Despite financial institutions’ unwavering efforts to safeguard their customers, scammers continually evolve to exploit advancements in technology. For example, the number of scams and cybercrimes reported to the police in Singapore increased by a staggering 49.6% to 50,376 at an estimated cost of USD 482M in 2023. GenAI represents the latest challenge to the industry, providing fraudsters with new avenues for deception.
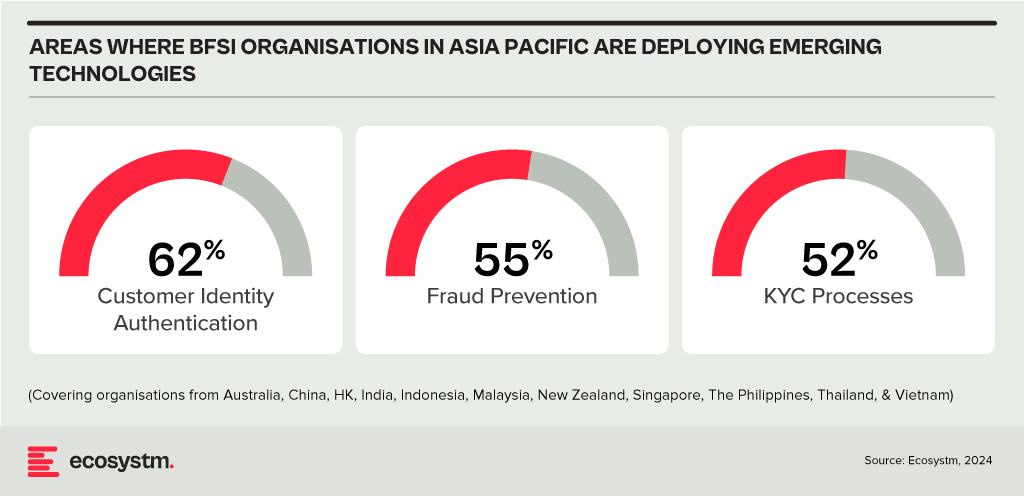
Ecosystm research shows that BFSI organisations in Asia Pacific are spending more on technologies to authenticate customer identity and prevent fraud, than they are in their Know Your Customer (KYC) processes.
The Evolution of the Threat Landscape in BFSI
Synthetic Identity Fraud. This involves the creation of fictitious identities by combining real and fake information, distinct from traditional identity theft where personal data is stolen. These synthetic identities are then exploited to open fraudulent accounts, obtain credit, or engage in financial crimes, often evading detection due to their lack of association with real individuals. The Deloitte Centre for Financial Services predicts that synthetic identity fraud will result in USD 23B in losses by 2030. Synthetic fraud is posing significant challenges for financial institutions and law enforcement agencies, especially with the emergence of advanced technologies like GenAI being used to produce realistic documents blending genuine and false information, undermining Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols.
AI-Enhanced Phishing. Ecosystm research reveals that in Asia Pacific, 71% of customer interactions in BFSI occur across multiple digital channels, including mobile apps, emails, messaging, web chats, and conversational AI. In fact, 57% of organisations plan to further improve customer self-service capabilities to meet the demand for flexible and convenient service delivery. The proliferation of digital channels brings with it an increased risk of phishing attacks.
While these organisations continue to educate their customers on how to secure their accounts in a digital world, GenAI poses an escalating threat here as well. Phishing schemes will employ widely available LLMs to generate convincing text and even images. For many potential victims, misspellings and strangely worded appeals are the only hint that an email from their bank is not what it seems. The maturing of deepfake technology will also make it possible for malicious agents to create personalised voice and video attacks.
Identity Fraud Detection and Prevention
Although fraudsters are exploiting every new vulnerability, financial organisations also have new tools to protect their customers. Organisations should build a layered defence to prevent increasingly sophisticated attempts at fraud.
- Behavioural analytics. Using machine learning, financial organisations can differentiate between standard activities and suspicious behaviour at the account level. Data that can be analysed includes purchase patterns, unusual transaction values, VPN use, browser choice, log-in times, and impossible travel. Anomalies can be flagged, and additional security measures initiated to stem the attack.
- Passive authentication. Accounts can be protected even before password or biometric authentication by analysing additional data, such as phone number and IP address. This approach can be enhanced by comparing databases populated with the details of suspicious actors.
- SIM swap detection. SMS-based MFA is vulnerable to SIM swap attacks where a customer’s phone number is transferred to the fraudster’s own device. This can be prevented by using an authenticator app rather than SMS. Alternatively, SIM swap history can be detected before sending one-time passwords (OTPs).
- Breached password detection. Although customers are strongly discouraged to reuse passwords across sites, some inevitably will. By employing a service that maintains a database of credentials leaked during third-party breaches, it is possible to compare with active customer passwords and initiate a reset.
- Stronger biometrics. Phone-based fingerprint recognition has helped financial organisations safeguard against fraud and simplify the authentication experience. Advances in biometrics continue with recognition for faces, retina, iris, palm print, and voice making multimodal biometric protection possible. Liveness detection will grow in importance to combat against AI-generated content.
- Step-up validation. Authentication requirements can be differentiated according to risk level. Lower risk activities, such as balance check or internal transfer, may only require minimal authentication while higher risk ones, like international or cryptocurrency transactions may require a step up in validation. When anomalous behaviour is detected, even greater levels of security can be initiated.
Recommendations
- Reduce friction. While it may be tempting to implement heavy handed approaches to prevent fraud, it is also important to minimise friction in the authentication system. Frustrated users may abandon services or find risky ways to circumvent security. An effective layered defence should act in the background to prevent attackers getting close.
- AI Phishing Awareness. Even the savviest of customers could fall prey to advanced phishing attacks that are using GenAI. Social engineering at scale becomes increasingly more possible with each advance in AI. Monitor emerging global phishing activities and remind customers to be ever vigilant of more polished and personalised phishing attempts.
- Deploy an authenticator app. Consider shifting away from OTP SMS as an MFA method and implement either an authenticator app or one embedded in the financial app instead.
- Integrate authentication with fraud analytics. Select an authentication provider that can integrate its offering with analytics to identify fraud or unusual behaviour during account creation, log in, and transactions. The two systems should work in tandem.
- Take a zero-trust approach. Protecting both customers and employees is critical, particularly in the hybrid work era. Implement zero trust tools to prevent employees from falling victim to malicious attacks and minimising damage if they do.

Over the past year, many organisations have explored Generative AI and LLMs, with some successfully identifying, piloting, and integrating suitable use cases. As business leaders push tech teams to implement additional use cases, the repercussions on their roles will become more pronounced. Embracing GenAI will require a mindset reorientation, and tech leaders will see substantial impact across various ‘traditional’ domains.
AIOps and GenAI Synergy: Shaping the Future of IT Operations
When discussing AIOps adoption, there are commonly two responses: “Show me what you’ve got” or “We already have a team of Data Scientists building models”. The former usually demonstrates executive sponsorship without a specific business case, resulting in a lukewarm response to many pre-built AIOps solutions due to their lack of a defined business problem. On the other hand, organisations with dedicated Data Scientist teams face a different challenge. While these teams can create impressive models, they often face pushback from the business as the solutions may not often address operational or business needs. The challenge arises from Data Scientists’ limited understanding of the data, hindering the development of use cases that effectively align with business needs.
The most effective approach lies in adopting an AIOps Framework. Incorporating GenAI into AIOps frameworks can enhance their effectiveness, enabling improved automation, intelligent decision-making, and streamlined operational processes within IT operations.
This allows active business involvement in defining and validating use-cases, while enabling Data Scientists to focus on model building. It bridges the gap between technical expertise and business requirements, ensuring AIOps initiatives are influenced by the capabilities of GenAI, address specific operational challenges and resonate with the organisation’s goals.
The Next Frontier of IT Infrastructure
Many companies adopting GenAI are openly evaluating public cloud-based solutions like ChatGPT or Microsoft Copilot against on-premises alternatives, grappling with the trade-offs between scalability and convenience versus control and data security.
Cloud-based GenAI offers easy access to computing resources without substantial upfront investments. However, companies face challenges in relinquishing control over training data, potentially leading to inaccurate results or “AI hallucinations,” and concerns about exposing confidential data. On-premises GenAI solutions provide greater control, customisation, and enhanced data security, ensuring data privacy, but require significant hardware investments due to unexpectedly high GPU demands during both the training and inferencing stages of AI models.
Hardware companies are focusing on innovating and enhancing their offerings to meet the increasing demands of GenAI. The evolution and availability of powerful and scalable GPU-centric hardware solutions are essential for organisations to effectively adopt on-premises deployments, enabling them to access the necessary computational resources to fully unleash the potential of GenAI. Collaboration between hardware development and AI innovation is crucial for maximising the benefits of GenAI and ensuring that the hardware infrastructure can adequately support the computational demands required for widespread adoption across diverse industries. Innovations in hardware architecture, such as neuromorphic computing and quantum computing, hold promise in addressing the complex computing requirements of advanced AI models.
The synchronisation between hardware innovation and GenAI demands will require technology leaders to re-skill themselves on what they have done for years – infrastructure management.
The Rise of Event-Driven Designs in IT Architecture
IT leaders traditionally relied on three-tier architectures – presentation for user interface, application for logic and processing, and data for storage. Despite their structured approach, these architectures often lacked scalability and real-time responsiveness. The advent of microservices, containerisation, and serverless computing facilitated event-driven designs, enabling dynamic responses to real-time events, and enhancing agility and scalability. Event-driven designs, are a paradigm shift away from traditional approaches, decoupling components and using events as a central communication mechanism. User actions, system notifications, or data updates trigger actions across distributed services, adding flexibility to the system.
However, adopting event-driven designs presents challenges, particularly in higher transaction-driven workloads where the speed of serverless function calls can significantly impact architectural design. While serverless computing offers scalability and flexibility, the latency introduced by initiating and executing serverless functions may pose challenges for systems that demand rapid, real-time responses. Increasing reliance on event-driven architectures underscores the need for advancements in hardware and compute power. Transitioning from legacy architectures can also be complex and may require a phased approach, with cultural shifts demanding adjustments and comprehensive training initiatives.
The shift to event-driven designs challenges IT Architects, whose traditional roles involved designing, planning, and overseeing complex systems. With Gen AI and automation enhancing design tasks, Architects will need to transition to more strategic and visionary roles. Gen AI showcases capabilities in pattern recognition, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making, promoting a symbiotic relationship with human expertise. This evolution doesn’t replace Architects but signifies a shift toward collaboration with AI-driven insights.
IT Architects need to evolve their skill set, blending technical expertise with strategic thinking and collaboration. This changing role will drive innovation, creating resilient, scalable, and responsive systems to meet the dynamic demands of the digital age.
Whether your organisation is evaluating or implementing GenAI, the need to upskill your tech team remains imperative. The evolution of AI technologies has disrupted the tech industry, impacting people in tech. Now is the opportune moment to acquire new skills and adapt tech roles to leverage the potential of GenAI rather than being disrupted by it.

As tech providers such as Microsoft enhance their capabilities and products, they will impact business processes and technology skills, and influence other tech providers to reshape their product and service offerings. Microsoft recently organised briefing sessions in Sydney and Singapore, to present their future roadmap, with a focus on their AI capabilities.

Ecosystm Advisors Achim Granzen, Peter Carr, and Tim Sheedy provide insights on Microsoft’s recent announcements and messaging.

Click here to download Ecosystm VendorSphere: Microsoft’s AI Vision – Initiatives & Impact
Ecosystm Question: What are your thoughts on Microsoft Copilot?
Tim Sheedy. The future of GenAI will not be about single LLMs getting bigger and better – it will be about the use of multiple large and small language models working together to solve specific challenges. It is wasteful to use a large and complex LLM to solve a problem that is simpler. Getting these models to work together will be key to solving industry and use case specific business and customer challenges in the future. Microsoft is already doing this with Microsoft 365 Copilot.
Achim Granzen. Microsoft’s Copilot – a shrink-wrapped GenAI tool based on OpenAI – has become a mainstream product. Microsoft has made it available to their enterprise clients in multiple ways: for personal productivity in Microsoft 365, for enterprise applications in Dynamics 365, for developers in Github and Copilot Studio, and to partners to integrate Copilot into their applications suites (E.g. Amdocs’ Customer Engagement Platform).
Ecosystm Question: How, in your opinion, is the Microsoft Copilot a game changer?
Microsoft’s Customer Copyright Commitment, initially launched as Copilot Copyright Commitment, is the true game changer.
Achim Granzen. It safeguards Copilot users from potential copyright infringement lawsuits related to data used for algorithm training or output results. In November 2023, Microsoft expanded its scope to cover commercial usage of their OpenAI interface as well.
This move not only protects commercial clients using Microsoft’s GenAI products but also extends to any GenAI solutions built by their clients. This initiative significantly reduces a key risk associated with GenAI adoption, outlined in the product terms and conditions.
However, compliance with a set of Required Mitigations and Codes of Conduct is necessary for clients to benefit from this commitment, aligning with responsible AI guidelines and best practices.
Ecosystm Question: Where will organisations need most help on their AI journeys?
Peter Carr. Unfortunately, there is no playbook for AI.
- The path to integrating AI into business strategies and operations lacks a one-size-fits-all guide. Organisations will have to navigate uncharted territories for the time being. This means experimenting with AI applications and learning from successes and failures. This exploratory approach is crucial for leveraging AI’s potential while adapting to unique organisational challenges and opportunities. So, companies that are better at agile innovation will do better in the short term.
- The effectiveness of AI is deeply tied to the availability and quality of connected data. AI systems require extensive datasets to learn and make informed decisions. Ensuring data is accessible, clean, and integrated is fundamental for AI to accurately analyse trends, predict outcomes, and drive intelligent automation across various applications.
Ecosystm Question: What advice would you give organisations adopting AI?
Tim Sheedy. It is all about opportunities and responsibility.
- There is a strong need for responsible AI – at a global level, at a country level, at an industry level and at an organisational level. Microsoft (and other AI leaders) are helping to create responsible AI systems that are fair, reliable, safe, private, secure, and inclusive. There is still a long way to go, but these capabilities do not completely indemnify users of AI. They still have a responsibility to set guardrails in their own businesses about the use and opportunities for AI.
- AI and hybrid work are often discussed as different trends in the market, with different solution sets. But in reality, they are deeply linked. AI can help enhance and improve hybrid work in businesses – and is a great opportunity to demonstrate the value of AI and tools such as Copilot.
Ecosystm Question: What should Microsoft focus on?
Tim Sheedy. Microsoft faces a challenge in educating the market about adopting AI, especially Copilot. They need to educate business, IT, and AI users on embracing AI effectively. Additionally, they must educate existing partners and find new AI partners to drive change in their client base. Success in the race for knowledge workers requires not only being first but also helping users maximise solutions. Customers have limited visibility of Copilot’s capabilities, today. Improving customer upskilling and enhancing tools to prompt users to leverage capabilities will contribute to Microsoft’s (or their competitors’) success in dominating the AI tool market.
Peter Carr. Grassroots businesses form the economic foundation of the Asia Pacific economies. Typically, these businesses do not engage with global SIs (GSIs), which drive Microsoft’s new service offerings. This leads to an adoption gap in the sector that could benefit most from operational efficiencies. To bridge this gap, Microsoft must empower non-GSI partners and managed service providers (MSPs) at the local and regional levels. They won’t achieve their goal of democratising AI, unless they do. Microsoft has the potential to advance AI technology while ensuring fair and widespread adoption.

I have spent many years analysing the mobile and end-user computing markets. Going all the way back to 1995 where I was part of a Desktop PC research team, to running the European wireless and mobile comms practice, to my time at 3 Mobile in Australia and many years after, helping clients with their end-user computing strategies. From the birth of mobile data services (GPRS, WAP, and so on to 3G, 4G and 5G), from simple phones to powerful foldable devices, from desktop computers to a complex array of mobile computing devices to meet the many and varied employee needs. I am always looking for the “next big thing” – and there have been some significant milestones – Palm devices, Blackberries, the iPhone, Android, foldables, wearables, smaller, thinner, faster, more powerful laptops.
But over the past few years, innovation in this space has tailed off. Outside of the foldable space (which is already four years old), the major benefits of new devices are faster processors, brighter screens, and better cameras. I review a lot of great computers too (like many of the recent Surface devices) – and while they are continuously improving, not much has got my clients or me “excited” over the past few years (outside of some of the very cool accessibility initiatives).
The Force of AI
But this is all about to change. Devices are going to get smarter based on their data ecosystem, the cloud, and AI-specific local processing power. To be honest, this has been happening for some time – but most of the “magic” has been invisible to us. It happened when cameras took multiple shots and selected the best one; it happened when pixels were sharpened and images got brighter, better, and more attractive; it happened when digital assistants were called upon to answer questions and provide context.
Microsoft, among others, are about to make AI smarts more front and centre of the experience – Windows Copilot will add a smart assistant that can not only advise but execute on advice. It will help employees improve their focus and productivity, summarise documents and long chat threads, select music, distribute content to the right audience, and find connections. Added to Microsoft 365 Copilot it will help knowledge workers spend less time searching and reading – and more time doing and improving.
The greater integration of public and personal data with “intent insights” will also play out on our mobile devices. We are likely to see the emergence of the much-promised “integrated app”– one that can take on many of the tasks that we currently undertake across multiple applications, mobile websites, and sometimes even multiple devices. This will initially be through the use of public LLMs like Bard and ChatGPT, but as more custom, private models emerge they will serve very specific functions.
Focused AI Chips will Drive New Device Wars
In parallel to these developments, we expect the emergence of very specific AI processors that are paired to very specific AI capabilities. As local processing power becomes a necessity for some AI algorithms, the broad CPUs – and even the AI-focused ones (like Google’s Tensor Processor) – will need to be complemented by specific chips that serve specific AI functions. These chips will perform the processing more efficiently – preserving the battery and improving the user experience.
While this will be a longer-term trend, it is likely to significantly change the game for what can be achieved locally on a device – enabling capabilities that are not in the realm of imagination today. They will also spur a new wave of device competition and innovation – with a greater desire to be on the “latest and greatest” devices than we see today!
So, while the levels of device innovation have flattened, AI-driven software and chipset innovation will see current and future devices enable new levels of employee productivity and consumer capability. The focus in 2023 and beyond needs to be less on the hardware announcements and more on the platforms and tools. End-user computing strategies need to be refreshed with a new perspective around intent and intelligence. The persona-based strategies of the past have to be changed in a world where form factors and processing power are less relevant than outcomes and insights.

It is not hyperbole to state that AI is on the cusp of having significant implications on society, business, economies, governments, individuals, cultures, politics, the arts, manufacturing, customer experience… I think you get the idea! We cannot understate the impact that AI will have on society. In times gone by, businesses tested ideas, new products, or services with small customer segments before they went live. But with AI we are all part of this experiment on the impacts of AI on society – its benefits, use cases, weaknesses, and threats.
What seemed preposterous just six months ago is not only possible but EASY! Do you want a virtual version of yourself, a friend, your CEO, or your deceased family member? Sure – just feed the data. Will succession planning be more about recording all conversations and interactions with an executive so their avatar can make the decisions when they leave? Why not? How about you turn the thousands of hours of recorded customer conversations with your contact centre team into a virtual contact centre team? Your head of product can present in multiple countries in multiple languages, tailored to the customer segments, industries, geographies, or business needs at the same moment.
AI has the potential to create digital clones of your employees, it can spread fake news as easily as real news, it can be used for deception as easily as for benefit. Is your organisation prepared for the social, personal, cultural, and emotional impacts of AI? Do you know how AI will evolve in your organisation?
When we focus on the future of AI, we often interview AI leaders, business leaders, futurists, and analysts. I haven’t seen enough focus on psychologists, sociologists, historians, academics, counselors, or even regulators! The Internet and social media changed the world more than we ever imagined – at this stage, it looks like these two were just a rehearsal for the real show – Artificial Intelligence.
Lack of Government or Industry Regulation Means You Need to Self-Regulate
These rapid developments – and the notable silence from governments, lawmakers, and regulators – make the requirement for an AI Ethics Policy for your organisation urgent! Even if you have one, it probably needs updating, as the scenarios that AI can operate within are growing and changing literally every day.
- For example, your customer service team might want to create a virtual customer service agent from a real person. What is the policy on this? How will it impact the person?
- Your marketing team might be using ChatGPT or Bard for content creation. Do you have a policy specifically for the creation and use of content using assets your business does not own?
- What data is acceptable to be ingested by a public Large Language Model (LLM). Are are you governing data at creation and publishing to ensure these policies are met?
- With the impending public launch of Microsoft’s Co-Pilot AI service, what data can be ingested by Co-Pilot? How are you governing the distribution of the insights that come out of that capability?
If policies are not put in place, data tagged, staff trained, before using a tool such as Co-Pilot, your business will be likely to break some privacy or employment laws – on the very first day!
What do the LLMs Say About AI Ethics Policies?
So where do you go when looking for an AI Ethics policy? ChatGPT and Bard of course! I asked the two for a modern AI Ethics policy.
You can read what they generated in the graphic below.
I personally prefer the ChatGPT4 version as it is more prescriptive. At the same time, I would argue that MOST of the AI tools that your business has access to today don’t meet all of these principles. And while they are tools and the ethics should dictate the way the tools are used, with AI you cannot always separate the process and outcome from the tool.
For example, a tool that is inherently designed to learn an employee’s character, style, or mannerisms cannot be unbiased if it is based on a biased opinion (and humans have biases!).
LLMs take data, content, and insights created by others, and give it to their customers to reuse. Are you happy with your website being used as a tool to train a startup on the opportunities in the markets and customers you serve?
By making content public, you acknowledge the risk of others using it. But at least they visited your website or app to consume it. Not anymore…
A Policy is Useless if it Sits on a Shelf
Your AI ethics policy needs to be more than a published document. It should be the beginning of a conversation across the entire organisation about the use of AI. Your employees need to be trained in the policy. It needs to be part of the culture of the business – particularly as low and no-code capabilities push these AI tools, practices, and capabilities into the hands of many of your employees.
Nearly every business leader I interview mentions that their organisation is an “intelligent, data-led, business.” What is the role of AI in driving this intelligent business? If being data-driven and analytical is in the DNA of your organisation, soon AI will also be at the heart of your business. You might think you can delay your investments to get it right – but your competitors may be ahead of you.
So, as you jump head-first into the AI pool, start to create, improve and/or socialise your AI Ethics Policy. It should guide your investments, protect your brand, empower your employees, and keep your business resilient and compliant with legacy and new legislation and regulations.




















