The tech industry is experiencing a strategic convergence of AI, data management, and cybersecurity, driving a surge in major M&A activity. As enterprises tackle digital transformation, these three pillars are at the forefront, accelerating the race to acquire and integrate critical technologies.
Here are this year’s key consolidation moves, showcasing how leading tech companies are positioning themselves to capitalise on the rising demand for AI-driven solutions, robust data infrastructure, and enhanced cybersecurity.
AI Convergence: Architecting the Intelligent Enterprise
From customer service to supply chain management, AI is being deployed across the entire enterprise value chain. This widespread demand for AI solutions is creating a dynamic M&A market, with tech companies acquiring specialised AI capabilities.
IBM’s AI Power Play
IBM’s acquisitions of HashiCorp and DataStax mark a decisive step in its push to lead enterprise AI and hybrid cloud. The USD 6.4B HashiCorp deal that got finalised this year, brings Terraform, a top-tier infrastructure-as-code tool that streamlines multi-cloud deployments – key to integrating IBM’s Red Hat OpenShift and Watsonx AI. Embedding Terraform enhances automation, making hybrid cloud infrastructure more efficient and AI-ready.
The DataStax acquisition strengthens IBM’s AI data strategy. With AstraDB and Apache Cassandra, IBM gains scalable NoSQL solutions for AI workloads, while Langflow simplifies AI app development. Together, these moves position IBM as an end-to-end AI and cloud powerhouse, offering enterprises seamless automation, data management, and AI deployment at scale.
MongoDB’s RAG Focus
MongoDB’s USD 220M acquisition of Voyage AI signals a strategic push toward enhancing AI reliability. At the core of this move is retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), a technology that curbs AI hallucinations by grounding responses in accurate, relevant data.
By integrating Voyage AI into its Atlas cloud database, MongoDB is making AI applications more trustworthy and reducing the complexity of RAG implementations. Enterprises can now build AI-driven solutions directly within their database, streamlining development while improving accuracy. This move consolidates MongoDB’s role as a key player in enterprise AI, offering both scalable data management and built-in AI reliability.
Google’s 1B Bet on Anthropic
Google’s continued investment in Anthropic reinforces its commitment to foundation model innovation and the evolving GenAI landscape. More than a financial move, this signals Google’s intent to shape the future of AI by backing one of the field’s most promising players.
This investment aligns with a growing trend among cloud giants securing stakes in foundation model developers to drive AI advancements. By deepening ties with Anthropic, Google not only gains access to cutting-edge AI research but also strengthens its position in developing safe, scalable, and enterprise-ready AI. This solidifies Google’s long-term AI strategy, ensuring its leadership in GenAI while seamlessly integrating these capabilities into its cloud ecosystem.
ServiceNow’s AI Automation Expansion
ServiceNow’s USD 2.9B acquisition of Moveworks completed this year, marking a decisive push into AI-driven service desk automation. This goes beyond feature expansion – it redefines enterprise support operations by embedding intelligent automation into workflows, reducing resolution times, and enhancing employee productivity.
The acquisition reflects a growing shift: AI-powered service management is no longer optional but essential. Moveworks’ AI-driven capabilities – natural language understanding, machine learning, and automated issue resolution – will enable ServiceNow to deliver a smarter, more proactive support experience. Additionally, gaining Moveworks’ customer base strengthens ServiceNow’s market reach.
Data Acquisition Surge: Fuelling Digital Transformation
Data has transcended its role as a byproduct of operations, becoming the lifeblood that fuels digital transformation. This fundamental shift has triggered a surge in strategic acquisitions focused on enhancing data management and storage capabilities.
Lenovo Scaling Enterprise Storage
Lenovo’s USD 2B acquisition of Infinidat strengthens its position in enterprise storage as data demands surge. Infinidat’s AI-driven InfiniBox delivers high-performance, low-latency storage for AI, analytics, and HPC, while InfiniGuard ensures advanced data protection.
By integrating these technologies, Lenovo expands its hybrid cloud offerings, challenging Dell and NetApp while reinforcing its vision as a full-stack data infrastructure provider.
Databricks Streamlining Data Warehouse Migrations
Databricks’ USD 15B acquisition of BladeBridge accelerates data warehouse migrations with AI-driven automation, reducing manual effort and errors in migrating legacy platforms like Snowflake and Teradata. BladeBridge’s technology enhances Databricks’ SQL platform, simplifying the transition to modern data ecosystems.
This strengthens Databricks’ Data Intelligence Platform, boosting its appeal by enabling faster, more efficient enterprise data consolidation and supporting rapid adoption of data-driven initiatives.
Cybersecurity Consolidation: Fortifying the Digital Fortress
The escalating sophistication of cyber threats has transformed cybersecurity from a reactive measure to a strategic imperative. This has fuelled a surge in M&A aimed at building comprehensive and integrated security solutions.
Turn/River Capital’s Security Acquisition
Turn/River Capital’s USD 4.4 billion acquisition of SolarWinds underscores the enduring demand for robust IT service management and security software. This acquisition is a testament to the essential role SolarWinds plays in enterprise IT infrastructure, even in the face of past security breaches.
This is a bold investment, in the face of prior vulnerability and highlights a fundamental truth: the need for reliable security solutions outweighs even the most public of past failings. Investors are willing to make long term bets on companies that provide core security services.
Sophos Expanding Managed Detection & Response Capabilities
Sophos completed the acquisition of Secureworks for USD 859M significantly strengthens its managed detection and response (MDR) capabilities, positioning Sophos as a major player in the MDR market. This consolidation reflects the growing demand for comprehensive cybersecurity solutions that offer proactive threat detection and rapid incident response.
By integrating Secureworks’ XDR products, Sophos enhances its ability to provide end-to-end protection for its customers, addressing the evolving threat landscape with advanced security technologies.
Cisco’s Security Portfolio Expansion
Cisco completed the USD 28B acquisition of SnapAttack further expanding its security business, building upon its previous acquisition of Splunk. This move signifies Cisco’s commitment to creating a comprehensive security portfolio that can address the diverse needs of its enterprise customers.
By integrating SnapAttack’s threat detection capabilities, Cisco strengthens its ability to provide proactive threat intelligence and incident response, solidifying its position as a leading provider of security solutions.
Google’s Cloud Security Reinforcement
Google’s strategic acquisition of Wiz, a leading cloud security company, for USD 32B demonstrates its commitment to securing cloud-native environments. Wiz’s expertise in proactive threat detection and remediation will significantly enhance Google Cloud’s security offerings. This move is particularly crucial as organisations increasingly migrate their workloads to the cloud.
By integrating Wiz’s capabilities, Google aims to provide its customers with a robust security framework that can protect their cloud-based assets from sophisticated cyber threats. This acquisition positions Google as a stronger competitor in the cloud security market, reinforcing its commitment to enterprise-grade cybersecurity.
The Way Ahead
The M&A trends of 2025 underscore the critical role of AI, data, and security in shaping the technology landscape. Companies that prioritise these core areas will be best positioned for long-term success. Strategic acquisitions, when executed with foresight and agility, will serve as essential catalysts for navigating the complexities of the evolving digital world.

As AI adoption continues to surge, the tech infrastructure market is undergoing a significant transformation. Traditional IT infrastructure providers are facing increasing pressure to innovate and adapt to the evolving demands of AI-powered applications. This shift is driving the development of new technologies and solutions that can support the intensive computational requirements and data-intensive nature of AI workloads.
At Lenovo’s recently held Asia Pacific summit in Shanghai they detailed their ‘AI for All’ strategy as they prepare for the next computing era. Building on their history as a major force in the hardware market, new AI-ready offerings will be prominent in their enhanced portfolio.
At the same time, Lenovo is adding software and services, both homegrown and with partners, to leverage their already well-established relationships with client IT teams. Sustainability is also a crucial message as it seeks to address the need for power efficiency and zero waste lifecycle management in their products.
Ecosystm Advisor Darian Bird comment on Lenovo’s recent announcements and messaging.
Click here to download Lenovo’s Innovation Roadmap: Takeaways from the APAC Analyst Summit as a PDF
1. Lenovo’s AI Strategy
Lenovo’s AI strategy focuses on launching AI PCs that leverage their computing legacy.
As the adoption of GenAI increases, there’s a growing need for edge processing to enhance privacy and performance. Lenovo, along with Microsoft, is introducing AI PCs with specialised components like CPUs, GPUs, and AI accelerators (NPUs) optimised for AI workloads.
Energy efficiency is vital for AI applications, opening doors for mobile-chip makers like Qualcomm. Lenovo’s latest ThinkPads, featuring Qualcomm’s Snapdragon X Elite processors, support Microsoft’s Copilot+ features while maximising battery life during AI tasks.
Lenovo is also investing in small language models (SLMs) that run directly on laptops, offering GenAI capabilities with lower resource demands. This allows users to interact with PCs using natural language for tasks like file searches, tech support, and personal management.
2. Lenovo’s Computer Vision Solutions
Lenovo stands out as one of the few computing hardware vendors that manufactures its own systems.
Leveraging precision engineering, Lenovo has developed solutions to automate production lines. By embedding computer vision in processes like quality inspection, equipment monitoring, and safety supervision, Lenovo customises ML algorithms using customer-specific data. Clients like McLaren Automotive use this technology to detect flaws beyond human capability, enhancing product quality and speeding up production.
Lenovo extends their computer vision expertise to retail, partnering with Sensormatic and Everseen to digitise branch operations. By analysing camera feeds, Lenovo’s solutions optimise merchandising, staffing, and design, while their checkout monitoring system detects theft and scanning errors in real-time. Australian customers have seen significant reductions in retail shrinkage after implementation.
3. AI in Action: Autonomous Robots
Like other hardware companies, Lenovo is experimenting with new devices to futureproof their portfolio.
Earlier this year, Lenovo unveiled the Daystar Bot GS, a six-legged robotic dog and an upgrade from their previous wheeled model. Resembling Boston Dynamics’ Spot but with added legs inspired by insects for enhanced stability, the bot is designed for challenging environments. Lenovo is positioning it as an automated monitoring assistant for equipment inspection and surveillance, reducing the need for additional staff. Power stations in China are already using the robot to read meters, detect temperature anomalies, and identify defective equipment.
Although it is likely to remain a niche product in the short term, the robot is an avenue for Lenovo to showcase their AI wares on a physical device, incorporating computer vision and self-guided movement.
Considerations for Lenovo’s Future Growth
Lenovo outlined an AI vision leveraging their expertise in end user computing, manufacturing, and retail. While the strategy aligns with Lenovo’s background, they should consider the following:
Hybrid AI. Initially, AI on PCs will address performance and privacy issues, but hybrid AI – integrating data across devices, clouds, and APIs – will eventually dominate.
Data Transparency & Control. The balance between convenience and privacy in AI is still unclear. Evolving transparency and control will be crucial as users adapt to new AI tools.
AI Ecosystem. AI’s value lies in data, applications, and integration, not just hardware. Hardware vendors must form deeper partnerships in these areas, as Lenovo’s focus on industry-specific solutions demonstrates.
Enhanced Experience. AI enhances operational efficiency and customer experience. Offloading level one support to AI not only cuts costs but also resolves issues faster than live agents.

The Manufacturing industry is at crossroads today. It faces challenges such as geopolitical risks, supply chain disruptions, changing regulatory environments, workforce shortages, and changing consumer demands. Overcoming these requires innovation, collaboration, and proactive adaptation.
Fortunately, many of these challenges can be mitigated by technology. The future of Manufacturing will be shaped by advanced technology, automation, and AI. We are seeing early evidence of how smart factories, robotics, and 3D printing are transforming production processes for increased efficiency and customisation.
Manufacturing is all set to become more agile, efficient, and sustainable.
Read on to find out the changing priorities and key trends in Manufacturing; about the World Economic Forum’s Global Lighthouse Network initiative; and where Ecosystm advisor Kaushik Ghatak sees as the Future of Manufacturing.
Click here to download ‘The Future of Manufacturing’ as a PDF

The Future of Work is here, now. Organisations were faced with unprecedented challenges of coping with the work-from-home model, when COVID-19 hit earlier this year. Many organisations managed the pivot very successfully, but all organisations were impacted in some way. Various trends have emerged over the last few months, that are likely to persist long after the immediate COVID-19 measures are removed by countries. In the Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal study, we find that organisations will continue to cater for remote employees (Figure 1) and keep a firm eye on employee experience (EX).
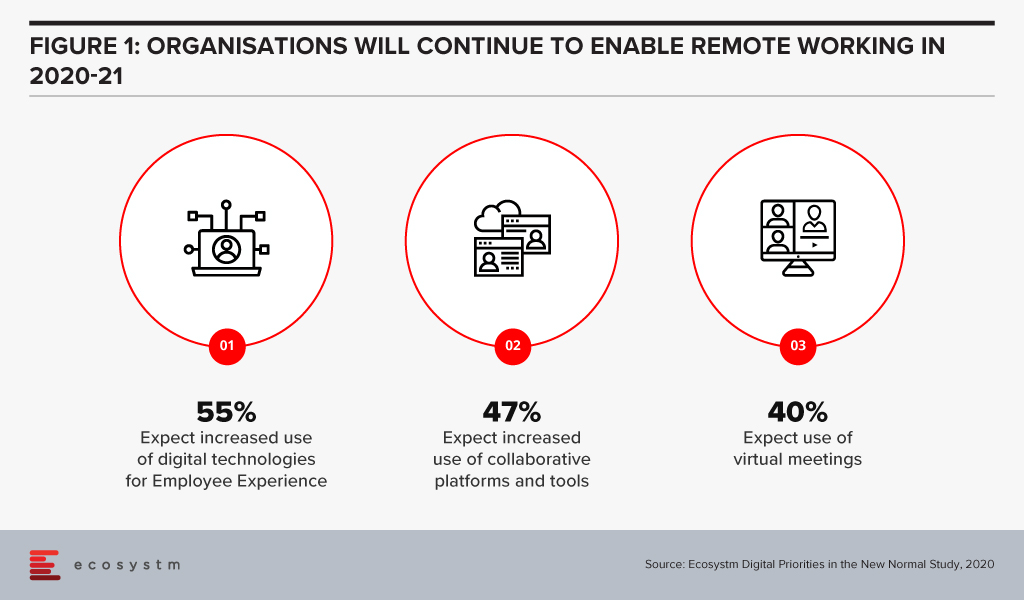
August has seen these clear trends in the Future of Work
#1 Tech companies leading from the front in embracing the Future of Work
As the pandemic continued to spread across the globe, various companies adopted the work from home model at a scale never seen before. While it is still unclear how the work model will look like, many companies continue to extend their remote working policies for the remaining year, and some are even thinking of making it a permanent move.
Tech companies appear to be the most proactive in extending remote working. Google, Microsoft, and AWS have all extended their work from home model till the end of the year or till the middle of next year. Earlier in the month Facebook extended its work from home program until mid-2021 and are also giving employees USD 1,000 to equip their home offices. This appears to be a long-term policy, with the company announcing in May that in the next 5-10 years, they expect 50% of their employees to be remote. Similarly, Salesforce and Uber also announced that they would be extending remote working till the mid-next year, and are providing funding for employees to set up the right work environment.
In Australia, Atlassian has made work from home a permanent option for their employees. They will continue to operate their physical offices but have given employees the option to choose where they want to work from.
Some organisations have gone beyond announcing these measures. Slack has talked about how they are evolving their corporate culture. For example, they have evolved their hiring policies and most new roles are open to remote candidates. Going forward, they are evaluating a more asynchronous work environment where employees can work the hours that make sense for them. In their communique, they are open about the fluid nature of the work environment and the challenges that employees and organisations might face as their shift their work models.
Organisations will have to evaluate multiple factors before coming up with the right model that suits their corporate culture and nature of work, but it appears that tech companies are showing the industry how it can be done.
#2 Tech companies evolve their capabilities to enable the Future of Work
Right from the start of the crisis, we have seen organisations make technology-led pivots. Technology providers are responding – and fast – to the changing environment and are evolving their capabilities to help their customers embrace the digital Future of Work.
Many of these responses have included strengthening their ecosystems and collaborating with other technology providers. Wipro and Intel announced a collaboration between Wipro’s LIVE Workspace digital workspace solution and the Intel vPro platform to enable remote IT support and solution. The solution provides enhanced protection and security against firmware-level attacks. Slack and Atlassian strengthened their alliance with app integrations and an account ‘passport’ in a joint go-to-market move, to reduce the time spent logging into separate services and products. This will enable both vendors to focus on their strengths in remote working tools and provide seamless services to their customers.
Tech companies have also announced product enhancements and new capabilities. CBTS has evolved their cloud-based unified communications, collaboration and networking solutions, with an AI-powered Secure Remote Collaboration solution, powered by Cisco Webex. With seamless integration of Cisco Webex software, Cisco Security software, and endpoints that combine high-definition cameras, microphones, and speakers, with automatic noise reduction, the solution now offers features such real-time transcription, closed captioning, and recording for post-meeting transcripts.
Communication and Collaboration tools have been in the limelight since the start of the crisis with providers such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams and Slack introducing new features throughout. In August Microsoft enhanced the capabilities of Teams and introduced a range of new features to the Teams Business Communications System. It now offers the option to host calls of up to 20,000 participants with a limit to 1,000 for interactive meetings, after which the call automatically shifts to a “view only” mode. With the possibility of remote working becoming a reality even after the crisis is over, Microsoft is looking to make Teams relevant for a range of meeting needs – from one-on-one meetings up to large events and conferences. In the near future, the solution will also allow organisations to add corporate branding, starting with branded meeting lobbies, followed by branded meeting experiences.
While many of these solutions are aimed at large enterprises, tech providers are also aware that they are now receiving a lot of business from small and medium enterprises (SMEs), struggling to make changes to their technology environment with limited resources. Juniper has expanded their WiFi 6 access points to include 4 new access points aimed at outdoor environments, SMEs, retail sites, K-12 schools, medical clinics and even the individual remote worker. While WiFi 6 is designed for high-density public or private environments, it is also designed for IoT deployments and in workplaces that use videoconferencing and other applications that require high bandwidth.
#3 The Future of Work is driving up hardware sales
Ecosystm research shows that at the start of the crisis, 76% of organisations increased investments in hardware – including PCs, devices, headsets, and conferencing units – and 67% of organisations expect their hardware spending to go up in 2020-21. Remote working remains a reality across enterprises. Despite the huge increase in demand, it became difficult for hardware providers to fulfil orders initially, with a disrupted supply chain, store closures and a rapid shift to eCommerce channels. This quarter has seen a steady rise in hardware sales, as providers overcome some of their initial challenges.
Apart from enterprise sales, there has been a surge in the consumer demand for PCs and devices. While remote working is a key contributor, online education and entertainment are mostly prompting homebound people to invest more in hardware. Even accessories such as joysticks are in short supply – a trend that seems to have been accelerated by the Microsoft Flight Simulator launch earlier this month.
The demand for both iPad and Mac saw double-digit growth in this quarter. Around half of the customers purchasing these devices were new to the product. Apple sees the rise in demand from remote workers and students. Lenovo reported a 31% increase in Q1 net profits with demand surges in China, Europe, the Middle East and Africa.
#4 The impact on Real Estate is beginning to show
The demand for prime real estate has been hit by remote working and organisations not renewing leases or downsizing – both because most employees are working remotely and because of operational cost optimisation during the crisis. This is going to have a longer-term impact on the market, as organisations re-evaluate their need for physical office space. Some organisations will reduce office space, and many will re-design their offices to cater to virtual interactions (Figure 1). While now, Ecosystm research shows that only 16% of enterprises are expecting a reduction of commercial space, this might well change over the months to come. Organisations might even feel the need to have multiple offices in suburbs to make it convenient for their hybrid workers to commute to work on the days they have to. Amazon is offering employees additional choices for smaller offices outside the city of Seattle.
But the Future of Work and the rise of a distributed workforce is beginning to show an initial impact on the real estate industry. Last week saw Pinterest cancel a large office lease at a building to be constructed near its headquarters in San Francisco. The company felt that it might not be the right time to go ahead with the deal, as they are re-evaluating where employees would like to work from in the future. Even the termination fees of USD 89.5 million did not discourage them. They will continue to maintain their existing work premises but do not see feel that it is the right time to make additional real estate investments, as they re-evaluate where employees would like to work from in the future.
There is a need for organisations to prepare themselves for the Future of Work – now! Ecosystm has launched a new 360o Future of Work practice, leveraging real-time market data from our platform combined with insights from our industry practitioners and experienced analysts, to guide organisations as they shift and define their new workplace strategies.























