Governments worldwide struggle with intricate social, economic, and environmental challenges. Tight budgets often leave them with limited resources to address these issues head-on. However, innovation offers a powerful path forward.
By embracing new technologies, adapting to cultural shifts, and fostering new skills, structures, and communication methods, governments can find solutions within existing constraints.
Find out how public sector innovation is optimising internal operations, improving service accessibility, bridging the financial gap, transforming healthcare, and building a sustainable future.
Click here to download ‘Innovation in Government: Social, Economic, and Environmental Wins’ as a PDF
Optimising Operations: Tech-Driven Efficiency
Technology is transforming how governments operate, boosting efficiency and allowing employees to focus on core functions.
Here are some real-world examples.
Singapore Streamlines Public Buses. A cloud-based fleet management system by the Land Transport Authority (LTA) improves efficiency, real-time tracking, data analysis, and the transition to electric buses.
Dubai Optimises Utilities Through AI. The Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) leverages AI for predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, and grid management. This enhances service reliability, operational efficiency, and resource allocation for power and water utilities.
Automation Boosts Hospital Efficiency. Singapore hospitals are using automation to save man-hours and boost efficiency. Tan Tock Seng Hospital automates bacteria sample processing, increasing productivity without extra staff, while Singapore General Hospital tracks surgical instruments digitally, saving thousands of man-hours.
Tech for Citizens
Digital tools and emerging technologies hold immense potential to improve service accessibility and delivery for citizens. Here’s how governments are leveraging tech to benefit their communities.
Faster Cross-Border Travel. Malaysia’s pilot QR code clearance system expedites travel for factory workers commuting to Singapore, reducing congestion at checkpoints.
Metaverse City Planning. South Korea’s “Metaverse 120 Center” allows residents to interact with virtual officials and access services in a digital environment, fostering innovative urban planning and infrastructure management.
Streamlined Benefits. UK’s HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) launched an online child benefit claim system that reduces processing time from weeks to days, showcasing the efficiency gains possible through digital government services.
Bridging the Financial Gap
Nearly 1.7 billion adults or one-third globally, remain unbanked.
However, innovative programs are bridging this gap and promoting financial inclusion.
Thailand’s Digital Wallet. Aimed at stimulating the economy and empowering underserved citizens, Thailand disburses USD 275 via digital wallets to 50 million low-income adults, fostering financial participation.
Ghana’s Digital Success Story. The first African nation to achieve 100% financial inclusion through modernised platforms like Ghana.gov and GhanaPay, which facilitate payments and fee collection through various digital channels.
Philippines Embraces QR Payments. The City of Alaminos leverages the Paleng-QR Ph Plus program to promote QR code-based payments, aligning with the central bank’s goal of onboarding 70% of Filipinos into the formal financial system by 2024.
Building a Sustainable Future
Governments around the world are increasingly turning to technology to address environmental challenges and preserve natural capital.
Here are some inspiring examples.
World’s Largest Carbon Capture Plant. Singapore and UCLA joined forces to build Equatic-1, a groundbreaking facility that removes CO2 from the ocean and creates carbon-negative hydrogen.
Tech-Enhanced Disaster Preparedness. The UK’s Lincolnshire County Council uses cutting-edge geospatial technology like drones and digital twins. This empowers the Lincolnshire Resilience Forum with real-time data and insights to effectively manage risks like floods and power outages across their vast region.
Smart Cities for Sustainability. Bologna, Italy leverages the digital twins of its city to optimise urban mobility and combat climate change. By analysing sensor data and incorporating social factors, the city is strategically developing infrastructure for cyclists and trams.
Tech for a Healthier Tomorrow
Technology is transforming healthcare delivery, promoting improved health and fitness monitoring.
Here’s a glimpse into how innovation is impacting patient care worldwide.
Robotic Companions for Seniors. South Korea tackles elder care challenges with robots. Companion robots and safety devices provide companionship and support for seniors living alone.
VR Therapy for Mental Wellness. The UAE’s Emirates Health Services Corporation implements a Virtual Reality Lab for Mental Health, that creates interactive therapy sessions for individuals with various psychological challenges. VR allows for personalised treatment plans based on data collected during sessions.

Leaders Roundtable: Decoding the GenAI Value Chain: Best Practices for Industry Leaders
We’ve concluded another successful event! Thanks to everyone for their Valuable contributions.
->Click here to explore hightlights and key takeaways from this Roundtable session.
Southeast Asia’s massive workforce – 3rd largest globally – faces a critical upskilling gap, especially with the rise of AI. While AI adoption promises a USD 1 trillion GDP boost by 2030, unlocking this potential requires a future-proof workforce equipped with AI expertise.
Governments and technology providers are joining forces to build strong AI ecosystems, accelerating R&D and nurturing homegrown talent. It’s a tight race, but with focused investments, Southeast Asia can bridge the digital gap and turn its AI aspirations into reality.
Read on to find out how countries like Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, and The Philippines are implementing comprehensive strategies to build AI literacy and expertise among their populations.
Download ‘Upskilling for the Future: Building AI Capabilities in Southeast Asia’ as a PDF
Big Tech Invests in AI Workforce
Southeast Asia’s tech scene heats up as Big Tech giants scramble for dominance in emerging tech adoption.
Microsoft is partnering with governments, nonprofits, and corporations across Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam to equip 2.5M people with AI skills by 2025. Additionally, the organisation will also train 100,000 Filipino women in AI and cybersecurity.
Singapore sets ambitious goal to triple its AI workforce by 2028. To achieve this, AWS will train 5,000 individuals annually in AI skills over the next three years.
NVIDIA has partnered with FPT Software to build an AI factory, while also championing AI education through Vietnamese schools and universities. In Malaysia, they have launched an AI sandbox to nurture 100 AI companies targeting USD 209M by 2030.
Singapore Aims to be a Global AI Hub
Singapore is doubling down on upskilling, global leadership, and building an AI-ready nation.
Singapore has launched its second National AI Strategy (NAIS 2.0) to solidify its global AI leadership. The aim is to triple the AI talent pool to 15,000, establish AI Centres of Excellence, and accelerate public sector AI adoption. The strategy focuses on developing AI “peaks of excellence” and empowering people and businesses to use AI confidently.
In keeping with this vision, the country’s 2024 budget is set to train workers who are over 40 on in-demand skills to prepare the workforce for AI. The country will also invest USD 27M to build AI expertise, by offering 100 AI scholarships for students and attracting experts from all over the globe to collaborate with the country.
Thailand Aims for AI Independence
Thailand’s ‘Ignite Thailand’ 2030 vision focuses on boosting innovation, R&D, and the tech workforce.
Thailand is launching the second phase of its National AI Strategy, with a USD 42M budget to develop an AI workforce and create a Thai Large Language Model (ThaiLLM). The plan aims to train 30,000 workers in sectors like tourism and finance, reducing reliance on foreign AI.
The Thai government is partnering with Microsoft to build a new data centre in Thailand, offering AI training for over 100,000 individuals and supporting the growing developer community.
Building a Digital Vietnam
Vietnam focuses on AI education, policy, and empowering women in tech.
Vietnam’s National Digital Transformation Programme aims to create a digital society by 2030, focusing on integrating AI into education and workforce training. It supports AI research through universities and looks to address challenges like addressing skill gaps, building digital infrastructure, and establishing comprehensive policies.
The Vietnamese government and UNDP launched Empower Her Tech, a digital skills initiative for female entrepreneurs, offering 10 online sessions on GenAI and no-code website creation tools.
The Philippines Gears Up for AI
The country focuses on investment, public-private partnerships, and building a tech-ready workforce.
With its strong STEM education and programming skills, the Philippines is well-positioned for an AI-driven market, allocating USD 30M for AI research and development.
The Philippine government is partnering with entities like IBPAP, Google, AWS, and Microsoft to train thousands in AI skills by 2025, offering both training and hands-on experience with cutting-edge technologies.
The strategy also funds AI research projects and partners with universities to expand AI education. Companies like KMC Teams will help establish and manage offshore AI teams, providing infrastructure and support.

It’s been barely one year since we entered the Generative AI Age. On November 30, 2022, OpenAI launched ChatGPT, with no fanfare or promotion. Since then, Generative AI has become arguably the most talked-about tech topic, both in terms of opportunities it may bring and risks that it may carry.
The landslide success of ChatGPT and other Generative AI applications with consumers and businesses has put a renewed and strengthened focus on the potential risks associated with the technology – and how best to regulate and manage these. Government bodies and agencies have created voluntary guidelines for the use of AI for a number of years now (the Singapore Framework, for example, was launched in 2019).
There is no active legislation on the development and use of AI yet. Crucially, however, a number of such initiatives are currently on their way through legislative processes globally.
EU’s Landmark AI Act: A Step Towards Global AI Regulation
The European Union’s “Artificial Intelligence Act” is a leading example. The European Commission (EC) started examining AI legislation in 2020 with a focus on
- Protecting consumers
- Safeguarding fundamental rights, and
- Avoiding unlawful discrimination or bias
The EC published an initial legislative proposal in 2021, and the European Parliament adopted a revised version as their official position on AI in June 2023, moving the legislation process to its final phase.
This proposed EU AI Act takes a risk management approach to regulating AI. Organisations looking to employ AI must take note: an internal risk management approach to deploying AI would essentially be mandated by the Act. It is likely that other legislative initiatives will follow a similar approach, making the AI Act a potential role model for global legislations (following the trail blazed by the General Data Protection Regulation). The “G7 Hiroshima AI Process”, established at the G7 summit in Japan in May 2023, is a key example of international discussion and collaboration on the topic (with a focus on Generative AI).
Risk Classification and Regulations in the EU AI Act
At the heart of the AI Act is a system to assess the risk level of AI technology, classify the technology (or its use case), and prescribe appropriate regulations to each risk class.
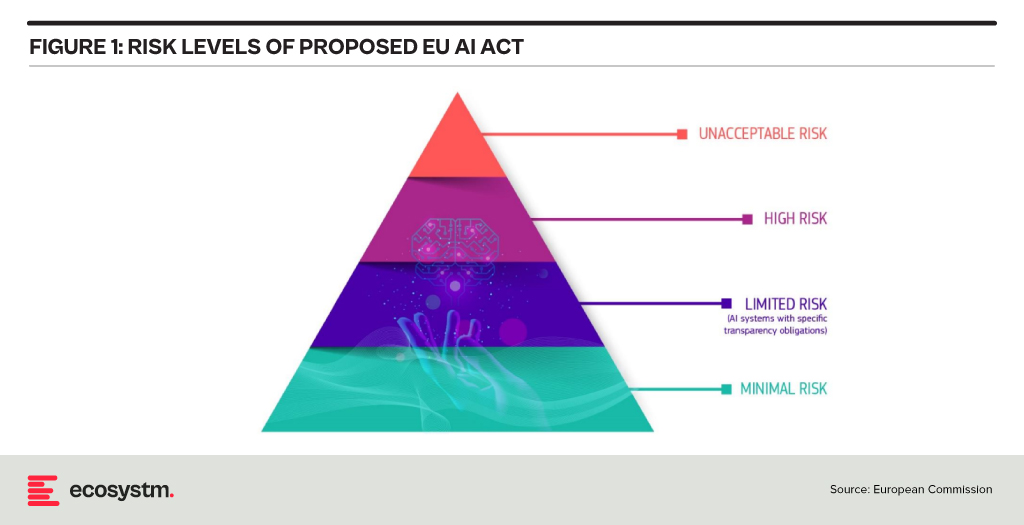
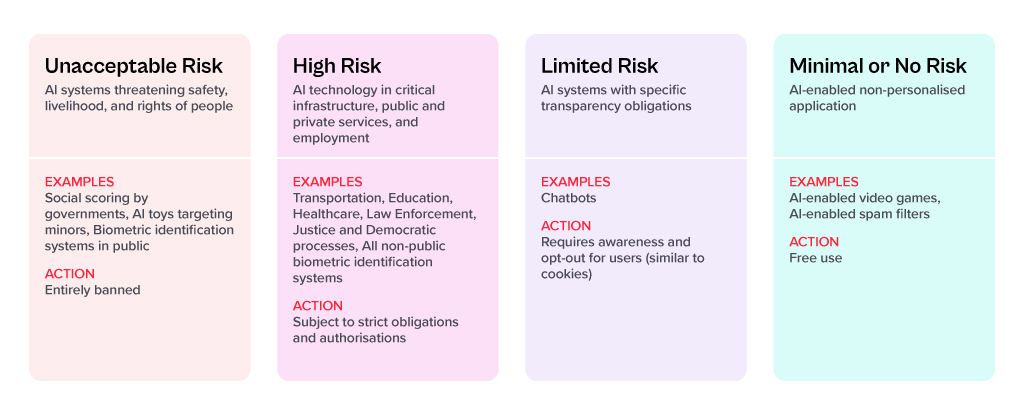
For each of these four risk levels, the AI Act proposes a set of rules and regulations. Evidently, the regulatory focus is on High-Risk AI systems.
Contrasting Approaches: EU AI Act vs. UK’s Pro-Innovation Regulatory Approach
The AI Act has received its share of criticism, and somewhat different approaches are being considered, notably in the UK. One set of criticism revolves around the lack of clarity and vagueness of concepts (particularly around person-related data and systems). Another set of criticism revolves around the strong focus on the protection of rights and individuals and highlights the potential negative economic impact for EU organisations looking to leverage AI, and for EU tech companies developing AI systems.
A white paper by the UK government published in March 2023, perhaps tellingly, named “A pro-innovation approach to AI regulation” emphasises on a “pragmatic, proportionate regulatory approach … to provide a clear, pro-innovation regulatory environment”, The paper talks about an approach aiming to balance the protection of individuals with economic advancements for the UK on its way to become an “AI superpower”.
Further aspects of the EU AI Act are currently being critically discussed. For example, the current text exempts all open-source AI components not part of a medium or higher risk system from regulation but lacks definition and considerations for proliferation.
Adopting AI Risk Management in Organisations: The Singapore Approach
Regardless of how exactly AI regulations will turn out around the world, organisations must start today to adopt AI risk management practices. There is an added complexity: while the EU AI Act does clearly identify high-risk AI systems and example use cases, the realisation of regulatory practices must be tackled with an industry-focused approach.
The approach taken by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) is a primary example of an industry-focused approach to AI risk management. The Veritas Consortium, led by MAS, is a public-private-tech partnership consortium aiming to guide the financial services sector on the responsible use of AI. As there is no AI legislation in Singapore to date, the consortium currently builds on Singapore’s aforementioned “Model Artificial Intelligence Governance Framework”. Additional initiatives are already underway to focus specifically on Generative AI for financial services, and to build a globally aligned framework.
To Comply with Upcoming AI Regulations, Risk Management is the Path Forward
As AI regulation initiatives move from voluntary recommendation to legislation globally, a risk management approach is at the core of all of them. Adding risk management capabilities for AI is the path forward for organisations looking to deploy AI-enhanced solutions and applications. As that task can be daunting, an industry consortium approach can help circumnavigate challenges and align on implementation and realisation strategies for AI risk management across the industry. Until AI legislations are in place, such industry consortia can chart the way for their industry – organisations should seek to participate now to gain a head start with AI.

Technology is reshaping the Public Sector worldwide, optimising operations, improving citizen services, and fostering data-driven decision-making. Government agencies are also embracing innovation for effective governance in this digital era.
Public sector organisations worldwide recognise the need for swift and agile interventions. With citizen expectations resembling those of commercial customers, public sector organisations face mounting pressure to break down the barriers to provide seamless service experiences.
Read on to find out how public sector organisations in countries such as Australia, Vietnam, the Philippines, South Korea, and Singapore are innovating to stay ahead of the curve; and what Ecosystm VP Consulting, Peter Carr sees as the Future of Public Sector.
Click here to Download ‘The Future of the Public Sector’ as a PDF