Over a century ago, the advent of commercial flights marked a pivotal moment in globalisation, shrinking the time-distance between cities and nations. Less than a century later, the first video call foreshadowed a future where conversations could span continents in real time, compressing the space-distance between people.
The world feels smaller, not literally, but in how we experience space and time. Messages that once took days to deliver arrive instantly. Distances between cities are now measured in hours, not miles. A product designed in New York is manufactured in Shenzhen and reaches London shelves within weeks. In essence, things traverse the world with far less friction than it once did.
Welcome to The Immediate Economy!
The gap between desire and fulfilment has narrowed, driven by technology’s speed and convenience. This time-space annihilation has ushered in what we now call The Immediate Economy.
Such transformations haven’t gone unnoticed, at the click of a button is now a native (sort of cliché) expression. Amidst all this innovation, a new type of consumer has emerged – one whose attention is fleeting and easy to lose. Modern consumers have compelled industries, especially retail and ecommerce, to evolve, creating experiences that not only capture but also hold their interest.
Beyond Usability: Crafting a Memorable User Experience
Selling a product is no longer about just the product itself; it’s about the lifestyle, the experience, and the rush of dopamine with every interaction. And it’s all because of technology.
In a podcast interview with the American Psychological Association, Professor Gloria Mark from the University of California, Irvine, revealed a significant decline in attention spans on screens, from 150 seconds in 2004 to 40 seconds in the last five years. Social media platforms have spoiled the modern consumer by curating content that caters instantly to desires. Influence spills into the retail sector, compelling retailers to create experiences matching the immediacy and personalisation people now expect.
Modern consumers require modern retail experiences. Take Whole Foods, and their recent partnership with Amazon’s Dash Cart, transforming the mundane act of grocery shopping into a seamless dance of efficiency. Shoppers can now glide through aisles with carts that tally selections and debit totals directly from their accounts, rendering checkout lines obsolete. It’s more than convenience; it reimagines retail – a choreography of consumerism where every step is both effortless and calculated.
Whole Foods can analyse data from their Dash Cart technology to gain valuable insights into shopping patterns. The Immediate Economy revolutionises retail, transforming it into a hyper-efficient, personalised experience.
Retail’s new Reality: The Rise of Experiential Shopping
Just as Netflix queues up a binge-worthy series; retailers create shopping experiences as engaging and addictive as your favourite shows.
It’s been a financially rough year for Nike, but that hasn’t stopped them from expanding their immersive retail experience. Nike’s “House of Innovation” leverages 3D holographic tech. Customers can inspect intricate details of sneakers, including the texture of the fabric, the design of the laces, and the construction of the sole. The holographic display can also adjust to different lighting conditions and present the sneaker in various colours, providing a truly immersive and personalised shopping experience.
Fashion commerce platforms like Farfetch are among many integrating Virtual Try-On (VTO) technology. Leveraging the camera and sensors of customer devices, their AR technology overlays a digital image of a handbag onto a live view of a customer, enabling them to see how different styles and sizes would look on you. This approach to ecommerce enhances experiences, elevating interaction.
The 3D holographic display and the AR tech, are unique and visually appealing ways to showcase products, allowing customers to interact with products in a way that is not possible with traditional displays. Each shopping trip feels like the next episode of retail therapy.
The Evolution of Shopptertainment
The bar for quick content consumption is higher than ever thanks to platforms like TikTok and Instagram.
A prime example of this trend is Styl, a tech startup from two Duke students, with their “Tinder for shopping” application. Styl offers a swipeable interface for discovering and purchasing fashion items, seamlessly integrating the convenience and engagement of social media into the retail experience.
Styl goes beyond a simple swipe. By leveraging AI algorithms, it learns your preferences and curates a personalised feed of clothing items that align with your taste. Streamlining the shopping process, they deliver a tailored experience that caters to the modern consumer’s desire for convenience and personalisation.
Interestingly, Styl isn’t even a retail company; it pools items from websites, redirecting the users with relevant interest. They combine ecommerce with AI, creating the ultimate shopping experience for today’s customer. It’s fast, customised, and changing the way we shop.
Styl is not the first ones to do this, Instagram and TikTok provide individualised suggestions within their marketplace. But they differ by selling an experience, a vibe. That’s what sets them apart.
Tech-Powered Retail: The Heart of the Immediate Economy
History is filled with examples of societal innovation, but the Immediate Economy is transforming retail in exciting ways. In the 21st century, technology is both the catalyst and the consequence of the retail industry transformation. It began by capturing and fragmenting the average consumer’s attention, and now it’s reshaping consumer-brand relationships.
Today’s consumers crave personalised shopping. Whole Foods, with its AI-driven Dash Carts, is redefining convenience. Nike and Farfetch, through immersive AR and 3D tech, is making shopping an interactive adventure. Meanwhile, startups like Styl are leveraging AI to bring personalized fashion choices directly to consumers’ smartphones. The world is shrinking, not just in miles, but in the milliseconds it takes to satisfy a desire. From the aisles of Whole Foods to the virtual showrooms of Farfetch, The Immediate Economy offers an immersive world, where time and space bend to technology’s will, and instant gratification is no longer a perk; it’s an expectation. The Immediate Economy is here, and it’s changing how we interact with the world around us. Welcome to the future of retail, and everything else.

Historically, data scientists have been the linchpins in the world of AI and machine learning, responsible for everything from data collection and curation to model training and validation. However, as the field matures, we’re witnessing a significant shift towards specialisation, particularly in data engineering and the strategic role of Large Language Models (LLMs) in data curation and labelling. The integration of AI into applications is also reshaping the landscape of software development and application design.
The Growth of Embedded AI
AI is being embedded into applications to enhance user experience, optimise operations, and provide insights that were previously inaccessible. For example, natural language processing (NLP) models are being used to power conversational chatbots for customer service, while machine learning algorithms are analysing user behaviour to customise content feeds on social media platforms. These applications leverage AI to perform complex tasks, such as understanding user intent, predicting future actions, or automating decision-making processes, making AI integration a critical component of modern software development.
This shift towards AI-embedded applications is not only changing the nature of the products and services offered but is also transforming the roles of those who build them. Since the traditional developer may not possess extensive AI skills, the role of data scientists is evolving, moving away from data engineering tasks and increasingly towards direct involvement in development processes.
The Role of LLMs in Data Curation
The emergence of LLMs has introduced a novel approach to handling data curation and processing tasks traditionally performed by data scientists. LLMs, with their profound understanding of natural language and ability to generate human-like text, are increasingly being used to automate aspects of data labelling and curation. This not only speeds up the process but also allows data scientists to focus more on strategic tasks such as model architecture design and hyperparameter tuning.
The accuracy of AI models is directly tied to the quality of the data they’re trained on. Incorrectly labelled data or poorly curated datasets can lead to biased outcomes, mispredictions, and ultimately, the failure of AI projects. The role of data engineers and the use of advanced tools like LLMs in ensuring the integrity of data cannot be overstated.
The Impact on Traditional Developers
Traditional software developers have primarily focused on writing code, debugging, and software maintenance, with a clear emphasis on programming languages, algorithms, and software architecture. However, as applications become more AI-driven, there is a growing need for developers to understand and integrate AI models and algorithms into their applications. This requirement presents a challenge for developers who may not have specialised training in AI or data science. This is seeing an increasing demand for upskilling and cross-disciplinary collaboration to bridge the gap between traditional software development and AI integration.
Clear Role Differentiation: Data Engineering and Data Science
In response to this shift, the role of data scientists is expanding beyond the confines of traditional data engineering and data science, to include more direct involvement in the development of applications and the embedding of AI features and functions.
Data engineering has always been a foundational element of the data scientist’s role, and its importance has increased with the surge in data volume, variety, and velocity. Integrating LLMs into the data collection process represents a cutting-edge approach to automating the curation and labelling of data, streamlining the data management process, and significantly enhancing the efficiency of data utilisation for AI and ML projects.
Accurate data labelling and meticulous curation are paramount to developing models that are both reliable and unbiased. Errors in data labelling or poorly curated datasets can lead to models that make inaccurate predictions or, worse, perpetuate biases. The integration of LLMs into data engineering tasks is facilitating a transformation, freeing them from the burdens of manual data labelling and curation. This has led to a more specialised data scientist role that allocates more time and resources to areas that can create greater impact.
The Evolving Role of Data Scientists
Data scientists, with their deep understanding of AI models and algorithms, are increasingly working alongside developers to embed AI capabilities into applications. This collaboration is essential for ensuring that AI models are effectively integrated, optimised for performance, and aligned with the application’s objectives.
- Model Development and Innovation. With the groundwork of data preparation laid by LLMs, data scientists can focus on developing more sophisticated and accurate AI models, exploring new algorithms, and innovating in AI and ML technologies.
- Strategic Insights and Decision Making. Data scientists can spend more time analysing data and extracting valuable insights that can inform business strategies and decision-making processes.
- Cross-disciplinary Collaboration. This shift also enables data scientists to engage more deeply in interdisciplinary collaboration, working closely with other departments to ensure that AI and ML technologies are effectively integrated into broader business processes and objectives.
- AI Feature Design. Data scientists are playing a crucial role in designing AI-driven features of applications, ensuring that the use of AI adds tangible value to the user experience.
- Model Integration and Optimisation. Data scientists are also involved in integrating AI models into the application architecture, optimising them for efficiency and scalability, and ensuring that they perform effectively in production environments.
- Monitoring and Iteration. Once AI models are deployed, data scientists work on monitoring their performance, interpreting outcomes, and making necessary adjustments. This iterative process ensures that AI functionalities continue to meet user needs and adapt to changing data landscapes.
- Research and Continued Learning. Finally, the transformation allows data scientists to dedicate more time to research and continued learning, staying ahead of the rapidly evolving field of AI and ensuring that their skills and knowledge remain cutting-edge.
Conclusion
The integration of AI into applications is leading to a transformation in the roles within the software development ecosystem. As applications become increasingly AI-driven, the distinction between software development and AI model development is blurring. This convergence needs a more collaborative approach, where traditional developers gain AI literacy and data scientists take on more active roles in application development. The evolution of these roles highlights the interdisciplinary nature of building modern AI-embedded applications and underscores the importance of continuous learning and adaptation in the rapidly advancing field of AI.

Over the past 3-4 weeks I have spent some time using Samsung DeX (shortened from “Desktop eXperience”) as my primary desktop environment. DeX has been around for a number of years, and I have dabbled with it from time-to-time – but I have never really taken it seriously. My (incorrect!) opinion was that a mobile chipset isn’t powerful enough for a PC-like experience. But for most of the last year, I have been using a Samsung Galaxy Book S laptop as my primary computing device – and this Windows 10 laptop runs an ARM processor which is the very same processor that powers many Samsung and other Android phones. Microsoft also has an ARM-based PC that I have used successfully (the Surface Pro X) which prompted me to rethink the opportunities for DeX. A number of clients also asked for my thoughts on DeX so I figured it is time to take it seriously as a potential end-user computing environment.
This Ecosystm Insight is a summary of the client report and is the first of a few Insights into DeX. In future, I plan to trial the dual-monitor ability for DeX (developed by VoIP – an Australian ICT consultancy). These Ecosystm Insights won’t cover how to use Samsung DeX. If you are looking for this information, Gizmodo has published a good piece here.
The Trial
In trialling Samsung DeX I attempted to cover all usage scenarios, including:
- Native DeX with the phone connected to a DeX station and both wired and wireless keyboard/mouse, using both wi-fi and 4G (I live literally 50 metres outside of 5G coverage!)
- DeX through Windows 10 using both wi-fi and 4G and a wired mouse and keyboard
- Native DeX connected to a monitor using the Microsoft wireless display adapter (again using both wi-fi and 4G)
In the native DeX environment I worked in the traditional Microsoft productivity apps, collaboration apps (such as Teams, Zoom, Webex, Google Meet), Google productivity apps, web applications (sales, CRM & ERP), file sharing applications (OneDrive, Google Drive), imaging applications (photos, video, image sharing), social applications (Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram etc) and other native Android apps – some of which were optimised for DeX, and some of which were not. I tried to imitate the information worker’s experience; and that of a site or specialist user. I used it as a primary computing environment for most of my work for 3-4 weeks. I didn’t just consume content, but also created content – I needed to be able to sign and attach Adobe documents, create new reports, conduct deep data analysis in Excel and create figures and move them between Excel, Word and PowerPoint. I created and shared leads in CRM systems, did company accounting in a financial application and even had some time to try out some gaming applications.
I have also trialled a Citrix and Amazon virtual desktop in all environments – running productivity applications, finance applications, graphics intensive applications and web apps.
Findings
My broad finding is that DeX is not a desktop replacement for power users – but there are plenty of roles within your business who would find that DeX is a capable environment that will allow them to get their job done.
I was planning to discuss the positive features of DeX, but the reality is that it is simpler to understand its limitations. And, most limitations are related to the Android applications or network lag introduced in virtual desktop environments using 4G.
- The Microsoft productivity applications in Android are all scaled back versions of the desktop applications. They do not contain many of the features and functions that the desktop versions have. For example, when I needed to format headings in a report, the fast format options (e.g. to make text a “heading 2”) don’t exist in the Android version of Microsoft Word. Power users will find these applications don’t deliver all of the functions they need to get their job done.
- Those who need broader functionality beyond the Android applications will benefit from a virtual desktop environment. Both Citrix Workspace and Amazon Workspaces delivered a very usable Windows 10 experience (although I found the base configuration to be a little slow). For existing users of virtual desktops, it is a no-brainer to roll them out to mobile devices if required. But would you add a virtual desktop environment to your existing desktop fleet just to enable DeX? I can’t answer that – as it is another environment to manage and support for your end-user computing and IT support teams. But again, for power users, this is not an ideal environment. It does EVERYTHING you want it to do – but it might not do it fast enough to satisfy all users.
- It’s not a mobile environment. This isn’t something you use on your phone (although I believe you can use it on some Samsung tablets). You need a monitor, keyboard, and ideally a separate mouse for DeX to work. It doesn’t replace a laptop for a mobile worker.
- DeX does not natively support dual screens or monitors. I found that I would switch back to my PC when I needed the productivity of two screens, as I personally find application switching on a single screen to be a productivity killer. BUT – this is changing – VoIP has developed a capability to run DeX across dual monitors (I will be testing this shortly and will post the results).
- When using DeX natively and not using a virtual desktop, the screen sharing features of collaboration apps don’t work in the way you expect. The screen that is shared is NOT the DeX desktop screen but the horizontal mobile phone screen. This is a significant issue if you want to share a Word, PowerPoint, or Excel file or another “full desktop screen” application. DeX users can view other people’s shared screens, but not share the screen effectively themselves.
- DeX introduces a new environment for your helpdesk to support. DeX isn’t Windows, it isn’t cloud, and it isn’t exactly native Android. Your tech support team will need to be trained on DeX and be required to learn a new user environment. It introduces an additional OS into the mix. That means at least some service desk technicians will need to be trained on the environment. As it is still running in Android, it doesn’t particularly require specific QA or testing for your business mobile applications. But to take full advantage of the larger screen real estate that DeX facilitates, you may need to make some changes to how applications perform in DeX.
Despite these challenges, DeX is a very capable environment. Running a virtual desktop was a breeze and performed far better than I would have imagined. I was worried about lag and had introduced many opportunities for it to run slowly – a wireless mouse and keyboard, wireless display adapter, running over wi-fi, and 4G using a virtual desktop in the cloud – and the lag was barely noticeable. I was impressed with this and understand how DeX could even be used to support legacy applications and environments too.
The convenience of having your phone at your fingertips – being able to respond to text messages on the large screen, taking calls using the same Bluetooth headphones that you use to watch video content on the larger screen, not to mention the security of taking your “PC” with you in your pocket when you head out to lunch or home for the day – adds to the value of DeX. The concept of a “PC in your pocket” has been around for a while – however most Samsung mobile users don’t realise that they have one there already!
Target Roles

Who are the business roles or personas who could benefit from it? The simple answer is that anyone who uses a desktop part-time would benefit from DeX. Many businesses have shared PCs for multiple users or dedicated PCs for users who don’t use a PC full-time. These might be site managers in constriction, store managers in retail, nurses, security staff, librarians, government or council workers. The significant factors that define potential DeX users are:
- They spend a fair amount of time away from a PC
- They still need a PC for reporting, document sharing, content creation etc
- They return to a fixed site regularly (like a store, office, site office etc)
Again, it is worth noting that DeX doesn’t replace a laptop or tablet. It is not for mobile computing – it replicates fixed computing environments in a more mobile and potentially cost-effective form factor. Remember that the employees need a screen, mouse, and keyboard (you can use the phone as a mouse, but it is not ideal). They also need the charging cable to connect to the computer. If they are making regular video calls then I suggest a phone holder that allows the charging cable to stay connected and the phone to be angled so as others can see their face (wireless chargers tend to sit too far back).
And while DeX is a secure solution, and can benefit from Samsung’s Knox security platform and capabilities, pairing DeX with a secure branch of one style solution – such as that offered by Asavie, now a part of Akamai – has the ability to add end-to-end security and secure application/data access that your employees desire and your business needs.
The opportunities for DeX outweigh the challenges. I am certain that most businesses have potential DeX users – employees who reluctantly carry around a laptop, or who have to come back to a location for their computing. They might be employees who use their phones for image capture and spend much of their time transferring photos to a PC to store them into a corporate system (such as an OH&S team member, or a repair and maintenance provider for a company). It could be a brand salesperson who spends time in various retailers or on the road but still need computing for product training, entering sales figures, and other administrative tasks.
If your business already offers Samsung devices to your employees, switching on DeX is a no-brainer. Start with a trial in a limited employee pool to determine the specific challenges and opportunities within your business. If you are already using virtual desktops, then this is the easiest way to start – roll out the app to your Samsung mobile devices and you have a ready-made portable computer in your employees’ pockets.
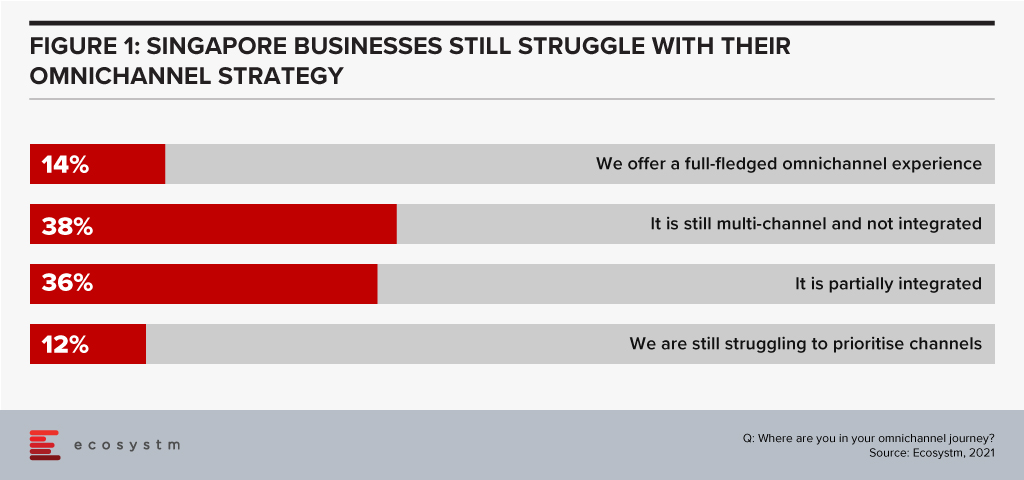
Customer needs are changing. Quickly. In 2020 having a great digital strategy went from being a nice-to-have to an absolute necessity. And in 2021, businesses that have great omnichannel experiences will go from a small minority to a majority as customers demand that they are served on their terms in their chosen platform. Only 14% of businesses in Singapore offer a complete omnichannel experience today – serving customers on their terms regardless of the location or platform (Figure 1). These businesses are setting the benchmark that the rest of the market needs to meet soon.
The Growing Importance of Social Media in Delivering Customer Experience
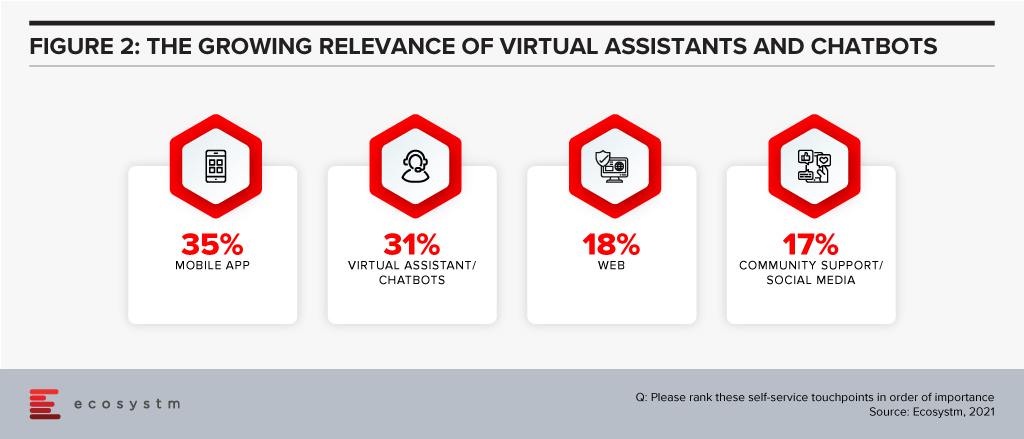
Chat and messaging are quickly becoming the normal way to interact with businesses – the view of a few years ago that “no one wants to chat with a bot” has quickly turned around. Now virtual assistants and chatbots are the second most important self-service channel for businesses in Singapore (Figure 2).
In fact, Zendesk’s global study shows that most customers (45%) use embedded messaging over social messaging apps (31%) and text/SMS (20%). That might be great for self-service, but for commerce, boundless opportunities exist to move to where the customer lives, communicates, and socialises today.
Smart businesses understand that customers spend their lives in other chat and social media platforms – such as Facebook Messenger, TikTok, Instagram, WeChat, Discord and WhatsApp. More customers expect to be served in these channels; they expect to be able to transact with their brands of choice. Why should they go to a mobile banking app to find their balance? Why can’t they get it in WhatsApp? They are often learning about the next Jordan or Yeezy shoe drop from their social network in Messenger – so why not transact with them there? Consider all your own personal WhatsApp, Messenger and other messaging platform groups discussing social activities, sporting teams, school activities or the latest fashion – these are ALL opportunities for commerce (Figure 3).

And there are use cases now. Airlines – such as KLM and Etihad Airways – are engaging customers on WeChat, Kakao Talk, and WhatsApp, helping them reschedule flights and answering customer service queries. Telecommunications providers are allowing customers to raise issues on messaging platforms – and are also using them to upsell and cross-sell new services. Transportation providers are making it easier to find a car or the the next scheduled bus right there in the messaging platforms. Retailers – such as 1-800 Flowers and Culture Kings – are not only serving customers but finding new customers on these messaging platforms.
Going beyond the messaging platforms, businesses are also looking to serve customers on their smart devices – such as Amazon Alexa/Echo and Google Nest/Home devices. Alerting customers to order updates, shipping details and product promotions is becoming standard practice for leading businesses. Digitally-savvy banks are allowing customers to not only track their balance but also make transfers and payments using these smart platforms.
Customers are more comfortable with these conversational commerce options – and they actually expect you to offer such services on your site, in your app, on their smart devices, and on their messaging platforms of choice. Your ability to provide outstanding customer experiences will not only be your ticket back to revenue growth but the recipe for long term business success. Meeting customer needs on their terms is a good place to start.
Delivering a Personalised Conversational Customer Experience
Customer experience (CX) decision-makers will have to rethink how they approach building richer CX capabilities to deliver personalised conversational interactions with customers.
Messaging should become part of a wider AI, Data, and Mobile strategy. Contact centre teams might feel that this is too ambitious a project and would prefer to continue to serve customers through the more traditional channels only. So, it is important to identify the key stakeholder/s who will drive the initiative. And the contact centre team should work with the Digital, Innovation and Marketing teams.
Designing the mobile experience and in app messaging for CX should have some of the following features:
- Ability to click a button to request for a service or escalate an issue that will, in turn, result in the company contacting the customer either by messaging or calling.
- Giving customers the option to contact through popular messaging platforms such as Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, LINE, WeChat, and others. Unifying these systems in a single interface that integrates with your customer service application is best practice.
- Having one single interface to manage and make payments – within the app itself or on the social messaging platform. Conversational commerce is about creating an ongoing relationship with customers throughout the entire customer journey. Don’t just focus on the sale or the post-sales experience – customers expect to be able to interact with your business from their platform of choice regardless of their need or stage in the customer journey.
- Embed deep analytics into the communication services to help the organisation better deliver a personalised CX.
- Ensure you have a solid, unified knowledge management interface at the backend so that all questions lead to the same answers regardless of channel, platform or touchpoint.
Your opportunity to drive greater business success lies in your ability to better win, serve and retain your customers. Refresh your customer strategy and capability today to make 2021 an exceptional year for your business.






