft and AWS is heating up in the Conversational AI. All of a sudden you have Microsoft as a powerhouse in this game.”

The COVID-19 pandemic has brought various changes in the healthcare processes. Many healthcare providers are transforming their practices with new trends and trying to stay at the forefront of healthcare innovation.
Ecosystm Healthcare experts and leaders give their verdict on what to expect in 2021.
Ecosystm Predicts – Key trends that will shape healthcare in 2021
The Healthcare industry has had to pivot completely this year and 2021 will see it emerge a transformed industry. The impact will be seen on policies, how ecosystems evolve, and most obviously on healthcare provider organisations. The Top 5 Ecosystm predictions for Healthcare Trends in 2021 is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform.

Microsoft introduced a second Vertical Cloud offering, last week – this time turning the focus on Retail, after having launched Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare in October 2020.
The Microsoft Cloud for Retail aims to offer integrated and intelligent capabilities to retailers and brands to improve their end-to-end customer journey. It brings industry-specific capabilities to the Microsoft suite including Microsoft Azure, Microsoft Power Platform, Microsoft 365, and Microsoft Dynamics 365 – and is aimed at the growing need for “intelligent retail’. Microsoft’s partner ecosystem will also be involved in the new platform to address challenges in the sector and future proof the retail evolution.
In The Top 5 Retail & eCommerce Trends for 2021, Ecosystm notes that while retailers will focus on the shift in customer expectations, a mere focus on customer experience will not be enough this year. From the customer experience angle, they will strongly focus on omnichannel, catering to ‘glocal’ consumption, using location-based services, and improving both their onsite and online customer experience. They will also have to work on their supply chain and pricing capabilities, as distribution woes continue. These trends are seeing a deeper need for transformational technologies and leading cloud providers are introducing solutions targeted at the industry. Google has introduced its cloud retail solutions aiming to help retailers get more from data. Similarly, AWS has cloud offerings for the retail industry leveraging its retail domain experience and cloud deployment services.
Ecosystm Comments

“Global cloud vendors continue to “move up the stack” to provide more of the technology landscape for organisations. The focus of these tech giants is on adding unique value to customers by tailoring the combination of the different cloud services they can provide to specific industries. Providing the full-stack will mean higher customer retention rates – as the implementation time should be lower than traditional on-premises implementations. Microsoft has a diverse range of capabilities. Having a software company and implementation partner that can deliver the full stack of technology and business processes should improve the time to value for organisations.
But I see three key difficulties in implementing systems such as these:
- People adapting effectively to use the new processes
- Migrating enough high-quality data to leverage the new capabilities
- Integrating the new capabilities into an organisation’s existing landscape.
This is why it is likely that initial use will come from Microsoft’s existing Retail customers as they expand the range of services they use. New adopters of these Microsoft solutions will find that much of the complexity and cost of implementing a new business solution will remain.
However, these value-added cloud services open access to smaller organisations. If Microsoft is able to work with their partners to simplify the implementation of these capabilities, it will allow smaller organisations to access these complex capabilities affordably.“

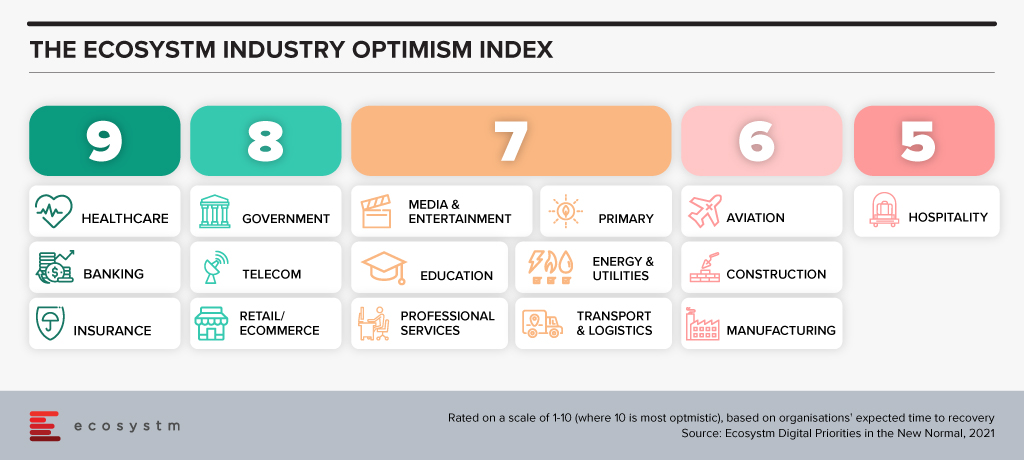
“The Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal Study aims to determine how optimistic industries are about successfully negotiating these uncertain times (Figure 1). The industries that are rated the most optimistic fall into two clear categories. In the first category, there are industries, such as Healthcare that had to transform urgently – mostly in an unplanned manner. This has led to a greater appetite for change and optimism in these industries. Then there are industries, such as Retail, that had some time to re-focus their technology roadmap when the crisis hit. These industries have a strong customer focus and had started their digital journeys before the pandemic.
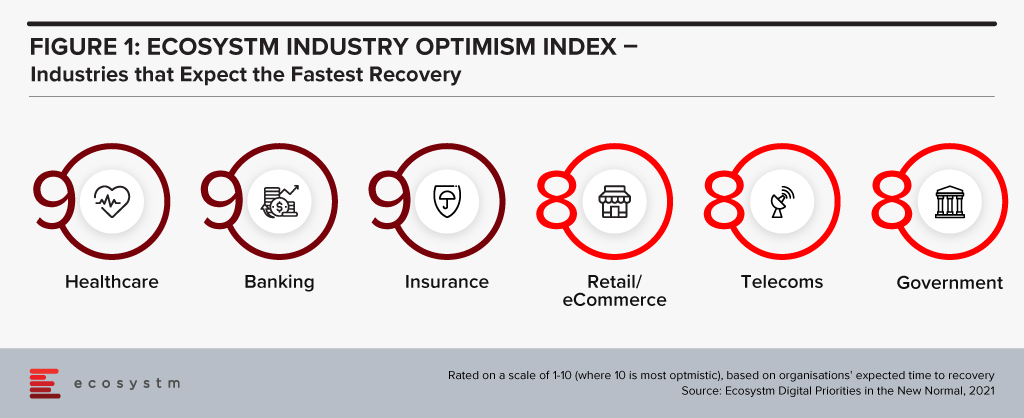
Microsoft’s industry focus appears to be spot-on. Their first two vertical clouds target enterprises that have had to – and will continue to – pivot. The ‘modular’ approach taken in the Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare offering allows providers to choose the right capability for their organisation – whether it is workflow automation, patient engagement through virtual health, collaboration within care teams or better clinical and operational insights. As healthcare organisations across the world negotiate the challenges of mass vaccination, they may well find themselves leveraging these industry-specific capabilities as they revamp their workflows, processes, and data use.”
Get to know the right research, insights and technologies for you to be one step ahead in this new world of retail in our top 5 retail trends for 2021 that represent the most significant shifts in 2021