Innovation is at the core of FinTechs. The Financial Services industry has been disrupted over the last few years because of the innovation and customer experience that FinTechs offer. But the FinTech world has become highly competitive, and there are many companies that do not make it, despite the innovations.
There are many factors that contribute to the success of a FinTech – and creating the right market differentiation is one of the key factors. This Ecosystm Snapshot looks at how FinTechs – such Earnest, Flock, Billd, Littlepay, Willa and AffiniPay – are disrupting industries as they build solutions targeted at those specific industries, to create the market differentiation required to succeed.

The rollout of 5G combined with edge computing in remote locations will change the way maintenance is carried out in the field. Historically, service teams performed maintenance either in a reactive fashion – fixing equipment when it broke – or using a preventative calendar-based approach. Neither of these methods is satisfactory, with the former being too late and resulting in failure while the latter is necessarily too early, resulting in excessive expenditure and downtime. The availability of connected sensors has allowed service teams to shift to condition monitoring without the need for taking equipment offline for inspections. The advent of analytics takes this approach further and has given us optimised scheduling in the form of predictive maintenance.
The next step is prescriptive maintenance in which AI can recommend action based on current and predicted condition according to expected usage or environmental circumstances. This could be as simple as alerting an operator to automatically ordering parts and scheduling multiple servicing tasks depending on forecasted production needs in the short term.
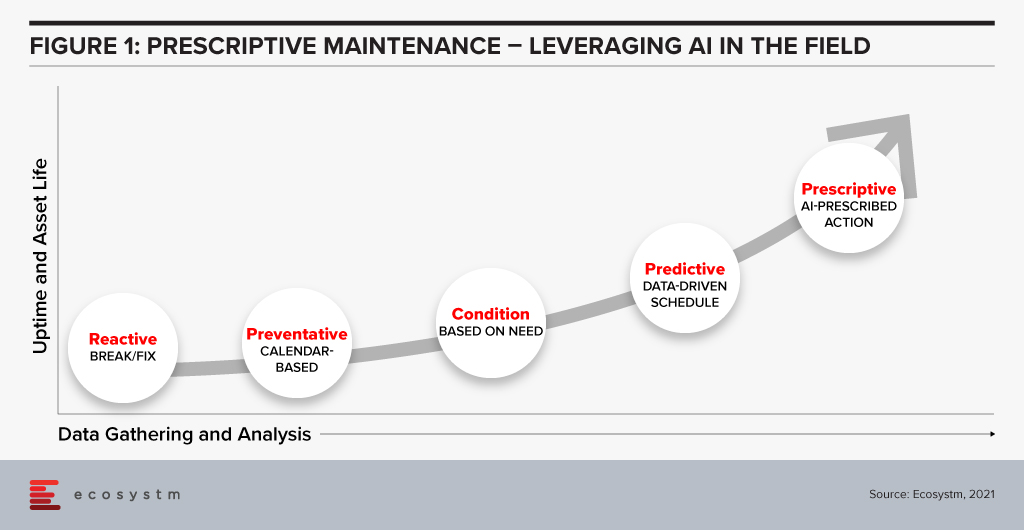
Prescriptive maintenance has only become possible with the advancement of AI and digital twin technology, but imminent improvements in connectivity and computing will take servicing to a new level. The rollout of 5G will give a boost to bandwidth, reduce latency, and increase the number of connections possible. Equipment in remote locations – such as transmission lines or machinery in resource industries – will benefit from the higher throughput of 5G connectivity, either as part of an operator’s network rollout or a private on-site deployment. Mobile machinery, particularly vehicles, which can include hundreds of sensors will no longer be required to wait until arrival before the condition can be assessed. Furthermore, vehicles equipped with external sensors can inspect stationary infrastructure as it passes by.
Edge computing – either carried out by miniature onboard devices or at smaller scale data centres embedded in 5G networks – ensure that intensive processing can be carried out closer to equipment than with a typical cloud environment. Bandwidth hungry applications, such as video and time series analysis, can be conducted with only meta data transmitted immediately and full archives uploaded with less urgency.
Prescriptive Maintenance with 5G and the Edge – Use Cases
- Transportation. Bridges built over railway lines equipped with high-speed cameras can monitor passing trains to inspect for damage. Data-intensive video analysis can be conducted on local devices for a rapid response while selected raw data can be uploaded to the cloud over 5G to improve inference models.
- Mining. Private 5G networks built-in remote sites can provide connectivity between fixed equipment, vehicles, drones, robotic dogs, workers, and remote operations centres. Autonomous haulage trucks can be monitored remotely and in the event of a breakdown, other vehicles can be automatically redirected to prevent dumping queues.
- Utilities. Emergency maintenance needs can be prioritised before extreme weather events based on meteorological forecasts and their impact on ageing parts. Machine learning can be used to understand location-specific effects of, for example, salt content in off-shore wind turbine cables. Early detection of turbine rotor cracks can recommend shutdown during high-load periods.

Data as an Asset
Effective prescriptive maintenance only becomes possible after the accumulation and integration of multiple data sources over an extended period. Inference models should understand both normal and abnormal equipment performance in various conditions, such as extreme weather, during incorrect operation, or when adjacent parts are degraded. For many smaller organisations or those deploying new equipment, the necessary volume of data will not be available without the assistance of equipment manufacturers. Moreover, even manufacturers will not have sufficient data on interaction with complementary equipment. This provides an opportunity for large operators to sell their own inference models as a new revenue stream. For example, an electrical grid operator in North America can partner with a similar, but smaller organisation in Europe to provide operational data and maintenance recommendations. Similarly, telecom providers, regional transportation providers, logistics companies, and smart cities will find industry players in other geographies that they do not naturally compete with.
Recommendations
- Employing multiple sensors. Baseline conditions and failure signatures are improved using machine learning based on feeds from multiple sensors, such as those that monitor vibration, sound, temperature, pressure, and humidity. The use of multiple sensors makes it possible to not only identify potential failure but also the reason for it and can therefore more accurately prescribe a solution to prevent an outage.
- Data assessment and integration. Prescriptive maintenance is most effective when multiple data sources are unified as inputs. Identify the location of these sources, such as ERP systems, time series on site, environmental data provided externally, or even in emails or on paper. A data fabric should be considered to ensure insights can be extracted from data no matter the environment it resides in.
- Automated action. Reduce the potential for human error or delay by automatically generating alerts and work orders for resource managers and service staff in the event of anomaly detection. Criticality measures should be adopted to help prioritise maintenance tasks and reduce alert noise.

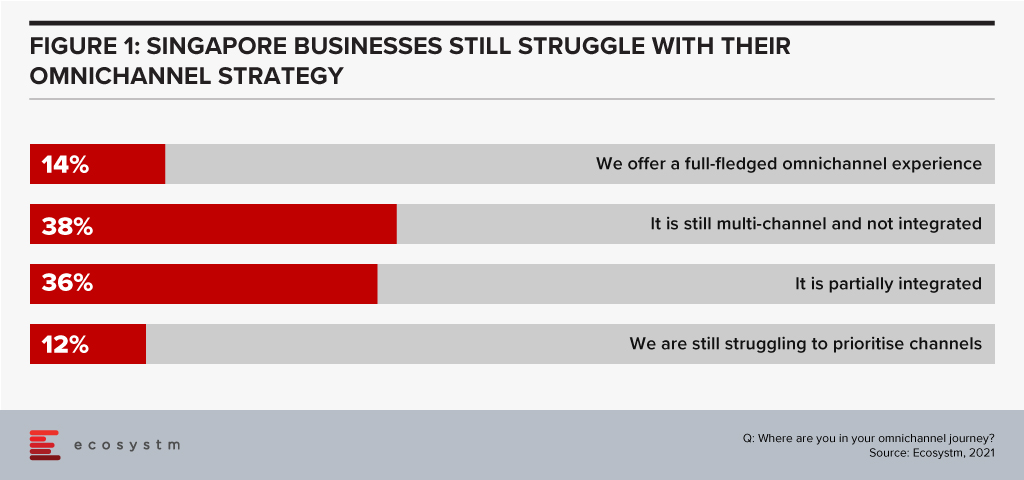
Customer needs are changing. Quickly. In 2020 having a great digital strategy went from being a nice-to-have to an absolute necessity. And in 2021, businesses that have great omnichannel experiences will go from a small minority to a majority as customers demand that they are served on their terms in their chosen platform. Only 14% of businesses in Singapore offer a complete omnichannel experience today – serving customers on their terms regardless of the location or platform (Figure 1). These businesses are setting the benchmark that the rest of the market needs to meet soon.
The Growing Importance of Social Media in Delivering Customer Experience
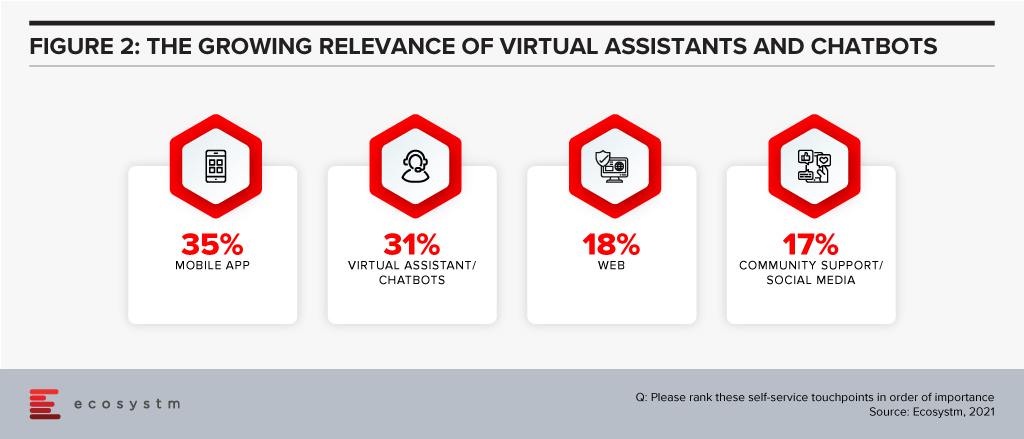
Chat and messaging are quickly becoming the normal way to interact with businesses – the view of a few years ago that “no one wants to chat with a bot” has quickly turned around. Now virtual assistants and chatbots are the second most important self-service channel for businesses in Singapore (Figure 2).
In fact, Zendesk’s global study shows that most customers (45%) use embedded messaging over social messaging apps (31%) and text/SMS (20%). That might be great for self-service, but for commerce, boundless opportunities exist to move to where the customer lives, communicates, and socialises today.
Smart businesses understand that customers spend their lives in other chat and social media platforms – such as Facebook Messenger, TikTok, Instagram, WeChat, Discord and WhatsApp. More customers expect to be served in these channels; they expect to be able to transact with their brands of choice. Why should they go to a mobile banking app to find their balance? Why can’t they get it in WhatsApp? They are often learning about the next Jordan or Yeezy shoe drop from their social network in Messenger – so why not transact with them there? Consider all your own personal WhatsApp, Messenger and other messaging platform groups discussing social activities, sporting teams, school activities or the latest fashion – these are ALL opportunities for commerce (Figure 3).

And there are use cases now. Airlines – such as KLM and Etihad Airways – are engaging customers on WeChat, Kakao Talk, and WhatsApp, helping them reschedule flights and answering customer service queries. Telecommunications providers are allowing customers to raise issues on messaging platforms – and are also using them to upsell and cross-sell new services. Transportation providers are making it easier to find a car or the the next scheduled bus right there in the messaging platforms. Retailers – such as 1-800 Flowers and Culture Kings – are not only serving customers but finding new customers on these messaging platforms.
Going beyond the messaging platforms, businesses are also looking to serve customers on their smart devices – such as Amazon Alexa/Echo and Google Nest/Home devices. Alerting customers to order updates, shipping details and product promotions is becoming standard practice for leading businesses. Digitally-savvy banks are allowing customers to not only track their balance but also make transfers and payments using these smart platforms.
Customers are more comfortable with these conversational commerce options – and they actually expect you to offer such services on your site, in your app, on their smart devices, and on their messaging platforms of choice. Your ability to provide outstanding customer experiences will not only be your ticket back to revenue growth but the recipe for long term business success. Meeting customer needs on their terms is a good place to start.
Delivering a Personalised Conversational Customer Experience
Customer experience (CX) decision-makers will have to rethink how they approach building richer CX capabilities to deliver personalised conversational interactions with customers.
Messaging should become part of a wider AI, Data, and Mobile strategy. Contact centre teams might feel that this is too ambitious a project and would prefer to continue to serve customers through the more traditional channels only. So, it is important to identify the key stakeholder/s who will drive the initiative. And the contact centre team should work with the Digital, Innovation and Marketing teams.
Designing the mobile experience and in app messaging for CX should have some of the following features:
- Ability to click a button to request for a service or escalate an issue that will, in turn, result in the company contacting the customer either by messaging or calling.
- Giving customers the option to contact through popular messaging platforms such as Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, LINE, WeChat, and others. Unifying these systems in a single interface that integrates with your customer service application is best practice.
- Having one single interface to manage and make payments – within the app itself or on the social messaging platform. Conversational commerce is about creating an ongoing relationship with customers throughout the entire customer journey. Don’t just focus on the sale or the post-sales experience – customers expect to be able to interact with your business from their platform of choice regardless of their need or stage in the customer journey.
- Embed deep analytics into the communication services to help the organisation better deliver a personalised CX.
- Ensure you have a solid, unified knowledge management interface at the backend so that all questions lead to the same answers regardless of channel, platform or touchpoint.
Your opportunity to drive greater business success lies in your ability to better win, serve and retain your customers. Refresh your customer strategy and capability today to make 2021 an exceptional year for your business.
















