The Healthcare industry has achieved much in the last two years, despite all the struggles and pivots. However, the impact of COVID-19 on the industry is far from over.
2020 was focused on finding a vaccine against the virus, setting treatment protocols, and workforce management to handle the emergency. 2021 was focused on vaccine distribution and administration. 2022 will be the year when we start seeing the second-order impacts of the pandemic – and see healthcare providers address these impacts.
In 2022 the key drivers of the ongoing transformation in Healthcare will be:
- Patients. Improved self-knowledge and ownership of personal health outcomes and data
- Technology. Widespread availability and adoption of digital and cognitive technologies
- Employees. The ongoing challenges of clinical and administrative staff
- The Life Sciences Industry. The recent investments in, and success of the sector
- Policy Makers. The sharp increase in focus on population health
- Continued Uncertainty. Around challenges such as new virus strains, anti-vaccine protests, supply chain disruptions etc.
Read on to find out what Ecosystm Analysts Amit Rana, Krish Krishnan, and Sash Mukherjee think are the key achievements of the industry and the future trends in 2022 and beyond.

In this Insight, our guest author Anupam Verma talks about how the Global Capability Centres (GCCs) in India are poised to become Global Transformation Centres. “In the post-COVID world, industry boundaries are blurring, and business models are being transformed for the digital age. While traditional functions of GCCs will continue to be providing efficiencies, GCCs will be ‘Digital Transformation Centres’ for global businesses.”

India has a lot to offer to the world of technology and transformation. Attracted by the talent pool, enabling policies, digital infrastructure, and competitive cost structure, MNCs have long embraced India as a preferred destination for Global Capability Centres (GCCs). It has been reported that India has more than 1,700 GCCs with an estimated global market share of over 50%.
GCCs employ around 1 million Indian professionals and has an immense impact on the economy, contributing an estimated USD 30 billion. US MNCs have the largest presence in the market and the dominating industries are BSFI, Engineering & Manufacturing, Tech & Consulting.
GCC capabilities have always been evolving
The journey began with MNCs setting up captives for cost optimisation & operational excellence. GCCs started handling operations (such as back-office and business support functions), IT support (such as app development and maintenance, remote IT infrastructure, and help desk) and customer service contact centres for the parent organisation.
In the second phase, MNCs started leveraging GCCs as centers of excellence (CoE). The focus then was product innovation, Engineering Design & R&D. BFSI and Professional Services firms started expanding the scope to cover research, underwriting, and consulting etc. Some global MNCs that have large GCCs in India are Apple, Microsoft, Google, Nissan, Ford, Qualcomm, Cisco, Wells Fargo, Bank of America, Barclays, Standard Chartered, and KPMG.
In the post-COVID world, industry boundaries are blurring, and business models are being transformed for the digital age. While traditional functions of GCCs will continue to be providing efficiencies, GCCs will be “Digital Transformation Centres” for global businesses.
The New Age GCC in the post-COVID world
On one hand, the pandemic broke through cultural barriers that had prevented remote operations and work. The world became remote everything! On the other hand, it accelerated digital adoption in organisations. Businesses are re-imagining customer experiences and fast-tracking digital transformation enabled by technology (Figure 1). High digital adoption and rising customer expectations will also be a big catalyst for change.
In last few years, India has seen a surge in talent pool in emerging technologies such as data analytics, experience design, AI/ML, robotic process automation, IoT, cloud, blockchain and cybersecurity. GCCs in India will leverage this talent pool and play a pivotal role in enabling digital transformation at a global scale. GCCs will have direct and significant impacts on global business performance and top line growth creating long-term stakeholder value – and not be only about cost optimisation.
GCCs in India will also play an important role in digitisation and automation of existing processes, risk management and fraud prevention using data analytics and managing new risks like cybersecurity.
More and more MNCs in traditional businesses will add GCCs in India over the next decade and the existing 1,700 plus GCCs will grow in scale and scope focussing on innovation. Shift of supply chains to India will also be supported by Engineering R & D Centres. GCCs passed the pandemic test with flying colours when an exceptionally large workforce transitioned to the Work from Home model. In a matter of weeks, the resilience, continuity, and efficiency of GCCs returned to pre-pandemic levels with a distributed and remote workforce.
A Final Take
Having said that, I believe the growth spurt in GCCs in India will come from new-age businesses. Consumer-facing platforms (eCommerce marketplaces, Healthtechs, Edtechs, and Fintechs) are creating digital native businesses. As of June 2021, there are more than 700 unicorns trying to solve different problems using technology and data. Currently, very few unicorns have GCCs in India (notable names being Uber, Grab, Gojek). However, this segment will be one of the biggest growth drivers.
Currently, only 10% of the GCCs in India are from Asia Pacific organisations. Some of the prominent names being Hitachi, Rakuten, Panasonic, Samsung, LG, and Foxconn. Asian MNCs have an opportunity to move fast and stay relevant. This segment is also expected to grow disproportionately.
New age GCCs in India have the potential to be the crown jewel for global MNCs. For India, this has a huge potential for job creation and development of Smart City ecosystems. In this decade, growth of GCCs will be one of the core pillars of India’s journey to a USD 5 trillion economy.
The views and opinions mentioned in the article are personal.
Anupam Verma is part of the Senior Leadership team at ICICI Bank and his responsibilities have included leading the Bank’s strategy in South East Asia to play a significant role in capturing Investment, NRI remittance, and trade flows between SEA and India.

The Healthcare industry has had to pivot completely this year and 2021 will see it emerge a transformed industry. The impact will be seen on policies, how ecosystems evolve, and most obviously on healthcare provider organisations. COVID-19 has shifted the business priorities of healthcare providers and how these organisations invest and use technology. There will be another reset in 2021. However, given the immense impact of the pandemic, it would be near-impossible to restrict the prediction to only one year; and several of the trends will firmly define the industry way beyond 2021.
Ecosystm Advisors Aga Manhao, Arun Sethuraman, Krish Krishnan and Sash Mukherjee present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for Healthcare Trends in 2021. This is a summary of the Healthcare predictions – the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform.
The Top 5 Healthcare Trends for 2021
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Public Health Will Create New Opportunities Well Beyond 2021
The impact of COVID-19 will be on all levels. Increasing pressure from patients will challenge healthcare providers (from primary through to tertiary) throughout 2021. There will be larger global impacts as well – average nourishment is likely to go down in most countries, and there will be lower average (seasonal) immune health in many countries.
This is not all doom and gloom – there will be new business opportunities. Enterprises and innovators will find opportunities in:
- Supply Chain Arbitrage. Continued asymmetrical supply and demand will drive the movement of healthcare related goods and services across geographies.
- Investment. Investments in pharma/ vaccine/ diagnostics manufacturing and distribution will be driven more by short-term horizons, defensive capacity building, and supply security concerns. Technology and IP acquisition by pharma and medtech leaders will also accelerate.
- Innovation. COVID-linked gaps in health, immunity, nourishment, and lifestyles will lead to new products within foods, supplements, medications, and pharmaceuticals; and in tech-enabled personal devices and health monitoring apps or systems.
- New Businesses. We will see an upsurge in demand and supply of alternative medicines and devices as well, although these may still not be accepted in conventional medicine.
- Healthcare Policies Will Focus on Product & Manufacturing Security and Supply Chain Control
The COVID-19 crisis has exposed the need for better collaboration and visibility of external resources to handle unprecedented scenarios. Governments in countries that have done well to manage the crisis took the vital step of encouraging and being the hub for cross-agency collaboration. Having a siloed view of resources and the supply chain is not sufficient in combating larger challenges. Healthcare policy makers will work towards a more collaborative, AI-driven, supply chain.
Some of the world’s largest economies have already begun to take steps to reduce manufacturing and supply chain dependencies in pharma, vaccines, diagnostics and medical devices. What has shown up as opportunistic stockpiling or supply chain arbitrage will become more entrenched. Various governments will either incentivise or centralise the establishment of manufacturing and long-term supply contracts for their countries.
- 2021 Will be a Breakout Year for Community Health
COVID-19 has significantly disrupted current standards of care for chronic diseases world-wide. Frequency and necessity of patient visits to hospitals and clinics for routine checkups and minor interventions are being evaluated by healthcare planners and providers. There are concerns about the increasing cost of providing basic services, allocation of healthcare capacity to higher priority needs, and the need to reduce risk of exposure to the vulnerable population.
Telehealth and Digital Health technologies have seen a marked increase in adoption during the pandemic, but the real effectiveness of these solutions to solve a healthcare delivery problem is still emerging. We predict 2021 will be a breakout year for Community Health, powered by these two technologies. There will be an increased focus on building resilient communities and early warning systems. Number of visits to hospitals and clinics for routine observations will drop by 15-20% or even more. Privacy and Data security concerns will increase, and this will also lead to better policy and practices to address these concerns. 2021 promises to be a better year for coordinated community care.
- Healthcare Providers Will be More Tech-Dependent Than Ever
In 2020, healthcare providers’ technology investments took off on unexpected trajectories and they have digressed from their technology and transformation roadmap. Many solutions would have gone through an initial ‘proof-of-concept’ without the formal rigours and protocols. Many of these will be adopted for longer term applications.
Healthcare organisations had to pivot their technology spending when COVID-19 hit. There were several changes that were required to be made, including implementing operational measures to ensure staff safety and cutting down on non-essential expenses. When it comes to digital initiatives, the key focus areas were evolving service delivery and empowering employees with the right technology for care delivery – often remote. What providers did not have the time or resources for was to digitalise processes and retain focus on their entire patient demography – and not just those impacted by COVID-19. In 2021, we see a clear indication that not only will their priorities be different, healthcare providers will ramp up their technology investments in all areas.
- Medtech and Providers Will Find New Synergies
Medical devices which generate clinical data and/or are driven by clinical data will attract greater investment and higher R&D expenditure; and will either dominate or begin to set the direction for future consumer devices in the Healthcare space.
The popularity of telehealth and digital health will put pressure on healthcare providers to further draw data-driven insights from personal devices. They are likely to mandate the devices that they would be willing to use the data from They will have greater power to demand Interoperability and operating system convergences in the next few years from device developers and manufacturers.
2021 will see an increased use of devices such phones, bracelets and even anklets to track the spread of COVID-19. It will also see the transition of the smartphone to a medical device. The collection, sharing of data, running AI/machine learning will make our smartphones an integral part of remote patient management.

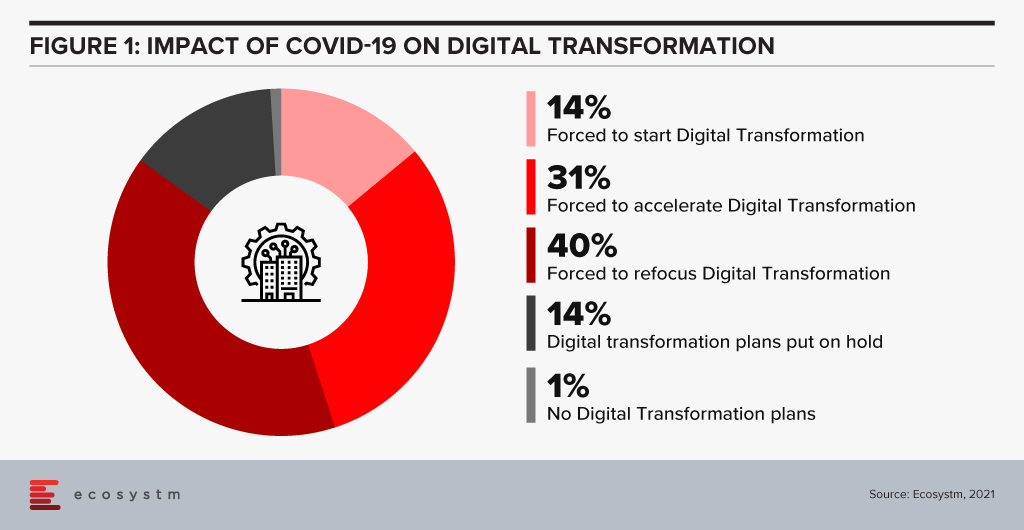
As the search for a COVID-19 vaccine intensifies, there is a global focus on the Life Sciences industry. The industry has been hit hard this year – having to deliver overtime through a disrupted supply chain, unexpected demand spikes, and reduction of revenues from their regular streams. Life sciences organisations are already challenged by the breadth of their focus – across R&D and clinical discovery; Manufacturing & Distribution; and Sales & Marketing. Increasingly, many pharmaceutical and medtech organisations choose to outsource some of these functions, which brings to fore the need for a robust compliance framework. In the Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal Study, two-thirds of life sciences organisations mention that they have either been forced to start, accelerate or refocus their Digital Transformation initiatives – the remaining one-third have put their Digital Transformation on hold. The industry is clearly at an inflection point.
Challenges of the Life Sciences Industry
Continued Focus on R&D. Life sciences companies operate in an extremely competitive global market where they have to work on new products against a backdrop of competition from generics and a global concern over rising healthcare expenditure. Apart from regulatory challenges, they also face immense competition from local manufacturers as they enter each new market.
Re-thinking their Distribution Strategy. Sales and distribution for many pharma and medtech organisations have been traditional – using agents, distributors, clinicians, and healthcare providers. But now they need to change their go-to-market strategies, target patients and consumers directly and package their product offerings into value-added services. This will require them to incorporate customer experience enhancers in their R&D, going beyond drug discovery and product innovation.
Tracking Global Regulations. Governments across the world are trying to manage their healthcare budgets. They are also more focused on chronic disease management. The focus has shifted to value-based medicine in general, but pharma and medtech products are being increasingly held accountable by health outcomes. Governments are increasingly implementing drug reforms around what clinicians can prescribe. Global Life Sciences organisations have to constantly monitor the regulations in the multiple countries where they operate and sell. They are also accountable for their entire supply chain, especially ensuring a high product quality and fraud prevention.
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for Life Sciences organisations, focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). They appear to be investing in emerging technology especially in their R&D and clinical discovery and Manufacturing functions.
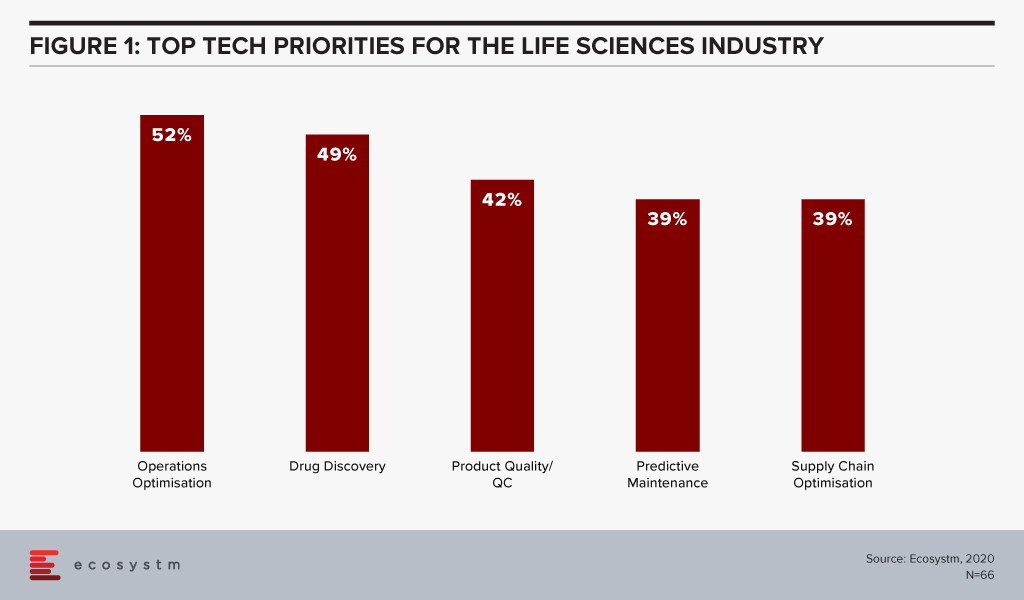
Technology as an Enabler of Life Sciences Transformation
Discovery and Development
With the evolution of technology, Life Sciences organisations are able to automate much of the mundane tasks around drug discovery and apply AI and machine learning to transform their drug discovery and development process. They are increasingly leveraging their ecosystem of smaller pharma and medtech companies, research laboratories, academic institutions, and technology providers to make the process more time and cost efficient.
Using an AI algorithm, the researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have discovered an antibiotic compound that can kill many species of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. MIT’s algorithm screens millions of chemical compounds and chooses the antibiotics which have the potential to eliminate bacteria resistant to existing drugs. Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering is manufacturing 3D printed organ-on-a-chip to give insights on cell, tissue, and organ biology to help the pharma sector with drug development, disease modelling and finally in the development of personalised medicine.
Life Sciences are also engaging more with technology partners – whether emerging start-ups or established players. Pfizer and Saama are working together on AI clinical data mining. The companies are developing and deploying an AI-based analytical tool where Pfizer provides clinical data and domain knowledge to train models on the Saama Life Science Analytics Cloud (LSAC). Saama was identified as a partner at a hackathon. Sanofi and Google have established a new virtual Innovation Lab to develop scientific and commercial solutions, using multiple Google capabilities from cloud computing to AI.
Tech providers also keep evolving their capabilities in the Life Sciences industry for more efficient drug discovery and better treatment protocols. Microsoft’s Project Hanover uses machine learning to develop a personalised drug protocol to manage acute myeloid leukaemia. Similarly, Apple’s ResearchKit – an open-source framework is meant to help researchers and developers create iOS-based applications in the field of medical research.
Manufacturing and Logistics
The industry also faces the challenges faced by any Manufacturing organisation and has the need to deploy manufacturing analytics, and advanced supply chain technology for better process and optimisation and agility. There is also the need for complete visibility over their supply chain and inventory for traceability, safety, and fraud prevention. Emerging technologies such as Blockchain will become increasingly relevant for real-time track and trace capability.
The MediLedger Network was established as an open network to the entire pharma supply chain. The project brings a consortium of some of the world’s largest pharmaceutical companies, and logistics providers to improve drug supply chain management.
Since the data on the distributed ledger is encrypted, it creates a secure system without any vulnerabilities. This eliminates counterfeit products and ultimately ensures the quality of the pharma products and promotes increased patient safety. To foster security and improve the supply chain, the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) successfully completed a pilot with a group including IBM, KPMG, Merck and Walmart to support U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) to trace vaccines and prescription medicines throughout the country.
Diagnostics and Personalised Healthcare
As more devices (consumer and enterprise) and applications enter the market, people will take ownership and interest in their own health outcomes. This is seeing a continued growth in online communities and comparison sites (on physicians, hospitals, and pharmaceutical products). Increasingly, insurance providers will use data from wearable devices for a more personalised approach; promoting and rewarding good health practices.
Beyond the use of wearables and health and wellness apps, we will also see an exponential increase of home-based healthcare products and services – whether for primary care and chronic disease management, or long-term and palliative care. As patients become more engaged with their care, the life sciences industry is beginning to serve them through personalised approach, medicines, right diagnosis and through advanced medical devices and products.
An online tool developed by the University of Virginia Health Systems helps identify patients that have a high risk of getting a stroke and helps them reduce that risk. This tool calculates the patient’s probability of suffering a stroke by measuring the severity of their metabolic syndrome – taking into account a number of conditions that include high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels and excess body fat. Life Sciences organisations are increasingly having to invest in customer-focused solutions such as these.
Wearables with special smart software to monitor health parameters, gauge drug compatibility and monitor complications are being implemented by Life Sciences organisations. The US FDA approved a pill called Abilify MyCite fitted with a tiny ingestible sensor that communicates with a patch worn by the patient to transmit data on a smartphone. Medtech companies continue to develop FDA approved health devices that can monitor chronic conditions. Smart continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and insulin pens send blood glucose level data to smartphone applications allowing the wearer to easily check their information and detect trends.
Technologies such as AR/VR are also enabling Life Sciences companies with their diagnostics. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals has created an AR/VR app called “In My Eyes” to better diagnose vision impairment in patients.
What is interesting about these personalised products is that not only do they improve clinical outcomes, they also give Life Sciences companies access to rich data that can be used for further product development and improvement.
The Life Sciences industry will continue to operate in an unpredictable and competitive market. This is evident by the several mergers and acquisitions that we witness in the industry. As they continue to use cutting-edge technology for their R&D practices, they will leverage technology to transform other functions as well.

The future of food, medicine, and digital technology has been marked as prime research targets to maintain Singapore’s competitiveness in the coming years. Recently, Singapore Government convened a panel discussion on the Research, Innovation and Enterprise (RIE) 2020 plan where Singapore’s Finance Minister Mr Heng Swee Keat delivered an update on Singapore’s science and technology research plan.
Mr. Heng conveyed that more than S$500 million is set-aside to shape up the artificial intelligence systems and to fulfill the nation’s cyber-security requirements. The fund will also improve Singapore’s supercomputing capabilities and the deployment of automation and robotics.
A further $144 million will be allocated towards food research to increase sustainable urban food production, and another $80 million will be contributed to the cell-therapy research in the biopharmaceutical sector.
How Singapore will benefit in terms of technology from this announcement?
The Government has clearly spent a lot of time to determine how to get Singaporean companies to invest in research that can benefit the country, and identifying areas that the industries can benefit in return.
Investment in Digital Technology
The Government believes that it is important to invest in the areas of Artificial Intelligence, Supercomputing and Robotics and hope that there will be more success stories for these industries. The S$500 million set aside will aim to increase the funding already set back in the RIE 2020 for the Digital Intelligence.
Speaking on the subject, Mervyn Cheah, Principal Advisor ,Ecosystm, says that “The Government aims to entice more Industry to invest in R&D in Singapore. PM Lee has mentioned that the industry today is investing just 1.2 to 1.4 of Singapore’s GDP in R&D in Singapore, and he wants the Industry to do more. It is a bit like playing roulette you place your bets on many numbers and hope that one of them will blossom and give you the returns and success. It is not possible that all R&D will come to fruition practically.”
Scenario for Businesses
The RIE 2020 is an initiative taken by the Singapore Government to make the nation a hub for R&D. By setting aside funds for both local industries and MNCs the government hopes that the industries will be able to invest and grow.
“There are a number of new start-ups being created as Singaporeans start to recognise that the government is putting in more R&D funding. At the same time, existing businesses will expand to take advantage of this announcement” says Cheah.
What to Expect – RIE2020
Currently, the local Industries in Singapore do not have a large appetite for investing in R&D in Singapore although there is a 50% spike from 2016 to 2018. The government’s aim is to invest in the Science, Engineering, and Biomedical fields industries, with the intent that they can increase their revenue.
Cheah says “the Government is looking at getting Multi-national Corporations (MNCs) to invest in Singapore for their R&D and believes that the industry can do better. So, the Government (National Research Foundation under the Prime Minister’s Office) is pushing the Industry to do more, and on their pro-active part, they have announced setting aside another S$700 million R&D funding to A*STAR, to the Singapore Food Agency, and other R&D agencies, with the hope that the Industries will further spend R&D in Singapore.”

















