In June, the Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) awarded 5G licenses to Singtel and JVCo (formed by Starhub and M1), after they completed the required regulatory processes – including the selection of their preferred frequency spectrums, vendor partners and other technical matters such as performance, coverage, resilience, and cybersecurity. They will be required to provide coverage for at least half of Singapore by end-2022, scaling up to nationwide coverage by end 2025. While Singtel and JVCo were allocated radio frequency spectrum to deploy nationwide 5G networks, other mobile operators, including MVNOs, can access these network services through a wholesale arrangement. The networks will also be supplemented by TPG who has been allocated the remaining mmWave spectrum and will be allowed to roll out localised 5G networks.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Shamir Amanullah says, “Singapore, along with Thailand, leads 5G adoption in Southeast Asia and major telecom operators Singtel and StarHub launched trials which gives customers an opportunity to experience 5G speeds and potential new services.”
Singtel’s Journey Forward
Earlier this month Singtel launched its 5G NSA infrastructure on a 3-month trial promising speeds of 1Gbps by use of 3.5GHz frequency coupled with the existing 2100 MHz spectrum. It has made it free for the first 20,000 customers with 5G-compatible smartphones. While the 5G signals initially cover certain central and southern parts of Singapore, the coverage is expected to increase over the trial period. Singtel is also working on the development of other 5G services and integrating its network with technologies such as AI, IoT, Cloud, AR and data technologies, in line with the Government’s vision for 5G.
Last week, Singtel unveiled a 24×7 unmanned 5G powered stall to transform and reshape the retail experience. Labelled as 5G NOW @ UNBOXED, the hyper-connected store is designed to provide a first-hand experience of 5G services and possibilities to retailers and consumers. The store aims to offer seamless service experience to visitors looking for services such as SIM card replacements, and device collection through self-service kiosks. To create a more personalised experience for visitors, a 5G virtual assistant Stella is deployed at the store, integrated with facial recognition and emotion reading capabilities which will work in tandem with UNBOXED’s 5G rover Stanley. The rover is connected with the kiosk’s security system and will manage the contactless experience for visitors through temperature checks and maintaining social distancing measures. The 5G service with wireless connectivity and high speeds makes the store movable in a sort of hybrid online and offline retail model.
Amanullah says, “Singtel has ramped up its digitalisation efforts and increased adoption of digital channels and services to improve their customer experience. The 5G NOW @ UNBOXED phygital experience is cutting edge and brings the physical and digital experience in a seamless fashion for its customers. Singtel will be able to integrate physical and digital marketing efforts which should increase sales opportunity. In a recent report, Singtel announced that more than 70% of customer service transactions are online while only 30% of sales are transacted online. The unmanned 5G powered phygital experience should see online sales rising.”
The 5G powered pop-up store follows the launch of Singtel’s 5G non-standalone (NSA) network in the 3.5 GHz frequency as well as existing 2.1 GHz spectrum integrating technologies such as dual connectivity. The trial based 5G network offers Singtel customers a sense of 5G services such as high-speed internet of more than 1Gbps, video streaming, cloud gaming, AR/VR and other consumer use-cases.
JVCo’s 5G Initiatives
JVCo has also launched its 5G connectivity services using the NSA 5G architecture in the country in partnership with Nokia. StarHub launched its trials in August 2020 which will end on 16 February 2021. The trial runs on an NSA 5G infrastructure on the 2100 MHz spectrum with the SA 5G infrastructure operating on the 3.5 GHz expected to be ready in mid-2021. The StarHub Mobile+ or Biz+ mobile plans, allows customers to automatically experience some early 5G benefits using compatible mobile devices. The 6-month, free trial is a lead up to the full commercial launch of 5G standalone services next year. The telecom operator has a planned investment of USD 146.4 million in 5G infrastructure over a five-year period.
Meanwhile, M1 is working closely with IMDA and is expected to roll out 5G trial services, soon.
Amanullah says, “In the challenging financial times due to the COVID-19 pandemic which has impacted roaming, prepaid segment, equipment sales among others, it is impressive that the leading operators in Singapore are bringing cutting-edge connectivity services which should drive digitalisation of consumers and enterprises.”

Never before has the world experienced a shutdown in both supply and demand which has effectively slammed the brakes on economic activities and forced a complete rethink on how to continue doing business and maintain social interactions. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated digitalisation of consumers and enterprises and the telecommunications industry has been the pillar which has kept the world ticking over.
It is unthinkable just how the human race would have coped with such massive disruption, two decades ago in the absence of broadband internet. The technology and telecom sector has seen a rise in their visible importance in recent months. Various findings show that peak level traffic was about 20-30% higher than the levels before the pandemic. The rise in traffic coupled with the fervent growth of the digital economy augurs well for the technology and telecom sector in Southeast Asia.
Revenues Hit Despite Rise in Traffic
Unfortunately, the rise in network traffic has not translated to an increase in revenue for many operators in the region. The winners, that enjoyed YoY growth in Q1 2020 despite challenging circumstances were: Maxis (4.9%) and DiGi (3.4%) in Malaysia; dtac (3.3%) and True (5.7%) in Thailand; PDLT (7.5%) and Globe (1.4%) in the Philippines; and Indosat Ooredoo (7.9%) and XL Axiata (8.8%) in Indonesia. The telecom operators that struggled include: Celcom (-6.1%) and TM (-8.0%) in Malaysia; Singapore’s trio of Singtel (-6.5%), StarHub (-15.2%) and M1 (-10.3%); and AIS (-1.0%) in Thailand.
Key market trends include a dip in prepaid subscribers due to fall in tourist numbers, roaming income losses due to travel restrictions, and a general decline in average revenue per user (ARPU) due to weaker customer spend. The postpaid customer segment was resilient while the fixed broadband revenue stream was stable due to the increase in work from home (WFH) practices. With fixed tariffs, there are no incremental gains with an increase in usage. Voice revenue has been hit with the increase in collaboration-based communication applications such as Zoom and Microsoft Teams.
Equipment sales fell as global supply chains were severely disrupted and impacted new sign-ups of the more premium customers. Most markets in Southeast Asia depend on retail outlets as a key channel to the market, which has been hampered.
With the job losses across the world, bad debts and weakened customer spend is inevitable and it is imperative that the operators provide for reflective pricing strategies, listen to new customer requirements to ensure customer retention and strengthening of their market position. In May, Verizon’s CEO Hans Vestberg said nearly 800,000 of their subscribers were unable to pay their monthly bills. Discussions with operators in Southeast Asia also highlighted this as a current concern.
Enterprise Segment Target for New Growth
Ecosystm research shows that enterprises in Southeast Asia are increasingly considering telecom operators as go-to-market partners (Figure 1). Enterprises are demanding more than just devices and connectivity and with the fervent digital transformation (DX) efforts underway, services such as managed services, business application services, cybersecurity and network services are in demand. Technology vendors have an opportunity to partner with the right telecom operator in each market to enhance their IT market offerings, ahead of the 5G rollouts.
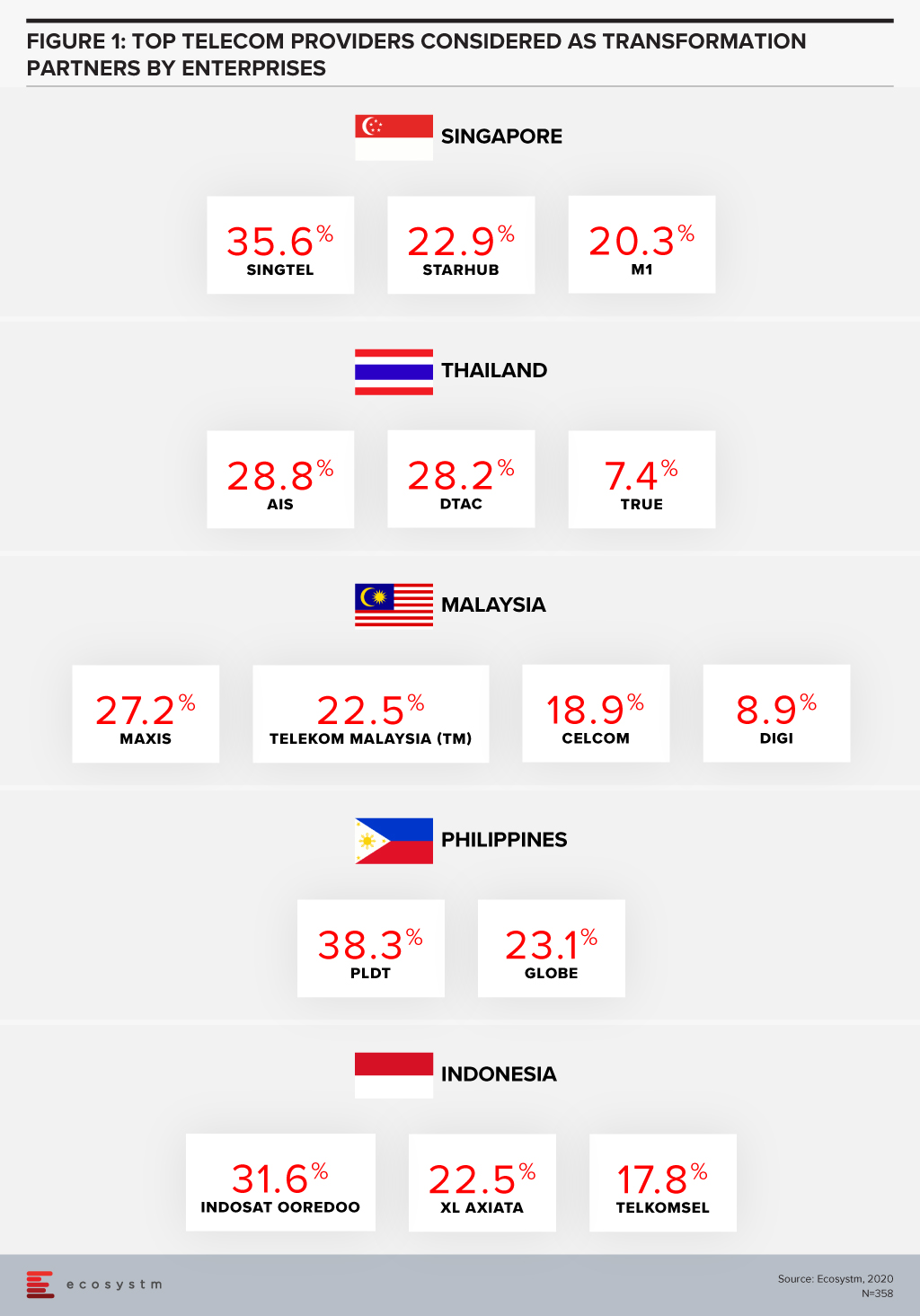
The broad 5G ecosystem inculcates cross-sector innovation and greater collaboration leading to new business models and exciting new opportunities. Singtel is the leading operator in the region and has the enterprise segment contributing approximately 65% to its revenue in its domestic market. In the World Communications Award 2019, Singtel won both “Best Enterprise Service” and “The Broadband Pioneer” awards. This places Singtel in a fine position to capitalise on the 5G enterprise services.
5G Needed Now More Than Ever
The pandemic has seen a rise in network traffic, onboarding of the digital customer and rapid DX of businesses which has whetted the appetite for faster broadband speeds and new services. Southeast Asia countries stand to profit from the trade war between the US and China and 5G features of low latency and higher security can boost adoption of IoT, Smart Manufacturing and broader Industry 4.0 goals to drive the economy.
Fixed Wireless in Southeast Asia is expected to be very popular considering the low penetration of fibre to the home (with the exception of Singapore) and will provide enterprises with a viable secondary connection to the internet. Popular applications – including video streaming and gaming – which are speed, latency and volume hungry will also be a target market for operators. Mobile operators that do not have a fixed broadband offering can enter this space and provide a serious “wireless fibre” alternative to homes and businesses.
Governments and telecom regulators ought to make spectrum available to the major telecom operators as soon as possible in order to ensure that the cutting edge 5G communications services are made available to consumers and businesses. Many experts believe 5G can raise the competitiveness of a nation.
Recent research from World Economic Forum (WEF) has found that significant economic and social value can be gained from the widespread deployment of 5G networks, with 5G facilitating industrial advances, productivity and improving the bottom line while enabling sustainable cities and communities. GSMA notes that mobile technologies and services in the wider Asia Pacific region generated USD 1.6 trillion of economic value while the mobile ecosystem supported 18 million jobs as well as contributing USD 180 billion of funding to the public sector through taxation.
US-China Trade War Threatens to Change Equipment Supplier Landscape
Despite severe pressures caused by the US-China trade war, Huawei posted an impressive 13.1% YoY growth in 1H 2020 registering revenue of USD 64.88 billion. Both Huawei and ZTE generate approximately 60% of their business from their domestic markets which is critical with the current unfavourable global sentiments. Huawei has diversified its business and built its consumer devices business which should withstand the disruptions caused by the political challenges.
Ericsson and Nokia stand to benefit from Huawei’s current global position and this was evident with the wins for the 5G contracts by Singtel and JVCo (Singtel and M1). The JVCo announced it selected Nokia to build the Radio Access Network (RAN) for the 5G standalone (SA) mmWave network infrastructure in the 3.5GHz radio frequency band. Singtel selected Ericsson to provide for the RAN on the same mmWave network.
However, while there is an opportunity for NEC and Samsung to join the party, Huawei is expected to do well in most other countries in Southeast Asia.
The Rise of the Digital Economy in Southeast Asia
A recent Google report valued the internet economy in Southeast Asia at USD 100 billion in 2019, more than tripling since 2015, and the sector is expected to hit USD 300 billion in 2025. With a population of approximately 570 million people, the region has some of the fastest-growing internet economies in the world.
The Indonesia market is the largest in the region and is expected to hit USD 133 billion from USD 40 billion in 2025. Indonesia’s lack of a world-class telecom infrastructure coupled with their slowness in 5G adoption has not impeded the country’s attractiveness for global technology investors who see the 270 million population as an immense opportunity. US tech giants, Facebook, Google, and PayPal have invested in Indonesia to reap the benefits from the growing digital economy powered by unicorns such as Gojek, Bukalapak, Tokopedia. In June 2020, Google Cloud launched in Jakarta, only the second in the region after Singapore with the four big unicorns being anchor customers.
In 2025, Google predicts Thailand to be the second-largest internet economy worth USD 50 billion. The internet economy for Singapore, Malaysia and the Philippines are estimated to be over USD 27 billion each. Shopee and Lazada are the top eCommerce apps in the region and have seen an increase in sales due to the disruption in the Retail industry. In-store shopping contributes to more than 50% of Retail in Singapore and Malaysia – this provides a tremendous opportunity for eCommerce players.
While movement restrictions are gradually being lifted, some things may never return where they were before COVID-19. Public debts have risen with numerous aids and handouts impacting economic growth forecast and rising unemployment is impacting customer spending power. On the plus side, DX of businesses and sharp onboarding of customers have redefined interactions, and sectors such as Education, are going online which will boost the digital economy. While the challenges are evident, exciting times are ahead for the technology and telecom sector in Southeast Asia.

Manufacturing is estimated to account for a fifth of Singapore’s GDP and is one of its growth pillars. Singapore has been talking about re-inventing the Manufacturing industry since 2017, when the Industry 4.0 initiatives to enable digitalisation and process automation of processes and to ensure global competitiveness were first launched. As part of the long-term strategy, the Government had spoken about investment into research and development (R&D) projects, developing transformation roadmaps and strengthening the skill sets of the workforce.
Singapore’s 5G Rollout
Last month, the Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) announced that Singtel and JVCo (formed by Starhub and M1) has won the 5G Call for Proposal. They will be required to provide coverage for at least half of Singapore by end-2022, scaling up to nationwide coverage by end 2025. While Singtel and JVCo will be allocated radio frequency spectrum to deploy nationwide 5G networks, other mobile operators, including MVNOs, can access these network services through a wholesale arrangement. The networks will also be supplemented by localised mmWave deployments that will provide high capacity 5G hotspots.
In October 2019, IMDA and the National Research Foundation had set aside $40 million to support 5G trials in strategic sectors such as maritime, aviation, smart estates, consumer applications, Industry 4.0 and government applications. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Jannat Maqbool says, “Reach, performance and robustness of connectivity and devices have long held back the ability to scale with the IoT as well as successful deployment of some solutions altogether. The integration of 5G with IoT has the potential to change that immensely. However, and possibly even more importantly, 5G will see the emergence of a true ‘Internet’, defined as ‘interconnected networks using standardised communication protocols’, made up of ‘things’ enabling never-before contemplated innovation – supporting economic development and community well-being.”
“While 5G offers enormous potential to produce economic and social benefits, to reach that potential we need to evaluate from a strategic perspective what it could mean for industries, employers and communities – then we need to invest in the infrastructure, innovation and associated development required to leverage the technology.”
Singapore’s Industry 4.0 Transformation
The Government is also focused on getting the industry ready for the transformation that 5G will bring. Last week, Singapore announced its first Industry 4.0 trial, where IMDA collaborates with IBM, M1 and Samsung to design, develop, test and benchmark 5G-enabled Industry 4.0 solutions that can be applied across various industries. The trials will begin at IBM’s facility in Singapore and involve open source infrastructure solutions from Red Hat to test Industry 4.0 use cases.
The project will test 5G-enabled use cases for Manufacturing, focusing on areas such as automated visual inspection using image recognition and video analytics, equipment monitoring and predictive maintenance, and the use of AR in increasing productivity and quality. The focus is also on leveraging 5G to reduce the cost of processing, by shifting the load from the edge device to centralised systems.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Kaushik Ghatak says, “For some time now, the Singapore Manufacturing industry has been in the quest for higher productivity in order to regain its foothold as a destination of choice for global manufacturing outsourcing. The 5G Industry 4.0 trial is a great initiative to fast-track identification and adoption of the right use cases in Manufacturing, in the areas of automation, visibility, analytics, as well as for opening new revenue streams through servitisation of smart products.”
5G will see increased collaboration in the Tech industry
With the advent of 5G, the market will see more collaboration between government agencies, telecom providers and cloud platform providers and network equipment providers. Governments globally have invested in 5G and so have the network and communications equipment providers. However, telecom providers are unsure of how to monetise 5G and cater to the shift in their customer profile from consumers to enterprises. IBM and Samsung had already announced the launch of a joint platform in late 2019. Collaborations such as these will be key to widespread 5G deployment and uptake.
Talking about the benefits of collaborative efforts such as this, Maqbool says, “Robustness and security built into 5G deployment from the outset is essential to enable the applications and innovation that many are promising the technology will deliver, including the ability to self-scale, automate fault management and support edge processing.”
It is interesting that the solutions developed will be featured at IBM’s Industry 4.0 Studio 5G Solutions Showcase, and that IBM and Samsung will evaluate successful solutions developed during the project for possible use in their operations in a broad range of markets and sectors. “Availability of proven use cases at IBM’s Solutions Showcase centre would benefit local manufactures greatly; in terms of easy access to right skills and proven technology architectures,” says Ghatak. “This initiative is a huge step towards realising the promise of the cyber physical world. The collaboration between the leaders in communications, equipment and software will ensure that the use case development is truly cutting edge.”





