Generative AI is seeing enterprise interest and early adoption enhancing efficiency, fostering innovation, and pushing the boundaries of possibility. It has the potential of reshaping industries – and fast!
However, alongside its immense potential, Generative AI also raises concerns. Ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and security come to the forefront, as powerful AI systems handle vast amounts of sensitive information.
Addressing these concerns through responsible AI development and thoughtful regulation will be crucial to harnessing the full transformative power of Generative AI.
Read on to find out the key challenges faced in implementing Generative AI and explore emerging use cases in industries such as Financial Services, Retail, Manufacturing, and Healthcare.
Download ‘Generative AI: Industry Adoption’ as a PDF

Verint has announced the intention to acquire Conversocial, a US-based social media management system provider for USD 50 million to integrate social messaging capabilities across Verint’s cloud platform. The deal is expected to be closed in Verint’s third quarter subject to customary closing conditions and regulatory clearances.
Verint has been expanding their digital engagement capabilities through acquisitions. In June, Verint expanded their Workforce Management (WFM) offerings to include AI-driven insights for better hiring decisions through the acquisition of HireIQ. To extend Verint’s omnichannel cloud Voice of the Customer (VoC) portfolio, Verint acquired Foresee. Verint is also building IVA capabilities and recently launched a low code version of their IVA solution to make it easier for brands to build the solution without the need for technical knowledge.
The Need to Enhance Digital Engagement
Using self-service and messaging as the first point of connection to engage with a brand is growing rapidly. It accelerated during the pandemic, and it is common now for individuals to engage with their financial institution, airlines, retail and others through social media. Now that customers are demanding it, brands are lifting their game and engaging with customers on the platform of their choices. This acquisition will allow Verint to deepen their digital engagement with customers across Marketing, Contact Centres and digital functions – it follows the pulse of today’s customers.
Digital discussions are accelerating and having a platform that can orchestrate as well as understand all the data from each digital and social messaging channel is important. Verint is taking the data discussion seriously and earlier this year they launched Engagement Data Management Solution (EDM). The ‘’data’’ piece is huge and cuts across functions – from back-office communications to gathering data across all channels and touchpoints. However, where this is going wrong for some enterprises is that all the data they collect sits in multiple repositories; in some instances the data has not been analysed for years! Managing the multiple social experiences, including data management and insights from these multiple sources, will be key to delivering proactive customer experience.
The data discussion is particularly significant for a vendor such as Verint – they are well known for their speech analytics and compliance management capabilities. These are all critical to managing multiple channels of conversation. They help agents to be accurate, efficient, and compliant; allow organisations to use asynchronous channels and social messaging and digital channels; immediately rectified errors through monitoring the data on the channels and so on. More importantly, they allow organisations to pick up points from conversations that can be passed on to Marketing to gauge the effectiveness of the messaging and campaigns. Organisations can ‘’identify and fix” problems by truly listening to customers.
Why Conversocial
If we look at the Conversocial customer stories, we realise how relevant their offerings are to industry requirements. They offer brands the ability to engage through an automated channel and chatbots. Whirlpool appears to have benefited by integrating channels to deliver better customer care as well as communicating with field engineers through WhatsApp. Another customer, Freshly – a meals delivery company – saw a spike in incoming queries at the start of the pandemic. They were able to use automation to ease of the load and say that 50% of the conversations were handled in-channel through automation without the need for human agent intervention. They were also able to use Facebook Messenger as a preferred contact channel and decreased their cost-per-contact.
This acquisition demonstrates how Verint is taking the digital and the data discussion seriously. CX Vendors that do not move fast in building end-to-end digital capabilities will find it hard to compete in a highly competitive CX market.

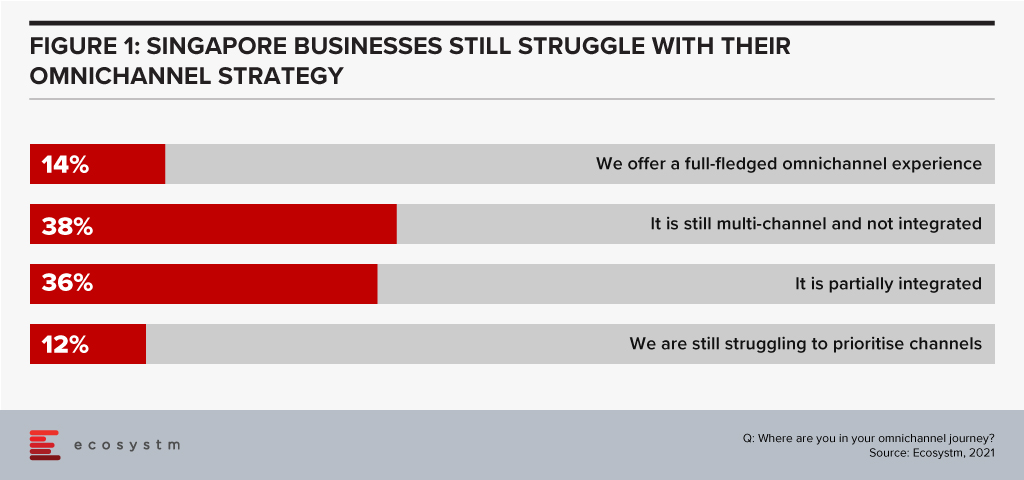
Customer needs are changing. Quickly. In 2020 having a great digital strategy went from being a nice-to-have to an absolute necessity. And in 2021, businesses that have great omnichannel experiences will go from a small minority to a majority as customers demand that they are served on their terms in their chosen platform. Only 14% of businesses in Singapore offer a complete omnichannel experience today – serving customers on their terms regardless of the location or platform (Figure 1). These businesses are setting the benchmark that the rest of the market needs to meet soon.
The Growing Importance of Social Media in Delivering Customer Experience
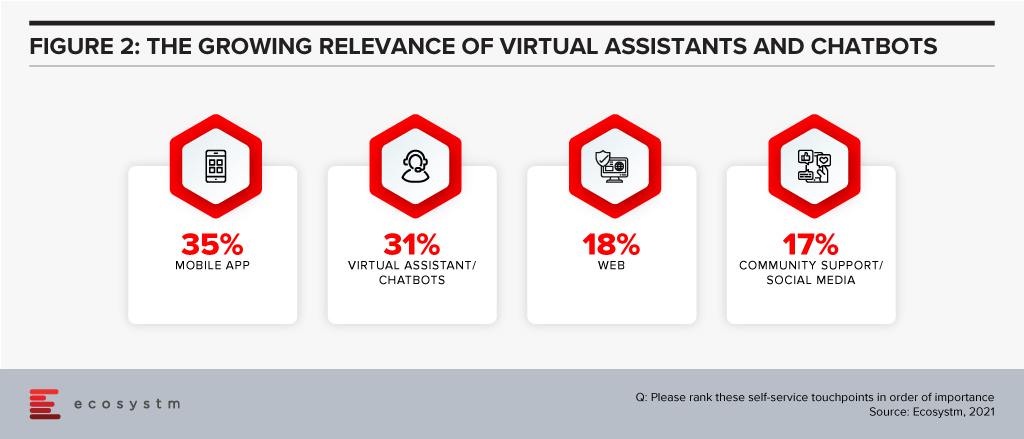
Chat and messaging are quickly becoming the normal way to interact with businesses – the view of a few years ago that “no one wants to chat with a bot” has quickly turned around. Now virtual assistants and chatbots are the second most important self-service channel for businesses in Singapore (Figure 2).
In fact, Zendesk’s global study shows that most customers (45%) use embedded messaging over social messaging apps (31%) and text/SMS (20%). That might be great for self-service, but for commerce, boundless opportunities exist to move to where the customer lives, communicates, and socialises today.
Smart businesses understand that customers spend their lives in other chat and social media platforms – such as Facebook Messenger, TikTok, Instagram, WeChat, Discord and WhatsApp. More customers expect to be served in these channels; they expect to be able to transact with their brands of choice. Why should they go to a mobile banking app to find their balance? Why can’t they get it in WhatsApp? They are often learning about the next Jordan or Yeezy shoe drop from their social network in Messenger – so why not transact with them there? Consider all your own personal WhatsApp, Messenger and other messaging platform groups discussing social activities, sporting teams, school activities or the latest fashion – these are ALL opportunities for commerce (Figure 3).

And there are use cases now. Airlines – such as KLM and Etihad Airways – are engaging customers on WeChat, Kakao Talk, and WhatsApp, helping them reschedule flights and answering customer service queries. Telecommunications providers are allowing customers to raise issues on messaging platforms – and are also using them to upsell and cross-sell new services. Transportation providers are making it easier to find a car or the the next scheduled bus right there in the messaging platforms. Retailers – such as 1-800 Flowers and Culture Kings – are not only serving customers but finding new customers on these messaging platforms.
Going beyond the messaging platforms, businesses are also looking to serve customers on their smart devices – such as Amazon Alexa/Echo and Google Nest/Home devices. Alerting customers to order updates, shipping details and product promotions is becoming standard practice for leading businesses. Digitally-savvy banks are allowing customers to not only track their balance but also make transfers and payments using these smart platforms.
Customers are more comfortable with these conversational commerce options – and they actually expect you to offer such services on your site, in your app, on their smart devices, and on their messaging platforms of choice. Your ability to provide outstanding customer experiences will not only be your ticket back to revenue growth but the recipe for long term business success. Meeting customer needs on their terms is a good place to start.
Delivering a Personalised Conversational Customer Experience
Customer experience (CX) decision-makers will have to rethink how they approach building richer CX capabilities to deliver personalised conversational interactions with customers.
Messaging should become part of a wider AI, Data, and Mobile strategy. Contact centre teams might feel that this is too ambitious a project and would prefer to continue to serve customers through the more traditional channels only. So, it is important to identify the key stakeholder/s who will drive the initiative. And the contact centre team should work with the Digital, Innovation and Marketing teams.
Designing the mobile experience and in app messaging for CX should have some of the following features:
- Ability to click a button to request for a service or escalate an issue that will, in turn, result in the company contacting the customer either by messaging or calling.
- Giving customers the option to contact through popular messaging platforms such as Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, LINE, WeChat, and others. Unifying these systems in a single interface that integrates with your customer service application is best practice.
- Having one single interface to manage and make payments – within the app itself or on the social messaging platform. Conversational commerce is about creating an ongoing relationship with customers throughout the entire customer journey. Don’t just focus on the sale or the post-sales experience – customers expect to be able to interact with your business from their platform of choice regardless of their need or stage in the customer journey.
- Embed deep analytics into the communication services to help the organisation better deliver a personalised CX.
- Ensure you have a solid, unified knowledge management interface at the backend so that all questions lead to the same answers regardless of channel, platform or touchpoint.
Your opportunity to drive greater business success lies in your ability to better win, serve and retain your customers. Refresh your customer strategy and capability today to make 2021 an exceptional year for your business.

Authored by Alea Fairchild and Audrey William
There is a lot of hope on AI and automation to create intellectual wealth, efficiency, and support for some level of process stability. After all, can’t we just ask Siri or Alexa and get answers so we can make a decision and carry on?
Automation has been touted as the wonder formula for workplace process optimisation. In reality it’s not the quick fix that many business leaders desire. But we keep raising the bar on expectations from automation. Investments in voice technologies, intelligent assistants, augmented reality and touchscreens are changing customer experience (Figure 1). Chatbots are ubiquitous, and everything has the potential to be personalised. But will they solve our problems?
100 percent automation is not effective
Let’s first consider using automation to replace face-to-face interactions. There was a time when people were raving about the check-in experience at some of the hotels in Japan where robots and automated systems would take care of the check-in, in-stay and check-out processes. Sounds simple and good? Till 2019, if you checked into the Henn-na Hotel in Japan, you would be served and taken care of by 243 robots. It was viewed by many as a template for what a fully automated hotel could look like in the future.
The hotel had an in-room voice assistant called Churi. It could cope with basic commands, such as turning the lights on and off, but it was found to be deficient when guests started asking questions about places to visit or other more sophisticated queries. It was not surprising that the hotel decided to retire their robots. In the end it created more work for the hotel staff on-site.
People love the personal touch when they are in a hotel; and talking to someone at the front desk, requesting assistance from hotel staff, or even just a short chat over breakfast are some of the small nuances of why the emotional connection matters. Many quarantine hotels today use robots for food delivery, but the hotel staff is still widely available for questions. That automation is good, but you need the human intervention. So, getting the balance right is key.
Empathy plays a big role in delivering great Customer Experience
Similarly, there was a time when many industry observers and technology providers said that a contact centre will be fully automated, reducing the number of agents. While technologies such as Conversational AI have come along where you can now automate common or repetitive questions and with higher accuracy levels, the human agent still plays a critical role in answering the more complex queries. When the customer has a complicated question or request, then they will WANT to speak to an agent.
When it reaches a point where the conversation with the chatbot starts getting complicated and the customers need more help there should be the option – within the app, website or any other channel – to escalate the call seamlessly to a human agent. Sometimes, a chat is where the good experience happens – the emotional side of the conversation, the laughter, the detailed explanation. This human touch cannot be replaced by machines. Disgruntled customers are happier when an agent shows empathy. Front line staff and human agents act as the face of a company’s brand. Complete automation will not allow the individual to understand the culture of the company. These can be attained through conversations.
Humans as supervisors for AI – The New Workplace
Empathy, intuitiveness, and creativity are all human elements in the intelligence equation. Workers in the future will need to make their niche in a fluid and unpredictable environment; and translating data into action in a non-replicable way is one of the values of human input. The essence of engineering is the capacity to design around human limitations. This requires an understanding of how humans behave and what they want. We call that empathy. It is the difference between the engineer who designs a product, and the engineer who delivers a solution. We don’t teach our computer scientists and engineering students a formula for empathy. But we do try to teach them respect for both the people and the process.
For efficiency, we turn to automation of processes, such as RPA. This is designed to try to eradicate human error and assist us in doing our job better, faster and at a lower cost by automating routine processes. If we design it right, humans take the role of monitoring or supervisory controlling, rather than active participation.
At present, AI is not seen as a replacement for our ingenuity and knowledge, but as a support tool. The value in AI is in understanding and translating human preferences. Humans-in-the-loop AI system building puts humans in the decision loop. They also shift pressure away from building “perfect” algorithms. Having humans involved in the ethical norms of the decision allows the backstop of overly orchestrated algorithms.
That being said, the astute use of AI can deepen insights into what truly makes us human and can humanise experiences by setting a better tone and a more trusted engagement. Using things like sentiment analysis can de-escalate customer service encounters to regain customer loyalty.
The next transformational activity for renovating work is to advance interactions with customers by interpreting what they are asking for and humanising the experience of acquiring it which may include actually dealing with a human contact centre agent – decisions that are supported at the edge by automation, but at the core by a human being.
Implications
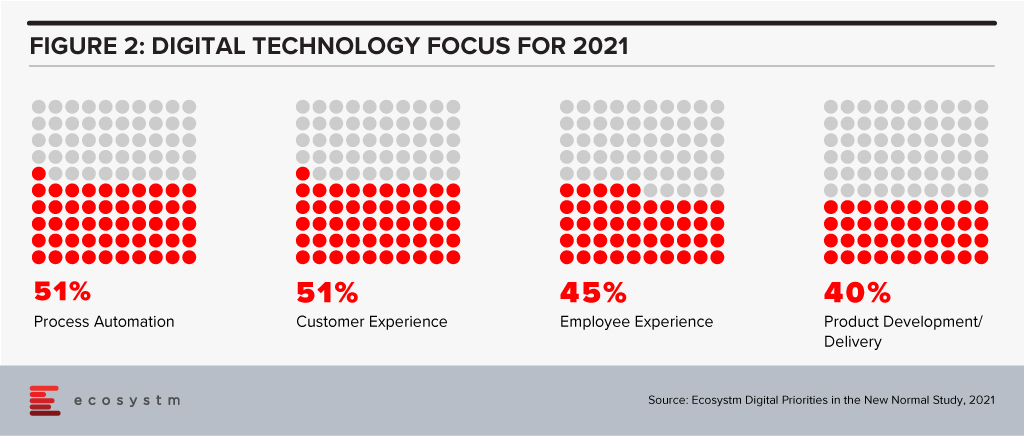
Ecosystm research shows that process automation will be a key priority for technology investments in 2021 (Figure 2).
With AI and automation, a priority in 2021, it will be important to keep these considerations in mind:
- Making empathy and the human connection the core of customer experiences will bring success.
- Rigorous, outcome-based testing will be required when process automation solutions are being evaluated. In areas where there are unsatisfactory results, human interactions cannot – and should not – be replaced.
- It may be easy to achieve 90% automation for dealing with common, repetitive questions and processes. But there should always be room for human intervention in the event of an issue – and it should be immediate and not 24 hours later!
- Employees can drive greater value by working alongside the chatbot, robot or machine.
Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Customer Experience Trends for 2021
Download Ecosystm’s complimentary report detailing the top 5 customer experience trends for 2021 that your company should pay attention to along with tips on how to stay ahead of the curve.

Running a contact centre has been extremely challenging in 2020. Contact centres have had to ensure business continuity, keep the focus on customer experience, and manage and motivate a largely remote workforce. Since the outbreak of COVID-19, not only have contact centres seen high inbound activity, but they have also had to manage agents who are dispersed and working remotely. 2020 has seen many contact centres starting, accelerating or re-focusing their digital transformation initiatives (Figure 1).
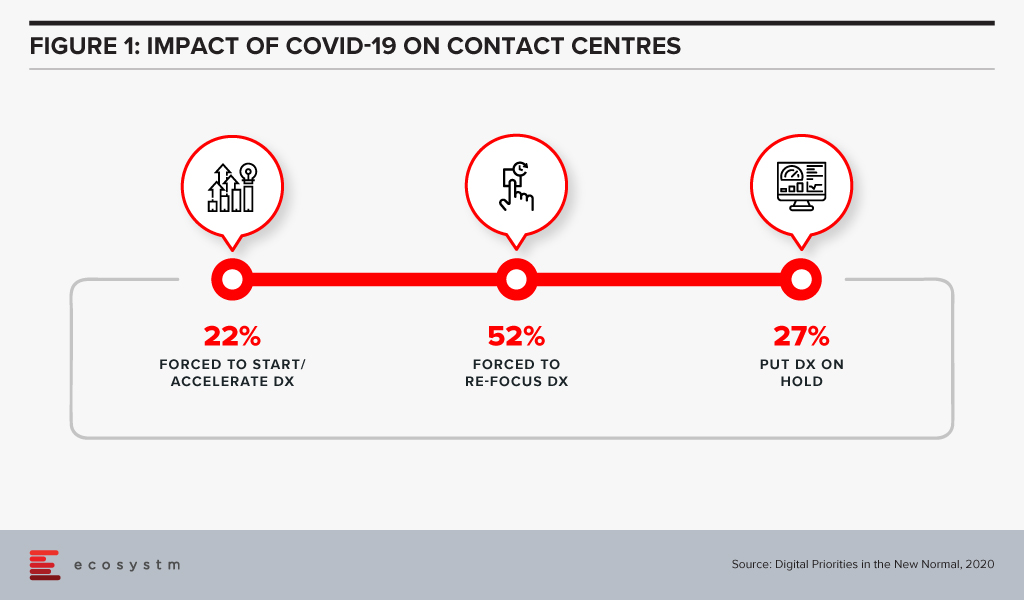
2021 will see contact centres focusing on transformation, not only to survive but also because their organisations and clients will expect more process efficiency and better customer experience. Ecosystm Advisors Audrey William and Ravi Bhogaraju present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for Contact Centres Trends in 2021.
This is a summary of our predictions on the top 5 Contact Centre Trends for 2021 – the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform here.
The Top 5 Contact Centre Trends for 2021
- Remote Working Will Force Contact Centres to Re-evaluate Security Measures
Security has always been a concern for contact centre leaders. Improper data use by agents and agents breaching confidentiality are the biggest security challenges for contact centres. This has been further heightened, especially the fear of agents purposely breaching confidentiality while working from home.
Contact centres are still trying to figure out the best security measures when managing customer data, especially in the work-from-home environment. There is greater scrutiny over security and compliance measures – what agents view, how agents access the data, when agents log in and out of the system. Outsourcing providers will also have to guarantee high levels of security – a trusted relationship and defining the best practices on working from home will not be sufficient.
Many contact centres will trial different methods – from installing video surveillance cameras, desktop monitoring tools and access controls. Others will test technologies that can mask the information captured through mobile devices. This presents immense opportunities for vendors, as contact centres will rely heavily on technology to re-invent their security practices.
- Contact Centres will Invest in Conversational AI – Chatbots will No Longer be Enough
Many enterprises have rushed into deploying chatbots with expectations that these engines can solve the problem of high call volumes. The outcomes have often been poor, leaving customers frustrated and opting to interact with a live agent instead. Implementing a basic chatbot does not fully solve the problem and will force companies back to the drawing board.
Conversational AI offers a different experience by designing multiple forms of dialogues and conversations. It requires conversational design and the algorithms go through rigour from the start. The aim should be to make the channel irresistible – one that customers have confidence in, and that can reduce the need to email or call an agent. Successful uses cases have shown that conversational AI can reduce calls and repetitive queries by 70-90%. Ecosystm research finds that contact centres are ramping up their self-service capabilities and their adoption of AI and machine learning.
- Offshore Centres will Re-invent Themselves and Make a Comeback
2020 has seen contact centres in offshore locations struggle to offer services to global clients. Many of these operators have been plagued by poor internet connectivity at agents’ homes, and unfavourable home working environments. These outsourcing locations remain vital however, for multiple reasons – for example the range of services offered, agent specialisation, costs or diversity in agent profile.
Contact centre outsourcing providers will make a comeback in 2021 and we can expect new models to appear. Many providers across the globe have been running successful work-from-home only operations for years – other outsourcing providers will learn from these best practices. Organisations will find that bringing jobs back to high-cost locations will incur more costs. A full onshore model may not be the right model for business continuity, and organisations will prefer to have back-up locations to ensure continuity of services if another pandemic or catastrophe happens. Organisations will want to see the outsourcing providers offer them a choice of location – they will prefer some services to be delivered from offshore locations and others to remain onshore.
- Digital and Mobile will be the Cornerstone of Deeper Customer Engagement
COVID-19 has changed how customers want to be served, and organisations have had to re-evaluate how they use their channels – e.g. email, web, chat and voice. Customer profiles and expectations have changed over the year and they are more digital savvy and are more likely to interact with brands through digital and mobile apps. They will expect a single point of interaction – for their enquiries and to complete their transactions. For instance, they will expect to chat while filling up shopping carts. Introducing chat capabilities within mobile apps is a good way to impress customers – this can be an effective way to push promotions and upsell. Capabilities such as the ability to directly place a call from a website will make the customer experience exceptional. Customers will expect to move between channels easily when interacting with a brand.
- Workplace Collaboration Will be Fully Integrated into Contact Centres
Contact centres will reassess their business and talent models. The focus on employees will be in two major areas:
- Productivity. The contact centre floor dynamics have changed in how agents are spread out across outsourcing locations and in-house contact centres. Agents are no longer located in the same room or floor and do not have access to their usual way of work – continual training, digital signage that provides guidance and demonstrates KPIs, conversations with supervisors, managers, and team members for guidance or assistance, easy access to back-office functions and so on. This can impact their productivity.
- Engagement. Contact centre staff often work in high-stress environments -chasing sales targets and deadlines, handling complaints – and it is important for managers and supervisors to be able to engage and motivate them constantly. Remote working has further exacerbated the stress for those agents who do not have a conducive working environment at home.
Contact centres will increasingly look to workplace collaboration platforms and tools to improve employee productivity and experience.

The pandemic crisis has rapidly accelerated digitalisation across all industries. Organisations have been forced to digitalise entire processes more rapidly, as face-to-face engagement becomes restricted or even impossible.
The most visible areas where face-to-face activity is being swiftly replaced by digital alternatives include conferencing and collaboration, and the use of digital channels to engage with customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders.
For example, the crisis has made it difficult – even impossible, sometimes – for contact centre agents to physically work in contact centres, and they often do not have the tools to work effectively from home. This challenge is particularly apparent for offshore contact centres in the Philippines and India. The creation of chatbots has reduced the need for customer service staff and enabled data to by entered into front-office systems, and analysed immediately.
Less visible are back-office processes which are commonly inefficient and labour-intensive. Remote working makes some back-office workflows challenging or impossible. For example, some essential finance and accounting workflows involve a mix of digital communications, printing, scanning, copying and storage of physical documents – making these workflows inefficient, difficult to scale and labour-intensive. This has been highlighted during the pandemic. RPA adoption has grown faster than expected as organisations seek to resolve these and other challenges – often caused by inefficient workflows being scrambled by the crisis.
The RPA Market in Asia Pacific
There are many definitions of the RPA market, but it can broadly be defined as the use of software bots to execute processes which involve high volumes of repeatable tasks, that were previously executed by humans. When processes are automated, the physical location of employees and other stakeholders becomes less important. RPA makes these processes more agile and flexible and makes businesses more resilient. It can also increase operational efficiency, drive business growth, and enhance customer and employee experience.
RPA is a comparatively new and fast-growing market – this is leading to rapid change. In its infancy, it was basically the digitalisation of BPO. It was viewed as a way of automating repetitive tasks, many of which had been outsourced. While its cost saving benefits remain important as with BPOs, customers are now seeking more. They want RPA to help them to improve or transform front-office, back-office and industry-specific processes throughout the organisation. RPA vendors are addressing these enhanced requirements by blending RPA with AI and re-branding their offerings as intelligent automation or hyper-automation.
Asia Pacific organisations have been relatively slow to adopt RPA, but this is changing fast. The findings of the Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal study show that in the next 12 months, organisations will continue to focus on digital technologies for process automation (Figure 1).

The market is growing rapidly with large global RPA specialists such as UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism and AntWorks experiencing high rates of growth in the region.
RPA vendors in Asia Pacific, are typically addressing immediate, short-term requirements. For example, healthcare companies are automating the reporting of COVID-19 tests and ordering supplies. Chatbots are being widely used to address unprecedented call centre volumes for airlines, travel companies, banks and telecom providers. Administrative tasks increasingly require automation as workflows become disrupted by remote working.
Companies can also be expected to scale their current deployments and increase the rate at which AI capabilities are integrated into their offerings
RPA often works in conjunction with major software products provided by companies such as Salesforce, SAP, Microsoft and IBM. For example, some invoicing processes involve the use of Salesforce, SAP and Microsoft products. Rather than having an operative enter data into multiple systems, a bot can be created to do this.
Large software vendors such as IBM, Microsoft, Salesforce and SAP are taking advantage of this opportunity by trying to own entire workflows. They are increasingly integrating RPA into their offerings as well as competing directly in the RPA market with pureplay RPA vendors. RPA may soon be integrated into larger enterprise applications, unless pureplay RPA vendors can innovate and continually differentiate their offerings.

Governments face multiple challenges which are further getting highlighted by the ongoing global crisis. They have to manage the countries’ financial performances, reducing fiscal deficits. Every economy – whether emerging or mature – face challenges in bridging economic and social divides and ensuring equal access to infrastructure across the population. Most governments have challenges associated with the changes in demographics – whether because of rapid urbanisation, a fast ageing population or those associated with immigration policies.
Government agencies have the task of ensuring reliable public service, keeping their citizens safe, and striving for cost optimisation. In this constantly evolving world, agencies need to rely on technology to manage ever-growing citizen expectations and rising costs. Several government agencies have started their digital transformation (DX) journey replacing their legacy systems to transform the way they deliver services to their citizens.
Drivers of Transformation in Public Sector
Creating cross-agency synergies
Government agencies have access to enormous quantities of citizen data. But much of that data resides with individual agencies, often with no real synergies between them. For improved cost management and better utilisation of the data, it is imperative for governments to think of cross-agency collaboration systems and tools which give the larger entity a better visibility of their resources, contracts and citizen information. This involves, developing procedures, frameworks and working beyond their limited boundaries, leveraging technology to share information, applications, platform and processes. While this has been in discussion for nearly a decade now, most government agencies still work in departmental siloes and find it hard to work as a networked entity. The Ecosystm AI study finds that nearly three-quarters of public sector organisations find data access a challenge for their AI projects.
Improving citizen engagement
Increasingly, citizens are becoming tech-savvy and are expecting digital services from their government agencies. Not only that, but they are also ready to have conversations with agencies and provide feedback on matters of convenience and public safety. With the popularity of social media, citizens now have the capability to take their feedback to a wider open forum, if the agency fails to engage with them. Public sector organisations have to streamline and automate the services they provide, including payments, and provide real-time services that require collaborative feedback and increased participation from citizens. Smart governments are successfully able to leverage their citizen engagement to use open data platforms – Data.gov and data.gov.uk, are allowing communities to target and solve problems for which governments do not have the bandwidth. With citizen centricity and open government policies, there is also an ever-increasing need for greater accountability and transparency.
Managing project performance and costs
Most government projects involve several stakeholders and are complex in terms of the data, infrastructure and investments required. To take better decisions in terms of project complexity, risks and investments, public sector agencies need to have a structured project management framework, using an optimum mix of physical. technical, financial and human resources. In an environment where citizens expect more accountability and transparency, and where projects are often funded by citizens’ taxes, running these projects become even more complicated. Government agencies struggle to get funding, optimise costs (especially in projects that run over multiple years and political environments), and demonstrate some form of ROI. There is also an overwhelming requirement to detect and prevent frauds.
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for public sector, that are focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). It is very clear that the key areas of focus are cost optimisation (including fraud detection and project performance management) and having access to better data to provide improved citizen services (such as public safety and predicting citizen behaviour).
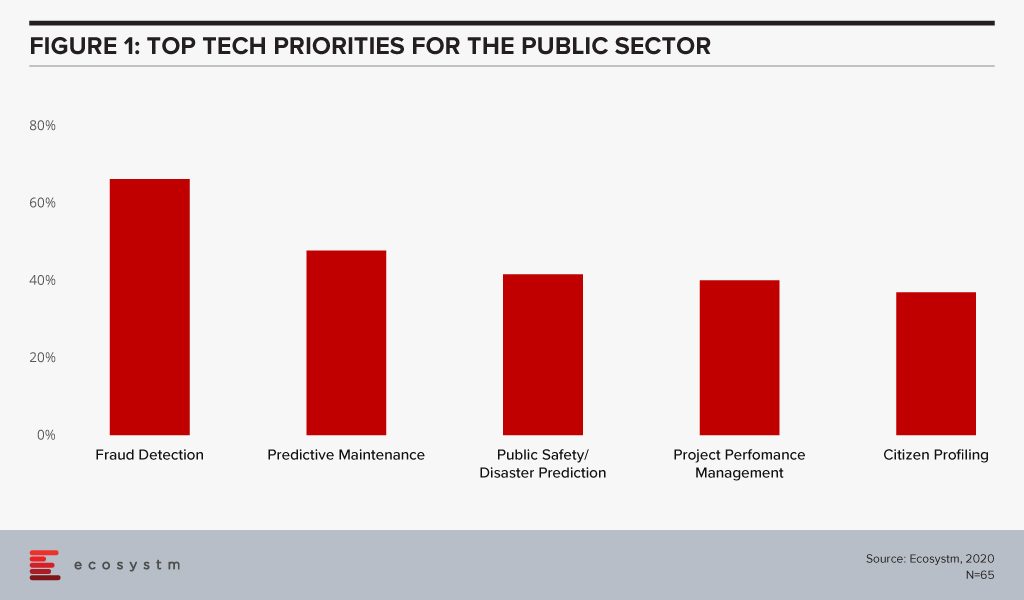
Technology as an Enabler of Public Sector transformation
Several emerging technologies are being used by government agencies as they look towards DX in the public sector.
The Push to Adopt Cloud
To prepare for the data surge that governments are facing and will continue to face, there is a push towards replacing legacy systems and obsolete infrastructure. The adoption of cloud services for data processing and storage is helping governments to provide efficient services, improve productivity, and reduce maintenance costs. Moreover, cloud infrastructure and services help governments provide open citizen services. The Government of India has built MeghRaj, India’s national cloud initiative to host government services and applications including local government services to promote eGovernance and better citizen services. The New Zealand Government has sent a clear directive to public sector organisations that public cloud services are preferred over traditional IT systems, in order to enhance customer experiences, streamline operations and create new delivery models. The objective is to use public cloud services for Blockchain, IoT, AI and data analytics.
Transparency through Communication & Collaboration technologies
Since the 1990s, the concept of eGovernment has required agencies to not only digitise citizen services but also work on how they communicate better with their citizens. While earlier modes of communication with citizens were restricted to print, radio or television, digital government initiatives have introduced more active communication using mobile applications, discussion forums, online feedback forms, eLearning, social media, and so on. Australia’s Just Ask Once allows citizens to access information on various government services at one place for better accessibility. More and more government agencies are implementing an omnichannel communication platform, which allows them to disseminate information across channels such as web, mobile apps, social media and so on. In the blog The Use of Technology in Singapore’s COVID-19 Response, Ecosystm analysts spoke about the daily updates shared by the Government through mobile phones. Demonstrating cross-agency collaboration, the information disseminated comes from multiple government agencies – the same channel is also used to drip-feed hygiene guidelines and the evolving government policies on travel, trade and so on.
AI & Automation for Process Efficiency and Actionable Intelligence
Governments are focusing on leveraging centralised resources and making processes smarter through the adoption of AI platforms. Initiatives such as the Singapore Government’s concept of Single Sources of Truth (SSOT), where all decision-making agencies have access to the same data, is the first step in efficient AI adoption. Singapore’s government agencies also have three data aggregators – Trusted Centers (TCs). This enables initiatives such as Vault-Gov.SG which allows government officials to browse a metadata catalogue and download sample data to run exploratory analytics. To push the adoption of AI, several governments are focusing on roadmaps and strategies such as Singapore’s National AI Strategies to transform the country by 2030, and the Government of Australia’s AI Roadmap and framework to help in the field of industry, science, energy, and education.
The first step of AI adoption is often through automation tools, such as virtual assistants and chatbots. The US Citizen and Immigration Service (USCIS) introduced an AI powered chatbot Emma to better support citizens through self-service options and reduce the workload of their customer service agents. The department of Human Services in Australia rolled out various chatbots named Roxy, Sam, Oliver, Charles and the most latest in progress PIPA (Platform Independent Personal Assistant) to provide information on various services and assist on queries.
Real-time data access with IoT
Governments have the responsibility of enforcing law and order, infrastructure management and disaster management. Real-time information data access is key to these initiatives. IoT sensors are being used in various government applications in object detection, and risk assessment in cities as well as remote areas. For example, IoT-enabled traffic monitoring and surveillance systems are embedded to provide real-time updates and continuous monitoring that can be used to solve issues, as well as provide real-time information to citizens. In a futuristic step, the US Department of Transportation (USDOT) is working with auto manufacturers on embedding vehicle to vehicle communication capabilities in all vehicles to avoid collision with emergency braking and vehicle speed monitoring. In an effort to promoting smart city initiatives and for infrastructure maintenance, New Zealand has installed smart cameras with automated processing capabilities, and IoT based street lighting system. IoT has tremendously benefited the supply chain and logistics sector. The US Army’s Logistics Support Activity (LOGSA) is using IoT for one of the Government’s biggest logistics systems. and military hardware with on-board sensors to analyse data directly from the vehicles for better asset maintenance. Again like in AI, there is a need for a clear roadmap for government adoption of emerging technologies, especially considering the safety and ethics angle. The Government of UK has introduced IoTUK, a program to help the public sector and private enterprises to come together and develop IoT technologies considering aspects such as privacy, security, and reliability.
Blockchain enabled Traceability & Transparency
Moving paper-based systems to digitised systems makes processes efficient to a degree. However, more is required for full traceability and transparency. Managing the data flow and safeguarding the information is vital for government organisations, especially as there is an increase in cross-agency collaboration. Government agencies and departments across the globe are increasingly collaborating using Blockchain technology, while at the same time maintaining the security of the data. For instance, in Georgia, the government department of Land, Property and Housing Management is using Blockchain to maintain land and property records. The blockchain-based land registry allows speedier approvals with no involvement of paperwork or multi-party signatures on physical documents. This is enhancing service quality while offering better security measures as the data is digitally stored in the National Agency of Public Registry’s land title database. Estonia is using Blockchain to protect their digital services such as electronic health records, legal records, police records, banking information, covering data and devices from attacks, misuse, and corruption.
Technology-led digital transformation has become the norm for public sector organisations across both emerging and mature economies. However, agencies need to create clear roadmaps and frameworks, including RoI considerations (which may not only be financial but should include citizen experience) and avoid ad-hoc implementations. The key consideration that government agencies should keep in mind is citizen security and ethics when adopting emerging technologies.

The FMCG industry has always been competitive given the need to drive high sales volume because of the low profit margins of the products. As the industry faces changes – such as the demographics of the consumer base and the need to introduce newer sales channels – technology is playing an important role in ensuring that the organisations can remain competitive.
eCommerce Disrupting the FMCG Industry
The concept of online retail is said to have originated in some form in the 1960s. But with the growth of the access to the Internet in the 1990s and Amazon’s competitive business model, it has disrupted the retail and FMCG industries. As we see a steady growth in smartphone usage, digital payments, online banking and app-based platforms, online retail is becoming mainstream. While initially thought to be ideal for the purchase of durables and entertainment products and services (where price comparison is key), it has become common for FMCG companies to use eCommerce platforms. Even perishables are being purchased online with the rise in the number of online grocery stores. This is impacting the FMCG industry in a number of ways:
Change in Marketing Strategy
FMCG companies need to continue their traditional marketing strategy for in-store consumers. But at the same time, they need to reach out to a wider base of consumers who shop online. The profile of these consumers is different – younger and technologically savvier. They do not necessarily believe in brand loyalty. While the browse-to-buy ratio for FMCG products is high, they are having to invest in digital marketing strategies including personalised campaigns and presence in social media and online forums. Even packaging for in-store and online products need to be different for some products.
Increased Competition
An online presence means that your brand can reach a wider audience – this also means that the competition becomes tougher. Now global brands compete with brands from other countries as well as local brands on the same online platform. This raises the bar, with companies competing not only on price and product but also on delivery services and better customer feedback.
Increased Complexity of the Supply Chain
No longer can an FMCG company depend solely on trucks delivering their products to stores at a fixed time of day. As they play increasingly in the B2C space, they have to constantly be aware of seasonality and spikes. This means that their supply chain operations become that much more complicated, and they are having to spend more on logistics and transportation. There is also the need to handle a larger volume of data.
Changing Consumer Profile
As mentioned earlier, the consumer profile of the FMCG industry has changed to include younger consumers who want to shop online. It also includes consumers in newer markets made possible by eCommerce platforms. FMCG companies also have to cater to consumers who are conscious about product quality, the environment and ethics. This means they want to know where the products were grown or manufactured, their carbon footprints and generally want more traceability of the products they are purchasing. This has led governments to come up with guidelines to protect consumer rights. Recently, the UK government issued guidelines on the quality, labelling, standards and food safety including the right logos, health and identification marks.
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for FMCG companies, focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). It is clear that their key priority is to handle the competitive market by focusing both on the consumer and the supply chain. Supply chain optimisation through demand forecasting ensures that they are not managing extra stock, and simultaneously not losing out on customers because of lack of stock. This just-in-time inventory management includes initiatives such as pricing optimisation in response to market demand, competition and – especially in the case of perishables – ensuring that stock closer to the use by date is cleared.
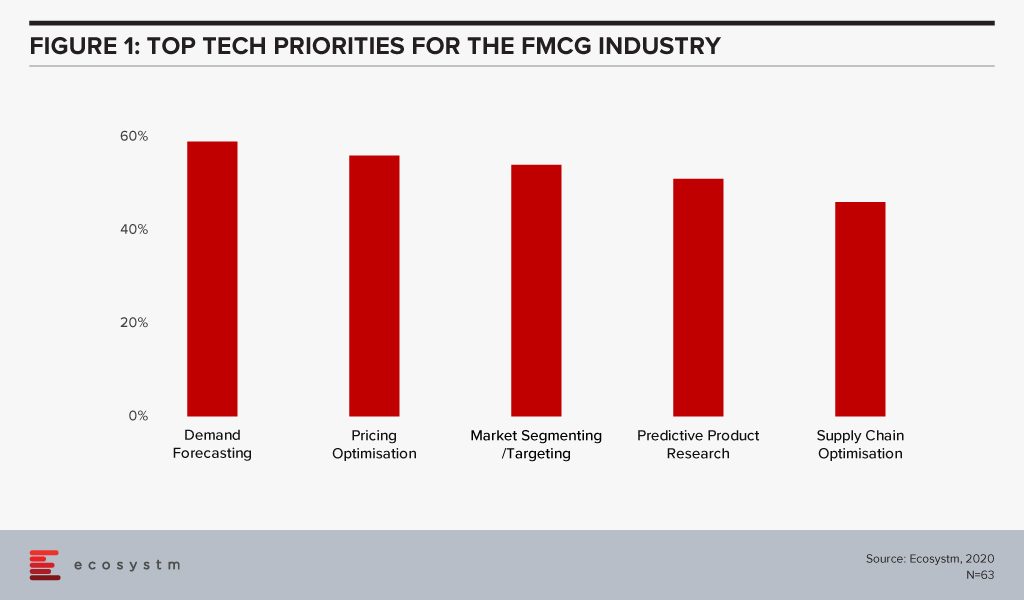
Technology as an Enabler of FMCG Transformation
The one advantage that FMCG companies have today is they have access to enormous customer and inventory data. As a result, they are able to leverage several emerging technologies to transform.
Digital Marketing
One area that is transforming the industry is digital marketing which includes multiple aspects such as search engine marketing, video marketing, social media activity and email marketing. While several technologies come together for a digital marketing solution and AI is a key component of the solutions, there are platforms that provide an end-to-end solution.
Digital marketing is most effective with a targeted group of customers and when organisations can identify digital or social champions. Johnson & Johnson’s Babycenter.com is a good example of how creating a digital community can help market products. The core idea behind the website is to give expecting and new mothers advice on early childhood. While on the surface it appears disassociated from Johnson & Johnson, the site almost exclusively carries their advertisements. This gives them a targeted base to push their products to. Dollar Shave Club is another example of how brands can leverage digital marketing. Their social media engagement has been so successful that they got bought over by Unilever. The digital campaign includes incentivising members with their products for posting about them on Instagram or Facebook.
Blockchain
FMCG companies are investing in Blockchain and digital ledger technologies for track and trace functionalities and operational efficiency. The technology not only helps manage the supply chain better by effective shipping timelines maintenance, delivery management and inventory management; it also helps build trust in a brand. It helps in compliance management, reduces the number or need for middlemen, easier handling of cross-border transactions and brings about an end-to-end accountability.
Danone initiated a Track & Connect service for their baby formula using Blockchain for transparency and traceability to show the authenticity of their products to parents and for a better customer experience. FMCG companies will benefit immensely from the farm-to-fork accountability concept initiated by Agriculture.
AI
From predictive analysis to machine learning to deep learning, AI is bringing a lot of benefits to FMCG companies. AI is enabling companies to discover gaps (both in their consumer interactions and in the supply chain) and make their processes intelligent – including demand forecasting, supply chain optimisation, personalised product offerings, social media analytics, consumer sentiment analytics and recommendation engines.
FMCG organisations are analysing internal and external data sources for both sales and improved customer experience. As FMCGs are forced to sell online to remain competitive, they have access to a high volume of the consumer as well as supply chain and inventory management data. Coca-Cola remains one of the leaders in the FMCG market by leveraging this data, including product research and social data mining. Even their vending machines are looking to leverage AI for personalised offerings and for loyalty programs.
The need to enhance the customer experience has also seen innovations like the Maggi Chatbot – “Kim”- that helps customers learn about Maggi recipes, ingredients, and dietary requirements, through Facebook Messenger.
FMCG companies that cannot afford to invest in technologies such as AI also have the option of leveraging the technology offerings of their online retail platform. eBay offers analytics as a service to the sellers – offering them data, metrics, and analytics to help them succeed. They also introduced computer vision technology to help sellers create clearer and more attractive images for the platform.
In this competitive market, we will see FMCG companies – and not just the big global brands but also the local producers – embrace more technology.

Artificial intelligence (AI) is perhaps the most electrifying and controversial of the so-called “disruptive” technologies. As AI becomes more sophisticated and the technology evolves, it will increasingly help to perform more complex tasks whether for personal or commercial use.
Today’s AI machines can replicate certain elements of intellectual ability and they are constantly striving to achieve more. This includes applications of autonomous vehicles, domestic and industrial robots, surveillance and security, automation, personal assistants, forecasting, data analysis and more.
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals top drivers of AI adoption. Organisations are trying to incorporate AI in their existing processes for better competitor analysis and insights, cost-effectiveness, deeper customer engagement to provide personalised service/product offerings, and for process redesign or automation.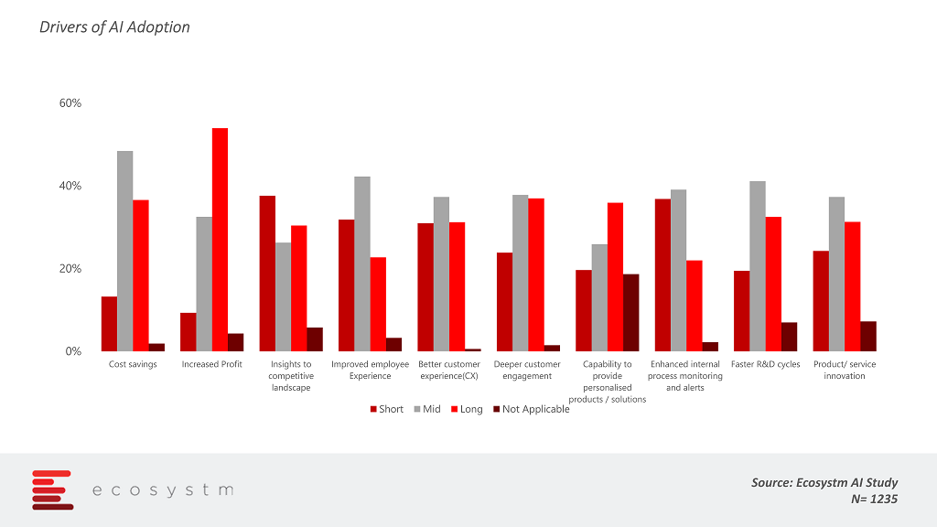
AI supporting technologies
AI is driving important technologies and processes and driving better, faster and more accurate decisions which help processes run more effectively and efficiently. With AI insights, business strategies will be more information-driven, efficient and consistent.
There are certainly many benefits that organisations are deriving from AI. Ecosystm AI study reveals that organisations implementing AI are using it to drive various business solutions including billing management, supply chain optimisation, predictive maintenance, enhancing operations and more.
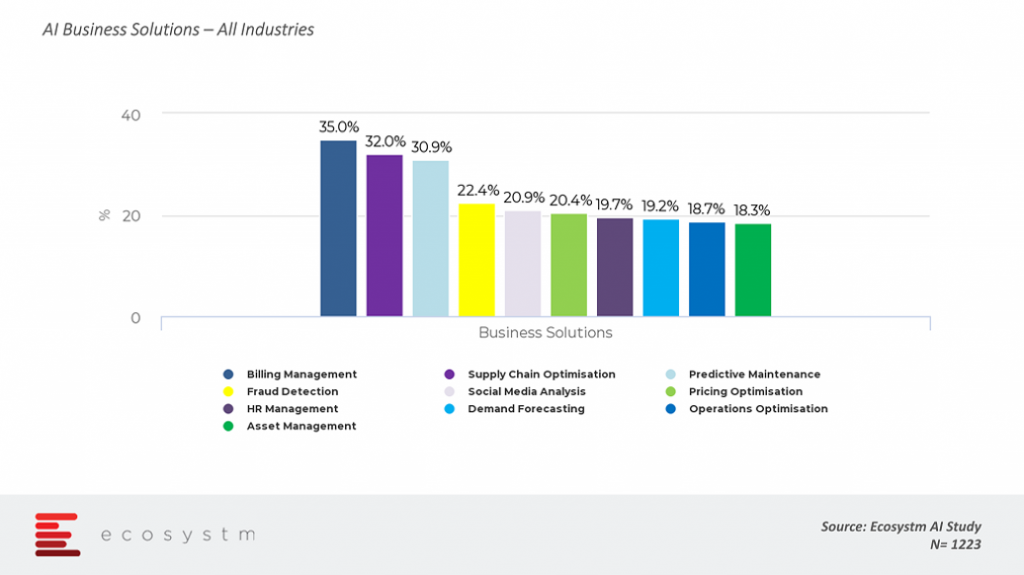
Below is a list of some hot technologies driven by AI.
Advanced Analytics
The proliferation of Big Data has led to the creation of massive data sets that can only be effectively analysed with AI tools and statistical models. AI can spot complex patterns in the data which is difficult for humans to understand. AI’s usefulness as an analytics tool is highly gaining importance in the use of predictive analytics and decision automation. Once sufficient data is available for use by AI, which is further filtered and processed thoroughly, the system can suggest actions or outcomes based on various parameters such as trends, patterns, historical information, frequency and more.
For example, the financial services industry is using advanced analytics to evaluate how customers earn, invest, spend and make financial decisions, which is useful for the organisations to customise their customers’ preference and offerings accordingly.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and speech recognition
NLP involves the learning of languages by machine through the means of interaction between computers and unstructured speech/text. NLP requires massive processing power and complex algorithms to reinforce learning mechanisms. To help in NLP, AI generates models, which are further improved to create NLP and speech simulations. Nowadays, Natural language is being implemented and used in various conversational interfaces, such as those with bots, artificial learning agents that can generalise to new environments, and autonomous vehicles.
Cognitive processing
Otherwise known as semantic computing, refers to a digital processing that attempts to mimic the operation of the human brain. In general, semantics means the meaning and interpretation of words and sentence structure and how words relate to other words. So, how is semantic related and what is the semantic analysis used for in AI? Semantic technology processes the logical structure of sentences to identify the most relevant elements in the text to understand the topic. It is especially suited to the analysis of large unstructured datasets with high efficiency.
Vantagepoint has an artificial intelligence tool to improve their trading results. It has a patented tool which can forecast stocks, futures, commodities, Forex and ETFs and claims an accuracy of up to 86%. The tool can predict changes in market trend direction up to three days in advance thus enabling traders to get in and out of trades at optimal times with confidence.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA has grown out of Business Process Automation (BPA) and refers to the use of AI to automate workflow and business processes. The advantages of RPA demonstrate it to be a solid tool in attaining higher quality output at lower costs which is much quicker than traditional methods. RPA can be used in IT support processes, back-office work, and workflow processes. The rules are programmed, and bots extract structured inputs from applications like Excel and enter them into other software such as CRM, SCM or accounting. A good example is the use of NLP to scan incoming emails and undertake the appropriate action, such as generating an invoice or flagging a complaint in an automated manner.
Machine Learning
Machine learning is an application of artificial intelligence (AI) which involves a combination of raw computing power and logic-based models to simulate the human learning process. Machine Learning is proving to be a successful approach to AI. When humans learn, they alter the way they relate information and the world, similarly when machines learn, they alter the data and form it into a piece of information.
An example, Image recognition is a popular application of machine learning in which images are fed into an algorithm, which attempts to recognise the contents of the image based on patterns. For instance, Yelp’s machine learning algorithms help the company’s human staff deal with tens of millions of photos to compile, categorise, and label the images more efficiently.
Chatbots and virtual assistants
Chatbots are robotic processes which simulate human conversation and automate functions. The technology is also used for so-called ‘virtual assistants’, which uses AI to interact with humans and aid with specific queries. They are increasingly being used to handle simple conversation and tasks in B2B and B2C environments. The addition of chatbots reduces human assistants and they can work throughout the clock. Chatbots and Virtual assistants improve with AI and can be trained to review conversations, past transactions and to draft a response based on context. If the user interacts with the bot through voice, then the chatbot requires a speech recognition engine.
Chatbots have been used in instant messaging (IM) applications and online interactive platforms. To exemplify, chatbots are deployed to assist online shoppers by answering noncomplex product questions, pricing, FAQ’s, order processing steps or forwarding information to human agents on complicated questions such as shipping delays or faults.
With AI technology evolving and improving so rapidly, many organisations are looking to use AI in their business, but there are still many questions to which adopters are seeking answers such as how to integrate AI into their existing systems, how to get access to data that will enable AI as well as the persistent technology concerns around cybersecurity and cost. The goal of many AI providers is to reach a stage where AI will support humans, control machines for us and automate repetitive tasks and processes.





















