In AI’s early days, enterprise leaders asked a straightforward question: “What can this automate?” The focus was on speed, scale, and efficiency and AI delivered. But that question is evolving. Now, the more urgent ask is: “Can this AI understand people?”
This shift – from automation to emotional intelligence – isn’t just theoretical. It’s already transforming how organisations connect with customers, empower employees, and design digital experiences. We’re shifting to a phase of humanised AI – systems that don’t just respond accurately, but intuitively, with sensitivity to mood, tone, and need.
One of the most unexpected, and revealing, AI use cases is therapy. Millions now turn to AI chat tools to manage anxiety, process emotions, and share deeply personal thoughts. What started as fringe behaviour is fast becoming mainstream. This emotional turn isn’t a passing trend; it marks a fundamental shift in how people expect technology to relate to them.
For enterprises, this raises a critical challenge: If customers are beginning to turn to AI for emotional support, what kind of relationship do they expect from it? And what does it take to meet that expectation – not just effectively, but responsibly, and at scale?
The Rise of Chatbot Therapy
Therapy was never meant to be one of AI’s first mass-market emotional use cases; and yet, here we are.
Apps like Wysa, Serena, and Youper have been quietly reshaping the digital mental health landscape for years, offering on-demand support through chatbots. Designed by clinicians, these tools draw on established methods like Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) and mindfulness to help users manage anxiety, depression, and stress. The conversations are friendly, structured, and often, surprisingly helpful.
But something even more unexpected is happening; people are now using general-purpose AI tools like ChatGPT for therapeutic support, despite them not being designed for it. Increasingly, users are turning to ChatGPT to talk through emotions, navigate relationship issues, or manage daily stress. Reddit threads and social posts describe it being used as a therapist or sounding board. This isn’t Replika or Wysa, but a general AI assistant being shaped into a personal mental health tool purely through user behaviour.
This shift is driven by a few key factors. First, access. Traditional therapy is expensive, hard to schedule, and for many, emotionally intimidating. AI, on the other hand, is always available, listens without judgement, and never gets tired.
Tone plays a big role too. Thanks to advances in reinforcement learning and tone conditioning, models like ChatGPT are trained to respond with calm, non-judgmental empathy. The result feels emotionally safe; a rare and valuable quality for those facing anxiety, isolation, or uncertainty. A recent PLOS study found that not only did participants struggle to tell human therapists apart from ChatGPT, they actually rated the AI responses as more validating and empathetic.
And finally, and perhaps surprisingly, is trust. Unlike wellness apps that push subscriptions or ads, AI chat feels personal and agenda-free. Users feel in control of the interaction – no small thing in a space as vulnerable as mental health.
None of this suggests AI should replace professional care. Risks like dependency, misinformation, or reinforcing harmful patterns are real. But it does send a powerful signal to enterprise leaders: people now expect digital systems to listen, care, and respond with emotional intelligence.
That expectation is changing how organisations design experiences – from how a support bot speaks to customers, to how an internal wellness assistant checks in with employees during a tough week. Humanised AI is no longer a niche feature of digital companions. It’s becoming a UX standard; one that signals care, builds trust, and deepens relationships.
Digital Companionship as a Solution for Support
Ten years ago, talking to your AI meant asking Siri to set a reminder. Today, it might mean sharing your feelings with a digital companion, seeking advice from a therapy chatbot, or even flirting with a virtual persona! This shift from functional assistant to emotional companion marks more than a technological leap. It reflects a deeper transformation in how people relate to machines.
One of the earliest examples of this is Replika, launched in 2017, which lets users create personalised chatbot friends or romantic partners. As GenAI advanced, so did Replika’s capabilities, remembering past conversations, adapting tone, even exchanging voice messages. A Nature study found that 90% of Replika users reported high levels of loneliness compared to the general population, but nearly half said the app gave them a genuine sense of social support.
Replika isn’t alone. In China, Xiaoice (spun off from Microsoft in 2020) has hundreds of millions of users, many of whom chat with it daily for companionship. In elder care, ElliQ, a tabletop robot designed for seniors has shown striking results: a report from New York State’s Office for the Aging cited a 95% drop in loneliness among participants.
Even more freeform platforms like Character.AI, where users converse with AI personas ranging from historical figures to fictional characters, are seeing explosive growth. People are spending hours in conversation – not to get things done, but to feel seen, inspired, or simply less alone.
The Technical Leap: What Has Changed Since the LLM Explosion
The use of LLMs for code editing and content creation is already mainstream in most enterprises but use cases have expanded alongside the capabilities of new models. LLMs now have the capacity to act more human – to carry emotional tone, remember user preferences, and maintain conversational continuity.
Key advances include:
- Memory. Persistent context and long-term recall
- Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). Empathy and safety by design
- Sentiment and Emotion Recognition. Reading mood from text, voice, and expression
- Role Prompting. Personas using brand-aligned tone and behaviour
- Multimodal Interaction. Combining text, voice, image, gesture, and facial recognition
- Privacy-Sensitive Design. On-device inference, federated learning, and memory controls
Enterprise Implications: Emotionally Intelligent AI in Action
The examples shared might sound fringe or futuristic, but they reveal something real: people are now open to emotional interaction with AI. And that shift is creating ripple effects. If your customer service chatbot feels robotic, it pales in comparison to the AI friend someone chats with on their commute. If your HR wellness bot gives stock responses, it may fall flat next to the AI that helped a user through a panic attack the night before.
The lesson for enterprises isn’t to mimic friendship or romance, but to recognise the rising bar for emotional resonance. People want to feel understood. Increasingly, they expect that even from machines.
For enterprises, this opens new opportunities to tap into both emotional intelligence and public comfort with humanised AI. Emerging use cases include:
- Customer Experience. AI that senses tone, adapts responses, and knows when to escalate
- Brand Voice. Consistent personality and tone embedded in AI interfaces
- Employee Wellness. Assistants that support mental health, coaching, and daily check-ins
- Healthcare & Elder Care. Companions offering emotional and physical support
- CRM & Strategic Communications. Emotion-aware tools that guide relationship building
Ethical Design and Guardrails
Emotional AI brings not just opportunity, but responsibility. As machines become more attuned to human feelings, ethical complexity grows. Enterprises must ensure transparency – users should always know they’re speaking to a machine. Emotional data must be handled with the same care as health data. Empathy should serve the user, not manipulate them. Healthy boundaries and human fallback must be built in, and organisations need to be ready for regulation, especially in sensitive sectors like healthcare, finance, and education.
Emotional intelligence is no longer just a human skill; it’s becoming a core design principle, and soon, a baseline expectation.
Those who build emotionally intelligent AI with integrity can earn trust, loyalty, and genuine connection at scale. But success won’t come from speed or memory alone – it will come from how the experience makes people feel.

Advanced technology and the growing interconnectedness of devices are no longer futuristic concepts in health and life sciences – they’re driving a powerful transformation. Technology, combined with societal demands, is reshaping drug discovery, clinical trials, patient care, and even our understanding of the human body.
The potential to create more efficient, personalised, and effective healthcare solutions has never been greater.
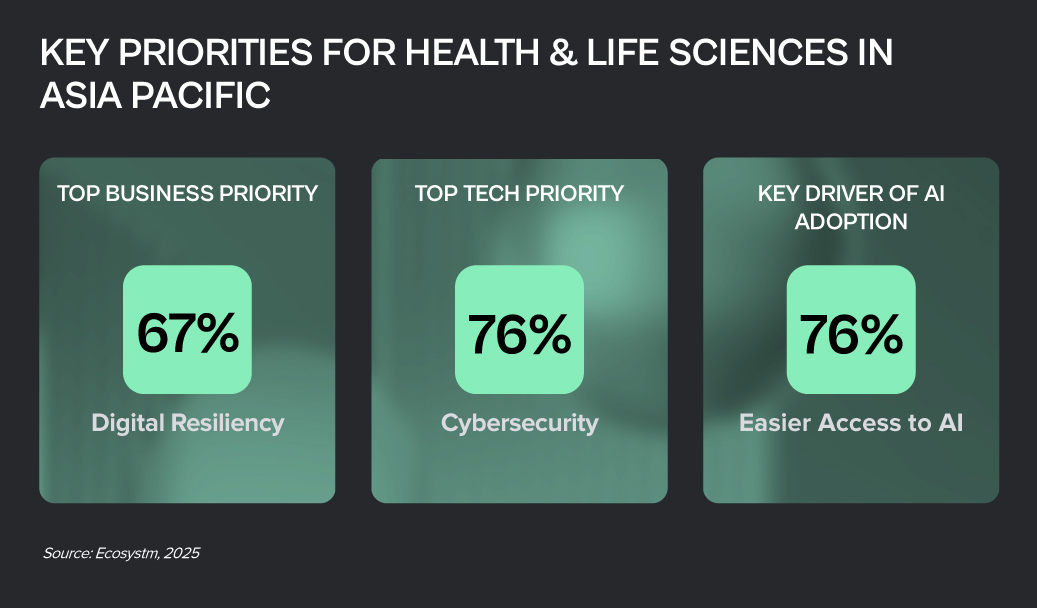
Click here to download “Future Forward: Reimagining Health & Life Sciences” as a PDF.
Modernising HR for Enhanced Efficiency & Employee Experience
The National Healthcare Group (NHG), a leading public healthcare provider in Singapore, recognised the need to modernise their HR system to better support 20,000+ healthcare professionals and improve patient services.
The iConnect@NHG initiative was launched to centralise HR functions, providing mobile access and self-service capabilities, and streamlining workflows across NHG’s integrated network of hospitals, polyclinics, and specialty centres.
The solution streamlined HR processes, giving employees easy access to essential data, career tools, and claims. The cloud-based platform improved data accuracy, reduced admin work, and integrated analytics for better decision-making and engagement. With 95% adoption, productivity and job satisfaction surged, enabling staff to focus on care delivery.
Automating Workflows for Better Patient Outcomes
Gold Coast Health handles a high volume of patient interactions across a wide range of medical services. The challenge was to streamline operations and reduce administrative burdens to improve patient care.
The solution involved automating the patient intake process by replacing paper forms with electronic versions, freeing up significant staff time.
A new clinical imaging solution also automates the uploading of wound images and descriptions into patient records, further saving time. Additionally, Gold Coast Health implemented a Discharge to Reassess system to automate follow-ups for long-term outpatient care. They are also exploring AI to simplify tasks and improve access to information, allowing clinical teams to focus more on patient care.
Streamlining Operations, Improving Care
IHH Healthcare, a global provider with over 80 hospitals across 10 countries, faced a fragmented IT landscape that hindered data management and patient care.
To resolve this, IHH migrated their core application workloads, including EMRs, to a next-gen cloud platform, unifying data across their network and enhancing analytics.
Additionally, they adopted an on-prem cloud solution to comply with local data residency requirements. This transformation reduced report generation time from days to hours, boosting operational efficiency and improving patient and clinician experiences. By leveraging advanced cloud technologies, IHH is strengthening their commitment to delivering world-class healthcare.
Creating Seamless & Compassionate Patient Journeys
The Narayana Health group in India is committed to providing accessible, high-quality care. However, they faced challenges with fragmented patient data, which hindered personalised care and efficient interactions.
To address this, Narayana Health centralised patient data, providing agents with a 360-degree view to offer more informed and compassionate service.
By automating tasks like call routing and form-filling, the organisation reduced average handling times and increased appointment conversions. Additionally, automated communication tools delivered timely, sensitive updates, strengthening patient relationships. The initiative has improved operational efficiency and deepened the organisation’s patient-centric focus.
Reimagining Location Services for Digital Healthcare
Halodoc, a leading digital health platform in Indonesia, connects millions of users with healthcare professionals and pharmacies.
To improve key services like home lab appointments and medicine delivery, Halodoc sought a more cost-effective and secure location service.
The transition resulted in an 88% reduction in costs for geocoding and places functionalities while enhancing data security. With better performance monitoring, Halodoc processed millions of geocoding and place requests with no major issues. This migration not only optimised costs but also resolved long-standing technical challenges, positioning Halodoc for future innovation, including machine learning and AI. The move strengthened their data security and provided a solid foundation for continued growth and high-quality healthcare delivery across Indonesia.
Driving Efficiency & Accessibility through Integrated Systems
Lupin, a global pharma leader, aimed to boost patient care, streamline operations, and enhance accessibility. By integrating systems and centralising data, Lupin wanted seamless interactions between patients, doctors, and the salesforce.
The company implemented a scalable infrastructure optimised for critical business applications, backed by high-performance server and storage technologies.
This integration improved data-driven decision-making, leading to optimised operations, reduced costs, and improved medicine quality and affordability. The robust infrastructure also ensured near-zero downtime, enhancing reliability and efficiency. Through this transformation, Lupin reinforced its commitment to providing patient-centred, affordable healthcare with faster, more efficient outcomes.
Leveraging AI for Cloud Security
Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma’s “VISION 30” seeks to deliver personalised healthcare by 2030, focusing on precision medicine and digital solutions. The company is investing in advanced digital technologies and secure data infrastructure to achieve these goals.
To secure their expanding cloud platform, the company adopted a zero-trust model and enhanced identity management.
A security assessment identified gaps in cloud configuration, prompting tailored security improvements. GenAI was introduced to translate and summarise security alerts, reducing processing time from 10 minutes to just one minute, improving efficiency and security awareness across the team. The company is actively exploring further AI-driven solutions to strengthen security and drive their digital transformation, advancing the vision for personalised healthcare.

AI has already had a significant impact on the tech industry, rapidly evolving software development, data analysis, and automation. However, its potential extends into all industries – from the precision of agriculture to the intricacies of life sciences research, and the enhanced customer experiences across multiple sectors.
While we have seen the widespread adoption of AI-powered productivity tools, 2025 promises a bigger transformation. Organisations across industries will shift focus from mere innovation to quantifiable value. In sectors where AI has already shown early success, businesses will aim to scale these applications to directly impact their revenue and profitability. In others, it will accelerate research, leading to groundbreaking discoveries and innovations in the years to come. Regardless of the specific industry, one thing is certain: AI will be a driving force, reshaping business models and competitive landscapes.
Ecosystm analysts Alan Hesketh, Clay Miller, Peter Carr, Sash Mukherjee, and Steve Shipley present the top trends shaping key industries in 2025.
Click here to download ‘AI’s Impact on Industry in 2025’ as a PDF
1. GenAI Virtual Agents Will Reshape Public Sector Efficiency
Operating within highly structured, compliance-driven environments, public sector organisations are well-positioned to benefit from GenAI Agents.
These agents excel when powered LLMs tailored to sector-specific needs, informed by documented legislation, regulations, and policies. The result will be significant improvements in how governments manage rising service demands and enhance citizen interactions. From automating routine enquiries to supporting complex administrative processes, GenAI Virtual Agents will enable public sector to streamline operations without compromising compliance. Crucially, these innovations will also address jurisdictional labour and regulatory requirements, ensuring ethical and legal adherence. As GenAI technology matures, it will reshape public service delivery by combining scalability, precision, and responsiveness.

2. Healthcare Will Lead in Innovation; Lag in Adoption
In 2025, healthcare will undergo transformative innovations driven by advancements in AI, remote medicine, and biotechnology. Innovations will include personalised healthcare driven by real-time data for tailored wellness plans and preventive care, predictive AI tackling global challenges like aging populations and pandemics, virtual healthcare tools like VR therapy and chatbots enhancing accessibility, and breakthroughs in nanomedicine, digital therapeutics, and next-generation genomic sequencing.
Startups and innovators will often lead the way, driven by a desire to make an impact.
However, governments will lack the will to embrace these technologies. After significant spending on crisis management, healthcare ministries will likely hesitate to commit to fresh large-scale investments.

3. Agentic AI Will Move from Bank Credit Recommendation to Approval
Through 2024, we have seen a significant upturn in Agentic AI making credit approval recommendations, providing human credit managers with the ability to approve more loans more quickly. Yet, it was still the mantra that ‘AI recommends—humans approve.’ That will change in 2025.
AI will ‘approve’ much more and much larger credit requests.
The impact will be multi-faceted: banks will greatly enhance client access to credit, offering 24/7 availability and reducing the credit approval and origination cycle to mere seconds. This will drive increased consumer lending for high-value purchases, such as major appliances, electronics, and household goods.

4. AI-Powered Demand Forecasting Will Transform Retail
There will be a significant shift away from math-based tools to predictive AI using an organisation’s own data. This technology will empower businesses to analyse massive datasets, including sales history, market trends, and social media, to generate highly accurate demand predictions. Adding external influencing factors such as weather and events will be simplified.
The forecasts will enable companies to optimise inventory levels, minimise stockouts and overstock situations, reduce waste, and increase profitability. Early adopters are already leveraging AI to anticipate fashion trends and adjust production accordingly.
No more worrying about capturing “Demand Influencing Factors” – it will all be derived from the organisation’s data.

5. AI-Powered Custom-Tailored Insurance Will Be the New Norm
Insurers will harness real-time customer data, including behavioural patterns, lifestyle choices, and life stage indicators, to create dynamic policies that adapt to individual needs. Machine learning will process vast datasets to refine risk predictions and deliver highly personalised coverage. This will produce insurance products with unparalleled relevance and flexibility, closely aligning with each policyholder’s changing circumstances. Consumers will enjoy transparent pricing and tailored options that reflect their unique risk profiles, often resulting in cost savings. At the same time, insurers will benefit from enhanced risk assessment, reduced fraud, and increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
This evolution will redefine the customer-insurer relationship, making insurance a more dynamic and responsive service that adjusts to life’s changes in real-time.


Over the past year, Ecosystm has conducted extensive research, including surveys and in-depth conversations with industry leaders, to uncover the most pressing topics and trends. And unsurprisingly, AI emerged as the dominant theme. Here are some insights from our research on the Healthcare industry.
Click here to download ‘AI in Healthcare: Success Stories & Insights’ as a PDF
AI is transforming the healthcare industry, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve patient outcomes and streamline operations. However, the successful implementation of AI in healthcare is not without its challenges. Those who can navigate these complexities and harness the power of AI will emerge as industry leaders, driving innovation and shaping the future of healthcare.

Despite the challenges, Healthcare organisations are witnessing early AI success in these 3 areas:
- 1. Diagnostics
- 2. Care Management
- 3. Operational Efficiency & Optimisation
Diagnostics
- Image Analysis. Analysing medical images (e.g., X-rays, MRIs) to detect diseases and abnormalities
- Diagnosis. Assisting clinicians in identifying and diagnosing diseases
- Early Detection. Detecting diseases at an early stage for more effective treatment
“Diagnostics is where our AI journey began – starting with image analysis for eye diseases, evolving to x-ray screening tools, and most recently, investing in digital stethoscopes for our doctors and nurses.” – CLINICIAN LEADER
Care Management
- Clinical Decision Support. Providing clinicians with recommendations and insights to improve patient care
- Personalised Treatment Plans. Personalising treatment protocols based on patient data and genetics
- Chronic Disease Management. Monitoring chronic diseases over multiple years
“Clinical decision support isn’t new, but AI has revolutionised it by enabling the system to send alerts and warnings proactively, rather than only when prompted.” – CLINICIAN LEADER
Operational Efficiency & Optimisation
- Supply Chain Management. Optimising inventory and supply chain processes
- Appointment Scheduling. Automating appointment booking and management
- Workflow Optimisation. Streamlining workflows and improving efficiency of clinical staff
“Patient satisfaction extends beyond clinical outcomes. Aspects like shorter waiting times during appointments, the availability of medications, and automated responses to common queries significantly enhance patient satisfaction. These are areas where we have successfully implemented AI.” – COO

India is undergoing a remarkable transformation across various industries, driven by rapid technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and a dynamic economic landscape. From the integration of new-age technologies like GenAI to the adoption of sustainable practices, industries in India are redefining their operations and strategies to stay competitive and relevant.
Here are some organisations that are leading the way.
Download ‘From Tradition to Innovation: Industry Transformation in India’ as a PDF
Redefining Customer Experience in the Financial Sector
Financial inclusion. India’s largest bank, the State Bank of India, is leading financial inclusion with its YONO app, to enhance accessibility. Initial offerings include five core banking services: cash withdrawals, cash deposits, fund transfers, balance inquiries, and mini statements, with plans to include account opening and social security scheme enrollments.
Customer Experience. ICICI Bank leverages RPA to streamline repetitive tasks, enhancing customer service with its virtual assistant, iPal, for handling queries and transactions. HDFC Bank customer preference insights to offer tailored financial solutions, while Axis Bank embraces a cloud-first strategy to digitise its platform and improve customer interfaces.
Indian banks are also collaborating with fintechs to harness new technologies for better customer experiences. YES Bank has partnered with Paisabazaar to simplify loan applications, and Canara HSBC Life Insurance has teamed up with Artivatic.AI to enhance its insurance processes via an AI-driven platform.
Improving Healthcare Access
Indian healthcare organisations are harnessing technology to enhance efficiency, improve patient experiences, and enable remote care.
Apollo Hospitals has launched an automated patient monitoring system that alerts experts to health deteriorations, enabling timely interventions through remote monitoring. Manipal Hospitals’ video consultation app reduces emergency department pressure by providing medical advice, lab report access, bill payments, appointment bookings, and home healthcare requests, as well as home medication delivery and Fitbit monitoring. Omni Hospitals has also implemented AI-based telemedicine for enhanced patient engagement and remote monitoring.
The government is also driving the improvement of healthcare access. eSanjeevani is the world’s largest government-owned telemedicine system, with the capacity to handle up to a million patients a day.
Driving Retail Agility & Consumer Engagement
India’s Retail sector, the fourth largest globally, contributes over 10% of the nation’s GDP. To stay competitive and meet evolving consumer demands, Indian retailers are rapidly adopting digital technologies, from eCommerce platforms to AI.
Omnichannel Strategies. Reliance Retail integrates physical stores with digital platforms like JioMart to boost sales and customer engagement. Tata CLiQ’s “phygital” approach merges online and offline shopping for greater convenience while Shoppers Stop uses RFID and data analytics for improved in-store experiences, online shopping, and targeted marketing.
Retail AI. Flipkart’s AI-powered shopping assistant, Flippi uses ML for conversational product discovery and intuitive guidance. BigBasket employs IoT-led AI to optimise supply chain and improve product quality.
Reshaping the Automotive Landscape
Tech innovation, from AI/ML to connected vehicle technologies, is revolutionising the Automotive sector. This shift towards software-defined vehicles and predictive supply chain management underscores the industry’s commitment to efficiency, transparency, safety, and environmental sustainability.
Maruti Suzuki’s multi-pronged approach includes collaborating with over 60 startups through its MAIL program and engaging Accenture to drive tech change. Maruti has digitised 24 out of 26 customer touchpoints, tracking every interaction to enhance customer service. In the Auto OEM space, they are shifting to software-defined vehicles and operating models.
Tata Motors is leveraging cloud, AI/ML, and IoT to enhancing efficiency, improving safety, and driving sustainability across its operations. Key initiatives include connected vehicles, automated driving, dealer management, cybersecurity, electric powertrains, sustainability, and supply chain optimisation.
Streamlining India’s Logistics Sector
India’s logistics industry is on the cusp of a digital revolution as it embraces cutting-edge technologies to streamline processes and reduce environmental impact.
Automation and Predictive Analytics. Automation is transforming warehousing operations in India, with DHL India automating sortation centres to handle 6,000 shipments per hour. Predictive analytics is reshaping logistics decision-making, with Delhivery optimising delivery routes to ensure timely service.
Sustainable Practices. The logistics sector contributes one-third of global carbon emissions. To combat this, Amazon India will convert its delivery fleet to 100% EVs by 2030 to reduce emissions and fuel costs. Blue Energy Motors is also producing 10,000 heavy-duty LNG trucks annually for zero-emission logistics.

The rapid adoption of technology in India is driving a surge in demand for AI solutions across sectors like finance, education, healthcare, and agriculture. AI is revolutionising these industries by making services more efficient, personalised, and accessible. This growing dependence on AI has created a fertile ground for innovation, propelling India’s emergence as a global hub for AI startups. With over 6,200 AI startups operating in the country, India offers a dynamic and challenging landscape for entrepreneurs seeking to make a meaningful impact.
Fuelling AI Innovation: India’s Strategic Investment
Earlier this year, the government allocated USD 1.3 billion for the India AI Mission, solidifying its commitment to AI. This comprehensive program is designed to catalyse the AI innovation ecosystem within the country. At the heart of this ecosystem’s development lies the expansion of compute infrastructure, a critical resource for AI startups. By providing access to powerful computing resources, the India AI Mission is empowering startups to scale their solutions and compete on a global level.
Beyond infrastructure, the initiative focuses on fostering collaborations between academia, industry, and startups to drive R&D. By creating a supportive environment that promotes knowledge sharing and resource accessibility, the India AI Mission aims to position India as a leader in the AI landscape.
A Spotlight on Indian Startups
Driving Industry Innovation
Healthcare. India’s vibrant AI startup ecosystem is driving innovation in healthcare, with companies leveraging AI to address critical challenges and improve patient outcomes.
- Cancer-Focused AI Startups. Several startups are revolutionising cancer care with AI-driven innovations. Niramai, globally recognised for its innovation, uses AI and thermal imaging for early breast cancer detection, particularly effective in younger women and dense breast tissue. Onward Assist provides predictive analytics for oncology, helping oncologists manage patient data and improve the accuracy of cancer care decisions. Similarly, Atom360 focuses on oral cancer screening with an AI-powered app that offers quick, affordable access to critical information, enhancing oral healthcare in underserved areas.
- AI-Driven Diagnostic Solutions. AI is significantly advancing diagnostics, enhancing accuracy, and reducing misdiagnosis. SigTuple develops AI-driven diagnostic solutions for medical imaging and pathology, improving accuracy and efficiency in disease detection. Endimension Technology, incubated at IIT Bombay, develops algorithms for detecting abnormalities in medical scans, aiming to reduce misdiagnosis and radiologist workload. Tricog Health delivers AI solutions for rapid heart attack diagnosis, reducing diagnosis time and improving outcomes, especially in underserved regions.
Financial Services. Fintechs have been at the forefront of AI-led innovations, offering innovative solutions for insurance, lending, and microfinance. Artivatic uses AI to transform traditional insurance systems into digital, personalised offerings, making coverage more accessible and affordable for a broader range of consumers. ZestMoney leverages AI for digital lending, providing credit to individuals without a credit history through easy EMI plans, and enhancing financial access. Meanwhile, mPokket offers instant micro-loans to students and young professionals, addressing short-term financial needs with flexible loan options and minimal documentation.
Other Industries. Beyond healthcare and financial services, AI startups are driving innovation across various industries, tackling critical challenges. Entropik uses AI to analyse human emotions and behaviour, helping businesses gain deeper insights into consumer preferences for market research and optimising user experiences. In agriculture, Intello Labs applies AI and computer vision to assess the quality of fresh produce, reducing food waste and improving supply chain efficiency. Similarly, AgNext enhances food value chains by offering AI-driven, real-time quality assessments through its SaaS platform, promoting safety and transparency in agribusiness.
Transforming Businesses
Technology for Security & Fraud. AI startups are offering innovative solutions tailored to organisations’ needs. SpoofSense combats deepfakes and identity fraud with advanced facial liveness detection, ensuring secure user verification by distinguishing between real users and spoofed images. Eagle Eye Networks provides cloud-based video surveillance solutions, using AI to offer real-time monitoring and analytics. In the e-commerce space, ThirdWatch uses AI to detect and prevent fraud in real-time by analysing user behaviour and transaction patterns, reducing financial losses for online retailers.
Tech Development. AI startups are empowering organisations to accelerate innovation and enhance productivity. Haptik helps businesses build intelligent virtual assistants, powering chatbots and voice bots across industries to improve customer engagement. DhiWise automates the development process, enabling faster app creation by converting designs into code. Additionally, Fluid AI provides advanced AI solutions like predictive analytics and natural language processing for sectors like finance, retail, and healthcare. Mihup enhances contact centre performance with its conversation intelligence platform, while Yellow.ai enables enterprises to automate customer engagement through its GenAI-powered platform, creating seamless and scalable customer service experiences.
Empowering People
AI startups are empowering individuals by providing personalised services that enhance learning, creativity, and financial management. SuperKalam and ZuAI offer students tailored learning experiences, using AI to create interactive lessons and assessments that adapt to individual learning styles, improving student engagement and outcomes. For creative professionals, Mugafi combines AI with human mentoring to assist writers in generating ideas and developing scripts, enabling them to create intellectual property with greater efficiency. Wright Research empowers individuals to make informed financial decisions through AI-powered investment advice, while Vahan simplifies job searches for blue-collar workers by using AI to match candidates with suitable employment opportunities via WhatsApp.
Promoting ESG
AI startups are driving meaningful change by optimising processes and creating economic opportunities. Ossus Biorenewables enhances biofuel production through AI, reducing waste and increasing efficiency in renewable energy generation, while Ishitva Robotic Systems promotes sustainability by automating waste sorting and recycling, contributing to a more efficient and circular economy. Karya connects rural workers with digital tasks, offering fair wages and skills development by matching them to tasks suited to their abilities using machine learning. In agriculture, KissanAI helps farmers improve crop yields and manage resources effectively through personalised, data-driven recommendations. ElasticRun improves last-mile delivery logistics in rural areas, enabling businesses to reach underserved markets.
Conclusion
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang noted India’s potential to become the “largest exporter of AI,” signalling vast global opportunities. India’s AI startups are at the forefront of innovation but face hurdles such as fierce competition for skilled talent, navigating complex regulations, and securing funding. With strategic focus on these challenges and the backing of initiatives like Digital India and Startup India, India’s AI ecosystem can seize emerging market opportunities, accelerate tech advancements, and make a substantial impact on the global AI landscape.

India’s digital journey has been nothing short of remarkable, driven by a robust Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) framework known as the India Stack. Over the past decade, the government, in collaboration with public and private entities, has built this digital ecosystem to empower citizens, improve governance, and foster economic growth.
The India Stack is a set of open APIs and platforms that provide a foundation for large-scale public service delivery and innovation. It enables governments, businesses, startups, and developers to leverage technology to offer services to millions of Indians, especially those in underserved areas.
The India Stack is viewed as a layered infrastructure, addressing identity, payments, data, and services.
Click here to download The India Stack: A Foundation for Digital India as a PDF
Four Pillars of the Digital Stack
The four layers of India Stack include:
- Presenceless Layer. Aadhaar enables remote authentication, providing a digital ID that requires only a 12-digit number and a fingerprint or iris scan, eliminating the need for physical documents. It prevents duplicate and fake identities.
- Paperless Layer. Reliance on digital records, using Aadhaar eKYC, eSign, and Digital Locker. It enables secure digital storage and retrieval, creating a paperless system for verifying and accessing documents anytime, on any device.
- Cashless Layer. Led by NPCI, this aims to universalise digital payments. UPI enables instant, secure money transfers between bank accounts using a simple Virtual Payment Address (VPA), moving transactions into the digital age for transparency and ease of use.
- Consent Layer. Enables secure, user-controlled data sharing through electronic consent, allowing data to flow freely. The Account Aggregator ecosystem benefits most, with AA acting as a thin data aggregation layer between Financial Information Providers (FIPs) and Financial Information Users (FIUs).
The Impact of the India Stack
The India Stack has played a pivotal role in the country’s rapid digitalisation:
Financial Inclusion. Aadhaar-enabled payment systems (AePS) and UPI have significantly expanded financial access, increasing inclusion from 25% in 2008 to 80% in 2024, particularly benefiting rural and underserved communities.
Boost to Digital Payments. The India Stack has fuelled exponential growth in digital payments, with UPI processing 10 billion monthly transactions. This has driven the rise of digital wallets, fintech platforms, and digitisation of small businesses.
Better Government Services. Aadhaar authentication has improved the delivery of government schemes like Direct Benefit Transfers (DBTs), Public Distribution System (PDS), and pensions, ensuring transparency and reducing leakages.
The India Stack: A Catalyst for Startup Success
The India Stack is fuelling startup innovation by providing a robust digital infrastructure. It enables entrepreneurs to build services like digital payments, eCommerce, and financial solutions for underserved populations. Platforms such as Aadhaar and UPI have paved the way for businesses to offer secure, seamless transactions, allowing startups like Paytm and BharatPe to thrive. These innovations are driving financial inclusion, empowering rural entrepreneurs, and creating opportunities in sectors like lending and healthtech, supported by global and domestic investments.

From Local Success to Global Inspiration
The impact of the India Stack’s success is being felt worldwide. Global giants such as Google Pay, WhatsApp, and Amazon Pay are drawing inspiration from it to enhance their global payment systems. Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai plans to apply lessons from Google Pay’s Indian experience to other markets.
While India Stack has achieved significant success, there is still room for improvement. Strengthening data privacy and security is crucial as personal data collection continues to expand. The Digital Personal Data Protection Act aims to address these issues, but balancing innovation with privacy protection remains a challenge.
Bridging the digital divide by expanding Internet access and improving digital literacy, especially for rural and older populations, is key to ensuring that everyone can benefit from the India Stack’s advantages.

Healthcare delivery and healthtech have made significant strides; yet, the fundamental challenges in healthcare have remained largely unchanged for decades. The widespread acceptance and integration of digital solutions in recent years have supported healthcare providers’ primary goals of enhancing operational efficiency, better resource utilisation (with addressing skill shortages being a key driver), improving patient experience, and achieving better clinical outcomes. With governments pushing for advancements in healthcare outcomes at sustainable costs, the concept of value-based healthcare has gained traction across the industry.
Technology-driven Disruption
Healthcare saw significant disruptions four years ago, and while we will continue to feel the impact for the next decade, one positive outcome was witnessing the industry’s ability to transform amid such immense pressure. I am definitely not suggesting another healthcare calamity! But disruptions can have a positive impact – and I believe that technology will continue to disrupt healthcare at pace. Recently, my colleague Tim Sheedy shared his thoughts on how 2024 is poised to become the year of the AI startup, highlighting innovative options that organisations should consider in their AI journeys. AI startups and innovators hold the potential to further the “good disruption” that will transform healthcare.
Of course, there are challenges associated, including concerns on ethical and privacy-related issues, the reliability of technology – particularly while scaling – and on professional liability. However, the industry cannot overlook the substantial number of innovative startups that are using AI technologies to address some of the most pressing challenges in the healthcare industry.
Why Now?
AI is not new to healthcare. Many would cite the development of MYCIN – an early AI program aimed at identifying treatments for blood infections – as the first known example. It did kindle interest in research in AI and even during the 1980s and 1990s, AI brought about early healthcare breakthroughs, including faster data collection and processing, enhanced precision in surgical procedures, and research and mapping of diseases.
Now, healthcare is at an AI inflection point due to a convergence of three significant factors.
- Advanced AI. AI algorithms and capabilities have become more sophisticated, enabling them to handle complex healthcare data and tasks with greater accuracy and efficiency.
- Demand for Accessible Healthcare. Healthcare systems globally are striving for better care amid resource constraints, turning to AI for efficiency, cost reduction, and broader access.
- Consumer Demand. As people seek greater control over their health, personalised care has become essential. AI can analyse vast patient data to identify health risks and customise care plans, promoting preventative healthcare.
Promising Health AI Startups
As innovative startups continue to emerge in healthcare, we’re particularly keeping an eye on those poised to revolutionise diagnostics, care delivery, and wellness management. Here are some examples.
DIAGNOSTICS
- Claritas HealthTech has created advanced image enhancement software to address challenges in interpreting unclear medical images, improving image clarity and precision. A cloud-based platform with AI diagnostic tools uses their image enhancement technology to achieve greater predictive accuracy.
- Ibex offers Galen, a clinical-grade, multi-tissue platform to detect and grade cancers, that integrate with third-party digital pathology software solutions, scanning platforms, and laboratory information systems.
- MEDICAL IP is focused on advancing medical imaging analysis through AI and 3D technologies (such as 3D printing, CAD/CAM, AR/VR) to streamline medical processes, minimising time and costs while enhancing patient comfort.
- Verge Genomics is a biopharmaceutical startup employing systems biology to expedite the development of life-saving treatments for neurodegenerative diseases. By leveraging patient genomes, gene expression, and epigenomics, the platform identifies new therapeutic gene targets, forecasts effective medications, and categorises patient groups for enhanced clinical efficacy.
- X-Zell focuses on advanced cytology, diagnosing diseases through single atypical cells or clusters. Their plug-and-play solution detects, visualises, and digitises these phenomena in minimally invasive body fluids. With no complex specimen preparation required, it slashes the average sample-to-diagnosis time from 48 hours to under 4 hours.
CARE DELIVERY
- Abridge specialises in automating clinical notes and medical discussions for physicians, converting patient-clinician conversations into structured clinical notes in real time, powered by GenAI. It integrates seamlessly with EMRs such as Epic.
- Waltz Health offers AI-driven marketplaces aimed at reducing costs and innovative consumer tools to facilitate informed care decisions. Tailored for payers, pharmacies, and consumers, they introduce a fresh approach to pricing and reimbursing prescriptions that allows consumers to purchase medication at the most competitive rates, improving accessibility.
- Acorai offers a non-invasive intracardiac pressure monitoring device for heart failure management, aimed at reducing hospitalisations and readmissions. The technology can analyse acoustics, vibratory, and waveform data using ML to monitor intracardiac pressures.
WELLNESS MANAGEMENT
- Anya offers AI-driven support for women navigating life stages such as fertility, pregnancy, parenthood, and menopause. For eg. it provides support during the critical first 1,001 days of the parental journey, with personalised advice, tracking of developmental milestones, and connections with healthcare professionals.
- Dacadoo’s digital health engagement platform aims to motivate users to adopt healthier lifestyles through gamification, social connectivity, and personalised feedback. By analysing user health data, AI algorithms provide tailored insights, goal-setting suggestions, and challenges.
Conclusion
There is no question that innovative startups can solve many challenges for the healthcare industry. But startups flourish because of a supportive ecosystem. The health innovation ecosystem needs to be a dynamic network of stakeholders committed to transforming the industry and health outcomes – and this includes healthcare providers, researchers, tech companies, startups, policymakers, and patients. Together we can achieve the longstanding promise of accessible, cost-effective, and patient-centric healthcare.

In the Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Healthcare Trends in 2022 we have said that 2022 will be the year when we start seeing the second-order impacts of the pandemic and we will see healthcare providers address these impacts. This means an increase in tech adoption and a greater (and in some cases, renewed) interest in tech providers to focus on the Healthcare industry.
Last month, we saw announcements of Francisco Partners acquiring the healthcare data and analytics assets from the IBM Watson Health business unit. This was neither unexpected nor an isolated news – it follows a series of significant Healthcare tech news from last year.
Here are some announcements from 2021 that I feel give us an indication of where the Healthcare tech market is headed.
- Oracle’s acquisition of Cerner
- Microsoft’s continued focus on Healthcare with the Nuance acquisition
- The acquisition of athenahealth by private equity firms
- Examples of the focus on mental health such as the creation of Headspace Health
- The interest of consumer apps in Healthcare as witnessed by Peloton’s corporate wellness programme.
Read on to find out more about these announcements. And let me know what you think is the most interesting Healthcare tech announcement in the last year.
Download “Where is Healthcare Tech Headed?” slides as a PDF.






























































