The Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) industry, known for its cautious stance on technology, is swiftly undergoing a transformational modernisation journey. Areas such as digital customer experiences, automated fraud detection, and real-time risk assessment are all part of a technology-led roadmap. This shift is transforming the cybersecurity stance of BFSI organisations, which have conventionally favoured centralising everything within a data centre behind a firewall.
Ecosystm research finds that 75% of BFSI technology leaders believe that a data breach is inevitable. This requires taking a new cyber approach to detect threats early, reduce the impact of an attack, and avoid lateral movement across the network.
BFSI organisations will boost investments in two main areas over the next year: updating infrastructure and software, and exploring innovative domains like digital workplaces and automation. Cybersecurity investments are crucial in both of these areas.
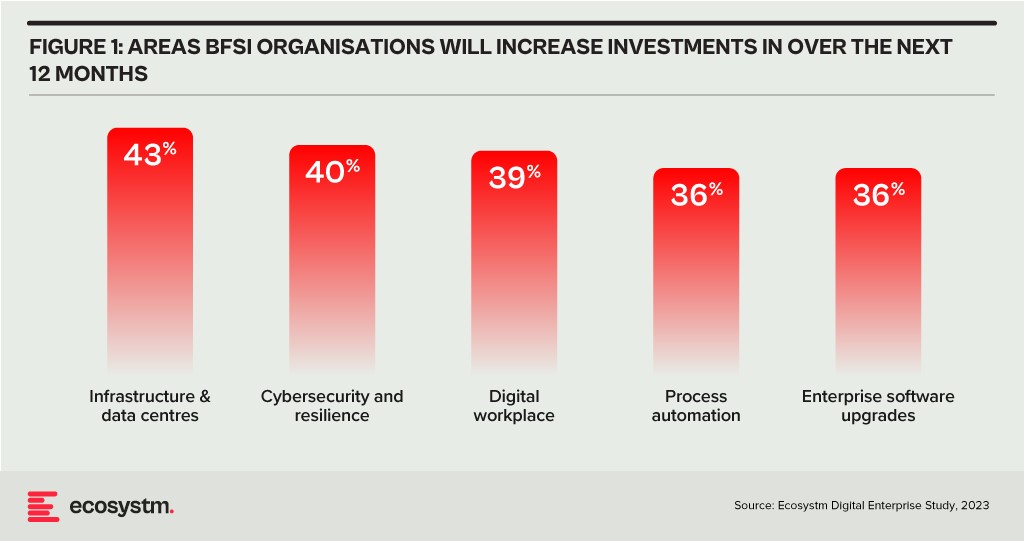
As a regulated industry, breaches come with significant cost implications, underscoring the need to prioritise cybersecurity. BFSI cybersecurity and risk teams need to constantly reassess their strategies for safeguarding data and fulfilling compliance obligations, as they explore ways to facilitate new services for customers, partners, and employees.
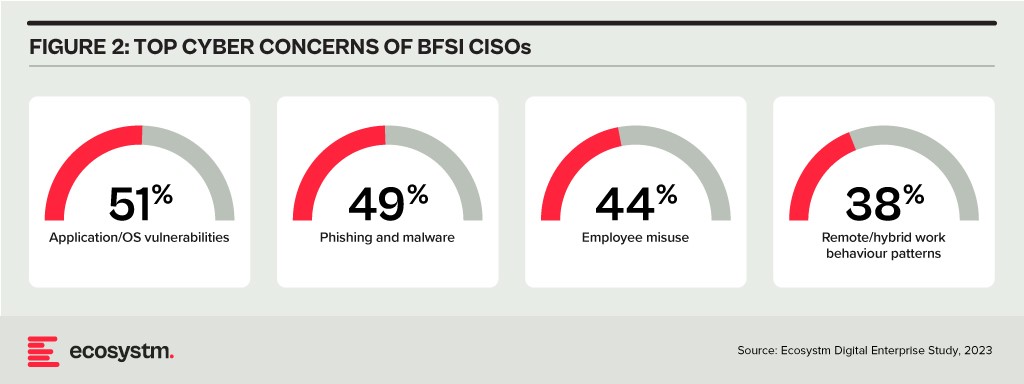
The primary concerns of BFSI CISOs can be categorised into two distinct groups:
- Expanding Technology Use. This includes the proliferation of applications and devices, as well as data access beyond the network perimeter.
- Employee-Related Vulnerabilities. This involves responses to phishing and malware attempts, as well as intentional and unintentional misuse of technology.
Vulnerabilities Arising from Employee Actions
Security vulnerabilities arising from employee actions and unawareness represent a significant and ongoing concern for businesses of all sizes and industries – the risks are just much bigger for BFSI. These vulnerabilities can lead to data breaches, financial losses, damage to reputation, and legal ramifications. A multi-pronged approach is needed that combines technology, training, policies, and a culture of security consciousness.
Training and Culture. BFSI organisations prioritise comprehensive training and awareness programs, educating employees about common threats like phishing and best practices for safeguarding sensitive data. While these programs are often ongoing and adaptable to new threats, they can sometimes become mere compliance checklists, raising questions about their true effectiveness. Conducting simulated phishing attacks and security quizzes to assess employee awareness and identify areas where further training is required, can be effective.
To truly educate employees on risks, it’s essential to move beyond compliance and build a cybersecurity culture throughout the organisation. This can involve setting organisation-wide security KPIs that cascade from the CEO down to every employee, promoting accountability and transparency. Creating an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting security concerns is critical for early threat detection and mitigation.
Policies. Clear security policies and enforcement are essential for ensuring that employees understand their roles within the broader security framework, including responsibilities on strong password use, secure data handling, and prompt incident reporting. Implementing the principle of least privilege, which restricts access based on specific roles, mitigates potential harm from insider threats and inadvertent data exposure. Policies should evolve through routine security audits, including technical assessments and evaluations of employee protocol adherence, which will help organisations with a swifter identification of vulnerabilities and to take the necessary corrective actions.
However, despite the best efforts, breaches do happen – and this is where a well-defined incident response plan, that is regularly tested and updated, is crucial to minimise the damage. This requires every employee to know their roles and responsibilities during a security incident.
Tech Expansion Leading to Cyber Complexity
Cloud. Initially hesitant to transition essential workloads to the cloud, the BFSI industry has experienced a shift in perspective due to the rise of inventive SaaS-based Fintech tools and hybrid cloud solutions, that have created new impetus for change. This new distributed architecture requires a fresh look at cyber measures. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) providers are integrating a range of cloud-delivered safeguards, such as FWaaS, CASB, and ZTNA with SD-WAN to ensure organisations can securely access the cloud without compromising on performance.
Data & AI. Data holds paramount importance in the BFSI industry for informed decision-making, personalised customer experiences, risk assessment, fraud prevention, and regulatory compliance. AI applications are being used to tailor products and services, optimise operational efficiency, and stay competitive in an evolving market. As part of their technology modernisation efforts, 47% of BFSI institutions are refining their data and AI strategies. They also acknowledge the challenges associated – and satisfying risk, regulatory, and compliance requirements is one of the biggest challenges facing BFSI organisations in the AI deployments.
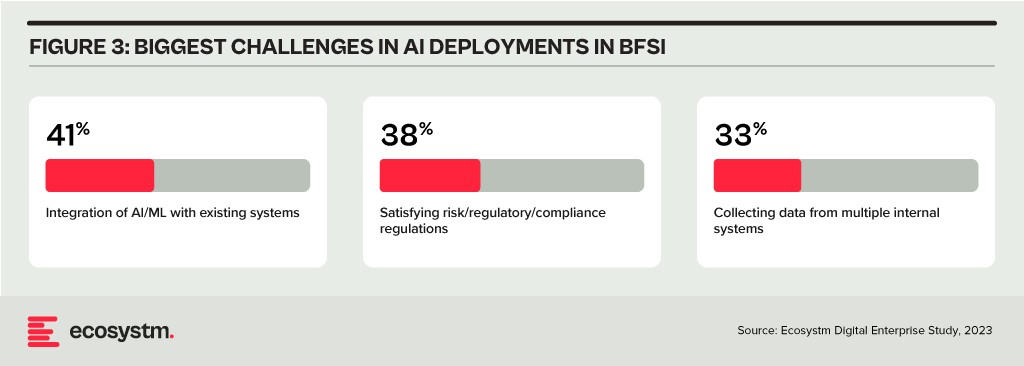
The rush to experiment with Generative AI and foundation models to assist customers and employees is only heightening these concerns. There is an urgent need for policies around the use of these emerging technologies. Initiatives such as the Monetary Authority of Singapore’s Veritas that aim to enable financial institutions to evaluate their AI and data analytics solutions against the principles of fairness, ethics, accountability, and transparency (FEAT) are expected to provide the much-needed guidance to the industry.
Digital Workplace. As with other industries with a high percentage of knowledge workers, BFSI organisations are grappling with granting remote access to staff. Cloud-based collaboration and Fintech tools, BYOD policies, and sensitive data traversing home networks are all creating new challenges for cyber teams. Modern approaches, such as zero trust network access, privilege management, and network segmentation are necessary to ensure workers can seamlessly but securely perform their roles remotely.

Looking Beyond Technology: Evaluating the Adequacy of Compliance-Centric Cyber Strategies
The BFSI industry stands among the most rigorously regulated industries, with scrutiny intensifying following every collapse or notable breach. Cyber and data protection teams shoulder the responsibility of understanding the implications of and adhering to emerging data protection regulations in areas such as GDPR, PCI-DSS, SOC 2, and PSD2. Automating compliance procedures emerges as a compelling solution to streamline processes, mitigate risks, and curtail expenses. Technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA), low-code development, and continuous compliance monitoring are gaining prominence.
The adoption of AI to enhance security is still emerging but will accelerate rapidly. Ecosystm research shows that within the next two years, nearly 70% of BFSI organisations will have invested in SecOps. AI can help Security Operations Centres (SOCs) prioritise alerts and respond to threats faster than could be performed manually. Additionally, the expanding variety of network endpoints, including customer devices, ATMs, and tools used by frontline employees, can embrace AI-enhanced protection without introducing additional onboarding friction.
However, there is a need for BFSI organisations to look beyond compliance checklists to a more holistic cyber approach that can prioritise cyber measures continually based on the risk to the organisations. And this is one of the biggest challenges that BFSI CISOs face. Ecosystm research finds that 72% of cyber and technology leaders in the industry feel that there is limited understanding of cyber risk and governance in their organisations.
In fact, BFSI organisations must look at the interconnectedness of an intelligence-led and risk-based strategy. Thorough risk assessments let organisations prioritise vulnerability mitigation effectively. This targeted approach optimises security initiatives by focusing on high-risk areas, reducing security debt. To adapt to evolving threats, intelligence should inform risk assessment. Intelligence-led strategies empower cybersecurity leaders with real-time threat insights for proactive measures, actively tackling emerging threats and vulnerabilities – and definitely moving beyond compliance-focused strategies.

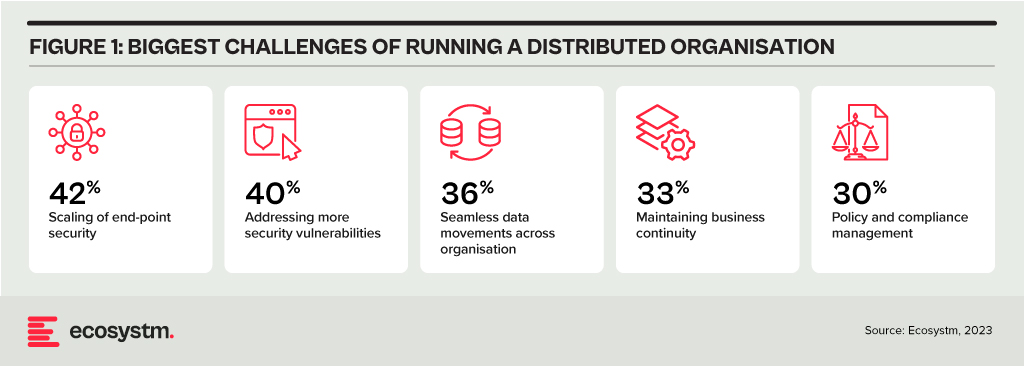
Traditional network architectures are inherently fragile, often relying on a single transport type to connect branches, production facilities, and data centres. The imperative for networks to maintain resilience has grown significantly, particularly due to the delivery of customer-facing services at branches and the increasing reliance on interconnected machines in operational environments. The cost of network downtime can now be quantified in terms of both lost customers and reduced production.
Distributed Enterprises Face New Challenges
As the importance of maintaining resiliency grows, so does the complexity of network management. Distributed enterprises must provide connectivity under challenging conditions, such as:
- Remote access for employees using video conferencing
- Local breakout for cloud services to avoid backhauling
- IoT devices left unattended in public places
- Customers accessing digital services at the branch or home
- Sites in remote areas requiring the same quality of service
Network managers require intelligent tools to remain in control without adding any unnecessary burden to end users. The number of endpoints and speed of change has made it impossible for human operators to manage without assistance from AI.
AI-Enhanced Network Management
Modern network operations centres are enhancing their visibility by aggregating data from diverse systems and consolidating them within a unified management platform. Machine learning (ML) and AI are employed to analyse data originating from enterprise networks, telecom Points of Presence (PoPs), IoT devices, cloud service providers, and user experience monitoring. These technologies enable the early identification of network issues before they reach critical levels. Intelligent networks can suggest strategies to enhance network resilience, forecast how modifications may impact performance, and are increasingly capable of autonomous responses to evolving conditions.
Here are some critical ways that AI/ML can help build resilient networks.
- Alert Noise Reduction. Network operations centres face thousands of alerts each day. As a result, operators battle with alert fatigue and are challenged to identify critical issues. Through the application of ML, contemporary monitoring tools can mitigate false positives, categorise interconnected alerts, and assist operators in prioritising the most pressing concerns. An operations team, augmented with AI capabilities could potentially de-prioritise up to 90% of alerts, allowing a concentrated focus on factors that impact network performance and resilience.
- Data Lakes. Networking vendors are building their own proprietary data lakes built upon telemetry data generated by the infrastructure they have deployed at customer sites. This vast volume of data allows them to use ML to create a tailored baseline for each customer and to recommend actions to optimise the environment.
- Root Cause Analysis. To assist network operators in diagnosing an issue, AIOps can sift through thousands of data points and correlate them to identify a root cause. Through the integration of alerts with change feeds, operators can understand the underlying causes of network problems or outages. By using ML to understand the customer’s unique environment, AIOps can progressively accelerate time to resolution.
- Proactive Response. As management layers become capable of recommending corrective action, proactive response also becomes possible, leading to self-healing networks. With early identification of sub-optimal conditions, intelligent systems can conduct load balancing, redirect traffic to higher performing SaaS regions, auto-scale cloud instances, or terminate selected connections.
- Device Profiling. In a BYOD environment, network managers require enhanced visibility to discover devices and enforce appropriate policies on them. Automated profiling against a validated database ensures guest access can be granted without adding friction to the onboarding process. With deep packet inspection, devices can be precisely classified based on behaviour patterns.
- Dynamic Bandwidth Aggregation. A key feature of an SD-WAN is that it can incorporate diverse transport types, such as fibre, 5G, and low earth orbit (LEO) satellite connectivity. Rather than using a simple primary and redundant architecture, bandwidth aggregation allows all circuits to be used simultaneously. By infusing intelligence into the SD-WAN layer, the process of path selection can dynamically prioritise traffic by directing it over higher quality or across multiple links. This approach guarantees optimal performance, even in the face of network degradation.
- Generative AI for Process Efficiency. Every tech company is trying to understand how they can leverage the power of Generative AI, and networking providers are no different. The most immediate use case will be to improve satisfaction and scalability for level 1 and level 2 support. A Generative AI-enabled service desk could provide uninterrupted support during high-volume periods, such as during network outages, or during off-peak hours.
Initiating an AI-Driven Network Management Journey
Network managers who take advantage of AI can build highly resilient networks that maximise uptime, deliver consistently high performance, and remain secure. Some important considerations when getting started include:
- Data Catalogue. Take stock of the data sources that are available to you, whether they come from network equipment telemetry, applications, or the data lake of a managed services provider. Understand how they can be integrated into an AIOps solution.
- Start Small. Begin with a pilot in an area where good data sources are available. This will help you assess the impact that AI could have on reducing alerts, improving mean time to repair (MTTR), increasing uptime, or addressing the skills gap.
- Develop an SD-WAN/SASE Roadmap. Many advanced AI benefits are built into an SD-WAN or SASE. Most organisations already have or will soon adopt SD-WAN but begin assessing the SASE framework to decide if it is suitable for your organisation.

Generative AI is seeing enterprise interest and early adoption enhancing efficiency, fostering innovation, and pushing the boundaries of possibility. It has the potential of reshaping industries – and fast!
However, alongside its immense potential, Generative AI also raises concerns. Ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and security come to the forefront, as powerful AI systems handle vast amounts of sensitive information.
Addressing these concerns through responsible AI development and thoughtful regulation will be crucial to harnessing the full transformative power of Generative AI.
Read on to find out the key challenges faced in implementing Generative AI and explore emerging use cases in industries such as Financial Services, Retail, Manufacturing, and Healthcare.
Download ‘Generative AI: Industry Adoption’ as a PDF

I have spent many years analysing the mobile and end-user computing markets. Going all the way back to 1995 where I was part of a Desktop PC research team, to running the European wireless and mobile comms practice, to my time at 3 Mobile in Australia and many years after, helping clients with their end-user computing strategies. From the birth of mobile data services (GPRS, WAP, and so on to 3G, 4G and 5G), from simple phones to powerful foldable devices, from desktop computers to a complex array of mobile computing devices to meet the many and varied employee needs. I am always looking for the “next big thing” – and there have been some significant milestones – Palm devices, Blackberries, the iPhone, Android, foldables, wearables, smaller, thinner, faster, more powerful laptops.
But over the past few years, innovation in this space has tailed off. Outside of the foldable space (which is already four years old), the major benefits of new devices are faster processors, brighter screens, and better cameras. I review a lot of great computers too (like many of the recent Surface devices) – and while they are continuously improving, not much has got my clients or me “excited” over the past few years (outside of some of the very cool accessibility initiatives).
The Force of AI
But this is all about to change. Devices are going to get smarter based on their data ecosystem, the cloud, and AI-specific local processing power. To be honest, this has been happening for some time – but most of the “magic” has been invisible to us. It happened when cameras took multiple shots and selected the best one; it happened when pixels were sharpened and images got brighter, better, and more attractive; it happened when digital assistants were called upon to answer questions and provide context.
Microsoft, among others, are about to make AI smarts more front and centre of the experience – Windows Copilot will add a smart assistant that can not only advise but execute on advice. It will help employees improve their focus and productivity, summarise documents and long chat threads, select music, distribute content to the right audience, and find connections. Added to Microsoft 365 Copilot it will help knowledge workers spend less time searching and reading – and more time doing and improving.
The greater integration of public and personal data with “intent insights” will also play out on our mobile devices. We are likely to see the emergence of the much-promised “integrated app”– one that can take on many of the tasks that we currently undertake across multiple applications, mobile websites, and sometimes even multiple devices. This will initially be through the use of public LLMs like Bard and ChatGPT, but as more custom, private models emerge they will serve very specific functions.
Focused AI Chips will Drive New Device Wars
In parallel to these developments, we expect the emergence of very specific AI processors that are paired to very specific AI capabilities. As local processing power becomes a necessity for some AI algorithms, the broad CPUs – and even the AI-focused ones (like Google’s Tensor Processor) – will need to be complemented by specific chips that serve specific AI functions. These chips will perform the processing more efficiently – preserving the battery and improving the user experience.
While this will be a longer-term trend, it is likely to significantly change the game for what can be achieved locally on a device – enabling capabilities that are not in the realm of imagination today. They will also spur a new wave of device competition and innovation – with a greater desire to be on the “latest and greatest” devices than we see today!
So, while the levels of device innovation have flattened, AI-driven software and chipset innovation will see current and future devices enable new levels of employee productivity and consumer capability. The focus in 2023 and beyond needs to be less on the hardware announcements and more on the platforms and tools. End-user computing strategies need to be refreshed with a new perspective around intent and intelligence. The persona-based strategies of the past have to be changed in a world where form factors and processing power are less relevant than outcomes and insights.

Zurich will be the centre of attention for the Financial and Regulatory industries from June 26th to 28th as it hosts the second edition of the Point Zero Forum. Organised by Elevandi and the Swiss State Secretariat for International Finance, this event serves as a platform to encourage dialogue on policy and technology in Financial Services, with a particular emphasis on adopting transformative technologies and establishing the necessary governance and risk frameworks.
As a knowledge partner, Ecosystm is deeply involved in the Point Zero Forum. Throughout the event, we will actively engage in discussions and closely monitor three key areas: ESG, digital assets, and Responsible AI.
Read on to find out what our leaders — Amit Gupta (CEO, Ecosystm Group), Ullrich Loeffler (CEO and Co-Founder, Ecosystm), and Anubhav Nayyar (Chief Growth Advisor, Ecosystm) — say about why this will be core to building a sustainable and innovative future.
Download ‘Building Synergy Between Policy & Technology’ as a PDF

In 2021, Ecosystm Principal Advisor Niloy Mukherjee wrote about the evolving partner landscape and the rise of non-traditional partners. This trend has continued to grow, and the “partner” has now evolved to include many of the things mentioned in that article.
These new avenues provide opportunities for growth but also bring with them some challenges. Building a successful partner program that considers the growing importance of new kinds of “partners” while managing the existing partner network can be a difficult task – one that many providers are still struggling to perfect.
Simultaneously, the expectations from traditional channel partners have also changed. The role of these partners is changing as platformisation and access make it easy to transact without an intermediary.
The partner world in 2023 is in an extraordinary state of flux.
Read on to find out Niloy’s thoughts on why the partner landscape is in a state of flux; how partners are evolving away from traditional roles and what is motivating the shifts: and the impact on both traditional partners and the partner strategies of large technology providers.
Download “The Evolving Partner Landscape: 2023 Edition” as a PDF

After the resounding success of the inaugural event last year, Ecosystm is once again partnering with Elevandi and the State Secretariat for International Finance SIF as a knowledge partner for the Point Zero Forum 2023. In this Ecosystm Insights, our guest author Jaskaran Bhalla, Content Lead, Elevandi talks about the Point Zero Forum 2023 and how it is all set to explore digital assets, sustainability, and AI in an ever-evolving Financial Services landscape.

The Point Zero Forum is returning for its second edition between 26 to 28 June 2023 in Zurich, Switzerland. The inaugural Forum held in June 2022 attracted over 1,000 leaders and featured more than 200 esteemed speakers from Europe, Asia Pacific, the USA, and MENA. The Forum represents a collaboration between the Swiss State Secretariat for International Finance (SIF) and Elevandi and is organised in cooperation with the BIS Innovation Hub, the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), and the Swiss National Bank.
As we gear up for this year’s Point Zero Forum, let’s take a moment to reflect on some of the pivotal developments that have shaped the Financial Services industry since the previous Forum and also moulded the three key themes that will take centre stage this year: Sustainability, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Digital Assets.
COP27, the rise of blended finance and the groundbreaking Net-Zero Public Data Utility
In November 2022, the Government of the Arab Republic of Egypt hosted the 27th session of the Conference of the Parties of the UNFCCC (COP27), with a view to accelerate the transition to a low-carbon future. In the build-up to COP27, Ravi Menon, the Managing Director of the MAS spoke at the inaugural Transition Finance towards Net-Zero conference and shared with the audience that the world is currently not on a trajectory to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. And according to the UN Emissions Gap report 2021, based on the current policies in place, the world is 55% short of the emissions reduction target for 2030. He also elaborated on the significant role that blended finance can play in tackling climate change, a theme that widely resonated with the global leaders at COP27. To enable easy and transparent reporting on climate commitments, the Climate Data Steering Committee (CDSC) outlined the next steps on its recommended plans for the Net-Zero Data Public Utility (NZDPU) at COP 27. NZDPU aims to aid efforts to transition to a net-zero economy by addressing data gaps, inconsistencies, and barriers to information that slow climate action.
The Point Zero Forum 2023 will deep-dive into the data, technologies, and capital and risk management solutions that can accelerate the fair transition towards a low-carbon future.
Panel Discussion Highlight: The opening panel discussion, “Data for Net-Zero: Views from the Climate Data Steering Committee,” scheduled for 26 June, will feature members of the CDSC, which include the Financial Conduct Authority, the MAS, Glasgow Financial Alliance for Net Zero (GFANZ), and the Swiss State Secretariat for International Finance. The panel will discuss the role of new technologies and collaborative platforms in promoting greater accessibility of transition data and innovative business models.
The launch of ChatGPT by OpenAI and its record for the fastest 100M monthly active users
The launch of ChatGPT by OpenAI on 30 November, 2022 led to widespread adoption by users globally – eventually setting the record for the fastest-growing, active users, hitting 100M monthly active users by Feb 2023. While on one hand users rushed to share enormous efficiency gains achieved by the use of ChatGPT, on the other hand ChatGPT soon became a disruptive tool to spread fake news.
The Point Zero Forum 2023 will deep-dive into Generative AI’s potential for enhancing efficiency, improving risk management, and providing better customer experience in the Financial Services industry, while highlighting the need for ensuring fair, ethical, accountable, and transparent use of these technologies.
Panel Discussion Highlight: The session “Breaking New Ground with Generative AI: Project MindForge”, scheduled for 27 June, will feature global leaders from NVIDIA, the MAS, Citigroup and Bloomberg. The panel will discuss the opportunities of Generative AI for the Financial Services sector.
MiCA regulation gets adopted by the EU lawmakers and sets a precedent for digital asset regulations
More than 2.5 years after it was first proposed, the EU Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation was approved in April 2023 by EU Parliament. While there is still work to be done to implement MiCA and measure its success, and to answer open questions around regulation for out-of-scope assets (like DeFI and NFTs), the digital assets industry is keenly observing whether MiCA could serve as a template for global crypto regulation. In May 2023, the International Organization Of Securities Commissions (IOSCO), the global standard setter for securities markets, also joined the global discussion on digital asset regulation by issuing for consultation detailed recommendations to jurisdictions across the globe as to how to regulate crypto assets.
The Point Zero Forum 2023 will do a stocktake on key global regulatory frameworks, market infrastructure, and use cases for the widespread adoption of digital assets, asset tokenisation, and distributed ledger technology.
Panel Discussion Highlight: The sessions “State of Global Digital Asset Regulation: Navigating Opportunities in an Evolving Landscape” and “Interoperability and Regulatory Compliance: Building the Future of Digital Asset Infrastructure”, scheduled on 26 and 27 June respectively, will feature global leaders from both public sector (such as the MAS, Bank of Italy, Bank of Thailand, U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission, EU Parliament) and private sector organisations (such as JP Morgan, Sygnum, SBI Digital Assets, Chainalysis, GBBC, SIX Digital Exchange). The discussions will centre around digital asset regulations and key considerations in the rapidly evolving world of digital assets.

Register here at https://www.pointzeroforum.com/registration. Receive 10% off the Industry Pass by entering the code ‘JB10’ at check out. (Policymakers, regulators, think tanks, and academics receive complimentary access/ Founders of tech companies (incorporated for less than 3 years) can apply for a discounted Founder’s Pass)
Organisations are moving beyond digitalisation to a focus on building market differentiation. It is widely acknowledged that customer-centric strategies lead to better business outcomes, including increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, competitiveness, growth, and profitability.
AI is the key enabler driving personalisation at scale. It has also become key to improving employee productivity, empowering them to focus on high-value tasks and deepening customer engagements.
Over the last month – at the Salesforce World Tour and over multiple analyst briefings – Salesforce has showcased their desire to solve customer challenges using AI innovations. They have announced a range of new AI innovations across Data Cloud, their integrated CRM platform.
Ecosystm Advisors Kaushik Ghatak, Niloy Mukherjee, Peter Carr, and Sash Mukherjee comment on Salesforce’s recent announcements and messaging.
Read on to find out more.
Download Ecosystm VendorSphere: Salesforce AI Innovations Transforming CRM as a PDF

It is not hyperbole to state that AI is on the cusp of having significant implications on society, business, economies, governments, individuals, cultures, politics, the arts, manufacturing, customer experience… I think you get the idea! We cannot understate the impact that AI will have on society. In times gone by, businesses tested ideas, new products, or services with small customer segments before they went live. But with AI we are all part of this experiment on the impacts of AI on society – its benefits, use cases, weaknesses, and threats.
What seemed preposterous just six months ago is not only possible but EASY! Do you want a virtual version of yourself, a friend, your CEO, or your deceased family member? Sure – just feed the data. Will succession planning be more about recording all conversations and interactions with an executive so their avatar can make the decisions when they leave? Why not? How about you turn the thousands of hours of recorded customer conversations with your contact centre team into a virtual contact centre team? Your head of product can present in multiple countries in multiple languages, tailored to the customer segments, industries, geographies, or business needs at the same moment.
AI has the potential to create digital clones of your employees, it can spread fake news as easily as real news, it can be used for deception as easily as for benefit. Is your organisation prepared for the social, personal, cultural, and emotional impacts of AI? Do you know how AI will evolve in your organisation?
When we focus on the future of AI, we often interview AI leaders, business leaders, futurists, and analysts. I haven’t seen enough focus on psychologists, sociologists, historians, academics, counselors, or even regulators! The Internet and social media changed the world more than we ever imagined – at this stage, it looks like these two were just a rehearsal for the real show – Artificial Intelligence.
Lack of Government or Industry Regulation Means You Need to Self-Regulate
These rapid developments – and the notable silence from governments, lawmakers, and regulators – make the requirement for an AI Ethics Policy for your organisation urgent! Even if you have one, it probably needs updating, as the scenarios that AI can operate within are growing and changing literally every day.
- For example, your customer service team might want to create a virtual customer service agent from a real person. What is the policy on this? How will it impact the person?
- Your marketing team might be using ChatGPT or Bard for content creation. Do you have a policy specifically for the creation and use of content using assets your business does not own?
- What data is acceptable to be ingested by a public Large Language Model (LLM). Are are you governing data at creation and publishing to ensure these policies are met?
- With the impending public launch of Microsoft’s Co-Pilot AI service, what data can be ingested by Co-Pilot? How are you governing the distribution of the insights that come out of that capability?
If policies are not put in place, data tagged, staff trained, before using a tool such as Co-Pilot, your business will be likely to break some privacy or employment laws – on the very first day!
What do the LLMs Say About AI Ethics Policies?
So where do you go when looking for an AI Ethics policy? ChatGPT and Bard of course! I asked the two for a modern AI Ethics policy.
You can read what they generated in the graphic below.
I personally prefer the ChatGPT4 version as it is more prescriptive. At the same time, I would argue that MOST of the AI tools that your business has access to today don’t meet all of these principles. And while they are tools and the ethics should dictate the way the tools are used, with AI you cannot always separate the process and outcome from the tool.
For example, a tool that is inherently designed to learn an employee’s character, style, or mannerisms cannot be unbiased if it is based on a biased opinion (and humans have biases!).
LLMs take data, content, and insights created by others, and give it to their customers to reuse. Are you happy with your website being used as a tool to train a startup on the opportunities in the markets and customers you serve?
By making content public, you acknowledge the risk of others using it. But at least they visited your website or app to consume it. Not anymore…
A Policy is Useless if it Sits on a Shelf
Your AI ethics policy needs to be more than a published document. It should be the beginning of a conversation across the entire organisation about the use of AI. Your employees need to be trained in the policy. It needs to be part of the culture of the business – particularly as low and no-code capabilities push these AI tools, practices, and capabilities into the hands of many of your employees.
Nearly every business leader I interview mentions that their organisation is an “intelligent, data-led, business.” What is the role of AI in driving this intelligent business? If being data-driven and analytical is in the DNA of your organisation, soon AI will also be at the heart of your business. You might think you can delay your investments to get it right – but your competitors may be ahead of you.
So, as you jump head-first into the AI pool, start to create, improve and/or socialise your AI Ethics Policy. It should guide your investments, protect your brand, empower your employees, and keep your business resilient and compliant with legacy and new legislation and regulations.




















































