In the Ecosystm Predicts: Building an Agile & Resilient Organisation: Top 5 Trends in 2024, Principal Advisor Darian Bird said, “The emergence of Generative AI combined with the maturing of deepfake technology will make it possible for malicious agents to create personalised voice and video attacks.” Darian highlighted that this democratisation of phishing, facilitated by professional-sounding prose in various languages and tones, poses a significant threat to potential victims who rely on misspellings or oddly worded appeals to detect fraud. As we see more of these attacks and social engineering attempts, it is important to improve defence mechanisms and increase awareness.
Understanding Deepfake Technology
The term Deepfake is a combination of the words ‘deep learning’ and ‘fake’. Deepfakes are AI-generated media, typically in the form of images, videos, or audio recordings. These synthetic content pieces are designed to appear genuine, often leading to the manipulation of faces and voices in a highly realistic manner. Deepfake technology has gained spotlight due to its potential for creating convincing yet fraudulent content that blurs the line of reality.
Deepfake algorithms are powered by Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and continuously enhance synthetic content to closely resemble real data. Through iterative training on extensive datasets, these algorithms refine features such as facial expressions and voice inflections, ensuring a seamless emulation of authentic characteristics.
Deepfakes Becoming Increasingly Convincing
Hyper-realistic deepfakes, undetectable to the human eye and ear, have become a huge threat to the financial and technology sectors. Deepfake technology has become highly convincing, blurring the line between real and fake content. One of the early examples of a successful deepfake fraud was when a UK-based energy company lost USD 243k through a deepfake audio scam in 2019, where scammers mimicked the voice of their CEO to authorise an illegal fund transfer.
Deepfakes have evolved from audio simulations to highly convincing video manipulations where faces and expressions are altered in real-time, making it hard to distinguish between real and fake content. In 2022, for instance, a deepfake video of Elon Musk was used in a crypto scam that resulted in a loss of about USD 2 million for US consumers. This year, a multinational company in Hong Kong lost over USD 25 million when an employee was tricked into sending money to fraudulent accounts after a deepfake video call by what appeared to be his colleagues.
Regulatory Responses to Deepfakes
Countries worldwide are responding to the challenges posed by deepfake technology through regulations and awareness campaigns.
- Singapore’s Online Criminal Harms Act, that will come into effect in 2024, will empower authorities to order individuals and Internet service providers to remove or block criminal content, including deepfakes used for malicious purposes.
- The UAE National Programme for Artificial Intelligence released a deepfake guide to educate the public about both harmful and beneficial applications of this technology. The guide categorises fake content into shallow and deep fakes, providing methods to detect deepfakes using AI-based tools, with a focus on promoting positive uses of advanced technologies.
- The proposed EU AI Act aims to regulate them by imposing transparency requirements on creators, mandating them to disclose when content has been artificially generated or manipulated.
- South Korea passed a law in 2020 banning the distribution of harmful deepfakes. Offenders could be sentenced to up to five years in prison or fined up to USD 43k.
- In the US, states like California and Virginia have passed laws against deepfake pornography, while federal bills like the DEEP FAKES Accountability Act aim to mandate disclosure and counter malicious use, highlighting the diverse global efforts to address the multifaceted challenges of deepfake regulation.
Detecting and Protecting Against Deepfakes
Detecting deepfake becomes increasingly challenging as technology advances. Several methods are needed – sometimes in conjunction – to be able to detect a convincing deepfake. These include visual inspection that focuses on anomalies, metadata analysis to examine clues about authenticity, forensic analysis for pattern and audio examination, and machine learning that uses algorithms trained on real and fake video datasets to classify new videos.
However, identifying deepfakes requires sophisticated technology that many organisations may not have access to. This heightens the need for robust cybersecurity measures. Deepfakes have seen an increase in convincing and successful phishing – and spear phishing – attacks and cyber leaders need to double down on cyber practices.
Defences can no longer depend on spotting these attacks. It requires a multi-pronged approach which combines cyber technologies, incidence response, and user education.
Preventing access to users. By employing anti-spoofing measures organisations can safeguard their email addresses from exploitation by fraudulent actors. Simultaneously, minimising access to readily available information, particularly on websites and social media, reduces the chance of spear-phishing attempts. This includes educating employees about the implications of sharing personal information and clear digital footprint policies. Implementing email filtering mechanisms, whether at the server or device level, helps intercept suspicious emails; and the filtering rules need to be constantly evaluated using techniques such as IP filtering and attachment analysis.
Employee awareness and reporting. There are many ways that organisations can increase awareness in employees starting from regular training sessions to attack simulations. The usefulness of these sessions is often questioned as sometimes they are merely aimed at ticking off a compliance box. Security leaders should aim to make it easier for employees to recognise these attacks by familiarising them with standard processes and implementing verification measures for important email requests. This should be strengthened by a culture of reporting without any individual blame.
Securing against malware. Malware is often distributed through these attacks, making it crucial to ensure devices are well-configured and equipped with effective endpoint defences to prevent malware installation, even if users inadvertently click on suspicious links. Specific defences may include disabling macros and limiting administrator privileges to prevent accidental malware installation. Strengthening authentication and authorisation processes is also important, with measures such as multi-factor authentication, password managers, and alternative authentication methods like biometrics or smart cards. Zero trust and least privilege policies help protect organisation data and assets.
Detection and Response. A robust security logging system is crucial, either through off-the shelf monitoring tools, managed services, or dedicated teams for monitoring. What is more important is that the monitoring capabilities are regularly updated. Additionally, having a well-defined incident response can swiftly mitigate post-incident harm post-incident. This requires clear procedures for various incident types and designated personnel for executing them, such as initiating password resets or removing malware. Organisations should ensure that users are informed about reporting procedures, considering potential communication challenges in the event of device compromise.
Conclusion
The rise of deepfakes has brought forward the need for a collaborative approach. Policymakers, technology companies, and the public must work together to address the challenges posed by deepfakes. This collaboration is crucial for making better detection technologies, establishing stronger laws, and raising awareness on media literacy.

Ecosystm research reveals a stark reality: 75% of technology leaders in Financial Services anticipate data breaches.
Given the sector’s regulatory environment, data breaches carry substantial financial implications, emphasising the critical importance of giving precedence to cybersecurity. This is compelling a fresh cyber strategy focused on early threat detection and reduction of attack impact.
Read on to find out how tech leaders are building a culture of cyber-resilience, re-evaluating their cyber policies, and adopting technologies that keep them one step ahead of their adversaries.
Download ‘Cyber-Resilience in Finance: People, Policy & Technology’ as a PDF

There are two types of organisations – those that know that they have had a cybersecurity breach and those that don’t. With ransomware accounting for a rapidly growing proportion of breaches, not knowing you have been breached is less likely. In the last two months, we have seen a series of devastating ransomware attacks. These have included attacks on critical infrastructure, Colonial Pipeline and JBS, and the more recent supply chain attack on Kaseya, infecting its customers’ customers with ransomware. We’ve also seen an increase in attacks on soft targets such as schools and hospitals.
What is ransomware? Well, it’s a type of malware that specialises in encrypting the victim’s data and demands a ransom for a decryption key which may or may not work. If the victim fails to pay, their data could be sold or published online. More worryingly, if the victim pays, their data could still be sold or published online, prolonging the agony. Common ransomware families include REvil, Locky, Wannacry, Cerber, NotPetya, Maze and Darkside.
Why is Ransomware Becoming more Widespread?
Increased digitisation, remote working, accelerated adoption of cloud computing and growth in IoT devices, have expanded the attack surface for threat actors – offering more vulnerabilities that can be exploited. Launching a ransomware attack is a relatively easy and low-risk way to make money for cyber-criminals. Threat actors are usually outside the jurisdiction where the attack takes place and are typically protected by the absence of extradition treaties between the country where the crime occurred and the country from where the attack was launched. As well as posing a remarkably low risk to the attacker the rewards from a successful ransomware attack are potentially very large. Ransomware as a service (RaaS) kits can be purchased on the dark web for a few hundred dollars and if used repeatedly are likely to find at least one victim. Cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin make it virtually impossible for law enforcement authorities to track ransom payments. Consequently, the rapid growth in ransoms combined with the increasing risk of successful ransomware attacks is leading to banks stocking up on bitcoin. This allows their customers to quickly pay ransoms.

How to Mitigate the Risks?
Companies will not be able to completely eliminate the risk of ransomware attacks. They can, however, mitigate the risk of these attacks with a zero-trust approach to cybersecurity, renewed focus on training and awareness programs, and well-prepared and rehearsed incident response plans.
Rigorously applying the principle of least privilege will make it harder for threat actors to gain the credentials that they need to move laterally within systems and networks. Segmenting networks and isolating workloads will limit the blast radius of attacks. Training and awareness campaigns will make employees less likely to download malware via phishing attacks or other social engineering activities. Ensuring that all sensitive data is classified and encrypted will make double extortion more difficult – a miserable scenario where the victim pays a ransom for a decryption key and is then asked to pay a further ransom for the dubious promise that stolen data will not be leaked.
Protecting against supply chain ransomware attacks, such as the Kaseya breach, is fiendishly difficult. In the case of Kaseya, attackers identified a zero-day vulnerability in its VSA IT management and monitoring tool. An update was then infected with ransomware and shared with managed service providers, who, in turn infected their customers with the ransomware.
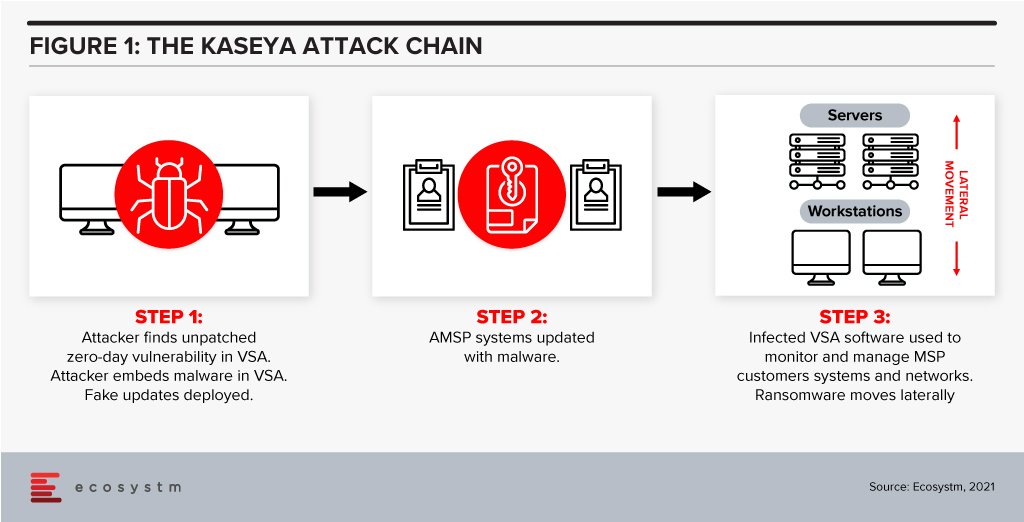
Rehearsed incident response plans that prepare for a successful ransomware attack are essential controls against such threats. A critical component of such a plan is backup and recovery. Backups are increasingly being targeted in well-orchestrated attacks so companies must find ways of ensuring that their data is stored in at least one immutable destination. This means that they can recover quickly – often almost instantly if the process is automated.
If companies follow cybersecurity best practices such as those outlined above, they should be able to manage ransomware risk and the misery associated with these attacks. If a ransomware attack occurs, well-prepared companies will be able to recover rapidly and be comfortable in the knowledge that the data which has been stolen is of little or no value to the attackers.

Ecosystm recently partnered with Asavie to conduct a study on the opportunity and outlook for the “Branch of One“. The results of the study make us question whether organisations’ mobile security strategies are appropriate for the evolving business priorities, the ever-changing threat landscape, and a seamless employee experience.
To answer this question, organisations will need to examine their security frameworks.
COVID-19 has forced organisations to realise that cybersecurity is not only a business enabler – it is a business prerequisite. Our research shows that businesses world-wide no longer see the pandemic as something that we need to get through to get back to “business as usual”. Most acknowledge that remote working and access from anywhere will be the new normal for many employees and that means they need to revisit and reprioritise their spending and their focus.
In many cases, existing procedures and policies are not sufficient to cover this new working environment – and often the policies have not been clearly communicated to all employees. Moreover, many organisations still rely on legacy WAN technologies that make secure and flexible access difficult – something that my colleague, Tim Sheedy touched upon in his recent blog post.
The choice of WAN technology is an important part of any mobile security strategy, but so is the approach to securing endpoints on the WAN and – what is perhaps the weakest link – the behaviour of employees.
The Global CxO Study 2020: The Future of Secure Office Anywhere showed us that when it came to mobile security, organisations were mostly worried about phishing and malware – but 4 out of the top 5 mobile security concerns involved human error and failure to follow corporate IT security policies and guidelines (Figure 1).

Time to Evaluate New Mobile Security Features
This highlights the importance of a couple of “security features” that many IT organisations still tend to overlook – convenience and ease-of-use. When employees ignore IT policies, bypass security steps, use unsanctioned personal devices to process work data etc., they tend to do so for mainly one reason: because it is convenient for them. Employees just want to get the work done and following security protocols, making sure that devices have the right security software installed etc. is simply seen as too cumbersome or as slowing down the work process.
To counter this, ease-of-use and convenience need to an integral part of any security framework – especially when employees are no longer working in the office. IT managers tend to be a bit ego-centric when they think of these terms, i.e. for them ease-of-use relates to their experience in implementing and running the systems, but they really need to be extending the ease to their users – the employees – as well.
This is where Branch of One comes to the fore. It offers the convenience of employees not having to install or connect software or hardware on the mobile device and it allows administrators to easily scale and manage their mobile security framework. Security frameworks do not have to be in the way of getting the work done. Branch of One shows us that comprehensive mobile security can be nearly seamless.
Download the report based on ‘The Global CxO Study 2020: The Future of the Secure Office Anywhere’, conducted by Ecosystm on behalf of Asavie. The report presents the key findings of the study and analyses the market perceptions of Office Anywhere and the need for a ‘Branch of One’, which will be the foundation of enterprise mobile security in the future.
















