Organisations are increasingly investing in digital. However, they are at different stages of their digital maturity. Some companies are in the early transitional stages while others are investing to upgrade capabilities they instituted long ago. An understanding of the digital maturity of a typical organisation in your market/industry can help you benchmark your technology and. digital roadmap.
This ebook presents some key findings for financial services within Indonesia. You will get insights on impact of COVID-19 on transformation journeys, key business priorities for 2021, and the shift in engagement strategies and channels.
Click below to download the eBook

(Clicking on this link will take you to Sitecore website where you can download the eBook)

Since the start of this millennium, no region has transformed as much as Asia. There has been significant paradigm shifts in the region and the perception that innovation starts in the US or in Europe and percolates through to Asia after a time lag, has been shattered. Asia is constantly demonstrating how dynamic, and technology-focused it is. This is getting fueled by the impact of the growing middle class on consumerism and the spirit of innovation across the region. The region has also seen a surge in new and upcoming business leaders who are embracing change and looking beyond success to creating impact.
What is Driving Innovation in Asia?
The “If you ain’t got it, build it” attitude. One of the key drivers of this shift is the age of the average population in Asia. According to the UN the Asia Pacific region has nearly 60% of the world’s youth population (between the age of 17-24). With youth comes dynamism, a desire to change the world, and innovation. As this age group enters the workforce, they will transform their lives and the companies they work in. They are already showing a spirit of agility when it comes to solving challenges – they will build what they do not have.
The Need to enable Foundational Shifts. The younger generation is more aware of environmental, social and governance issues that the world continues to face. Many of the countries in the region are emerging economies, where these issues become more apparent. COVID-19 has also inculcated an empathy in people and they are thinking of future success in terms of impact. The desire to enable foundational shifts is giving direction to the transformation journey in the region. The wonderful new paradigm that is the Digital Economy allows us to cut across all segments; and technology and its advancements has immense potential to create a more sustainable and inclusive future for the world.
Realising the Power of Momentum. The pandemic has caused major disruptions in the region. But every crisis also presents an opportunity to perhaps re-imagine a brighter world through a digital lens. The other thing that the pandemic has done is made people and organisations realise that to succeed they need to be open to change – and that momentum is important. As organisations had to pivot fast, they realised what I have been saying for years – we shouldn’t “let perfect get in the way of better”. This adaptability and the readiness to fail fast and learn from the mistakes early for eventual success, is leading to faster and more agile transformation journeys.
Where are we seeing the most impact?
Industries are Transforming. There are industries such as Healthcare and Education that had to transform out of a necessity and urgency brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic. This has led to a greater impetus for change and optimism in these industries. These industries will continue to transform as governments focus significantly on creating “Social Safety Nets” and technology plays a key role in enabling critical services across Health, Education and Food Security. Then there are industries, such as the Financial Services and Retail, that had a strong customer focus and were well on their digital journeys before the pandemic. The pandemic boosted these efforts.
But these are not the only industries that are transforming. There are industries that have been impacted more than others. There are several instances of how organisations in these industries are demonstrating not only resilience but innovation. The Travel & Hospitality industry has had several such instances. As business models evolve the industry will see significant changes in digital channels to market, booking engines, corporate service offerings and others, as the overall Digital Strategy is overhauled.
Technologies are Evolving. Organisations depended on their tech partners to help them make the fast pivot required to survive and succeed in the last year – and tech companies have not disappointed. They have evolved their capabilities and continue to offer innovative solutions that can solve many of the ongoing business challenges that organisations face in their innovation journey. More and more technologies such as AI, machine learning, robotics, and digital twins are getting enmeshed together to offer better options for business growth, process efficiency and customer engagement. And the 5G rollouts will only accelerate that. The initial benefits being realized from early adoption of 5G has been for consumers. But there is a much bigger impact that is waiting to be realised as 5G empowers governments and businesses to make critical decisions at the edge.
Tech Start-ups are Flourishing. There are immense opportunities for technology start-ups to grow their market presence through innovative products and services. To succeed these companies need to have a strong investment roadmap; maintain a strong focus on customer engagement; and offer technology solutions that can fulfil the global needs of their customers. Technologies that promote efficiency and eliminate mundane tasks for humans are the need of the hour. However, as the reliance on technology-led transformation increases, tech vendors are becoming acutely aware that they cannot be best-in-class across the different technologies that an organisation will require to transform. Here is where having a robust partner ecosystem helps. Partnerships are bringing innovation to scale in Asia.
We can expect Asia to emerge as a powerhouse as businesses continue to innovate, embed technology in their product and service offerings – and as tech start-ups continue to support their innovation journeys.
Ecosystm CEO Amit Gupta gets face to face with Garrett Ilg, President Asia Pacific & Japan, Oracle to discuss the rise of the Asia Digital economies, the impact of the growing middle class on consumerism and the spirit of innovation across the region.

In this blog, our guest author Shameek Kundu talks about the importance of making AI/ machine learning models reliable and safe. “Getting data and algorithms right has always been important, particularly in regulated industries such as banking, insurance, life sciences and healthcare. But the bar is much higher now: more data, from more sources, in more formats, feeding more algorithms, with higher stakes.”

Building trust in algorithms is essential. Not (just) because regulators want it, but because it is good for customers and business. The good news is that with the right approach and tooling, it is also achievable.
Getting data and algorithms right has always been important, particularly in regulated industries such as banking, insurance, life sciences and healthcare. But the bar is much higher now: more data, from more sources, in more formats, feeding more algorithms, with higher stakes. With the increased use of Artificial Intelligence/ Machine Learning (AI/ML), today’s algorithms are also more powerful and difficult to understand.
A false dichotomy
At this point in the conversation, I get one of two reactions. One is of distrust in AI/ML and a belief that it should have little role to play in regulated industries. Another is of nonchalance; after all, most of us feel comfortable using ‘black-boxes’ (e.g., airplanes, smartphones) in our daily lives without being able to explain how they work. Why hold AI/ML to special standards?
Both make valid points. But the skeptics miss out on the very real opportunity cost of not using AI/ML – whether it is living with historical biases in human decision-making or simply not being able to do things that are too complex for a human to do, at scale. For example, the use of alternative data and AI/ML has helped bring financial services to many who have never had access before.
On the other hand, cheerleaders for unfettered use of AI/ML might be overlooking the fact that a human being (often with a limited understanding of AI/ML) is always accountable for and/ or impacted by the algorithm. And fairly or otherwise, AI/ML models do elicit concerns around their opacity – among regulators, senior managers, customers and the broader society. In many situations, ensuring that the human can understand the basis of algorithmic decisions is a necessity, not a luxury.
A way forward
Reconciling these seemingly conflicting requirements is possible. But it requires serious commitment from business and data/ analytics leaders – not (just) because regulators demand it, but because it is good for their customers and their business, and the only way to start capturing the full value from AI/ML.
1. ‘Heart’, not just ‘Head’
It is relatively easy to get people excited about experimenting with AI/ML. But when it comes to actually trusting the model to make decisions for us, we humans are likely to put up our defences. Convincing a loan approver, insurance under-writer, medical doctor or front-line sales-person to trust an AI/ML model – over their own knowledge or intuition – is as much about the ‘heart’ as the ‘head’. Helping them understand, on their own terms, how the alternative is at least as good as their current way of doing things, is crucial.
2. A Broad Church
Even in industries/ organisations that recognise the importance of governing AI/ML, there is a tendency to define it narrowly. For example, in Financial Services, one might argue that “an ML model is just another model” and expect existing Model Risk teams to deal with any incremental risks from AI/ML.
There are two issues with this approach:
First, AI/ML models tend to require a greater focus on model quality (e.g., with respect to stability, overfitting and unjust bias) than their traditional alternatives. The pace at which such models are expected to be introduced and re-calibrated is also much higher, stretching traditional model risk management approaches.
Second, poorly designed AI/ML models create second order risks. While not unique to AI/ML, these risks become accentuated due to model complexity, greater dependence on (high-volume, often non-traditional) data and ubiquitous adoption. One example is poor customer experience (e.g., badly communicated decisions) and unfair treatment (e.g., unfair denial of service, discrimination, misselling, inappropriate investment recommendations). Another is around the stability, integrity and competitiveness of financial markets (e.g., unintended collusion with other market players). Obligations under data privacy, sovereignty and security requirements could also become more challenging.
The only way to respond holistically is to bring together a broad coalition – of data managers and scientists, technologists, specialists from risk, compliance, operations and cyber-security, and business leaders.
3. Automate, Automate, Automate
A key driver for the adoption and effectiveness of AI/ ML is scalability. The techniques used to manage traditional models are often inadequate in the face of more data-hungry, widely used and rapidly refreshed AI/ML models. Whether it is during the development and testing phase, formal assessment/ validation or ongoing post-production monitoring, it is impossible to govern AI/ML at scale using manual processes alone.
o, somewhat counter-intuitively, we need more automation if we are to build and sustain trust in AI/ML. As humans are accountable for the outcomes of AI/ ML models, we can only be ‘in charge’ if we have the tools to provide us reliable intelligence on them – before and after they go into production. As the recent experience with model performance during COVID-19 suggests, maintaining trust in AI/ML models is an ongoing task.
***
I have heard people say “AI is too important to be left to the experts”. Perhaps. But I am yet to come across an AI/ML practitioner who is not keenly aware of the importance of making their models reliable and safe. What I have noticed is that they often lack suitable tools – to support them in analysing and monitoring models, and to enable conversations to build trust with stakeholders. If AI is to be adopted at scale, that must change.
Shameek Kundu is Chief Strategy Officer and Head of Financial Services at TruEra Inc. TruEra helps enterprises analyse, improve and monitor quality of machine
Have you evaluated the tech areas on your AI requirements? Get access to AI insights and key industry trends from our AI research.

The disruption that we faced in 2020 has created a new appetite for adoption of technology and digital in a shorter period. Crises often present opportunities – and the FinTech and Financial Services industries benefitted from the high adoption of digital financial services and eCommerce. In 2021, there will be several drivers to the transformation of the Financial Services industry – the rise of the gig economy will give access to a larger talent pool; the challenges of government aid disbursement will be mitigated through tech adoption; compliance will come sharply back into focus after a year of ad-hoc technology deployments; and social and environmental awareness will create a greater appetite for green financing. However, the overarching driver will be the heightened focus on the individual consumer (Figure 1).
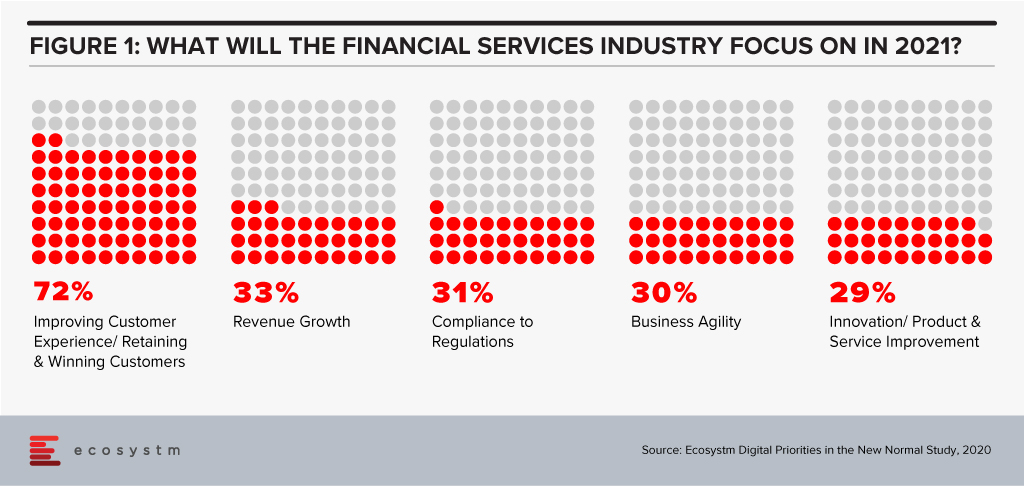
2021 will finally see consumers at the core of the digital financial ecosystem.
Ecosystm Advisors Dr. Alea Fairchild, Amit Gupta and Dheeraj Chowdhry present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for FinTech in 2021 – written in collaboration with the Singapore FinTech Festival. This is a summary of the predictions; the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform.
The Top 5 FinTech Trends for 2021
#1 The New Decade of the ‘Empowered’ Consumer Will Propel Green Finance and Sustainability Considerations Beyond Regulators and Corporates
We have seen multiple countries set regulations and implement Emissions Trading Systems (ETS) and 2021 will see Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) considerations growing in importance in the investment decisions for asset managers and hedge funds. Efforts for ESG standards for risk measurement will benefit and support that effort.
The primary driver will not only be regulatory frameworks – rather it will be further propelled by consumer preferences. The increased interest in climate change, sustainable business investments and ESG metrics will be an integral part of the reaction of the society to assist in the global transition to a greener and more humane economy in the post-COVID era. Individuals and consumers will demand FinTech solutions that empower them to be more environmentally and socially responsible. The performance of companies on their ESG ratings will become a key consideration for consumers making investment decisions. We will see corporate focus on ESG become a mainstay as a result – driven by regulatory frameworks and the consumer’s desire to place significant important on ESG as an investment criterion.
#2 Consumers Will Truly Be ‘Front and Centre’ in Reshaping the Financial Services Digital Ecosystems
Consumers will also shape the market because of the way they exercise their choices when it comes to transactional finance. They will opt for more discrete solutions – like microfinance, micro-insurances, multiple digital wallets and so on. Even long-standing customers will no longer be completely loyal to their main financial institutions. This will in effect take away traditional business from established financial institutions. Digital transformation will need to go beyond just a digital Customer Experience and will go hand-in-hand with digital offerings driven by consumer choice.
As a result, we will see the emergence of stronger digital ecosystems and partnerships between traditional financial institutions and like-minded FinTechs. As an example, platforms such as the API Exchange (APIX) will get a significant boost and play a crucial role in this emerging collaborative ecosystem. APIX was launched by AFIN, a non-profit organisation established in 2018 by the ASEAN Bankers Association (ABA), International Finance Corporation (IFC), a member of the World Bank Group, and the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS). Such platforms will create a level playing field across all tiers of the Financial Services innovation ecosystem by allowing industry participants to Discover, Design and rapidly Deploy innovative digital solutions and offerings.
#3 APIfication of Banking Will Become Mainstream
2020 was the year when banks accepted FinTechs into their product and services offerings – 2021 will see FinTech more established and their technology offerings becoming more sophisticated and consumer-led. These cutting-edge apps will have financial institutions seeking to establish partnerships with them, licensing their technologies and leveraging them to benefit and expand their customer base. This is already being called the “APIficiation” of banking. There will be more emphasis on the partnerships with regulated licensed banking entities in 2021, to gain access to the underlying financial products and services for a seamless customer experience.
This will see the growth of financial institutions’ dependence on third-party developers that have access to – and knowledge of – the financial institutions’ business models and data. But this also gives them an opportunity to leverage the existent Fintech innovations especially for enhanced customer engagement capabilities (Prediction #2).
#4 AI & Automation Will Proliferate in Back-Office Operations
From quicker loan origination to heightened surveillance against fraud and money laundering, financial institutions will push their focus on back-office automation using machine learning, AI and RPA tools (Figure 3). This is not only to improve efficiency and lower risks, but to further enhance the customer experience. AI is already being rolled out in customer-facing operations, but banks will actively be consolidating and automating their mid and back-office procedures for efficiency and automation transition in the post COVID-19 environment. This includes using AI for automating credit operations, policy making and data audits and using RPA for reducing the introduction of errors in datasets and processes.
There is enormous economic pressure to deliver cost savings and reduce risks through the adoption of technology. Financial Services leaders believe that insights gathered from compliance should help other areas of the business, and this requires a completely different mindset. Given the manual and semi-automated nature of current AML compliance, human-only efforts slow down processing timelines and impact business productivity. KYC will leverage AI and real-time environmental data (current accounts, mortgage payment status) and integration of third-party data to make the knowledge richer and timelier in this adaptive economic environment. This will make lending risk assessment more relevant.
#5 Driven by Post Pandemic Recovery, Collaboration Will Shape FinTech Regulation
Travel corridors across border controls have started to push the boundaries. Just as countries develop new processes and policies based on shared learning from other countries, FinTech regulators will collaborate to harmonise regulations that are similar in nature. These collaborative regulators will accelerate FinTech proliferation and osmosis i.e. proliferation of FinTechs into geographies with lower digital adoption.
Data corridors between countries will be the other outcome of this collaboration of FinTech regulators. Sharing of data in a regulated environment will advance data science and machine learning to new heights assisting credit models, AI, and innovations in general. The resulting ‘borderless nature’ of FinTech and the acceleration of policy convergence across several previously siloed regulators will result in new digital innovations. These Trusted Data Corridors between economies will be further driven by the desire for progressive governments to boost the Digital Economy in order to help the post-pandemic recovery.

Organisations are finding that the ways to do work and conduct business are evolving rapidly. It is evident that we cannot use the perspectives from the past as a guide to the future. As a consequence both leaders and employees are discovering and adapting both their work and their expectations from it. In general, while job security concerns still command a big mindshare, the simpler productivity measures are evolving to more nuanced wellness measures. This puts demands on the CHRO and the leadership team to think about company, customer and people strategy as one holistic way of working and doing business.
Organisations will have to re-think their people and technology to evolve their Future of Work policies and strategise their Future of Talent. There are multiple dimensions that will require attention.
Hybrid is Becoming Mainstream
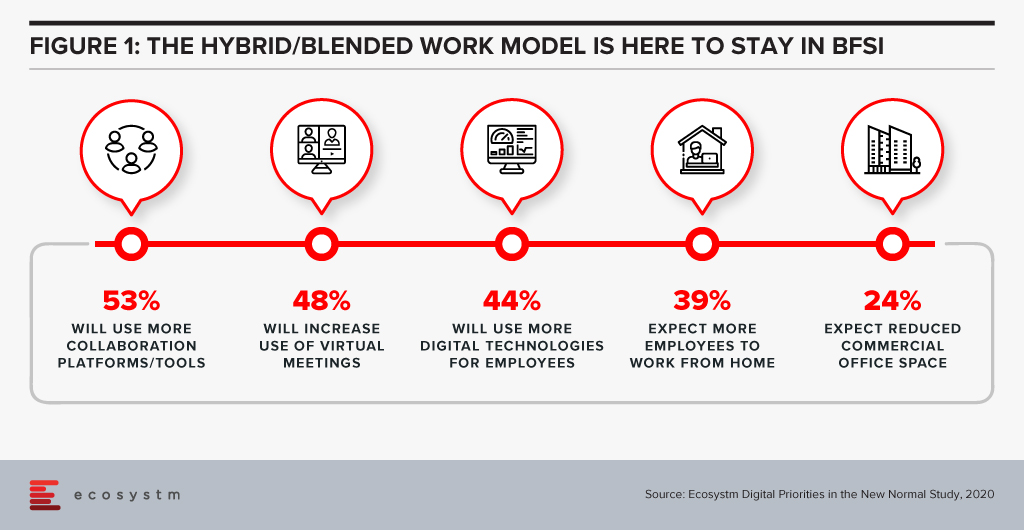
It is clear that hybrid workplaces are here to stay. Ecosystm research finds that in 2021 BFSI organisations will use more collaboration tools and platforms, and virtual meetings (Figure 1). Nearly 40% expect more employees to work from home, but only about a quarter of organisations are looking to reduce their physical workspaces. Organisations will give more choice to employees in the location of their work – and employees will choose to work from where they are more productive. The Hybrid model will be more mainstream than it has been in the last few months.
Companies are coming to terms with the fact that there is no single answer to operating in the new world. Experimentation and learnings are continuously captured to create the right workforce and workplace model that works best. Agility both in terms of being able to undersand the market as well as quickly adapt is becoming quite important. Thus being able to use different models and ways of working at the same time is the new norm.
Technology and Talent are Core
Talent and tech are the two core pillars that companies need to look at to be successful against their competition. It is becoming imperative to create synergy between the two to deliver a superior value proposition to customers. Companies that are able to bring the customer and employee experience journeys together will be able to create better value. HR tech stacks need to evolve to be more deliberate in the way they link the employee experience, customer experience, and the culture of the organisation. That’s how the Employee Value Proposition (EVP) comes to life on a day-to-day basis to the employers. With evolving work models, the tech stack is a key EVP pillar.
Governments will also need to partner with industry to make such talent available. Singapore is rolling out a new “Tech.Pass” to support the entry of up to 500 proven founders, leaders and experts from top tech companies into Singapore. Its an extension of the Tech@SG program launched in 2019, to provide fast-growing companies greater assurance and access to the talent they need. The EDB will administer the pass, supported by the Ministry of Manpower.
Attracting the Right Talent
Talent has always been difficult to find. Even with globalisation, significant investment of time and resources is needed to find and relocate talent to the right geography. In many instances this was not possible given the preferences of the candidates and/or the hiring managers. COVID-19 has changed this drastically. Remote working and distributed teams have become acceptable. With limitations on immigration and travel for work, there is a lot more openness to finding and hiring talent from outside the traditional talent pool.
However it is not as simple as it seems. The cost per applicant (CPA) – the cost to convert a job seeker to a job applicant – had been averaging US$11-12 throughout 2019 according to recruiting benchmark data from programmatic recruitment advertising provider, Appcast. But, the impact of COVID-19 saw the CPA reach US$19 in June – a 60% increase. I expect that finding right talent is going to be a “needle in a haystack” issue. But this is only one side of the coin – the other aspect is that the talent profile needed to be successful in roles that are all remote or hybrid is also significantly different from what it was before. Companies need to pay special attention to what kind of people they would like to hire in these new roles. Without this due consideration it is very likely that there would be difficulty in on-boarding and making these new hires successful within the organisation.
Automation Augmentation and Skills
The pace at which companies are choosing to automate or apply AI is increasing. This is changing the work patterns and job requirements for many roles within the industry. According to the BCG China AI study on the financial sector 23% of the roles will be replaced by AI by 2027. The roles that will not be replaced will need a higher degree of soft skills, critical thinking and creativity. However, automation is not the endgame. Firms that go ahead with automation without considering the implications on the business process, and the skills and roles it impacts will end up disrupting the business and customer experience. Firms will have to really design their customer journeys, their business processes along with roles and capabilities needed. Job redesign and reskilling will be key to ensuring a great customer experience
Analytics is Inadequate Without the Right Culture
Data-driven decision-making as well as modelling is known to add value to business. We have great examples of analytics and data modelling being used successfully in Attrition, Recruitment, Talent Analytics, Engagement and Employee Experience. The next evolution is already underway with advanced analytics, sentiment analysis, organisation network analysis and natural language processing (NLP) being used to draw better insights and make people strategies predictive. Being able to use effective data models to predict and and draw insights will be a key success factor for leadership teams. Data and bots do not drive engagement and alignment to purpose – leaders do. Working to promote transparency of data insights and decisions, for faster response, to champion diversity, and give everyone a voice through inclusion will lead to better co-creation, faster innovation and an overall market agility.
Creating a Synergy
We are seeing a number of resets to what we used to know, believe and think about the ways of working. It is a good time to rethink what we believe about the customer, business talent and tech. Just like customer experience is not just about good sales skills or customer service – the employee experience and role of Talent is also evolving rapidly. As companies experiment with work models, technology and work environment, there will a need to constantly recalibrate business models, job roles, job technology and skills. With this will come the challenge of melding the pieces together within the context of the entire business without falling into the trap of siloed thinking. Only by bringing together businesses processes, talent, capability evolution, culture and digital platforms together as one coherent ecosystem can firms create a winning formula to create a competitive edge.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Talent Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit which will cover topics on Founders success and failure stories, pandemic impact on founders and talent development, upskilling and reskilling for the future of work.

In this blog, our guest author Chandru Pingali talks about the potential benefits of the Blended working model and the impact it will have on FinTech and financial services organisations. “FinTech innovation and performance is here to stay and thrive. It needs to be backed by a well-oiled machine to support implementation of a blended workforce plan to institutionalise and scale.”

When under pressure to reduce costs and survive, we reimagine everything we do to build resilience and thrive. Never before have the buzzwords frugality, prudence and agility gained as much prominence – not just in one country or industry, but across global economies simultaneously (a phenomenon not seen since the Great Depression). And these words have sliced through the employment opportunities ruthlessly, leaving an abundance of talent to be gainfully employed differently.
So, is the freelance economy surging? Statistics appear to say yes. In 2018, freelancers had contributed almost USD 1.40 trillion to the US economy; 162 million freelancers work across US and EU-15. So, who are these people? Why is blended workforce new or relevant for the Asia Pacific? Why is it gaining more prominence now? How can enterprises create and implement a blended workforce strategy to reduce costs more permanently, while running and scaling businesses? What does the Future of Work and workforce mean? How can FinTech enterprises successfully implement a blended workforce strategy?
Let us take Singapore as an example. With 1000+ FinTech firms and increasing investments, the “smart financial centre” initiative of Singapore is a huge success story, recognised globally. To sustain this, apart from innovation and technology, the main ingredient is consistent availability of talent as the demand for expertise in technology and financial services increases, while the supply is inconsistent, uncurated and fragmented. Recent data from the Singapore government job portals reveal that there are several hundred jobs at any point in time posted by FinTech companies that are open for months! This invariably slows down the ability to build businesses, innovate or scale. Interestingly, while the local talent for technology and BFSI may be limited in Singapore, the crisis this year presented a significant opportunity to reimagine the Future of Work and workforce. While efforts should continue to upskill and reskill local talent, it is now possible to create dedicated local and cross-border talent hubs to work part-time, fulltime-short term with the option of working physically or remotely. We expect the plug and play of freelance management experts and expertise to cost 25-30% less to an enterprise, keeps costs flexible and dramatically shortens time to “hire and deploy” from an average of 120 days to 15 days.

Gigs and Generations – Conceptual Clarity of Who We Need
Culturally, the US and Europe are more accepting of freelancing as full-time careers compared to the Asia Pacific. It is predicted that by 2027 the majority of the workforce in the US will be freelancers overtaking traditional employment. The buzz in the Asia Pacific has just started with both employers and employable talent accepting a new reality – learning to run businesses with a blended workforce, starting at the top of the pyramid. Particularly, since the ratio of new jobs to lost jobs is skewed in the wrong direction.
Power of Blended Workforce
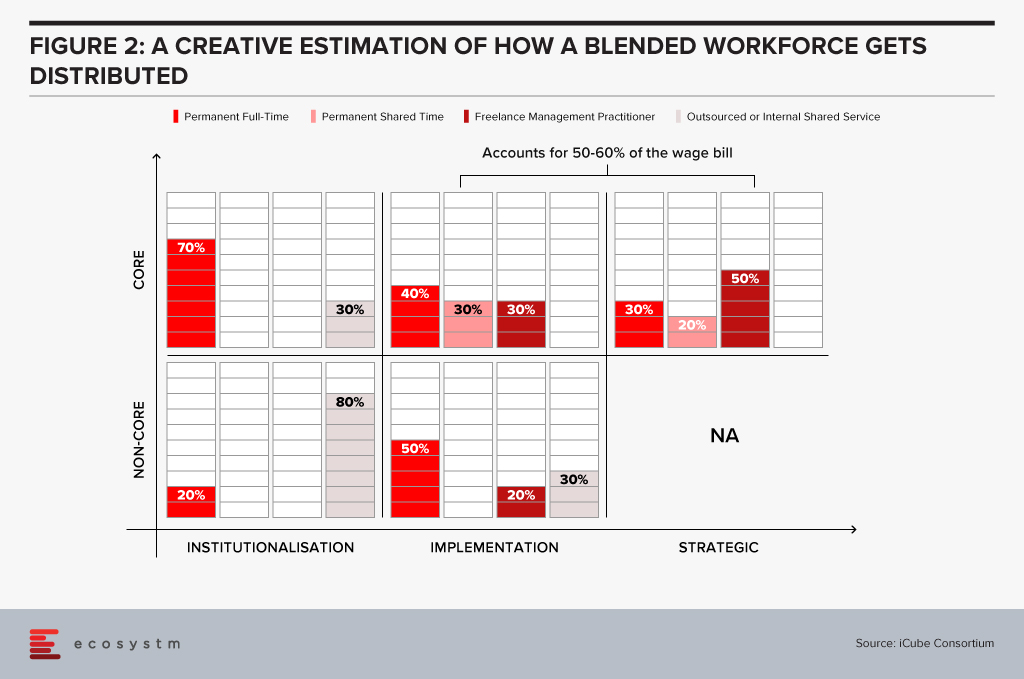
A blended workforce is a combination of permanent, part-time, full time-short term and turnkey practitioners, working as a single collaborative workforce. It is built around business activity clusters – Strategy, Implementation and Institutionalisation, applied to create a plan for core and non-core workforce to drive business.
A creative estimation of how a blended workforce gets distributed across the three business clusters is depicted below (Figure 2). What is important here is to recognise that the ratio of permanent to flexible workforce has to start at 10-15% across different levels. Enterprises will gain the most on cost optimisation when they focus on the management layer to go blended. Not an easy change to drive but then change is often driven by some tough calls and some low hanging fruits to build a sustainable cost model.
Developing & Implementing a Blended Workforce Strategy: What to Consider
Fix the core and flex the non-core should be the mantra
- Identify roles by each business and function
- Segregate core and non-core roles by job profiles
- Classify them into buckets of permanent full time, permanent part time, cyclical, and freelance on demand, based on:
- Time demand for the roles
- Importance to business goals
- Criticality to daily business output
- Criticality to daily or weekly business continuity
- Set up a process to engage and create a blended workforce strategy
- Implement the plan with a blend of a common self-service platform and a central client service team to source, engage and deploy workforces
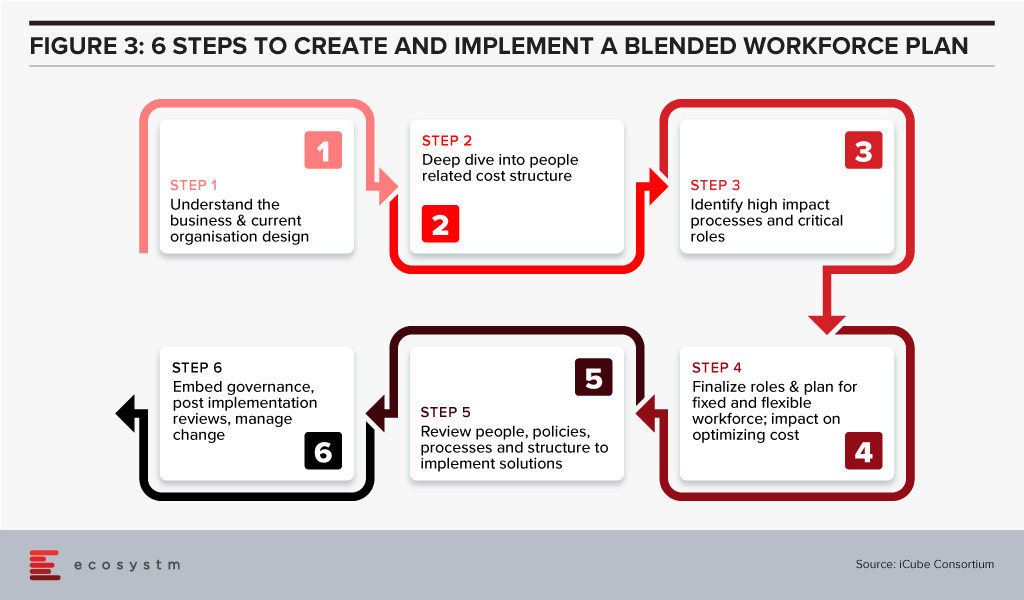
Once the process review is completed, the organisation structures will be finalised. Creation of a strategy and the process are the easier parts. A disciplined fulfilment of the plan is critical to success. So, is this the new normal? Pretty much yes, if organisations need to optimise costs and be agile to reduce or scale with freelance experts and shared talent pools.
The Potential Benefits of a Blended Workforce
A Blended Workforce will help reduce your talent scarcity gap, while providing thousands of work opportunities to locals who are freelance experts. So, what are these benefits that can make you sleep better at night better?
- Cost optimisation. Freelance experts do not need the fully loaded costs. They can work remotely or physically and do not need investment in regular training, insurance, or other related benefits.
- Targeted purpose-hire for short term. With deliverables specified upfront, measurable, results focused and tracked for closure.
- Job Sharing. Two or may be three, for the prize of one! Jobs can be dismantled to tasks or activity clusters to hire more than one expert in place of a full-time role. Enables razor sharp focus on sourcing for expertise, increases employment opportunities and accelerates productivity.
- Boundaryless with an opportunity to find cross-border talent pools to work on-demand, remotely. It cuts both ways- Singaporean talent finding work opportunities outside the country whilst the best talent from other countries made available to grow Singapore’s economy.
- Speed of hire is dramatically reduced (we have several client cases, with a reduction from an average of 120 days to 15 days, to clients’ delight!)
- Reduced infrastructure costs because the workforce works remotely or at best part-time physically. Easy to implement with hot desking, if needed but enables permanent cost reduction.
- Builds resilience by staying agile and nimble in the cost line, with an ability to scale up or down rapidly based on business needs.
How Open is the Financial Services Industry to Blended Workforce and Future of Work?
SolvecubeHR conducted a recent survey with CXOs across 22 countries, predominantly focused on the Asia Pacific region. Some key findings for the financial services industry are:
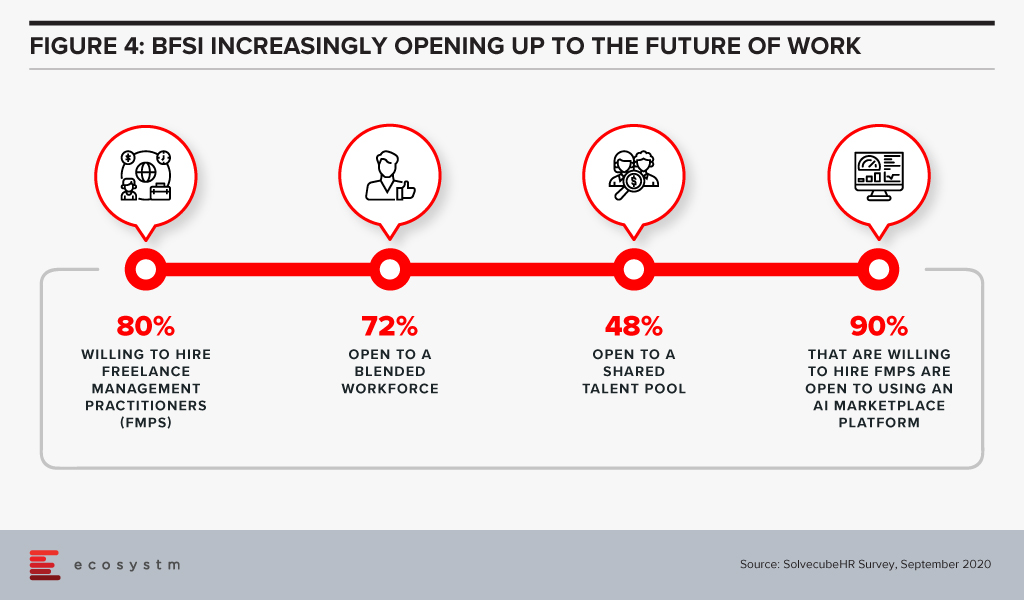
In summary, a blended workforce is the Future of Work. Asia Pacific will see a massive shift in its mindset from “jobs to work opportunities”. Employers and talent pools will embrace new ways of working to remain agile and prudent. The power of aggregation, curation, and collaboration by leveraging an AI matchmaking platform, backed by creation of shared talent pools, will be a game changer.
FinTech innovation and performance is here to stay and thrive. It needs to be backed by a well-oiled machine to support implementation of a blended workforce plan to institutionalise and scale.
We can build technologies to disintermediate people dependency, but we cannot take humans out of the human capital needed to build these technologies.
About iCube: iCube Consortium is a Singapore based, Human Capital Management (HCM) solutions firm, with an award-winning AI platform to source and manage freelance management experts and execute turnkey assignments in Asia and Middle East
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Talent Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit which will cover topics on Founders success and failure stories, pandemic impact on founders and talent development, upskilling and reskilling for the future of work.

Identifying and selecting a vendor for your tech project can be a daunting task – especially when it comes to emerging technologies or when implementing a tech solution for the first time. Organisations look for a certain degree of alignment with their tech vendors – in terms of products and pricing, sure, but also in terms of demonstrable areas of expertise and culture. Several factors are involved in the selection process – vendors’ ability to deliver, to match expected quality standards, to offer the best pricing, to follow the terms of the contract and so on. They are also evaluated based on favourable reviews from the tech buyer community.
Often businesses in a particular industry tend to have their unique challenges; for example, the Financial Services industries have their specific set of compliance laws which might need to be built into their CRM systems. Over the years, vendors have built on their industry expertise and have industry teams that can advise organisations on how their business requirements can be met through technology adoption. These experts speak in the language of the industry and understand their business and technology pain points. They are able to customise their product and service offerings to the needs of the industry for a single client – which can then be repeated for other businesses in that industry. Vendors arm themselves with a portfolio of industry use cases, especially when they are entering a new market – and this often gives them an upper hand at the evaluation stage. In the end, organisations want less customisations to keep the complexity and costs down.
Do organisations evaluate vendors on industry experience?
Ecosystm research finds that industry experience can be a significant vendor selection criterion for some tech areas (Figure 1), especially in emerging technologies such as AI. AI and automation applications and algorithms are considered to be distinctive to each industry. While a vendor may have the right certifications and a team of skilled professionals, there is no substitute for experience. With that in mind, a vendor with experience in building machine learning models for the Telecommunications industry might not be perceived as the right fit for a Utilities industry implementation.
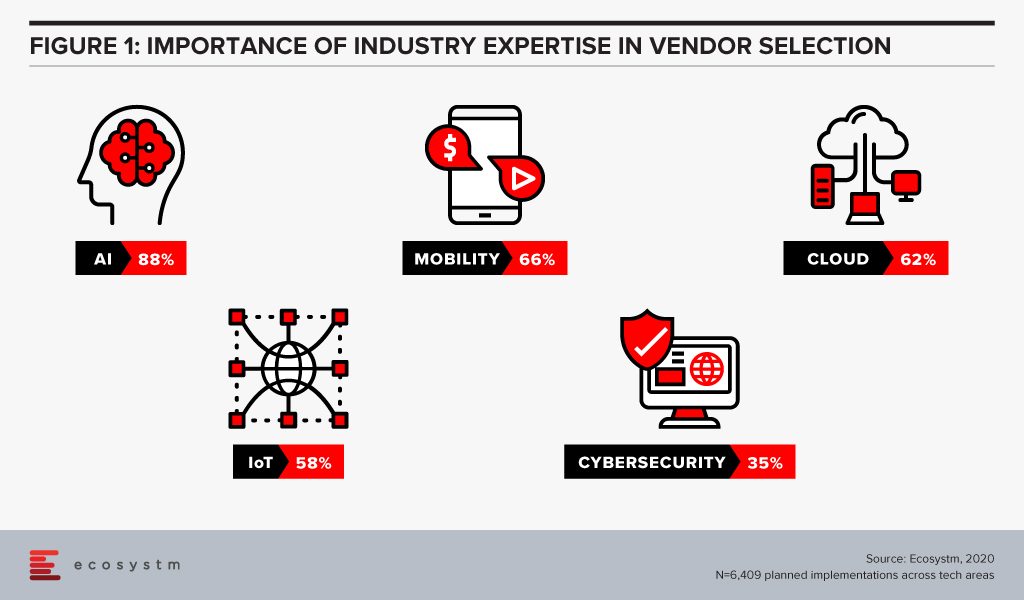
Whereas, we find that cybersecurity is at the other end of the spectrum, and organisations perceive that industry expertise is not required as network, applications and data protection requirements are not considered unique to any industry.
Is that necessarily the right approach?
Yes and no. If we look at the history of the ERP solution, as an example, we find that it was initially meant for and deeply entrenched in Manufacturing organisations. In fact, the precursor to modern-day ERP is the Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) software of the 1980s. Now, we primarily look at ERP as a cross-industry solution. Every business has taken lessons on inventory and supply chain management from the Manufacturing industry and has an enterprise-wide system. However, there are industries such as Hospitality and Healthcare that have their niche vendors who bundle in ERP features with their industry-specific solutions. This will be the general pattern that all tech solutions will follow: a) an industry use case will become popular; b) other industries will try to incorporate that solution, and in the process; c) create their own industry-specific customisations. It is important, therefore, for those who are evaluating emerging technologies to cast their net wide to identify use cases from other industries.
AI and automation is one such tech area where organisations should look to leverage cross-industry expertise. They should ask their vendors about their implementations in other allied industries and, in some cases, in industries that are not allied.
For cybersecurity, their approach should be entirely different. As companies move on from network security to more specific areas such as data security and emerging areas such as GRC communication, it will be important to evaluate industry experience. Data protection and compliance laws are often specific to industries – for example, while customer-focused industries are mandated on how to handle customer data, the Banking, Insurance, Healthcare and Public Sector industries have the need to store more sensitive data than other industries. They should look at solutions that have in-built checks and balances in place, incorporating their GRC requirements.
So, the answer to whether organisations should look for industry expertise in their vendors is that they should for more mature tech areas. An eCommerce company should look for industry experience when choosing a web hosting partner, but should look for experience in other industries such as Banking, when they are looking to invest in virtual assistants.
Are some industries more focused on industry experience than others?
Ecosystm research also sought to find out which industries look for industry expertise more than others (Figure 2). Surprisingly, there are no clear differences across industries. The Services, Healthcare and Public Sector industries emphasise marginally more on industry expertise – but the differences are almost negligible.
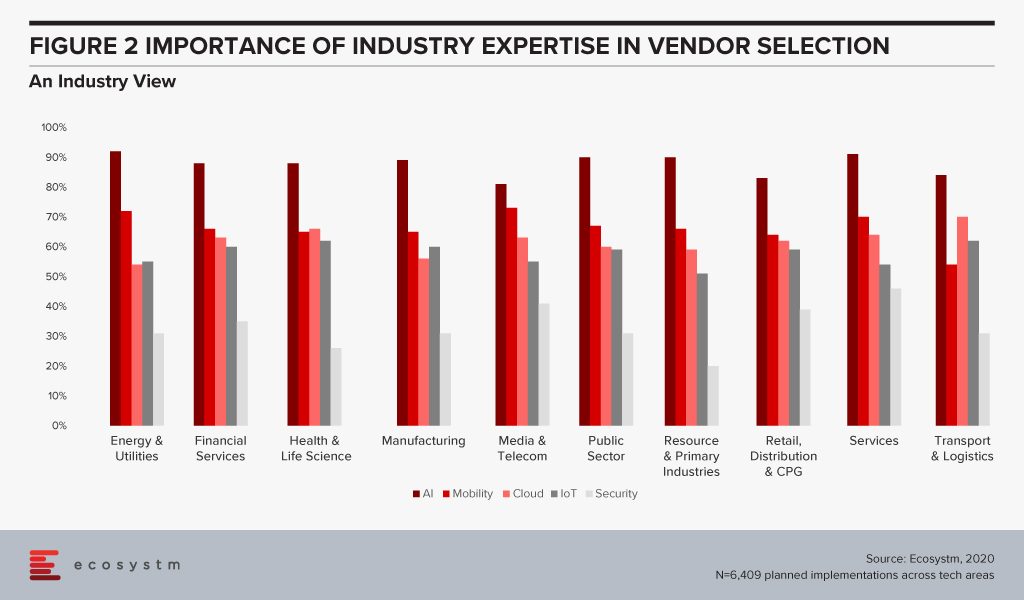
There are some differences when we look at specific tech areas, however. For example, industries that may be considered early adopters of IoT – Transportation, Manufacturing and Healthcare – tend to give more credit to industry experience because there are previous use cases that they can leverage. There are industries that are still formulating standards when it comes to IoT and they will be more open to evaluating vendors that have a successful solution for their requirement – irrespective of the industry.
The Healthcare Industry Example
Ecosystm Principal Analyst, Sash Mukherjee says, “In today’s fast-evolving technology market, it is important to go beyond use cases in only your industries and look for vendors that have a demonstrated history of innovation and experience in delivering measurable results, irrespective of the industry.” Mukherjee takes the example of the Healthcare industry. “No one vendor can provide the entire gamut of functionalities required for patient lifecycle management. In spite of recent trends of multi-capability vendors, hospitals need multiple vendors for the hospital information systems (HIS), ERP, HR systems, document management systems, auxiliary department systems and so on. For some areas such as electronic health records (EHR) systems, obviously industry expertise is paramount. However, if healthcare organisations continue to look for industry expertise and partner with the same vendors, they miss out on important learnings from other industries.”
Talking about industries that have influenced and will influence the Healthcare industry in the very near future, Mukherjee says, “Healthcare providers have learnt a lot from the Manufacturing industry – and several organisations have evaluated and implemented Lean Healthcare and Six Sigma to improve clinical outcomes. The industry has also learnt from the Retail and Hospitality industries on how to be customer focused. In the Top 5 Healthtech trends for 2020, I had pointed out the similarities between the Financial and Healthcare industries (stringent regulations, process-based legacy systems and so on). As the Healthcare industry focuses on value-based outcomes, governments introduce more regulations around accountability and transparency, and people expect the experience that they get out of their retail interactions, Healthtech start-ups will become as mainstream as Fintech start-ups.”
It is time for tech buyers to re-evaluate whether they are restricting themselves by looking at industry use cases, especially for emerging technologies. While less industry customisations mean easier deployments, it may also hamper innovation.