In this Insight, guest author Anupam Verma talks about how a smart combination of technologies such as IoT, edge computing and AI/machine learning can be a game changer for the Financial Services industry. “With the rise in the number of IoT devices and increasing financial access, edge computing will find its place in the sun and complement (and not compete) with cloud computing.”

The number of IoT devices have now crossed the population of planet earth. The buzz around the Internet of Things (IoT) refuses to go down and many believe that with 5G rollouts and edge computing, the adoption will rise exponentially in the next 5 years.
The IoT is described as the network of physical objects (“things”) embedded with sensors and software to connect and exchange data with other devices over the internet. Edge computing allows IoT devices to process data near the source of generation and consumption. This could be in the device itself (e.g. sensors), or close to the device in a small data centre. Typically, edge computing is advantageous for mission-critical applications which require near real-time decision making and low latency. Other benefits include improved data security by avoiding the risk of interception of data in transfer channels, less network traffic and lower cost. Edge computing provides an alternative to sending data to a centralised cloud.
In the 5G era, a smart combination of technologies such as IoT, edge computing and AI/machine learning will be a game changer. Multiple uses cases from self-driving vehicles to remote monitoring and maintenance of machinery are being discussed. How do we see IoT and the Edge transforming Financial Services?
Before we go into how these technologies can transforming the industry, let us look at current levels of perception and adoption (Figure 1).
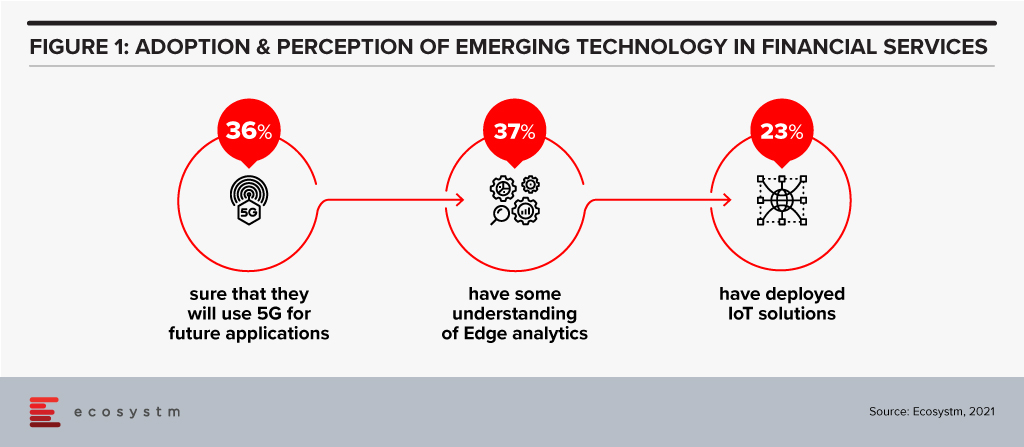
There is definitely a need for greater awareness of the capabilities and limitations of these emerging technologies in the Financial Services.
Transformation of Financial Services
The BFSI sector is increasingly moving away from selling a product to creating a seamless customer journey. Financial transactions, whether it is payment, transfer of money, or a loan can be invisible, and Edge computing will augment the customer experience. This cannot be achieved without having real-time data and analytics to create an updated 360-degree profile of the customer at all times. This data could come from multiple IoT devices, channels and partners that can interface and interact with the customer. A lot of use cases around personalisation would not be possible without edge computing. The Edge here would mean faster processing and smoother experience leading to customer delight and a higher trust quotient.
With IoT, customers can bank anywhere anytime using connected devices like wearables (smartwatches, fitness trackers etc). People can access account details, contextual offers at their current location or make payments without even needing a smartphone.

Use Cases of IoT & Edge in Financial Services
IT and Digital Leaders in Financial Services are aware of the benefits of IoT and there are some use cases that most of them think will help transform Financial Services (Figure 2).
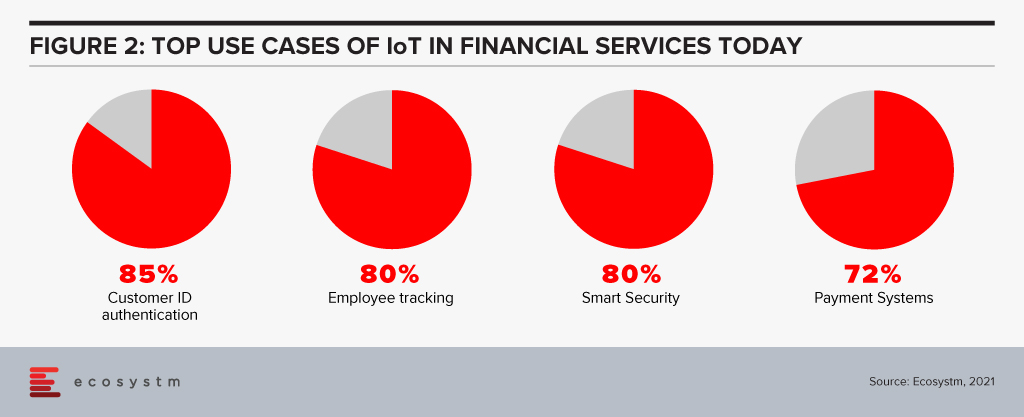
However, there are many more potential use cases. Here are some use cases whose volume will only grow every day to fuel incessant data generation, consumption and processing at the Edge.
- Smart Homes. IoT devices like Alexa/Google Home have capabilities to become “bank in a speaker” with edge computing.
- In-Sync Omnichannels. IoT devices can be synced with other banking channels. A customer may start a transaction on an IoT device and complete it in a branch. Facial recognition can be used to identify the customer after he/she walks in and synced IoT devices will ensure that the transaction is completed without any steps repeated (zero re-work) thereby enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Virtual Relationship Managers. In a digital branch, the customer may use Virtual Reality (VR) headsets to engage with virtual relationship managers and relevant experts. Gamification using VR can be amazingly effective in the area of financial literacy and financial planning.
- Home and Auto Purchase. VR may also find use in home and auto purchase processes with financing built into it. The entire customer journey will have a much smoother experience with edge computing.
- Auto and Health Insurance. Companies can use IoT (device installed in the vehicle) plus edge computing to monitor and improve driving behaviour, eventually rewarding safety with lower premiums. The growth in electric mobility will continue to provide the basis for auto insurance. Companies can use wearables to monitor crucial health parameters and exercising habits. The creation of real-time dynamic rewards around it can change behaviour towards a healthier lifestyle. Awareness, longevity, rising costs and pandemic will only fuel this sector’s growth.
- Payments. Device to device contactless payment protocol is picking up and IoT and edge computing can create next-gen revolution in payments. Your EV could have an embedded wallet and pay for its parking and toll.
- Branch/ATM. IoT sensors and CCTV footage from branches/ATMs can be utilised in real-time to improve branch productivity as well as customer engagement, at the same time enhancing security. It could also help in other situations like low cash levels in ATMs and malfunctions. Sending live video streams for video analytics to the cloud can be expensive. By processing data within the device or on-premises, the Edge can help lower costs and reduce latency.
- Trading in Securities. Another area where response time matters is algorithmic trading. Edge computing will help to quickly process and analyse a large amount of data streaming real-time from multiple feeds and react appropriately.
- Trade Finance. Real-time tracking of goods may add a different dimension to the risk, pricing and transparency of supply chains.
Cloud vs Edge
The decision to use cloud or edge will depend on multiple considerations. At the same time, all the data from IoT devices need not go to the cloud for processing and choke network bandwidth. In fact, some of this data need not be stored forever (like video feeds etc). As a result, with the rise in the number of IoT devices and increasing financial access, edge computing will find its place in the sun and complement (and not compete) with cloud computing.
The views and opinions mentioned in the article are personal.
Anupam Verma is part of the Leadership team at ICICI Bank and his responsibilities have included leading the Bank’s strategy in South East Asia to play a significant role in capturing Investment, NRI remittance, and trade flows between SEA and India.

The ongoing global crisis is expected to drive more investments in Fintech, especially in the area of digital payments, as more organisations and consumers adopt eCommerce. Fintech will also continue to grow in areas such as Regtech and Blockchain for ease of reporting and enhanced transaction security.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Paul Gestro says, “In the environment, we find ourselves in now – and will be for some time – we have likely already switched to a number of new online channels, or at the very least increased the use of them. Fintech has played a big role already with online shopping & delivery, contactless payments and the general reduction in face to face transacting. Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) may gain the most as Fintech has enabled credit to be approved and distributed faster, either by banks or governments.”
“Fintech have been able to develop bespoke applications based on their open platforms to provide immediate channels to get much-needed capital flowing through the economy. Governments have often turned to the Fintechs first rather than traditional financial institutions. If Fintechs can still access investment capital to survive and keep growing, they will continue to disrupt the intermediaries across all sectors. It is yet to be seen if this will accelerate or be curtailed, but that will depend on how the financial institutions react to whatever the new normal will be.”
The Role of Blockchain in Financial Services
Talking about the role of Blockchain in Financial Services, Gestro says, “Overall Blockchain will lead to a more open and interconnected economy that is borderless, transparent and does not need counter-party trust to operate. To date, banks and other financial institutions have been the intermediary to make this happen but, in many areas, it can be slow and costly. Blockchain has the advantage of eliminating the intermediary or ‘middleman’.”
“One particular area is the use of ‘Smart Contracts’. Financial contracts involve legal work, document handling, sighting, signing and sending them to the right people. All of this involves both time and people and proves to be an expensive option eventually. Blockchain can speed this process up in a secure (with no failure points), interoperable and risk-free environment. Trade finance, lending and Islamic Banking are all potential areas that will benefit immensely.”
However, Gestro also extends a word of caution. “On paper, a cross-border Blockchain ecosystem makes perfect sense. However financial institutions have strict and long-standing governance and compliance boundaries that do not make it so easy to ‘switch’ to Blockchain overnight. The entire rationale of Blockchain is decentralising the legacy of competing rules and regulations and different agendas – this would mean that without a decision-maker, bottlenecks will form,” says Gestro. “On the other hand, financial institutions have also developed rapid transactional processing capability and Blockchain technology may be a long way from replicating that speed. So, even though Blockchain will prove immensely beneficial, scalability, risk management and compliance are the three areas that are inhibiting financial institutions from a full-blown adoption.”
Blockchain in Islamic Banking
One of the key benefits of Fintech is to drive financial inclusion. This is particularly true when it comes to widespread access to Islamic Banking facilities. With Fintech, Islamic Banking becomes more accessible to a larger population who do not bank because the banking and financial practices are not Shariah-compliant. Gestro sees a clear role of Blockchain in Islamic Banking. “The two key principles of Islamic Banking are the sharing of profit/loss and the prohibition of interest collection/payment. A key principle of Blockchain finance is smart contracts. With smart contracts, the entire contractual process can be automated quickly and transparently with the terms of each contract enforced as it should. A smart contract will be in compliance with the Shariah objective of ensuring transparency in a deal with clear asset definitions, payment terms and enforcement – all aligned with the principles of trust.”
UAE has been the hub of global Islamic financial services and there have been a few initiatives in 2019 to drive the adoption of Fintech in Banking and Financial Services. Etisalat Digital – the digital arm of Etisalat focused on transformational technologies – has developed the UAE Trade Connect (UTC), a nationwide platform that uses disruptive technologies to digitalise trade in the UAE. The initial phase will focus on addressing the risks of double financing and invoice fraud before turning to other key areas of trade finance. Created in partnership with First Abu Dhabi Bank (FAB) and Avanza Innovations, the platform has since seen the participation of 7 other major banks in the UAE. The goal of UTC is to drive transformation in trading practices by enabling banks, enterprises and governments to collaboratively evaluate technologies such as Blockchain, AI, machine learning and robotics.
Later in the year, during the Middle East Banking Forum in Abu Dhabi, the Central Bank of the UAE (CBUAE) announced the formation of a Fintech office to develop countrywide regulations for financial technology firms. The country has clearly been evaluating Fintech as a means of growth in the financial sector. Last week, the Abu Dhabi Islamic Bank (ADIB), in the UAE announced that they had successfully executed a Digital Ledger Technology (DLT) trade transaction with TradeAssets, a trade finance e-marketplace powered by Blockchain technology. It became the first Islamic Bank to transact on DLT.
As the global Islamic banking market heats up – with countries such as Malaysia openly vying to be a market leader – we will see higher adoption of Regtech and Blockchain in this sector.
Blockchain in China’s Financial Industry
Gestro says, “China is at the forefront of Blockchain technology development. Xi Jinping has announced that Blockchain is one of China’s technological priorities with the impending launch of the Blockchain Service Network (BCN). This is similar to the Belt and Road Initiative to provide infrastructure for the world to use, be a first mover and gain a strong foothold. It is no coincidence that China has filed the most Blockchain patents in the world. It has the collective power of the banking system, telecommunications behemoths and internet giants – all collaborating to realise China’s Blockchain vision.”
Last year, China unveiled plans to adopt and develop Blockchain to reduce banking fraud, offer secure loans, and streamline transactions in the financial industry. A Blockchain committee called the National Blockchain and Distributed Accounting Technology Standardisation Technical Committee was set up to explore the possibilities. The primary goal of the committee is to set standards for the adoption of Blockchain and involved big tech companies, such as Huawei, Tencent, Baidu, Ant Financial Services, and JD.com.
Ant Financial Services – Alibaba’s Fintech arm – recently created a new consortium Blockchain platform called Open Alliance Chain aimed at SMEs and developers. The available Blockchain tools would be able to help supply chain, invoices, donations, financial transactions and promote various other Blockchain uses across financial services.
There appears to be an interest in global financial services around Blockchain. It will be interesting to watch this space to see if Blockchain adoption in the Financial Services industry becomes mainstream, as the global economy adjusts to the new normal.



