Earlier this month, I had the privilege of attending Oracle’s Executive Leadership Forum, to mark the launch of the Oracle Cloud Singapore Region. Oracle now has 34 cloud regions worldwide across 17 countries and intends to expand their footprint further to 44 regions by the end of 2022. They are clearly aiming for rapid expansion across the globe, leveraging their customers’ need to migrate to the cloud. The new Singapore region aims to support the growing demand for enterprise cloud services in Southeast Asia, as organisations continue to focus on business and digital transformation for recovery and future success.
Here are my key takeaways from the session:
#1 Enabling the Digital Futures
The theme for the session revolved around Digital Futures. Ecosystm research shows that 77% of enterprises in Southeast Asia are looking at technology to pivot, shift, change and adapt for the Digital Futures. Organisations are re-evaluating and accelerating the use of digital technology for back-end and customer workloads, as well as product development and innovation. Real-time data access lies at the backbone of these technologies. This means that Digital & IT Teams must build the right and scalable infrastructure to empower a digital, data-driven organisation. However, being truly data-driven requires seamless data access, irrespective of where they are generated or stored, to unlock the full value of the data and deliver the insights needed. Oracle Cloud is focused on empowering this data-led economy through data sovereignty, lower latency, and resiliency.
The Oracle Cloud Singapore Region brings to Southeast Asia an integrated suite of applications and the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) platform that aims to help run native applications, migrate, and modernise them onto cloud. There has been a growing interest in hybrid cloud in the region, especially in large enterprises. Oracle’s offering will give companies the flexibility to run their workloads on their cloud and/or on premises. With the disruption that the pandemic has caused, it is likely that Oracle customers will increasingly use the local region for backup and recovery of their on-premises workloads.
#2 Partnering for Success
Oracle has a strong partner ecosystem of collaboration platforms, consulting and advisory firms and co-location providers, that will help them consolidate their global position. To begin with they rely on third-party co-location providers such as Equinix and Digital Realty for many of their data centres. While Oracle will clearly benefit from these partnerships, the benefit that they can bring to their partners is their ability to build a data fabric – the architecture and services. Organisations are looking to build a digital core and layer data and AI solutions on top of the core; Oracle’s ability to handle complex data structures will be important to their tech partners and their route to market.
#3 Customers Benefiting from Oracle’s Core Strengths
The session included some customer engagement stories, that highlight Oracle’s unique strengths in the enterprise market. One of Oracle’s key clients in the region, Beyonics – a precision manufacturing company for the Healthcare, Automotive and Technology sectors – spoke about how Oracle supported them in their migration and expansion of ERP platform from 7 to 22 modules onto the cloud. Hakan Yaren, CIO, APL Logistics says, “We have been hosting our data lake initiative on OCI and the data lake has helped us consolidate all these complex data points into one source of truth where we can further analyse it”.
In both cases what was highlighted was that Oracle provided the platform with the right capacity and capabilities for their business growth. This demonstrates the strength of Oracle’s enterprise capabilities. They are perhaps the only tech vendor that can support enterprises equally for their database, workloads, and hardware requirements. As organisations look to transform and innovate, they will benefit from the strength of these enterprise-wide capabilities that can address multiple pain points of their digital journeys.
#4 Getting Front and Centre of the Start-up Ecosystem
One of the most exciting announcements for me was Oracle’s focus on the start-up ecosystem. They make a start with a commitment to offer 100 start-ups in Singapore USD 30,000 each, in Oracle Cloud credits over the next two years. This is good news for the country’s strong start-up community. It will be good to see Oracle build further on this support so that start-ups can also benefit from Oracles’ enterprise offerings. This will be a win-win for Oracle. The companies they support could be “soonicorns” – the unicorns of tomorrow; and Oracle will get the opportunity to grow their accounts as these companies grow. Given the momentum of the data economy, these start-ups can benefit tremendously from the core differentiators that OCI can bring to their data fabric design. While this is a good start, Oracle should continue to engage with the start-up community – not just in Singapore but across Southeast Asia.
#5 Commitment to Sustainability at the Core of the Digital Futures
Another area where Oracle is aligning themselves to the future is in their commitment to sustainability. Earlier this year they pledged to power their global operations with 100% renewable energy by 2025, with goals set for clean cloud, hardware recycling, waste reduction and responsible sourcing. As Jacqueline Poh, Managing Director, EDB Singapore pointed out, sustainability can no longer be an afterthought and must form part of the core growth strategy. Oracle has aligned themselves to the SG Green Plan that aims to achieve sustainability targets under the UN’s 2030 Sustainable Development Agenda.
Cloud infrastructure is going to be pivotal in shaping the future of the Digital Economy; but the ability to keep sustainability at its core will become a key differentiator. To quote Sir David Attenborough from his speech at COP26, “In my lifetime, I’ve witnessed a terrible decline. In yours, you could and should witness a wonderful recovery”
Conclusion
Oracle operates in a hyper competitive world – AWS, Microsoft and Google have emerged as the major hyperscalers over the last few years. With their global expansion plans and targeted offerings to help enterprises achieve their transformation goals, Oracle is positioned well to claim a larger share of the cloud market. Their strength lies in the enterprise market, and their cloud offerings should see them firmly entrenched in that segment. I hope however, that they will keep an equal focus on their commitment to the start-up ecosystem. Most of today’s hyperscalers have been successful in building scale by deeply entrenching themselves in the core innovation ecosystem – building on the ‘possibilities’ of the future rather than just on the ‘financial returns’ today.

Recognising FinTechs that are changing lives, creating impact, demonstrating innovation, and building ecosystems to shape the Digital Future.
CATEGORIES:
Global Platform. Organisations that provide a platform to bring together industry stakeholders such as financial services institutions and FinTechs to drive ease of collaboration and innovation by accelerating proof of concept deployments
Financial Inclusion Impact. Organisations that promote financial inclusion in the unbanked and the underbanked with a focus on bridging the economic divide
Sustainable Finance Impact. Organisations that promote sustainable finance and have ESG values
Global Banking. Banks and financial services organisations that embrace digital technology for excellence in customer experience, process efficiency and/or compliance
Global Payments. Innovative use of technology and business models in payment areas
Global Lending. Innovation in alternative finance in areas such as microfinance for individuals and small & medium enterprises, P2P lending and crowdfunding
Customer Experience. Organisations that are driving an exceptional experience for their customers and setting new benchmarks within the industry
Global InsureTech. Excellence and innovation in InsureTech in areas such as micro-insurance, usage-based pricing, process optimisation and underwriting efficiency
To find out about the winners, read on.
To download Ecosystm Red: Global Digital Futures Awards for FinTech Awards Winners as a PDF, please click here.
Our financial system plays a central role in crystallising priorities and incentives for businesses and other stakeholders across the globe. So, many of us breathed a sigh of relief as the financial community got behind the Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) movement in recent years, signalling a very visible acceleration in ESG as a hot button issue for investors and lenders.
Unfortunately, the growth of ESG as a priority for investors, lenders and consumers has driven many companies to oversell their green and/or social credentials in order to burnish their brands and attract investment. This is referred to as “greenwashing” and “social washing”.
As sustainability becomes a critical pillar for investors and consumers in their decision-making, data, analytics and technology play an increasingly critical role in enabling better decisions based on credible, accurate and more real-time information.
Read on to find out the three themes for technology enablement in sustainable finance, together with examples and potential use cases including companies such as IBM, Triodos Bank, Alipay, Floodmapp, and Data Gumbo.

We are seeing a rise in social and environmental consciousness – especially in the younger generation. Their awareness of human rights, the environment and inclusion is growing exponentially – they want to create impact. Organisations are being driven to develop and demonstrate an Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) consciousness in their actions and investments.
In this Ecosystm Snapshot, we cover some of the recent examples of how governments and individual advocates are creating a difference; and how financial organisations and tech providers are embracing ESG.
Read how organisations such as Sun Cable, Equinix, Microsoft, NVIDIA, Prologis, Zensung, Ergo, Munich Re, Natwest, JPMorgan, Credit Suisse and others are working to make the world a better place.

The disruption that we faced in 2020 has created a new appetite for adoption of technology and digital in a shorter period. Crises often present opportunities – and the FinTech and Financial Services industries benefitted from the high adoption of digital financial services and eCommerce. In 2021, there will be several drivers to the transformation of the Financial Services industry – the rise of the gig economy will give access to a larger talent pool; the challenges of government aid disbursement will be mitigated through tech adoption; compliance will come sharply back into focus after a year of ad-hoc technology deployments; and social and environmental awareness will create a greater appetite for green financing. However, the overarching driver will be the heightened focus on the individual consumer (Figure 1).
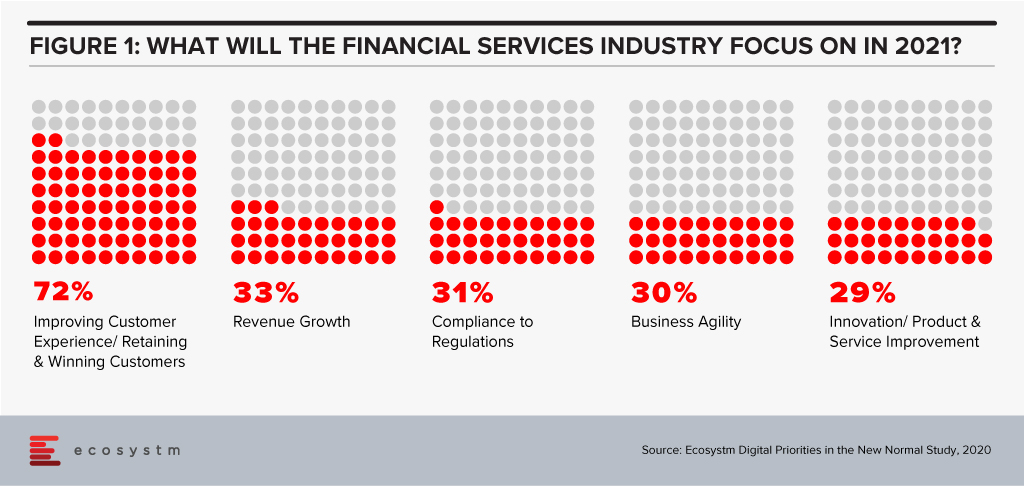
2021 will finally see consumers at the core of the digital financial ecosystem.
Ecosystm Advisors Dr. Alea Fairchild, Amit Gupta and Dheeraj Chowdhry present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for FinTech in 2021 – written in collaboration with the Singapore FinTech Festival. This is a summary of the predictions; the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform.
The Top 5 FinTech Trends for 2021
#1 The New Decade of the ‘Empowered’ Consumer Will Propel Green Finance and Sustainability Considerations Beyond Regulators and Corporates
We have seen multiple countries set regulations and implement Emissions Trading Systems (ETS) and 2021 will see Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) considerations growing in importance in the investment decisions for asset managers and hedge funds. Efforts for ESG standards for risk measurement will benefit and support that effort.
The primary driver will not only be regulatory frameworks – rather it will be further propelled by consumer preferences. The increased interest in climate change, sustainable business investments and ESG metrics will be an integral part of the reaction of the society to assist in the global transition to a greener and more humane economy in the post-COVID era. Individuals and consumers will demand FinTech solutions that empower them to be more environmentally and socially responsible. The performance of companies on their ESG ratings will become a key consideration for consumers making investment decisions. We will see corporate focus on ESG become a mainstay as a result – driven by regulatory frameworks and the consumer’s desire to place significant important on ESG as an investment criterion.
#2 Consumers Will Truly Be ‘Front and Centre’ in Reshaping the Financial Services Digital Ecosystems
Consumers will also shape the market because of the way they exercise their choices when it comes to transactional finance. They will opt for more discrete solutions – like microfinance, micro-insurances, multiple digital wallets and so on. Even long-standing customers will no longer be completely loyal to their main financial institutions. This will in effect take away traditional business from established financial institutions. Digital transformation will need to go beyond just a digital Customer Experience and will go hand-in-hand with digital offerings driven by consumer choice.
As a result, we will see the emergence of stronger digital ecosystems and partnerships between traditional financial institutions and like-minded FinTechs. As an example, platforms such as the API Exchange (APIX) will get a significant boost and play a crucial role in this emerging collaborative ecosystem. APIX was launched by AFIN, a non-profit organisation established in 2018 by the ASEAN Bankers Association (ABA), International Finance Corporation (IFC), a member of the World Bank Group, and the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS). Such platforms will create a level playing field across all tiers of the Financial Services innovation ecosystem by allowing industry participants to Discover, Design and rapidly Deploy innovative digital solutions and offerings.
#3 APIfication of Banking Will Become Mainstream
2020 was the year when banks accepted FinTechs into their product and services offerings – 2021 will see FinTech more established and their technology offerings becoming more sophisticated and consumer-led. These cutting-edge apps will have financial institutions seeking to establish partnerships with them, licensing their technologies and leveraging them to benefit and expand their customer base. This is already being called the “APIficiation” of banking. There will be more emphasis on the partnerships with regulated licensed banking entities in 2021, to gain access to the underlying financial products and services for a seamless customer experience.
This will see the growth of financial institutions’ dependence on third-party developers that have access to – and knowledge of – the financial institutions’ business models and data. But this also gives them an opportunity to leverage the existent Fintech innovations especially for enhanced customer engagement capabilities (Prediction #2).
#4 AI & Automation Will Proliferate in Back-Office Operations
From quicker loan origination to heightened surveillance against fraud and money laundering, financial institutions will push their focus on back-office automation using machine learning, AI and RPA tools (Figure 3). This is not only to improve efficiency and lower risks, but to further enhance the customer experience. AI is already being rolled out in customer-facing operations, but banks will actively be consolidating and automating their mid and back-office procedures for efficiency and automation transition in the post COVID-19 environment. This includes using AI for automating credit operations, policy making and data audits and using RPA for reducing the introduction of errors in datasets and processes.
There is enormous economic pressure to deliver cost savings and reduce risks through the adoption of technology. Financial Services leaders believe that insights gathered from compliance should help other areas of the business, and this requires a completely different mindset. Given the manual and semi-automated nature of current AML compliance, human-only efforts slow down processing timelines and impact business productivity. KYC will leverage AI and real-time environmental data (current accounts, mortgage payment status) and integration of third-party data to make the knowledge richer and timelier in this adaptive economic environment. This will make lending risk assessment more relevant.
#5 Driven by Post Pandemic Recovery, Collaboration Will Shape FinTech Regulation
Travel corridors across border controls have started to push the boundaries. Just as countries develop new processes and policies based on shared learning from other countries, FinTech regulators will collaborate to harmonise regulations that are similar in nature. These collaborative regulators will accelerate FinTech proliferation and osmosis i.e. proliferation of FinTechs into geographies with lower digital adoption.
Data corridors between countries will be the other outcome of this collaboration of FinTech regulators. Sharing of data in a regulated environment will advance data science and machine learning to new heights assisting credit models, AI, and innovations in general. The resulting ‘borderless nature’ of FinTech and the acceleration of policy convergence across several previously siloed regulators will result in new digital innovations. These Trusted Data Corridors between economies will be further driven by the desire for progressive governments to boost the Digital Economy in order to help the post-pandemic recovery.

Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) ratings towards investment criteria have become popular for potential investors to evaluate companies in which they might want to invest. As younger investors and others have shown an interest in investing based on their personal values, brokerage firms and mutual fund companies have begun to offer exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and other financial products that follow specifically stated ESG criteria. Passive investing with robo-advisors such as Betterment and Wealthfront have also used ESG criteria to appeal to this group.
The disruption caused by the pandemic has highlighted for many of us the importance of building sustainable and resilient business models based on multi-stakeholder considerations. It has also created growing investor interest in ESG.
ESG signalling for institutional investors
The increased interest in climate change, sustainable business investments and ESG metrics is partly a reaction of the society to assist in the global transition to a greener and more humane economy in the post-COVID era. Efforts for ESG standards for risk measurement will benefit and support that effort.
A recent study of asset managers by the investment arm of Institutional Shareholder Services (ISS) showed that more than 12% of respondents reported heightened importance of ESG considerations in their investment decisions or stewardship activities compared to before the pandemic.
In the area of hedge funds, there has been an increased demand for ESG-integrated investments since the start of COVID-19, according to 50% of all respondents of a hedge fund survey conducted by BNP Paribas Corporate and Institutional Banking of 53 firms with combined assets under management (AUM) of at least USD 500B.
ESG criteria may have a practical purpose beyond any ethical concerns, as these criteria may be able to help avoidance of companies whose practices could signal risk. As ESG gets more traction, investment firms such as JPMorgan Chase, Wells Fargo, and Goldman Sachs have published annual reports that highlight and review their ESG approaches and the bottom-line results.
But even with more options, the need for clarity and standards on ESG has never been so important. In my opinion, there must be an enhanced effort to standardise and harmonise ESG rating metrics.
How are ESG ratings made?
ESG ratings need both quantitative and qualitative/narrative disclosures by companies in order to be calculated. And if no data is disclosed or available, companies then move to estimations.
No global standard has been defined for what is included in a given company’s ESG rating. Attempts at standardising the list of ESG topics to consider include the materiality map developed by the Sustainable Accounting Standard Board (SASB) or the reporting standards created by the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI). But most ESG rating providers have been defining their own materiality matrices to calculate their scores.
Can ESG scoring be automatically integrated?
Just this month, Morningstar equity research analysts announced they will employ a globally consistent framework to capture ESG risk across over 1,500 stocks. Analysts will identify valuation-relevant risks for each company using Sustainalytics’ ESG Risk Ratings, which measure a company’s exposure to material ESG risks, then evaluate the probability those risks materialise and the associated valuation impact. ESG rating firms such as MSCI, Sustainalytics, RepRisk, and ISS use a rules-based methodology to identify industry leaders and laggards according to their exposure to ESG risks, as well as how well they manage those risks relative to peers.
Their ESG Risk Ratings measure a company’s exposure to industry-specific material ESG risks and how well a company is managing those risks. This approach to measuring ESG risk combines the concepts of management and exposure to arrive at an assessment of ESG risk – the ESG Risk Rating – which should be comparable across all industries. But some critics of this form of approach feel it is still too subjective and too industry-specific to be relevant. This criticism is relevant when you understand that the use of the ESG ratings and underlying scores may in future inform asset allocation. How might this better automated and controlled? Perhaps adding some AI might be useful to address this?
In one example, Deutsche Börse has recently led a USD 15 million funding round in Clarity AI, a Spanish FinTech firm that uses machine learning and big data to help investors understand the societal impact of their investment portfolios. Clarity AI’s proprietary tech platform performs sustainability assessments covering more than 30,000 companies,198 countries,187 local governments and over 200,000 funds. Where companies like Cooler Future are working on an impact investment app for everyday individual users, Clarity AI has attracted a client network representing over $3 trillion of assets and funding from investors such as Kibo Ventures, Founders Fund, Seaya Ventures and Matthew Freud.
What about ESG Indices? What do they tell us about risk?
Core ESG indexing is the use of indices designed to apply ESG screening and ESG scores to recognised indices such as the S&P 500®, S&P/ASX 200, or S&P/TSX Composite. SAM, part of S&P Global, annually conducts a Corporate Sustainability Assessment, an ESG analysis of over 7,300 companies. Core ESG indices can then become actionable components of asset allocation when a fund or separately managed accounts (SMAs) provider tracks the index.
Back in 2017, the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN) and the State Secretariat for International Finance (SIF) made it possible for all Swiss pension funds and insurance firms to measure the environmental impact of their stocks and portfolios for free. Currently, these federal bodies are testing use case with banks and asset managers. Its initial activities will be recorded in an action plan, which is due to be published in Spring 2021.
How can having a body of sustainable firms help create ESG metrics?
Creating ESG standard metrics and methodologies will be aided when there is a network of sustainable companies to analyse, which leads us to green fintech networks (GFN) of companies interested in exploring how their own technology investments can be supportive of ESG objectives. Switzerland is setting up a Green Fintech Network to help the country take advantage of the “great opportunity” presented by sustainable finance. The network has been launched by SIF alongside industry players, including green FinTech companies, universities, and consulting and law firms. Stockholm also has a Green Fintech Network that allows collaboration towards sustainability goals.
Concluding Thought
We should be curious about how ESG can provide decision-oriented information about intangible assets and non-financial risks and opportunities. More information and data from ESG data providers like SAM, combined with automation or AI tools can potentially provide a more complete picture of how to measure the long-term sustainable performance of equity and fixed income asset classes.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Investor Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Investor Summit which will cover topics tied to 2021 Investor Priorities, and Fundraising and exit strategies

Authored by Alea Fairchild and Mike Zamora
There have been a few articles recently about investment companies looking to buy large national US retail companies, for example, JC Penney and Dillards. Their historical approach was to purchase the land and develop the sites as a retail centre and operate their stores. They then lease the remaining retail space to other retailers. It is a business model which has been in use for many decades.
Historically a long and deep negative economic cycle has caused some retail operators/developers to sell part of their operations. This happened in the US in 1995 with Sears. The real estate development and investment companies’ interest is in exploring if there is a higher and better use for the properties. That is the essence of land economics, going from a lower economic use to a higher income/value use.
A key difference this time is the use of advanced technology. We see this in many dimensions: building systems and operations; retail management, social media, entertainment and food and beverage (F&B) operations.
The Smart Building revolution in Retail is about changing the management philosophy of buildings and using technology to aid in the process. The defining characteristic of building smarter is not the application of technology or a function of outcomes on energy use or maintenance. Instead, it is a commitment to leveraging the overall footprint to achieve the goals that perhaps inspired the building in the first place.
Evolution of Space for Retail Activities
The old axiom of real estate is location, location, location. This means that every retail centre will have to be assessed for its best purpose for its locations and surrounding environment. Retail has been morphing in the past few years from a traditional purpose of picking something up to an intersection of shopping and entertainment. This combines on-premise activities with a buying transaction which can be handled either onsite or online. Technology infrastructure investment opportunities are driven by optimising the customer retail experience.
Retail centres are seeking new functionality, including the adaptation of both design and use. Below are four approaches we believe can be used to assess each retail centre.
Reuse: Retail Lifecycle – Consumption to Redemption
There is a shift from consumers discovering and experiencing products in a physical retail space to retailers delivering on-demand. Many smaller retailers have capitalised on this by becoming pick-up points for online orders. They hope to increase footfall by drawing the customer into their own premises when retrieving their online delivery.
Retail centres need to expand on this trend to become a fulfilment location rather than a retail shopping space. Consumers could pick up online orders, recycle used goods, get products maintained and repaired, have appointments for personal services (dental, eye, hair, dry cleaning, etc.), try and test goods in mini-showrooms and collect points and benefits from gamification activities. By having a centralised exchange facility with multiple functionalities, consumer data can be leveraged to create marketing pull activities such as exclusive shopping events, and personalised customer service based on preferences and purchase history.
The current square meterage can be reallocated for distribution including the use of dark stores, green recycling centres for 3D printed product disposal and retail pick-up and exchange points. Staff will not be salespeople, but customer delivery service managers. The technology opportunities in this area would be re-allocation of network resources; focus on efficiency in delivery and customer satisfaction; and automation tools for customer service staff.
Redesign: Blended – Community Environment and Retail Experience
An alternative and more involved development approach would be to redesign the retail centre with deeper use cases to get more customers to come and stay longer. If a consumer stays onsite longer, there is a higher probability they will spend more at the retail centre. The future retail centre (Figure 1) would include additional space usages for a community space, a distribution centre for pick-ups, expanded F&B and remote working.
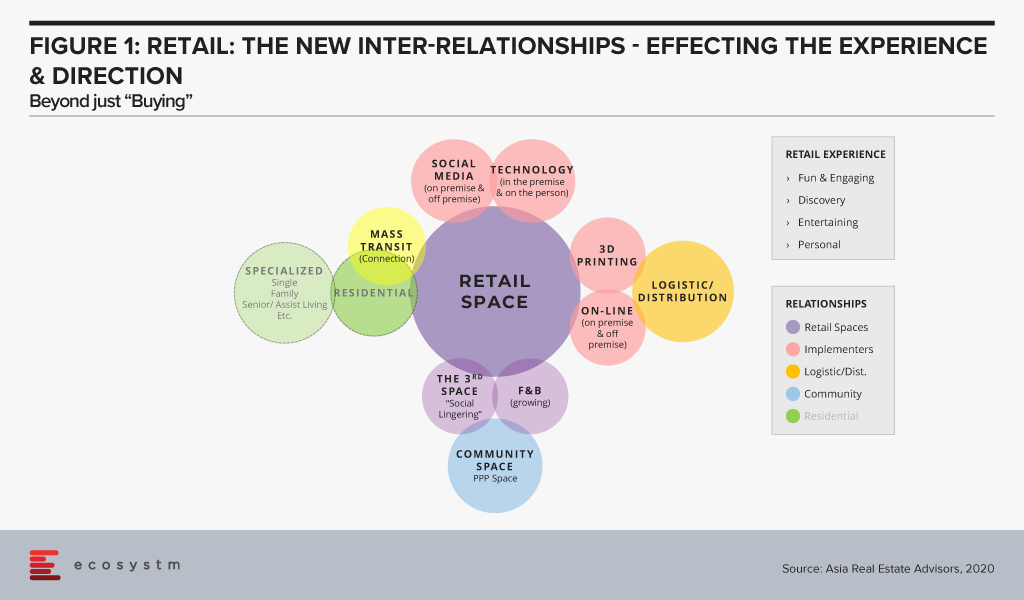
The technology opportunities are in two areas: customer experience and building operations. From a customer perspective, some technology examples would include entertainment and gaming in the F&B area, digital signage and mobile device technology to further engage people. For building operations examples could include technologies to control climate, lighting, security, energy management and building management.
Redevelop – Living Space for a Quality of Life
In some locations, the retail environment could have an oversupply of newly development retail centres. This means the optimal use for the centre would be to change it to a ‘Village Community’ – a community where people can live, work, learn and play. It would encompass multiple uses – multi-family residential units, a community centre, learning centres for younger children and a co-working area. The technology opportunies would be identical to a connected Smart City – at a lesser scale. Smart residential solutions would make the living environmental more user friendly. Retail could include digital media, mobile push features, enhanced and operational technology, energy management, climate control and security. Schools could include interactive and collaborative tools. Parks would have Wi-Fi and enhanced security. Connected Services (eg utilities, fire life safety, security and communications) could include operational technology systems for utilities, audio and video security systems and communication.
Repurpose: Knowledge & Learning Environment
For some retail centres a redevelopment may not be required, but would instead need a major repurposing of the space. The repurpose could be as a learning or healthcare centre. Learning environments require large open spaces with high ceilings for auditoriums or class rooms; common areas for gathering in between classes; onsite housing for students; food courts; and adequate parking for commuters. A healthcare environment would require patient reception, examination rooms, inpatient rooms, surgical units, and administrative offices. It could also include a medical learning centre.
The technology opportunities would be to develop a 24×7 site, with technologies to support the key purpose of the centre. The learning environment could include collaborative audio/video tools for Smart Classrooms. The social areas could including advanced food ordering and delivery systems and multiple player gaming centres for entertainment. The living areas would include systems and technology for smart living. The parking area could include enhanced security and surveillance systems, and smart parking systems. Behind the scenes, the building operations would need to upgrade energy management, building maintenance and management, digital food court operations, and a wellness air quality system.
The Future of Sustainable Retail Space
The decline of a retail centre is not necessarily a bad thing for a community. It is just the “Circle of Life” as an area evolves. Locations morph over the long-term. This has been seen in all the large cities around the world which have stood the test of time, eg. London, Paris, Amsterdam, New York, Tokyo and Beijing. The transformation also breathes fresh air into the surrounding environment. There are multiple layers of technology available to provide for an incredible Sustainable and Smart Community. It is large opportunity, not only for real estate developers, but also for technology vendors who understand the transformation process into the multiple variations of smart environments. Large real estate players and REITs will buy these retail portfolios and begin to transform older, low revenue, semi-vacant shopping centres into vibrant destination centres. Technology vendors should bring their ideas and systems to the attention of retail real estate owners early on in the the process. This will increase their chances of having their systems incorporated into the overall design concept and operational approach. It is a physical and digital transformation which improves neighborhoods, businesses and the city. It is a win for all.

Telstra and Microsoft have extended their partnership to jointly build solutions harnessing the capabilities of AI, IoT, and Digital Twin technologies in Australia. The partnership will also enable both companies to work on sustainability, emission reduction, and digital transformation initiatives.
The adoption of cloud and 5G technology is already on the rise and creating opportunities across the globe. The Microsoft-Telstra partnership is set to bring together the capabilities of both providers for businesses in Australia and globally. Their focus on AI, IoT, cloud and 5G will enable Australia’s developers and independent software vendors (ISVs) to leverage AI with low latency 5G access to drive efficiency, and enhance decision making. This will also see practical applications and new solutions in areas like asset tracking, supply chain management, and smart spaces to enhance customer experience.
Technology Enhancing the Built Environment
Microsoft Azure and Telstra’s 5G capabilities will come together to develop new industry solutions – the combination of cloud computing power and telecom infrastructure will enable businesses and industries to leverage a unified IoT platform where they can get information through sensors, and perform real-time compute and data operations. Telstra and Microsoft will also build digital twins for Telstra’s customers and Telstra’s own commercial buildings which will be initially deployed at five buildings. Upon completion, the digital twin will enable Telstra to form a digital nerve centre and map physical environments in a virtual space based on real-world models and plot what-if scenarios.
Telstra CEO, Andy Penn says, “If you think about the physical world – manufacturing, cities, buildings, mining, logistics – the physical world hasn’t really been digitised yet. So, how do you digitise the physical world? Well, what you do is put sensors into physical assets. Those sensors can draw information around that physical asset, which you can then capture and then understand.”
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Mike Zamora finds the comment interesting and says, “It isn’t so much that the physical world is digitized – it is more about how digital tools enhance and enable the physical world to be more effective to help the occupier of the space. This has been the history of the physical space. There have been many ‘tools’ over time to help the physical world – the elevator in the late 1880s enabled office buildings to be taller; the use of steel improved structural support, allowing structural walls to be thinner and buildings taller. These two ‘tools’ enabled the modern skyscraper to be born. The HVAC system developed in the early 1900s, enabled occupants to be more comfortable inside a building year-round in any climate.”
“Digital tools (sensors, etc) are just the latest to be used to enhance the physical space for the occupant. Digital twins enable an idea to be replicated in 3D – prior to having to spend millions of dollars and hundreds of man hours to see if a new idea is viable. Its advent and use enable more experimentation at a lower cost and faster set up. This equates into a lower risk. It is a welcomed tool which will propel the experimentation in the physical world.”
Talking about emerging technologies, Zamora says, “Digital twins along with other digital tools, such as 3D printing, AI, drones with 4K cameras and others will enable the built environment to develop at a very quick pace. It is the pace that will be welcomed, as the built environment is typically a slow-moving asset (pardon the pun).”
“Expect the Built Environment developers, designers, investors, and occupiers to welcome the concept. It will allow them to dream of the possible.”
Telstra and Microsoft – Joint Goals
Telstra and Microsoft have partnered over the years over multiple projects. Last year, the companies partnered to bring Telstra’s eSIM functionality to Windows devices for data and wireless connectivity; they have also worked on Telstra Data Hub for secured data sharing between data producers, businesses and government agencies; and most recently collaborated on Telstra’s exclusive access to Xbox All Access subscription service to Australian gamers with the announcement of Microsoft’s Xbox Series X and Xbox Series S gaming consoles expected to release in November.
This announcement also sees them work jointly towards their sustainability goals. Both companies are committed to sustainability and addressing climate change. Earlier this year, Microsoft announced its plans to be carbon negative by 2030, while Telstra has also set a target to generate 100% renewable energy by 2025 and reducing its absolute carbon emissions by 50% by the same time. To enable sustainability, Telstra and Microsoft are exploring technology to reduce carbon emissions. This includes further adoption of cloud for operations and services, remote working, and piloting on real-time data reporting solutions.
Telstra also aims to leverage Microsoft technology for its ongoing internal digital transformation, adopting Microsoft Azure as its cloud platform to streamline operations, and infrastructure modernisation, including transition from legacy and on-premise infrastructure to cloud based applications.

Today nearly 56% of the global population lives in an urban environment. The city has finally become the dominant place to live. Given the changing environment and increasing technology, the city has begun to dramatically change in the past 5-10 years. And it will continue to evolve and change at an increasingly faster pace.
As technology has developed and influenced the city, the term “Smart City” has become prevalent. Technology is an important attribute of a city’s evolution. However, it is just one of the attributes. A more encompassing and enduring term could be a “Sustainable City”. The definition of a Sustainable City that I subscribe to is:
“A vibrant community which can adapt and grow over the years, due to changing demographics and economic conditions. It is based upon multiple attributes.”
This definition begins to describe the holistic and long-term issues associated with the complexities of an urban environment. A Sustainable City has a goal of being an enduring and competitive place to work, live, learn, and play. It requires many aspects. Some of these are:
- Purpose. Entertain, eat, work, live, learn
- Activities. Walk, bike, play, work, learn, etc.
- Scale. Human scale not mega blocks
- Natural Environment. Location, terrain, water, etc.
- Environmental Implications. Resource usage, output disposal, environmental footprint, etc.
- Dynamic. Changing through the day/week as needed (festival, farmer’s markets, sporting event)
- Transportation. Walk, bike, mass transit – beyond cars
- Connectivity. Smart & effective infrastructure (utility & transportation coordination, etc.)
- Built Environment. Smart & efficiently operated buildings, spaces, etc.
A city is also a three-dimensional physical puzzle. It is composed of multiple layers: Subterranean level (utilities, transportation, walkways, retail); Ground level (streets, walkways, public spaces, open areas, building entrances); Concourse (walkways, retail, elevated rail, etc.); and Air Space (skyscrapers, bridges). This three-dimensional layout adds a level of complexity.
Key Stakeholders in a Sustainable City
Another important layer to consider consists of the four main players that need to work together:
- People (employees, students, families, tourists)
- Businesses (large, small/medium, start-ups, etc.)
- Built Environment (developers, real estate investors, consultants, designers, engineers, etc.)
- Government (local and regional)
For a city to be enduring and sustainable, the four main players need to work in a concerted effort. They need to discuss, advise, decide and provide for an environment which can change or be modified based upon a particular city’s needs. No one player truly has the ability to control how the city develops over time. Instead all of them work together along with the marketplace and land economics to determine the success of a city in the long run. Idea generation can come from any of these players and is tested in the marketplace. Figure 1 shows the interactions between these four key stakeholders. When all the groups work together, they are able to attain that “Sweet Spot” which enables a location to have the characteristics of a sustainable Global City. In the most simplistic terms, the Sweet Spot for a Sustainable City is the on-going quality of life that the city provides to its occupants.
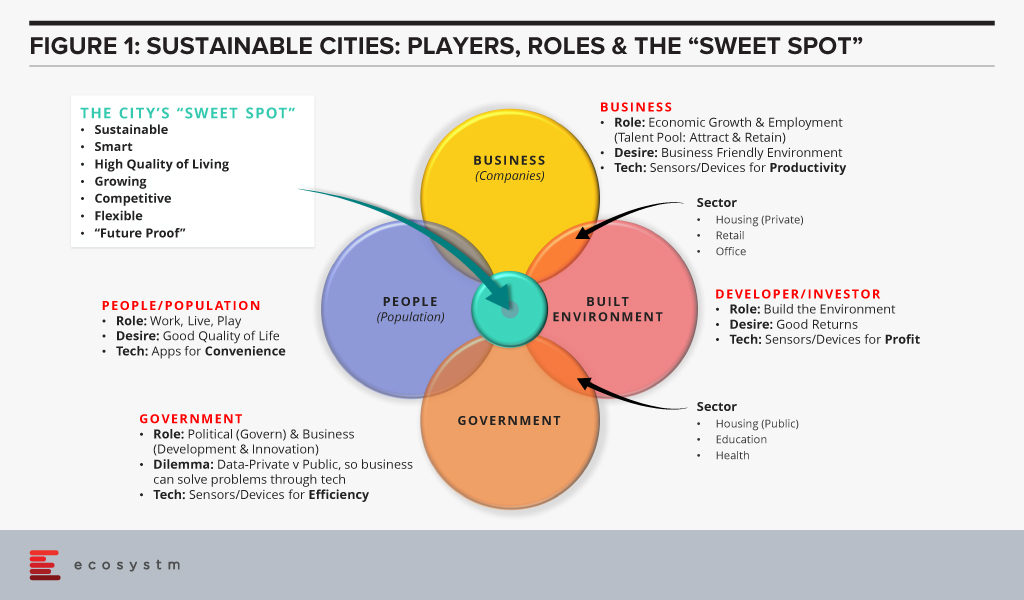
The Dynamic Nature of a Sustainable City
Some believe that once a city or regional masterplan has been developed and approved the only thing left is to implement and enjoy. As a city and its inhabitants are dynamic, a longer-term sustainable view might be that the completion of the environment is just a starting point. The cases in point are the great global cities whose origins have started many generations ago, such as London, New York, Berlin, Tokyo, and so on This means that through use, the environment and space will constantly be assessed to evaluate if they are meeting the changing needs of the city or location. The appropriate adjustments or modifications are required over time. This is what has been done over the past centuries for many global cities. The difference between then and now is that with technology permeating everywhere, the ability to assess and adjust the environment will now be done at a much faster rate.
As builders and/or occupants of the environment we are just the current Stewards of the urban environment. Stewardship is a delicate balance between Return on Investment and Return to Society. The city is a dynamic environment which will continue to evolve over time based upon its changing needs. We have to determine whether we are going to change and improve the environment or just “pluck the fruits” from the existing assets. We should make sure that when we design and develop the urban environments it is with long-term sustainability in mind.











































