As AI evolves, the supporting infrastructure has become a crucial consideration for organisations and technology companies alike. AI demands massive processing power and efficient data handling, making high-performance computing clusters and advanced data management systems essential. Scalability, efficiency, security, and reliability are key to ensuring AI systems handle increasing demands and sensitive data responsibly.
Data centres must evolve to meet the increasing demands of AI and growing data requirements.
Equinix recently hosted technology analysts at their offices and data centre facilities in Singapore and Sydney to showcase how they are evolving to maintain their leadership in the colocation and interconnection space.
Equinix is expanding in Latin America, Africa, the Middle East, and Asia Pacific. In Asia Pacific, they recently opened data centres in Kuala Lumpur and Johor Bahru, with capacity additions in Mumbai, Sydney, Melbourne, Tokyo, and Seoul. Plans for the next 12 months include expanding in existing cities and entering new ones, such as Chennai and Jakarta.
Ecosystm analysts comment on Equinix’s growth potential and opportunities in Asia Pacific.
Small Details, Big Impact
TIM SHEEDY. The tour of the new Equinix data centre in Sydney revealed the complexity of modern facilities. For instance, the liquid cooling system, essential for new Nvidia chipsets, includes backup cold water tanks for redundancy. Every system and process is designed with built-in redundancy.
As power needs grow, so do operational and capital costs. The diesel generators at the data centre, comparable to a small power plant, are supported by multiple fuel suppliers from several regions in Sydney to ensure reliability during disasters.
Security is critical, with some areas surrounded by concrete walls extending from the ceiling to the floor, even restricting access to Equinix staff.
By focusing on these details, Equinix enables customers to quickly set up and manage their environments through a self-service portal, delivering a cloud-like experience for on-premises solutions.
Equinix’s Commitment to the Environment
ACHIM GRANZEN. Compute-intensive AI applications challenge data centres’ “100% green energy” pledges, prompting providers to seek additional green measures. Equinix addresses this through sustainable design and green energy investments, including liquid cooling and improved traditional cooling. In Singapore, one of Equinix’s top 3 hubs, the company partnered with the government and Sembcorp to procure solar power from panels on public buildings. This improves Equinix’s power mix and supports Singapore’s renewable energy sector.
TIM SHEEDY Building and operating data centres sustainably is challenging. While the basics – real estate, cooling, and communications – remain, adding proximity to clients, affordability, and 100% renewable energy complicates matters. In Australia, reliant on a mixed-energy grid, Equinix has secured 151 MW of renewable energy from Victoria’s Golden Plains Wind Farm, aiming for 100% renewable by 2029.
Equinix leads with AIA-rated data centres that operate in warmer conditions, reducing cooling needs and boosting energy efficiency. Focusing on efficient buildings, sustainable water management, and a circular economy, Equinix aims for climate neutrality by 2030, demonstrating strong environmental responsibility.
Equinix’s Private AI Value Proposition
ACHIM GRANZEN. Most AI efforts, especially GenAI, have occurred in the public cloud, but there’s rising demand for Private AI due to concerns about data availability, privacy, governance, cost, and location. Technology providers in a position to offer alternative AI stacks (usually built on top of a GPU-as-a-service model) to the hyperscalers find themselves in high interest. Equinix, in partnership with providers such as Nvidia, offers Private AI solutions on a global turnkey AI infrastructure. These solutions are ideal for industries with large-scale operations and connectivity challenges, such as Manufacturing, or those slow to adopt public cloud.
SASH MUKHERJEE. Equinix’s Private AI value proposition will appeal to many organisations, especially as discussions on AI cost efficiency and ROI evolve. AI unites IT and business teams, and Equinix understands the need for conversations at multiple levels. Infrastructure leaders focus on data strategy capacity planning; CISOs on networking and security; business lines on application performance, and the C-suite on revenue, risk, and cost considerations. Each has a stake in the AI strategy. For success, Equinix must reshape its go-to-market message to be industry-specific (that’s how AI conversations are shaping) and reskill its salesforce for broader conversations beyond infrastructure.
Equinix’s Growth Potential
ACHIM GRANZEN. In Southeast Asia, Malaysia and Indonesia provide growth opportunities for Equinix. Indonesia holds massive potential as a digital-savvy G20 country. In Malaysia, the company’s data centres can play a vital part in the ongoing Mydigital initiative, having a presence in the country before the hyperscalers. Also, the proximity of the Johor Bahru data centre to Singapore opens additional business opportunities.
TIM SHEEDY. Equinix is evolving beyond being just a data centre real estate provider. By developing their own platforms and services, along with partner-provided solutions, they enable customers to optimise application placement, manage smaller points of presence, enhance cloud interconnectivity, move data closer to hyperscalers for backup and performance, and provide multi-cloud networking. Composable services – such as cloud routers, load balancers, internet access, bare metal, virtual machines, and virtual routing and forwarding – allow seamless integration with partner solutions.
Equinix’s focus over the last 12 months on automating and simplifying the data centre management and interconnection services is certainly paying dividends, and revenue is expected to grow above tech market growth rates.
Innovation is at the core of Singapore’s ethos. The country has perfected the art of ‘structured innovation’ where pilots and proof of concepts are introduced and the successful ones scaled up by recalibrating technology, delivery systems, legislation, and business models. The country has adopted a similar approach to achieving its sustainability goals.
The Singapore Green Plan 2030 outlines the strategies to become a sustainable nation. It is driven by five ministries: Education, National Development, Sustainability and the Environment, Trade and Industry, and Transport, and includes five key pillars: City in Nature, Sustainable Living, Energy Reset, Green Economy, and Resilient Future. We will see a slew of new programs and initiatives in green finance, sustainability, solar energy, electric vehicles (EVs), and innovation, in the next couple of years.
Singapore’s Intentions of Becoming a Green Finance Leader
Singapore is serious about becoming a world leader in green finance. The Green Bonds Programme Office was set up last year, to work with statutory boards to develop a framework along with industry and investor stakeholders. We have seen a number of sustainable finance initiatives last year, such as the National Environment Agency (NEA) collaborating with DBS to raise USD 1.23 billion from its first green bond issuance. The proceeds will fund new and ongoing sustainable waste management initiatives. Temasek collaborated with HSBC for a USD 110 million debt financing platform for sustainable projects and Sembcorp issued sustainability bonds worth USD 490 million.
Building an Ecosystm of Sustainable Organisations
Sustainability has to be a collective goal that will require governments to work with enterprises, investors and consumers. To ensure that enterprises are focusing on Sustainability, governments have to keep in mind what drives these initiatives and the challenges organisations face in achieving their goals.
There are several reasons driving organisations in Singapore to adopt sustainability goals and ESG responsibilities (Figure 1)
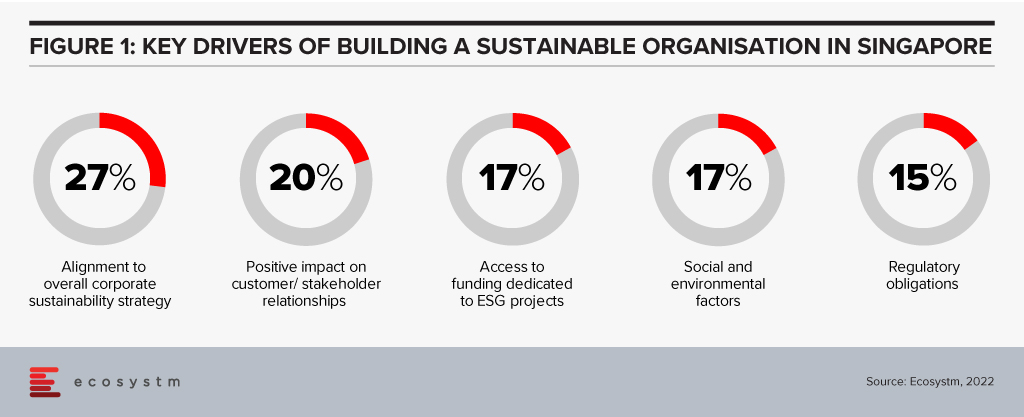
It is equally important to address organisations’ challenges in building sustainability in their business processes. Last week, the Institute of Banking and Finance (IBF) and the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) set out 12 Sustainable Finance Technical Skills and Competencies (SF TSCs) required by people in various roles in sustainable finance. This addresses the growing demand for sustainable finance talent in Singapore; and covers knowledge areas such as climate change policy developments, natural capital, green taxonomies, carbon markets and decarbonisation strategies. There are Financial Services related competencies as well, such as sustainability risk management, sustainability reporting, sustainable investment management, and sustainable insurance and reinsurance solutions. The SF TSCs are part of the IBF Skills Framework for Financial Services.
Sustainable Resources Initiatives
Singapore is not only focused on Sustainable Finance. If we look at NEA’s Green Bonds, there are specific criteria that projects must satisfy in order to qualify, including a focus on sustainable waste management.
Last week the Government announced that the National Research Fund (NRF) will allocate around USD 160 million to drive new initiatives in water, reuse and recycling technologies, as part of the Research, Innovation and Enterprise 2025 plan (RIE2025). Part of the fund will be allocated to the Closing the Resource Loop (CTRL) initiative, administered by the NEA that will fund sustainable resource recovery solutions.
Singapore faces severe resource constraints, and water security is not a new challenge for the country. The NRF funding will also be used partially for R&D in 3 water technology focus areas: desalination and water reuse; used water treatment; and waste reduction and resource recovery.
The Government is Leading the Way
The Government’s concerted efforts to make the Singapore Green Plan 2030 a success is seeing corporate participation in the vision. In February, Shell started supplying sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) to customers such as SIA Engineering Company and the Singapore Air Force in Singapore. Shell has also upgraded their Singapore facility to blend SAF at multiple, key locations. Last week, Atlas announced their commitment to Web 3.0 technologies and “tech for good”. They aim to increase their green energy use to 75% by 2022; 90% by 2023; and 100% by 2024. ESG consciousness is percolating down from the Government.
The success of Singapore’s Sustainability strategies will depend on innovation, the Government’s ongoing commitment, and the support provided to enterprises, investors, and consumers. The Singapore Government is poised to lead from the front in building a Sustainable Ecosystem.
















