The Retail industry has had to do a sharp re-think of its digital roadmap and transformation journey – Ecosystm research shows that about 75% of retail organisations had to start, accelerate, or re-focus their digital transformation initiatives. However, that will not be enough as organisations move beyond survival to recovery – and future successes. While retailers will focus on the shift in customer expectations, a mere focus on customer experience will not be enough in 2021. Ecosystm Principal Advisors, Alan Hesketh and Alea Fairchild present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for Retail & eCommerce in 2021.
This is a summary of the predictions, the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform here.
The Top 5 Retail & eCommerce Trends for 2021
- There Will Only be Omnichannel Retailers
The value of an omnichannel offer in Retail has become much clearer during the COVID-19 pandemic. Retailers that do not have the ability to deliver using the channel customers prefer will find it hard to compete. As the physical channel becomes less important new revenue opportunities will open up for businesses operating in adjacent market sectors – companies such as food and grocery wholesalers will increasingly sell direct to consumers, leveraging their existing online and distribution capabilities.
Most customers transact on mobile device – either a mobile phone or tablet. New capabilities will remove some of the barriers to using these mobile devices. For one, technologies such as Progressive Web Apps (PWA) and Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) will provide a better customer experience on mobile platforms than existing websites, while delivering a user experience at par or better than mobile apps. Also, as retailers become AI-enabled, machine learning engines will provide purchase recommendations through smartwatches or in-home, voice-enabled, smart devices.
- COVID-19 Will Continue to be an Influence Forcing Radical Shifts
In driving the economic recovery in 2021, we will see ‘glocal’ consumption – emphasis on local retailers and global players taking local actions to win the hearts and minds of local consumers. There will be significant actions within local communities to drive consumers to support local retailers. Location-based services (LBS) will be used extensively as consumers on the high street carry more LBS-enabled devices than ever before. Bluetooth beacon technology and proximity marketing will drive these efforts. Consumers will have to opt-in for this to work, so privacy and relationship management are also important to consider.
But people still want to “physically” browse, and design aesthetics of a store are still part of the attraction. In the next 18 months, the concept of virtual stores that are digital twins will take off, particularly in the holiday and Spring clearance sales. Innovators like Matterport can help local retailers gain a more global audience with a digital twin with a limited technological investment. At a minimum, Shopify or other intermediaries will be necessary for a digital shop window.
- The Industry will See Artificial Intelligence in Everything
AI will increase its impact on Retail with an uptake in two key areas.
- Customer interactions. Retail AI will use customer data to deliver much richer and targeted experiences. This may include the ability to get to a ‘segment of one’. Tools will include chatbots that are more functional and support for voice-based commerce using mobile and in-home edge devices. Also, in-store recognition of customers will become easier through enhanced device or facial recognition. Markets where privacy is less respected will lead in this area – other markets will also innovate to achieve the same outcomes without compromising privacy but will lag in their delivery. This mismatch of capability may allow early adopters to enter other geographic markets with competitive offers while meeting the privacy requirements of these markets.
- Supply chain and pricing capabilities. AI-based machine learning engines using both internal and increased sources of external data will replace traditional math-based forecasting and replenishment models. These engines will enable the identification of unexpected and unusual demand influencing factors, particularly from new sources of external data. Modelling of price elasticity using machine learning will be able to handle more complex models. Retailers using this capability will be in a better position to optimise their customer offers based on their pricing strategies. Supply chains will be re-engineered so products with high demand volatility are manufactured close to markets, and the procurement of products with stable demands will be cost-based.
- Distribution Woes Will Continue
Third party delivery platforms such as Wish and RoseGal are recruiting additional international non-Asian suppliers to expand their portfolios. Amazon and AliExpress are leaders here, but there are many niche eCommerce platforms taking up the slack due to the uneven distribution patterns from the ongoing economic situation. Expect to see a number of new entrants taking up niche spaces in the second half of 2021, sponsored by major retail product brands, to give Amazon a run for their money on a more local basis.
As the USPS continues to be under strain, delivery companies like FedEx in the US who partner with the USPS are already suffering from the USPS’s operational slowdown, in both their customer reputation and delivery speed. In 2021, COVID-19 – and workers’ unions – will continue to impact distribution activities. Increased spending in warehouse automation and new retail footprints such as dark stores will be seen to make up for worker shortfalls.
- China’s Retail Models Will Expand into Other Markets
China’s online businesses operate in a large domestic market that is comparatively free of international competitors. Given the scale of the domestic market, these online companies have been able to grow to become substantial businesses using advanced technologies. All the Chinese tech giants – among them Alibaba, ByteDance, DiDi Chuxing, and Tencent – are expanding internationally.
China’s rapidly recovering economy puts those businesses in a strong position to fund a competitive expansion into international markets using their domestic base, particularly with their Government’s promotion of the country’s tech sector. It is harder to impose restrictions on software-based businesses, unlike the approach that we have witnessed the US Government take for hardware companies such as Huawei – placing constraints on mobile phone components and operating systems.
These tech giants also have significant experience in a Big Data environment that provides little privacy protection, as well as leading-edge AI capabilities. While they will not be able to operate with the same freedom in global markets, and there will be other large challenges in translating Chinese experience to other markets – these tech players will be able to compete very effectively with incumbent global companies. Chinese companies also continue to raise capital from US stock exchanges with The Economist reporting Chinese listings have raised close to USD 17 billion since January 2020.

Contact centres were already on a path to modernisation – which got accelerated by the COVID-19 crisis. The need for omnichannel delivery and better insights from customer data has forced contact centres to adopt cloud solutions. Ecosystm Principal Advisor Audrey William says, “There is still a disconnect between integrating and synchronising customer data between Sales, Marketing and Customer Teams. However, the market is starting to see contact centre vendors work closer with vendors in customer experience management segment.”
Genesys and Adobe are collaborating on integrating Genesys cloud and the Adobe Experience Platform. The deeper integration of both platforms is aimed to give organisations a better omnichannel presence. The platform is live for users and Genesys and Adobe will introduce other features and capabilities throughout 2020. Genesys is already a partner of Adobe’s Exchange Program designed for technology partners to supplement Exchange Marketplace with extensions and applications for Adobe Creative Cloud users.
Augmenting the CX journey through Data Synchronization
Ecosystm data finds that 62% of contact centres have driving omnichannel experience as a key customer experience (CX) priority and 57% want to analyse data across multiple data repositories. However, when asked about the challenges of driving consistent CX, data access and integration appears to be a barrier in achieving their priorities. These challenges are the reason why getting a “true view” of the customer data has been an arduous task and achieving consistent CX continues to be a struggle.
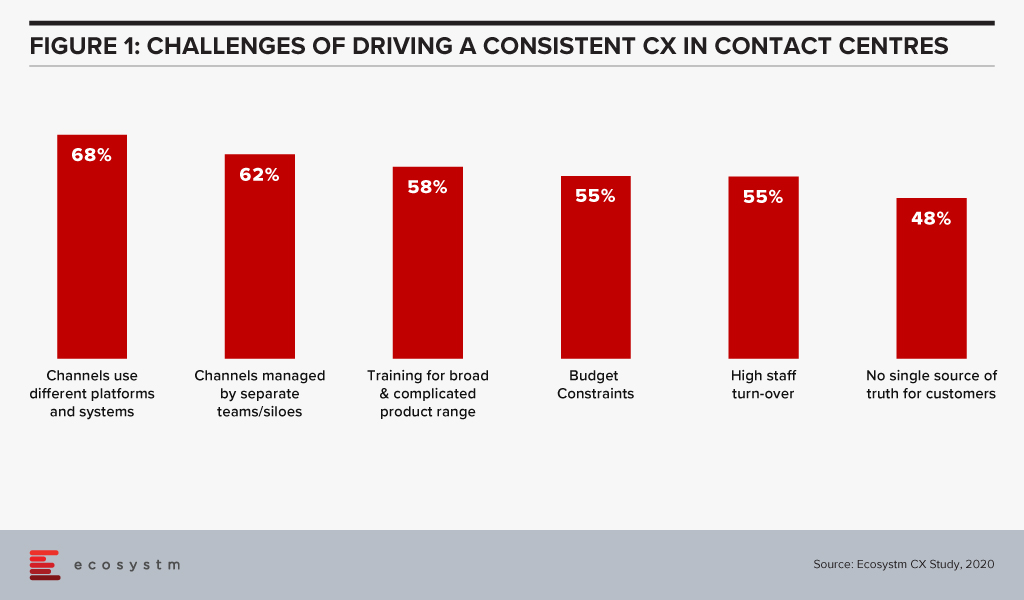
William says. “The customer data collected by a particular service or department does not always move along in real-time with the customer interactions across different touchpoints. This complicates maintaining a real-time customer profile and impacts the CX.”
“Sales and Marketing have different KPIs and tend to view customer data from different angles. The data from in-store, Marketing and Sales interactions sits within departmental silos. They may deal with the same customers and not follow them through their entire journey. This leads to missed opportunities in reaching out to them at the right time with the right products to upsell, resell or provide better CX. Data synchronisation across channels, would solve that problem.”
Integrating Genesys and Adobe Experience Platform will give organisations the capability to provide contact centre agents with real-time customer data and profiles from a single point to provide an personalised experience. The platform is powered by Genesys Predictive Engagement that uses AI to provide more intelligence based on past interactions to drive effective, data-driven conversations. In addition to this, the partnership also enables businesses and marketing departments to customise campaigns and extend their digital and voice capabilities for optimal conversions. William says, “The ability to use AI to understand customer intent, behaviour and patterns is critical as it will allow brands to re-look at how to design the customer journey. When you keep using the same and outdated profile, it will be hard to have discussions around intent, customer interest and assess how customer priorities have changed. Accurate and automate data profiling will lead to more targeted and accurate marketing campaigns.”
Genesys Deepening Industry Partnerships
Genesys is re-shaping its strategy on Contact Centre as a Service (CCaaS) offerings through partnerships and working on its vision of providing Experience as a Service to its global clients. The need for CCaaS has been accelerated by the pandemic. Last month Genesys signed a five year deal with Infosys to develop and deploy cloud CX and contact centre solutions.
Earlier this year, Genesys partnered with MAXIMUS, a US Government services provider to set up the MAXIMUS Genesys Engagement Platform, an integrated, cloud-based omnichannel contact centre solution driven by the government requirement for public sector organisations to provide seamless customer experiences similar to those offered in the private sector.
The company has also partnered with various other industry leaders like Microsoft, Google Cloud, and Zoom to roll out cloud-based innovations to benefit customers.
Click below to access insights from the Ecosystm Contact Centre Study on visibility into organisations’ priorities when running a Contact Centre (both in-house and outsourced models) and the technologies implemented and being evaluated
This week, Vodafone New Zealand launched a contact centre solution known as Vodafone Connect that runs on AWS cloud infrastructure. The solution is designed for contact centres and customer service providers to reduce their operating cost and deliver an improved customer experience (CX).
The move comes as many businesses and governments are witnessing a spike in inbound contact centre volumes since the outbreak of the pandemic. The telecom company aims to help the contact centre industry through its on-demand contact centre suite of solutions that can be scaled up or down according to the organisations’ requirements. It can be combined with existing CRM platforms in a single dashboard for better access to data and resolution support.
Vodafone Connect is built on the AWS Connect cloud contact centre solution and uses data analytics and machine learning tools to automate customer interactions across multiple channels – email, messaging and social media – to support the contact centre agents with real-time information.
COVID-19 has accelerated the move to the cloud
The recent pandemic has seen many organisations make a leap almost overnight to cloud contact centre technologies. Many organisations that previously had concerns around data privacy, and securing customer data – and were thus hesitant about deploying cloud contact centre solutions – have moved to the cloud model. The cloud model helped get agents that were forced to work from home up and running in a short duration. The immediate urgency was primarily due to a massive spike in voice calls and non-voice activity such as emails. During the COVID-19 crisis, many organisations used Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections to their legacy on-premises phone system to enable the remote agents. However, there have been challenges reported by many organisations with that approach such as increases to IT budget, difficulty in scaling easily, and the requirement for more IT support that could have been avoided.
Ecosystm research finds that only 30% of organisations have fully migrated their cloud contact centre solutions on the cloud. 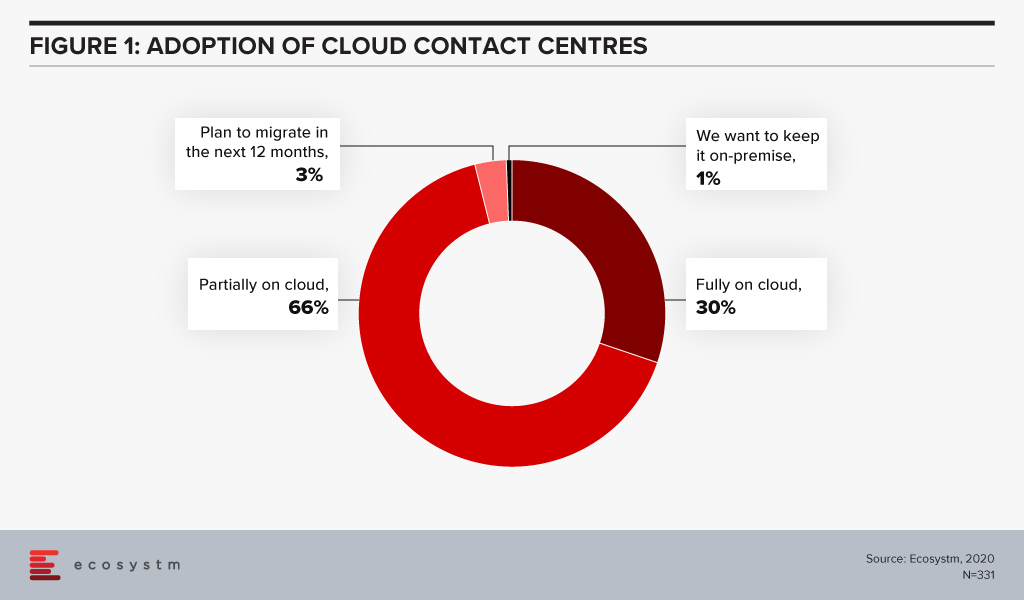
This indicates a market opportunity for vendors in the cloud contact centre space. The COVID-19 pandemic has definitely triggered a strong move towards the cloud model. It has become imperative for vendors and solutions providers to strengthen their cloud capabilities.
Driving an Omni-Channel Experience has become increasingly difficult
Ecosystm research also finds that organisations find siloed organisational data as one of the biggest challenges in driving consistent customer experience.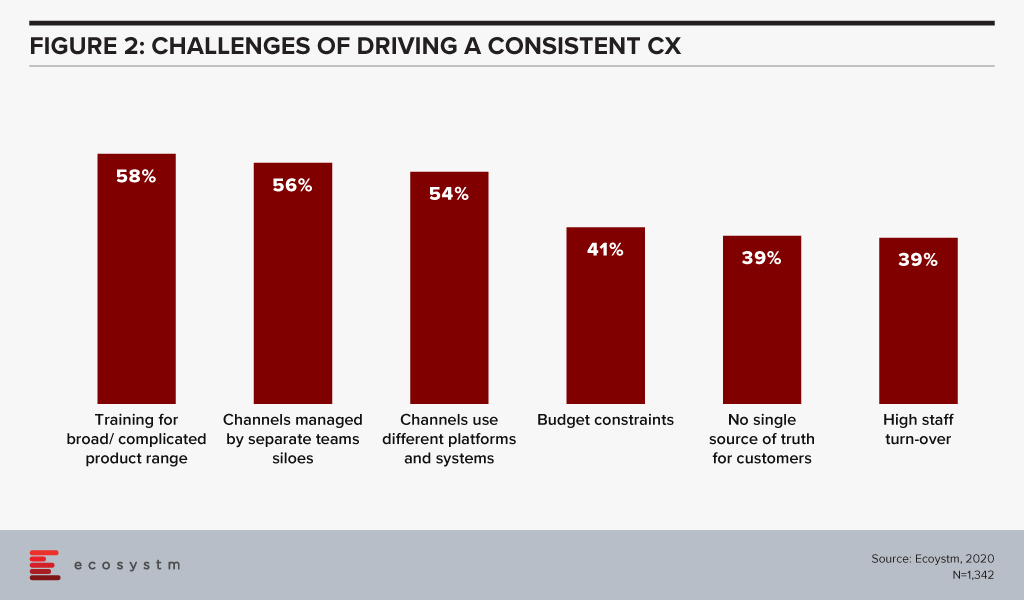
This has been further exacerbated by the high volume of interactions that organisations have been having with their customers, and the need to accommodate work-from-home policies for their customer care agents. At the same time, nearly 60% of organisations want to drive an omni-channel experience to improve CX. This provides a huge opportunity for contact centre vendors and partners to offer consulting services to help organisations bridge the gaps in achieving an omni-channel experience. For many organisations there has been a greater push to integrate CRM, the voice of the customer/surveys, customer journey analytics to the contact centre technologies and this is not an easy task as it involves different stakeholders with different sets of KPIs. Having a single platform that can manage this omni-channel experience will be a huge benefit for many organisations.
New Players in the Competitive Landscape
AWS is a relatively new player in the contact centre market, but it is starting to disrupt the existing players, with a global installed base. However, it is worth noting that Avaya, Cisco and Genesys have a higher installed base and they continue to win new deals. The move to the cloud is witnessing more service providers, telecom providers and other contact centre partners push more cloud-based solutions in the market. Apart from AWS, other important players include NICEinContact, 8×8, Talkdesk, Twillio, Five9, and UJet. The competitive battleground is heating up and there are a lot of options for customers to choose from. It will all come down to working with a vendor that can help them achieve their desired CX outcomes.
There are other important elements in CX that are growing in importance and these include conversational AI, voice biometrics, knowledge management systems, machine learning and CX management solutions. Contact centre solution providers are having discussions around these areas with tech buyers. This will mean that we can expect deeper partnerships and acquisitions in the short to medium term. Security has also emerged as an important issue to be resolved, especially with agents working from home. This is from a compliance perspective and pertaining to how agents are viewing and handling customer data. These new trends indicate that customers will need to work with different vendors to solve the variety of issues they are facing.
The Vodafone Connect solution on AWS Connect is one of the many examples of how more partners of contact centre solutions are gearing up for the rapid move to the cloud. Globally, Vodafone also sells contact centre solutions from Cisco and Genesys. The next 3 years will see a great movement in the market and this will include vendors from North America that will set up operations to push their offerings across Europe and the Asia Pacific.





