Despite financial institutions’ unwavering efforts to safeguard their customers, scammers continually evolve to exploit advancements in technology. For example, the number of scams and cybercrimes reported to the police in Singapore increased by a staggering 49.6% to 50,376 at an estimated cost of USD 482M in 2023. GenAI represents the latest challenge to the industry, providing fraudsters with new avenues for deception.
Ecosystm research shows that BFSI organisations in Asia Pacific are spending more on technologies to authenticate customer identity and prevent fraud, than they are in their Know Your Customer (KYC) processes.
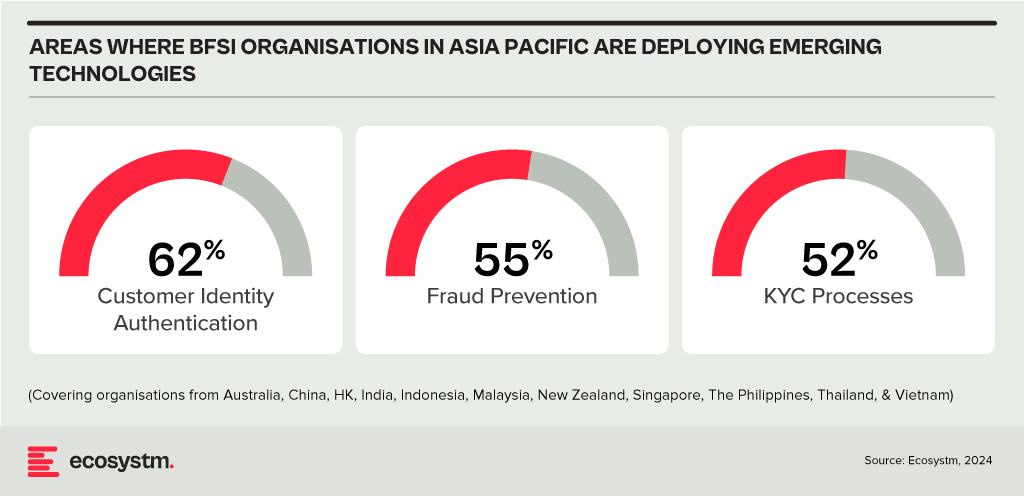
The Evolution of the Threat Landscape in BFSI
Synthetic Identity Fraud. This involves the creation of fictitious identities by combining real and fake information, distinct from traditional identity theft where personal data is stolen. These synthetic identities are then exploited to open fraudulent accounts, obtain credit, or engage in financial crimes, often evading detection due to their lack of association with real individuals. The Deloitte Centre for Financial Services predicts that synthetic identity fraud will result in USD 23B in losses by 2030. Synthetic fraud is posing significant challenges for financial institutions and law enforcement agencies, especially with the emergence of advanced technologies like GenAI being used to produce realistic documents blending genuine and false information, undermining Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols.
AI-Enhanced Phishing. Ecosystm research reveals that in Asia Pacific, 71% of customer interactions in BFSI occur across multiple digital channels, including mobile apps, emails, messaging, web chats, and conversational AI. In fact, 57% of organisations plan to further improve customer self-service capabilities to meet the demand for flexible and convenient service delivery. The proliferation of digital channels brings with it an increased risk of phishing attacks.
While these organisations continue to educate their customers on how to secure their accounts in a digital world, GenAI poses an escalating threat here as well. Phishing schemes will employ widely available LLMs to generate convincing text and even images. For many potential victims, misspellings and strangely worded appeals are the only hint that an email from their bank is not what it seems. The maturing of deepfake technology will also make it possible for malicious agents to create personalised voice and video attacks.
Identity Fraud Detection and Prevention
Although fraudsters are exploiting every new vulnerability, financial organisations also have new tools to protect their customers. Organisations should build a layered defence to prevent increasingly sophisticated attempts at fraud.
- Behavioural analytics. Using machine learning, financial organisations can differentiate between standard activities and suspicious behaviour at the account level. Data that can be analysed includes purchase patterns, unusual transaction values, VPN use, browser choice, log-in times, and impossible travel. Anomalies can be flagged, and additional security measures initiated to stem the attack.
- Passive authentication. Accounts can be protected even before password or biometric authentication by analysing additional data, such as phone number and IP address. This approach can be enhanced by comparing databases populated with the details of suspicious actors.
- SIM swap detection. SMS-based MFA is vulnerable to SIM swap attacks where a customer’s phone number is transferred to the fraudster’s own device. This can be prevented by using an authenticator app rather than SMS. Alternatively, SIM swap history can be detected before sending one-time passwords (OTPs).
- Breached password detection. Although customers are strongly discouraged to reuse passwords across sites, some inevitably will. By employing a service that maintains a database of credentials leaked during third-party breaches, it is possible to compare with active customer passwords and initiate a reset.
- Stronger biometrics. Phone-based fingerprint recognition has helped financial organisations safeguard against fraud and simplify the authentication experience. Advances in biometrics continue with recognition for faces, retina, iris, palm print, and voice making multimodal biometric protection possible. Liveness detection will grow in importance to combat against AI-generated content.
- Step-up validation. Authentication requirements can be differentiated according to risk level. Lower risk activities, such as balance check or internal transfer, may only require minimal authentication while higher risk ones, like international or cryptocurrency transactions may require a step up in validation. When anomalous behaviour is detected, even greater levels of security can be initiated.
Recommendations
- Reduce friction. While it may be tempting to implement heavy handed approaches to prevent fraud, it is also important to minimise friction in the authentication system. Frustrated users may abandon services or find risky ways to circumvent security. An effective layered defence should act in the background to prevent attackers getting close.
- AI Phishing Awareness. Even the savviest of customers could fall prey to advanced phishing attacks that are using GenAI. Social engineering at scale becomes increasingly more possible with each advance in AI. Monitor emerging global phishing activities and remind customers to be ever vigilant of more polished and personalised phishing attempts.
- Deploy an authenticator app. Consider shifting away from OTP SMS as an MFA method and implement either an authenticator app or one embedded in the financial app instead.
- Integrate authentication with fraud analytics. Select an authentication provider that can integrate its offering with analytics to identify fraud or unusual behaviour during account creation, log in, and transactions. The two systems should work in tandem.
- Take a zero-trust approach. Protecting both customers and employees is critical, particularly in the hybrid work era. Implement zero trust tools to prevent employees from falling victim to malicious attacks and minimising damage if they do.

As AI evolves rapidly, the emergence of GenAI technologies such as GPT models has sparked a novel and critical role: prompt engineering. This specialised function is becoming indispensable in optimising the interaction between humans and AI, serving as a bridge that translates human intentions into prompts that guide AI to produce desired outcomes. In this Ecosystm Insight, I will explore the importance of prompt engineering, highlighting its significance, responsibilities, and the impact it has on harnessing AI’s full potential.
Understanding Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering is an interdisciplinary role that combines elements of linguistics, psychology, computer science, and creative writing. It involves crafting inputs (prompts) that are specifically designed to elicit the most accurate, relevant, and contextually appropriate responses from AI models. This process requires a nuanced understanding of how different models process information, as well as creativity and strategic thinking to manipulate these inputs for optimal results.
As GenAI applications become more integrated across sectors – ranging from creative industries to technical fields – the ability to effectively communicate with AI systems has become a cornerstone of leveraging AI capabilities. Prompt engineers play a crucial role in this scenario, refining the way we interact with AI to enhance productivity, foster innovation, and create solutions that were previously unimaginable.
The Art and Science of Crafting Prompts
Prompt engineering is as much an art as it is a science. It demands a balance between technical understanding of AI models and the creative flair to engage these models in producing novel content. A well-crafted prompt can be the difference between an AI generating generic, irrelevant content and producing work that is insightful, innovative, and tailored to specific needs.
Key responsibilities in prompt engineering include:
- Prompt Optimisation. Fine-tuning prompts to achieve the highest quality output from AI models. This involves understanding the intricacies of model behaviour and leveraging this knowledge to guide the AI towards desired responses.
- Performance Testing and Iteration. Continuously evaluating the effectiveness of different prompts through systematic testing, analysing outcomes, and refining strategies based on empirical data.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration. Engaging with a diverse team of professionals, including data scientists, AI researchers, and domain experts, to ensure that prompts are aligned with project goals and leverage domain-specific knowledge effectively.
- Documentation and Knowledge Sharing. Developing comprehensive guidelines, best practices, and training materials to standardise prompt engineering methodologies within an organisation, facilitating knowledge transfer and consistency in AI interactions.
The Strategic Importance of Prompt Engineering
Effective prompt engineering can significantly enhance the efficiency and outcomes of AI projects. By reducing the need for extensive trial and error, prompt engineers help streamline the development process, saving time and resources. Moreover, their work is vital in mitigating biases and errors in AI-generated content, contributing to the development of responsible and ethical AI solutions.
As AI technologies continue to advance, the role of the prompt engineer will evolve, incorporating new insights from research and practice. The ability to dynamically interact with AI, guiding its creative and analytical processes through precisely engineered prompts, will be a key differentiator in the success of AI applications across industries.
Want to Hire a Prompt Engineer?
Here is a sample job description for a prompt engineer if you think that your organisation will benefit from the role.

Conclusion
Prompt engineering represents a crucial evolution in the field of AI, addressing the gap between human intention and machine-generated output. As we continue to explore the boundaries of what AI can achieve, the demand for skilled prompt engineers – who can navigate the complex interplay between technology and human language – will grow. Their work not only enhances the practical applications of AI but also pushes the frontier of human-machine collaboration, making them indispensable in the modern AI ecosystem.

AI has become a business necessity today, catalysing innovation, efficiency, and growth by transforming extensive data into actionable insights, automating tasks, improving decision-making, boosting productivity, and enabling the creation of new products and services.
Generative AI stole the limelight in 2023 given its remarkable advancements and potential to automate various cognitive processes. However, now the real opportunity lies in leveraging this increased focus and attention to shine the AI lens on all business processes and capabilities. As organisations grasp the potential for productivity enhancements, accelerated operations, improved customer outcomes, and enhanced business performance, investment in AI capabilities is expected to surge.
In this eBook, Ecosystm VP Research Tim Sheedy and Vinod Bijlani and Aman Deep from HPE APAC share their insights on why it is crucial to establish tailored AI capabilities within the organisation.

“AI Guardrails” are often used as a method to not only get AI programs on track, but also as a way to accelerate AI investments. Projects and programs that fall within the guardrails should be easy to approve, govern, and manage – whereas those outside of the guardrails require further review by a governance team or approval body. The concept of guardrails is familiar to many tech businesses and are often applied in areas such as cybersecurity, digital initiatives, data analytics, governance, and management.
While guidance on implementing guardrails is common, organisations often leave the task of defining their specifics, including their components and functionalities, to their AI and data teams. To assist with this, Ecosystm has surveyed some leading AI users among our customers to get their insights on the guardrails that can provide added value.
Data Security, Governance, and Bias
- Data Assurance. Has the organisation implemented robust data collection and processing procedures to ensure data accuracy, completeness, and relevance for the purpose of the AI model? This includes addressing issues like missing values, inconsistencies, and outliers.
- Bias Analysis. Does the organisation analyse training data for potential biases – demographic, cultural and so on – that could lead to unfair or discriminatory outputs?
- Bias Mitigation. Is the organisation implementing techniques like debiasing algorithms and diverse data augmentation to mitigate bias in model training?
- Data Security. Does the organisation use strong data security measures to protect sensitive information used in training and running AI models?
- Privacy Compliance. Is the AI opportunity compliant with relevant data privacy regulations (country and industry-specific as well as international standards) when collecting, storing, and utilising data?
Model Development and Explainability
- Explainable AI. Does the model use explainable AI (XAI) techniques to understand and explain how AI models reach their decisions, fostering trust and transparency?
- Fair Algorithms. Are algorithms and models designed with fairness in mind, considering factors like equal opportunity and non-discrimination?
- Rigorous Testing. Does the organisation conduct thorough testing and validation of AI models before deployment, ensuring they perform as intended, are robust to unexpected inputs, and avoid generating harmful outputs?
AI Deployment and Monitoring
- Oversight Accountability. Has the organisation established clear roles and responsibilities for human oversight throughout the AI lifecycle, ensuring human control over critical decisions and mitigation of potential harm?
- Continuous Monitoring. Are there mechanisms to continuously monitor AI systems for performance, bias drift, and unintended consequences, addressing any issues promptly?
- Robust Safety. Can the organisation ensure AI systems are robust and safe, able to handle errors or unexpected situations without causing harm? This includes thorough testing and validation of AI models under diverse conditions before deployment.
- Transparency Disclosure. Is the organisation transparent with stakeholders about AI use, including its limitations, potential risks, and how decisions made by the system are reached?
Other AI Considerations
- Ethical Guidelines. Has the organisation developed and adhered to ethical principles for AI development and use, considering areas like privacy, fairness, accountability, and transparency?
- Legal Compliance. Has the organisation created mechanisms to stay updated on and compliant with relevant legal and regulatory frameworks governing AI development and deployment?
- Public Engagement. What mechanisms are there in place to encourage open discussion and engage with the public regarding the use of AI, addressing concerns and building trust?
- Social Responsibility. Has the organisation considered the environmental and social impact of AI systems, including energy consumption, ecological footprint, and potential societal consequences?
Implementing these guardrails requires a comprehensive approach that includes policy formulation, technical measures, and ongoing oversight. It might take a little longer to set up this capability, but in the mid to longer term, it will allow organisations to accelerate AI implementations and drive a culture of responsible AI use and deployment.

For many organisations migrating to cloud, the opportunity to run workloads from energy-efficient cloud data centres is a significant advantage. However, carbon emissions can vary from one country to another and if left unmonitored, will gradually increase over time as cloud use grows. This issue will become increasingly important as we move into the era of compute-intensive AI and the burden of cloud on natural resources will shift further into the spotlight.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that data centres are responsible for up to 1.5% of global electricity use and 1% of GHG emissions. Cloud providers have recognised this and are committed to change. Between 2025 and 2030, all hyperscalers – AWS, Azure, Google, and Oracle included – expect to power their global cloud operations entirely with renewable sources.
Chasing the Sun
Cloud providers are shifting their sights from simply matching electricity use with renewable power purchase agreements (PPA) to the more ambitious goal of operating 24/7 on carbon-free sources. A defining characteristic of renewables though is intermittency, with production levels fluctuating based on the availability of sunlight and wind. Leading cloud providers are using AI to dynamically distribute compute workloads throughout the day to regions with lower carbon intensity. Workloads that are processed with solar power during daylight can be shifted to nearby regions with abundant wind energy at night.
Addressing Water Scarcity
Many of the largest cloud data centres are situated in sunny locations to take advantage of solar power and proximity to population centres. Unfortunately, this often means that they are also in areas where water is scarce. While liquid-cooled facilities are energy efficient, local communities are concerned on the strain on water sources. Data centre operators are now committing to reduce consumption and restore water supplies. Simple measures, such as expanding humidity (below 20% RH) and temperature tolerances (above 30°C) in server rooms have helped companies like Meta to cut wastage. Similarly, Google has increased their reliance on non-potable sources, such as grey water and sea water.
From Waste to Worth
Data centre operators have identified innovative ways to reuse the excess heat generated by their computing equipment. Some have used it to heat adjacent swimming pools while others have warmed rooms that house vertical farms. Although these initiatives currently have little impact on the environmental impact of cloud, they suggest a future where waste is significantly reduced.
Greening the Grid
The giant facilities that cloud providers use to house their computing infrastructure are also set to change. Building materials and construction account for an astonishing 11% of global carbon emissions. The use of recycled materials in concrete and investing in greener methods of manufacturing steel are approaches the construction industry are attempting to lessen their impact. Smaller data centres have been 3D printed to accelerate construction and use recyclable printing concrete. While this approach may not be suitable for hyperscale facilities, it holds potential for smaller edge locations.
Rethinking Hardware Management
Cloud providers rely on their scale to provide fast, resilient, and cost-effective computing. In many cases, simply replacing malfunctioning or obsolete equipment would achieve these goals better than performing maintenance. However, the relentless growth of e-waste is putting pressure on cloud providers to participate in the circular economy. Microsoft, for example, has launched three Circular Centres to repurpose cloud equipment. During the pilot of their Amsterdam centre, it achieved 83% reuse and 17% recycling of critical parts. The lifecycle of equipment in the cloud is largely hidden but environmentally conscious users will start demanding greater transparency.
Recommendations
Organisations should be aware of their cloud-derived scope 3 emissions and consider broader environmental issues around water use and recycling. Here are the steps that can be taken immediately:
- Monitor GreenOps. Cloud providers are adding GreenOps tools, such as the AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool, to help organisations measure the environmental impact of their cloud operations. Understanding the relationship between cloud use and emissions is the first step towards sustainable cloud operations.
- Adopt Cloud FinOps for Quick ROI. Eliminating wasted cloud resources not only cuts costs but also reduces electricity-related emissions. Tools such as CloudVerse provide visibility into cloud spend, identifies unused instances, and helps to optimise cloud operations.
- Take a Holistic View. Cloud providers are being forced to improve transparency and reduce their environmental impact by their biggest customers. Getting educated on the actions that cloud partners are taking to minimise emissions, water use, and waste to landfill is crucial. In most cases, dedicated cloud providers should reduce waste rather than offset it.
- Enable Remote Workforce. Cloud-enabled security and networking solutions, such as SASE, allow employees to work securely from remote locations and reduce their transportation emissions. With a SASE deployed in the cloud, routine management tasks can be performed by IT remotely rather than at the branch, further reducing transportation emissions.

In the Ecosystm Predicts: Building an Agile & Resilient Organisation: Top 5 Trends in 2024, Principal Advisor Darian Bird said, “The emergence of Generative AI combined with the maturing of deepfake technology will make it possible for malicious agents to create personalised voice and video attacks.” Darian highlighted that this democratisation of phishing, facilitated by professional-sounding prose in various languages and tones, poses a significant threat to potential victims who rely on misspellings or oddly worded appeals to detect fraud. As we see more of these attacks and social engineering attempts, it is important to improve defence mechanisms and increase awareness.
Understanding Deepfake Technology
The term Deepfake is a combination of the words ‘deep learning’ and ‘fake’. Deepfakes are AI-generated media, typically in the form of images, videos, or audio recordings. These synthetic content pieces are designed to appear genuine, often leading to the manipulation of faces and voices in a highly realistic manner. Deepfake technology has gained spotlight due to its potential for creating convincing yet fraudulent content that blurs the line of reality.
Deepfake algorithms are powered by Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and continuously enhance synthetic content to closely resemble real data. Through iterative training on extensive datasets, these algorithms refine features such as facial expressions and voice inflections, ensuring a seamless emulation of authentic characteristics.
Deepfakes Becoming Increasingly Convincing
Hyper-realistic deepfakes, undetectable to the human eye and ear, have become a huge threat to the financial and technology sectors. Deepfake technology has become highly convincing, blurring the line between real and fake content. One of the early examples of a successful deepfake fraud was when a UK-based energy company lost USD 243k through a deepfake audio scam in 2019, where scammers mimicked the voice of their CEO to authorise an illegal fund transfer.
Deepfakes have evolved from audio simulations to highly convincing video manipulations where faces and expressions are altered in real-time, making it hard to distinguish between real and fake content. In 2022, for instance, a deepfake video of Elon Musk was used in a crypto scam that resulted in a loss of about USD 2 million for US consumers. This year, a multinational company in Hong Kong lost over USD 25 million when an employee was tricked into sending money to fraudulent accounts after a deepfake video call by what appeared to be his colleagues.
Regulatory Responses to Deepfakes
Countries worldwide are responding to the challenges posed by deepfake technology through regulations and awareness campaigns.
- Singapore’s Online Criminal Harms Act, that will come into effect in 2024, will empower authorities to order individuals and Internet service providers to remove or block criminal content, including deepfakes used for malicious purposes.
- The UAE National Programme for Artificial Intelligence released a deepfake guide to educate the public about both harmful and beneficial applications of this technology. The guide categorises fake content into shallow and deep fakes, providing methods to detect deepfakes using AI-based tools, with a focus on promoting positive uses of advanced technologies.
- The proposed EU AI Act aims to regulate them by imposing transparency requirements on creators, mandating them to disclose when content has been artificially generated or manipulated.
- South Korea passed a law in 2020 banning the distribution of harmful deepfakes. Offenders could be sentenced to up to five years in prison or fined up to USD 43k.
- In the US, states like California and Virginia have passed laws against deepfake pornography, while federal bills like the DEEP FAKES Accountability Act aim to mandate disclosure and counter malicious use, highlighting the diverse global efforts to address the multifaceted challenges of deepfake regulation.
Detecting and Protecting Against Deepfakes
Detecting deepfake becomes increasingly challenging as technology advances. Several methods are needed – sometimes in conjunction – to be able to detect a convincing deepfake. These include visual inspection that focuses on anomalies, metadata analysis to examine clues about authenticity, forensic analysis for pattern and audio examination, and machine learning that uses algorithms trained on real and fake video datasets to classify new videos.
However, identifying deepfakes requires sophisticated technology that many organisations may not have access to. This heightens the need for robust cybersecurity measures. Deepfakes have seen an increase in convincing and successful phishing – and spear phishing – attacks and cyber leaders need to double down on cyber practices.
Defences can no longer depend on spotting these attacks. It requires a multi-pronged approach which combines cyber technologies, incidence response, and user education.
Preventing access to users. By employing anti-spoofing measures organisations can safeguard their email addresses from exploitation by fraudulent actors. Simultaneously, minimising access to readily available information, particularly on websites and social media, reduces the chance of spear-phishing attempts. This includes educating employees about the implications of sharing personal information and clear digital footprint policies. Implementing email filtering mechanisms, whether at the server or device level, helps intercept suspicious emails; and the filtering rules need to be constantly evaluated using techniques such as IP filtering and attachment analysis.
Employee awareness and reporting. There are many ways that organisations can increase awareness in employees starting from regular training sessions to attack simulations. The usefulness of these sessions is often questioned as sometimes they are merely aimed at ticking off a compliance box. Security leaders should aim to make it easier for employees to recognise these attacks by familiarising them with standard processes and implementing verification measures for important email requests. This should be strengthened by a culture of reporting without any individual blame.
Securing against malware. Malware is often distributed through these attacks, making it crucial to ensure devices are well-configured and equipped with effective endpoint defences to prevent malware installation, even if users inadvertently click on suspicious links. Specific defences may include disabling macros and limiting administrator privileges to prevent accidental malware installation. Strengthening authentication and authorisation processes is also important, with measures such as multi-factor authentication, password managers, and alternative authentication methods like biometrics or smart cards. Zero trust and least privilege policies help protect organisation data and assets.
Detection and Response. A robust security logging system is crucial, either through off-the shelf monitoring tools, managed services, or dedicated teams for monitoring. What is more important is that the monitoring capabilities are regularly updated. Additionally, having a well-defined incident response can swiftly mitigate post-incident harm post-incident. This requires clear procedures for various incident types and designated personnel for executing them, such as initiating password resets or removing malware. Organisations should ensure that users are informed about reporting procedures, considering potential communication challenges in the event of device compromise.
Conclusion
The rise of deepfakes has brought forward the need for a collaborative approach. Policymakers, technology companies, and the public must work together to address the challenges posed by deepfakes. This collaboration is crucial for making better detection technologies, establishing stronger laws, and raising awareness on media literacy.

2024 and 2025 are looking good for IT services providers – particularly in Asia Pacific. All types of providers – from IT consultants to managed services VARs and systems integrators – will benefit from a few converging events.
However, amidst increasing demand, service providers are also challenged with cost control measures imposed in organisations – and this is heightened by the challenge of finding and retaining their best people as competition for skills intensifies. Providers that service mid-market clients might find it hard to compete and grow without significant process automation to compensate for the higher employee costs.
Why Organisations are Opting for IT Service
- Organisations are seeking further cost reductions. Managed services providers will see more opportunities to take cost and complexity out of organisation’s IT functions. The focus in 2024 will be less on “managing” services and more on “transforming” them using ML, AI, and automation to reduce cost and improve value.
- Big app upgrades are back on the agenda. SAP is going above and beyond to incentivise their customers and partners to migrate their on-premises and hyperscale hosted instances to true cloud ERP. Initiatives such as Rise with SAP have been further expanded and improved to accelerate the transition. Salesforce customers are also looking to streamline their deployments while also taking advantage of the new AI and data capabilities. But many of these projects will still be complex and time-consuming.
- Cloud deployments are getting more complex. For many organisations, the simple cloud migrations are done. This is the stage of replatforming, retiring, and refactoring applications to take advantage of public and hybrid cloud capabilities. These are not simple lift and shift – or switch to SaaS – engagements.
- AI will drive a greater need for process improvement and transformation. This will happen along with associated change management and training programs. While it is still early days for GenAI, before the end of 2024, many organisations will move beyond experimentation to department or enterprise wide GenAI initiatives.
- Increasing cybersecurity and data governance demands will prolong the security skill shortage. More organisations will turn to managed security services providers and cybersecurity consultants to help them develop their strategy and response to the rising threat levels.
Choosing the Right Cost Model for IT Services
Buyers of IT services must implement strict cost-control measures and consider various approaches to align costs with business and customer outcomes, including different cost models:
Fixed-Price Contracts. These contracts set a firm price for the entire project or specific deliverables. Ideal when project scope is clear, they offer budget certainty upfront but demand detailed specifications, potentially leading to higher initial quotes due to the provider assuming more risk.
Time and Materials (T&M) Contracts with Caps. Payment is based on actual time and materials used, with negotiated caps to prevent budget overruns. Combining flexibility with cost predictability, this model offers some control over total expenses.
Performance-Based Pricing. Fees are tied to service provider performance, incentivising achievement of specific KPIs or milestones. This aligns provider interests with client goals, potentially resulting in cost savings and improved service quality.
Retainer Agreements with Scope Limits. Recurring fees are paid for ongoing services, with defined limits on work scope or hours within a given period. This arrangement ensures resource availability while containing expenses, particularly suitable for ongoing support services.
Other Strategies for Cost Efficiency and Effective Management
Technology leaders should also consider implementing some of the following strategies:
Phased Payments. Structuring payments in phases, tied to the completion of project milestones, helps manage cash flow and provides a financial incentive for the service provider to meet deadlines and deliverables. It also allows for regular financial reviews and adjustments if the project scope changes.
Cost Transparency and Itemisation. Detailed billing that itemises the costs of labour, materials, and other expenses provides transparency to verify charges, track spending against the budget, and identify areas for potential savings.
Volume Discounts and Negotiated Rates. Negotiating volume discounts or preferential rates for long-term or large-scale engagements, makes providers to offer reduced rates for a commitment to a certain volume of work or an extended contract duration.
Utilisation of Shared Services or Cloud Solutions. Opting for shared or cloud-based solutions where feasible, offers economies of scale and reduces the need for expensive, dedicated infrastructure and resources.
Regular Review and Adjustment. Conducting regular reviews of the services and expenses with the provider to ensure alignment with the budget and objectives, prepares organisations to adjust the scope, renegotiate terms, or implement cost-saving measures as needed.
Exit Strategy. Planning an exit strategy that include provisions for contract termination, transition services, protects an organisation in case the partnership needs to be dissolved.
Conclusion
Many businesses swing between insourcing and outsourcing technology capabilities – with the recent trend moving towards insourcing development and outsourcing infrastructure to the public cloud. But 2024 will see demand for all types of IT services across nearly every geography and industry. Tech services providers can bring significant value to your business – but improved management, monitoring, and governance will ensure that this value is delivered at a fair cost.

2024 will be another crucial year for tech leaders – through the continuing economic uncertainties, they will have to embrace transformative technologies and keep an eye on market disruptors such as infrastructure providers and AI startups. Ecosystm analysts outline the key considerations for leaders shaping their organisations’ tech landscape in 2024.
Navigating Market Dynamics

Continuing Economic Uncertainties. Organisations will focus on ongoing projects and consider expanding initiatives in the latter part of the year.
Popularity of Generative AI. This will be the time to go beyond the novelty factor and assess practical business outcomes, allied costs, and change management.
Infrastructure Market Disruption. Keeping an eye out for advancements and disruptions in the market (likely to originate from the semiconductor sector) will define vendor conversations.
Need for New Tech Skills. Generative AI will influence multiple tech roles, including AIOps and IT Architecture. Retaining talent will depend on upskilling and reskilling.
Increased Focus on Governance. Tech vendors are guide tech leaders on how to implement safeguards for data usage, sharing, and cybersecurity.
5 Key Considerations for Tech Leaders
#1 Accelerate and Adapt: Streamline IT with a DevOps Culture
Over the next 12-18 months, advancements in AI, machine learning, automation, and cloud-native technologies will be vital in leveraging scalability and efficiency. Modernisation is imperative to boost responsiveness, efficiency, and competitiveness in today’s dynamic business landscape.
The continued pace of disruption demands that organisations modernise their applications portfolios with agility and purpose. Legacy systems constrained by technical debt drag down velocity, impairing the ability to deliver new innovative offerings and experiences customers have grown to expect.
Prioritising modernisation initiatives that align with key value drivers is critical. Technology leaders should empower development teams to move beyond outdated constraints and swiftly deploy enhanced applications, microservices, and platforms.

#2 Empowering Tomorrow: Spring Clean Your Tech Legacy for New Leaders
Modernising legacy systems is a strategic and inter-generational shift that goes beyond simple technical upgrades. It requires transformation through the process of decomposing and replatforming systems – developed by previous generations – into contemporary services and signifies a fundamental realignment of your business with the evolving digital landscape of the 21st century.
The essence of this modernisation effort is multifaceted. It not only facilitates the integration of advanced technologies but also significantly enhances business agility and drives innovation. It is an approach that prepares your organisation for impending skill gaps, particularly as the older workforce begins to retire over the next decade. Additionally, it provides a valuable opportunity to thoroughly document, reevaluate, and improve business processes. This ensures that operations are not only efficient but also aligned with current market demands, contemporary regulatory standards, and the changing expectations of customers.

#3 Employee Retention: Consider the Strategic Role of Skills Acquisition
The agile, resilient organisation needs to be able to respond at pace to any threat or opportunity it faces. Some of this ability to respond will be related to technology platforms and architectures, but it will be the skills of employees that will dictate the pace of reform. While employee attrition rates will continue to decline in 2024 – but it will be driven by skills acquisition, not location of work.
Organisations who offer ongoing staff training – recognising that their business needs new skills to become a 21st century organisation – are the ones who will see increasing rates of employee retention and happier employees. They will also be the ones who offer better customer experiences, driven by motivated employees who are committed to their personal success, knowing that the organisation values their performance and achievements.

#4 Next-Gen IT Operations: Explore Gen AI for Incident Avoidance and Predictive Analysis
The integration of Generative AI in IT Operations signifies a transformative shift from the automation of basic tasks, to advanced functions like incident avoidance and predictive analysis. Initially automating routine tasks, Generative AI has evolved to proactively avoiding incidents by analysing historical data and current metrics. This shift from proactive to reactive management will be crucial for maintaining uninterrupted business operations and enhancing application reliability.
Predictive analysis provides insight into system performance and user interaction patterns, empowering IT teams to optimise applications pre-emptively, enhancing efficiency and user experience. This also helps organisations meet sustainability goals through accurate capacity planning and resource allocation, also ensuring effective scaling of business applications to meet demands.

#5 Expanding Possibilities: Incorporate AI Startups into Your Portfolio
While many of the AI startups have been around for over five years, this will be the year they come into your consciousness and emerge as legitimate solutions providers to your organisation. And it comes at a difficult time for you!
Most tech leaders are looking to reduce technical debt – looking to consolidate their suppliers and simplify their tech architecture. Considering AI startups will mean a shift back to more rather than fewer tech suppliers; a different sourcing strategy; more focus on integration and ongoing management of the solutions; and a more complex tech architecture.
To meet business requirements will mean that business cases will need to be watertight – often the value will need to be delivered before a contract has been signed.


Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Juniper Networks for USD 40 per share, totaling an equity value of about USD 14 Billion. This strategic move is aimed to enhance HPE’s portfolio by focusing on higher-growth solutions and reinforcing their high-margin networking business. HPE expects to double their networking business, positioning the combined entity as a leader in networking solutions. With the growing demand for secure, unified technology driven by AI and hybrid cloud trends, HPE aims to offer comprehensive, disruptive solutions that connect, protect, and analyse data from edge to cloud.
This would also be the organisation’s largest deal since becoming an independent company in 2015. The acquisition is expected to be completed by late 2024 or early 2025.
Ecosystm analysts Darian Bird and Richard Wilkins provide their insights on the HPE acquisition and its implications for the tech market.

Converging Networking and Security
One of the big drawcards for HPE is Juniper’s Mist AI. The networking vendors have been racing to catch up – both in capabilities and in marketing. The acquisition though will give HPE a leadership position in network visibility and manageability. With GreenLake and soon Mist AI, HPE will have a solid AIOps story across the entire infrastructure.
HPE has been working steadily towards becoming a player in the converged networking-security space. They integrated Silver Peak well to make a name for themselves in SD-WAN and last year acquiring Axis Security gave them the Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), Secure Web Gateway (SWG), and Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) modules in the Secure Service Edge (SSE) stack. Bringing all of this to the market with Juniper’s networking prowess positions HPE as a formidable player, especially as the Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) market gains momentum.
As the market shifts towards converged SASE, there will only be more interest in the SD-WAN and SSE vendors. In just over one year, Cato Networks and Netskope have raised funds, Check Point acquired Perimeter 81, and Versa Networks has made noises about an IPO. The networking and security players are all figuring out how they can deliver a single-vendor SASE.
Although HPE’s strategic initiatives signal a robust market position, potential challenges arise from the overlap between Aruba and Juniper. However, the distinct focus on the edge and data center, respectively, may help alleviate these concerns. The acquisition also marks HPE’s foray into the telecom space, leveraging its earlier acquisition of Athonet and establishing a significant presence among service providers. This expansion enhances HPE’s overall market influence, posing a challenge to the long-standing dominance of Cisco.

The strategic acquisition of Juniper Networks by HPE can make a transformative leap in AIOps and Software-Defined Networking (SDN). There is a potential for this to establish a new benchmark in IT management.
AI in IT Operations Transformation
The integration of Mist’s AI-driven wireless solutions and HPE’s SDN is a paradigm shift in IT operations management and will help organisations transition from a reactive to a predictive and proactive model. Mist’s predictive analytics, coupled with HPE’s SDN capabilities, empower networks to dynamically adjust to user demands and environmental changes, ensuring optimal performance and user experience. Marvis, Mist’s Virtual Network Assistant (VNA), adds conversational troubleshooting capabilities, enhancing HPE’s network solutions. The integration envisions an IT ecosystem where Juniper’s AI augments HPE’s InfoSight, providing deeper insights into network behaviour, preemptive security measures, and more autonomous IT operations.
Transforming Cloud and Edge Computing
The incorporation of Juniper’s AI into HPE’s cloud and edge computing solutions promises a significant improvement in data processing and management. AI-driven load balancing and resource allocation mechanisms will significantly enhance multi-cloud environment efficiency, ensuring robust and seamless cloud services, particularly vital in IoT applications where real-time data processing is critical. This integration not only optimises cloud operations but also has the potential to align with HPE’s commitment to sustainability, showcasing how AI advancements can contribute to energy conservation.
In summary, HPE’s acquisition of Juniper Networks, and specifically the integration of the Mist AI platform, is a pivotal step towards an AI-driven, efficient, and predictive IT infrastructure. This can redefine the standards in AIOps and SDN, creating a future where IT systems are not only reactive but also intuitively adaptive to the evolving demands of the digital landscape.

































