
Singapore maintains its competitiveness through strong Government support and an environment that encourages trade and investments. The economy sees a huge contribution from start-ups and small and medium enterprises (SMEs), which receives financial incentives and technology guidance from the Government.
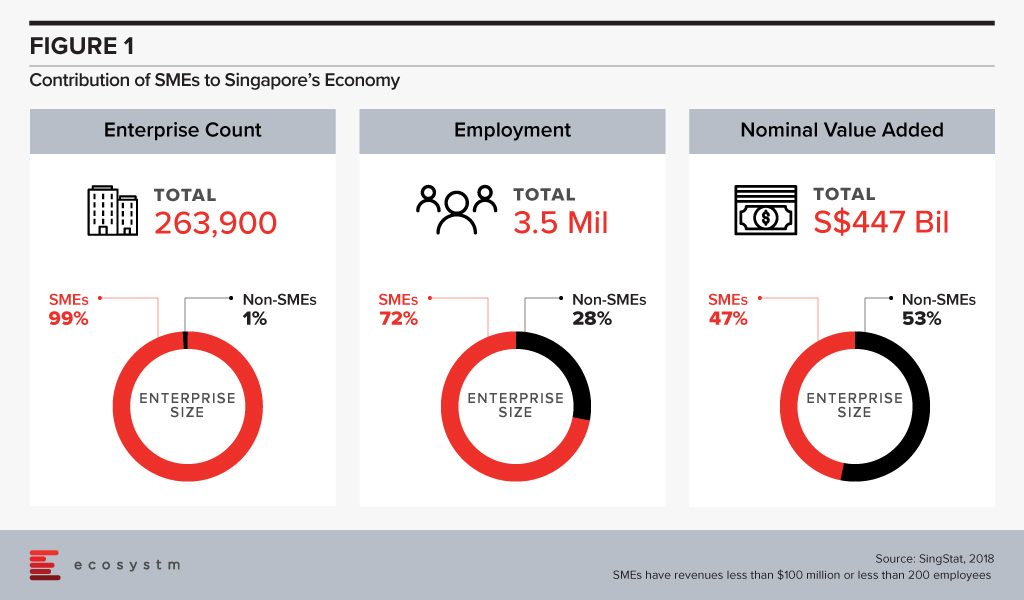
The success of SMEs in Singapore is at the core of national economic growth with approximately 261,000 SMEs contributing to nearly 50% of the country’s GDP.
A survey conducted by United Overseas Bank (UOB) in November 2019 illustrates that SMEs in Singapore are focusing on boosting productivity as they grapple with macro-economic and socio-political uncertainties this year. The UOB survey included 615 local SMEs with a revenue of less than S$100 million. Nearly half of the SMEs surveyed have a positive outlook for their business in 2020, while nearly a third are not so optimistic about it.
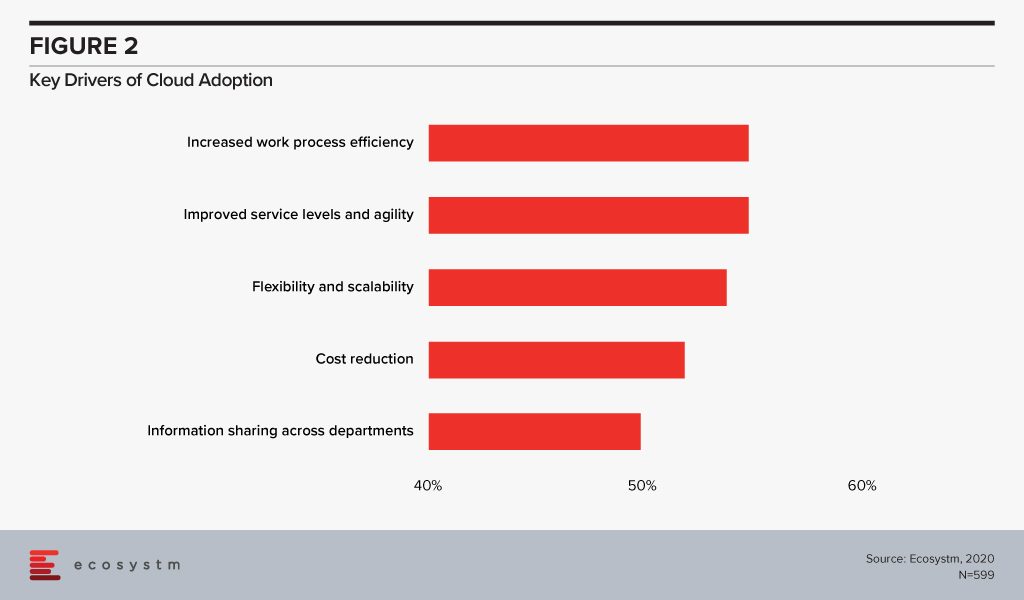
While cost reduction and new streams of revenue generation are top business priorities, more than half of the SMEs polled, mentioned increasing productivity as their top priority. Technology adoption has often been linked to an increase in productivity. SMEs in Singapore appear to be on the right track as currently 65% use digital solutions, mostly geared towards accounting, HR and customer relationship management. Digitalisation involves a widespread adoption of cloud and automation solutions. If we look at the key drivers of cloud adoption across all global organisations (Figure 2), we find that optimisation and productivity are key incentives.
Interestingly, the UOB survey also finds that more than half of SMEs in Singapore have sustainability goals. Resource optimisation and energy efficiency will also see higher adoption of technology in the future.
Government Initiatives Empowering SMEs
Government agencies and industry bodies have always been proactive in empowering SMEs with technological knowledge. There are various programs and initiatives to promote digitalisation, which have made Singapore SMEs competitive at a global level.
The Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) is helping Singapore SMEs to scale and improve their digital capabilities, expand their network and go global through collaboration with multinational companies (MNCs). The SMEs Go Digital program launched in 2017, has seen an estimated 4,000 SMEs adopting pre-approved digital solutions.
Several organisations in Singapore – such as A*Star and Enterprise Singapore – have targeted programs for the SME community. One of the key challenges for SMEs that impacts their ability to invest in technology is a lack of internal IT skills. Initiatives such as the Technology Adoption Programme (TAP) recognise this and bring in multiple industry and technology stakeholders to translate new technologies into Ready-to-Go (RTG) solutions, aimed at SMEs.
Apart from technology, access to financing is a key factor that determines the success of an SME and remains a key focus of Singapore’s banking and financial sector. The digital wholesale licenses are also aimed at SME financing, especially targeting those that are unable to procure funds from traditional sources.
Technologies Enabling Digitalisation in Singapore SMEs
Cloud
As mentioned earlier, cloud is the key enabler of digitalisation, giving organisations the ability to access solutions anywhere and anytime. Ecosystm research shows that 80% of SMEs in Singapore use an IaaS solution, while more than 75% use a SaaS solution.
There are programs that boost cloud adoption in Singapore SMEs as well. As an example, SMECEN, developed by the Association of Small & Medium Enterprises (ASME), and supported by Enterprise Singapore, Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) and Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) is a SaaS solution with accounting, HR and compliance modules – integration with other business tools is on the cards.
AI/Automation
Digitalisation will eventually involve investments in Automation and AI. For Singapore, AI is a key technology as it continues to focus on IoT, smart buildings, smart electricity, autonomous electric vehicles and other smart city solutions. The Government is working to open up access to data and AI tools so everyone can experiment. It especially wants to encourage SMEs to adopt AI and work on government use cases.
Singapore SMEs are ramping up their AI investments, especially in IoT sensor analytics (27%), machine learning (21%) and robotic process automation (16%), according to the Ecosystm AI study. Their key short-term drivers are insights into the competition and enhanced internal process monitoring. However, in the longer term, they are looking at cost reduction and better profit margins.
Fintech
According to an OCBC survey in 2018, which polled 200 such companies, two-thirds of SMEs in Singapore are likely to go cashless by 2023. It is estimated that over 75% of Fintech transactions in Singapore are digital payments and it receives over a quarter of Fintech funding. Government initiatives such as FAST and SGQR, have opened up digital payment options for consumer use as well as for SMEs.
However, the UOB survey notes some concerns that SMEs have over digital payments adoption, including customer/supplier acceptance and security. This is an encouraging sign, which indicates that SMEs are not just adopting technology because of the hype – but are evaluating the pros and cons of tech adoption before embarking on a digitalisation project.








Awesome post! Keep up the great work! 🙂