Two weeks ago, Michael Dell made the big announcement that Dell Technologies would spin off their shareholding in VMware, leading to a share price spike for both companies. A lot has already been written about the move – we would like to highlight a market-based view which we feel will be significant for the two companies going forward.
First let us break down the facts around the deal:
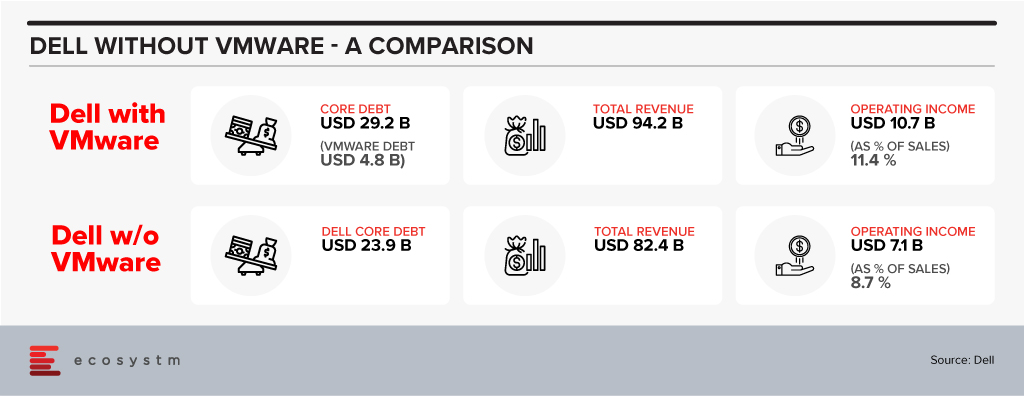
As has been analysed threadbare the deal reduces the total debt Dell is carrying and will even reduce the ratio of Dell debt to EBITDA. As a result, it is highly likely that Dell’s credit rating will move up from their current BB+ level to investment grade – which can have a lot of implications for future capital raising. There is also a buzz in the market that Dell Technologies may also sell off Boomi soon and write down another USD 3 Billion approximately in debt.
It is interesting to note that the company has been willing to let go off VMware even though it will dilute their profitability ratios – VMWare business being obviously more profitable than Dell’s traditional businesses which are heavily based on products.
The last few years has seen Dell reselling a fair amount of VMware products. From a number of perspectives Dell has been a key reseller for VMware and now contributes almost 34% of VMware’s revenues.
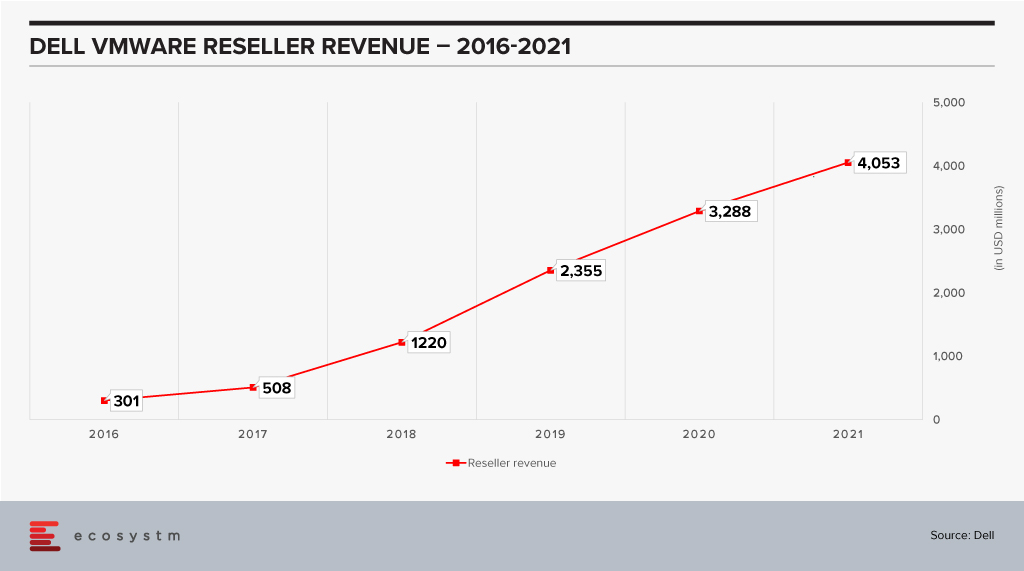
This chart is a testament to the power of execution that is inherent within Dell. This performance was aided by market growth – but even then it is remarkable how Dell has been able to scale up taking VMware to their customers. The two companies have very different sales cycles. A VMware sale typically has a longer cycle with a completely different set of touchpoints from the boxes that Dell is so good at selling – which have shorter cycles. The sales cycle for EMC products is closer to VMware’s which would have helped. The sales of the VXRail hyperconverged appliance have also jumped in recent times and this would have driven an equivalent spike in VMware revenues. It is still a remarkable achievement to be able to bring these three diverse groups together and grow revenue.
Market Impact of the Spin-Off
Does it make sense then for VMware to part with their largest reseller? Would it not be better for VMware to continue to drive this and use Dell’s execution skills to drive more growth? Data suggests that there could be another twist to this story.
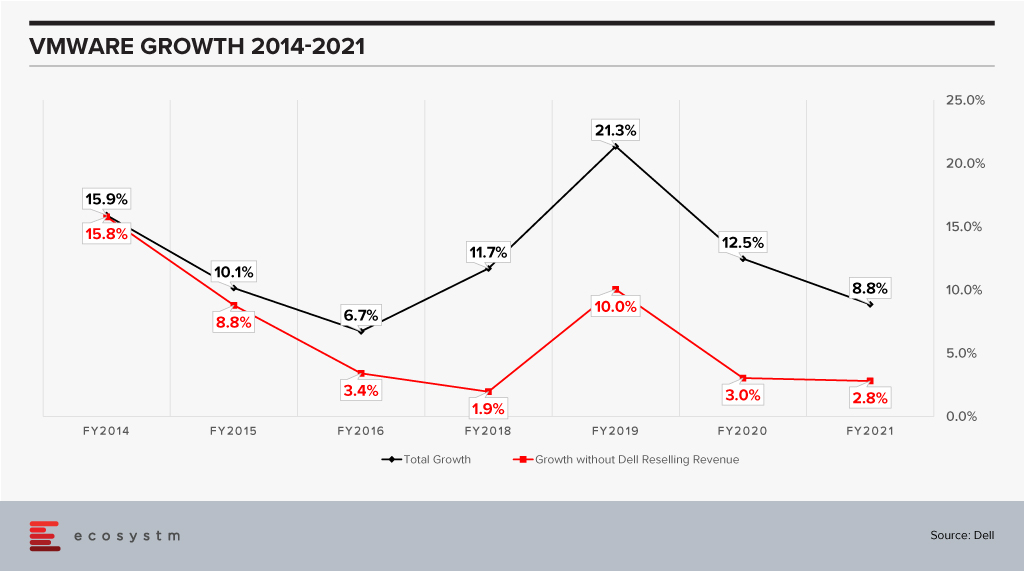
VMware has been growing impressively as a company when one looks at the black line and while the growth has slowed in percentage terms, this is on a much higher revenue base. FY2021 revenue is close to 2x the revenue in FY2014. However, when one considers it without the Dell reselling revenue (the red line) it looks a lot less impressive especially in the last couple of years when it is an anemic 3%. When comparing this growth we also see a slowdown of sorts in recent years for VMware.
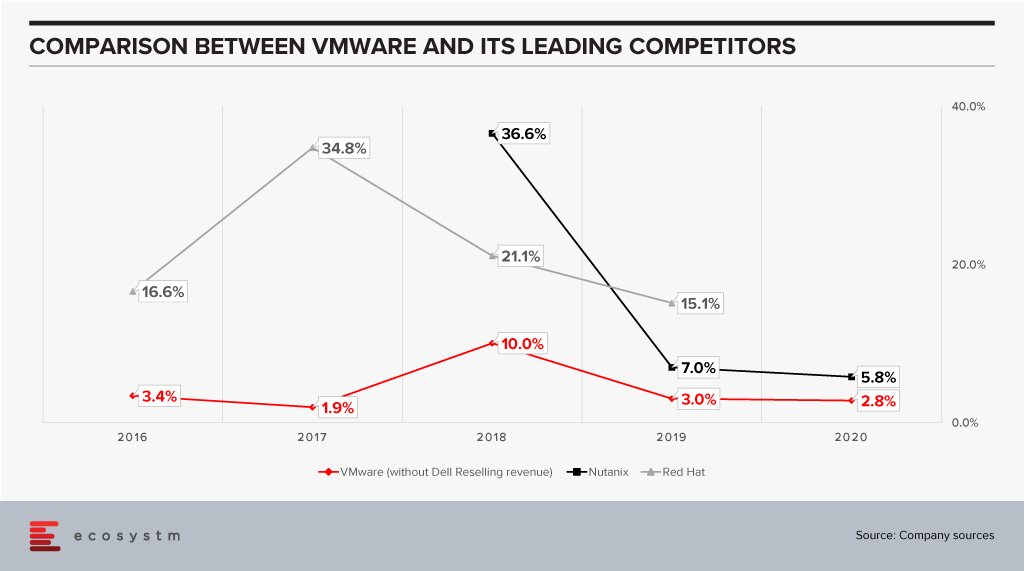
Til Dell acquired EMC – and VMware in consequence – they were working closely with other vendors such as Nutanix and driving solid growth for them. As they pivoted to doing more with VMware, did this then mean that other vendors – of either bare metal or cloud – drifted away from VMware?
Anecdotal evidence suggests that vendors such as HPE became more cautious and tried to diversify their business. It is entirely possible that if we looked at VMware as two separate businesses – one with Dell and one independent – the independent business has been losing share in the last few years.
The optical separation from Dell may then help VMware in rebuilding stronger relationships with the other players in the market including the hyperscalers. This may fuel further VMware growth. To do that VMware will have to manage a balancing act:
- On the one hand keep growing their reseller revenue with Dell. They are on a good wicket so far and need to make sure this continues. While the revenue from appliances – which come loaded with VMware – is a sure-fire proposition, other growth needs to be harvested carefully. Dell has a multitude of offerings and taking their eyes of the VMware ball is super easy.
- Build trust and closer ties with the other vendors to keep driving revenue. VMware’s leadership in the market means they already have ties with other industry leaders like HPE, AWS and so on. These will need to become much deeper; VMware will need to build the trust that they will give these vendors equal status even as they are building new appliances with Dell.
The one complicating factor here is that Michael Dell remains the Chairman of the Board of VMware. This may give other vendors pause and they may still want to keep their options open instead of putting all eggs into the VMware basket.
Ecosystm Comments
VMware is at a fairly critical inflection point in their business. The growth of cloud technologies still bodes well for virtual machines which has been their mainstay, but this is also likely to drive growth for more containerisation. They have great products for that part of the business also. However, as container adoption is likely to explode VMware would not want vendors to shift, to say Red Hat, and develop deeper partnerships with them or other competitors. They would like to keep the vendors on VMware – be it a virtual machine or a container. One does feel the future battle for VMware really rests on how well they will be able to grow in the container space. This will have to be done while continuing to innovate to keep the lead in the virtual machine space. Doing it will be quite a feat!!
Finally, what then of Dell? The company seems to have a talent for running businesses which are in long-term secular decline – but running those businesses well. Their PC business is delivering almost 7% operating income and has continued to show growth. The PC market last year was on fire thanks to the pandemic which dramatically increased the demand for devices – growth was double digits for a market which has declined almost every year since 2011. As Dell is fond of saying the PC industry has sold over 5 billion machines since the PC was declared dead!
The server market seems to have stagnated over the last couple of years which is a bit of a surprise given the growth in cloud. Dell’s revenue has declined two years in a row pointing to possible issues which need fixing in that part of the business.
As the company focuses on these key challenges in the market it probably makes sense for them to lower their debt and earn more freedom to operate. One never knows – given the number of surprises that Michael Dell has engineered over the last decade such as taking Dell private, acquiring EMC, stabilising it, then going public again, making a windfall in the process – if he has some other rabbits yet to be pulled out of his hat!!!
Access insights on adoption of key Cloud solutions in regions/countries and industries. Insights include drivers and inhibitors of adoption, budget allocation, and preferred implementation partners.

ServiceNow announced their intention to acquire robotic process automation (RPA) provider, Intellibot, for an undisclosed sum. Intellibot is a significant tier 2 player in the RPA market, that is rapidly consolidating into the hands of the big three – UiPath, Automation Everywhere, and Blue Prism – and other acquisition-hungry software providers. This is unlikely to be the last RPA acquisition that we see this year with smaller players looking to either go niche or sell out while the market is hot.
Expanding AI/Automation Capabilities
Intellibot is the latest in a string of purchases by ServiceNow that reveals their intention to embed AI and machine learning into offerings. In 2020, they acquired Loom Systems, Passage AI (both January), Sweagle (June), and Element AI (November) in addition to Attivio in 2019. These acquisitions were integrated into the latest version of their Now Platform, code-named Quebec, which was launched earlier this month. As a result, Predictive AIOps and AI Search were newly added to the platform while the low-code tools were expanded upon and became Creator Workflows. This means ServiceNow now offers four primary solutions – IT Workflows, Employee Workflows, Customer Workflows, and Creator Workflows – demonstrating the importance they are placing on low-code and RPA.
ServiceNow was quick to remind the market that although they will be able to offer RPA functionality natively once Intellibot is integrated into their platform, they are still willing to work with competitors. They specifically highlighted that they would continue partnering with UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism, suggesting they plan to use RPA as a complementary technology to their current offerings rather than going head-to-head with the Big Three. Only a month ago, UiPath announced deeper integration with ServiceNow, by expanding automation capabilities for Test Management 2.0 and Agile Development projects.
Expansion in India
The acquisition of Intellibot, based in Hyderabad, is part of ServiceNow’s expansion strategy in India – one of their fastest growing markets. The country is already home to their largest R&D centre outside of the US and they intend to launch a couple of data centres there by March 2022. The company plans to double their local staff levels by 2024, having already tripled the number of employees there in the last two years. The expansion in India means they can increasingly offer services from there to global customers.
Market Consolidation Accelerates
In the Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 AI & AUTOMATION Trends for 2021, Ecosystm had talked about technology vendors adding RPA functionality either organically or through acquisitions, this year.
“Buyers will find that many of the automation capabilities that they currently purchase separately will increasingly be integrated in their enterprise applications. This will resolve integration challenges and will be more cost-effective.”
ServiceNow’s purchase is one of several recent examples of low-code vendors acquiring their way into the RPA space. Last year, Appian acquired Novayre Solutions for their Jidoka product and Microsoft snapped up Softomotive. Speculation continues to build that Salesforce could also be assessing RPA targets. Considering RPA market leader, UiPath recently announced that their Series F funding round values the company at USD 35 billion, there is pressure on acquirers to gobble up the remaining smaller players before they are all gone or become prohibitively expensive.
The cloud hyperscalers are also likely to play a growing role in the RPA market over the next year. Microsoft and IBM have already entered the market, coming from the angle of office productivity and business process management (BPM), respectively. Google announced just last week that they will work closely with Automation Anywhere to integrate RPA into their cloud offerings, such as Apigee, AppSheet, and AI Platform. More interestingly, they plan to co-develop new solutions, which might for now satisfy Google’s appetite for RPA rather than requiring an acquisition.
Here are some of the trends to watch for RPA, AI and Automation in 2021. Signup for Free to download Ecosystm’s Top 5 AI & Automation Trends Report.

This week at Microsoft Ignite, there was a heavy emphasis on RPA and low code as the tools it sees as the future of productivity. It used its annual conference for developers and IT professionals to make a slew of announcements about its Power Platform. Most notable is that from this week, Power Automate Desktop will be bundled with Microsoft Windows and is available as a free download. This marks a major step in the direction of mass adoption of RPA.
By Microsoft’s estimates, 50% of tasks carried out by information workers could be automated by currently available technology but are instead performed manually. Moreover, 500 million apps will need to be built by 2026, more than were developed in the last 40 years. Slowing down the pace of automation and the roll out of apps to enable digital business, is the skills gap, with a shortage of 1 million developers in the US alone. This is of course why Microsoft is betting on RPA and low code tools to empower citizen developers to do it themselves.
Microsoft was arguably slow to focus on RPA and low code considering its breadth of applications and good standing with developers. It only announced the general availability of UI Flows in Power Automate less than a year ago. Moreover, its automation suite worked best in the Microsoft universe but had limited interoperability with third-party tools. In May 2020, it acquired Softomotive, which signalled that it was taking RPA seriously and was willing to expand beyond the automation of its own software. By then, acquiring one of the big three – UiPath, Automation Anywhere, or Blue Prism – would have been excessively costly but Softomotive ensured it had both attended and unattended RPA capabilities to build upon. Softomotive’s WinAutomation remerged as Power Automate Desktop in September and with this week’s announcement, it becomes a native component in Windows.
By providing Power Automate Desktop for free with Windows, Microsoft appears to be attempting to generate interest from users who may not have previously been exposed to RPA. For the widespread adoption of RPA beyond just functions like finance, HR, and procurement, these tools need to be put into the hands of average users that can find their own use cases. Eventually, some of these basic users will need more advanced functionality available in the cloud-based version of Power Automate. Microsoft has a range of pricing plans including per user, per flow, with AI Builder, and unattended RPA.
Security and Governance
While making free desktop-based automation available to all, may be an effective means of raising the profile of RPA, Microsoft realises that it must provide IT and security teams with tools for control. It also announced this week additional features, such as:
- Endpoint filtering to turn on selected connections but with restrictions
- Connector action controls, e.g. allowing read permission but not write in some connectors
- Tenant isolation to provide differentiated access to connectors according to business unit
- Usage dashboards
Power Fx – Microsoft’s Low Code Language
Microsoft is one of the best-placed vendors to address the needs of citizen developers; bringing together its dominance as a productivity software provider and an important part of the developer ecosystem. This week it also introduced Power Fx, a low-code programming language based on Microsoft Excel. The logic of this new, simple language should be familiar to the millions of spreadsheet users. Power Fx provides more advanced citizen developers with a bridge from the drag-and-drop features of the Power Platform to low-code development.
Is 2021 the year RPA finally goes mainstream?
Microsoft’s announcements this week are one of many signs in the last few months that the RPA market is on its way to gaining mainstream acceptance. Also garnering attention was the lofty valuation given to the market leader, UiPath, this year. It recently announced that in its Series F funding round, it closed at $750M, valuing the company at $35B. This is hot on the heels of confirmation that it plans to IPO, probably in the first half of 2021. Last year was also a rapid period of consolidation, with Appian, IBM, and Microsoft all making RPA acquisitions. It seems highly likely that in the next few months we could see acquisitions or RPA launches by some of the cloud and application vendors that have until now been waiting to see the technology mature.
How will RPA be a part of your automation strategy in 2021? The Top 5 AI & Automation Trends for 2021 are available for download from the Ecosystm platform. Signup for Free to download the report.

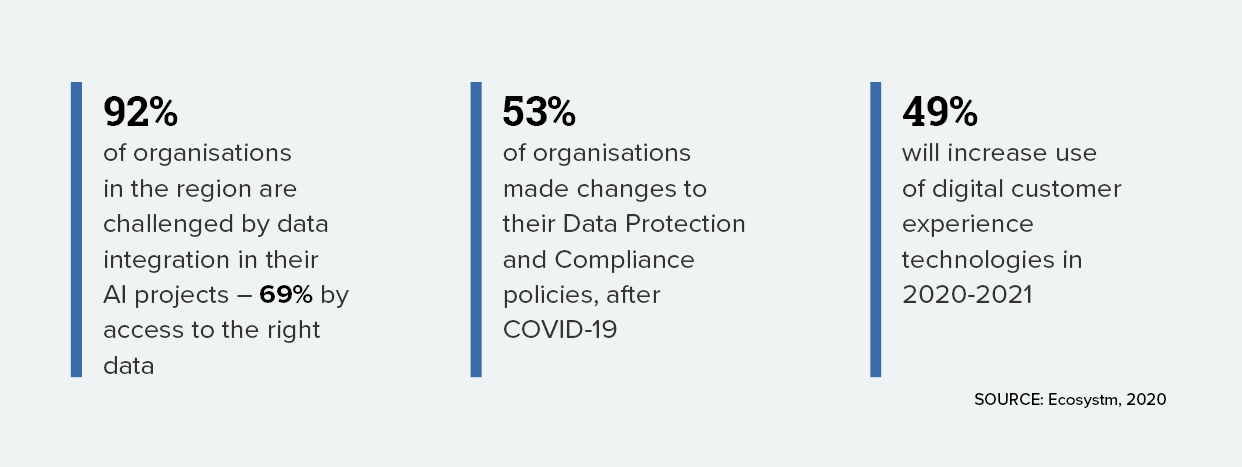
Ecosystm had predicted that in 2020, AI and analytics would be a top priority for organisations as they embarked or continued on their Digital Transformation journeys. What we saw instead was organisations collecting the right data – but handling more pressing matters this year. They focused more on cybersecurity frameworks, enabling remote employees and the shifts in product and service delivery. In 2021, as organisations work their way to recovery, they will re-evaluate their AI and automation roadmaps, more actively. Ecosystm Advisors Alea Fairchild, Andrew Milroy and Tim Sheedy present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for AI & Automation in 2021.
This is a summary of the AI & Automation predictions, the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform here.
The Top 5 AI & Automation Trends for 2021
- AI Will Move from a Competitive Advantage to a Must-Have
The best practices and leading-edge technology-centric implementations, over the years gives a very good indication of market trends. In 2018 and 2019 AI-centric engagements were few and far between – they were still in the “innovation stage” as trials and small projects. In 2020, AI was mentioned in most applications, showcased as best practices. AI is currently a competitive advantage for businesses. CIOs and their businesses are using AI to get ahead of their competitors and highlighting these practices for external recognition.
That also means that it is a matter of time before AI becomes a standard practice – processes are smart “out-of-the-box”; intelligent applications are an expectation, not the exception; systems learn because that is how they were designed, not as an overlay. If your competitors are using AI today to get ahead of you, then you need to also use AI to catch up and keep up. In 2021, having a smart business will not get you ahead of the pack – it will move you into it.
- AI Will Thrive in Areas where the Cost of Failure is Low
While organisations will be forced to adopt AI to remain competitive, initial exploration of AI solutions will be in areas that they consider low risk. The Financial Services, Retail, and other transaction-oriented industries will use AI to drive improved personalisation, increase customer retention, and improve their ability to lower risk and combat fraud. These are process-driven areas, where manual processes are being enhanced and enriched by AI. Although machine learning and other AI technologies will help improve the speed and quality of services, they will not be a replacement for many of the more complex business practices that companies and their employees frequently overlook to automate. The ‘low hanging fruit’ to add AI to will come first, with various degrees of success.
There will be industries and processes where organisations will be more skeptical about adopting AI. If Google finds a wrong translation or gives a wrong link, it is not a big concern, unlike a wrong diagnosis or wrong medication. In areas that are crucial to our well-being – such as healthcare – AI does not yet have the trust for acceptance of society. There are still questions around ethics and algorithm concerns.
- Technology Providers Will Stop Talking about AI
Technology vendors highlight what they consider their key differentiators, that show that they are ahead of the game. When every piece of software and hardware is intelligent, vendors will stop talking about the fact that they are intelligent. This may not fully happen in 2021 – but ENOUGH technology will be intelligent for those who have not yet made their software smart to understand that they cannot talk about its intelligent capabilities as that just shows they are behind the market.
The good news is that the less we hear about AI, the more intelligent applications will become. AI is quickly becoming a core capability and a base expectation. Systems that learn and adapt will be standard very soon – but be wary, as significant market changes can break these systems! Many companies learned that the pandemic broke their algorithms as times were no longer “normal”.
- Enterprises Will Seek Hyperautomation Solutions
RPA will increasingly become part of large enterprise application implementations. Technology vendors are adding RPA functionality either organically or through acquisitions to their enterprise application suites. RPA often works in conjunction with major software products provided by companies such as Salesforce, SAP, Microsoft, and IBM. Rather than having an operative enter data into multiple systems, a bot can be created to do this. Large software vendors are taking advantage of this opportunity by trying to own entire workflows. They are increasingly integrating RPA into their offerings as well as competing directly in the RPA market with pureplay RPA vendors.
As the RPA offerings continue to mature, enterprises seek to scale implementations and to automate non-repetitive processes, which require more intelligence. They will seek to automate more processes at scale. They will demand solutions that process unstructured data, handle exceptions, and continuously learn, further increasing productivity. Intelligent automation typically incorporates AI, particularly voice and vision capabilities and uses machine learning to optimise processes. Hyperautomation turbo charges intelligent automation by automating multiple processes at scale – and will become core to digital transformation initiatives in 2021.
- Businesses Will Put “Automation Targets” in Place
2020 was the year that many businesses started seeing some broad and tangible benefits from their automation initiatives. Automation was one of the big winners of the year, as many businesses took extra steps to take humans out of processes – particularly those humans that had to be in a specific location, such as a warehouse, the finance team, the front desk and so on (because of the pandemic, they were often working at home instead). Senior management is seeing the benefits of automation, and they will start to ask their teams why more processes are not automated Therefore we will start to see managers put targets around a certain percentage of tasks automated in an area – e.g. 70% of contact centre processes will be automated, 90% of the digital customer experience for a certain outcome will be automated and so on. Achieving these numbers may not be easy, but the targets will change the mindset of people designing, implementing, and improving processes.


Join this exclusive C-level virtual discussion, where alongside a handpicked gathering of your peers we will discuss:
- How application modernisation will have an immediate and long-term impact on your business
- Ensuring that app deployment and modernisation happens in a fast and agile manner by leveraging hybrid cloud environments
- Modernising technology implementations through APIs and containerisation
There has been a heightened interest in the cloud in EMEA in recent times, triggered by several regional and country level announcements.
The European Union (EU) founded the GAIA-X Foundation to build a unified system of cloud and data services to be protected by EU Laws – including GDPR, the free flow of non-personal data regulation and the Cybersecurity Act. France and Germany kicked off the GAIA-X cloud project last year and the system is open for participation to national and European initiatives for exchange of data across industries and services such as AI, IoT and data analytics. GAIA-X took another step towards becoming a real option for European organisations with the establishment as a legal entity in June. Founding members of GAIA-X include Atos, Bosch, BMW, Deutsche Telekom, EDF, German Edge Cloud, Orange, OVHcloud, SAP, and Siemens. Non-European providers, such as AWS, Microsoft, Google, and IBM will also have the opportunity to join GAIA-X. The UK Crown Commercial Service (CCS) has also been entering into agreements with public cloud platform providers to encourage increased cloud adoption in cash-strapped public sector organisations. It is a good time to evaluate organisations’ perception on cloud and their adoption patterns.
Ecosystm research finds that while most organisations have migrated at least some simple workloads to the cloud, the sophistication of these systems ranges from SaaS deployed as shadow IT, all the way up to cloud-native applications that are core to a digital business strategy. When asked about the maturity of their cloud deployments, 36% of organisations in EMEA consider themselves advanced, leaving the remaining 64% with more basic environments. These figures vary by business size with only 31% of SMEs considering their deployments advanced, rising to 40% for large enterprises.
Cloud technology providers should segment the market according to the maturity of their client’s systems. Those in the early stages of modernising their infrastructure will be seeking different benefits and will have different concerns than those already using cloud to underpin their digital transformation.
In the mature economies in the region, 75% of those with advanced deployments, considered improved service levels and agility as a key benefit of cloud. These organisations have moved beyond simply replacing legacy systems with cloud infrastructure and now look to the IT department to provide a platform on which new, client-facing services can be delivered. In the emerging economies, the most-reported benefits of cloud are flexibility and scalability, and standardised systems, both at 68% of respondents. These could be viewed as benefits expected from organisations not as far along in the cloud journey. The benefit of reduced IT costs was important in both mature EMEA (67%) and emerging EMEA (62%).
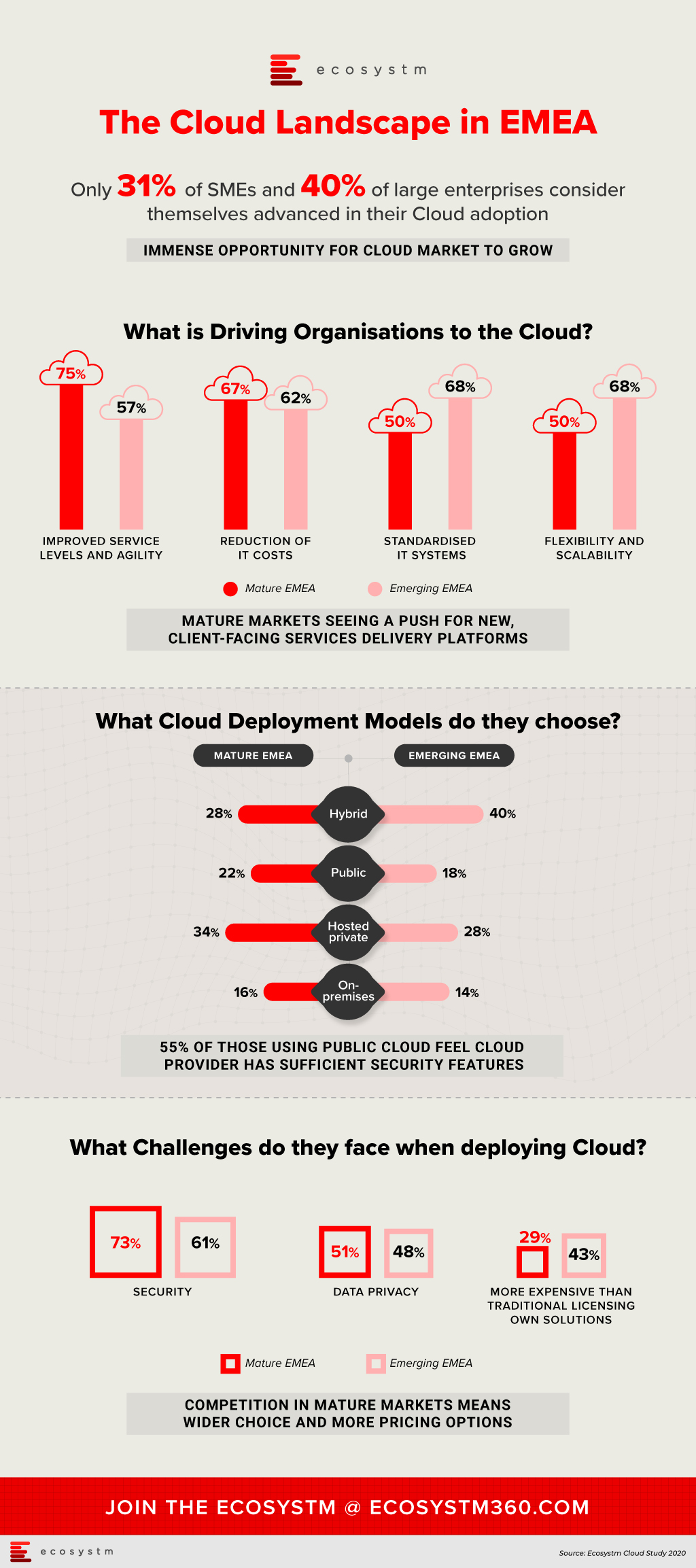
Looking at those who consider their cloud deployments as still basic, security is the leading challenge to greater adoption and by a large margin. Of those respondents in mature EMEA, 73% cited security as a key challenge, more than 20 percentage points higher than the next greatest difficulty. In emerging EMEA, a similar trend was evident, with 61% of respondents considering security as a key challenge. Moreover, data privacy is the second-most significant concern for those who do not consider their cloud deployments advanced. This was visible in both mature EMEA (51%) and emerging EMEA (48%). As organisations look to shift more critical workloads to the cloud, they will be increasing their attack surfaces and at the same time will face greater consequences if a breach does occur.
Services providers targeting organisations with less developed cloud environments should include security early in the conversation to push them along to the next stage of maturity.
The challenge that varied most according to market maturity and business size was the concern that cloud-based services were more expensive that traditional licencing or in-house solutions. Only 29% of respondents with basic cloud deployments in the mature economies, held this view, while in emerging economies the figure rose to 43%. Competition in those mature markets has in some cases put pressure on prices or at least resulted in wider choice. While 29% of SME respondents considered cost a key challenge, 41% of large enterprises did. Migrating larger, more complex environments to cloud will be viewed as more costly than the status quo due to organisational inertia.
The perception that cloud can be more costly, provides an opportunity for cloud management including expense optimisation services.
Organisations looking to move from a basic cloud environment to one that adopts a cloud-first model should begin with a maturity assessment. Understand what your systems will look like at the next stage, what the benefits will be, and what are the risks. More importantly, decide on the long-term business goal that you are trying to achieve, particularly how IT can be a critical player in the organisation’s digital strategy.
Note: Mature economies – France, Germany and the UK/ Emerging economies – Middle Eastern countries, Russia and South AfricaIdentify emerging cloud computing trends that can help you drive digital business decision making, vendor and technology platform selection and investment strategies.Gain access to more insights from the Ecosystm Cloud Study.

The pandemic crisis has rapidly accelerated digitalisation across all industries. Organisations have been forced to digitalise entire processes more rapidly, as face-to-face engagement becomes restricted or even impossible.
The most visible areas where face-to-face activity is being swiftly replaced by digital alternatives include conferencing and collaboration, and the use of digital channels to engage with customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders.
For example, the crisis has made it difficult – even impossible, sometimes – for contact centre agents to physically work in contact centres, and they often do not have the tools to work effectively from home. This challenge is particularly apparent for offshore contact centres in the Philippines and India. The creation of chatbots has reduced the need for customer service staff and enabled data to by entered into front-office systems, and analysed immediately.
Less visible are back-office processes which are commonly inefficient and labour-intensive. Remote working makes some back-office workflows challenging or impossible. For example, some essential finance and accounting workflows involve a mix of digital communications, printing, scanning, copying and storage of physical documents – making these workflows inefficient, difficult to scale and labour-intensive. This has been highlighted during the pandemic. RPA adoption has grown faster than expected as organisations seek to resolve these and other challenges – often caused by inefficient workflows being scrambled by the crisis.
The RPA Market in Asia Pacific
There are many definitions of the RPA market, but it can broadly be defined as the use of software bots to execute processes which involve high volumes of repeatable tasks, that were previously executed by humans. When processes are automated, the physical location of employees and other stakeholders becomes less important. RPA makes these processes more agile and flexible and makes businesses more resilient. It can also increase operational efficiency, drive business growth, and enhance customer and employee experience.
RPA is a comparatively new and fast-growing market – this is leading to rapid change. In its infancy, it was basically the digitalisation of BPO. It was viewed as a way of automating repetitive tasks, many of which had been outsourced. While its cost saving benefits remain important as with BPOs, customers are now seeking more. They want RPA to help them to improve or transform front-office, back-office and industry-specific processes throughout the organisation. RPA vendors are addressing these enhanced requirements by blending RPA with AI and re-branding their offerings as intelligent automation or hyper-automation.
Asia Pacific organisations have been relatively slow to adopt RPA, but this is changing fast. The findings of the Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal study show that in the next 12 months, organisations will continue to focus on digital technologies for process automation (Figure 1).

The market is growing rapidly with large global RPA specialists such as UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism and AntWorks experiencing high rates of growth in the region.
RPA vendors in Asia Pacific, are typically addressing immediate, short-term requirements. For example, healthcare companies are automating the reporting of COVID-19 tests and ordering supplies. Chatbots are being widely used to address unprecedented call centre volumes for airlines, travel companies, banks and telecom providers. Administrative tasks increasingly require automation as workflows become disrupted by remote working.
Companies can also be expected to scale their current deployments and increase the rate at which AI capabilities are integrated into their offerings
RPA often works in conjunction with major software products provided by companies such as Salesforce, SAP, Microsoft and IBM. For example, some invoicing processes involve the use of Salesforce, SAP and Microsoft products. Rather than having an operative enter data into multiple systems, a bot can be created to do this.
Large software vendors such as IBM, Microsoft, Salesforce and SAP are taking advantage of this opportunity by trying to own entire workflows. They are increasingly integrating RPA into their offerings as well as competing directly in the RPA market with pureplay RPA vendors. RPA may soon be integrated into larger enterprise applications, unless pureplay RPA vendors can innovate and continually differentiate their offerings.

As organisations come to terms with the “new normal”, technology companies are presenting unique offerings to help them tide over the situation and lead them towards economic and social recovery. These companies are also leading from the front and demonstrating how to transform with agility and pace – evolving their business and delivery models.
Organisations are dependent on digital technologies more than ever before. In 2020, we have already seen unprecedented and rapid adoption of technologies such as audio and video conferencing, collaboration tools to engage with employees and clients, contactless services, and AI/automation. This will have a wider impact on the technology industry, community, and redefining the workplace of the future.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Tim Sheedy hosted a virtual roundtable with business leaders from some of the world’s largest technology service providers to discuss how they managed the challenges during the pandemic; and the measures they implemented to support not only their business operations and working environment, but also to help their customers negotiate these difficult times.
The Role of Technology During the COVID-19 Crisis
When the COVID-19 crisis hit, IT teams found themselves largely unprepared. Ecosystm research finds that only 9% of organisations considered their IT fully prepared for the changes that had to be implemented (Figure 1). More than a third did not have the right technology solutions and 41% were unprepared for the scale of the changes required and the capacity to extend the existing technology to meet client and employee needs. 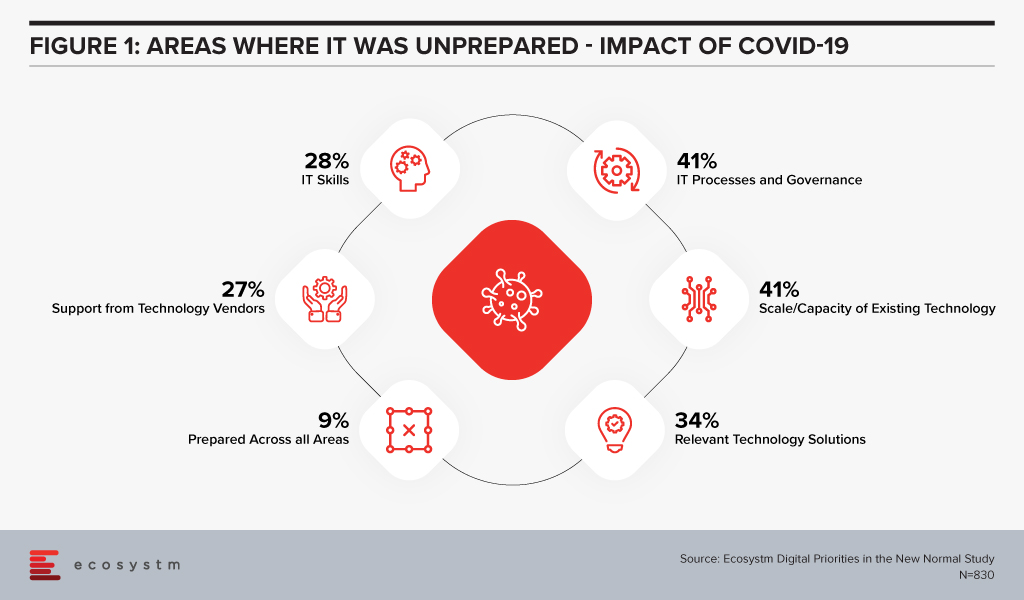
While 27% of organisations felt that they needed more support from their IT provider, further questioning reveals that only 4% switched technology providers for better support during these difficult times. Organisations are looking to their technology partners for guidance, as they negotiate the new normal.
Here are some of the discussion points that emerged in the conversation with the technology providers.
Business Continuity Planning is Still Evolving
One of the early impacts on businesses was due to their dependence on outsourced services and offshore models. Several concerns emerged – how could their provider continue to operate offsite; would they be able to access the network remotely; how should fully remote teams be managed and so on. In addition to this, there were other challenges such as supply chain disruptions and a sudden change in business. Even technology providers felt that they were navigating uncharted territory.
“Remote project delivery is not new, it’s been going on for a few years; but I think that there’s been a lot of non-believers out there. This experience has moved a lot of those non-believers to the believer category. A lot of our delivery can be done from home – think of the savings of time and money that can be realised through this.” – Andrew Campbell, Partner Asia Pacific for Talent and Transformation, IBM
Moreover, the rising workload and client expectation has led businesses to move towards exploring automation and AI.
“The thing that is changing now is, when we approach a new opportunity or an existing customer with a new requirement, we look at using automation. Typically, when you go in to design a solution you always think of the human aspect. We’re working very hard to move our thinking to automation first and then supplementing it with the human side as a backup.” – Michael Horton, Executive VP, ANZ, HCL Technologies
Data has become paramount in this time of crisis. The right use of data is helping organisations fulfil customer requirements, enhance their experience, and optimise services and products.
“Those organisations that have a good understanding of the data within their business, and how that data can be used to understand the impact on their business, are starting to have much better clarity on future requirements.” – Peter Lawther, Oceania Regional Technology Officer, Fujitsu
Organisations should take the learnings from managing this situation to keep evolving their business continuity plans – keeping in mind individual business needs and growth and business strategies.
Having the Right Infrastructure Means Employees are Productive
The lockdown and social distancing measures forced organisations to focus on the infrastructure that can support their remote and hybrid work environment.
“Before the pandemic around 20-30% of our staff logged on to a VPN, but with remote working, all of a sudden, we were at 90%.” – Lawther
The adoption of digital tools and online infrastructure led businesses to re-think how they were delivering their services. While some organisations had the tools, governance and the protocols in place, there is still a long way to go for organisations to solve their infrastructure and networking challenges.
“It gets down to the quality of the equipment that the staff use – which ranges from decent laptops, phones, and network connections. If you don’t have that now, people cannot work effectively.” – Horton
Several of these organisations, focused on ergonomics as well, when evaluating their employees’ infrastructural needs when working from home. This extra focus on infrastructural needs – with the employees firmly on their mind – ensured that there was minimal impact on delivery.
Caring for Your People is More Important than Ever
The pandemic has changed the way people work, socialise, and interact. While this appears to have become the new norm, adjusting to it can create emotional stress. Simultaneously, as organisations focus on survival and recovery, workloads have increased. Employees are working extended hours, without taking adequate hours. There is an immediate need to involve organisations’ HR practices in evaluating the emotional well-being of employees and finding better ways to engage with remote staff, to reduce stress.
“A key aspect of handling the crisis has been empathy, transparency and engagement with employees. In a business environment, we have all sorts of teams, cultures, clients, and so on. The common thread in this model is that everyone’s just become a lot friendlier, more empathic, more transparent.” – Sumit Nurpuri, COO, SE Asia Hong Kong and Taiwan, Capgemini
Organisations will have to be innovative in the way they manage these people challenges. For example, a common problem that has emerged is employees attending meetings, with interruptions from family, especially children.
“One of the things that we did as a part of our team meetings is that we assigned tasks to children at the beginning of the call and in the last few minutes, the children presented back to the teams on what they’ve been up to. It was a mechanism for us to make sure that we were involving our staff and understanding their current situation – and trying to make it as easy for them to work, as possible.” – Lawther
Taking the Opportunity to Drive Positive Outcomes
The other aspect businesses are trying to overcome is meeting the rising expectations of clients. This has led them to focus on skills training, mostly delivered through e-learning platforms. Organisations find that this has translated into increased employee performance and a future-ready workforce.
The crisis disrupted economies and societies across the globe, with business and industry coming to a standstill in most countries. Unexpected business benefits emerged from the necessity to comply with country regulations. By and large, employees have been more productive. Also, many organisations re-evaluated their commercial property requirements and many were able to reduce expenses on office rentals (for many this will not be immediate, but there is a future potentiality). Similarly, there were other areas where businesses saw reduced expenses – operational costs such as equipment maintenance and travel expenses.
“When you start global projects and global implementations, you typically do some kind of global design work and maybe fly in people from all over the world, typically to a centralised location. This has changed to virtual meetings and collaborative interactions on online global design. The amount of time and money that was saved – that would typically be spent on people traveling to manage these global design workshops – was great” – Campbell
Most organisations, across industries, will have to make considerable changes to their IT environment. The Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal study finds that 70% expect considerable to significant changes to their IT environment, going forward. Technology providers will remain a significant partner in organisations’ journey to transformation, recovery and success.