In my previous insights, I explained why organisations need to rethink their End-User Computing (EUC) strategies and shared a simple checklist to help them build smarter, more responsible plans tailored to their goals, users, and regions.
As that foundation is laid, it’s critical to put sustainability at the core. From laptops and desktops to peripherals and accessories, the choices made around devices impact not only IT budgets and user productivity but also environmental footprints and regulatory compliance.
Sustainable EUC means selecting devices that align with your company’s climate goals, regulatory mandates, and ethical commitments, while delivering reliability and performance in diverse working environments.
This guide offers a comprehensive sustainability checklist to help IT leaders embed responsible sourcing and lifecycle management into their EUC strategy.
What to Demand from Vendors & Devices
- Specify recognised eco-label tiers (e.g., TCO Gen 9, EPEAT Climate+). Ensures devices meet verified environmental and social standards, reducing overall carbon footprint.
- Request embodied-carbon disclosures (ISO 14067, PAS 2050). To understand full lifecycle emissions to inform refresh cycle decisions.
- Insist on vendor-funded take-back in all deployment regions. Supports responsible recycling and circular economy for end-user devices.
- Audit supply-chain ethics (latest RBA VAP score, Modern Slavery compliance). Certifies devices against verified environmental and social standards, cutting their overall carbon footprint.
- Set minimum firmware support periods and repairability targets. Extends usable device lifespan, lowering total cost of ownership and e-waste.
- Test devices for local climate conditions (humidity, altitude). Guarantees device reliability and energy efficiency in diverse workplaces.
Key Eco-Labels & Certifications for EUC Devices
Not all certifications are created equal. Here are the most relevant for end-user devices, what they mean, and recent updates to watch:

Regional Regulations & Compliance for EUC
EUC devices often span multiple jurisdictions; understanding regional regulations helps avoid compliance risks and future-proofs procurement:
Australia & New Zealand. Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) for monitors and power supplies; NTCRS take-back requirements; Modern Slavery Act disclosures
Singapore. Resource Sustainability Act (EPR for IT equipment) since 2021; green procurement guidelines for public sector
Japan. Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) for monitors and power supplies; NTCRS take-back requirements; Modern Slavery Act disclosures
China. China RoHS 2 with new 2024 testing standards for restricted substances
India. E-Waste (Management) Rules 2022 requiring OEMs/importers to collect 80% of products sold; ongoing amendments under legal review
South Korea. Eco-Label expansion to tablets and mini-PCs; EPR scheme in public tenders
Embedding Ethical Sourcing in Your EUC Strategy
Ethics matter beyond environmental impact; responsible sourcing reduces risk and protects brand reputation:
Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) Code of Conduct v8.0. Check for vendor audit results to ensure compliance.
Conflict Minerals / Responsible Minerals Initiative. Especially relevant for supply chains feeding US/EU markets.
Modern Slavery Legislation. Mandate supplier disclosures and risk assessments, especially in Australia and New Zealand.
Public Sector Procurement & EUC Sustainability
Many government buyers set strong sustainability expectations, which can serve as best-practice benchmarks:
Australia (Commonwealth & States). Preference for EPEAT Silver+, NTCRS take-back, and Modern Slavery compliance statements
Singapore GovTech. ENERGY STAR compliance, Resource Sustainability Act adherence, and use of low-halogen plastics
Japan National Procurement. Top Runner energy efficiency, Eco-Mark or equivalent certification
Why Sustainability Matters for End-User Computing
Sustainability in your EUC strategy drives more than just environmental benefits. It:
- Reduces Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) by extending device lifecycles and lowering energy consumption
- Mitigates Supply Chain Risks by ensuring ethical sourcing and regulatory compliance
- Supports Corporate Climate Commitments with transparent carbon accounting and circular economy practices
- Enhances User Satisfaction and Reliability by testing devices for local conditions and durability
By integrating these sustainability criteria into procurement, IT leaders can transform their EUC strategy into a powerful enabler of business value and responsible growth.

Typically, business leaders rely on forecasts to secure budgets for achieving their goals and objectives. Forecasts take historical trends and project them forward, with added assumptions about what may or may not change in the market or operating environment.
But in today’s volatile economic and political climate, traditional forecasting is increasingly unreliable.
The threat of tariffs, actual tariffs, ongoing and emerging conflicts, political transitions and rising authoritarianism, along with the uncertain impact of AI on employment and productivity, are all undermining not just business and consumer confidence, but also supply chains and manufacturing capacity.
Look at the PC market in Asia Pacific. Shipments have traditionally been relatively straightforward to forecast; but in 2025, projections have swung from a 10% decline to 12% growth, and everything in between! These forecasts continue to shift month by month as market conditions evolve. The same applies to tech and non-tech products and services across many industries. Forecasts are no longer reliable or trustworthy.
So, if we cannot trust forecasts, what can we do to secure budget for our short-, medium- and longer-term initiatives? For many leaders, the answer is “Backcasting”.
When Forecasts Break Down, Backcasting Steps Up
Put simply, backcasting is creating a future vision, and building a plan to make that vision a reality.
For example, imagine you are the Asia Pacific Managing Director of a US-based software company aiming to move from the fifth to the second-largest provider in the region by 2030. To reach this goal, you’ll need to build specific capabilities such as adding distributors; expanding implementation and systems integration partners across ASEAN and India (which means strengthening your partner management team); increasing sales and account managers in tier 2 cities; and developing localised product versions and language support. You might also need to choose a different cloud provider to access certain markets like China and adapt your software to meet local regulations.
Backcasting helps you plan all these steps by starting with your 2030 goal and working backwards to create a clear roadmap to get there.
The benefit of backcasting over forecasting is that it gives your organisation defendable goals, targets and initiatives. It moves the thinking beyond the traditional quarterly targets to a longer-term vision. When global leaders ask you to cut budgets, it provides them with clear insight into how those cuts will affect the organisation’s success in Asia Pacific over the medium to long term. It also helps to understand which resources will help you achieve the longer-term goals and which will not.
Ultimately, backcasting is a better way of helping you defend your budgets from the tactical cuts and short-sighted strategies and sharpens your capability to deliver results in the longer term.
Want to Know More?
You can access a detailed report on backcasting: what it is, how it differs from traditional forecasting, and how it can be applied within your organisation. The report includes examples of companies using backcasting to shape strategic initiatives and support innovation, as well as a scenario outlining how an Asia Pacific tech vendor might use the approach to meet growing regional demands.
We have also helped clients start their backcasting journeys through targeted workshops, internal presentations, training programs and helping them set the backcasting strategy and processes in place. These services can support organisations at a strategic level, by aligning long-term plans with overarching goals; or at a team level, by helping functions like sales and marketing meet specific performance expectations.
We welcome your feedback – feel free to contact me or Alea Fairchild. If backcasting could support your organisation’s growth or budget planning, we’d be happy to connect via call or in person to discuss specific needs.
Here’s how we can help:
- Workshops. In-person or virtual workshops designed to build backcasting capabilities, such as setting long-term goals, creating roadmaps, and shifting focus from short-term tactics to strategic outcomes.
- Training (Internal Presentations & Webinars). Sessions to introduce teams to backcasting, explaining what it is, how it can be used, and why it supports more effective mid- to long-term planning.
- Client-Facing Presentations. Presentations tailored for clients and customers to show how backcasting can support their planning and investment decisions, potentially strengthening alignment with available solutions.
- Podcasts & Videos. Co-created audio or video content with leadership to explore how backcasting fits into current workflows, where the value lies, and how teams can tailor their efforts to organisational priorities.

In a previous blog, I explored why organisations need to rethink their end-user computing strategies in light of shifting business demands, evolving user expectations, and operational challenges.
Building on that, this post offers a strategy template: a living framework to guide sustainable, responsible tech procurement. Use it to define clear requirements that reflect your business goals, regional context, and workforce needs. Then tailor it further to suit your industry standards and organisational realities, revisiting it regularly as your environment evolves.
Click here to download “End-User Computing Strategy Checklist” as a PDF.
1. Business Alignment and Objectives
- Primary business goals such as productivity, collaboration, security, and innovation.
- Strategic initiatives, including digital transformation, hybrid working, and compliance.
- Alignment between EUC objectives, overall business strategy, and industry-specific drivers.
2. Industry-Specific Considerations
- Regulatory requirements (Data privacy, compliance frameworks, cybersecurity).
- Industry-specific applications (e.g., finance platforms, healthcare EMR, retail POS).
- Business-critical workflows and processes supported by EUC.
3. Geographic & Regional Factors
- Infrastructure considerations (network availability, connectivity quality, 4G/5G, Wi-Fi).
- Regional compliance (local privacy laws, cybersecurity regulations, data residency requirements).
- Support and logistics (local vendor availability, language support, supply chain).
4. Persona-Based Device Strategy
- Employee personas including:
- Frontline/Mobile workers
- Knowledge workers
- Power users/Technical teams
- Executives
- Hybrid/Remote workers
- Device types, operating systems, and form factors suited to each persona.
5. Technology and Platform Choices
- Operating system selection (Windows, macOS, Chrome OS, Android, iOS).
- VDI/DaaS selection (Citrix, VMware Horizon, AWS WorkSpaces, Azure Virtual Desktop).
- Cloud-based productivity suite selection (Microsoft 365, Google Workspace).
- Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) platform selection.
6. Security and Compliance Strategy
- Endpoint security model (Zero Trust, EDR, MFA, biometrics).
- Data encryption and privacy management strategy.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies.
- Incident response and threat detection framework.
7. User Experience and Employee Engagement
- Employee experience objectives (ease-of-use, personalisation, productivity).
- Self-service portals and automation for IT support.
- End-user training, change management, and continuous feedback loops.
- Plans for local AI capabilities – Agents, Information and data management, etc.
8. Operational Excellence and Lifecycle Management
- Device procurement, deployment, and lifecycle policies.
- Automation and AI-driven analytics for device management.
- Sustainability and environmental impact (device recycling, energy efficiency).
- Other GRC requirements (anti-slavery etc).
9. Cost Optimisation and Budgeting
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) calculation framework.
- CAPEX vs OPEX considerations (purchase, lease, consumption-based).
- Vendor financing and budgeting strategies.
10. Vendor and Partner Management
- Vendor evaluation criteria (support, innovation, geographic coverage, pricing).
- Partnership strategy (managed services, system integrators, technology alliances).
- Vendor risk management and vendor performance monitoring framework.
11. Metrics and Measurement
- Outcome-focused success metrics (e.g., productivity, satisfaction, security).
- Monitoring and reporting structure.
- Continuous improvement plan based on metric analysis.
12. ESG
- Eco-labels, ISO 14067 or PAS 2050 carbon disclosures, and climate-condition testing to avoid energy waste.
- Vendor take-back in all regions, minimums for firmware support and repairability to slow refresh cycles.
- Supply-chain ethics evidence, including up-to-date RBA VAP scores or modern slavery reports.
- Tracking of tightening regulations to stay ahead of compliance risks.

We’re entering a new cycle of PC device growth, driven by the end-of-life of Windows 10 and natural enterprise upgrade cycles, brought into alignment by the COVID-era device boom. In Asia Pacific, PC shipments are expected to grow by 4-8% in 2025. The wide range reflects uncertainty linked to the US tariff regime, which could impact device pricing and availability in the region as manufacturers adjust to shifting demand globally.
To AI or Not to AI?
“AI PCs” (or Copilot PCs) are set to become a growing segment, but real AI benefits from these devices are still some way off. Microsoft’s announcement to embed Agentic AI capabilities into the OS marks the first step toward moving AI processing from the cloud to the desktop. However, for most organisations, these capabilities remain 12-24 months away.
This creates a strategic question: should organisations invest now in NPU-enabled devices that may not deliver immediate returns? Given typical refresh cycles of 3-5 years, it’s worth considering whether local AI processing could become relevant during that time. The safer bet is to invest in Copilot or AI PCs now, as the AI market is evolving rapidly; and the chances of NPUs becoming useful sooner rather than later are high.
Is the Desktop Being Left Behind?
PC market growth is concentrated in the laptop segment, drawing most manufacturers and chip providers to focus their innovation there. AI and Copilot PCs have yet to meaningfully enter the desktop space, where manufacturers remain largely focused on gaming.
This creates a gap for enterprises and SMEs. AI capabilities available on laptops may not be mirrored on desktops. Recent conversations with infrastructure and End-User Computing (EUC) managers suggest a shift in Asia Pacific toward laptops or cloud/ virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) devices, including thin clients and desktops. If this trend continues, organisations will need to re-evaluate employee experience and ensure applications are designed to match the capabilities of each device type and user persona.
Fundamental EUC Drivers are Changing
As EUC and infrastructure teams revisit their strategies, several foundational drivers are undergoing significant change:
- Remote work is no longer a default. Once considered the norm for information workers, remote work is now being reconsidered. With some organisations mandating full-time office returns, device strategies must adapt to a more hybrid and unpredictable working model.
- Employee Experience is losing budget priority. During the pandemic, keeping employees productive and engaged was critical. But with rising cost pressures, growing automation through GenAI and Agentic AI, and changing labour dynamics, EX is no longer a top enterprise priority and budgets reflect that shift.
- Cloud-based EUC solutions are now enterprise-ready. Since 2022, cloud adoption in EUC has accelerated. Solutions like Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, AWS WorkSpaces, and VMware Horizon Cloud now offer mature capabilities. Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) is increasingly cloud-managed, enabling more scalable and agile IT operations.
- Zero-trust is moving security closer to the user. EUC security is evolving from perimeter-based models to identity-centric, continuous verification approaches. Investments in EDR, AI-driven threat analytics, MFA, biometric authentication, and proactive threat hunting are now standard, driven by the shift to zero trust.
- Device diversity is increasing. Standardised device fleets are giving way to more diverse options – touchscreen laptops, foldables, and a broader mix of PC brands. Enterprise offerings are expanding beyond traditional tiers to meet varied needs across user personas.
- Metrics are shifting from technical to outcome-based. Traditional KPIs like uptime and cost are giving way to metrics tied to business value – employee productivity, experience, collaboration, cyber resilience, and adaptability. EUC success is now measured in terms of outcomes, not just infrastructure performance.
Build a Modern and Future-Ready EUC Strategy
Organisations must reassess their plans to align with changing business needs, user expectations, and operational realities. Modern EUC strategies must account for a broad set of considerations.
Key factors to consider:
Strategic Business Alignment
- Business Outcomes. EUC strategies must align with core business goals such as boosting productivity, enhancing employee experience, improving customer outcomes, and driving competitive advantage. Consider how device choices enable new work models, such as remote/hybrid setups, gig workforce enablement, and cross-border collaboration.
- Digital Transformation Fit. Ensure EUC refresh cycles are integrated with broader digital transformation efforts – cloud migration, AI adoption, automation, and innovation. Devices should be future-ready, capable of supporting the AI and automation needs of 2026 and beyond. While some workloads may shift to the cloud, others like GenAI-powered video and image creation, may demand stronger local processing across the broader workforce, not just specialist teams.
Technology Considerations
- Device Selection. Move beyond the old “one device per persona” approach. Build a flexible device ecosystem that supports a range of employee types, from frontline workers to power users, while allowing for broader device choices based on real usage patterns. Evaluate form factors like desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, and thin/zero clients. With the rise of Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS), thin clients are becoming more viable, offering cost savings and better security without compromising user experience.
- Flexibility of Choice. High-end features – lightweight design, long battery life, sleek aesthetics – are no longer limited to exec devices. I am currently writing this on a loan device – a Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 13 Aura Edition – a freakishly light, powerful and slim device with LONG battery life – a device typically targeted towards the top tier of business leaders. But today, many of the features of this device run through the entire Lenovo laptop ecosystem – the “Aura” tag appears in many of the device SKUs and ranges. Hopefully the days of senior management getting the great looking devices and everyone else getting ugly bricks are behind us!
- Operating Systems and Compatibility. Ensure compatibility with current and planned business applications, cloud services, and collaboration tools. Consider ease of management and integration into existing IT ecosystems (such as Windows, macOS, Android, Chrome OS, Linux environments).
- Cloud Integration. Evaluate cloud-readiness and seamless integration capabilities with popular productivity suites (Microsoft 365, Google Workspace), hybrid cloud, and SaaS applications. Leverage VDI, DaaS or application virtualisation solutions to reduce hardware dependency and streamline maintenance.
User Experience
- Employee Productivity and Engagement. Even as EX slips down the priority list – and the budget – EUC leaders must still champion intuitive, user-friendly devices to boost productivity and reduce training and support demands. Seamless collaboration is critical across physical, remote, and hybrid teams. In-office collaboration is back in focus, but its value depends on digitising outcomes: laptops, smartphones, and tablets must enable AI-driven transcription, task assignment, and follow-up tracking from physical or hybrid meetings.
- Personalisation and Mobility. Where practical, offer device personalisation through flexible BYOD or CYOD models. Even in industries or geographies where this isn’t feasible, small touches like device colour or accessories, can improve engagement. UEM tools are essential to enforce security while enabling flexibility.
- Performance and Reliability. Choose devices that deliver the right performance for the task, especially for users handling video, design, or AI workloads. Prioritise long battery life and reliable connectivity, including Wi-Fi 6/7 and 5G where available. While 5G laptops are still rare across many Asia Pacific markets, that’s likely to change as networks expand and manufacturers respond to demand.
- Localised Strategy. Given the distributed nature of many organisations in the region, support and warranty strategies should reflect local realities. Tiered service agreements may provide better value than one-size-fits-all premium coverage that’s difficult to deliver consistently.
Security and Compliance
- Cybersecurity Posture. EUC teams typically work hand-in-hand with their cyber teams in the development of a secure EUC strategy and the deployment of the preferred devices. Cybersecurity teams will likely provide specific guidance and require compliance with local and regional regulations and laws. They will likely require that EUC teams prioritise integrated security capabilities (such as zero-trust architectures, endpoint detection and response – EDR solutions, biometrics, hardware-based security features like TPM). Consider deploying AI-driven endpoint threat detection and response tools for proactive threat mitigation.
- Data Privacy and Regulatory Compliance. Assess devices and management systems to ensure adherence to local regulatory frameworks (such as Australia’s Privacy Act, Singapore’s PDPA, or the Philippines’ Data Privacy Act). Deploy robust policies and platforms for data encryption, remote wiping, and identity and access management (IAM).
Management, Sustainability and Operational Efficiency
- Unified Endpoint Management (UEM). Centralise device management through UEM platforms to streamline provisioning, policy enforcement, patching, updates, and troubleshooting. Boost efficiency further with automation and self-service tools to lower IT overhead and support costs.
- Asset Lifecycle Management (ALM). While many organisations have made progress in optimising ALM – from procurement to retirement – gaps remain, especially in geographies outside core operations. Use device analytics to monitor health, utilisation, and performance, enabling smarter refresh cycles and reduced downtime.
- Sustainable IT and CSR Alignment. Choose vendors with strong sustainability credentials such as energy-efficient devices, ethical manufacturing, and robust recycling programs. Apply circular economy principles to extend device lifespan, reduce e-waste, and lower your carbon footprint. Align EUC strategies with broader CSR and ESG goals, using device refresh cycles as opportunities to advance sustainability targets and reinforce your organisation’s values.
Cost and Investment Planning
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). Evaluate TCO holistically, factoring in purchase price, operations, software licensing, security, support, warranties, and end-of-life costs. TCO frameworks are widely available, but if you need help tailoring one to your business, feel free to reach out. Balance CapEx and OpEx across different deployment models – owned vs leased, cloud-managed vs on-premises.
- Budgeting & Financial Modelling. Clearly define ROI and benefit realisation timelines to support internal approvals. Explore vendor financing or consumption-based models to enhance flexibility. These often align with sustainability goals, with many vendors offering equipment recycling and resale programs that reduce overall costs and support circular IT practices.
Vendor and Partner Selection
- Vendor Support & Regional Coverage. Select vendors with strong regional support across Asia Pacific to ensure consistent service delivery across diverse markets. Many organisations rely on distributors and resellers for their extended reach into remote geographies. Others prefer working directly with manufacturers. While this can reduce procurement costs, it may increase servicing complexity and response times. Assess vendors not just on cost, but on local presence, partner network strength, and critically, their supply chain resilience.
- Innovation & Ecosystem Alignment. Partner with vendors whose roadmaps align with future technology priorities – AI, IoT, edge computing – and who continue to invest in advancing EUC capabilities. Long-term innovation alignment is just as important as short-term performance.
Building a modern, future-ready EUC strategy isn’t just about devices – it’s about aligning people, technology, security, sustainability, and business outcomes in a way that’s cost-effective and forward-looking. But we know investment planning can be tricky. At Ecosystm, we’ve helped organisations build ROI models that make a strong case for EUC investments. If you’d like guidance, feel free to reach out – we’re here to help you get it right.

GenAI AI has truly transformed content creation by automating text, image, and video generation from simple prompts, slashing the time and skills once needed. Canva leads this shift, blending an intuitive interface with expansive templates and cutting-edge AI tools. This empowers anyone – individuals or businesses – to produce professional-quality visuals with ease, breaking down barriers and making design truly accessible.
Canva’s “Create 2025” event in Los Angeles showcased its evolution from a simple design tool into a full enterprise platform for productivity, content creation, collaboration, and brand management – embedding visual communication across the modern workplace. For tech teams, marketers, and leaders, this shift brings opportunity but also demands careful strategy, integration, and governance to unlock Canva’s full potential in enterprise settings.
Canva Create 2025: Key Announcements
Visual Suite 2.0: A Unified Workspace & Single Design Canvas. Canva unveiled Visual Suite 2.0, a seamless platform combining presentations, documents, whiteboards, spreadsheets, and video editing into one design canvas. This unified workspace helps organisations streamline workflows, eliminate tool fragmentation, and ensure consistent visual communication across teams.
Canva Sheets: Where Data Meets Design. Canva Sheets reimagines the spreadsheet by focusing on visualising data with rich charts, colour-coded cells, smart templates, automation, and AI-powered insights. Designed for teams that share data rather than just analyse it, Sheets empowers every user – including the “data shy” – to become a confident data analyst.
Canva AI: GenAI for the Creative Enterprise. The enhanced Magic Studio integrates AI-driven writing, image editing, template creation, and video animation into one toolset. Features like Magic Write, Magic Design, and Magic Animate enable teams to create branded, engaging content at scale – quickly and cost-effectively – across the entire Canva platform.
Canva Code: Low/No-Code Interactive Content. Canva Code enables users to build interactive content such as calculators, quizzes, websites, apps, and chatbots without complex coding. Combining this with Canva’s design and brand management tools lets teams create on-brand digital experiences and publish them to customers in minutes – transforming everyone into a coder and accelerating customer-facing innovation.
Why Enterprises Should Adopt Canva
Canva’s evolution into an enterprise platform offers several key advantages for larger organisations:
- Streamlined Workflows. A unified workspace and single design canvas cuts the need to switch between tools, boosting efficiency and team collaboration.
- Brand Consistency at Scale. Centralised brand controls and template governance ensure all content – from marketing to regional sales – stays on-brand. For example, eXp Realty’s central design team creates assets that agents nationwide confidently use, maintaining brand integrity.
- Scalable Content Creation. GenAI accelerates content creation and localisation, while Canva Sheets lets designers update assets at scale, reducing days of work to a single click.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration. By making design accessible, Canva empowers marketing, operations, sales, and finance teams to collaborate seamlessly on visuals, cutting bottlenecks.
- Lower Barriers to Creativity. With an easy-to-learn platform, more employees can contribute to visual storytelling without needing design expertise.
Beyond Licensing: Strategic Enterprise Adoption
Successful enterprise adoption of tools such as Canva goes beyond licensing – it requires organisational change. Here’s how enterprises can prepare:
1. Integration with the Digital Workplace Ecosystem
Enterprises must integrate new platforms with the broader toolset employees use daily. Without this, they risk becoming just another siloed app, limiting adoption and ROI.
- Enable SSO and identity management (e.g. via Azure AD or Okta).
- Integrate with storage platforms like SharePoint, Google Drive, or Box.
- Connect to collaboration and productivity tools such as Slack, Teams, Trello, and Salesforce.
2. Structured Training and Enablement
Though intuitive, enterprise features require tailored training to boost adoption and build a self-sustaining user community. Customers benefit from dedicated support – including brand kit setup, onboarding, billing, SSO configuration, and company-wide training with a dedicated Customer Success Manager.
- Deliver role-based training for marketers, HR, sales, and support.
- Establish champions in each business unit to drive adoption.
- Provide regular updates and tips as new features launch.
3. Design Governance and Brand Control
Enterprises must address concerns around brand fragmentation. This ensures that the platform acts as brand enabler – not a brand risk.
- Set up Brand Kits to enforce logos, fonts, and colours.
- Use locked templates for consistency while enabling localisation.
- Create layered permission structures to reflect organisational hierarchy.
4. Data Security, Compliance and Governance
As with any enterprise SaaS platform, security and compliance must be foundational and built into the rollout plan from day one.
- Understand data residency and privacy policies.
- Use admin controls, usage analytics, and audit logs to maintain oversight.
- Define clear policies for external sharing and publishing.
5. Defining Success Metrics
Adoption should be measured by capturing metrics that enable IT and marketing leaders to demonstrate value to the C-suite.
- Benchmark operations before and after rollout.
- Track usage, asset creation, and publishing speed.
- Monitor template use versus freeform content to gauge brand adherence.
- Survey users on productivity improvements and satisfaction.
Driving Adoption and Innovation: The Tech Team’s Mandate
For the success of tools such as Canva in enterprise settings, technology teams must move beyond gatekeeping and become proactive enablers of adoption and innovation. This involves integrating them smoothly with identity management, storage, productivity, and collaboration tools to deliver a seamless user experience. At the same time, they must enforce strict security and access controls, manage user provisioning, and monitor usage to ensure compliance and safeguard sensitive data.
But technology’s role doesn’t stop at governance. Teams need to set clear internal service standards, build strong vendor relationships, and drive consistent rollout across the organisation. Crucially, they should partner with business units to co-develop templates, embed these tools into daily workflows, and experiment with new features like AI-powered design, localisation, and self-service content creation.
Ecosystm Opinion
Canva is no longer just a tool for simple social posts or pitch decks; with its latest updates at Create 2025, it has evolved into a core platform for modern, visual-first enterprise communication. To fully realise this potential, organisations must approach Canva like any other critical enterprise platform – implementing the right structure, strategy, security, and support. For companies aiming to empower teams, speed up content creation, and maintain brand consistency at scale, Canva is now poised to take centre stage.

The energy at ServiceNow’s Knowledge25 matched the company’s ambitious direction! ServiceNow is repositioning itself as more than just an IT service platform – aiming to be the orchestration layer for the modern enterprise. Over the past two days, I’ve seen a clear focus on platform extensibility, AI-driven automation, and a push into new functional territories like CRM and ERP.
Here are my key takeaways from Knowledge25.
Click here to download “ServiceNow Knowledge25: Big Moves, Bold Bets, and What’s Next” as a PDF.
AI Everywhere: Agents and Control Towers
ServiceNow goes all in on AI Agents – and makes it easy to adopt.
Like Google, Salesforce, and AWS, ServiceNow is betting big on agents. But with a key advantage: it’s already the enterprise layer where workflows live. Its AI Agents don’t just automate tasks; they amplify what’s already working, layer in intelligence, and collaborate with other agents across systems. ServiceNow becomes the orchestration hub, just as it already is for processes and change.
ServiceNow’s AI Control Tower is a critical accelerator for AI at scale. It enforces policies, ensures compliance with internal and regulatory standards, and provides the guardrails needed to deploy AI responsibly and confidently.
The bigger move? Removing friction. Most employees don’t know what agents can do – so they don’t ask. ServiceNow solves this with hundreds of prebuilt agents across finance, risk, IT, service, CRM, and more. No guesswork. Just plug and go.
Sitting Above Silos: ServiceNow’s Architectural Advantage
ServiceNow is finally highlighting its architectural edge.
It’s one of the few platforms that can sit above all systems of record – pulling in data as needed, delivering workflows to employees and customers, and pushing updates back into core systems. While most Asia Pacific customers use ServiceNow mainly for IT help desk and service requests, its potential extends much further. Virtually anything done in ERP, CRM, SCM, or HRM systems can be delivered through ServiceNow, often with far greater agility. Workflow changes that once took weeks or months can now happen instantly.
ServiceNow is leaning into this capability more forcefully than ever, positioning itself as the platform that can finally keep pace with constant business change.
Stepping into the Ring: ServiceNow’s CRM & ERP Ambitions
ServiceNow is expanding into CRM and ERP workflows – putting itself in competition with some of the industry’s biggest players.
ServiceNow is boldly targeting CRM as a growth area, despite Salesforce’s dominance, by addressing gaps traditional CRMs miss. Customer workflows extend far beyond sales and service, spanning fulfillment, delivery, supply chain, and compliance. A simple quoting process, for instance, often pulls data from multiple systems. ServiceNow covers the full scope, positioning itself as the platform that orchestrates end-to-end customer workflows from a fundamentally different angle.
Its Core Business Suite – an AI-powered solution that transforms core processes like HR, procurement, finance, and legal – also challenges traditional ERP providers, With AI-driven automation for tasks like case management, it simplifies workflows and streamlines operations across departments.
Closing the Skills Gap: ServiceNow University
To support its vision, ServiceNow is investing heavily in education.
The refreshed ServiceNow University aims to certify 3 million professionals by 2030. This is critical to build both demand (business leaders who ask for ServiceNow) and supply (professionals who can implement and extend the platform).
But the skills shortage is a now problem, not a 2030 problem. ServiceNow must go beyond online learning and push harder on in-person classes, tutorials, and train-the-trainer programs across Asia Pacific. Major cloud providers like AWS broke through when large enterprises started training their entire workforces – not just on usage, but on development. ServiceNow needs similar scale and commitment to hit the mainstream.
Asia Pacific: ServiceNow’s Next Growth Frontier
ServiceNow’s potential is massive – and its opportunities even bigger.
In Asia Pacific, many implementations are partner-led, but most partners are currently focused on the platform’s legacy IT capabilities. To unlock growth, ServiceNow needs to empower its partners to engage beyond IT and connect with business leaders.
Despite broader challenges like shrinking tech budgets, fragmented decision-making, and decentralised tech ownership, ServiceNow has a clear path forward. By upskilling partners, simplifying its narrative, and adapting quickly, it’s well-positioned to continue its growth and surpass the hurdles many other software vendors face.

A lot has been written and spoken about DeepSeek since the release of their R1 model in January. Soon after, Alibaba, Mistral AI, and Ai2 released their own updated models, and we have seen Manus AI being touted as the next big thing to follow.
DeepSeek’s lower-cost approach to creating its model – using reinforcement learning, the mixture-of-experts architecture, multi-token prediction, group relative policy optimisation, and other innovations – has driven down the cost of LLM development. These methods are likely to be adopted by other models and are already being used today.
While the cost of AI is a challenge, it’s not the biggest for most organisations. In fact, few GenAI initiatives fail solely due to cost.
The reality is that many hurdles still stand in the way of organisations’ GenAI initiatives, which need to be addressed before even considering the business case – and the cost – of the GenAI model.
Real Barriers to GenAI
• Data. The lifeblood of any AI model is the data it’s fed. Clean, well-managed data yields great results, while dirty, incomplete data leads to poor outcomes. Even with RAG, the quality of input data dictates the quality of results. Many organisations I work with are still discovering what data they have – let alone cleaning and classifying it. Only a handful in Australia can confidently say their data is fully managed, governed, and AI-ready. This doesn’t mean GenAI initiatives must wait for perfect data, but it does explain why Agentic AI is set to boom – focusing on single applications and defined datasets.
• Infrastructure. Not every business can or will move data to the public cloud – many still require on-premises infrastructure optimised for AI. Some companies are building their own environments, but this often adds significant complexity. To address this, system manufacturers are offering easy-to-manage, pre-built private cloud AI solutions that reduce the effort of in-house AI infrastructure development. However, adoption will take time, and some solutions will need to be scaled down in cost and capacity to be viable for smaller enterprises in Asia Pacific.
• Process Change. AI algorithms are designed to improve business outcomes – whether by increasing profitability, reducing customer churn, streamlining processes, cutting costs, or enhancing insights. However, once an algorithm is implemented, changes will be required. These can range from minor contact centre adjustments to major warehouse overhauls. Change is challenging – especially when pre-coded ERP or CRM processes need modification, which can take years. Companies like ServiceNow and SS&C Blue Prism are simplifying AI-driven process changes, but these updates still require documentation and training.
• AI Skills. While IT teams are actively upskilling in data, analytics, development, security, and governance, AI opportunities are often identified by business units outside of IT. Organisations must improve their “AI Quotient” – a core understanding of AI’s benefits, opportunities, and best applications. Broad upskilling across leadership and the wider business will accelerate AI adoption and increase the success rate of AI pilots, ensuring the right people guide investments from the start.
• AI Governance. Trust is the key to long-term AI adoption and success. Being able to use AI to do the “right things” for customers, employees, and the organisation will ultimately drive the success of GenAI initiatives. Many AI pilots fail due to user distrust – whether in the quality of the initial data or in AI-driven outcomes they perceive as unethical for certain stakeholders. For example, an AI model that pushes customers toward higher-priced products or services, regardless of their actual needs, may yield short-term financial gains but will ultimately lose to ethical competitors who prioritise customer trust and satisfaction. Some AI providers, like IBM and Microsoft, are prioritising AI ethics by offering tools and platforms that embed ethical principles into AI operations, ensuring long-term success for customers who adopt responsible AI practices.
GenAI and Agentic AI initiatives are far from becoming standard business practice. Given the current economic and political uncertainty, many organisations will limit unbudgeted spending until markets stabilise. However, technology and business leaders should proactively address the key barriers slowing AI adoption within their organisations. As more AI platforms adopt the innovations that helped DeepSeek reduce model development costs, the economic hurdles to GenAI will become easier to overcome.

The promise of AI agents – intelligent programs or systems that autonomously perform tasks on behalf of people or systems – is enormous. These systems will augment and replace human workers, offering intelligence far beyond the simple RPA (Robotic Process Automation) bots that have become commonplace in recent years.
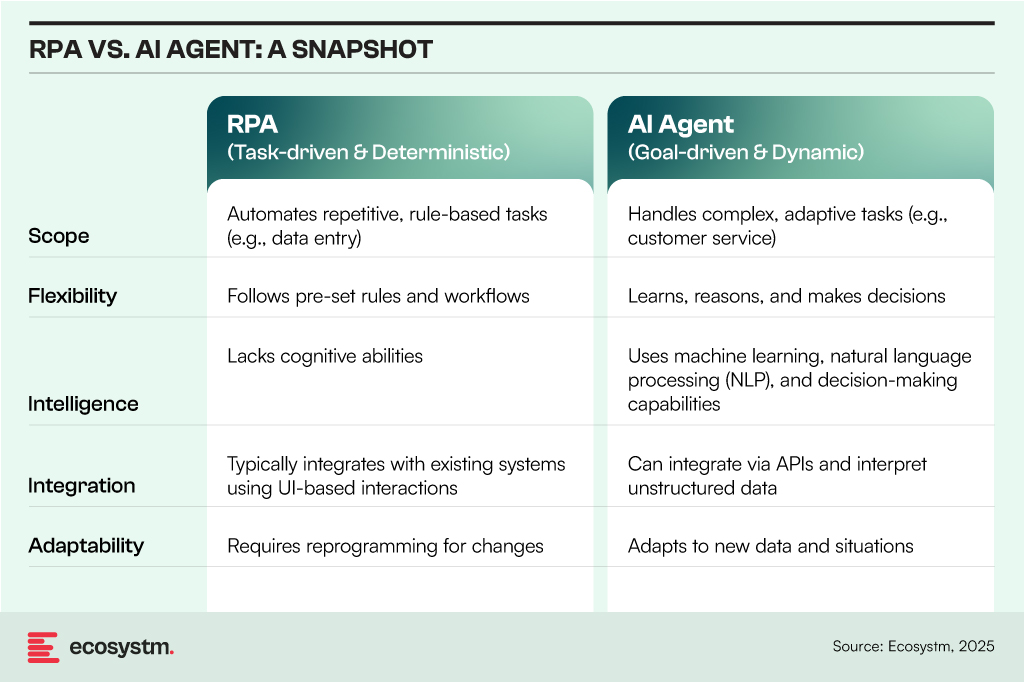
RPA and AI Agents both automate tasks but differ in scope, flexibility, and intelligence:
7 Lessons for AI Agents: Insights from RPA Deployments
However, in many ways, RPA and AI agents are similar – they both address similar challenges, albeit with different levels of automation and complexity. RPA adoption has shown that uncontrolled deployment leads to chaos, requiring a balance of governance, standardisation, and ongoing monitoring. The same principles apply to AI agent management, but with greater complexity due to AI’s dynamic and learning-based nature.
By learning from RPA’s mistakes, organisations can ensure AI agents deliver sustainable value, remain secure, and operate efficiently within a governed and well-managed environment.
#1 Controlling Sprawl with Centralised Governance
A key lesson from RPA adoption is that many organisations deployed RPA bots without a clear strategy, resulting in uncontrolled sprawl, duplicate bots, and fragmented automation efforts. This lack of oversight led to the rise of shadow IT practices, where business units created their own bots without proper IT involvement, further complicating the automation landscape and reducing overall effectiveness.
Application to AI Agents:
- Establish centralised governance early, ensuring alignment between IT and business units.
- Implement AI agent registries to track deployments, functions, and ownership.
- Enforce consistent policies for AI deployment, access, and version control.
#2 Standardising Development and Deployment
Bot development varied across teams, with different toolsets being used by different departments. This often led to poorly documented scripts, inconsistent programming standards, and difficulties in maintaining bots. Additionally, rework and inefficiencies arose as teams developed redundant bots, further complicating the automation process and reducing overall effectiveness.
Application to AI Agents:
- Standardise frameworks for AI agent development (e.g., predefined APIs, templates, and design patterns).
- Use shared models and foundational capabilities instead of building AI agents from scratch for each use case.
- Implement code repositories and CI/CD pipelines for AI agents to ensure consistency and controlled updates.
#3 Balancing Citizen Development with IT Control
Business users, or citizen developers, created RPA bots without adhering to IT best practices, resulting in security risks, inefficiencies, and technical debt. As a result, IT teams faced challenges in tracking and supporting business-driven automation efforts, leading to a lack of oversight and increased complexity in maintaining these bots.
Application to AI Agents:
- Empower business users to build and customise AI agents but within controlled environments (e.g., low-code/no-code platforms with governance layers).
- Implement AI sandboxes where experimentation is allowed but requires approval before production deployment.
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities between IT, AI governance teams, and business users.
#4 Proactive Monitoring and Maintenance
Organisations often underestimated the effort required to maintain RPA bots, resulting in failures when process changes, system updates, or API modifications occurred. As a result, bots frequently stopped working without warning, disrupting business processes and leading to unanticipated downtime and inefficiencies. This lack of ongoing maintenance and adaptation to evolving systems contributed to significant operational disruptions.
Application to AI Agents:
- Implement continuous monitoring and logging for AI agent activities and outputs.
- Develop automated retraining and feedback loops for AI models to prevent performance degradation.
- Create AI observability dashboards to track usage, drift, errors, and security incidents.
#5 Security, Compliance, and Ethical Considerations
Insufficient security measures led to data leaks and access control issues, with bots operating under overly permissive settings. Also, a lack of proactive compliance planning resulted in serious regulatory concerns, particularly within industries subject to stringent oversight, highlighting the critical need for integrating security and compliance considerations from the outset of automation deployments.
Application to AI Agents:
- Enforce role-based access control (RBAC) and least privilege access to ensure secure and controlled usage.
- Integrate explainability and auditability features to comply with regulations like GDPR and emerging AI legislation.
- Develop an AI ethics framework to address bias, ensure decision-making transparency, and uphold accountability.
#6 Cost Management and ROI Measurement
Initial excitement led to unchecked RPA investments, but many organisations struggled to measure the ROI of bots. As a result, some RPA bots became cost centres, with high maintenance costs outweighing the benefits they initially provided. This lack of clear ROI often hindered organisations from realising the full potential of their automation efforts.
Application to AI Agents:
- Define success metrics for AI agents upfront, tracking impact on productivity, cost savings, and user experience.
- Use AI workload optimisation tools to manage computing costs and avoid overconsumption of resources.
- Regularly review AI agents’ utility and retire underperforming ones to avoid AI bloat.
#7 Human Oversight and Hybrid Workflows
The assumption that bots could fully replace humans led to failures in situations where exceptions, judgment, or complex decision-making were necessary. Bots struggled to handle scenarios that required nuanced thinking or flexibility, often leading to errors or inefficiencies. The most successful implementations, however, blended human and bot collaboration, leveraging the strengths of both to optimise processes and ensure that tasks were handled effectively and accurately.
Application to AI Agents:
- Integrate AI agents into human-in-the-loop (HITL) systems, allowing humans to provide oversight and validate critical decisions.
- Establish AI escalation paths for situations where agents encounter ambiguity or ethical concerns.
- Design AI agents to augment human capabilities, rather than fully replace roles.
The lessons learned from RPA’s journey provide valuable insights for navigating the complexities of AI agent deployment. By addressing governance, standardisation, and ethical considerations, organisations
can shift from reactive problem-solving to a more strategic approach, ensuring AI tools deliver value while operating within a responsible, secure, and efficient framework.

In my previous Ecosystm Insight, I explored the Automation Paradox – how AI shifts human roles from routine tasks to more complex, high-pressure responsibilities. Now, let’s look at its impact on entry-level roles and what it means for those starting their careers.
AI is reshaping the skills mix in enterprises, automating many repetitive, lower-complexity tasks that traditionally serve as stepping stones for new professionals. Roles like Level 1 IT support or paralegal work – once common entry points – are increasingly being automated or significantly reduced.
The question now is: how will the next generation gain the experience needed to advance?
Click here to download “AI’s Unintended Consequences: Redefining Employee Skill Pathways” as a PDF
Why Are Entry-Level Roles Changing?
- Automation of Routine Tasks. AI-driven tools are taking over routine tasks. AI-driven tools and chatbots now handle common helpdesk issues instantly, eliminating the need for human intervention. Contract review software scans and analyses legal documents, cutting the workload of junior paralegals.
- Demand for Specialised Knowledge. As AI handles grunt work, remaining roles demand higher-level skills – technical, analytical, and interpersonal. For e.g., IT support shifts from password resets to configuring complex systems, interpreting AI diagnostics, and crafting custom solutions.
With routine tasks automated and remaining work more complex, traditional career entry points may shrink – or vanish entirely.
If an organisation no longer has a roster of junior positions, where will young professionals gain the foundational experience and institutional knowledge needed to excel?
The Ripple Effect on Talent & Development
Reduced Traditional Apprenticeships. Entry-level roles have historically provided new hires with an informal apprenticeship – learning basic skills, building relationships, and understanding organisational nuances. Without these roles, new talent may miss out on crucial developmental opportunities.
Potential Skills Gap. By removing the “lower rungs” of the career ladder, we risk ending up with professionals who lack broad foundational knowledge. A fully automated helpdesk, for example, might produce mid-level analysts who understand theory but have never troubleshot a live system under pressure.
Pressure to Upskill Quickly. New recruits may have to jump directly into more complex responsibilities. While this can accelerate learning, it may also create undue stress if the proper structures for training, mentoring, and support are not in place.
Strategies to Create New Skill Pathways
1. Reimagined Entry Pathways for New Employees
- Rotational Programs. One way to fill the void left by disappearing junior roles is through rotational programs. Over the course of a year, new hires cycle through different departments or projects, picking up hands-on experience even if traditional entry-level tasks are automated.
- Apprenticeship-Style Training. Instead of “on-the-job” experience tied to low-level tasks, companies can establish apprenticeship models where junior employees shadow experienced mentors on live projects. This allows them to observe complex work up close and gradually take on real responsibilities.
2. Blended Learning & Simulation
- AI-Driven Training. Ironically, AI can help solve the gap it creates. AI simulations and virtual labs can approximate real-world scenarios, giving novices a taste of troubleshooting or document review tasks.
- Certification & Micro-Credentials. More specialised skill sets may be delivered through structured learning, using platforms that provide bite-sized, verifiable credentials in areas like cybersecurity, analytics, or advanced software configuration.
- Knowledge Sharing Communities. Team chat channels, internal wikis, and regular “lunch and learn” sessions can help new employees gain the cultural and historical context they’d otherwise accumulate in junior roles.
3. Redefining Career Progression
- Competency-Based Pathways. Instead of relying on job titles (e.g. Level 1 Support), organisations can define career progression through skill mastery. Employees progress once they demonstrate competencies – through projects, assessments, or peer review – rather than simply ticking time-based boxes.
- Continuous Upskilling. Given the rapid evolution of AI, companies should encourage a culture of lifelong learning. Subsidised courses, conference attendance, and online platforms help maintain an agile, future-ready workforce.













































