Your CEO and Board are asking you to cut costs and do more with the IT budget.
This is the usual refrain you get used to as a Chief Digital or Information Officer. COVID-19 has increased the need for cost savings, without compromising your organisation’s mission. In Ecosystm’s on-going research, Digital Priorities in the New Normal – a COVID-19 Study, there are several common themes that emerge for retailers.

The impact of the cost-cutting measures that organisations are implementing, on CDOs and CIOs has been discussed in my report Managing Costs in the New Normal, where I provide guidance on how to address the necessary cuts.
Super Retail Group (SRG) recently presented at SalesForce Live on their success in using AI to improve their customer engagement – linking digital customer engagement and re-calibration of AI models. I want to highlight a couple of aspects of SRG’s experience for those retailers addressing these themes.
Increasing Customer Engagement
In a well-run online presence, retailers acquire a significant amount of data about their customers’ online behaviour. Data such as customer’s purchase history as well as how they traverse the site, how long they remain on the site and how they leave – often without purchasing. The challenge is how you can collect and use this data to improve the customer experience (CX) and increase sales in our new normal.
SRG, trading under banners such as Super Cheap Auto, BCF and Rebel across Australasia, has adopted a Salesforce tool called Einstein to address this challenge. SRG is using this AI engine to present product recommendations in several contexts across a customer’s online journey.
The impact of COVID-19 means overall sales across the group has declined. At the same time, online sales have grown to be generating almost 20% of the overall sales. Within these online sales, the AI recommendation engine has directly influenced 1 in 5 customer purchases.
SRG has developed a significant base of customer data since they introduced omnichannel and club offers; and are now seeing the return from this investment. Recommendation engines operate best when they have quality data in volume – and the proportion of and growth in, online customers using these recommendations is a guide to the quality of the platform.
Coping with Increasing Online Demands
Ecosystm research finds that over 56% of retailers are increasing their use of digital technologies for CX and will continue to invest after the immediate crisis. As always, getting the right value from this increased expenditure will be critical to a retailer’s price competitiveness and profitability.
With online sales growing dramatically, SRG’s online share of sales has more than doubled over April and May, the potential return from an engaging online CX has increased significantly. In turn, this has increased the importance of the online CX to a retailer’s competitive positioning and market share.
Tech leaders will be expected to provide direction on how to achieve this improvement, with AI engines offering an increasingly important tool in increasing the speed of response to changing customer behaviours.
With their mapping of customer journeys, SRG has been able to target specific stages in the journey for the use of the AI recommendation engine. Their focus on increasing the size and value of a customer’s basket provides the explicit measure of success. And SRG’s customers are showing their enthusiasm for these recommendations. The share of online sales influenced by the AI engine grew by over 600% in the past 12 months.
Customer expectations are continually being redefined by their experiences across the online environment, not just by retailers. In our new normal, with online becoming significantly important, retailers need to be consistently improving their offer to remain competitive.
Our study results shows that retailers are taking this step and will need to pay careful attention to their cost base and profitability while making these changes. SRG’s success with the AI engine shows that this is possible.
Lessons to Learn
COVID-19 has changed customer behaviour significantly, and tech leaders are identifying new tools and processes to improve their CX in line with these changes. SRG has continued its customer-focused omnichannel approach by adopting the Salesforce Einstein AI engine. By using one of their key sales metrics – size and value of basket – they have been able to assess the contribution of this tool.
There are some clear lessons for other retailers from their experience:
- Be very clear on why you are introducing the new tool – how you are going to achieve value.
- Understand the foundation that you need, to introduce new technology. You will find being successful using AI without quality data in volume will be difficult.
- Experiment and learn quickly from experience gained. In this cost-constrained world, don’t over-commit to a new approach without evidence.
- Use products and services that have a low cost of entry and a variable cost model. Cloud services generally provide this cost model.
Our research, along with press release such as SRG’s, show that retail leaders are continuously improving their customer engagement. As a tech leader, you need to be aware that customers will vote with their clicks, for retailers that are delivering.
And getting those non-essential costs out has never been more critical.

We continue to receive responses from the tech buyer community on the impact of COVID-19 on Digital Transformation initiatives, and the early business and technology measures that were implemented to combat the crisis. As the months go by, it is becoming apparent that organisations have implemented the early measures and are now looking ahead to their journey to recovery.
IT Teams realised that even if they had the right technology solutions, they were unprepared for the scale or capacity to extend these technology offerings to handle the sudden and enormous changes required to manage the crisis. Their cloud business applications, cybersecurity and collaboration solutions were simply not sufficient to meet the needs of the remote workforce. As organisations become more conscious of business continuity planning (BCP) for future eventualities, they will boost their technology capabilities, over the next 12 months.
Another area the study aims to explore is how optimistic is the business outlook, when it comes to expecting a return to normalcy. Only 3% of organisations are expecting a New Normal that is very different from where things were at the beginning of the year. About a third of organisations are expecting a return to normalcy by the end of the year, while the majority expect to recover by the middle of 2021. Also, some industries are more optimistic of a recovery than others. As an example, 35% of healthcare organisations expect a return to normalcy by the end of the year. This is a positive indicator, given that the industry has been in the forefront of the crisis, for nearly 6 months now.
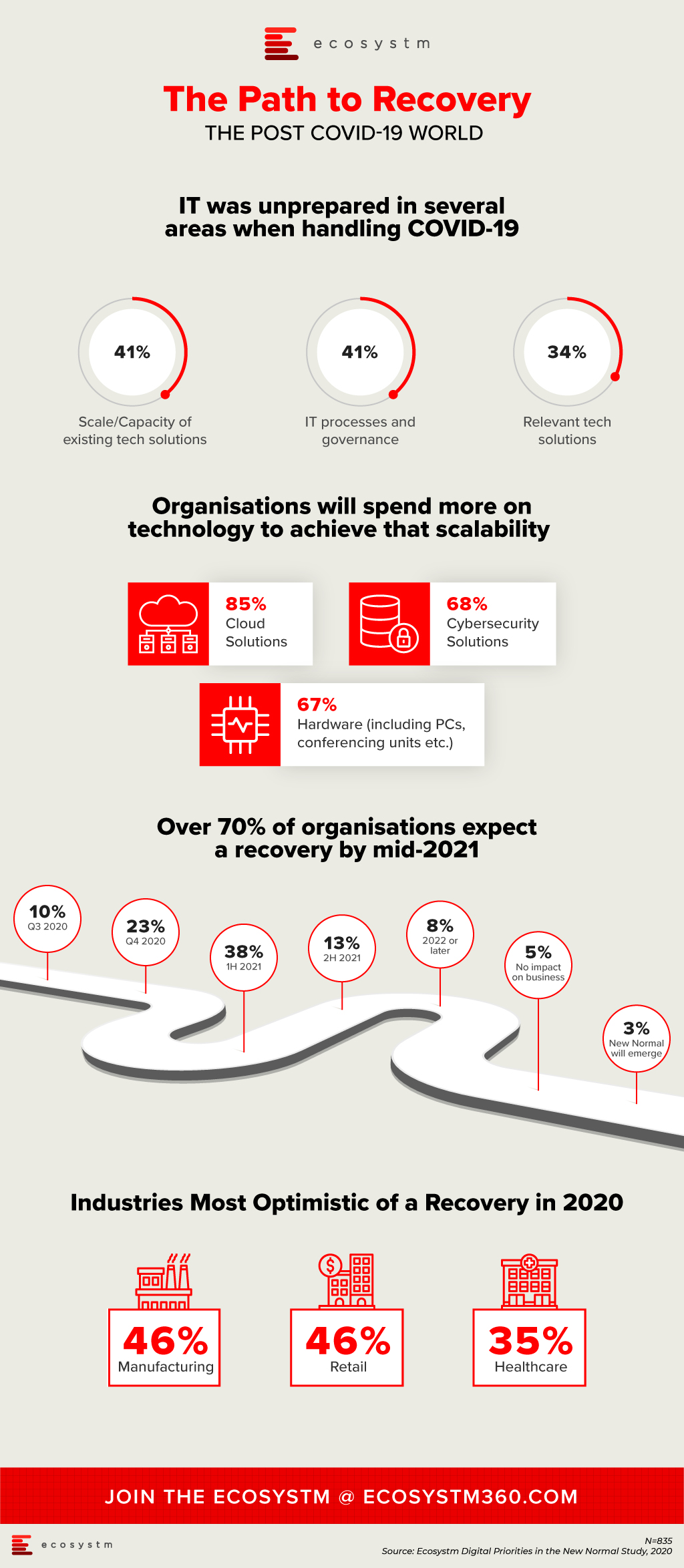
More insights on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and technology areas that will see continued investments, as organisations get into the recovery phase, can be found in the Digital Priorities in the New Normal Study.
A decade ago, the axiom of a successful business model was to identify a need, find the market and then develop an idea or product that fits into that chain. It was a process of inserting a product in the customer’s already existing experience journey with the hope that the product/idea would deliver efficiency to the client. This efficiency could be financial, operational, marketing or cost savings – the uni-product, uni-feature approach.
There has been enough said about the many companies that failed to innovate beyond their existing product/feature and failed to stay ahead of the game. Nokia and Blackberry remain at the centre of any discussion about “lack of innovation”. There are others like Kodak, Canon, Napster, Palm, Blockbuster – that were devoured by innovative competitors.
The predators were ones with the vision to see the entire value chain and not just their own product. Netflix created content and distributed it, Apple touched the lives of their customers in multiple ways and AirBnb provided accommodation inventory, choice and booking all in one. The new secret sauce is to provide the customer with an ecosystem and not a product!
The Need to Transform
Cut to the COVID era – there are many businesses facing the downturn and experiencing the “moments of truth” giving rise to a desperate attempt to innovate, transform, survive, and come out as the rising stars. Ecosystm research finds that 98% of organisations have re-evaluated their Transformation roadmap (Figure 1), while 75% have started, accelerated or refocused their DX initiatives.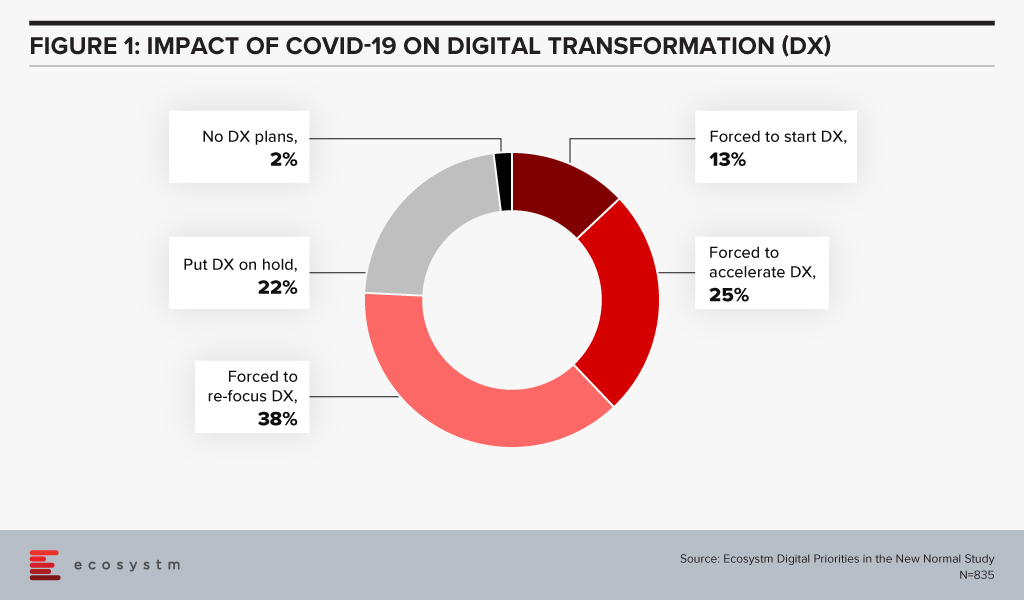
New business models are evolving, and accelerating digitalisation is the result. The digital movement, be it in food delivery or payments, is here to stay. This digital acceptance and absorption exaggerate the need for business models that capture holistic ecosystems and entire customer journeys, due to reasons that separate the hunter and the hunted.
- Margins will never be the same again as in the uni-product model. Using the F&B analogy; with the increasing number of customers wanting to dine in the comfort of their homes, restaurants cannot use ambiance as the price differentiator. Since most restaurants are available on food delivery services, customers are getting brand agnostic. This is the start of commoditisation of dining. Restaurants (or food caterers now!) will need to play the price card to remain competitive resulting in compressed margins. The food delivery market is expected to grow 4-fold to USD 8 billion by 2025 but with lower margins. This example of the food delivery model will be the same as experienced by retail, apparel and other industries.
- Customer experience will still be the differentiator and lever for loyalty and repeat purchase. Factors like proximity, parking, in-store experience, and store layout are fast getting replaced by the ease of navigation, user experience, seamless check out and finally efficient and timely delivery. The ease of transaction including multiple steps of search, assessment, evaluation, payment and delivery is of paramount importance. Customers do not want fractured journeys with multiple drop-offs. A unified seamless journey will win.
- Virtual, Digital and Automation are the three mantras that management consultants are betting on. However, this trilogy will not guarantee survival since the road to recovery is not a straight one. Different work schedules, observing various curves and on what point of the curve the business, its customer and the market are at, will add to the complexity of decision making and transformation.
Given the above, an obvious strategy to beat the existential crisis is to transform and seek out sustainable operating models. However, it may not be so simple since most businesses may not be able to change models as quickly as needed. There is an inherent cost to change since the existing processes and procedures have been well oiled and smoothed over time. The much-needed change requires the infusion of the 3Ts (time, technology, training) and associated costs. Most often, there is an inverse correlation noticed between the sturdiness of the business and its ability to be flexible to change. Businesses that are “rock-solid” and profitably sturdy and stable, have high inertia of transformation versus FinTech businesses, as an example, that pride themselves with nimble operations but are financially fragile and may not be able to absorb the cost of speedy transformation.
This Sturdy-Flexible continuum is the tight rope walk that businesses will need to walk in this need for transformation. Businesses that embark on this walk alone will find it extremely painful and lonely. Especially in the case of small business owners who are scared and low on all 3Ts.
The Rise of Ecosystems
The new world has manifested that businesses that use physical space or assets as their competitive advantage are more prone to be impacted. Retail, Education, Hospitality and Entertainment are some obvious examples that have been impacted by the physicality in their propositions. Digital businesses are more agile but have suffered in their inability to scale up in time to capture the increased demand.
Fashion retailer FJ Benjamin has decided to shut 300 physical stores and rely on online sales. This strategy also helps to utilise precious time to scale diversification. Other retailers too have been going down the FJ Benjamin path and ramping up eCommerce as this trend is expected to stick beyond COVID-19.
Zouk, the renowned nightclub with 30,000 square feet of space in Singapore uses this venue as a live streaming venue during the day to host bazaars for eCommerce vendors. From June 2020, it launched an online shop selling merchandise, bottled cocktails and food from its RedTail kitchen.
Transformation of businesses will require capabilities that were not created within their models. The instinct to survive in the short term will require businesses to create symbiotic partnerships. This will require some fresh thinking by business leaders.
- Change the “Build” obsession and not try to own every leg of the customer journey. That will not only take time but also distract capital and management.
- Rethink the customer needs – and this time think of the entire journey rather than an inward view of product-market fits. Customer needs are changing at breakneck speeds, so chasing and “building” these “fits” will always remain a common string amongst laggards.
- Connect with like-minded ecosystem players and complement strengths with a single-minded focus on solving customer problems.
- View technology stacks through the lens of your partners. There may be opportunities available from near open source technology solutions.
For example, FJ Benjamin will need the last-mile-delivery capability that will be provided by partners who have optimised in that field, Zouk has tied up with Lazada to host the bazaars and GrabFood is using underutilised taxi capacity to meet the increased demand for food delivery. There are many other examples in the O2O (Offline to Online) space.
This ecosystem approach is also relevant to other sectors like Financial Services. These firms also need to understand the changing consumer needs faster, with a mantra to deliver. Aspire, originally an alternate lending platform has gone through a metamorphosis and transformed into a Neobank. From a uni-product loan provider, it is now solving for a business account, card solution, integration with expense management solutions and continue to provide loans. Capabilities not necessarily built in-house.
The changing world will give rise to business models that will integrate and complement each other. Businesses with an ecosystem mindset will be winners while others might just be relegated to oblivion.

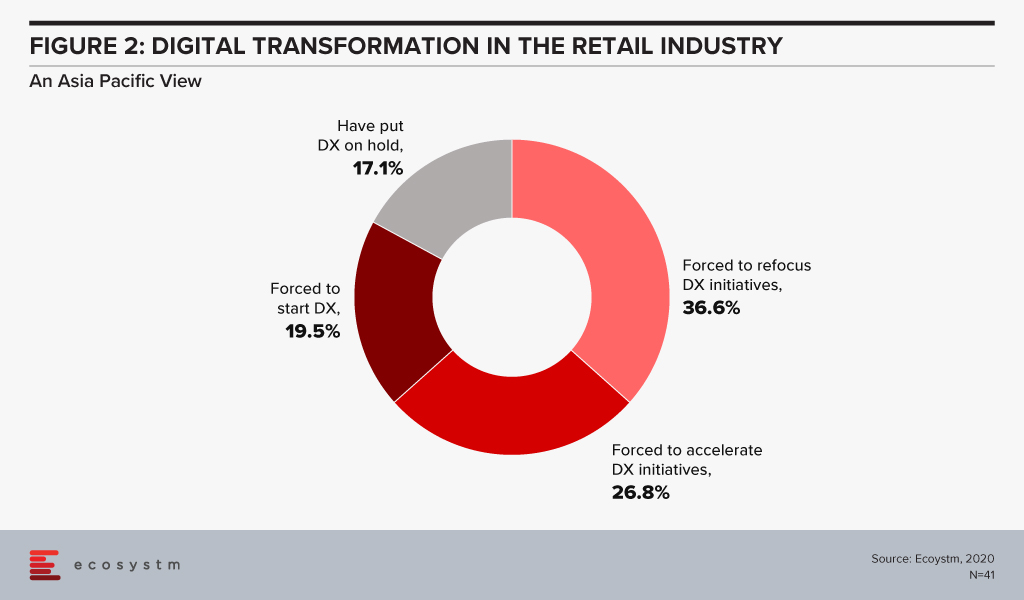
The Retail industry has been one of the hardest-hit industries during the COVID-19 crisis. The industry had to pivot faster than many to cater to an evolving market need and customer expectation, amidst social distancing measures and supply chain disruption. Ecosystm’s Digital Priorities in the New Normal study finds that nearly 83% of organisations in Asia Pacific’s Retail industries were forced to work on digital transformation (DX) in the aftermath of the crisis (Figure 1).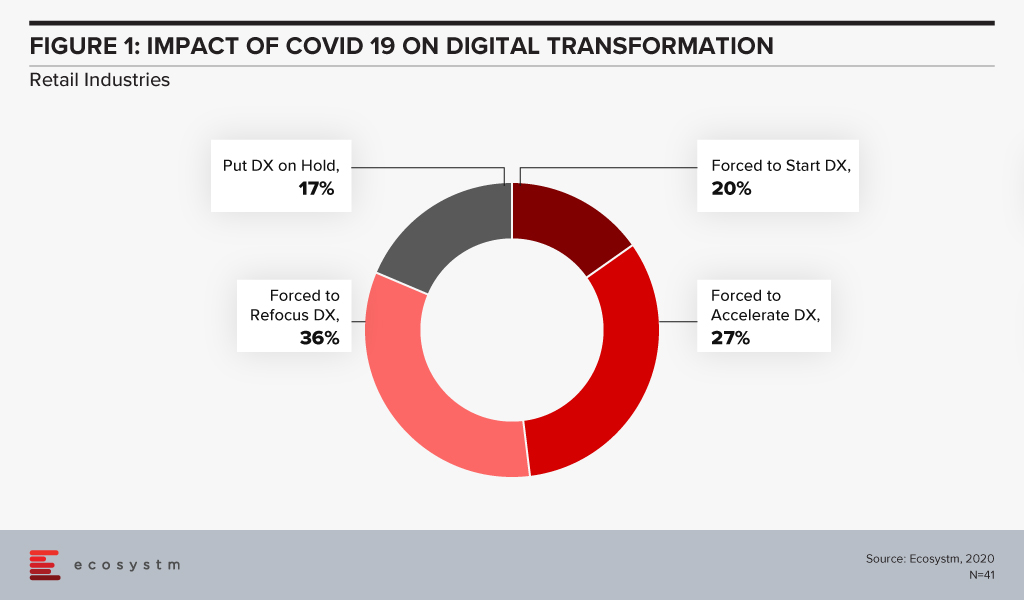
Retail organisations that had not walked the DX path found themselves struggling to cope in recent times. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Alan Hesketh says, “Digital transformation in retail, as represented by deep customer understanding and omnichannel operations, is far from new. Industry leaders launched these activities almost 20 years ago and continue to aggressively develop these capabilities. Retailers not actively leveraging these capabilities to understand their customer preferences are at a massive competitive disadvantage.”
Anta Group Accelerates DX
The Anta Group, a sports products manufacturer based in China with over 12,500 stores, has launched a group-wide digital platform designed and deployed by IBM Services based on SAP S/4HANA. The initial phase of Anta Group’s DX included creating intelligent workflows and was completed in January 2020. This enabled the company to adjust its retail operations and switch to quickly to online channels during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Like any retail organisation, the Anta Group realised that their product offerings had to be diverse to cater to an evolving customer base. This growth required an upgrade to a group-level management platform to help the business run more efficiently across the entire value chain of procurement, supply, production and sales. The SAP S/4HANA platform gives the senior management a single view of data across business units to help with better decision making regarding production and sales optimisation. The company claims to have improved its supply chain efficiency by 80%, that has led to faster delivery and business growth even in these difficult times.
IBM Services has a role to play in providing the business intelligence required for agile decision-making. By integrating data from multiple sources – retail stores, multi-brand products, channels, customers, suppliers and finance teams – on the one platform can help Anta Group to settle accounts quickly and issue business analysis reports for different entities as well as a real-time view of the operation across the organisation.
Hesketh says, “Retailers must have an accurate, timely understanding of their customers’ behaviour and resulting sales performance. COVID-19 has dramatically increased the volatility of sales, making rapid recognition of changes essential. For those lagging in their digital transformation to acquire this understanding, an attractive option is partnering with organisations with demonstrated relevant capabilities; in this case with SAP, for the capabilities and performance of their in-memory product, and IBM for their configuration and implementation expertise.”
IBM and SAP evolving their partnership
In 2016, IBM and SAP had expressed intentions of increasing investments to help their customers on their DX journeys. As some economies move into the recovery phase, all businesses will be forced to transform – or keep transforming if they are already along that path. Last month saw IBM and SAP announce the evolution of their partnership with new offerings to help businesses transform faster. The next evolution of the IBM and SAP partnership aims to focus on faster DX time to value, innovation through industry-specific offerings, customer and employee experiences and providing flexibility and choice to organisations to run their workloads in hybrid cloud environments.
Hesketh adds, “But the product and implementation partners are, while important, not the real determinant of the success of DX activity and time to value. Retailers must recognise and commit to the strategic reshaping of their business, taking their large workforces with them on the journey. This is a high-risk change. A strong relationship between product vendor and implementation partner, as SAP and IBM demonstrate here, assists in reducing, not removing, this risk.”

2020 has seen extreme disruption – and fast. The socio-economic impact will probably outlast the pandemic, but several industries have had to transform themselves to survive during these past months and to walk the path to recovery.
Against this backdrop, the Retail industry has been impacted early due to supply chain disruptions, measures such as lockdowns and social distancing, demand spikes in certain products (and diminished demands in others) and falling margins. Moreover, it is facing changed consumer buying behaviour. In the short-term consumers are focusing on essential retail and conservation of cash. The impact does not end there – in the medium and long term, the industry will face consumers who have acquired digital habits including buying directly from home through eCommerce platforms. They will expect a degree of digitalisation from retailers that the industry is not ready to provide at the moment. This raises the question on how they should transform to adapt to the New Normal and what could be a potential game-changer for them.
Translating Business Needs into Technology Capabilities
In his report, The Path to Retail’s New Normal, Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Kaushik Ghatak says, “Satisfying their old consumers, now set in their new ways, should be the ‘mantra’ for the retailers in order to survive in the New Normal.” To be able to do so they have to evaluate what their new business requirements are and translate them into technological requirements. Though it may sound simple, it may prove to be harder than usual to identify their evolving business requirements. This is especially difficult because even before the pandemic, the Retail industry was challenged with consumers who are becoming increasingly demanding, providing enhanced customer experience (CX), offering more choices and lowering prices. The market was already extremely competitive with large retailers fighting for market consolidation and smaller and more nimble retailers trying to carve out their niche.
In the New Normal, retailers will struggle to retain and grow their customer base. They will also have to focus aggressively on cost containment. A robust risk management process will become the new reality. But above all else, they will have to innovate – in their product range as well as in their processes. These are all areas where technology can help them. This can come in the form of technology partnerships, adopting hybrid models, increased usage of technology across all channels and investing in reskilling or upskilling the technology capabilities of employees.
Re-evaluating the Supply Chain
One of the first business operation to get disrupted by the current crisis was the supply chain. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Alea Fairchild says, “Retailers are finding themselves at the front-end of the broken supply chain in the current situation and there is an enormous gap between suppliers and buyers. Retailers will have to aim to combine inventory with local sourcing and become agile and adopt change quickly. This will highlight to them the importance of transparency of information, traceability, and information flow of goods.”
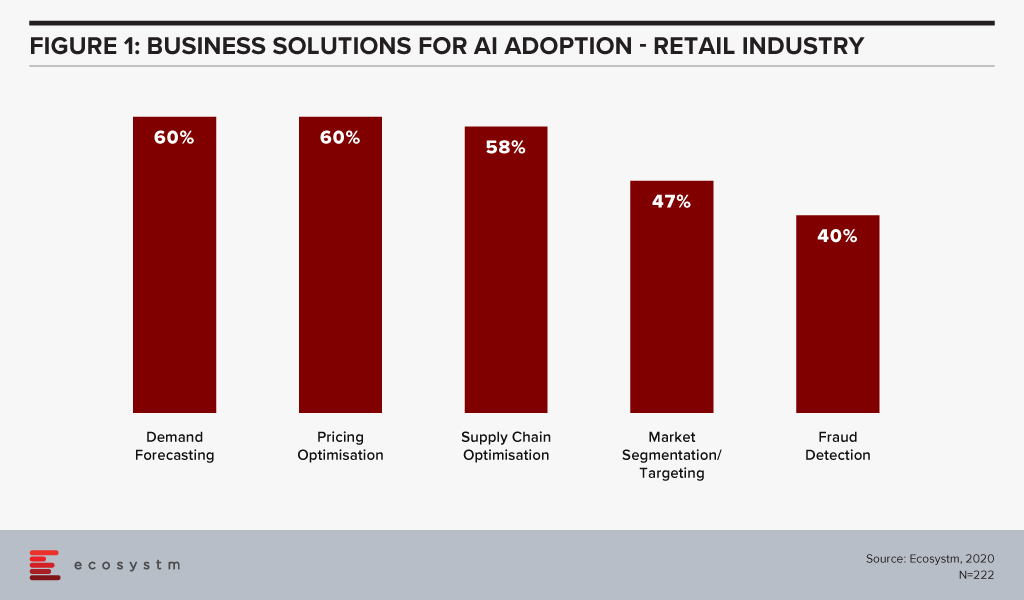
Ecosystm research shows that supply chain optimisation and demand forecasting among the top 5 business solutions that firms in Retail consider using AI for (Figure 1).
“In the New Normal, consumers are going to demand the same level of perfection that they have received and at the same cost. In order to make that possible, at the right time and at a lower cost, automation has to be implemented to improve the supply chain process, fulfill expectations and enhance visibility,” says Ghatak. “Providing differentiated CX is intimately dependent upon an aligned, flexible and efficient supply chain. Retailers will not only need to innovate at the store (physical or online) level and offer more innovative products – they will also need to have a high level of innovation in their supply chain processes.”
Digital Transformation in the Retail Industry
Ecosystm research reveals that only about 34% of global retailers had considered themselves to be digital-ready to face the challenges of the New Normal, before the pandemic. The vast majority of them admit that they still have a long way to go.
With COVID-19, the timeframes for digitalisation have imploded for most retailers. The study to evaluate the Digital Priorities in the New Normal reveals that in Asia Pacific nearly 83% of retailers have been forced to start, accelerate or refocus their Digital Transformation (DX) initiatives (Figure 2).
So, what technology areas will Retail see increased adoption oF?
Fairchild sees retailers adopt IoT, mobility, AI and solutions that deliver personalised experiences such as push notifications. What they are likely to do is blend different aspects of their physical and virtual environment to create a solution for customers. “To address in-store processing, hygiene, safety standards and compliance requirements, retailers will change their processes through a combination of resources, KPIs, automation, task management software and switching the information flow.”
Ghatak thinks automation has a significant role to play in improving both CX and the supply chain. “This is also an opportunity for retailers – both online and in-store – to create a solution experience where technologies such as Augment/Virtual Reality (AR/VR) can help. While retailers are adopting these technologies, with 5G rollouts, there is potential that the adoption will implode in a short time-frame.”
Those retailers that are not re-evaluating their business models and technology investments now will find themselves unprepared to handle the customer expectations when the global economy opens up.

During this pandemic, shoppers who have experienced new forms of delivery direct from manufacturers, curbside pickup and eCommerce via wholesalers will likely adopt at least some of those habits in their everyday lives in future. Why? Ease of use, convenience, hygiene and guaranteed product availability, all factor into this shift.
Most retailers were not ready for a rush of online shoppers or structured for a Buy Online Pickup In-Store (BOPIS) model. They struggled to pivot with their own delivery set-up, both in terms of staffing and infrastructure. Delivery slots were rare and required midnight countdowns to the next day’s set of slots with online confusion. Many grocery retailers initially stopped curbside deliveries due to lack of resources for fulfilment in store.
And for SME retail outlets, square meterage limits the number of customers inside at a time and social distancing measures limit handling curbside pickups. Supply chain issues and inventory management also played a role, with local inventory visibility a real factor in determining order placement.
As shown in Figure 1, Ecosystm research shows that supply chain optimisation and demand forecasting are both listed in the top five business solutions that firms in retail consider using AI for.
Hybrid Operations
How can retail firms, with both perishable and non-perishable goods, use AI, automation and other infrastructural investments to develop the near-term future of curbside retail? We suggest the use of hybrid operations.
Retailers are starting to look at developing hybrid operations: part retail space and part fulfilment centre. Allowing customers to enter only part of the store or pulling inventory off the shelf to a different part of the store for deliveries expands reach and allows fulfilment without decreasing the experience for customers who prefer to shop in-store. But it requires an IT infrastructural upgrade to make it happen.
In the medium term, leveraging automation will be one of the ways supermarkets and other retailers evolve their models to remain viable and profitable.
What can be automated?
Let’s define these automated delivery infrastructural options:
- Curbside pickup is the endpoint of manual sorting and selecting operation, and then the goods are ready for pickup with a vehicle outside the store.
- Micro-fulfilment centres are locations with a logistics company to maximise space in traditional stores and expand online options. Micro-fulfillment helps retailers solve the labour and last-mile costs conundrum as it brings the goods closer to the end customer.
- Dark stores are traditional retail stores that have been converted to local fulfilment centres.
None of these concepts are new, but as alternatives to traditional retail in the current environment, they are viable options. Having curbside pickup, micro-fulfilment centres or dark stores help ease transitions towards traditional operations while still protecting customers and employees. Figure 2 from our AI research at Ecosystm shows that better customer experience is a top short-term driver in retail AI deployment.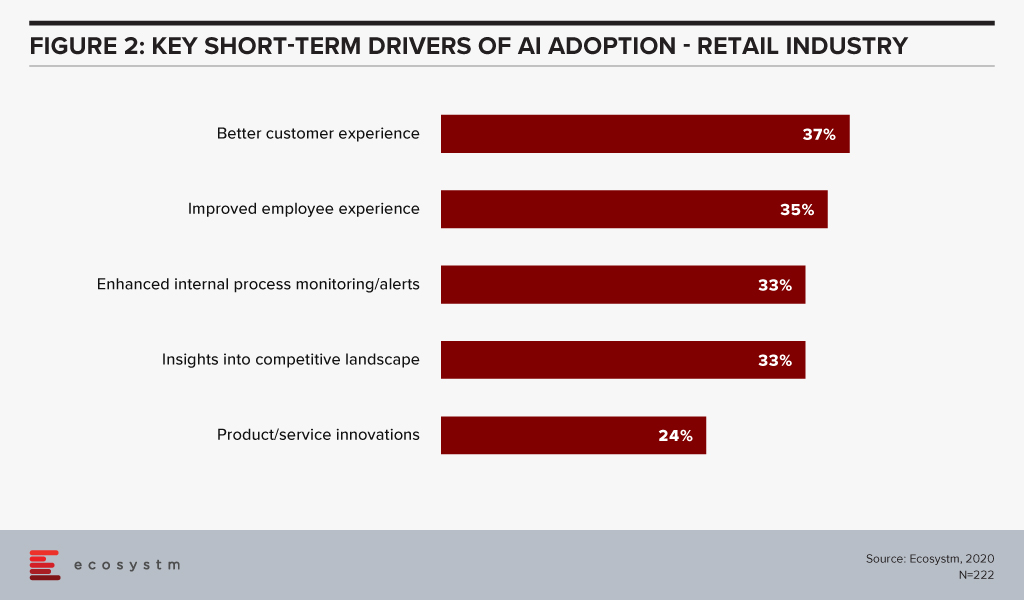
Restructuring the three factors of production
By using AI and inventory automation, retailers can focus on rightsizing the three factors of production:
- Labour. Reducing the staffing cost to produce the same volume of sales.
- Inventory. Giving the retailer the tools to replenish stores with more specific information on consumption and wastage.
- Physical Space. Enabling dynamic adjustments of product display allows alignment more closely with sales patterns within the physical store. This can be adjusted for within the week and even by day.
Retailers are looking to speed delivery by dispersing inventory closer to customers. They use automation to build more compact distribution operations by using hybrid operations.
Designing hybrid operations with technology
To develop a hybrid operation, what IT infrastructural elements need to be addressed?
Store layout. Hybrid operations should drive efficiency in delivery, based on time and motion, but without impacting in-store shoppers. Order pulling should structurally happen towards the back of the store, both for efficiency and ease of access to move goods. To maintain product quality, networks and sensors need to be installed.
Process training. Hybrid operations are system dependent. Skilled staff who pick items for delivery require systems that implement standard procedures for selection and bundling. Processes require system automation for checks to mitigate high levels of wastage. Operational implementations need to include systems that manage cut-off times and back-room management.
Order management and inventory management systems. Analytics help retailers to stock popular items. They can then ensure these are easily accessible both front and back of the store. Retailers need to prioritise inventory management to make the most of inventory visibility across hybrid operations. SKUs and barcodes should be simple, consistent and unique.
Learning from innovative IT models in Grocery
In California, Sysco expanded its direct-to-the-consumer pop-up format to help give shoppers in the area access to fresh grocery items. Whole Foods expanded its dark store concept in Texas in combination with Amazon. Aldi in the UK rolled out an online program to distribute grocery parcels to consumers who were self-isolating, with 22 different goods in the bundle including toilet paper and anti-bacterial gel.
Market ownership will come from a better shopping experience. Streamlining processes and automating order fulfilment using IT in a hybrid retail operation could help lessen the financial and logistical strain of maintaining social distancing and proper hygiene measures.







