Ecosystm and Bitstamp, conducted an invitation-only Executive ThinkTank at the Point Zero Forum in Zurich. A select group of regulators and senior leaders from financial institutions from across the globe came together to share their insights and experiences on Decentralised Finance (DeFi), innovations in the industry, and the outlook for the future.
Here are the 5 key takeaways from the ThinkTank.
- Regulators: Perception vs. Reality. Regulators are generally perceived as having a bias against innovations in the Financial Services industry. In reality, they want to encourage innovation, and the industry players welcome these regulations as guardrails against unscrupulous practices.
- Institutional Players’ Interest in DeFi. Many institutional players are interested in DeFi to enable the smooth running of processes and products and to reduce costs. It is being evaluated in areas such as lending, borrowing, and insurance.
- Evolving Traditional Regulations. In a DeFi world, participants and actors are connected by technology. Hence, setting the framework and imposing good practices when building projects will be critical. Regulations need to find the right balance between flexibility and rigidity.
- The Importance of a Digital Asset Listing Framework. There has been a long debate on who should be the gatekeeper of digital asset listings. From a regulator’s perspective, the liability of projects needs to shift from the consumer to the project and the gatekeeper.
- A Simplified Disclosure Document. Major players are willing to work with regulators to develop a simple disclosure document that describes the project for end-users or investors.
Read below to find out more.
Download Pathways for Aligning Innovation and Regulation in a DeFi World as a PDF

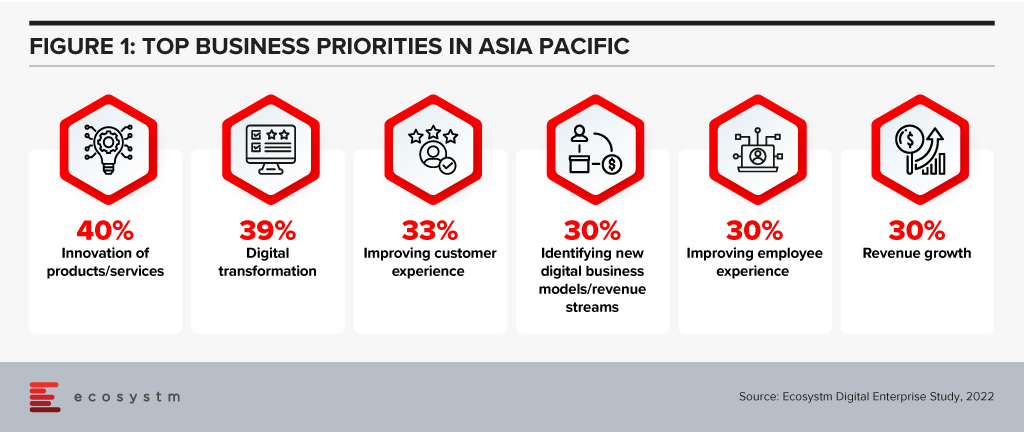
Life never gets any easier for the digital and information technology teams in organisations. The range and reach of the different technologies continue to open new opportunities for organisations that have the foresight and strategy to chase them. Improving offers for existing customers and reaching new segments depend on the organisation’s ability to innovate.
But the complexity of the digital ecosystem means this ability to innovate will be heavily constrained, causing improvements to take longer and cost more in many cases. Addressing the top business priorities expressed in the Ecosystm Digital Enterprise Study, 2022, will need tech teams to look to simplify as well as add features.
Complexity is Not Just an IT Issue
Many parts of an organisation have been making decisions on implementing new digital capabilities, particularly those involved in remote working. Frequently, the IT organisation has not been involved in the selection, implementation and use of these new facilities.
The number of start-up organisations delivering SaaS has continued to explode. A particular area has been the expansion of co-creation tools used by teams to deliver outcomes. In many cases, these have been introduced by enthusiastic users looking to improve their immediate working environment without the understanding of single-sign-on requirements, security and privacy of information or the importance of backup and business continuity planning.
SaaS tools such as Notion, monday.com and ClickUp (amongst many, many others), are being used to coordinate and manage teams across organisations of all sizes. While these are all cloud services, the support and maintenance of them ultimately will fall to the IT organisation. And they won’t be integrated at all with the tools the IT organisation uses to manage and improve user experience.
Every new component adds to the complexity of the tech environment – but with that complexity comes increased dependencies between components, which slows an organisation’s ability to adapt and evolve. This means each change needs more work to deliver, costs increase, and it takes longer to deliver value.
And this increasing complexity causes further problems with cybersecurity. Without regular attention, legacy systems will increase the attack surface of organisations, making it easier to compromise an organisation’s environment. At a recent executive forum with CISOs, attendees rated the risks caused by their legacy systems as their most significant concern.
An organisation’s leadership needs to both simplify and advance their organisation’s digital capabilities to remain competitive. This balance should not be left to the IT organisation to achieve as they will not be able to deliver both without wider support and recognition of the problems.
Discriminate on Differentiating Skills
One thing we can be sure of is that we won’t be able to employ all the skills we need for our future capabilities. We are not training enough people in the skills that we need now and for the future, and the range of technologies continues to expand, increasing the number of skills that we will need to keep an organisation running.
Most organisations are not removing or replacing ageing systems, preferring to keep them running at an apparently low cost. Often these legacy systems are fully depreciated, have low maintenance costs and have few changes made to them, as other areas of the organisation offer better investment options. But this also means that the old skills remain necessary.
So organisational leaders are adding new skills requirements on top of old, with the older skills being less attractive with so many new languages, frameworks and databases becoming available. Wikipedia has a very long list of languages that have been developed over the years. Some from the 1950s, like FORTRAN and LISP, continue to be used today.
Organisations will not be in a position to employ all the skills it needs to implement, develop and maintain for its digital infrastructure and applications. The choice is going to be which skills are most important to an organisation. This selection needs to be very discriminating and focus on differentiating skills – those that really make a difference within your ecosystem, particularly for your customers and employees.
Organisations will need a great partner who can deliver generic skills and more services. They will have better economies of scale and skill and will free management to attend to those things most important to customers and employees.
Hybrid Cloud has an Edge
Almost every organisation has a hybrid cloud environment. This is not a projection – it has already happened. And most organisations are not well equipped to deal with this situation.
Organisations may not be aware that they are using multiple public clouds. Many of the niche SaaS applications used by an organisation will use Microsoft Azure, AWS or GCP, so it is highly likely organisations are already using multiple public clouds. Not to mention the offerings from vendors such as Oracle, Salesforce, SAP and IBM. IT teams need to be able to monitor, manage and maintain this complex set of environments. But we are only in the early stages of integrating these different services and systems.
But there is a third leg to this digital infrastructure stool that is becoming increasingly important – what we call “the Edge” – where applications are deployed as part of the sensors that collect data in different environments. This includes applications such as pattern recognition systems embedded in cameras so that network and server delays cannot affect the performance of the edge systems. We can see this happening even in our homes. Google supports their Nest domestic products, while Alexa uses AWS. Not to mention Amazon’s Ring home security products.
With the sheer number of these edge devices that already exist, the complexity it adds to the hybrid environment is huge. And we expect IT organisations to be able to support and manage these.
Simplify, Specialise, Scale
The lessons for IT organisations are threefold:
- Simplify as much as possible while you are implementing new features and facilities. Retiring legacy infrastructure elements should be consistently included in the IT Team objectives. This should be done as part of implementing new capabilities in areas that are related to the legacy.
- Specialise in the skills that are the differentiators for your organisation with its customers and employees. Find great partners who can provide the more generic skills and services to take this load off your team.
- Scale your hybrid management environment so that you can automate as much of the running of your infrastructure as possible. You need to make your IT Team as productive as possible, and they will need power tools.
For IT vendors, the lessons are similar.
- Simplify customer offers as much as possible so that integration with your offering is fast and frugal. Work with them to reduce and retire as much of their legacy as possible as you implement your services. Duplication of even part of your offer will complicate your delivery of high-quality services.
- Understand where your customers have chosen to specialise and look to complement their skills. And consistently demonstrate that you are the best in delivering these generic capabilities.
- Scale your integration capabilities so that your customers can operate through that mythical single pane of glass. They will be struggling with the complexities of the hybrid infrastructure that include multiple cloud vendors, on-premises equipment, and edge services.

–
Innovation is at the core of Singapore’s ethos. The country has perfected the art of ‘structured innovation’ where pilots and proof of concepts are introduced and the successful ones scaled up by recalibrating technology, delivery systems, legislation, and business models. The country has adopted a similar approach to achieving its sustainability goals.
The Singapore Green Plan 2030 outlines the strategies to become a sustainable nation. It is driven by five ministries: Education, National Development, Sustainability and the Environment, Trade and Industry, and Transport, and includes five key pillars: City in Nature, Sustainable Living, Energy Reset, Green Economy, and Resilient Future. We will see a slew of new programs and initiatives in green finance, sustainability, solar energy, electric vehicles (EVs), and innovation, in the next couple of years.
Singapore’s Intentions of Becoming a Green Finance Leader
Singapore is serious about becoming a world leader in green finance. The Green Bonds Programme Office was set up last year, to work with statutory boards to develop a framework along with industry and investor stakeholders. We have seen a number of sustainable finance initiatives last year, such as the National Environment Agency (NEA) collaborating with DBS to raise USD 1.23 billion from its first green bond issuance. The proceeds will fund new and ongoing sustainable waste management initiatives. Temasek collaborated with HSBC for a USD 110 million debt financing platform for sustainable projects and Sembcorp issued sustainability bonds worth USD 490 million.
Building an Ecosystm of Sustainable Organisations
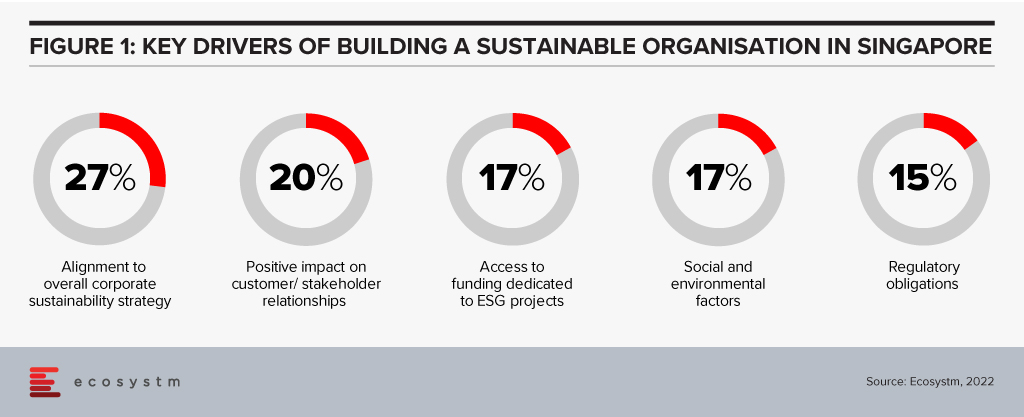
Sustainability has to be a collective goal that will require governments to work with enterprises, investors and consumers. To ensure that enterprises are focusing on Sustainability, governments have to keep in mind what drives these initiatives and the challenges organisations face in achieving their goals.
There are several reasons driving organisations in Singapore to adopt sustainability goals and ESG responsibilities (Figure 1)
It is equally important to address organisations’ challenges in building sustainability in their business processes. Last week, the Institute of Banking and Finance (IBF) and the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) set out 12 Sustainable Finance Technical Skills and Competencies (SF TSCs) required by people in various roles in sustainable finance. This addresses the growing demand for sustainable finance talent in Singapore; and covers knowledge areas such as climate change policy developments, natural capital, green taxonomies, carbon markets and decarbonisation strategies. There are Financial Services related competencies as well, such as sustainability risk management, sustainability reporting, sustainable investment management, and sustainable insurance and reinsurance solutions. The SF TSCs are part of the IBF Skills Framework for Financial Services.
Sustainable Resources Initiatives
Singapore is not only focused on Sustainable Finance. If we look at NEA’s Green Bonds, there are specific criteria that projects must satisfy in order to qualify, including a focus on sustainable waste management.
Last week the Government announced that the National Research Fund (NRF) will allocate around USD 160 million to drive new initiatives in water, reuse and recycling technologies, as part of the Research, Innovation and Enterprise 2025 plan (RIE2025). Part of the fund will be allocated to the Closing the Resource Loop (CTRL) initiative, administered by the NEA that will fund sustainable resource recovery solutions.
Singapore faces severe resource constraints, and water security is not a new challenge for the country. The NRF funding will also be used partially for R&D in 3 water technology focus areas: desalination and water reuse; used water treatment; and waste reduction and resource recovery.
The Government is Leading the Way
The Government’s concerted efforts to make the Singapore Green Plan 2030 a success is seeing corporate participation in the vision. In February, Shell started supplying sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) to customers such as SIA Engineering Company and the Singapore Air Force in Singapore. Shell has also upgraded their Singapore facility to blend SAF at multiple, key locations. Last week, Atlas announced their commitment to Web 3.0 technologies and “tech for good”. They aim to increase their green energy use to 75% by 2022; 90% by 2023; and 100% by 2024. ESG consciousness is percolating down from the Government.
The success of Singapore’s Sustainability strategies will depend on innovation, the Government’s ongoing commitment, and the support provided to enterprises, investors, and consumers. The Singapore Government is poised to lead from the front in building a Sustainable Ecosystem.

Since the start of this millennium, no region has transformed as much as Asia. There has been significant paradigm shifts in the region and the perception that innovation starts in the US or in Europe and percolates through to Asia after a time lag, has been shattered. Asia is constantly demonstrating how dynamic, and technology-focused it is. This is getting fueled by the impact of the growing middle class on consumerism and the spirit of innovation across the region. The region has also seen a surge in new and upcoming business leaders who are embracing change and looking beyond success to creating impact.
What is Driving Innovation in Asia?
The “If you ain’t got it, build it” attitude. One of the key drivers of this shift is the age of the average population in Asia. According to the UN the Asia Pacific region has nearly 60% of the world’s youth population (between the age of 17-24). With youth comes dynamism, a desire to change the world, and innovation. As this age group enters the workforce, they will transform their lives and the companies they work in. They are already showing a spirit of agility when it comes to solving challenges – they will build what they do not have.
The Need to enable Foundational Shifts. The younger generation is more aware of environmental, social and governance issues that the world continues to face. Many of the countries in the region are emerging economies, where these issues become more apparent. COVID-19 has also inculcated an empathy in people and they are thinking of future success in terms of impact. The desire to enable foundational shifts is giving direction to the transformation journey in the region. The wonderful new paradigm that is the Digital Economy allows us to cut across all segments; and technology and its advancements has immense potential to create a more sustainable and inclusive future for the world.
Realising the Power of Momentum. The pandemic has caused major disruptions in the region. But every crisis also presents an opportunity to perhaps re-imagine a brighter world through a digital lens. The other thing that the pandemic has done is made people and organisations realise that to succeed they need to be open to change – and that momentum is important. As organisations had to pivot fast, they realised what I have been saying for years – we shouldn’t “let perfect get in the way of better”. This adaptability and the readiness to fail fast and learn from the mistakes early for eventual success, is leading to faster and more agile transformation journeys.
Where are we seeing the most impact?
Industries are Transforming. There are industries such as Healthcare and Education that had to transform out of a necessity and urgency brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic. This has led to a greater impetus for change and optimism in these industries. These industries will continue to transform as governments focus significantly on creating “Social Safety Nets” and technology plays a key role in enabling critical services across Health, Education and Food Security. Then there are industries, such as the Financial Services and Retail, that had a strong customer focus and were well on their digital journeys before the pandemic. The pandemic boosted these efforts.
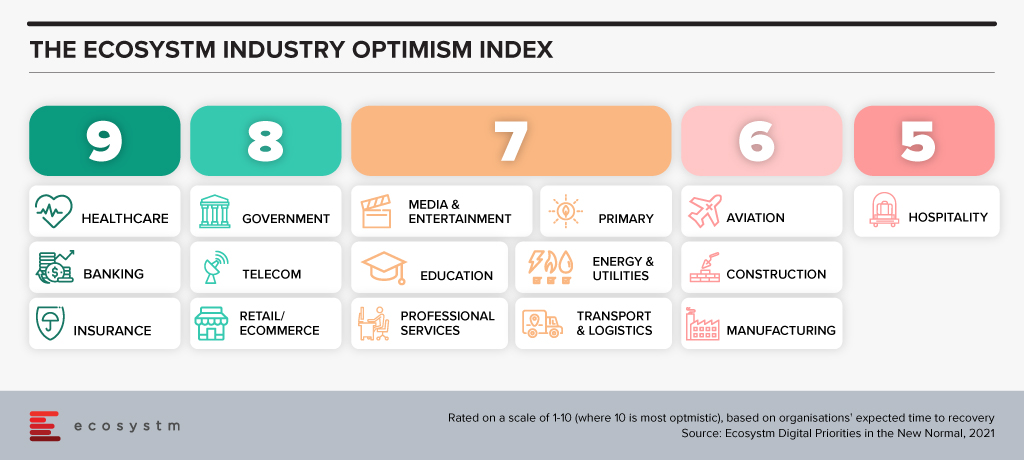
But these are not the only industries that are transforming. There are industries that have been impacted more than others. There are several instances of how organisations in these industries are demonstrating not only resilience but innovation. The Travel & Hospitality industry has had several such instances. As business models evolve the industry will see significant changes in digital channels to market, booking engines, corporate service offerings and others, as the overall Digital Strategy is overhauled.
Technologies are Evolving. Organisations depended on their tech partners to help them make the fast pivot required to survive and succeed in the last year – and tech companies have not disappointed. They have evolved their capabilities and continue to offer innovative solutions that can solve many of the ongoing business challenges that organisations face in their innovation journey. More and more technologies such as AI, machine learning, robotics, and digital twins are getting enmeshed together to offer better options for business growth, process efficiency and customer engagement. And the 5G rollouts will only accelerate that. The initial benefits being realized from early adoption of 5G has been for consumers. But there is a much bigger impact that is waiting to be realised as 5G empowers governments and businesses to make critical decisions at the edge.
Tech Start-ups are Flourishing. There are immense opportunities for technology start-ups to grow their market presence through innovative products and services. To succeed these companies need to have a strong investment roadmap; maintain a strong focus on customer engagement; and offer technology solutions that can fulfil the global needs of their customers. Technologies that promote efficiency and eliminate mundane tasks for humans are the need of the hour. However, as the reliance on technology-led transformation increases, tech vendors are becoming acutely aware that they cannot be best-in-class across the different technologies that an organisation will require to transform. Here is where having a robust partner ecosystem helps. Partnerships are bringing innovation to scale in Asia.
We can expect Asia to emerge as a powerhouse as businesses continue to innovate, embed technology in their product and service offerings – and as tech start-ups continue to support their innovation journeys.
Ecosystm CEO Amit Gupta gets face to face with Garrett Ilg, President Asia Pacific & Japan, Oracle to discuss the rise of the Asia Digital economies, the impact of the growing middle class on consumerism and the spirit of innovation across the region.

The disruption that we faced in 2020 has created a new appetite for adoption of technology and digital in a shorter period. Crises often present opportunities – and the FinTech and Financial Services industries benefitted from the high adoption of digital financial services and eCommerce. In 2021, there will be several drivers to the transformation of the Financial Services industry – the rise of the gig economy will give access to a larger talent pool; the challenges of government aid disbursement will be mitigated through tech adoption; compliance will come sharply back into focus after a year of ad-hoc technology deployments; and social and environmental awareness will create a greater appetite for green financing. However, the overarching driver will be the heightened focus on the individual consumer (Figure 1).
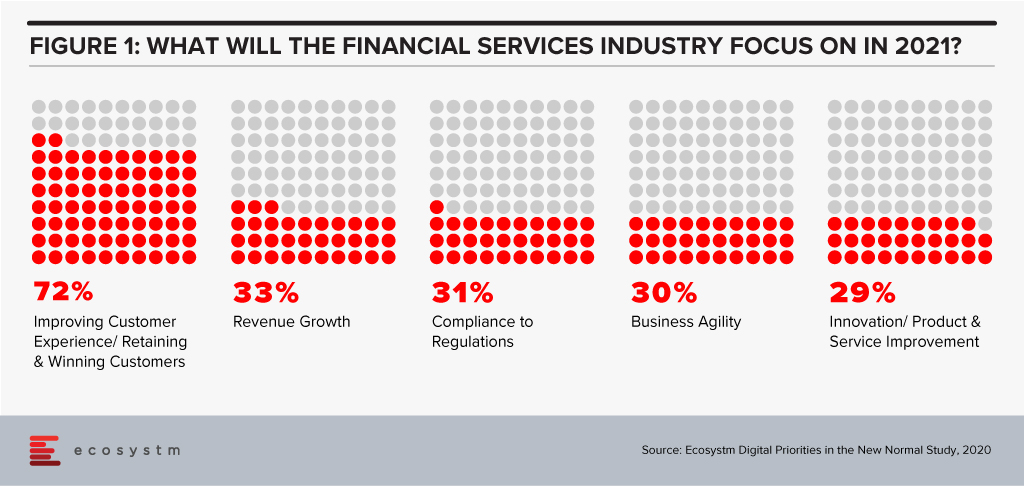
2021 will finally see consumers at the core of the digital financial ecosystem.
Ecosystm Advisors Dr. Alea Fairchild, Amit Gupta and Dheeraj Chowdhry present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for FinTech in 2021 – written in collaboration with the Singapore FinTech Festival. This is a summary of the predictions; the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform.
The Top 5 FinTech Trends for 2021
#1 The New Decade of the ‘Empowered’ Consumer Will Propel Green Finance and Sustainability Considerations Beyond Regulators and Corporates
We have seen multiple countries set regulations and implement Emissions Trading Systems (ETS) and 2021 will see Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) considerations growing in importance in the investment decisions for asset managers and hedge funds. Efforts for ESG standards for risk measurement will benefit and support that effort.
The primary driver will not only be regulatory frameworks – rather it will be further propelled by consumer preferences. The increased interest in climate change, sustainable business investments and ESG metrics will be an integral part of the reaction of the society to assist in the global transition to a greener and more humane economy in the post-COVID era. Individuals and consumers will demand FinTech solutions that empower them to be more environmentally and socially responsible. The performance of companies on their ESG ratings will become a key consideration for consumers making investment decisions. We will see corporate focus on ESG become a mainstay as a result – driven by regulatory frameworks and the consumer’s desire to place significant important on ESG as an investment criterion.
#2 Consumers Will Truly Be ‘Front and Centre’ in Reshaping the Financial Services Digital Ecosystems
Consumers will also shape the market because of the way they exercise their choices when it comes to transactional finance. They will opt for more discrete solutions – like microfinance, micro-insurances, multiple digital wallets and so on. Even long-standing customers will no longer be completely loyal to their main financial institutions. This will in effect take away traditional business from established financial institutions. Digital transformation will need to go beyond just a digital Customer Experience and will go hand-in-hand with digital offerings driven by consumer choice.
As a result, we will see the emergence of stronger digital ecosystems and partnerships between traditional financial institutions and like-minded FinTechs. As an example, platforms such as the API Exchange (APIX) will get a significant boost and play a crucial role in this emerging collaborative ecosystem. APIX was launched by AFIN, a non-profit organisation established in 2018 by the ASEAN Bankers Association (ABA), International Finance Corporation (IFC), a member of the World Bank Group, and the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS). Such platforms will create a level playing field across all tiers of the Financial Services innovation ecosystem by allowing industry participants to Discover, Design and rapidly Deploy innovative digital solutions and offerings.
#3 APIfication of Banking Will Become Mainstream
2020 was the year when banks accepted FinTechs into their product and services offerings – 2021 will see FinTech more established and their technology offerings becoming more sophisticated and consumer-led. These cutting-edge apps will have financial institutions seeking to establish partnerships with them, licensing their technologies and leveraging them to benefit and expand their customer base. This is already being called the “APIficiation” of banking. There will be more emphasis on the partnerships with regulated licensed banking entities in 2021, to gain access to the underlying financial products and services for a seamless customer experience.
This will see the growth of financial institutions’ dependence on third-party developers that have access to – and knowledge of – the financial institutions’ business models and data. But this also gives them an opportunity to leverage the existent Fintech innovations especially for enhanced customer engagement capabilities (Prediction #2).
#4 AI & Automation Will Proliferate in Back-Office Operations
From quicker loan origination to heightened surveillance against fraud and money laundering, financial institutions will push their focus on back-office automation using machine learning, AI and RPA tools (Figure 3). This is not only to improve efficiency and lower risks, but to further enhance the customer experience. AI is already being rolled out in customer-facing operations, but banks will actively be consolidating and automating their mid and back-office procedures for efficiency and automation transition in the post COVID-19 environment. This includes using AI for automating credit operations, policy making and data audits and using RPA for reducing the introduction of errors in datasets and processes.
There is enormous economic pressure to deliver cost savings and reduce risks through the adoption of technology. Financial Services leaders believe that insights gathered from compliance should help other areas of the business, and this requires a completely different mindset. Given the manual and semi-automated nature of current AML compliance, human-only efforts slow down processing timelines and impact business productivity. KYC will leverage AI and real-time environmental data (current accounts, mortgage payment status) and integration of third-party data to make the knowledge richer and timelier in this adaptive economic environment. This will make lending risk assessment more relevant.
#5 Driven by Post Pandemic Recovery, Collaboration Will Shape FinTech Regulation
Travel corridors across border controls have started to push the boundaries. Just as countries develop new processes and policies based on shared learning from other countries, FinTech regulators will collaborate to harmonise regulations that are similar in nature. These collaborative regulators will accelerate FinTech proliferation and osmosis i.e. proliferation of FinTechs into geographies with lower digital adoption.
Data corridors between countries will be the other outcome of this collaboration of FinTech regulators. Sharing of data in a regulated environment will advance data science and machine learning to new heights assisting credit models, AI, and innovations in general. The resulting ‘borderless nature’ of FinTech and the acceleration of policy convergence across several previously siloed regulators will result in new digital innovations. These Trusted Data Corridors between economies will be further driven by the desire for progressive governments to boost the Digital Economy in order to help the post-pandemic recovery.

I recently came across an article which makes 7 predictions for a post COVID world. Upon reflection, I agree with the predictions to varying degrees and decided to comment further.
First, let me share a couple of general observations. Currently, we are still in the eye of the storm. Many are unable to see any light at the end of the tunnel. There is quite a bit of negative sentiments, and some fail to see that the situation will ever improve. I am sure similar thoughts occurred during other crises: the 1918 Pandemic (Spanish Flu); the Great Depression of the 1930s; the Dot.com bust of 2001; SARS in 2003; and the Global Financial Crisis/Great US Recession of 2007. During each of these events, a sense of impending Armageddon came over much of the population. Certainly, in each instance, people did experience some personal and social permanent changes, with which they learned to adapt and cope. But, inevitably, the world did go on and Armageddon did not occur.
One of the basic truths I believe, is that humans require and crave interaction with other humans. Think about the videoconferencing applications. The use of these apps grew exponentially as the main communication channel. Instead of just audio, it was audio and video. These mediums greatly assisted society in coping and adapting. Mankind, and the Natural World, will always find a way.
Here are the predictions from the article:
- Companies that traffic in digital services and e-commerce will make immediate and lasting gains
- Remote work will become the default
- Many jobs will be automated, and the rest will be made remote-capable
- Telemedicine will become the new normal, signaling an explosion in med-tech innovation
- The nationwide student debt crisis will finally abate as higher education begins to move online
- Goods and people will move less often and less freely across national and regional borders
- After an initial wave of isolationism, multilateral cooperation may flourish
I very much agree with the author’s first prediction. This one is fairly obvious, as it has proven true throughout the crisis with providers such as Amazon, Zoom and others. It is expected to continue into the post COVID world. This is also evident from the findings of the Ecosystm research on the impacts of COVID-19. Organisations intend to continue to use digital technologies, even after the immediate crisis is over (Figure 1).
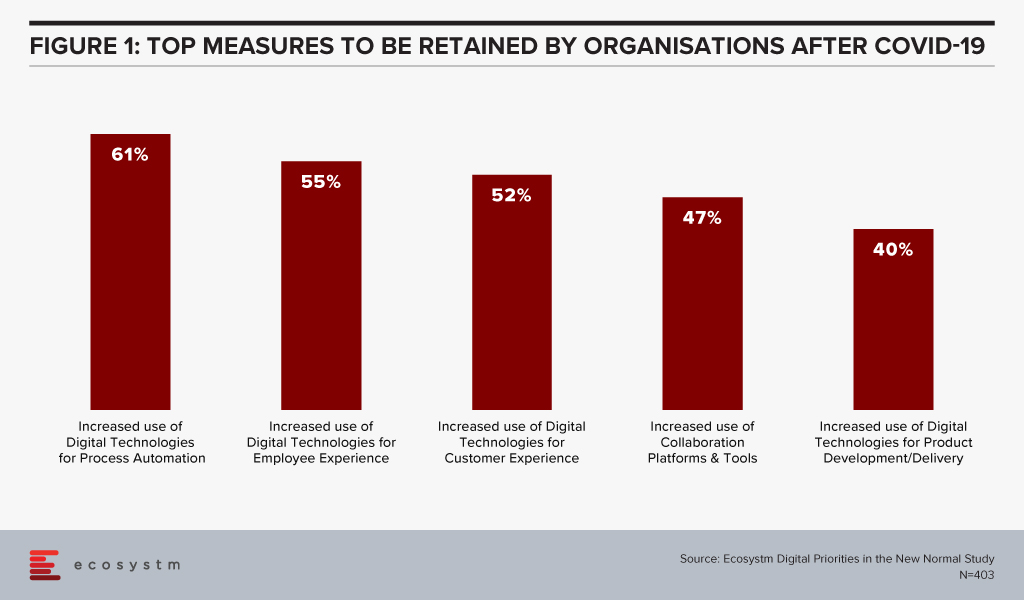
A Natural State of Equilibrium will Emerge
I believe for each of the areas described in the predictions, there will be various levels of long-term modification. None of them will return to their pre COVID-19 state, as we have all experienced going down the rabbit hole. During the pandemic, due largely to the lockdowns, the pendulum swung significantly towards one side. Many times, when people predict a new view, the current state is considered the New Normal. For me, the relevant question is: Will things stay as they are now, or will there be a new natural state of equilibrium? If so, what will it look like, in each of these areas? I don’t believe there is one answer, or one New Normal for all the dimensions being discussed. I believe a new normal state will potentially be different for each individual, each company/entity and each condition. In a post COVID-19 world there could be 50 shades of grey in each of these areas.
One of the predictions states that remote work will become the default. It must be remembered that part of work is a collaborative effort. While video conferencing has enabled collaborative efforts, the importance of the accidental interaction at the break room, printer, etc. can’t be under-estimated. It is these unscheduled interactions that enable accidental collaboration which can lead to great solutions. Thus, there will be many shades to the Future of Work – there will not be one absolute.
A similar example is a prediction for higher education. Part of the learning process a university offers is interacting with people who are not similar to your background or beliefs. That is one of the benefits of a diverse university. Similar to the corporate environment, many different types of learning environments will enable a person to gain great experiences from the time at university.
The advantage of all these alternatives will be the additional options and benefits to people post COVID compared to the pre COVID-19 world. It will present many great opportunities for entrepreneurs and innovators, as well as end-users and consumers. It will create new and iterative ‘middle spaces’. It will be possible for a David to emerge and challenge a Goliath(s).
The two Chinese characters for the word ‘crisis’ are “danger” and “opportunity”. Just as we are in a dangerous time now, it has also presented new and different opportunities. Those opportunities will continue to exist even when the danger has passed. I am also reminded of the old expression “May you live in interesting times”. It very much applies to all of us now and in the future. I wish the same for all of you.
Stay Safe. Stay Healthy. Stay Mentally Positive.

Global supply chains were impacted early and badly by the COVID-19 pandemic. The fact that the pandemic started in China – the leader in the Manufacturing industry – meant that many enterprises globally had to re-evaluate their supply chain and logistics. This was compounded by the impact on demand – for some sectors the demand went down significantly, while in others, especially for items required to fight the crisis, there was an unexpected spike in demand. There was also the need for many manufacturers and retailers to shift to eCommerce, to directly access the market and sustain their businesses. These sudden shifts that were required of the industry, opened up the need for a global supply chain that is more integrated, agile and responsive.
Last week, global heavyweights with a stake in the global supply chain, joined a consortium to work on creating that agility. This includes PepsiCo, BMW, Shopify, DHL, and the United States Postal Service and some emerging tech companies. The alliance will actively work on solutions to embed automation and digitalisation in the logistics and supply chain systems. While this consortium was formed last year, recent events have accelerated the need to fix a global problem.
Co-Creation and Innovation
LINK is a collaborative ecosystem, co-founded by Innovation Endeavors and Sidewalk Infrastructure Partners (SIP) to bring together emerging tech start-ups, institutions and global organisations to innovate and make supply chains resilient. The tech start-ups involved include the likes of Fabric, that has large automated micro-fulfillment centres for faster deliveries, and Third Wave Automation, that has developed automated forklifts with enhanced safety measures.
LINK aims to transform global supply chains, with the use of technologies such as automation, IoT, AI, and Robotics. The solutions developed by the start-ups will be tested in real-life situations, often in large organisations with complex operations. On the other hand, the start-ups will have access to the internal systems of these large organisations to understand the data and their organisational needs.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Kaushik Ghatak says, “COVID-19 has brought the need for supply chain agility and resilience to a completely new level of criticality. Companies in the ‘New Normal’ will need higher levels of nimbleness and flexibility to be able to recover from this crisis quickly and sustain in an increasing disruptive world. Increased ability to sense and respond to disruptions will be key to success. It will require better visibility of their entire supply chain, increasing efficiencies, building necessary redundancies (in form of inventory and capacity) where they are required the most – redundancy comes at a cost – and being flexible and innovative to cater to the rapid market and supply-side changes. Rapid digitalisation to build such capabilities will be a key to success.”
“Managing such rapid changes is usually a struggle for organisations with large and complex supply chains, because of the years of past practices, systems and culture. For them Innovation is a must, but the path to innovation is difficult. The LINK collaboration model is the right step towards addressing that challenge. Collaborating with start-ups can infuse new ideas, more innovative ways of solving a problem and rapid testing of use cases in the areas of IoT, AI and automation.”
Involving Start-ups for Innovation
This initiative is a great example of how larger enterprises are looking to leverage innovations by the start-up community. The Financial Services industry has been an early beneficiary, when it stopped competing with Fintech organisations, partnering with them instead. Other industries have started to recognise the benefits of fast pivots and the role start-ups can play.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Ravi Bhogaraju says, “Bringing together companies that have complementary and unique capabilities to solve industry issues is a great way to speed up experimentation and innovation.”
However, he recognises that forming alliances such as this, comes with its own set of challenges. “One of the key things to recognise in such a construct is that the team members from different possessions bring with them their unique belief systems, organisational and country cultural constructs. Expectations on how things should work, can become quite tricky to navigate. The talent and expertise in such an environment need to be facilitated be able to deliver high quality outcomes.”
Talking about how these constructs can work successfully, delivering what started out to deliver, Bhogaraju says, “An agile team setup can help tremendously as it uses two key principles – People and Interactions over processes; as well as Working models over documentation.”
“A clear expectation setting through contracting at the beginning of the project cycle can help establish the ways of working and rules of engagement. Increased regular feedback and problem solving should continuously fine tune the ways of working. This way teams can get through the norming process at pace and scale and eventually focus on outcomes, rather than fumble over each other and/or have ego flareups.”
“The key is to get to creative problem-solving working cohesively – the intent being to challenge the status quo – stepping outside the box and using all capabilities within the team. Blending the subcultures together using agile way of working and principles, can be a fantastic way to make that happen – failing which you have the challenge of trying to somehow bring together different work products, people and preferences.”
Innovation is quite an apt subject to write about – given we are coming to the close of an extremely innovative decade. Contrary to popular conception however, the word innovation is not limited to startups – corporates have ample opportunities to innovate and there are plenty of examples to inspire us.
In the technology industry, the turning point was the rapid scale-up of Amazon Web Services (AWS) – originating from the mothership, they defied all odds and forever changed the way we consume technology, making it more accessible through their cloud offerings. While AWS took the world by storm, most competitors have struggled because they are slow to adapt and transform. For them, this age of innovation has become a burden. The one exception is Microsoft – perhaps the true giant of the industry – that pivoted, and now constant innovation is seeing them consistently jostle for the leadership position. The underlying success factor for innovations is speed – it is of the essence when innovating.
Most companies are unable to promote a culture of innovation into their system, fast enough. Mainly because they are afraid of stumbling on the classic difficulties: “cannibalisation” of the existing business, impossibility to predict with certainty the results of innovation, lack of funding, internal conflict and one-upmanship, lack of understanding of technologies or the challenges of innovation management. Not to mention that taking risks isn’t well regarded in most companies. Most leaders fall in the long-standing tradition of annual P&L management. It’s that temptation of getting by another year of achieving targets. In the end, we are what we measure. The final metric always has to be increased profitability – but it’s all about defining the timescale. Once that’s sorted, the milestones and metrics make Success easier to measure.
The reality is also that the one rarest commodity for innovation is the vision and managed risk-taking ability of the leadership. For this reason, many companies prefer to create a dedicated independent team of corporate mavericks, specifically aimed at innovation. But eventually, the success of these teams is based on rapidly incorporating the innovations into the business – it must reflect in the core corporate ethos of the organisation. Experts debate the benefits of centralised versus decentralised innovation, but what’s most important is to have a dedicated capacity. If innovation is 10% of 100 people’s responsibility, you can rest assured that little innovation will take place. But if it’s 100% of 10 people’s jobs, things will start to happen. Speed is partly born of the priority that is put on it, so assigning - and incentivising - a dedicated team with the job of moving fast is an essential organisational step to innovation.
Easier said than done you say? It becomes even more challenging when you’re trying to achieve this in a large corporate environment. What AWS achieved is world-changing, and one cannot comprehend the vision, capabilities and execution par excellence of the leadership and the team. However, they were building from scratch with a blank canvas – they had the capital, a proven organisational culture of building and arguably one of the strongest leaderships in our generation. But for Microsoft, the storyboard was different. In order to innovate, they had to change the status quo. Yes, they had capital – tons of it – however, they also carried tremendous ‘baggage’. Ironically, it’s this baggage that corporations strive to achieve and only some manage – it’s called ‘legacy’. It can come back to bite you and hold you back when you need to rapidly adapt and innovate. But that is what Microsoft achieved – they overcame the fear of cannibalisation, put aside all the internal posturing and one-upmanship and more importantly, built a culture of innovation. Something that was led impeccably by Satya Nadella who allowed rapid innovation and ensured that the entire organisation got behind the ‘cloud-first’ vision.
Companies that are built for speed react more quickly to competitor moves or market shifts with their own product innovations. Fast innovators test prototypes with customers, worrying less about the imperfections that they know are there and focusing more on the insights they may gain from consumer reactions and feedback. They also fail several times – but they fail fast and cheap.
To sum it up, organisations that innovate successfully are fast to respond to the market, are led by a vision, have a culture of innovation, are not afraid to fail and they don’t ever let perfect get in the way of better!
As published in the tabla! (An SPH Publication)