How is conversational commerce changing customer engagement?
Listen to this Ecosystm Podcast where Ecosystm Principal Advisor Tim Sheedy talks to Sash Mukherjee about the importance of creating a consolidated view of customer interactions across myriads of social and messaging applications.
Podcast: Play in new window | Download (4.6MB)
Subscribe Spotify | Amazon Music | JioSaavn | Podchaser | RSS | More
Last week saw 8×8 and Verint announce a partnership that aims to deliver integrated cloud-based contact centre services and workforce management applications to medium and large enterprises worldwide. The integrated solution will leverage 8×8’s expertise in unified communications as a service (UCaaS) and contact centre as a service (CCaaS) with Verint’s workforce management solutions.
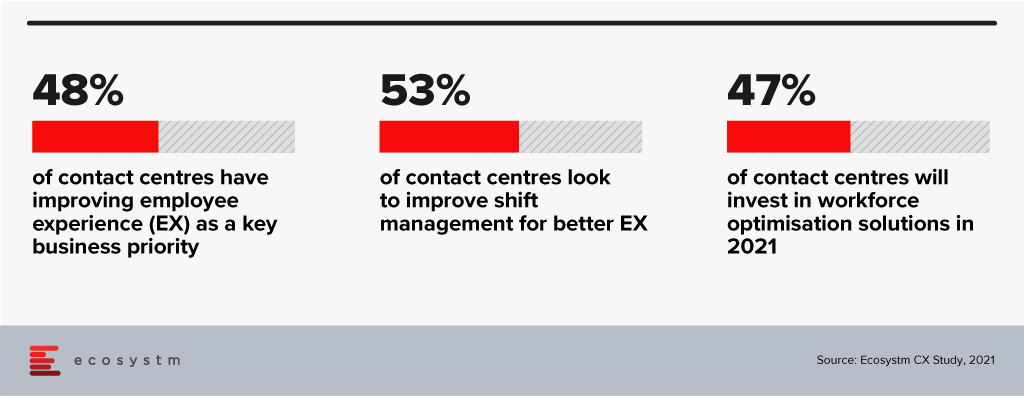
The Need for Better Workforce Optimisation Solutions
Talking about the need for integrated solutions such as this in the Contact Centre space, Ecosystm Principal Advisor for Enterprise Communications and Contact Centres, Audrey William, says, “With agents working from both their homes and the office, contact centres will be challenged with managing staffing requirements and scheduling. The key to delivering exceptional customer experience will be to have the right agent working on the right assignments, across the right channels. On top of that, contact centres have to manage shifts, flexible work hours and part-time agents working across multiple locations. This does not make workforce optmisation an easy task!”
“Driving better employee experience is a top priority for contact centres – and this will include investments in solutions that can alleviate stress for the agent. The industry continues to be challenged by agent attrition – the most common causes being work overload and stress. To provide a consistently good customer experience, contact centres have to listen better to their agents, understand their workloads better, show empathy, and monitor their emotional well-being A workforce optimisation solution will ensure that inbound enquiries are not impacted, and agents’ times are better utilised, through forecasting and better scheduling.”
Synergy between 8×8 and Verint
The single-vendor integrated communications and contact centre solution is anticipated to create better customer engagement and smoother remote operations by empowering employees and agents to plan, forecast and schedule contact centre activities and manage workloads through omnichannel routing.
William says, “8×8 has been establishing its presence in the unified communications and contact centre solutions space in Asia Pacific, particularly in small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Partnering with a market leader in workforce management such as Verint is a positive step. Verint’s strengths in gap analysis from historical data patterns and predicting will help 8×8’s customers to drive optimisation and accuracy in planning in the contact centre. This will have an impact on reducing overstaffing and overtime. Additionally, it will give agents greater control over their schedules and the flexibility to plan their shifts around their desired hours of work.”
“While 8×8 has its own workforce engagement solution, this partnership demonstrates how 8×8 is elevating its game and wants to offer its customers a more robust workforce management solution through Verint Monet and Verint Enterprise. This solution is also out of the box for 8×8’s customers without the need for professional services. That is a plus!”, says William.

As the economy looks to recover from the devastating impact of COVID-19 in 2020, businesses in Singapore are gaining momentum through technology leverage, and wider adoption of digital platforms. The disruption has led to a higher dependence on and appetite for technology to rebuild industries such as Healthcare, Financial Services and Manufacturing. Organisations are re-engineering their processes to go digital and this has driven the need to re-skill and upskill.
Growing Need for Tech Talent
Even before the pandemic, there was a shift of business focus on the Asian and Southeast Asian economies, that has led global companies and investors to flock to Singapore as a regional hub. Many of these companies are technology providers and as Singapore looks well-positioned to recover from the pandemic, these companies find themselves delivering on multiple transformation projects across industries. This has led to an increased demand for tech experts, The growing demand, combined with travel restrictions and a focus on ensuring Singaporeans are a priority for employment opportunities, has made the tech community anxious about the talent availability and the possibility of a talent crunch.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor Ravi Bhogaraju says, “Tech talent crunch is very palpable in the Singapore market today. The primary drivers of the crunch have been the change in the immigration policies due to the COVID-19 disruption followed by the huge increase in the demand for technology skills in the last 12-18 months. This gap will continue to rise over the next years as more technology firms expand or set up their base in Singapore.”
Skill Development Efforts and Programs
With this in mind, the Government of Singapore is focused on addressing this concern through various innovation and skills development programs. For instance, the Economic Development Board (EDB) has introduced programs to grow the talent pool, partnered with institutions and organisations for reskilling programs and supporting skills development with help of other companies.
Some more Government-supported initiatives to bridge the skills shortage include Singapore’s Global Ready Talent Programme (GRT) which aims to build talent pipeline by exposing Singaporeans to internships and work opportunities overseas, TechSkills Accelerator (TeSA) and Professional Conversion Programmes (PCP), to provide training on knowledge and skills to support expansion plans.
The Government has also increased its spending on digital initiatives to help SMEs and empower them to hire more specialised manpower in focus areas such as AI, cloud, IoT, and data analytics.
Singapore’s Tech.Pass visa program is another initiative to invite qualified individuals to work and operate in Singapore. It supports the entry of up to 500 proven founders, leaders and experts from top tech companies into Singapore.
Bhogaraju says, “The skills gap needs to be bridged with talent that is ready to step up and take on the new roles. To that end we see that the Singapore Government is making the right investments in the Skills Future program. There are a few pillars currently in play that are addressing different elements of the talent skilling initiatives. The key pillars are talent reskilling, experiential training, work-learn programs, and implementing new education curriculum. These are well designed in line with the skills frameworks and are meant to address the skills development for mid-career professionals to students in polytechnics and university programs.”
Tech Companies Need a Long-term View
However, Bhogaraju notes, “That’s only one side of the equation – the other element of the partnership is the companies that need these skills and how they are thinking of approaching the skills they need. Here there are some good examples of public private partnerships to help bridge the skills. However, in many cases the companies are still struggling to fill the positions – and that is because they use an age-old strategy of ‘let’s attract the talent’ to come work for us. In a time when there is limited talent in the pool – this strategy will only result in spinning wheels and expending energy.”
“Companies need to fundamentally rethink their talent pooling and development strategies to be able to deliver good quality talent. They need to develop a strategy that focuses on reskilling, finding new talent pools, leveraging the gig economy and developing their existing talents into adjoining pools to be able to fill these gaps effectively.”
As the nature of work transforms, many professionals will be challenged to learn new skills to address the skills gaps. Create your free account on Ecosystm Platform to access research, data and insights on the emerging technologies, the supply of skills and the demand for tech talent to address the mismatch.

Microsoft introduced a second Vertical Cloud offering, last week – this time turning the focus on Retail, after having launched Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare in October 2020.
The Microsoft Cloud for Retail aims to offer integrated and intelligent capabilities to retailers and brands to improve their end-to-end customer journey. It brings industry-specific capabilities to the Microsoft suite including Microsoft Azure, Microsoft Power Platform, Microsoft 365, and Microsoft Dynamics 365 – and is aimed at the growing need for “intelligent retail’. Microsoft’s partner ecosystem will also be involved in the new platform to address challenges in the sector and future proof the retail evolution.
In The Top 5 Retail & eCommerce Trends for 2021, Ecosystm notes that while retailers will focus on the shift in customer expectations, a mere focus on customer experience will not be enough this year. From the customer experience angle, they will strongly focus on omnichannel, catering to ‘glocal’ consumption, using location-based services, and improving both their onsite and online customer experience. They will also have to work on their supply chain and pricing capabilities, as distribution woes continue. These trends are seeing a deeper need for transformational technologies and leading cloud providers are introducing solutions targeted at the industry. Google has introduced its cloud retail solutions aiming to help retailers get more from data. Similarly, AWS has cloud offerings for the retail industry leveraging its retail domain experience and cloud deployment services.
Ecosystm Comments

“Global cloud vendors continue to “move up the stack” to provide more of the technology landscape for organisations. The focus of these tech giants is on adding unique value to customers by tailoring the combination of the different cloud services they can provide to specific industries. Providing the full-stack will mean higher customer retention rates – as the implementation time should be lower than traditional on-premises implementations. Microsoft has a diverse range of capabilities. Having a software company and implementation partner that can deliver the full stack of technology and business processes should improve the time to value for organisations.
But I see three key difficulties in implementing systems such as these:
- People adapting effectively to use the new processes
- Migrating enough high-quality data to leverage the new capabilities
- Integrating the new capabilities into an organisation’s existing landscape.
This is why it is likely that initial use will come from Microsoft’s existing Retail customers as they expand the range of services they use. New adopters of these Microsoft solutions will find that much of the complexity and cost of implementing a new business solution will remain.
However, these value-added cloud services open access to smaller organisations. If Microsoft is able to work with their partners to simplify the implementation of these capabilities, it will allow smaller organisations to access these complex capabilities affordably.“

“The Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal Study aims to determine how optimistic industries are about successfully negotiating these uncertain times (Figure 1). The industries that are rated the most optimistic fall into two clear categories. In the first category, there are industries, such as Healthcare that had to transform urgently – mostly in an unplanned manner. This has led to a greater appetite for change and optimism in these industries. Then there are industries, such as Retail, that had some time to re-focus their technology roadmap when the crisis hit. These industries have a strong customer focus and had started their digital journeys before the pandemic.
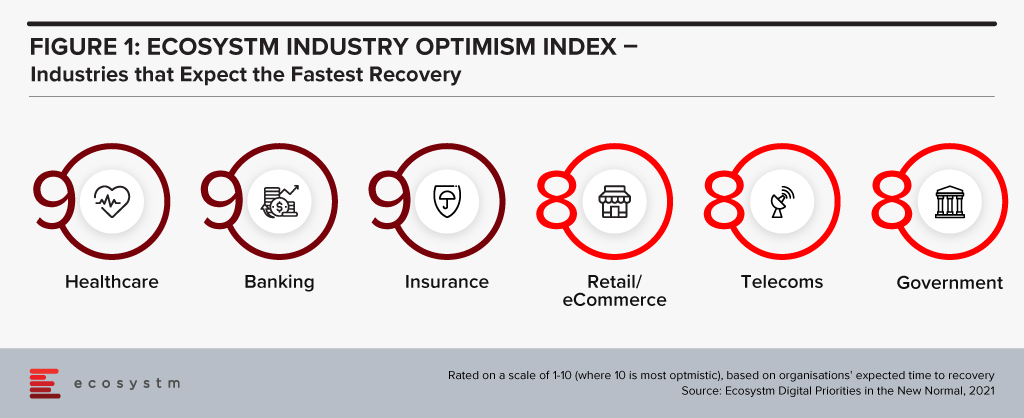
Microsoft’s industry focus appears to be spot-on. Their first two vertical clouds target enterprises that have had to – and will continue to – pivot. The ‘modular’ approach taken in the Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare offering allows providers to choose the right capability for their organisation – whether it is workflow automation, patient engagement through virtual health, collaboration within care teams or better clinical and operational insights. As healthcare organisations across the world negotiate the challenges of mass vaccination, they may well find themselves leveraging these industry-specific capabilities as they revamp their workflows, processes, and data use.”
Get to know the right research, insights and technologies for you to be one step ahead in this new world of retail in our top 5 retail trends for 2021 that represent the most significant shifts in 2021

Authored by Alea Fairchild and Audrey William
There is a lot of hope on AI and automation to create intellectual wealth, efficiency, and support for some level of process stability. After all, can’t we just ask Siri or Alexa and get answers so we can make a decision and carry on?
Automation has been touted as the wonder formula for workplace process optimisation. In reality it’s not the quick fix that many business leaders desire. But we keep raising the bar on expectations from automation. Investments in voice technologies, intelligent assistants, augmented reality and touchscreens are changing customer experience (Figure 1). Chatbots are ubiquitous, and everything has the potential to be personalised. But will they solve our problems?
100 percent automation is not effective
Let’s first consider using automation to replace face-to-face interactions. There was a time when people were raving about the check-in experience at some of the hotels in Japan where robots and automated systems would take care of the check-in, in-stay and check-out processes. Sounds simple and good? Till 2019, if you checked into the Henn-na Hotel in Japan, you would be served and taken care of by 243 robots. It was viewed by many as a template for what a fully automated hotel could look like in the future.
The hotel had an in-room voice assistant called Churi. It could cope with basic commands, such as turning the lights on and off, but it was found to be deficient when guests started asking questions about places to visit or other more sophisticated queries. It was not surprising that the hotel decided to retire their robots. In the end it created more work for the hotel staff on-site.
People love the personal touch when they are in a hotel; and talking to someone at the front desk, requesting assistance from hotel staff, or even just a short chat over breakfast are some of the small nuances of why the emotional connection matters. Many quarantine hotels today use robots for food delivery, but the hotel staff is still widely available for questions. That automation is good, but you need the human intervention. So, getting the balance right is key.
Empathy plays a big role in delivering great Customer Experience
Similarly, there was a time when many industry observers and technology providers said that a contact centre will be fully automated, reducing the number of agents. While technologies such as Conversational AI have come along where you can now automate common or repetitive questions and with higher accuracy levels, the human agent still plays a critical role in answering the more complex queries. When the customer has a complicated question or request, then they will WANT to speak to an agent.
When it reaches a point where the conversation with the chatbot starts getting complicated and the customers need more help there should be the option – within the app, website or any other channel – to escalate the call seamlessly to a human agent. Sometimes, a chat is where the good experience happens – the emotional side of the conversation, the laughter, the detailed explanation. This human touch cannot be replaced by machines. Disgruntled customers are happier when an agent shows empathy. Front line staff and human agents act as the face of a company’s brand. Complete automation will not allow the individual to understand the culture of the company. These can be attained through conversations.
Humans as supervisors for AI – The New Workplace
Empathy, intuitiveness, and creativity are all human elements in the intelligence equation. Workers in the future will need to make their niche in a fluid and unpredictable environment; and translating data into action in a non-replicable way is one of the values of human input. The essence of engineering is the capacity to design around human limitations. This requires an understanding of how humans behave and what they want. We call that empathy. It is the difference between the engineer who designs a product, and the engineer who delivers a solution. We don’t teach our computer scientists and engineering students a formula for empathy. But we do try to teach them respect for both the people and the process.
For efficiency, we turn to automation of processes, such as RPA. This is designed to try to eradicate human error and assist us in doing our job better, faster and at a lower cost by automating routine processes. If we design it right, humans take the role of monitoring or supervisory controlling, rather than active participation.
At present, AI is not seen as a replacement for our ingenuity and knowledge, but as a support tool. The value in AI is in understanding and translating human preferences. Humans-in-the-loop AI system building puts humans in the decision loop. They also shift pressure away from building “perfect” algorithms. Having humans involved in the ethical norms of the decision allows the backstop of overly orchestrated algorithms.
That being said, the astute use of AI can deepen insights into what truly makes us human and can humanise experiences by setting a better tone and a more trusted engagement. Using things like sentiment analysis can de-escalate customer service encounters to regain customer loyalty.
The next transformational activity for renovating work is to advance interactions with customers by interpreting what they are asking for and humanising the experience of acquiring it which may include actually dealing with a human contact centre agent – decisions that are supported at the edge by automation, but at the core by a human being.
Implications
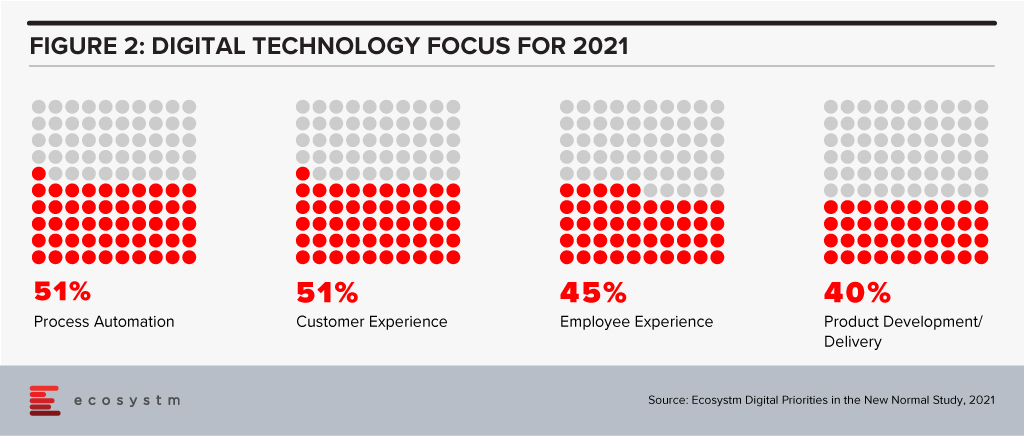
Ecosystm research shows that process automation will be a key priority for technology investments in 2021 (Figure 2).
With AI and automation, a priority in 2021, it will be important to keep these considerations in mind:
- Making empathy and the human connection the core of customer experiences will bring success.
- Rigorous, outcome-based testing will be required when process automation solutions are being evaluated. In areas where there are unsatisfactory results, human interactions cannot – and should not – be replaced.
- It may be easy to achieve 90% automation for dealing with common, repetitive questions and processes. But there should always be room for human intervention in the event of an issue – and it should be immediate and not 24 hours later!
- Employees can drive greater value by working alongside the chatbot, robot or machine.
Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Customer Experience Trends for 2021
Download Ecosystm’s complimentary report detailing the top 5 customer experience trends for 2021 that your company should pay attention to along with tips on how to stay ahead of the curve.

The disruption that we faced in 2020 has created a new appetite for adoption of technology and digital in a shorter period. Crises often present opportunities – and the FinTech and Financial Services industries benefitted from the high adoption of digital financial services and eCommerce. In 2021, there will be several drivers to the transformation of the Financial Services industry – the rise of the gig economy will give access to a larger talent pool; the challenges of government aid disbursement will be mitigated through tech adoption; compliance will come sharply back into focus after a year of ad-hoc technology deployments; and social and environmental awareness will create a greater appetite for green financing. However, the overarching driver will be the heightened focus on the individual consumer (Figure 1).
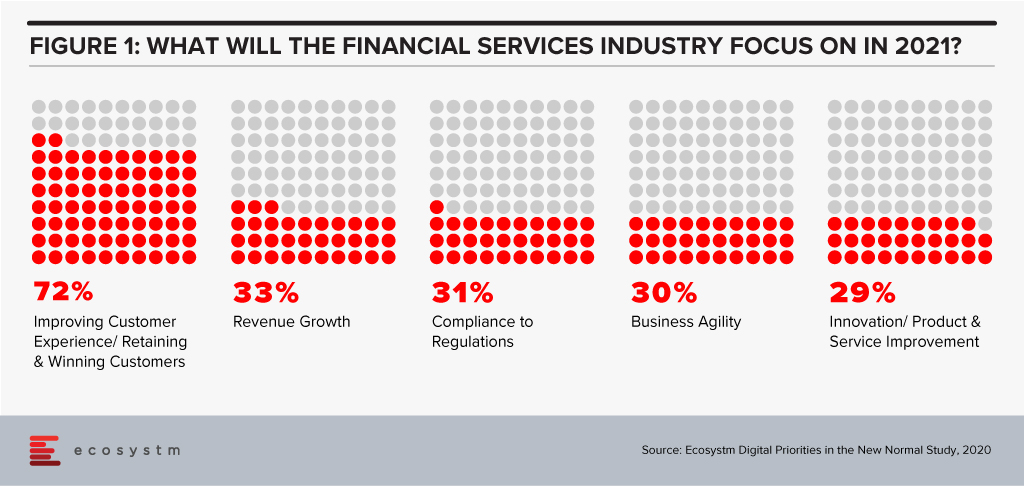
2021 will finally see consumers at the core of the digital financial ecosystem.
Ecosystm Advisors Dr. Alea Fairchild, Amit Gupta and Dheeraj Chowdhry present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for FinTech in 2021 – written in collaboration with the Singapore FinTech Festival. This is a summary of the predictions; the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform.
The Top 5 FinTech Trends for 2021
#1 The New Decade of the ‘Empowered’ Consumer Will Propel Green Finance and Sustainability Considerations Beyond Regulators and Corporates
We have seen multiple countries set regulations and implement Emissions Trading Systems (ETS) and 2021 will see Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) considerations growing in importance in the investment decisions for asset managers and hedge funds. Efforts for ESG standards for risk measurement will benefit and support that effort.
The primary driver will not only be regulatory frameworks – rather it will be further propelled by consumer preferences. The increased interest in climate change, sustainable business investments and ESG metrics will be an integral part of the reaction of the society to assist in the global transition to a greener and more humane economy in the post-COVID era. Individuals and consumers will demand FinTech solutions that empower them to be more environmentally and socially responsible. The performance of companies on their ESG ratings will become a key consideration for consumers making investment decisions. We will see corporate focus on ESG become a mainstay as a result – driven by regulatory frameworks and the consumer’s desire to place significant important on ESG as an investment criterion.
#2 Consumers Will Truly Be ‘Front and Centre’ in Reshaping the Financial Services Digital Ecosystems
Consumers will also shape the market because of the way they exercise their choices when it comes to transactional finance. They will opt for more discrete solutions – like microfinance, micro-insurances, multiple digital wallets and so on. Even long-standing customers will no longer be completely loyal to their main financial institutions. This will in effect take away traditional business from established financial institutions. Digital transformation will need to go beyond just a digital Customer Experience and will go hand-in-hand with digital offerings driven by consumer choice.
As a result, we will see the emergence of stronger digital ecosystems and partnerships between traditional financial institutions and like-minded FinTechs. As an example, platforms such as the API Exchange (APIX) will get a significant boost and play a crucial role in this emerging collaborative ecosystem. APIX was launched by AFIN, a non-profit organisation established in 2018 by the ASEAN Bankers Association (ABA), International Finance Corporation (IFC), a member of the World Bank Group, and the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS). Such platforms will create a level playing field across all tiers of the Financial Services innovation ecosystem by allowing industry participants to Discover, Design and rapidly Deploy innovative digital solutions and offerings.
#3 APIfication of Banking Will Become Mainstream
2020 was the year when banks accepted FinTechs into their product and services offerings – 2021 will see FinTech more established and their technology offerings becoming more sophisticated and consumer-led. These cutting-edge apps will have financial institutions seeking to establish partnerships with them, licensing their technologies and leveraging them to benefit and expand their customer base. This is already being called the “APIficiation” of banking. There will be more emphasis on the partnerships with regulated licensed banking entities in 2021, to gain access to the underlying financial products and services for a seamless customer experience.
This will see the growth of financial institutions’ dependence on third-party developers that have access to – and knowledge of – the financial institutions’ business models and data. But this also gives them an opportunity to leverage the existent Fintech innovations especially for enhanced customer engagement capabilities (Prediction #2).
#4 AI & Automation Will Proliferate in Back-Office Operations
From quicker loan origination to heightened surveillance against fraud and money laundering, financial institutions will push their focus on back-office automation using machine learning, AI and RPA tools (Figure 3). This is not only to improve efficiency and lower risks, but to further enhance the customer experience. AI is already being rolled out in customer-facing operations, but banks will actively be consolidating and automating their mid and back-office procedures for efficiency and automation transition in the post COVID-19 environment. This includes using AI for automating credit operations, policy making and data audits and using RPA for reducing the introduction of errors in datasets and processes.
There is enormous economic pressure to deliver cost savings and reduce risks through the adoption of technology. Financial Services leaders believe that insights gathered from compliance should help other areas of the business, and this requires a completely different mindset. Given the manual and semi-automated nature of current AML compliance, human-only efforts slow down processing timelines and impact business productivity. KYC will leverage AI and real-time environmental data (current accounts, mortgage payment status) and integration of third-party data to make the knowledge richer and timelier in this adaptive economic environment. This will make lending risk assessment more relevant.
#5 Driven by Post Pandemic Recovery, Collaboration Will Shape FinTech Regulation
Travel corridors across border controls have started to push the boundaries. Just as countries develop new processes and policies based on shared learning from other countries, FinTech regulators will collaborate to harmonise regulations that are similar in nature. These collaborative regulators will accelerate FinTech proliferation and osmosis i.e. proliferation of FinTechs into geographies with lower digital adoption.
Data corridors between countries will be the other outcome of this collaboration of FinTech regulators. Sharing of data in a regulated environment will advance data science and machine learning to new heights assisting credit models, AI, and innovations in general. The resulting ‘borderless nature’ of FinTech and the acceleration of policy convergence across several previously siloed regulators will result in new digital innovations. These Trusted Data Corridors between economies will be further driven by the desire for progressive governments to boost the Digital Economy in order to help the post-pandemic recovery.

In this blog, our guest author Chandru Pingali talks about the potential benefits of the Blended working model and the impact it will have on FinTech and financial services organisations. “FinTech innovation and performance is here to stay and thrive. It needs to be backed by a well-oiled machine to support implementation of a blended workforce plan to institutionalise and scale.”

When under pressure to reduce costs and survive, we reimagine everything we do to build resilience and thrive. Never before have the buzzwords frugality, prudence and agility gained as much prominence – not just in one country or industry, but across global economies simultaneously (a phenomenon not seen since the Great Depression). And these words have sliced through the employment opportunities ruthlessly, leaving an abundance of talent to be gainfully employed differently.
So, is the freelance economy surging? Statistics appear to say yes. In 2018, freelancers had contributed almost USD 1.40 trillion to the US economy; 162 million freelancers work across US and EU-15. So, who are these people? Why is blended workforce new or relevant for the Asia Pacific? Why is it gaining more prominence now? How can enterprises create and implement a blended workforce strategy to reduce costs more permanently, while running and scaling businesses? What does the Future of Work and workforce mean? How can FinTech enterprises successfully implement a blended workforce strategy?
Let us take Singapore as an example. With 1000+ FinTech firms and increasing investments, the “smart financial centre” initiative of Singapore is a huge success story, recognised globally. To sustain this, apart from innovation and technology, the main ingredient is consistent availability of talent as the demand for expertise in technology and financial services increases, while the supply is inconsistent, uncurated and fragmented. Recent data from the Singapore government job portals reveal that there are several hundred jobs at any point in time posted by FinTech companies that are open for months! This invariably slows down the ability to build businesses, innovate or scale. Interestingly, while the local talent for technology and BFSI may be limited in Singapore, the crisis this year presented a significant opportunity to reimagine the Future of Work and workforce. While efforts should continue to upskill and reskill local talent, it is now possible to create dedicated local and cross-border talent hubs to work part-time, fulltime-short term with the option of working physically or remotely. We expect the plug and play of freelance management experts and expertise to cost 25-30% less to an enterprise, keeps costs flexible and dramatically shortens time to “hire and deploy” from an average of 120 days to 15 days.

Gigs and Generations – Conceptual Clarity of Who We Need
Culturally, the US and Europe are more accepting of freelancing as full-time careers compared to the Asia Pacific. It is predicted that by 2027 the majority of the workforce in the US will be freelancers overtaking traditional employment. The buzz in the Asia Pacific has just started with both employers and employable talent accepting a new reality – learning to run businesses with a blended workforce, starting at the top of the pyramid. Particularly, since the ratio of new jobs to lost jobs is skewed in the wrong direction.
Power of Blended Workforce
A blended workforce is a combination of permanent, part-time, full time-short term and turnkey practitioners, working as a single collaborative workforce. It is built around business activity clusters – Strategy, Implementation and Institutionalisation, applied to create a plan for core and non-core workforce to drive business.
A creative estimation of how a blended workforce gets distributed across the three business clusters is depicted below (Figure 2). What is important here is to recognise that the ratio of permanent to flexible workforce has to start at 10-15% across different levels. Enterprises will gain the most on cost optimisation when they focus on the management layer to go blended. Not an easy change to drive but then change is often driven by some tough calls and some low hanging fruits to build a sustainable cost model.
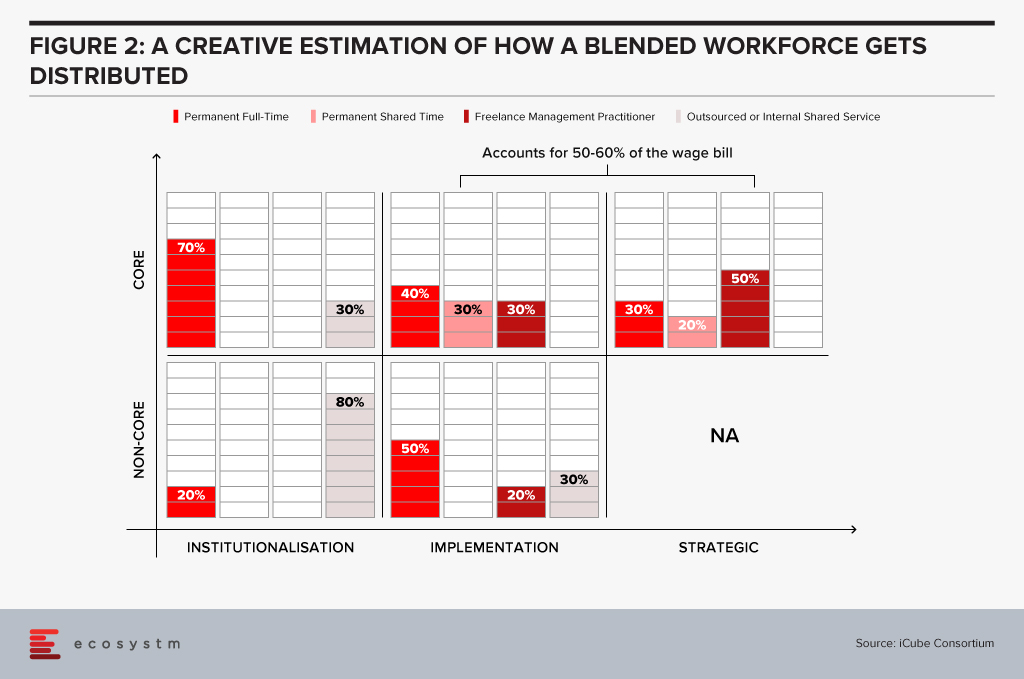
Developing & Implementing a Blended Workforce Strategy: What to Consider
Fix the core and flex the non-core should be the mantra
- Identify roles by each business and function
- Segregate core and non-core roles by job profiles
- Classify them into buckets of permanent full time, permanent part time, cyclical, and freelance on demand, based on:
- Time demand for the roles
- Importance to business goals
- Criticality to daily business output
- Criticality to daily or weekly business continuity
- Set up a process to engage and create a blended workforce strategy
- Implement the plan with a blend of a common self-service platform and a central client service team to source, engage and deploy workforces
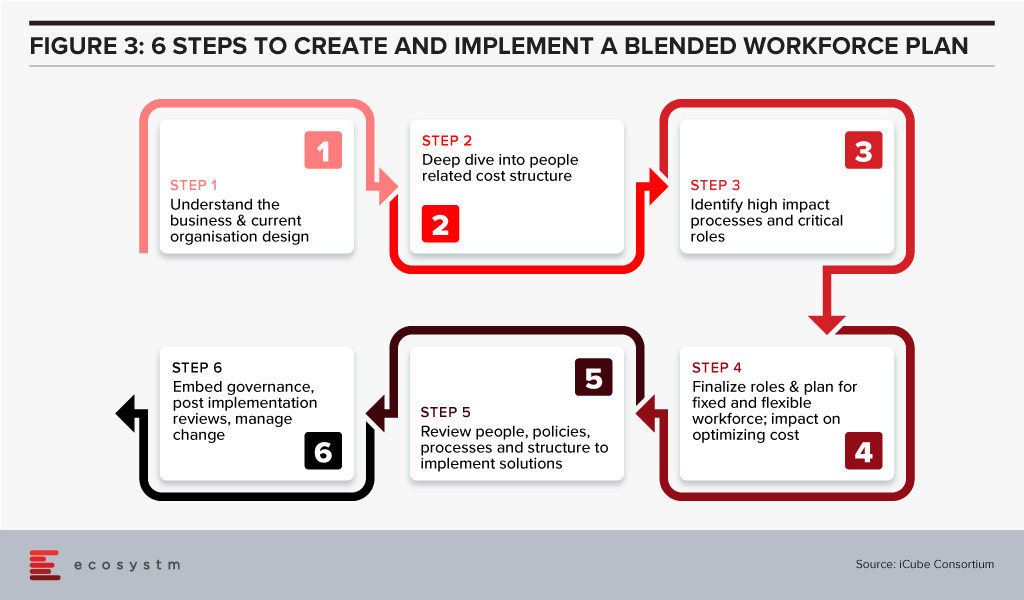
Once the process review is completed, the organisation structures will be finalised. Creation of a strategy and the process are the easier parts. A disciplined fulfilment of the plan is critical to success. So, is this the new normal? Pretty much yes, if organisations need to optimise costs and be agile to reduce or scale with freelance experts and shared talent pools.
The Potential Benefits of a Blended Workforce
A Blended Workforce will help reduce your talent scarcity gap, while providing thousands of work opportunities to locals who are freelance experts. So, what are these benefits that can make you sleep better at night better?
- Cost optimisation. Freelance experts do not need the fully loaded costs. They can work remotely or physically and do not need investment in regular training, insurance, or other related benefits.
- Targeted purpose-hire for short term. With deliverables specified upfront, measurable, results focused and tracked for closure.
- Job Sharing. Two or may be three, for the prize of one! Jobs can be dismantled to tasks or activity clusters to hire more than one expert in place of a full-time role. Enables razor sharp focus on sourcing for expertise, increases employment opportunities and accelerates productivity.
- Boundaryless with an opportunity to find cross-border talent pools to work on-demand, remotely. It cuts both ways- Singaporean talent finding work opportunities outside the country whilst the best talent from other countries made available to grow Singapore’s economy.
- Speed of hire is dramatically reduced (we have several client cases, with a reduction from an average of 120 days to 15 days, to clients’ delight!)
- Reduced infrastructure costs because the workforce works remotely or at best part-time physically. Easy to implement with hot desking, if needed but enables permanent cost reduction.
- Builds resilience by staying agile and nimble in the cost line, with an ability to scale up or down rapidly based on business needs.
How Open is the Financial Services Industry to Blended Workforce and Future of Work?
SolvecubeHR conducted a recent survey with CXOs across 22 countries, predominantly focused on the Asia Pacific region. Some key findings for the financial services industry are:
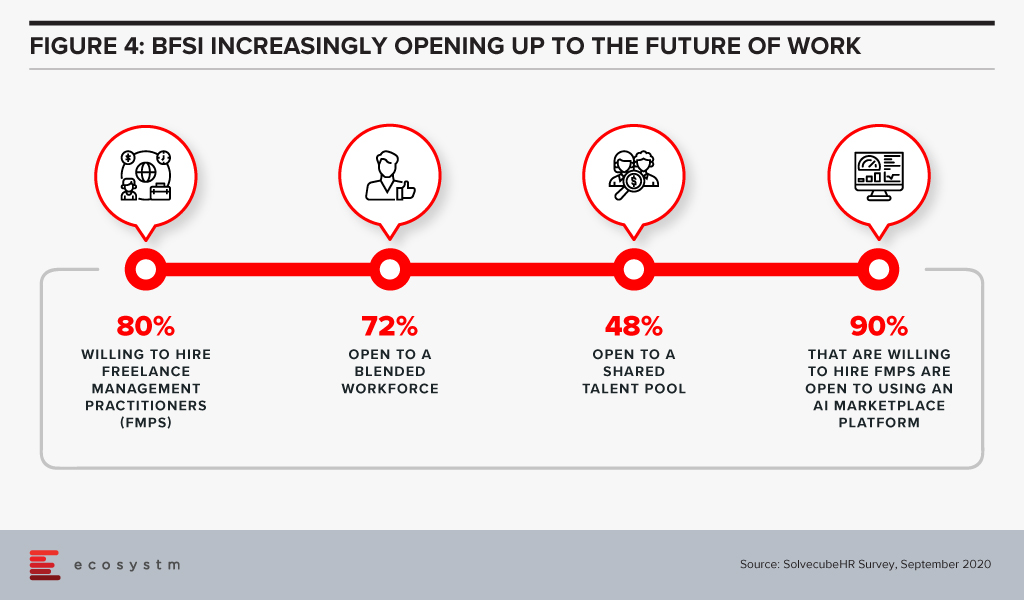
In summary, a blended workforce is the Future of Work. Asia Pacific will see a massive shift in its mindset from “jobs to work opportunities”. Employers and talent pools will embrace new ways of working to remain agile and prudent. The power of aggregation, curation, and collaboration by leveraging an AI matchmaking platform, backed by creation of shared talent pools, will be a game changer.
FinTech innovation and performance is here to stay and thrive. It needs to be backed by a well-oiled machine to support implementation of a blended workforce plan to institutionalise and scale.
We can build technologies to disintermediate people dependency, but we cannot take humans out of the human capital needed to build these technologies.
About iCube: iCube Consortium is a Singapore based, Human Capital Management (HCM) solutions firm, with an award-winning AI platform to source and manage freelance management experts and execute turnkey assignments in Asia and Middle East
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Talent Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit which will cover topics on Founders success and failure stories, pandemic impact on founders and talent development, upskilling and reskilling for the future of work.

In 2020, much of the focus for organisations were on business continuity, and on empowering their employees to work remotely. Their primary focus in managing customer experience was on re-inventing their product and service delivery to their customers as regular modes were disrupted. As they emerge from the crisis, organisations will realise that it is not only their customer experience delivery models that have changed – but customer expectations have also evolved in the last few months. They are more open to digital interactions and in many cases the concept of brand loyalty has been diluted. This will change everything for organisations’ customer strategies. And digital technology will play a significant role as they continue to pivot to succeed in 2021 – across regions, industries and organisations.
Ecosystm Advisors Audrey William, Niloy Mukherjee and Tim Sheedy present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for Customer Experience in 2021. This is a summary of the predictions – the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform.
The Top 5 Customer Experience Trends for 2021
- Customer Experience Will Go Truly Digital
COVID-19 made the few businesses that did not have an online presence acutely aware that they need one – yesterday! We have seen at least 4 years of digital growth squeezed into six months of 2020. And this is only the beginning. While in 2020, the focus was primarily on eCommerce and digital payments, there will now be a huge demand for new platforms to be able to interact digitally with the customer, not just to be able to sell something online.
Digital customer interactions with brands and products – through social media, online influencers, interactive AI-driven apps, online marketplaces and the like will accelerate dramatically in 2021. The organisations that will be successful will be the ones that are able to interact with their customers and connect with them at multiple touchpoints across the customer journey. Companies unable to do that will struggle.
- Digital Engagement Will Expand Beyond the Traditional Customer-focused Industries
One of the biggest changes in 2020 has been the increase in digital engagement by industries that have not traditionally had a strong eye on CX. This trend is likely to accelerate and be further enhanced in 2021.
Healthcare has traditionally been focused on improving clinical outcomes – and patient experience has been a byproduct of that focus. Many remote care initiatives have the core objective of keeping patients out of the already over-crowded healthcare provider organisations. These initiatives will now have a strong CX element to them. The need to disseminate information to citizens has also heightened expectations on how people want their healthcare organisations and Public Health to interact with them. The public sector will dramatically increase digital interactions with citizens, having been forced to look at digital solutions during the pandemic.
Other industries that have not had a traditional focus on CX will not be far behind. The Primary & Resources industries are showing an interest in Digital CX almost for the first time. Most of these businesses are looking to transform how they manage their supply chains from mine/farm to the end customer. Energy and Utilities and Manufacturing industries will also begin to benefit from a customer focus – primarily looking at technology – including 3D printing – to customise their products and services for better CX and a larger share of the market.
- Brands that Establish a Trusted Relationship Can Start Having Fun Again
Building trust was at the core of most businesses’ CX strategies in 2020 as they attempted to provide certainty in a world generally devoid of it. But in the struggle to build a trusted experience and brand, most businesses lost the “fun”. In fact, for many businesses, fun was off the agenda entirely. Soft drink brands, travel providers, clothing retailers and many other brands typically known for their fun or cheeky experiences moved the needle to “trust” and dialed it up to 11. But with a number of vaccines on the horizon, many CX professionals will look to return to pre-pandemic experiences, that look to delight and sometimes even surprise customers.
However, many companies will get this wrong. Customers will not be looking for just fun or just great experiences. Trust still needs to be at the core of the experience. Customers will not return to pre-pandemic thinking – not immediately anyway. You can create a fun experience only if you have earned their trust first. And trust is earned by not only providing easy and effective experiences, but by being authentic.
- Customer Data Platforms Will See Increased Adoption
Enterprises continue to struggle to have a single view of the customer. There is an immense interest in making better sense of data across every touchpoint – from mobile apps, websites, social media, in-store interactions and the calls to the contact centre – to be able to create deeper customer profiles. CRM systems have been the traditional repositories of customer data, helping build a sales pipeline, and providing Marketing teams with the information they need for lead generation and marketing campaigns. However, CRM systems have an incomplete view of the customer journey. They often collect and store the same data from limited touchpoints – getting richer insights and targeted action recommendations from the same datasets is not possible in today’s world. And organisations struggled to pivot their customer strategies during COVID-19. Data residing in silos was an obstacle to driving better customer experience.
We are living in an age where customer journeys and preferences are becoming complex to decipher. An API-based CDP can ingest data from any channel of interaction across multiple journeys and create unique and detailed customer profiles. A complete overhaul of how data can be segregated based on a more accurate and targeted profile of the customer from multiple sources will be the way forward in order to drive a more proactive CX engagement.
- Voice of the Customer Programs Will be Transformed
Designing surveys and Voice of Customer programs can be time-consuming and many organisations that have a routine of running these surveys use a fixed pattern for the data they collect and analyse. However, some organisations understand that just analysing results from a survey or CSAT score does not say much about what customers’ next plan of action will be. While it may give an idea of whether particular interactions were satisfactory, it gives no indication of whether they are likely to move to another brand; if they needed more assistance; if there was an opportunity to upsell or cross sell; or even what new products and services need to be introduced. Some customers will just tick the box as a way of closing off a feedback form or survey. Leading organisations realise that this may not be a good enough indication of a brand’s health.
Organisations will look beyond CSAT to other parameters and attributes. It is the time to pay greater attention to the Voice of the Customer – and old methods alone will not suffice. They want a 360-degree view of their customers’ opinions.

In this blog, our guest authors Randeep Sudan and Yamin Oo talk about the pervasiveness of the Digital Economy, and the key trends that will determine its future trajectory. “That the world in 2030 will be very different from today is obvious. We may, however, be surprised by the extent and sweep of the change ahead of us.”


The Digital Economy – a term first coined by Don Tapscott in 1994 – is not easy to define or measure. At one end, it is limited to the production and consumption of digital goods and services. On the other end, according to the European Parliament, “The digital economy is increasingly interwoven with the physical or offline economy making it more and more difficult to clearly delineate the digital economy“. We are, however, witnessing the Digital Economy transitioning to an economy that is digital.
Given the pervasiveness of the Digital Economy, its future will be determined by the complex interplay of several trends. Some of the trends that illustrate the future trajectory of the Digital Economy are:
Technology
We will see AI becoming ubiquitous as it is leveraged in every sector and sphere of activity. According to one estimate, AI is estimated to contribute USD 15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, which is more than the current GDP of China and India combined! We are also likely to see rapid progress in technologies related to Extended Reality (XR) in the coming years. COVID-19 is accelerating this trend, as we can see from the offerings of companies like Spatial and MeetinVR that facilitate virtual business meetings. The analog world’s rendering into its digital twin will see us moving towards a metaverse – a virtual shared space imagined in Neal Stephenson’s novel Snowcrash. Some of the biggest names in the tech industry – Apple (Apple glass), Facebook (Oculus), Sony (Playstation) – are assiduously working towards this direction.
Given the importance of telecom infrastructure to the Digital Economy, 5G networks are being rolled out in countries worldwide (Figure 1). However, even as 5G is being deployed, the buzz around 6G is getting louder. 6G may transmit data 100 times faster than 5G and may see deployment by 2030 given the decadal cycles for telecom: 1G in the 80s, 2G in the 90s, 3G in the decade following 2000, 4G in the decade starting 2010, and 5G beginning in the 2020s.
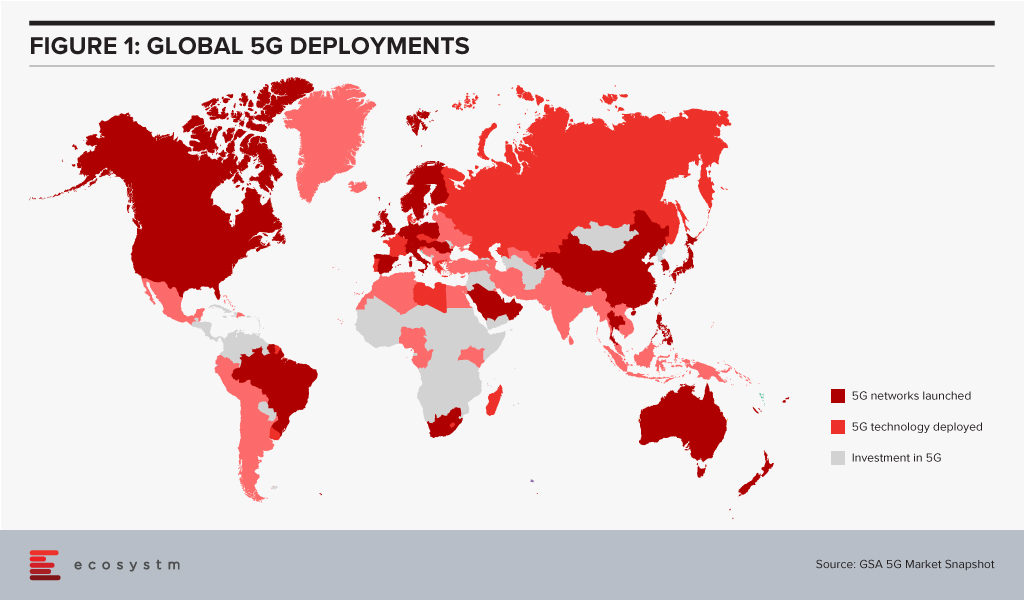
The availability of high bandwidth, low latency networks could lead to newer applications and further breakthroughs in innovative technologies.
The Future of Work
With the rapid growth in automation and AI, we are likely to see significant labour market disruptions. Moreover, COVID-19 has been a watershed for the global economy – its impacts will continue to be felt for many years to come. According to the International Labor Organization, 495 million full-time jobs were lost in the first two quarters of 2020 due to COVID-19. Lower and middle-income countries have suffered the most, with an estimated 23.3% drop in working hours – equivalent to 240 million jobs.
A recent report from the World Economic Forum estimates that by 2025, 85 million jobs may be displaced due to automation and AI, while 97 million new roles may emerge. We will see significant changes and turbulence in labour markets across multiple industries and geographies in the years ahead. If we look at how the top ten skills required by the top 10 US companies have been changing over time, we get an indication of the Future of Work. Companies are more focused on “soft” skills, that are not easily addressed by AI & Automation.
We are also likely to see a shift from humans adapting to technology to technologies adapting to humans. For example, the acceleration in digital twins combined with advancements in XR could allow unskilled workers to do skilled jobs. AR could guide a worker to repair a piece of mechanical equipment without long years of previous training. Similarly, the emergence of ‘Low Code No Code’ (LCNC) applications will allow ordinary individuals to do tasks that previously required specialised training.
Climate Change
Scientists have long focused our attention to limit the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere to 450 parts per million to avoid catastrophic climate change. In 2016, the World Meteorological Organization reported this concentration had crossed 400 parts per million, leaving us with a shorter runway to prevent calamitous climate change. We are, therefore, likely to see increased efforts to tackle climate change in the decade ahead.
Digital technologies can impact the global climate agenda in multiple ways: smart grids, smart buildings, smart appliances, intelligent transport systems, shared mobility, and 3D printing, to name a few. Digital technologies will also allow new sources of renewable energy to be tapped. For example, the molten core of the earth is over 6,000°C. “Just 0.1% of the heat content of Earth could supply humanity’s total energy needs for 2 million years,” according to AltaRock Energy. Advances in the use of digital technologies that allow for precise directional drilling will allow for advanced geothermal systems to be established as reliable power sources.
Splinternet
Tech bloggers like Doc Searls and Stephen Lewis had begun to theorise about a Splinternet as early as 2008. There was a danger of governments carving the world into geopolitical blocks and creating technology barriers. China’s Great Firewall and the US’s recent responses under the Trump administration are likely to hurtle us in the direction of a fractured internet. We may end up with the US dominating the western internet and China dominating a competing block of countries. The Digital Economy’s evolution would fracture into different camps, making it very different from what it is today.
Tech Regulation
The most valuable companies in the world today are in tech. Seven of the top ten companies in the world by market cap in 2020 are tech companies.
The recent investigation into competition in digital markets undertaken by the US House Judiciary Committee observed: “Over the past decade, the digital economy has become highly concentrated and prone to monopolisation. Several markets investigated by the Subcommittee – such as social networking, general online search, and online advertising – are dominated by just one or two firms. The companies investigated by the Subcommittee – Amazon, Apple, Facebook, and Google – have captured control over key channels of distribution and have come to function as gatekeepers. Just a decade into the future, 30% of the world’s gross economic output may lie with these firms, and just a handful of others.“
We have also witnessed the rapid diversification of data monopolies into other sectors. See, for example, the diversification of VC investments by Alibaba’s Ant Group over time. In 2015 they were investing in 5 areas, which has doubled in the last 5 years.
The call for the regulation of big tech will gain momentum in the coming years. The European Union is likely to lead here, just the way just it did in the case of its General Data Protection Regulation.
Governments will also require data monopolies to share data. China mandates its automakers to share data generated by electric vehicles with a government research institute. This data is essential for public safety and planning battery-recharging stations. The Australian Government promotes the concept of sharing “designated datasets” that could include data held by the private sector that has significant community benefits. Similarly, France’s Law for a Digital Republic requires the sharing data by certain categories of the private sector. Such blurring of boundaries between public and private data will become more important.
We will also see the growing importance of data trusts. These are structures where data is placed in the custody of a “Board of Trustees” who have a fiduciary responsibility to look after the interests of data owners. Such data trusts might give individuals better control over their data.
Every aspect of the economy is being digitalised today. In the next decade we are likely to witness foundational shifts in how the Digital or Data Economy is structured. It will also see increasing risks as cyber threats grow exponentially from cybercriminals and state actors. That the world in 2030 will be very different from today is obvious. We may, however, be surprised by the extent and sweep of the change ahead of us.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Economic Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Economic Summit which will cover topics tied to the state of the economy, path to recovery and re-framing the new financial services landscape











