As technology vendors, their channel partners and organisations deal with the tech talent crunch, there are consequences for the entire technology ecosystem. Vendor solutions are less impactful than their potential; their channel partners are losing a lot of time in closing sales cycles and their customers are left with sub-optimal deployments.
Here is how vendors and their channel partners can bridge the gap:
Re-evaluating Certification Programs
The first step is to move to a case-based training model with the participant needing to respond to a situation rather than answering multiple-choice questions. We do not discount the usefulness of standard testing, but it needs to be mixed with evaluating the situational awareness and subjective understanding of the participant. This will require more detailed answers and case studies and will require a knowledgeable evaluator at the other end who will need more time than that required to assess MCQ answers. While AI tools are starting to address this, for now, this means a fairly large investment in resources.

While giving the tech talent – whether Sales or Delivery – a greater context of competitors’ strengths will give them a better chance to win deals, it has the potential to open up a host of issues that are best avoided. However, part of that knowledge can be provided as a general solution context – focusing on customer benefits in doing a certain transition and the kind of use cases that would be most appropriate for each transition. This will require, in most cases, a redesign of the curriculum.
Rethinking Partner Sales Support
A much bigger initiative by the vendors could be to set up sales support specialist groups within their own organisations that can be booked for customer meetings by channel partners. This has become easier now with most organisations being quite accustomed to video conferences and virtual meetings.
The set-up of such a “centre” will require careful planning, expertise, and investment in systems. Most vendors do have something like this for escalations and technical support, but few have a comprehensive program to assist with sales opportunities.

The resources at these centres should be highly specialised and well-paid. This will add cost. However, a group like this can pay for itself as long as more deals are converted. We do not recommend using gold-plated costs, but penny pinching, especially on the quality of resources and systems used here will be a classic case of penny wise, pound foolish. Success here will come from increasing revenue, not decreasing cost.
Clarifying Hiring Policies
Finally, vendors need to be clear about the policies of hiring staff from their channel partners. It is unlikely that this practice is going to stop. For one, if they don’t hire these talents, their competitors might. And channel partners often attract more talent if they are able to hold out the carrot, that the employee can eventually get employed by the vendor.
However, there should be clearer policies, such as only hiring those who have spent a minimum specified time with the partner; providing a longer than normal off-ramp period; seconding the talent to the channel partner for a period during which the employee gets additional training on the vendor’s solutions while working for the channel partner. Incentivising channel partners for providing successful candidates might also be a good idea.
Having bad policies, an attitude of poaching or not cooperating just leads to the channel partners underinvesting in people which harms the vendor as well as the channel. Innovative strategies here can deliver a solution where the channel partner is able to attract better talent and manage the talent while they are in their formative stages. Essentially, they are rewarded for incubating talent. The best talent eventually “graduate” to working for the vendor. This will be a true win-win for both.
Making Upskilling a Norm
The leadership of channel partner organisations need to embrace upskilling of their teams. Employees need technological capability building as well as certification.
Upskilling is a slower burn process than some of the steps discussed earlier, but for partners, this is the key. Partners will need help to put together a full program that nurtures employees at different levels of experience and capability and builds them up with a step-by-step approach. This is actually the job of a full-fledged Learning and Development organisation. Very few partners today either invest in such an organisation or have the ability to work this into their HR practices.
Finding an outsourced partner who can help to design and implement such a program might be the way to go. There is also an opportunity here for multiple channel partners to coordinate and engage one agency, in effect paying to hire an outsider as a joint Chief Learning Officer for all their companies.

In an exploding market where the skill of the employee can land the extra contracts, reel in the customers, whose lifetime value can be enormous, upskilling is vital – it is not really a choice.
Conclusion
There is a need to do things differently and to invest a lot more in talent. In a growing market, channel partners are getting by as revenue is moving upwards anyway. A smart step-by-step investment approach, however, can dramatically change this growth trajectory. That will alter the fortunes of the vendors too. Maintaining the status quo and not spending more on tech talent is actually a poison pill – the market growth is just hiding that fact.

Digital and IT organisations are going through some dramatic changes as they adopt cloud and as-a-service capabilities. In this post, I want to write about two of these – one that is very much a consequence of the other.
Contract Numbers are Exploding
We’re seeing an explosion in the number of IT suppliers to a typical organisation.
Pre-cloud, the typical organisation probably had five to ten contracts that covered most of the external services that were in use. With suppliers increasingly providing niche functionality and the increased use of credit cards to buy external services, it is often difficult to determine exactly how many contracts are in place. Or, indeed, have a clear understanding of the terms and conditions of each of these contracts.
Where once an organisation might have had contracts for an on-premises ERP and CRM system, a typical organisation will still have those contracts as well as a supply chain forecasting service, a marketing email management tool, not to mention online spreadsheets and task management capabilities.
So with many more contracts in place, the complexity of managing these contracts and understanding the technical, legal and business risks encapsulated in these contracts has become dramatically more difficult.
I’ll return to this point in a later post, as most organisations struggle with this increasing complexity.
What Is Happening to Your People?
The existence of these contracts means that you are increasingly becoming dependent on the people employed by these external organisations. But when you sign up for these contracts, do you investigate how these suppliers develop their talent?
The New Zealand Herald recently carried an interesting article on one organisation that has developed a paid intern program. Something very rare in the industry.
The article prompted me to think through some of the implications of using cloud services. Tech buyer organisations will have less need for technical capabilities as increasingly these are delivered by the cloud suppliers.
But the growth in demand for digital and IT skills just continues to increase as more and more industries digitalise. In the past, tech buyer organisations would have invested (at least the good employers did!) in the development of their people. The cloud suppliers are increasingly doing this talent development.
Most contract negotiations are based on cost, quality and customer service. A significant proportion of cloud contracts are now boilerplate – you pay with a credit card for a monthly service and have little or no ability to negotiate terms and conditions.
The trade-off is required to get a short commitment term and a variable cost profile. No tech vendor can afford to negotiate bespoke contracts for this type of commercial arrangement.
This situation leaves the question of how tech buyers can influence tech vendors to develop their people’s talent appropriately. Some would say that the tech vendors will do this as a matter of course, but the statistics, as highlighted in the Ecosystm research data in Figure 1, show that we are not bringing people in at the rate the industry requires.
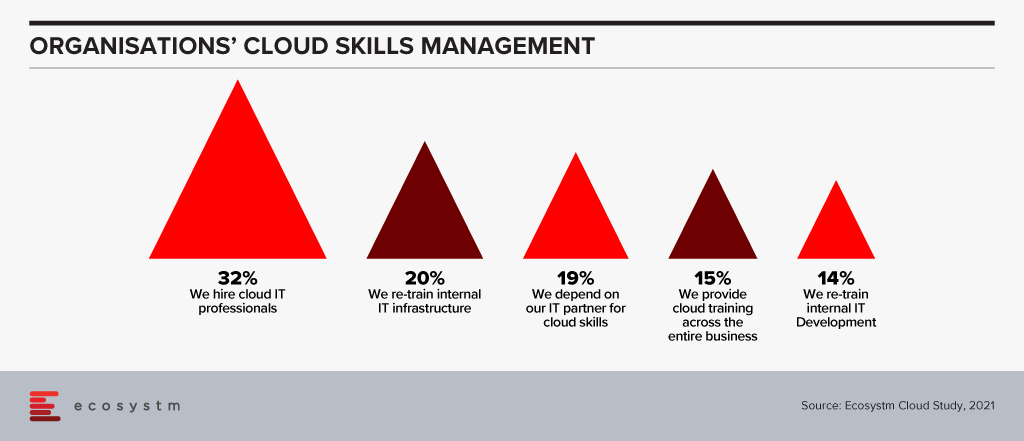
Advice for Tech Buyers
I recommend you look closely at using two tactics with the tech vendors that you are working with:
- First, look to consolidate as much workload as practical under a single contract with the supplier. This is not a new recommendation for contracts – but with the increasing use of boilerplate contracts, it is one of the few ways an organisation can increase its value and importance to a tech vendor.
- Second, start finding those tech vendors that are developing new and existing talent in practical ways and favour these organisations in any purchase decision.
Most organisations, individually, do not have the commercial power to dictate terms to the cloud providers. Still, if enough tech buyers adopt this critical criterion, the cloud providers may see the value in investing in the industry’s talent development in meaningful ways.
The downside? Talent development does not come free. Tech buyers may need to pay a higher fee to encourage the suppliers but paying a low-cost provider who does not develop their talent sounds like a recipe for poor quality service.
If you would like to discuss any of these thoughts or issues further, please feel free to reach out and contact me. This is an industry issue and one for our broader society, so I would be interested in hearing how your organisations are addressing this challenge.




