In his blog, The Cybercrime Pandemic, Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Andrew Milroy says, “Remote working has reached unprecedented levels as organisations try hard to keep going. This is massively expanding the attack surface for cybercriminals, weakening security and leading to a cybercrime pandemic. Hacking activity and phishing, inspired by the COVID-19 crisis, are growing rapidly.” Remote working has seen an increase in adoption of cloud applications and collaborative tools, and organisations and governments are having to re-think their risk management programs.
We are seeing the market respond to this need and May saw initiatives from governments and enterprises on strengthening risk management practices and standards. Tech vendors have also stepped up their game, strengthening their Cybersecurity offerings.
Market Consolidation through M&As Continues
The Cybersecurity market is extremely fragmented and is ripe for consolidation. The last couple of years has seen some consolidation of the market, especially through acquisitions by larger platform players (wishing to provide an end-to-end solution) and private equity firms (who have a better view of the Cybersecurity start-up ecosystem). Cybersecurity providers continue to acquire niche providers to strengthen their end-to-end offering and respond to market requirements.
As organisations cope with remote working, network security, threat identification and identity and access management are becoming important. CyberArk acquired Identity as a Service provider Idaptive to work on an AI-based identity solution. The acquisition expands its identity management offerings across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Quick Heal invested in Singapore-based Ray, a start-up specialising in next-gen wireless and network technology. This would benefit Quick Heal in building a safe, secure, and seamless digital experience for users. This investment also shows Quick Heal’s strategy of investing in disruptive technologies to maintain its market presence and to develop a full-fledged integrated solution beneficial for its users.
Another interesting deal was Venafi acquiring Jetstack. Jetstack’s open-source Kubernetes certificate manager controller – cert-manager – with a thriving developer community of over 200 contributors, has been used by many global organisations as the go-to tool for using certificates in the Kubernetes space. The community has provided feedback through design discussion, user experience reports, code and documentation contributions as well as serving as a source for free community support. The partnership will see Venafi’s Machine Identity Protection having cloud-native capabilities. The deal came a day after VMware announced its intent to acquire Octarine to extend VMware’s Intrinsic Security Capabilities for Containers and Kubernetes and integrate Octarine’s technology to VMware’s Carbon Black, a security company which VMware bought last year.
Cybersecurity vendors are not the only ones that are acquiring niche Cybersecurity providers. In the wake of a rapid increase in user base and a surge in traffic, that exposed it to cyber-attacks (including the ‘zoombombing’ incidents), Zoom acquired secure messaging service Keybase, a secure messaging and file-sharing service to enhance their security and to build end-to-end encryption capability to strengthen their overall security posture.
Governments actively working on their Cyber Standards
Governments are forging ahead with digital transformation, providing better citizen services and better protection of citizen data. This has been especially important in the way they have had to manage the COVID-19 crisis – introducing restrictions fast, keeping citizens in the loop and often accessing citizens’ health and location data to contain the disaster. Various security guidelines and initiatives were announced by governments across the globe, to ensure that citizen data was being managed and used securely and to instil trust in citizens so that they would be willing to share their data.
Singapore, following its Smart Nation initiative, introduced a set of enhanced data security measures for public sector. There have been a few high-profile data breaches (especially in the public healthcare sector) in the last couple of years and the Government rolled out a common security framework for public agencies and their officials making them all accountable to a common code of practice. Measures include clarifying the roles and responsibilities of public officers involved in managing data security, and mandating that top public sector leadership be accountable for creating a strong organisational data security regime. The Government has also empowered citizens to raise a flag against unauthorised data disclosures through a simple incident report form available on Singapore’s Smart Nation Website.
Australia is also ramping up measures to protect the public sector and the country’s data against threats and breaches by issuing guidelines to Australia’s critical infrastructure providers from cyber-attacks. The Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) especially aims key employees working in services such as power and water distribution networks, and transport and communications grids. In the US agencies such as the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the Department of Energy (DOE) have issued guidelines on safeguarding the country’s critical infrastructure. Similarly, UK’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) issued cybersecurity best practices for Industrial Control Systems (ICS).
Cyber Awareness emerges as the need of the hour
While governments will continue to strengthen their Cybersecurity standards, the truth is Cybersecurity breaches often happen because of employee actions – sometimes deliberate, but often out of unawareness of the risks. As remote working becomes a norm for more organisations, there is a need for greater awareness amongst employees and Cybersecurity caution should become part of the organisational culture.
Comtech received a US$8.4 million in additional orders from the US Federal Government for a Joint Cyber Analysis Course. The company has been providing cyber-training to government agencies in the communications sector. Another public-private partnership to raise awareness on Cybersecurity announced in May was the MoU between Europol’s European Cybercrime Centre (EC3) and Capgemini Netherlands. With this MoU, Capgemini and Europol are collaborating on activities such as the development of cyber simulation exercises, capacity building, and prevention and awareness campaigns. They are also partnered on a No More Ransomware project by National High Tech Crime Unit of the Netherlands’ Police, Kaspersky and McAfee to help victims fight against ransomware threats.
The Industry continues to gear up for the Future
Technology providers, including Cybersecurity vendors, continue to evolve their offerings and several innovations were reported in May. Futuristic initiatives such as these show that technology vendors are aware of the acute need to build AI-based cyber solutions to stay ahead of cybercriminals.
Samsung introduced a new secure element (SE) Cybersecurity chip to protect mobile devices against security threats. The chip received an Evaluation Assurance Level (EAL) 6+ certification from CC EAL – a technology security evaluation agency which certifies IT products security on a scale of EAL0 to EAL7. Further applications of the chip could include securing e-passports, crypto hardware wallets and mobile devices based on standalone hardware-level security. Samsung also introduced a new smartphone in which Samsung is using a chipset from SK Telecom with quantum-crypto technology. This involves Quantum Random Number Generator (QRNG) to enhance the security of applications and services instead of using normal random number generators. The technology uses LED and CMOS sensor to capture quantum randomness and produce unpredictable strings and patterns which are difficult to hack. This is in line with what we are seeing in the findings of an Ecosystm business pulse study to gauge how organisations are prioritising their IT investments to adapt to the New Normal. 36% of organisations in the Asia Pacific region invested significantly in Mobile Security is a response to the COVID-19 crisis.
The same study reveals that nearly 40% of organisations in the region have also increased investments in Threat Analysis & Intelligence. At the Southern Methodist University in Texas, engineers at Darwin Deason Institute for Cybersecurity have created a software to detect and prevent ransomware threats before they can occur. Their detection method known as sensor-based ransomware detection can even spot new ransomware attacks and terminates the encryption process without relying on the signature of past infections. The university has filed a patent for this technique with the US Patent and Trademark Office.
Microsoft and Intel are working on a project called STAMINA (static malware-as-image network analysis). The project involves a new deep learning approach that converts malware into grayscale images to scan the text and structural patterns specific to malware. This works by converting a file’s binary form into a stream of raw pixel data (1D) which is later converted into a photo (2D) to feed into image analysis algorithms based on a pre-trained deep neural network to scan and classify images as clean or infected.

Manufacturing is estimated to account for a fifth of Singapore’s GDP and is one of its growth pillars. Singapore has been talking about re-inventing the Manufacturing industry since 2017, when the Industry 4.0 initiatives to enable digitalisation and process automation of processes and to ensure global competitiveness were first launched. As part of the long-term strategy, the Government had spoken about investment into research and development (R&D) projects, developing transformation roadmaps and strengthening the skill sets of the workforce.
Singapore’s 5G Rollout
Last month, the Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) announced that Singtel and JVCo (formed by Starhub and M1) has won the 5G Call for Proposal. They will be required to provide coverage for at least half of Singapore by end-2022, scaling up to nationwide coverage by end 2025. While Singtel and JVCo will be allocated radio frequency spectrum to deploy nationwide 5G networks, other mobile operators, including MVNOs, can access these network services through a wholesale arrangement. The networks will also be supplemented by localised mmWave deployments that will provide high capacity 5G hotspots.
In October 2019, IMDA and the National Research Foundation had set aside $40 million to support 5G trials in strategic sectors such as maritime, aviation, smart estates, consumer applications, Industry 4.0 and government applications. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Jannat Maqbool says, “Reach, performance and robustness of connectivity and devices have long held back the ability to scale with the IoT as well as successful deployment of some solutions altogether. The integration of 5G with IoT has the potential to change that immensely. However, and possibly even more importantly, 5G will see the emergence of a true ‘Internet’, defined as ‘interconnected networks using standardised communication protocols’, made up of ‘things’ enabling never-before contemplated innovation – supporting economic development and community well-being.”
“While 5G offers enormous potential to produce economic and social benefits, to reach that potential we need to evaluate from a strategic perspective what it could mean for industries, employers and communities – then we need to invest in the infrastructure, innovation and associated development required to leverage the technology.”
Singapore’s Industry 4.0 Transformation
The Government is also focused on getting the industry ready for the transformation that 5G will bring. Last week, Singapore announced its first Industry 4.0 trial, where IMDA collaborates with IBM, M1 and Samsung to design, develop, test and benchmark 5G-enabled Industry 4.0 solutions that can be applied across various industries. The trials will begin at IBM’s facility in Singapore and involve open source infrastructure solutions from Red Hat to test Industry 4.0 use cases.
The project will test 5G-enabled use cases for Manufacturing, focusing on areas such as automated visual inspection using image recognition and video analytics, equipment monitoring and predictive maintenance, and the use of AR in increasing productivity and quality. The focus is also on leveraging 5G to reduce the cost of processing, by shifting the load from the edge device to centralised systems.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Kaushik Ghatak says, “For some time now, the Singapore Manufacturing industry has been in the quest for higher productivity in order to regain its foothold as a destination of choice for global manufacturing outsourcing. The 5G Industry 4.0 trial is a great initiative to fast-track identification and adoption of the right use cases in Manufacturing, in the areas of automation, visibility, analytics, as well as for opening new revenue streams through servitisation of smart products.”
5G will see increased collaboration in the Tech industry
With the advent of 5G, the market will see more collaboration between government agencies, telecom providers and cloud platform providers and network equipment providers. Governments globally have invested in 5G and so have the network and communications equipment providers. However, telecom providers are unsure of how to monetise 5G and cater to the shift in their customer profile from consumers to enterprises. IBM and Samsung had already announced the launch of a joint platform in late 2019. Collaborations such as these will be key to widespread 5G deployment and uptake.
Talking about the benefits of collaborative efforts such as this, Maqbool says, “Robustness and security built into 5G deployment from the outset is essential to enable the applications and innovation that many are promising the technology will deliver, including the ability to self-scale, automate fault management and support edge processing.”
It is interesting that the solutions developed will be featured at IBM’s Industry 4.0 Studio 5G Solutions Showcase, and that IBM and Samsung will evaluate successful solutions developed during the project for possible use in their operations in a broad range of markets and sectors. “Availability of proven use cases at IBM’s Solutions Showcase centre would benefit local manufactures greatly; in terms of easy access to right skills and proven technology architectures,” says Ghatak. “This initiative is a huge step towards realising the promise of the cyber physical world. The collaboration between the leaders in communications, equipment and software will ensure that the use case development is truly cutting edge.”

As we get into the second month of Circuit Breaker here in Singapore and most people are working from home, we are hearing a lot more about the difficulties that organisations and individuals have faced when it comes to operating as a remote workforce – or what is commonly called working from home or “WFH”.
As the CEO of technology research and advisory platform, I am lucky to have some of the global experts and thought-leaders in remote working as part of our team. While it is not an easy ask of staff, and some find it harder than others, remote working is going to be an increasingly important component of our work lives in the future, and something we need to get right in order to “Survive to Thrive”.
People and Engagement
Let’s face it – we are in a humanitarian crisis, foremost and the economic crisis is just a fallout of it. So impact on People has to be the number one consideration. Working from home can be a real culture shock. Gone is the ability to quickly speak to the colleague next to you, meet someone for lunch or even just have a discussion in the pantry. Taking away these social interactions can impact employee morale and therefore productivity. Putting an effort into team-building – as hard as it is to do remotely – is very important.
Groups on social messaging apps (outside of the work-related ones) can help rebuild that camaraderie and strengthen social bonds. Plan team-building exercises such as quizzes, virtual drinks, or even networking lunches that can be done remotely. Remember, the wellness of your teams is directly proportionate to the well-being of the business.
Process and Practice
Working from home requires a different mindset to being in the office, and it is easy to get dragged into an endless cycle of emails and conference calls. This often means that the act of planning and discussing replaces the act of doing!
This is where good-practice from the pre-COVID-19 era becomes an essential practice right now. Note-taking, summarising discussions, and recapping roles and responsibilities for project execution becomes paramount. Documenting and tracking progress will have a positive impact on productivity and ensure that teams are focused on their collective and individual responsibilities.
While there are many applications that you may consider to manage and monitor projects, you may also want to explore appointing dedicated people whose role is to identify how processes have been affected by remote working, and how bottlenecks can be cleared with more effective use of collaboration software.
Technology to get Digital Ready
Teams need the applications to communicate and carry out their responsibilities diligently. Luckily, in the age of cloud computing, most organisations were able to quite easily transition to a work from home environment. Those that struggled were the companies that had not embraced digital and were not using any cloud-based software (for email, collaboration, bookkeeping, HR or CRM); or those that are mandated by strict compliance and cybersecurity measures that cannot be enforced in employees’ homes.
While many organisations were already using a variety of communication & collaboration solutions, in the new work from home setups, you may want to consider additional solutions to help you get through your current challenges. The good news is that many technology providers have made their offerings available for free trials during this period, so the financial outlay may be minimal or non-existent.
You should also not overlook the importance of cybersecurity at this time. Regulations around data privacy are still applicable, and home-networks are not as secure as enterprise networks. At the same time, social-engineering and phishing attacks are also on the rise. So be sure to provide regular updates to your teams with guidance on how they can help maintain the security of your data and networks.
In conclusion, as we come to terms with the current normal, and get a glimpse of what the future normal may look like; we continue to see the old adage that it’s people, process and technology – in that order – which will guide us through the current situation and set us up for continued success. While no one has a crystal ball, it is actions – how you interact with your colleagues and the processes you put in place – and not technology that will ultimately best position your organisation to thrive in the future.
As published in the tabla! (An SPH Publication)
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of the telecommunications industry which has now become the backbone of the new normal, both in a social and business sense. The last few months have seen a number of changes including more video usage, location of traffic and time of traffic. Network usage is on the rise and telecom carriers are prioritising on the resilience of their networks and the quality of services offered to their customers.
What goes up must come down
According to Speedtest, global mobile and broadband speeds have suffered as a result of the increase in traffic with speeds dropping in March 2020 for mobile to 30.47 Mbps (from 31.62 Mbps in February) and fixed broadband to 74.64 Mbps (from 75.41 Mbps in February). In Southeast Asia, only Singapore and Vietnam averaged mobile speeds of 54.37 Mbps and 33.97 Mbps respectively, exceeding the global average speeds. As for fixed broadband, Singapore ranked highest globally achieving 197.26 Mbps while Thailand and Malaysia clocked 149.95 Mbps and 79.86 Mbps respectively, trumping the global average speeds.
Southeast Asian carriers increase network efficiency and quality
Singapore. The country’s ICT regulator, Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA), reported an increase in internet usage and its intentions to support telecom carriers in boosting network capacity to ensure essential services run smoothly. Priority will be given to high traffic and residential areas where a larger proportion of the population are working from home. The Ministry of Communications and Information (MCI) reported that Singapore has at least 30 percent buffer in network capacity even during peak periods. Major TV operators Mediacorp, Singtel and Starhub have made more content available for free during this period. This may further impact network speeds as customers are consuming more content over wifi (on mobile apps) or over the fibre networks.
Thailand. Part of the country’s public assistance measures during the pandemic, include offering about 30 million mobile subscribers 10GB free data. The National Broadcasting and Telecommunications Commission (NBTC) will also upgrade the speeds of fixed broadband to at least 100 Mbps which is expected to benefit 1.2 million household subscribers. Leading operator Advanced Info Service (AIS) recently announced that it has deployed 5G networks at hospitals to boost network capacity and speeds, and is deploying robots for telemedicine to empower the healthcare system to fight COVID-19.
Malaysia. Maxis and Telekom Malaysia (TM) reported a surge in traffic since the movement control order (MCO) was implemented by the Government on the 18th March 2020. The MCO is expected to run at least until 28th April 2020. TM cited a 30 percent increase in usage attributed to the increase in traffic for streaming, online games and teleconferencing. Leading operators Maxis, Digi, Celcom and U Mobile have offered 1GB free data during the MCO period as part of the Government’s stimulus package. Maxis, TM, Digi and Celcom have also committed significant manpower to ensure that the networks are operating efficiently and to ensure customer support. Leading TV operator Astro has made all movie, news and cartoon networks available to all its customers until the 28th April 2020.
Social distancing fillip for video conferencing
The rise of social distancing has made us all seek new ways to connect, mainly through video chat. Video conferencing traffic is on the rise as it is the next best thing to face-to-face meetings. Microsoft Teams and Zoom have been big benefactors. The American Economic Institute (AEI) notes that Zoom hit some 200 million users daily from a daily average 10 million. Microsoft Teams added some 12 million registrations to a total of 44 million.
Many predict that the home working trend will continue in the recovery stage and beyond, due to improvements in the telecommunications infrastructure and impending rollout of 5G. It is also predicted that the commercial property sector is likely to suffer due to this trend. This period also highlights the critical importance of cybersecurity with increasing occurrences of hacking and fraud. Zoom is being forced to reinforce their privacy and security measures, as an example.
COVID-19 has changed the way we web
On the social front, many are also using video conferencing to communicate with friends and family. Operators relaxing and offering additional data has undoubtedly contributed to the increase in this usage too. Now that many are homebound, network traffic in residential areas are higher than ever. In the past, peak hours of traffic at homes were at night – this has changed with adults and children homebound. Adults are using video conferencing and more voice calls; while children are using elearning, playing games or streaming videos. The European Commission had asked Netflix and other streaming platforms to reduce streaming quality to standard definition (SD). Netflix has assured that it has the capability to manage levels of streaming quality in accordance with the networks quality requirement of individual countries.
Online gaming and video streaming have emerged as winners and have seen an increase in consumption in these times as they provide for entertainment for millions stuck at home. There is tremendous opportunity for both telecom operators and content providers to increase their number of services in this area. Netflix, YouTube, Microsoft Xbox and PlayStation are among the winners in this sector. YouTube provides for a primary news source and commentary on the epidemic for many. Netflix’s stocks are near an all-time high at present.
eCommerce boost for essentials goods and services
The eCommerce sector should see a major improvement in Southeast Asia as physical channels to market have reduced. Emerging economies such as Malaysia and Thailand should see an improvement in services and embrace eCommerce like their mature counterparts. Statista reports that the average Malaysian eCommerce shopper spent just US$159 and Thailand just US$100 on online consumer goods purchases in 2018, considerably lower than the global average of US$634. There is huge opportunity to provide for basic necessities such as online grocery, food and delivery of goods. As a consequence, contactless payment and the transport and logistics sector will be forced to adapt their business operations to ride this wave successfully. As eCommerce transactions diversify and increase in emerging markets, it will give telecom providers an opportunity to keep engaging with platform players.
Telecom carriers are likely to suffer financial losses due to the scale of the disruption COVID-19 has brought about. However, there are some positives takeaways from this period. The increase of network traffic and the changing patterns have driven carriers to better understand network traffic management. The sharp consumer and business onboarding as far as applications and digital services are concerned, has given the digital economy and 5G use cases a shot in the arm. This is likely to spur innovation in services including communications, eCommerce, payments, logistics and healthcare among others.

Deep Tech companies are aiming to transform the world through scientific, engineering and technological advances. As technology evolves, researchers are looking to apply engineering and technological advances in areas such as processing and computing architecture, semiconductors and electronics, materials science, vision and speech technologies, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, and so on – for the greater good. For example, finding a cure to a disease, developing new medical devices, sensors and analytics to help farmers increase yield, or developing clean energy solutions to reduce the environmental impact are some of the areas that Deep Tech is finding real-world applications.
Deep Tech Impacting Industries Today
There are several industries that are benefitting from Deep Tech innovations today. Here are only a few examples of Deep Tech innovations in some industries:
Healthcare
The combination of computational and biotechnology is accelerating the development of new cures, augmenting R&D and improving health outcomes. Deep Tech in healthcare has multiple applications from the manufacturing of affordable medical devices to redefining healthcare. Vibrosonic, has designed what they call a “contact lens for the ear” which can be directly placed on the eardrum. Unlike other hearing aids speakers are not used to transport sound through the ear canal but the eardrums are stimulated through electric impulses. A Singapore-based biotech company X Zell has patented a “liquid biopsy”- detecting cancer from a 10ml blood sample by measuring the presence of tumour-derived Circulating Endothelial Cells (tCEC) – which reduces the need for invasive cancer detection processes.
Food and Agriculture
Food crisis is a reality today with factors such as overpopulation, urbanisation, decreasing land per capita, extreme climates and so on impacting the food and agriculture industry immensely. Deep Tech companies are working to bring us sustainable food options and building climate resilience. Cell-based meat options are being researched globally, and companies such as foodtech start-up Shiok Meats is producing meat by harvesting cells from animals with a view to be environmentally friendly and to reduce the impact on biodiversity. In agriculture, Deep Tech companies are working on technologies to develop better farming methods to improve yield and precision sensors for weather forecasting. Examples such as UbiQD, that has worked on a greenhouse quantum dot film that improves crop quality by optimising sunlight spectrum for plants to improve production, show how Deep Tech will continue to transform the industry.
Environment and Energy
Deep Tech continues to come up with solutions that will help us in climate change mitigation, development of sustainable energy and energy efficiency. Innovations include Carbon Upcycling Technologies’ solution to capture and neutralise carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide-enriched nanoparticles are used to make commercial construction materials and even consumer products such as jewellery. Celadyne Technologies has developed hydrogen fuel cells and electrolysers with nanocomposite membranes for a more efficient, cost-effective and eco-friendly energy source.
Advanced Computing
As technology evolves, there will be a need to support even greater compute and data-intensive tasks. Deep Tech has impacted and will continue to impact advanced computing. The semiconductor and microchip industry is getting disrupted by cutting-edge global research, many by the top universities. MIT, for example, has developed a process called “remote epitaxy” to manufacture flexible chips. Potential use cases include VR-enabled contact lenses, electronic fabrics that respond to the weather, and other flexible electronics. Atom Computing is working on scalable quantum computing that will be able to scale millions of qubits using individual atoms – without scaling up the physical resources – in a single architecture.
Communication and Security
Communication and connectivity have seen a sea change in the last decade. As we wait for 5G to take off, this industry has become a playground for inventions. Aircision, is working on making 5G more accessible using its laser-based communications technology. The technology is developed to enable high-bandwidth communication and beam data between buildings thus aiming to eliminate the need for optical fibre installations and microwave. Another area that will keep getting a lot of attention from Deep Tech firms is communication security. Speqtral is working on space-based quantum networks to deliver secure encryption keys.
Examples such as these are an indication that Deep Tech is a reality today and has the potential to disrupt several industries and impact the lives of millions.
Where is Deep Tech Headed?
Government Interest in Deep Tech
Since Deep Tech is aimed at leveraging technology and engineering for sustainability and greater good, several countries are promoting Deep Tech R&D and initiatives. From emerging to mature economies, governments are supporting their Deep Tech industry. The New Zealand Government has formed a Deep Tech Incubator program. The program is headed by the Government’s innovation agency to help Deep Tech companies and to create new tech jobs.
Singapore has created a strong Deep Tech ecosystem leveraging the funding ecosystem, the presence of global corporations, research and higher learning organisations and the Government that promotes innovation and entrepreneurship. Agencies such as SGInnovate and Enterprise Singapore are working with Deep Tech startups in advanced manufacturing, urban solutions and sustainability, and healthcare and biomedical sciences. Partnerships between universities, industry bodies and research organisations further fuel this ecosystem – the Critical Analytics for Manufacturing Personalised-Medicine (CAMP) is a partnership between Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART) and A*STAR for cell therapy manufacturing. The Government also funds and incentivises Deep Tech startups. The 2020 budget announced additional funding to support Deep Tech companies under the Start-up SG Equity scheme.
As global governments get serious about the quality of their citizens’ lives and sustainability goals, they will invest in Deep Tech research.
Challenges of the Deep Tech Industry
While Deep Tech has enormous potential, mainstream adoption is still some way off. There are some unique challenges that the industry faces today. Future uptake will depend heavily on how fast the industry can circumvent these challenges. The key challenges are:
- Securing Finances. Despite initiatives by several global governments, Deep Tech projects often find it difficult to secure funding. Very often the research duration can stretch without any real guarantee of success. Funding is likelier to go to organisations developing consumer products as the ROI are seen earlier and are easier to quantify, especially in the early stages.
- Identifying Market Opportunities. Researchers who develop Deep Tech solutions and products might not be able to identify opportunities to present their development from a marketing as well as an economic perspective. Very often these companies rely on other channels or third-party services for a proper marketing and planning strategy. This is where working with incubators or government bodies becomes crucial – countries that give that opportunity through a well-defined ecosystem, will lead the Deep Tech revolution.
- Scalable Development. Many Deep Tech innovations get stuck at the proof-of-concept stage – not because they are not innovative enough, but because they are not scalable to mass production. That requires the right infrastructure as well as a deep understanding of how the products and services can be commercialised.
There are several global companies trying to disrupt entire industries with their inventive offerings. We are witnessing some novel innovations in autonomous vehicles, foodtech, computer vision, AI, weather predictions, Clean Energy solutions – the list continues – that we will benefit from in the future.
Let us know which Deep Tech companies have impressed you in the comments below.

Singapore maintains its competitiveness through strong Government support and an environment that encourages trade and investments. The economy sees a huge contribution from start-ups and small and medium enterprises (SMEs), which receives financial incentives and technology guidance from the Government.
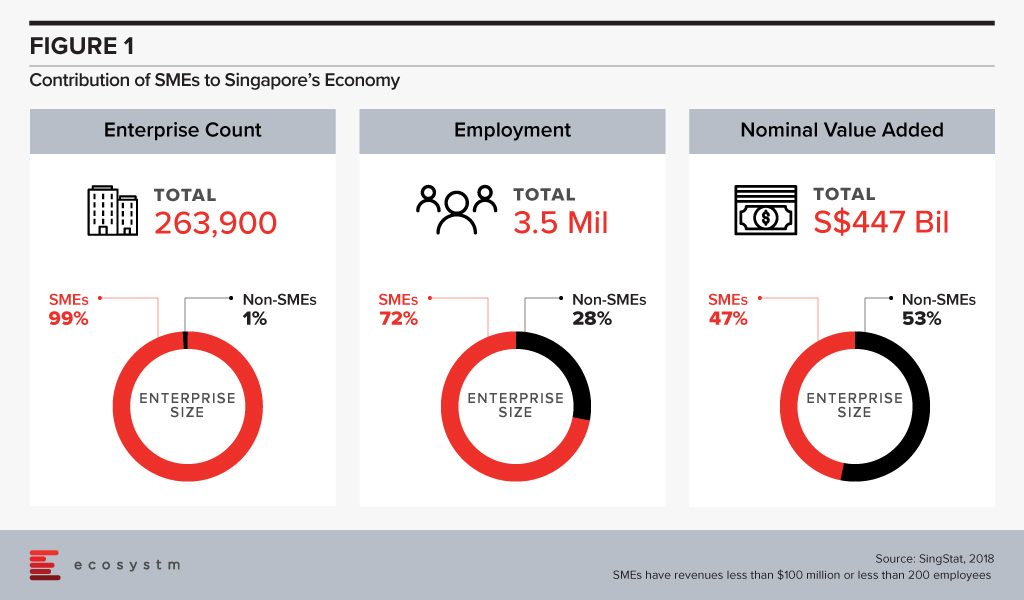
The success of SMEs in Singapore is at the core of national economic growth with approximately 261,000 SMEs contributing to nearly 50% of the country’s GDP.
A survey conducted by United Overseas Bank (UOB) in November 2019 illustrates that SMEs in Singapore are focusing on boosting productivity as they grapple with macro-economic and socio-political uncertainties this year. The UOB survey included 615 local SMEs with a revenue of less than S$100 million. Nearly half of the SMEs surveyed have a positive outlook for their business in 2020, while nearly a third are not so optimistic about it.
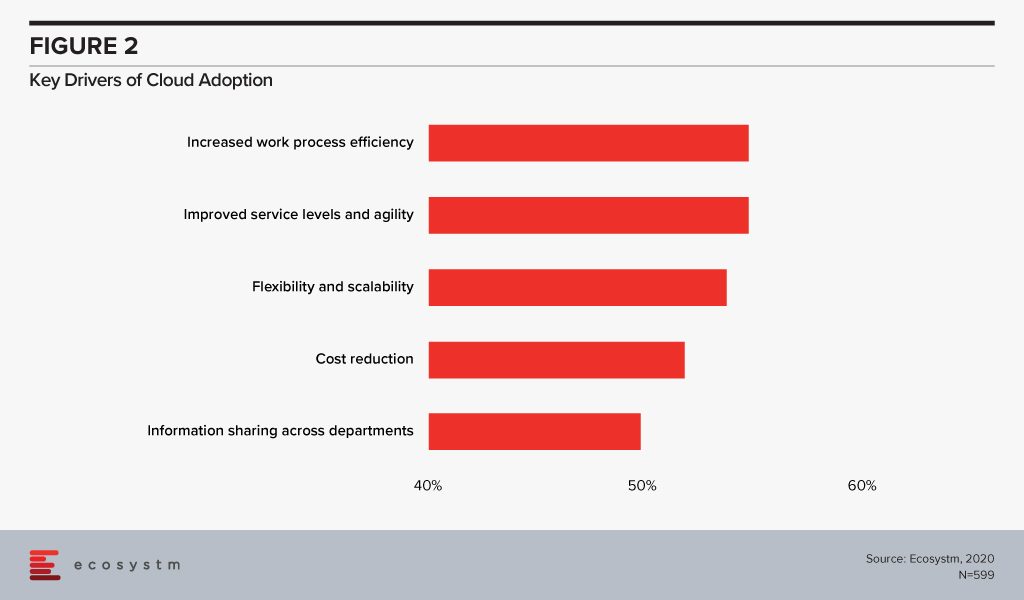
While cost reduction and new streams of revenue generation are top business priorities, more than half of the SMEs polled, mentioned increasing productivity as their top priority. Technology adoption has often been linked to an increase in productivity. SMEs in Singapore appear to be on the right track as currently 65% use digital solutions, mostly geared towards accounting, HR and customer relationship management. Digitalisation involves a widespread adoption of cloud and automation solutions. If we look at the key drivers of cloud adoption across all global organisations (Figure 2), we find that optimisation and productivity are key incentives.
Interestingly, the UOB survey also finds that more than half of SMEs in Singapore have sustainability goals. Resource optimisation and energy efficiency will also see higher adoption of technology in the future.
Government Initiatives Empowering SMEs
Government agencies and industry bodies have always been proactive in empowering SMEs with technological knowledge. There are various programs and initiatives to promote digitalisation, which have made Singapore SMEs competitive at a global level.
The Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) is helping Singapore SMEs to scale and improve their digital capabilities, expand their network and go global through collaboration with multinational companies (MNCs). The SMEs Go Digital program launched in 2017, has seen an estimated 4,000 SMEs adopting pre-approved digital solutions.
Several organisations in Singapore – such as A*Star and Enterprise Singapore – have targeted programs for the SME community. One of the key challenges for SMEs that impacts their ability to invest in technology is a lack of internal IT skills. Initiatives such as the Technology Adoption Programme (TAP) recognise this and bring in multiple industry and technology stakeholders to translate new technologies into Ready-to-Go (RTG) solutions, aimed at SMEs.
Apart from technology, access to financing is a key factor that determines the success of an SME and remains a key focus of Singapore’s banking and financial sector. The digital wholesale licenses are also aimed at SME financing, especially targeting those that are unable to procure funds from traditional sources.
Technologies Enabling Digitalisation in Singapore SMEs
Cloud
As mentioned earlier, cloud is the key enabler of digitalisation, giving organisations the ability to access solutions anywhere and anytime. Ecosystm research shows that 80% of SMEs in Singapore use an IaaS solution, while more than 75% use a SaaS solution.
There are programs that boost cloud adoption in Singapore SMEs as well. As an example, SMECEN, developed by the Association of Small & Medium Enterprises (ASME), and supported by Enterprise Singapore, Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) and Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) is a SaaS solution with accounting, HR and compliance modules – integration with other business tools is on the cards.
AI/Automation
Digitalisation will eventually involve investments in Automation and AI. For Singapore, AI is a key technology as it continues to focus on IoT, smart buildings, smart electricity, autonomous electric vehicles and other smart city solutions. The Government is working to open up access to data and AI tools so everyone can experiment. It especially wants to encourage SMEs to adopt AI and work on government use cases.
Singapore SMEs are ramping up their AI investments, especially in IoT sensor analytics (27%), machine learning (21%) and robotic process automation (16%), according to the Ecosystm AI study. Their key short-term drivers are insights into the competition and enhanced internal process monitoring. However, in the longer term, they are looking at cost reduction and better profit margins.
Fintech
According to an OCBC survey in 2018, which polled 200 such companies, two-thirds of SMEs in Singapore are likely to go cashless by 2023. It is estimated that over 75% of Fintech transactions in Singapore are digital payments and it receives over a quarter of Fintech funding. Government initiatives such as FAST and SGQR, have opened up digital payment options for consumer use as well as for SMEs.
However, the UOB survey notes some concerns that SMEs have over digital payments adoption, including customer/supplier acceptance and security. This is an encouraging sign, which indicates that SMEs are not just adopting technology because of the hype – but are evaluating the pros and cons of tech adoption before embarking on a digitalisation project.

The race for digital bank licenses in Singapore is on as the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) deadline for applications closed at the end of last year.
The Singapore Government continues to promote fintech initiatives in the banking industry such as the FAST network (giving fintech and non-banking organisations access to the real-time payments network) and Project Ubin (focusing on inter-bank funds transfer using Blockchain). The digital bank licenses continue in the same vein and will offer the same banking services as traditional banks but operate online and without any physical infrastructure.
“The biggest gamechanger of the app-based and shared economy is that it puts the power of decision making and choice in the hands of the consumer. It also removes entry barriers for non-traditional market entrants, but the flipside is it also weakens a number of regulatory barriers that were put in place for safeguarding the consumer,” says Amit Gupta, Ecosystm CEO. “With digital banking at the verge of becoming mainstream, it will help spur the app-based economy with the advent of more complete ecosystems and the added benefit of stronger governance measures and frameworks that will come into play simply because financial regulators in Singapore are driving it.”
Digital banking is not new, and MAS has been encouraging banks to offer digital services since 2000. Taking it a step forward, in June 2019, MAS announced their intentions to issue 5 digital bank licences in Singapore, opening up the banking industry to the non-banking sector.
Following the announcement, in August 2019, MAS invited applications for 2 digital full banks (DFBs) aimed primarily at retail banking, and 3 digital wholesale banks (DWBs) primarily for SMEs and other non-retail segments. While DFB licenses are restricted to Singapore based companies (including foreign joint ventures with a Singapore entity and headquarters), DWB licenses have no such restrictions, opening the market to overseas players.
Applicants for the New Digital Bank License
MAS announced on January 7, 2020, that it had received 21 applications (7 for DFB and 14 for DWB licenses). A list of applicants has not been made available, and confirmation of application has typically come from the applicants themselves. The licences will be issued in mid-2020 with the commencement of business expected about a year later.
The race for the digital bank license in Singapore has seen several non-banking contenders. MAS has mentioned that applicants will be selected based on their market reputation, a proven track record, financial strength, innovative business models, and a commitment to develop the skills of the Singaporean workforce. The contenders who have announced their applications cover a wide range – from the Sea Group (whose eCommerce site, Shoppee has a strong presence in Singapore) to the Enigma Group (a financial organisation based in the UK). Here are some organisations that may well be ahead of the race:
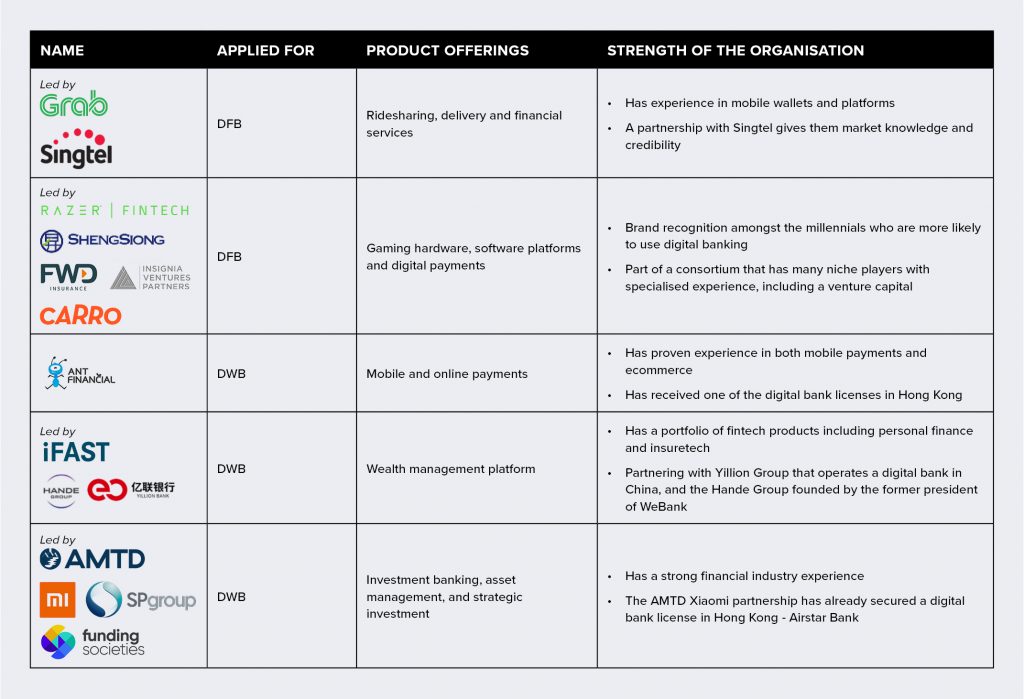
“From the nature of consortium of bidders for DFBs and DFWs in Singapore, we can safely anticipate that the financial ecosystems will be aligned very closely with certain consumer demographics that make up the core target segments. As an example, Razer will be in a position to meet the specific needs of the millennial consumer base,” adds Gupta. “In saying that, it will also be important to evaluate how digital banks deal with educating consumers on wealth creation offerings and financial literacy, which is currently being achieved through personal touchpoints by the traditional banks.”
Ecosystm Comments
Singapore has emerged as one of the global leaders in fintech due largely to the maturity of the technology infrastructure, the banking sector and data compliance laws, as well as the tech-savviness of its citizens. The buzz created in the market when MAS announced the initiative last year is partly because a successful implementation in Singapore carries weight globally, especially in the relatively untapped Southeast Asian market.
Singapore also collaborates with the countries in the region empowering them with talent development and co-creation of fintech solutions. Initiatives such as the ASEAN Financial Innovation Network (AFIN) further promote fintech adoption through its open-architecture platform. Several countries in the region will take inspiration from Singapore and evaluate digital banks as a means to better financial inclusion. Thailand’s central bank has already indicated its interest in digital banks, prompted by the Singapore and Hong Kong initiatives.
Talking specifically about the competition in the Singapore financial industry, Gupta says, “Unlike some of the other markets, traditional banks in Singapore will continue to offer competing digital offerings as local banks such as DBS have been very savvy in building their digital offerings over the years. If their digital innovation keeps evolving at the pace they have been setting in recent years, they will present very stiff competitive barriers to the new digital bank entrants, especially given their ability to continue offering personalised service and touchpoints, coupled with compelling digital offerings.”
Data Management and Digital Transformation: Inextricably Intertwined
Digital transformation (DX) is at the top of the strategic objectives list for most organisations. However, one key aspect of DX that is often overlooked and causes problems if not adequately prepared for, is the issue of data management. Before you can reap the benefits of your data – which is the core of DX – you need to have control over it first.
Most enterprise data is scattered across multiple locations on-premise and in various clouds (public, private, hybrid). It is trapped in infrastructure silos or buried in long-forgotten storage systems, or back-up devices. This makes it difficult and time-consuming for IT to control or access and hinders data exploitation for the business.
The topic of data management, although not as exciting sounding as DX, or analytics, is substantially more critical to business success, so I invite you to join Ecosystm, HPE, Cohesity, and PTC at our Executive Luncheon on “Data Management & Digital Transformation: Inextricably Intertwined”. In a collegiate and sharing environment, we will discuss how you can take back control of your data and simplify the way your company protects, controls and extracts value from your data across all sources.
This session is designed to share and learn with your peers and industry experts on some of the following topics:
- Relevance and importance of Data Management to your Digital Transformation initiatives and enabling your business to derive competitive advantage from all of your data
- Discussion on the key issues around data management including data collection, storage, coping with growth, data protection and privacy, and management and use of data from the center to the edge
- Best practices in data management – based on a short interactive roundtable discussion format where you workshop one of a selection of data management challenges as a table and exchange ideas and solutions
++Update: A few days after we added this story, Australia released its AI roadmap focused on future investment in AI and machine learning, and Artificial Intelligence: Australia’s Ethics Framework.
Over the last few years, many countries have created plans to harness Artificial Intelligence (AI) for better citizen services. At this week’s SFFXSWITCH (Singapore FinTech Festival and Singapore Week of Innovation and TeCHnology), Singapore announced the next step in its Smart Nation initiative with the release of the “National AI Strategy”. The AI strategy will focus on social and economic benefits by providing modern infrastructure, intelligent services, and an excellent education system to citizens.
Commenting on Singapore’s AI adoption and implementation strategies, Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Tim Sheedy said “being a smaller country, Singapore is one of the few around the globe that can make investments into AI at a ‘country level’. Singapore has the luxury of having a progressive public sector that operates at the same speed as the private sector, and has the opportunity to become one of the leading economies in the world for both the deployment of AI in everyday services AND in ensuring the economy has the required skills.”
The key approach of the AI strategy
Singapore is aiming to position itself as a global hub for the development and implementation of AI solutions. National AI Office established under the Smart Nation and Digital Government Office (SNDGO) will be heading Singapore’s AI initiatives.
To begin with, the SNDGO will be initially working on key high-value sectors:
- Transport and Logistics: Intelligent Freight Planning
- Smart Cities and Municipal Services: Infra management and smart services
- Healthcare: Chronic Disease Prediction and Management
- Education: Personalised Education
- Safety and Security: Seamless border clearance operations
Speaking on AI strategies devised for transportation, smart cities, healthcare, education and safety and security in Singapore, Sheedy said “all of these investments are ones that you would make as an economy if you had the opportunity. They are all logical and will all benefit the lives of citizens and the success of the overall economy.”
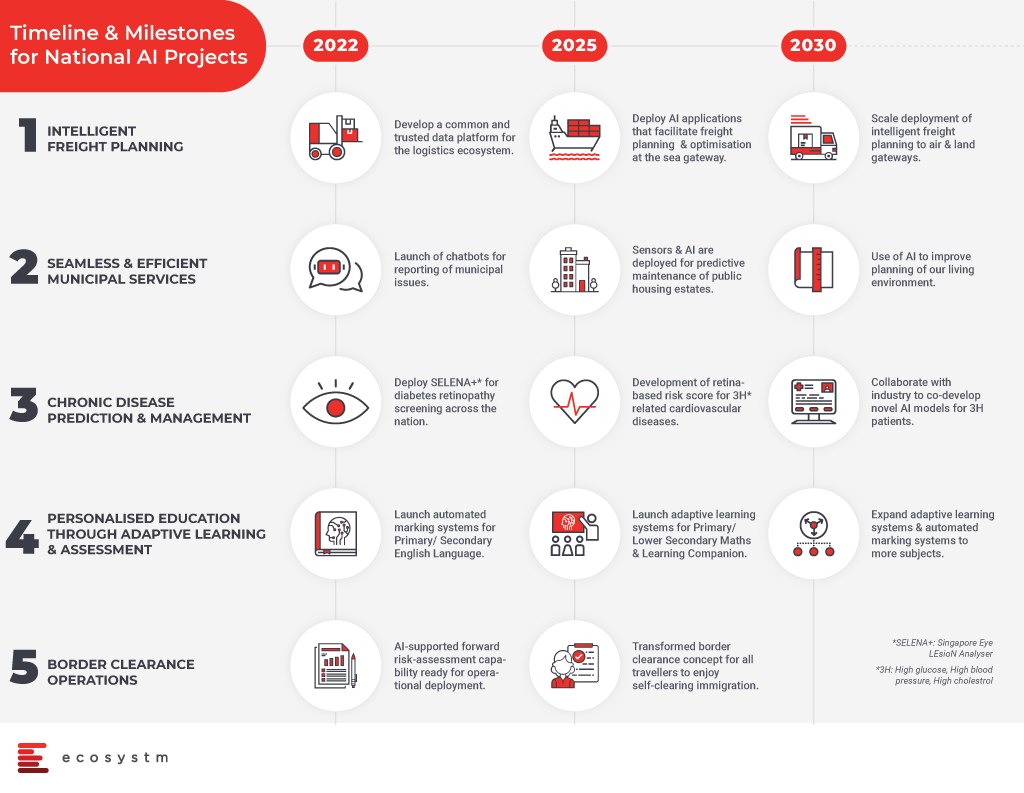
Transport and Logistics: To optimise the freight and delivery services, a common data platform will be built. The aim is to bring in efficient transportation and logistics with intelligent AI systems in place by 2022 and further AI developments will scale deployment, enable optimised delivery processes and routing of services for freight planning.
Smart Cities and Estates: The country aims to launch AI powered chatbots by 2022 to record municipal issues and allocate them to the responsible authorities. AI powered services will be introduced to better serve the residents. By 2025, efforts will be established to optimise estate maintenance through AI and sensors and by the year 2030, data driven insights will be used to improve the infrastructure and living environment in Singapore.
Healthcare: An all-new AI system known as SELENA+ will be in place to screen and detect diabetic eye disease. SELENA+ is a first artificial intelligence algorithm which performs automated retinal photo analysis to detect retinopathy and systemic complications in diabetics. In addition to this, AI capabilities will also be used to predict cardiovascular diseases and create personalised chronic risk scores. All of these will help to detect diseases and take early preventive measures by the healthcare teams for the welfare of country and betterment of the economy.
“This could detect chronic issues early, and reduce the impact of them on individuals, families and the economy. Being able to make investments at a macro level – like this happening in Singapore – will make sure everyone benefits” said Sheedy.
Education: AI in education will bring the benefits of automated marking systems for English language in primary and secondary education. Further, AI-enabled learning systems will help students on learning and mastery of topics. The government has planned to expand automated AI and adaptive learning systems to more subjects at a later stage.
Sheedy said, “with the government being able to influence and change the syllabus in schools and universities, as well as the skills in the public and private sector, Singapore is uniquely positioned to drive real economic benefit from their investment into AI.”
Safety and Security: AI systems will help in border security and clearance procedures. AI will enhance travel experience with automated immigration clearance systems involving face and iris scans. The immigration processes will develop into seamless self-clearance systems and become faster.
“A few countries have the ability to drive this level of planning – most countries have many levels of government which make this planning – or execution of plans – difficult.” said Sheedy. “Many are also leaving the investment to the private sector, which means it will happen eventually, but may see many competing initiatives or different capabilities emerge that only benefit a single company, not an entire economy.”
Smart Nation drive
Singapore’s government is highly active in transforming the country into a smart nation. Singapore was working with the World Economic Forum’s Centre for Fourth Industrial Revolution (WEF C4IR) in order to come out with a framework for ethical and responsible AI adoption and deployment by the Asian governments.
Singapore is also set to invest US$ 360 million on AI and other digital technologies through 2020 and has invited Chinese and American companies to be a part of this.
According to Sheedy, there are many benefits of having deep investments in AI and AI capabilities in an economy.
It will make Singapore a more attractive investment location. If access to government and other services are seamless, then the barriers to entry to starting a new business or creating a new business capability will be much lower. It will mean that it is easier to build a business case for businesses to move to Singapore or start in Singapore – attracting investment funds and employment into the island state.
It will boost export capabilities – both for the skills that will be in demand through technology and business service providers and for the intelligent products and services that will likely emerge from the early AI investments. If Singapore can make more of the products and services that they produce “smart” – then these products and services will see increased demand – both locally and outside of Singapore.
It will make Singapore a better place to live and visit. With seamless government services, easier travel into and out of the country, and a government that anticipates the needs of its citizens, the quality of life for residents will increase.
The country can get ahead of the challenges and downsides of AI – and legislate or plan for these challenges, to ensure these challenges are understood and managed before they become problems.
In the escalating initiatives to become an AI superpower, Singapore has clearly indicated they are fully committed to leveraging AI to drive growth and citizen services.
++Update
An AI roadmap report was published by the Australian Government in November 2019, co-developed by CSIRO’s Data61 and the Department of Industry, Innovation and Science. The report identifies the opportunities and benefits of AI that Australia could capture.
The report classifies the strategies to help develop AI capabilities to boost the productivity of industry, generate jobs, bring economic growth, and enhance the quality of citizens’ life. To drive this, Australia has identified 3 key areas where it has the best opportunity to create new value-
Health, Ageing, and Disability – To develop AI to improve healthcare, aged care, and disability services while reducing healthcare costs.
Cities, Towns, and Infrastructure – To develop an AI system for the cities and infrastructure to provide better services, safety efficiency in a smart and cost-effective way.
Natural resource and environment management – Develop AI for better natural resource management and improve the productivity of agriculture, mining, fisheries, forestry, and environmental management.











