The Philippines, renowned as a global contact centre hub, is experiencing heightened pressure on the global stage, leading to intensified competition within the country. Smaller BPOs are driving larger players to innovate, requiring a stronger focus on empowering customer experience (CX) teams, and enhancing employee experience (EX) in organisations in the Philippines.

As the Philippines expands its global footprint, organisations must embrace progressive approaches to outpace rivals in the CX sector.
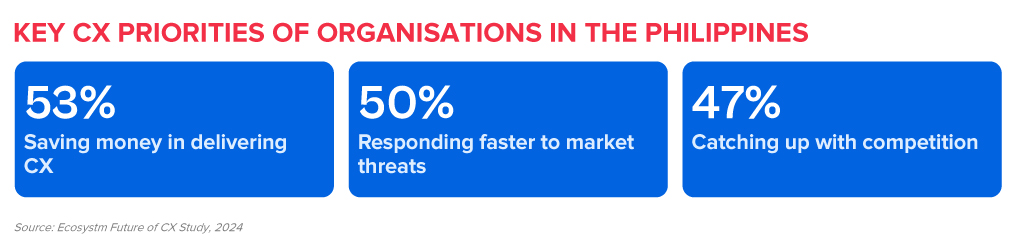
These priorities can be achieved through a robust data strategy that empowers CX teams and contact centres to glean actionable insights.
Here are 5 ways organisations in the Philippines can achieve their CX objectives.
Download ‘Securing the CX Edge: 5 Strategies for Organisations in the Philippines’ as a PDF.
#1 Modernise Voice and Omnichannel Orchestration
Ensuring that all channels are connected and integrated at the core is critical in delivering omnichannel experiences. Organisations must ensure that the conversation can be continued seamlessly irrespective of the channel the customer chooses, without losing the context.
Voice must be integrated within the omnichannel strategy. Even with the rise of digital and self-service, voice remains crucial, especially for understanding complex inquiries and providing an alternative when customers face persistent challenges on other channels.
Transition from a siloed view of channels to a unified and integrated approach.

#2 Empower CX Teams with Actionable Customer Data
An Intelligent Data Hub aggregates, integrates, and organises customer data across multiple data sources and channels and eliminates the siloed approach to collecting and analysing customer data.
Drive accurate and proactive conversations with your customers through a unified customer data platform.
- Unifies user history across channels into a single customer view.
- Enables the delivery of an omnichannel experience.
- Identifies behavioural trends by understanding patterns to personalise interactions.
- Spots real-time customer issues across channels.
- Uncovers compliance gaps and missed sales opportunities from unstructured data.
- Looks at customer journeys to proactively address their needs.

#3 Transform CX & EX with AI/Automation
AI and automation should be the cornerstone of an organisation’s CX efforts to positively impact both customers and employees.
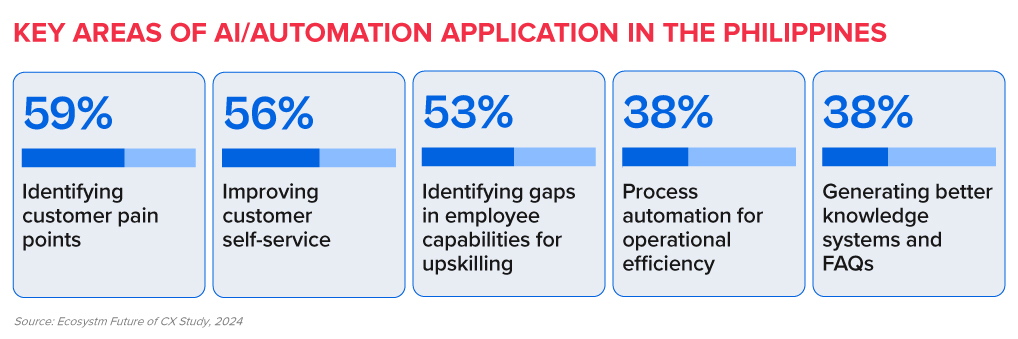
Evaluate all aspects of AI/automation to enhance both customer and employee experience.
- Predictive AI algorithms analyse customer data to forecast trends and optimise resource allocation.
- AI-driven identity validation reduces fraud risk.
- Agent Assist Solutions offer real-time insights to agents, enhancing service delivery and efficiency.
- GenAI integration automates post-call activities, allowing agents to focus on high-value tasks.
#4 Augment Existing Systems for Success
Many organisations face challenges in fully modernising legacy systems and reducing reliance on multiple tech providers.
CX transformation while managing multiple disparate systems will require a platform that integrates desired capabilities for holistic CX and EX experiences.
A unified platform streamlines application management, ensuring cohesion, unified KPIs, enhanced security, simplified maintenance, and single sign-on for agents. This approach offers consistent experiences across channels and early issue detection, eliminating the need to navigate multiple applications or projects.
Capabilities that a platform should have:
- Programmable APIs to deliver messages across preferred social and messaging channels.
- Modernisation of outdated IVRs with self-service automation.
- Transformation of static mobile apps into engaging experience tools.
- Fraud prevention across channels through immediate phone number verification APIs.

#5 Focus on Proactive CX
In the new CX economy, organisations must meet customers on their terms, proactively engaging them before they initiate interactions. This requires a re-evaluation of all aspects of CX delivery.
- Redefine the Contact Centre. Transforming it into an “Intelligent” Data Hub providing unified and connected experiences; leveraging intelligent APIs to proactively manage customer interactions seamlessly across journeys.
- Reimagine the Agent’s Role. Empowering agents to be AI-powered brand ambassadors, with access to prior and real-time interactions, instant decision-making abilities, and data-led knowledge bases.
- Redesign the Channel and Brand Experience. Ensuring consistent omnichannel experiences through unified and coherent data; using programmable APIs to personalise conversations and discern customer preferences for real-time or asynchronous messaging; integrating innovative technologies like video to enrich the channel experience.

In 2024, business and technology leaders will leverage the opportunity presented by the attention being received by Generative AI engines to test and integrate AI comprehensively across the business. Many organisations will prioritise the alignment of their initial Generative AI initiatives with broader AI strategies, establishing distinct short-term and long-term goals for their AI investments.
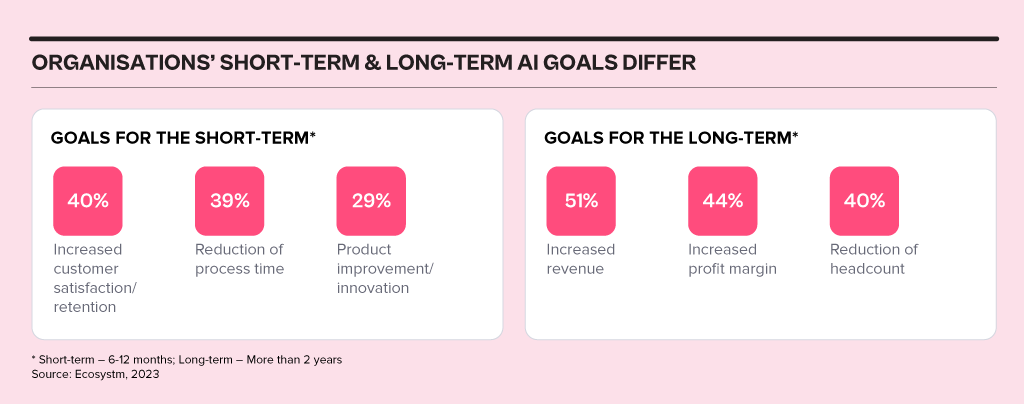
AI adoption will influence business processes, technology skills, and, in turn, reshape the product/service offerings of AI providers.
Ecosystm analysts Achim Granzen, Peter Carr, Richard Wilkins, Tim Sheedy, and Ullrich Loeffler present the top 5 AI trends in 2024.
Click here to download ‘Ecosystm Predicts: Top 5 AI Trends in 2024.
#1 By the End of 2024, Gen AI Will Become a ‘Hygiene Factor’ for Tech Providers
AI has widely been commended as the ‘game changer’ that will create and extend the divide between adopters and laggards and be the deciding factor for success and failure.
Cutting through the hype, strategic adoption of AI is still at a nascent stage and 2024 will be another year where companies identify use cases, experiment with POCs, and commit renewed efforts to get their data assets in order.
The biggest impact of AI will be derived from integrated AI capability in standard packaged software and products – and this will include Generative AI. We will see a plethora of product releases that seamlessly weave Generative AI into everyday tools generating new value through increased efficiency and user-friendliness.
Technology will be the first industry where AI becomes the deciding factor between success and failure; tech providers will be forced to deliver on their AI promises or be left behind.

#2 Gen AI Will Disrupt the Role of IT Architects
Traditionally, IT has relied on three-tier architectures for applications, that faced limitations in scalability and real-time responsiveness. The emergence of microservices, containerisation, and serverless computing has paved the way for event-driven designs, a paradigm shift that decouples components and use events like user actions or data updates as triggers for actions across distributed services. This approach enhances agility, scalability, and flexibility in the system.
The shift towards event-driven designs and advanced architectural patterns presents a compelling challenge for IT Architects, as traditionally their role revolved around designing, planning and overseeing complex systems.
Generative AI is progressively demonstrating capabilities in architectural design through pattern recognition, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making.
With the adoption of Generative AI, the role of an IT Architect will change into a symbiotic relationship where human expertise collaborates with AI insights.

#3 Gen AI Adoption Will be Confined to Specific Use Cases
A little over a year ago, a new era in AI began with the initial release of OpenAI’s ChatGPT. Since then, many organisations have launched Generative AI pilots.
In its second-year enterprises will start adoption – but in strictly defined and limited use cases. Examples such as Microsoft Copilot demonstrate an early adopter route. While productivity increases for individuals can be significant, its enterprise impact is unclear (at this time).
But there are impactful use cases in enterprise knowledge and document management. Organisations across industries have decades (or even a century) of information, including digitised documents and staff expertise. That treasure trove of information can be made accessible through cognitive search and semantic answering, driven by Generative AI.
Generative AI will provide organisations with a way to access, distill, and create value out of that data – a task that may well be impossible to achieve in any other way.

#4 Gen AI Will Get Press Inches; ‘Traditional’ AI Will Do the Hard Work
While the use cases for Generative AI will continue to expand, the deployment models and architectures for enterprise Generative AI do not add up – yet.
Running Generative AI in organisations’ data centres is costly and using public models for all but the most obvious use cases is too risky. Most organisations opt for a “small target” strategy, implementing Generative AI in isolated use cases within specific processes, teams, or functions. Justifying investment in hardware, software, and services for an internal AI platform is challenging when the payback for each AI initiative is not substantial.
“Traditional AI/ML” will remain the workhorse, with a significant rise in use cases and deployments. Organisations are used to investing for AI by individual use cases. Managing process change and training is also more straightforward with traditional AI, as the changes are implemented in a system or platform, eliminating the need to retrain multiple knowledge workers.

#5 AI Will Pioneer a 21st Century BPM Renaissance
As we near the 25-year milestone of the 21st century, it becomes clear that many businesses are still operating with 20th-century practices and philosophies.
AI, however, represents more than a technological breakthrough; it offers a new perspective on how businesses operate and is akin to a modern interpretation of Business Process Management (BPM). This development carries substantial consequences for digital transformation strategies. To fully exploit the potential of AI, organisations need to commit to an extensive and ongoing process spanning the collection, organisation, and expansion of data, to integrating these insights at an application and workflow level.
The role of AI will transcend technological innovation, becoming a driving force for substantial business transformation. Sectors that specialise in workflow, data management, and organisational transformation are poised to see the most growth in 2024 because of this shift.


Earlier in the year, Microsoft unveiled its vision for Copilot, a digital companion that aims to provide a unified user experience across Bing, Edge, Microsoft 365, and Windows. This vision includes a consistent user experience. The rollout began with Windows in September and expanded to Microsoft 365 Copilot for enterprise customers this month.
Many organisations across Asia Pacific will soon face the question on whether to invest in Microsoft 365 Copilot – despite its current limitations in supporting all regional languages. Copilot is currently supported in English (US, GB, AU, CA, IN), Japanese, and Chinese Simplified. Microsoft plans to support more languages such as Arabic, Chinese Traditional, Korean and Thai over the first half of 2024. There are still several languages used across Asia Pacific that will not be supported until at least the second half of 2024 or later.
Access to Microsoft 365 Copilot comes with certain prerequisites. Organisations need to have either a Microsoft 365 E3 or E5 license and an Azure Active Directory account. F3 licenses do not currently have access to 365 Copilot. For E3 license holders the cost per user for adding Copilot would nearly double – so it is a significant extra spend and will need to deliver measurable and tangible benefits and a strong business case. It is doubtful whether most organisations will be able to justify this extra spend.
However, Copilot has the potential to significantly enhance the productivity of knowledge workers, saving them many hours each week, with hundreds of use cases already emerging for different industries and user profiles. Microsoft is offering a plethora of information on how to best adopt, deploy, and use Copilot. The key focus when building a business case should revolve around how knowledge workers will use this extra time.
Maximising Copilot Integration: Steps to Drive Adoption and Enhance Productivity
Identifying use cases, building the business proposal, and securing funding for Copilot is only half the battle. Driving the change and ensuring all relevant employees use the new processes will be significantly harder. Consider how employees currently use their productivity tools compared to 15 years ago, with many still relying on the same features and capabilities in their Office suites as they did in earlier versions. In cases where new features were embraced, it typically occurred because knowledge workers didn’t have to make any additional efforts to incorporate them, such as the auto-type ahead functions in email or the seamless integration of Teams calls.
The ability of your organisation to seamlessly integrate Copilot into daily workflows, optimising productivity and efficiency while harnessing AI-generated data and insights for decision-making will be of paramount importance. It will be equally important to be watchful to mitigate potential risks associated with an over-reliance on AI without sufficient oversight.
Implementing Copilot will require some essential steps:
- Training and onboarding. Provide comprehensive training to employees on how to use Copilot’s features within Microsoft 365 applications.
- Integration into daily tasks. Encourage employees to use Copilot for drafting emails, documents, and generating meeting notes to familiarise them with its capabilities.
- Customisation. Tailor Copilot’s settings and suggestions to align with company-specific needs and workflows.
- Automation. Create bots, templates, integrations, and other automation functions for multiple use cases. For example, when users first log onto their PC, they could get a summary of missed emails, chats – without the need to request it.
- Feedback loop. Implement a feedback mechanism to monitor how Copilot is used and to make adjustments based on user experiences.
- Evaluating effectiveness. Gauge how Copilot’s features are enhancing productivity regularly and adjust usage strategies accordingly. Focus on the increased productivity – what knowledge workers now achieve with the time made available by Copilot.
Changing the behaviours of knowledge workers can be challenging – particularly for basic processes that they have been using for years or even decades. Knowledge of use cases and opportunities for Copilot will not just filter across the organisation. Implementing formal training and educational programs and backing them up with refresher courses is important to ensure compliance and productivity gains.

Ecosystm research reveals a stark reality: 75% of technology leaders in Financial Services anticipate data breaches.
Given the sector’s regulatory environment, data breaches carry substantial financial implications, emphasising the critical importance of giving precedence to cybersecurity. This is compelling a fresh cyber strategy focused on early threat detection and reduction of attack impact.
Read on to find out how tech leaders are building a culture of cyber-resilience, re-evaluating their cyber policies, and adopting technologies that keep them one step ahead of their adversaries.
Download ‘Cyber-Resilience in Finance: People, Policy & Technology’ as a PDF

The Manufacturing industry is at crossroads today. It faces challenges such as geopolitical risks, supply chain disruptions, changing regulatory environments, workforce shortages, and changing consumer demands. Overcoming these requires innovation, collaboration, and proactive adaptation.
Fortunately, many of these challenges can be mitigated by technology. The future of Manufacturing will be shaped by advanced technology, automation, and AI. We are seeing early evidence of how smart factories, robotics, and 3D printing are transforming production processes for increased efficiency and customisation.
Manufacturing is all set to become more agile, efficient, and sustainable.
Read on to find out the changing priorities and key trends in Manufacturing; about the World Economic Forum’s Global Lighthouse Network initiative; and where Ecosystm advisor Kaushik Ghatak sees as the Future of Manufacturing.
Click here to download ‘The Future of Manufacturing’ as a PDF

Organisations are uncertain about how 2023 will shape up for them, amidst concerns about recessions, supply chain uncertainties, continued geopolitical volatility, energy crisis, and labour disruptions. At the same time, they have to continue to evolve their products and services, the customer experiences they deliver, and overall brand image.
If you are a tech leader, your first instinct would be to cut down on technology spend to align with your organisation’s cost optimisation strategy. And that is where you would make the first mistake – this is the time to invest in the right technologies to help your organisation face the uncertainties with agility.
Here are 5 things that you should keep in mind when shaping your organisation’s tech landscape in 2023.
- Focus on the shortest time to value. Choose a few smart digital improvements that are aligned with the strategic goals of the business and deliver value quickly.
- Drive better corporate outcomes through Sustainability programs. The transition to smart and sustainable digital assets and infrastructure should be a top priority for today’s technology leaders.
- Build resilience by improving value chain visibility. Digital technologies will continue to play an important role in providing visibility and insights across the value chains for risk management and resilience.
- Treat location data as a feedstock for AI & Automation. With the increasing importance of automation, especially to contemporary service models like digital twins and metaverse, incorporating spatial and location data into your strategy is essential for staying ahead of the competition and driving meaningful business outcomes.
- Find allies against cyber adversaries. Join the cybersecurity communities that exist in your geography and industry. Participate openly as possible so that lessons are shared quickly and widely. Don’t try to defeat the flood on your own.
Read on to find more.
Download Making the Right Tech Decisions for Better Value as a PDF

Customer experience (CX) is an integral part of a brand today – and excellence in CX is a moving target (think how tools such as ChatGPT can revolutionise communications and CX). Organisations will find themselves aiming for personalised CX across channels of preference, with convenience, empathy, and speed at the core.
Here are the top 5 trends for the Experience Economy for 2023 according to Ecosystm analysts Audrey William, Melanie Disse, and Tim Sheedy.
- Organisations Will Focus on Building a “One CX Workforce”
- AI Will Lead Voice of Customer Programs
- Metadata Will Become Important
- The Conversational AI Market Will Mature
- Organisations Will Go Back to Focusing on Web Experience
Read on for more details.
Download Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Trends for the Experience Economy in 2023 as a PDF

Organisations will continue their quest to become digital and data-first in 2023. Business process automation will be a priority for the majority; but many will look at their data strategically to derive better business value.
As per Ecosystm’s Digital Digital Enterprise Study 2022, organisations will focus equally on Automation and Strategic AI in 2023.
Here are the top 5 trends for the Intelligent Enterprise in 2023 according to Ecosystm analysts, Alan Hesketh, Peter Carr, Sash Mukherjee and Tim Sheedy.
- Cloud Will Be Replaced by AI as the Right Transformation Goal
- Adoption of Data Platform Architecture Will See an Uptick
- Tech Teams Will Finally Focus on Internal Efficiency
- Data Retention/Deletion and Records Management Will Be Top Priority
- AI Will Replace Entire Human Jobs
Read on for more details.
Download Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Trends for the Intelligent Enterprise in 2023 as a PDF

In the rush towards digital transformation, individual lines of business in organisations, have built up collections of unconnected systems, each generating a diversity of data. While these systems are suitable for rapidly launching services and are aimed at solving individual challenges, digital enterprises will need to take a platform approach to unlock the full value of the data they generate.
Data-driven enterprises can increase revenue and shift to higher margin offerings through personalisation tools, such as recommendation engines and dynamic pricing. Cost cutting can be achieved with predictive maintenance that relies on streaming sensor data integrated with external data sources. Increasingly, advanced organisations will monetise their integrated data by providing insights as a service.
Digital enterprises face new challenges – growing complexity, data explosion, and skills gap.
Here are 5 ways in which IT teams can mitigate these challenges.
- Data & AI projects must focus on data access. When the organisation can unify data and transmit it securely wherever it needs to, it will be ready to begin developing applications that utilise machine learning, deep learning, and AI.
- Transformation requires a hybrid cloud platform. Hybrid cloud provides the ability to place each workload in an environment that makes the most sense for the business, while still reaping the benefits of a unified platform.
- Application modernisation unlocks future value. The importance of delivering better experiences to internal and external stakeholders has not gone down; new experiences need modern applications.
- Data management needs to be unified and automated. Digital transformation initiatives result in ever-expanding technology estates and growing volumes of data that cannot be managed with manual processes.
- Cyber strategy should be Zero Trust – backed by the right technologies. Organisations have to build Digital Trust with privacy, protection, and compliance at the core. The Zero Trust strategy should be backed by automated identity governance, robust access and management policies, and least privilege.
Read below to find out more.
Download The Future of Business: 5 Ways IT Teams Can Help Unlock the Value of Data as a PDF