Google recently extended its Generative AI, Bard, to include coding in more than 20 programming languages, including C++, Go, Java, Javascript, and Python. The search giant has been eager to respond to last year’s launch of ChatGPT but as the trusted incumbent, it has naturally been hesitant to move too quickly. The tendency for large language models (LLMs) to produce controversial and erroneous outputs has the potential to tarnish established brands. Google Bard was released in March in the US and the UK as an LLM but lacked the coding ability of OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Microsoft’s Bing Chat.
Bard’s new features include code generation, optimisation, debugging, and explanation. Using natural language processing (NLP), users can explain their requirements to the AI and ask it to generate code that can then be exported to an integrated development environment (IDE) or executed directly in the browser with Google Colab. Similarly, users can request Bard to debug already existing code, explain code snippets, or optimise code to improve performance.
Google continues to refer to Bard as an experiment and highlights that as is the case with generated text, code produced by the AI may not function as expected. Regardless, the new functionality will be useful for both beginner and experienced developers. Those learning to code can use Generative AI to debug and explain their mistakes or write simple programs. More experienced developers can use the tool to perform lower-value work, such as commenting on code, or scaffolding to identify potential problems.
GitHub Copilot X to Face Competition
While the ability for Bard, Bing, and ChatGPT to generate code is one of their most important use cases, developers are now demanding AI directly in their IDEs.
In March, Microsoft made one of its most significant announcements of the year when it demonstrated GitHub Copilot X, which embeds GPT-4 in the development environment. Earlier this year, Microsoft invested $10 billion into OpenAI to add to the $1 billion from 2019, cementing the partnership between the two AI heavyweights. Among other benefits, this agreement makes Azure the exclusive cloud provider to OpenAI and provides Microsoft with the opportunity to enhance its software with AI co-pilots.
Currently, under technical preview, when Copilot X eventually launches, it will integrate into Visual Studio — Microsoft’s IDE. Presented as a sidebar or chat directly in the IDE, Copilot X will be able to generate, explain, and comment on code, debug, write unit tests, and identify vulnerabilities. The “Hey, GitHub” functionality will allow users to chat using voice, suitable for mobile users or more natural interaction on a desktop.
Not to be outdone by its cloud rivals, in April, AWS announced the general availability of what it describes as a real-time AI coding companion. Amazon CodeWhisperer, integrates with a range of IDEs, namely Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ IDEA, CLion, GoLand, WebStorm, Rider, PhpStorm, PyCharm, RubyMine, and DataGrip, or natively in AWS Cloud9 and AWS Lambda console. While the preview worked for Python, Java, JavaScript, TypeScript, and C#, the general release extends support for most languages. Amazon’s key differentiation is that it is available for free to individual users, while GitHub Copilot is currently subscription-based with exceptions only for teachers, students, and maintainers of open-source projects.
The Next Step: Generative AI in Security
The next battleground for Generative AI will be assisting overworked security analysts. Currently, some of the greatest challenges that Security Operations Centres (SOCs) face are being understaffed and overwhelmed with the number of alerts. Security vendors, such as IBM and Securonix, have already deployed automation to reduce alert noise and help analysts prioritise tasks to avoid responding to false threats.
Google recently introduced Sec-PaLM and Microsoft announced Security Copilot, bringing the power of Generative AI to the SOC. These tools will help analysts interact conversationally with their threat management systems and will explain alerts in natural language. How effective these tools will be is yet to be seen, considering hallucinations in security is far riskier than writing an essay with ChatGPT.
The Future of AI Code Generators
Although GitHub Copilot and Amazon CodeWhisperer had already launched with limited feature sets, it was the release of ChatGPT last year that ushered in a new era in AI code generation. There is now a race between the cloud hyperscalers to win over developers and to provide AI that supports other functions, such as security.
Despite fears that AI will replace humans, in their current state it is more likely that they will be used as tools to augment developers. Although AI and automated testing reduce the burden on the already stretched workforce, humans will continue to be in demand to ensure code is secure and satisfies requirements. A likely scenario is that with coding becoming simpler, rather than the number of developers shrinking, the volume and quality of code written will increase. AI will generate a new wave of citizen developers able to work on projects that would previously have been impossible to start. This may, in turn, increase demand for developers to build on these proofs-of-concept.
How the Generative AI landscape evolves over the next year will be interesting. In a recent interview, OpenAI’s founder, Sam Altman, explained that the non-profit model it initially pursued is not feasible, necessitating the launch of a capped-for-profit subsidiary. The company retains its values, however, focusing on advancing AI responsibly and transparently with public consultation. The appearance of Microsoft, Google, and AWS will undoubtedly change the market dynamics and may force OpenAI to at least reconsider its approach once again.

Innovation and collaboration are the cornerstones of FinTech success stories. Successful FinTechs have identified market gaps and designed innovative solutions to address these gaps. They have also built an ecosystem of partners – such as other FinTechs, large corporates and financial services organisations – to deliver better customer experiences, create process efficiencies and make compliance easier.
As FinTechs have become mainstream over the years the innovations and the collaborations continue to make technology and business headlines.
Here are some recent trends:
- The Growth of Cross-border Finance. Globalisation and the rise of eCommerce have created a truly global marketplace – and financial agencies such as the MAS and those in the EU are responding to the need.
- Transparency through Smart Contracts. As businesses and platforms scale applications and capabilities through global partnerships, there is a need for trusted, transparent transactions. Symbiont‘s partnership with Swift and BNB Chain‘s tie-up with Google Cloud are some recent examples.
- Evolution of Digital Payments. Digital payments have come a long way from the early days of online banking services and is now set to move beyond digital wallets such as the Open Finance Association and EU initiatives to interlink domestic CBDCs.
- Banks Continue to Innovate. They are responding to market demands and focus on providing their customers with easy, secure, and enhanced experiences. NAB is working on digital identity to reduce fraud, while Standard Chartered Bank is collaborating with Bukalapak to introduce new digital services.
- The Emergence of Embedded Finance. In the future, we will see more instances of embedded financial services within consumer products and services that allows seamless financial transactions throughout customer journeys. LG Electronics‘ new NFT offering is a clear instance.
Read below to find out more.
Download The Future of Finance: FinTech Innovations & Collaborations as a PDF

Last week, Kyndryl became a Premier Global Alliance Partner for AWS. This follows other recent similar partnerships for Kyndryl with Google and Microsoft. This now gives Kyndryl premier or similar partner status at the big three hyperscalers.
The Partnership
This new partnership was essential for Kyndryl to provide legitimacy to their independent reputation and their global presence. And in many respects, it is a partnership that AWS needs as much as Kyndryl does. As one of the largest global managed services providers, Kyndryl manages a huge amount of infrastructure and thousands of applications. Today, most of these applications sit outside public cloud environments, but at some stage in the future, many of these applications will move to the public cloud. AWS has positioned itself to benefit from this transition – as Kyndryl will be advising clients on which cloud environment best suits their needs, and in many cases Kyndryl will also be running the application migration and managing the application when it resides in the cloud. To that end, the further investment in developing an accelerator for VMware Cloud on AWS will also help to differentiate Kyndryl on AWS. With a high proportion of Kyndryl customers running VMware, this capability will help VMware users to migrate these workloads to the cloud and run core businesses services on AWS.
The Future
Beyond the typical partnership activities, Kyndryl will build out its own internal infrastructure in the cloud, leveraging AWS as its preferred cloud provider. This experience will mean that Kyndryl “drinks its own champagne” – many other managed services providers have not yet taken the majority of their infrastructure to the cloud, so this experience will help to set Kyndryl apart from their competitors, along with providing deep learning and best practices.
By the end of 2022, Kyndryl expects to have trained more than 10,000 professionals on AWS. Assuming the company hits these targets, they will be one of AWS’s largest partners. However, experience trumps training, and their relatively recent entry into the broader cloud ecosystem space (after coming out from under IBM’s wing at the end of 2021) means they have some way to go to have the depth and breadth of experience that other Premier Alliance Partners have today.
Ecosystm Opinion
In my recent interactions with Kyndryl, what sets them apart is the fact that they are completely customer-focused. They start with a client problem and find the best solution for that problem. Yes – some of the “best solutions” will be partner specific (such as SAP on Azure, VMware on AWS), but they aren’t pushing every customer down a specific path. They are not just an AWS partner – where every solution to every problem starts and ends with AWS. The importance of this new partnership is it expands the capabilities of Kyndryl and hence expands the possibilities and opportunities for Kyndryl clients to benefit from the best solutions in the market – regardless of whether they are on-premises or in one of the big three hyperscalers.

COP26 has firmly put environmental consciousness as a leading global priority. While we have made progress in the last 30 odd years since climate change began to be considered as a reality, a lot needs to be done.
No longer is it enough for only governments to lead on green initiatives. Now is the time for non-profit organisations, investors, businesses – corporate and SMEs – and consumers to come together to ensure we leave a safer planet for our children.
February saw examples of how technology providers and large corporates are delivering on their environmental consciousness and implementing meaningful change.
Here are some announcements that show how tech providers and corporates are strengthening the Sustainability cause:
- IBM launches Sustainability Accelerator Program
- Microsoft boosts their Sustainability offerings by extending extend their EID tool for Microsoft 365
- Salesforce officially announce sustainability as a core company value
- Google enables Sustainable AIOps
- The Aviation industry (Southwest Airlines, ANA, Norwegian Air and Singapore Airlines) appears to be making a concerted effort to reduce carbon footprint.
Read on to find more.
Click here to download a copy of The Future of Sustainability as a PDF.

Since officially separating from IBM in November last year, Kyndryl has been busy cementing some heavyweight partnerships. The alliances with Microsoft, Google, and VMware demonstrate its intention to build hybrid cloud solutions with whoever it needs to, rather than favouring the Big Blue or Red Hat. The SAP tie-up hints at a future of migrating ERP workloads to the cloud and even an eye on moving up the application stack. Last week Kyndryl announced it is working with Nokia to provide private 5G and LTE networks to enable Industry 4.0 solutions. The first customer reference for the partnership is Dow, deploying both real-world and proof-of-concept applications for worker safety and collaboration and asset tracking.
The Partnership
Kyndryl has a competitive networking services unit, particularly in partnership with Cisco. Its focus has been on SD-WAN, campus networks, and network management as part of broader cloud services deals. This 5G partnership with Nokia is its first serious effort to work with one of the major carrier-grade vendors using cellular technology. It creates an opportunity for Kyndryl to position itself as a provider of services that underpin IoT and edge applications, rather than only cloud, which has until now been its main strength.
Prior to the Kyndryl announcement, Nokia was already developing private 5G solutions under the moniker Digital Automation Cloud (DAC). A key customer is Volkswagen, using the network to connect robots and wireless assembly tools. Over-the-air vehicle updates are also tested over the private network. Volkswagen operates in a dedicated 3.7-3.8 GHz band, which was allocated by the Federal Network Agency in Germany. This illustrates a third option for accessing spectrum, which will become an important consideration in private 5G rollouts.
Private 5G Use Cases
Private 5G has several benefits such as low latency, long-range, support for many users per access point, and provision for devices that are mobile due to handover. It is unlikely that it will completely replace other technologies, like wireless LAN, but it is very compelling for certain use cases.
Private 5G is useful on large sites, like mines, ports, farms, and warehouses where connected machines are moving about or some devices – like perimeter security cameras – are just out of reach. Utilities, like power, gas, and water, with infrastructure that needs to be monitored over long distances, will also start looking at it as a part of their predictive maintenance and resiliency systems. Low latency will become increasingly important as we see more and more customer-facing digital services delivered on-site and autonomous robots in the production environment.
Another major benefit of private 5G compared to operating on public service is that data can remain within the organisation’s own network for as long as possible, providing more security and control.
Private 5G Gaining Popularity
There has been a lot of activity over the last year in this space, with the hyperscalers, telecom providers and network equipment vendors developing private 5G offerings.
Last year, the AWS Private 5G was announced, a managed service that includes core network hardware, small-cell radio units, SIM cards, servers, and software. The service operates over a shared spectrum, like the Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) in the US, where the initial preview will be available. CBRS is considered a lightly licenced band. This builds on AWS’s private multi-access edge compute (MEC) solution, released in conjunction with Verizon to integrate AWS Outposts with private 5G operating in licenced spectrum. A customer reference highlighted was low latency, high throughput analysis of video feeds from manufacturing robots at Corning.
Similarly, Microsoft launched a private MEC offering last year, a cloud and software stack designed for operators, systems integrators, and ISVs to deploy private 5G solutions. The system is built up of components from Azure and its acquisition of Metaswitch. AT&T is an early partner bringing a solution to the market built on Microsoft’s technology and the operator’s licenced spectrum. Microsoft highlighted use cases such as asset tracking in logistics, factory operations in manufacturing, and experiments with AI-infused video analytics to improve worker safety.
The Future
Organisations are likely to begin testing private 5G this year for Industry 4.0 applications, either at single sites in the case of factories or in select geographic areas for Utilities. Early applications will mostly focus on simple connectivity for mobile machines or remote equipment. In the longer term, however, the benefits of private 5G will become more apparent as AI applications, such as video analysis and autonomous machines become more prevalent. This will require the full ecosystem of players, including telecom providers, network vendors, cloud hyperscalers, systems integrators, and IoT providers.

It is true that the Retail industry is being forced to evolve the experiences they deliver to their customers. However, if Retail organisations are only focused on creating digital experiences, they are not creating the differentiation that will be required to leap ahead of the competition. It is time for Retail organisations to leverage data to empower multiple roles across the organisation to prepare for the different ways customers want to engage with their brands.
Another trend that is creating a shift in the industry is the rise of small and medium-sized retailers. Traditionally, larger retailers have made larger investments in technology – they simply had deeper pockets for the on-premise investments. However, with the rise of SaaS, size may no longer be such an advantage in Retail.
Here is how organisations such as Walmart, Adobe, GoDaddy and Google are empowering the SME retailer.

Last week AWS announced their plans to invest USD 5.3 billion to launch new data centres in New Zealand’s Auckland region by 2024. Apart from New Zealand, AWS has recently added new regions in Beijing, Hong Kong, Mumbai, Ningxia, Seoul, Singapore, Sydney and Tokyo; and are set to expand into Indonesia, Israel, UAE and Spain.
In a bid to deliver secure and low latency data centre capabilities, the infrastructure hub will comprise three Availability Zones (AZ) and will be owned and operated by the local AWS entity in New Zealand. The new region will enable local businesses and government entities to run workloads and store data using their local data residency preferences.
It is estimated that the new cloud region will create nearly 1,000 jobs over the next 15 years. They will continue to train and upskill the local developers, students and next-gen leaders through the AWS re/Start, AWS Academy, and AWS Educate programs. To support the launch and build new businesses, the AWS Activate program will provide web-based trainings, cloud computing credits, and business mentorship.
New Zealand is becoming attractive to cloud and data centre providers. Last year, Microsoft had also announced their Azure data centre investments and skill development programs in New Zealand. To support the future of cloud services and to fulfil the progressive data centre demands, Datagrid and Meridian Energy partnered to build the country’s first hyperscale data centre, last year. Similarly, CDC Data Centres have plans to develop two new hyperscale data centres in Auckland.
An Opportunity for New Zealand to Punch Above its Weight as the New Data Economy Hub

“The flurry of data centre related activity in New Zealand is not just a reflection of the local opportunity given that the overall IT Market size of a sub-5 million population will always be modest, even if disproportionate. Trust, governance, transparency are hallmarks of the data centre business. Consider this – New Zealand ranks #1 on Ease of Doing Business rankings globally and #1 on the Corruptions Perception Index – not as a one-off but consistently over the years.
Layered on this is a highly innovative business environment, a cluster of high-quality data science skills and an immense appetite to overcome the tyranny of distance through a strong digital economy. New Zealand has the opportunity to become a Data Economy hub as geographic proximity will become less relevant in the new digital economy paradigm.
New Zealand is strategically located between Latin America and Asia, so could act as a data hub for both regions, leveraging undersea cables. The recently initiated and signed Digital Economy Partnership Agreement between Singapore and New Zealand – with Chile as the 3rd country – is a testimony to New Zealand’s ambitions to be at the core of a digital and data economy. The DEPA is a template other countries are likely to sign up to and should enhance New Zealand’s ability to be a trusted custodian of data.
Given the country’s excellent data governance practices, access to clean energy, conducive climate for data centres, plenty of land and an exceptional innovation mindset, this is an opportunity for global businesses to leverage New Zealand as a Data Economy hub.“
New Zealand’s Data Centre Market is Becoming Attractive

“The hyperscale cloud organisations investing in New Zealand-based data centres is both a great opportunity and a significant challenge for both local data centre providers and the local digital industry. With AWS and Microsoft making significant investments in the Auckland region the new facilities, will improve access to the extensive facilities provided by Azure and AWS with reduced latency.
To date, there have not been significant barriers for most non-government organisations to access any of the hyperscalers, with latency of trans-Tasman already reasonably low. However, large organisations, particularly government departments, concerned about data sovereignty are going to welcome this announcement.
With fibre to the premise available in significant parts of New Zealand, with cost-effective 1GB+ symmetrical services available, and hyperscalers on-shore, the pressure to grow New Zealand’s constrained skilled workforce can only increase. Skills development has to be a top priority for the country to take advantage of this infrastructure. While immigration can address part of the challenge, increasing the number of skilled citizens is really needed. It is good to see the commitment that AWS is making with the availability of training options. Now we need to encourage people to take advantage of these options!“
Top Cloud Providers Continue to Drive Data Centre Investment

“Capital investments in data centres have soared in recent quarters. For the webscale sector, spending on data centres and related network technology account for over 40% of total CapEx. The webscale sector’s big cloud providers have accounted for much of the recent CapEx surge. AWS, Google, and Microsoft have been building larger facilities, expanding existing campuses and clusters, and broadening their cloud region footprint into smaller markets. These three account for just under 60% of global webscale tech CapEx over the last four quarters. The facilities these webscale players are building can be immense.
The largest webscalers – Google, AWS, Facebook and Microsoft – clearly prefer to design and operate their own facilities. Each of them spends heavily on both external procurement and internal design for the technology that goes into their data centres. Custom silicon and the highest speed, most advanced optical interconnect solutions are key. As utility costs are a huge element of running a data centre, webscalers also seek out the lowest cost (and, increasingly, greenest) power solutions, often investing in new power sources directly. Webscalers aim to deploy facilities which are on the bleeding edge of technology.
An important part of the growth in cloud adoption is the construction of infrastructure closer to the end-user. AWS’s investment in New Zealand will benefit their positioning and should help deliver more responsive and resilient services to New Zealand’s enterprise market.“

The emergence of COVID-19 last year caused a rapid shift towards work and study from home, and a pickup in eCommerce and social media usage. Tech companies running large data centre-based “webscale” networks have eagerly exploited these changes. Already flush with cash, the webscalers invested aggressively in expanding their networks, in an effort to blanket the globe with rapid, responsive connectivity. Capital investments have soared. For the webscale sector, spending on data centres and related network technology accounts for over 40% of the total CapEx.
Here are the 3 key emerging trends in the data centre market:
#1 Top cloud providers drive webscale investment but are not alone
The webscale sector’s big cloud providers have accounted for much of the recent CapEx surge. AWS, Google, and Microsoft have been building larger facilities, expanding existing campuses and clusters, and broadening their cloud region footprint into smaller markets. These three account for just under 60% of global webscale tech CapEx over the last four quarters. Alibaba and Tencent have been reinforcing their footprints in China and expanding overseas, usually with partners. Numerous smaller cloud providers – notably Oracle and IBM – are also expanding their cloud services offerings and coverage.
Facebook and Apple, while they don’t provide cloud services, also continue to invest aggressively in networks to support large volumes of customer traffic. If we look at Facebook, the reason becomes clear: as of early 2021, they needed to support 65 billion WhatsApp messages per day, over 2 billion minutes of voice and video calls per day, and on a monthly basis their Messenger platform carries 81 billion messages.
The facilities these webscale players are building can be immense. For instance, Microsoft was scheduled to start construction this month on two new data centres in Des Moines Iowa, each of which costs over USD 1 billion and measures over 167 thousand square metres. And Microsoft is not alone in building these large facilities.

#2 Building it all alone is not an option for even the biggest players
The largest webscalers – Google, AWS, Facebook and Microsoft – clearly prefer to design and operate their own facilities. Each of them spends heavily on both external procurement and internal design for the technology that goes into their data centres. Custom silicon and the highest speed, most advanced optical interconnect solutions are key. As utility costs are a huge element of running a data centre, webscalers also seek out the lowest cost (and, increasingly, greenest) power solutions, often investing in new power sources directly. Webscalers aim to deploy facilities that are on the bleeding edge of technology. Nonetheless, in order to reach the far corners of the earth, they have to also rely on other providers’ network infrastructure. Most importantly, this means renting out space in data centres owned by carrier-neutral network operators (CNNOs) in which to install their gear.
The Big 4 webscalers do this as little as possible. For many smaller webscalers though, piggybacking on other networks is the norm. Of course, they want some of their own data centres – usually the largest ones closest to their main concentrations of customers and traffic generators. But leasing space – and functionalities like cloud on-ramps – in third-party facilities helps enormously with time to market.
Oracle is a case in point. They have expanded their cloud services business dramatically in the last few years and attracted some marquee names to their client list, including Zoom, FedEx and Cisco. To ramp up, Oracle reported a rise in CapEx, growing to USD 2.1 billion in the 12 months ended June 2021, which represents a 31% increase from the previous year. However, when compared to Microsoft’s spending this appears modest. Microsoft reported having spent USD 20.6 billion in the 12 months ended June 2021 – a 33% increase over the previous year – to help drive the growth of their Azure cloud service.
One reason behind Oracle’s more modest spending is how heavily the company has relied on colocation partners for their cloud buildouts. Oracle partners with Equinix, Digital Realty, and other providers of neutral data centre space to speed their cloud time to market. Oracle rents space in 29 Digital Realty locations, for instance, and while Equinix doesn’t quantify its partnership with Oracle, Oracle’s cloud regions across the globe access the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) via the Equinix Cloud Exchange Fabric. Oracle also works with telecom providers; their Dubai cloud region, launched in October 2020, is hosted out of an Etisalat owned data centre.
#3 Carrier-neutral data centre investment is surging in concert with webscale/cloud growth
As the webscale sector has raced to expand over the last 2 years, companies that specialise in carrier-neutral data centres have benefited. Industry sources estimate that as much as 50% or more of the cloud sector’s total data centre footprint is actually in these third-party data centres. That is unlikely to change, especially as some CNNOs are explicitly aiming to build out their networks in areas where webscalers have less incentive to devote resources. It’s not just about the webscalers’ need for space; the need for highly responsive, low latency networks is also key, and interconnection closer to the end-user is a driver.
Looking at the biggest publicly traded carrier-neutral providers in the data centre sector shows that their capacity has expanded significantly in the last few years (Figure 1)
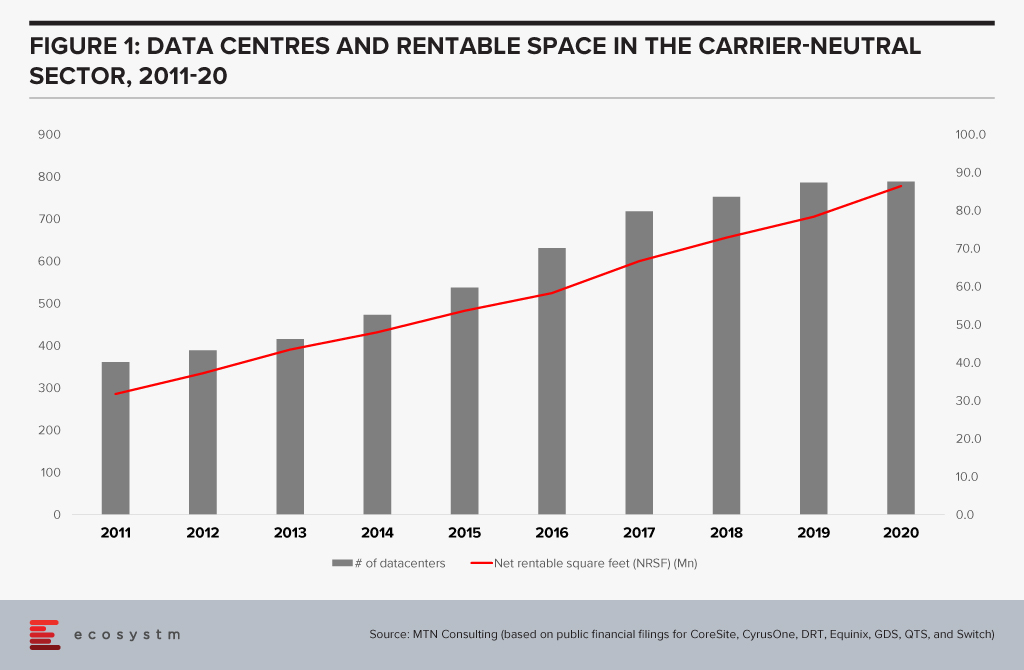
By my estimation, for the first 6 months of 2021, CapEx reported publicly for these CNNOs increased 18% against 1H20, to an estimated USD 4.1 Billion. Beyond the big public names, private equity investment is blossoming in the data centre market, in part aimed at capturing some of the demand growth generated by webscalers. Examples include Blackstone’s acquisition of QTS Realty Trust, Goldman Sachs setting up a data centre-focused venture called Global Compute Infrastructure; and Macquarie Capital’s strategic partnership with Prime Data Centers.
Some of this new investment target core facilities in the usual high-traffic clusters, but some also target smaller country markets (e.g. STT’s new Bangkok-based data centre), and the network edge (e.g. EdgeConneX, a portfolio company of private equity fund EQT Infrastructure).
EdgeConneX is a good example of the flexibility required by the market. They build smaller size facilities and deploy infrastructure closer to the edge of the network, including a PoP in Boston’s Prudential Tower. The company offers data centre solutions “ranging from 40kW to 40MW or more.” They have built over 40 data centres in recent years, including both edge data centres and a number of regional and hyperscale facilities across North America, Europe, and South America. Notably, EdgeConneX recently created a joint venture with India’s property group Adani – AdaniConneX – which looks to leverage India’s status of being the current hotspot for carrier-neutral data centre investment.
As enterprises across many vertical markets continue to adopt cloud services, and their requirements grow more stringent, the investment climate for new data centre capacity is likely to remain strong. Webscale providers will provide much of this capacity, but carrier-neutral specialists have an important role to play.






































