In this edition of Ecosystm RNx – an objective vendor ranking based on in-depth, quantified ratings from technology decision-makers on the Ecosystm platform – we rank the Top 10 Global Cybersecurity Vendors.
If you are an End User, you are having to re-evaluate your Cybersecurity risks and measures as both solution capabilities and the threat landscape become more complex. In a fragmented market, it is difficult to select the right Cybersecurity partner to safeguard your organisation. This vendor ranking will help you evaluate your buying decisions based on key evaluation ratings by your peers across a number of key metrics and benchmarks, including customer experience.
If you are Cybersecurity Vendor, you are aware that end users are looking more for Cybersecurity services than solutions – this is an opportunity to understand how your customers rate you on capabilities and their overall customer experience.

Ecosystm RNx is an objective vendor ranking based on in-depth, quantified ratings from technology decision-makers on the Ecosystm platform. In this edition, we rank the Top 10 Global AI & Automation Vendors.
If you are an End-User, you are realising that the right investments in Data & AI now will be the key to your future success. This vendor ranking will help you evaluate your buying decisions based on key evaluation ratings by your peers across a number of key metrics and benchmarks, including customer experience.
If you are an AI & Automation Vendor, it’s an opportunity to understand how your customers rate you on capabilities and their overall customer experience.

In this first edition of Ecosystm RNx we rank the Top 10 Global Cloud Vendors.
Ecosystm RNx is an objective vendor ranking based on in-depth and quantified ratings from technology decision-makers on the Ecosystm platform.
If you are an technology user, this Cloud Vendor ranking will help you evaluate your buying decisions based on key evaluation ratings by your peers across a number of key metrics and benchmarks, including customer experience.
If you are a Cloud Vendor, this is an opportunity to understand how your customers rate you on capabilities and their overall customer experience.

Industries continue to innovate and disrupt to create and maintain a competitive edge – and their technology partners evolve their solution offerings to empower them.
We bring to you latest industry news from the Healthcare, Financial Services, Retail, Travel & Hospitality and Entertainment & Media industries to show you how organisations are leveraging technology. Find out more about organisations such as Services Australia, Paypal, Walmart, Zara and Amex – and how tech providers such as IBM, Oracle, Google and Uplift are supporting organisations across industries.
View the latest Ecosystm Bytes on Industries of the Future below, and reach out to our experts if you have questions.
For more ‘byte sized’ insights click on the link below

Two weeks ago, Michael Dell made the big announcement that Dell Technologies would spin off their shareholding in VMware, leading to a share price spike for both companies. A lot has already been written about the move – we would like to highlight a market-based view which we feel will be significant for the two companies going forward.
First let us break down the facts around the deal:
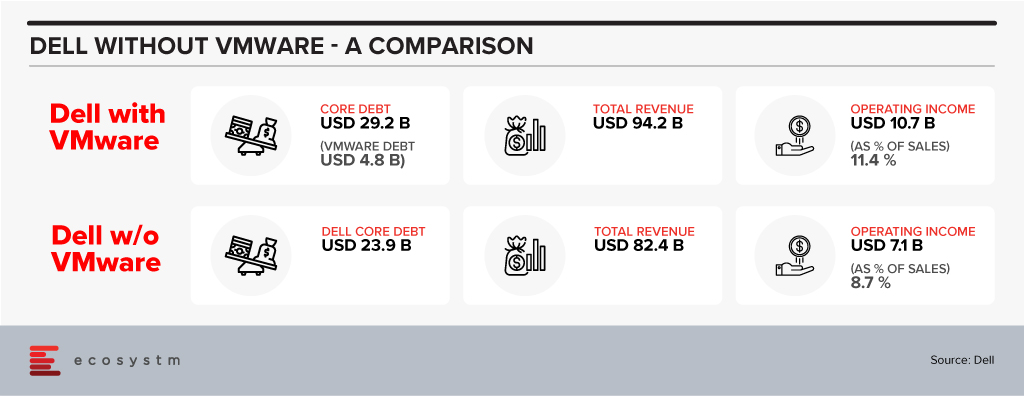
As has been analysed threadbare the deal reduces the total debt Dell is carrying and will even reduce the ratio of Dell debt to EBITDA. As a result, it is highly likely that Dell’s credit rating will move up from their current BB+ level to investment grade – which can have a lot of implications for future capital raising. There is also a buzz in the market that Dell Technologies may also sell off Boomi soon and write down another USD 3 Billion approximately in debt.
It is interesting to note that the company has been willing to let go off VMware even though it will dilute their profitability ratios – VMWare business being obviously more profitable than Dell’s traditional businesses which are heavily based on products.
The last few years has seen Dell reselling a fair amount of VMware products. From a number of perspectives Dell has been a key reseller for VMware and now contributes almost 34% of VMware’s revenues.
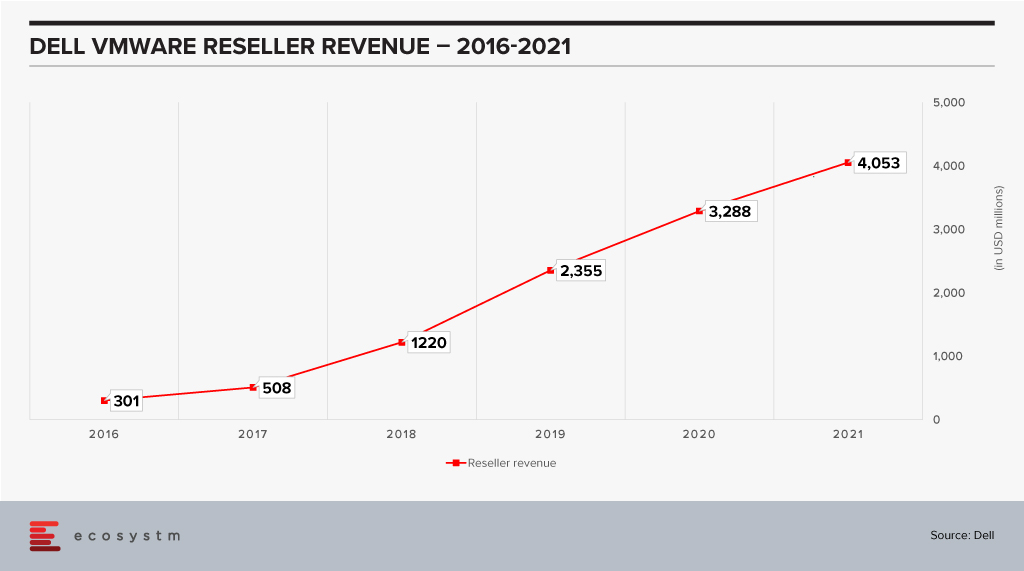
This chart is a testament to the power of execution that is inherent within Dell. This performance was aided by market growth – but even then it is remarkable how Dell has been able to scale up taking VMware to their customers. The two companies have very different sales cycles. A VMware sale typically has a longer cycle with a completely different set of touchpoints from the boxes that Dell is so good at selling – which have shorter cycles. The sales cycle for EMC products is closer to VMware’s which would have helped. The sales of the VXRail hyperconverged appliance have also jumped in recent times and this would have driven an equivalent spike in VMware revenues. It is still a remarkable achievement to be able to bring these three diverse groups together and grow revenue.
Market Impact of the Spin-Off
Does it make sense then for VMware to part with their largest reseller? Would it not be better for VMware to continue to drive this and use Dell’s execution skills to drive more growth? Data suggests that there could be another twist to this story.
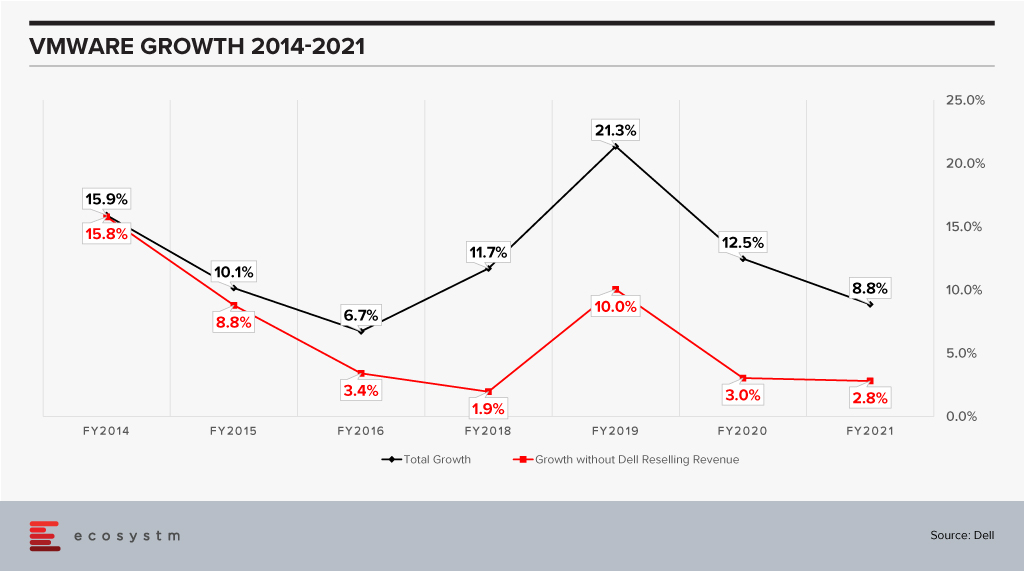
VMware has been growing impressively as a company when one looks at the black line and while the growth has slowed in percentage terms, this is on a much higher revenue base. FY2021 revenue is close to 2x the revenue in FY2014. However, when one considers it without the Dell reselling revenue (the red line) it looks a lot less impressive especially in the last couple of years when it is an anemic 3%. When comparing this growth we also see a slowdown of sorts in recent years for VMware.
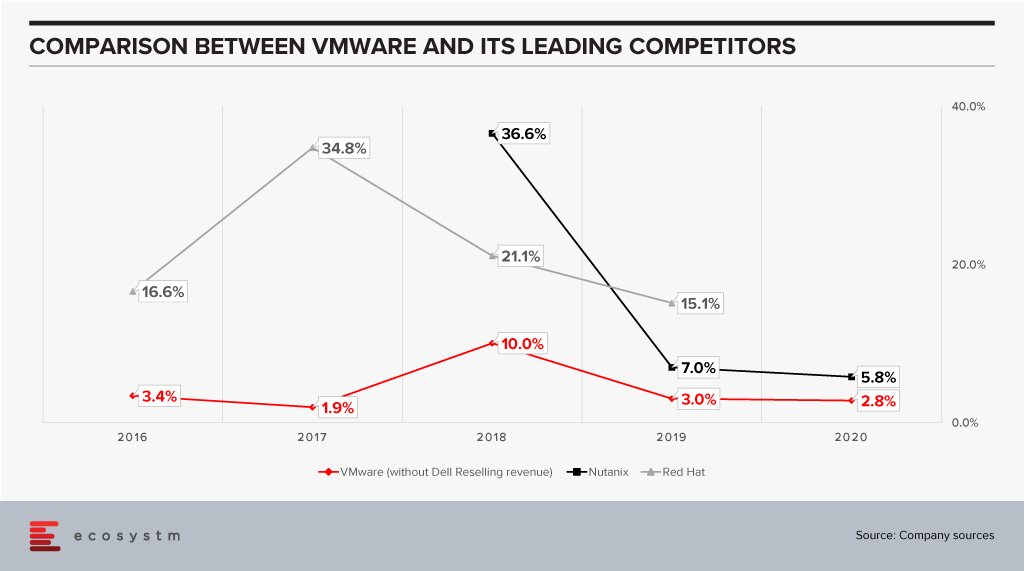
Til Dell acquired EMC – and VMware in consequence – they were working closely with other vendors such as Nutanix and driving solid growth for them. As they pivoted to doing more with VMware, did this then mean that other vendors – of either bare metal or cloud – drifted away from VMware?
Anecdotal evidence suggests that vendors such as HPE became more cautious and tried to diversify their business. It is entirely possible that if we looked at VMware as two separate businesses – one with Dell and one independent – the independent business has been losing share in the last few years.
The optical separation from Dell may then help VMware in rebuilding stronger relationships with the other players in the market including the hyperscalers. This may fuel further VMware growth. To do that VMware will have to manage a balancing act:
- On the one hand keep growing their reseller revenue with Dell. They are on a good wicket so far and need to make sure this continues. While the revenue from appliances – which come loaded with VMware – is a sure-fire proposition, other growth needs to be harvested carefully. Dell has a multitude of offerings and taking their eyes of the VMware ball is super easy.
- Build trust and closer ties with the other vendors to keep driving revenue. VMware’s leadership in the market means they already have ties with other industry leaders like HPE, AWS and so on. These will need to become much deeper; VMware will need to build the trust that they will give these vendors equal status even as they are building new appliances with Dell.
The one complicating factor here is that Michael Dell remains the Chairman of the Board of VMware. This may give other vendors pause and they may still want to keep their options open instead of putting all eggs into the VMware basket.
Ecosystm Comments
VMware is at a fairly critical inflection point in their business. The growth of cloud technologies still bodes well for virtual machines which has been their mainstay, but this is also likely to drive growth for more containerisation. They have great products for that part of the business also. However, as container adoption is likely to explode VMware would not want vendors to shift, to say Red Hat, and develop deeper partnerships with them or other competitors. They would like to keep the vendors on VMware – be it a virtual machine or a container. One does feel the future battle for VMware really rests on how well they will be able to grow in the container space. This will have to be done while continuing to innovate to keep the lead in the virtual machine space. Doing it will be quite a feat!!
Finally, what then of Dell? The company seems to have a talent for running businesses which are in long-term secular decline – but running those businesses well. Their PC business is delivering almost 7% operating income and has continued to show growth. The PC market last year was on fire thanks to the pandemic which dramatically increased the demand for devices – growth was double digits for a market which has declined almost every year since 2011. As Dell is fond of saying the PC industry has sold over 5 billion machines since the PC was declared dead!
The server market seems to have stagnated over the last couple of years which is a bit of a surprise given the growth in cloud. Dell’s revenue has declined two years in a row pointing to possible issues which need fixing in that part of the business.
As the company focuses on these key challenges in the market it probably makes sense for them to lower their debt and earn more freedom to operate. One never knows – given the number of surprises that Michael Dell has engineered over the last decade such as taking Dell private, acquiring EMC, stabilising it, then going public again, making a windfall in the process – if he has some other rabbits yet to be pulled out of his hat!!!
Access insights on adoption of key Cloud solutions in regions/countries and industries. Insights include drivers and inhibitors of adoption, budget allocation, and preferred implementation partners.

ServiceNow announced their intention to acquire robotic process automation (RPA) provider, Intellibot, for an undisclosed sum. Intellibot is a significant tier 2 player in the RPA market, that is rapidly consolidating into the hands of the big three – UiPath, Automation Everywhere, and Blue Prism – and other acquisition-hungry software providers. This is unlikely to be the last RPA acquisition that we see this year with smaller players looking to either go niche or sell out while the market is hot.
Expanding AI/Automation Capabilities
Intellibot is the latest in a string of purchases by ServiceNow that reveals their intention to embed AI and machine learning into offerings. In 2020, they acquired Loom Systems, Passage AI (both January), Sweagle (June), and Element AI (November) in addition to Attivio in 2019. These acquisitions were integrated into the latest version of their Now Platform, code-named Quebec, which was launched earlier this month. As a result, Predictive AIOps and AI Search were newly added to the platform while the low-code tools were expanded upon and became Creator Workflows. This means ServiceNow now offers four primary solutions – IT Workflows, Employee Workflows, Customer Workflows, and Creator Workflows – demonstrating the importance they are placing on low-code and RPA.
ServiceNow was quick to remind the market that although they will be able to offer RPA functionality natively once Intellibot is integrated into their platform, they are still willing to work with competitors. They specifically highlighted that they would continue partnering with UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism, suggesting they plan to use RPA as a complementary technology to their current offerings rather than going head-to-head with the Big Three. Only a month ago, UiPath announced deeper integration with ServiceNow, by expanding automation capabilities for Test Management 2.0 and Agile Development projects.
Expansion in India
The acquisition of Intellibot, based in Hyderabad, is part of ServiceNow’s expansion strategy in India – one of their fastest growing markets. The country is already home to their largest R&D centre outside of the US and they intend to launch a couple of data centres there by March 2022. The company plans to double their local staff levels by 2024, having already tripled the number of employees there in the last two years. The expansion in India means they can increasingly offer services from there to global customers.
Market Consolidation Accelerates
In the Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 AI & AUTOMATION Trends for 2021, Ecosystm had talked about technology vendors adding RPA functionality either organically or through acquisitions, this year.
“Buyers will find that many of the automation capabilities that they currently purchase separately will increasingly be integrated in their enterprise applications. This will resolve integration challenges and will be more cost-effective.”
ServiceNow’s purchase is one of several recent examples of low-code vendors acquiring their way into the RPA space. Last year, Appian acquired Novayre Solutions for their Jidoka product and Microsoft snapped up Softomotive. Speculation continues to build that Salesforce could also be assessing RPA targets. Considering RPA market leader, UiPath recently announced that their Series F funding round values the company at USD 35 billion, there is pressure on acquirers to gobble up the remaining smaller players before they are all gone or become prohibitively expensive.
The cloud hyperscalers are also likely to play a growing role in the RPA market over the next year. Microsoft and IBM have already entered the market, coming from the angle of office productivity and business process management (BPM), respectively. Google announced just last week that they will work closely with Automation Anywhere to integrate RPA into their cloud offerings, such as Apigee, AppSheet, and AI Platform. More interestingly, they plan to co-develop new solutions, which might for now satisfy Google’s appetite for RPA rather than requiring an acquisition.
Here are some of the trends to watch for RPA, AI and Automation in 2021. Signup for Free to download Ecosystm’s Top 5 AI & Automation Trends Report.

This week at Microsoft Ignite, there was a heavy emphasis on RPA and low code as the tools it sees as the future of productivity. It used its annual conference for developers and IT professionals to make a slew of announcements about its Power Platform. Most notable is that from this week, Power Automate Desktop will be bundled with Microsoft Windows and is available as a free download. This marks a major step in the direction of mass adoption of RPA.
By Microsoft’s estimates, 50% of tasks carried out by information workers could be automated by currently available technology but are instead performed manually. Moreover, 500 million apps will need to be built by 2026, more than were developed in the last 40 years. Slowing down the pace of automation and the roll out of apps to enable digital business, is the skills gap, with a shortage of 1 million developers in the US alone. This is of course why Microsoft is betting on RPA and low code tools to empower citizen developers to do it themselves.
Microsoft was arguably slow to focus on RPA and low code considering its breadth of applications and good standing with developers. It only announced the general availability of UI Flows in Power Automate less than a year ago. Moreover, its automation suite worked best in the Microsoft universe but had limited interoperability with third-party tools. In May 2020, it acquired Softomotive, which signalled that it was taking RPA seriously and was willing to expand beyond the automation of its own software. By then, acquiring one of the big three – UiPath, Automation Anywhere, or Blue Prism – would have been excessively costly but Softomotive ensured it had both attended and unattended RPA capabilities to build upon. Softomotive’s WinAutomation remerged as Power Automate Desktop in September and with this week’s announcement, it becomes a native component in Windows.
By providing Power Automate Desktop for free with Windows, Microsoft appears to be attempting to generate interest from users who may not have previously been exposed to RPA. For the widespread adoption of RPA beyond just functions like finance, HR, and procurement, these tools need to be put into the hands of average users that can find their own use cases. Eventually, some of these basic users will need more advanced functionality available in the cloud-based version of Power Automate. Microsoft has a range of pricing plans including per user, per flow, with AI Builder, and unattended RPA.
Security and Governance
While making free desktop-based automation available to all, may be an effective means of raising the profile of RPA, Microsoft realises that it must provide IT and security teams with tools for control. It also announced this week additional features, such as:
- Endpoint filtering to turn on selected connections but with restrictions
- Connector action controls, e.g. allowing read permission but not write in some connectors
- Tenant isolation to provide differentiated access to connectors according to business unit
- Usage dashboards
Power Fx – Microsoft’s Low Code Language
Microsoft is one of the best-placed vendors to address the needs of citizen developers; bringing together its dominance as a productivity software provider and an important part of the developer ecosystem. This week it also introduced Power Fx, a low-code programming language based on Microsoft Excel. The logic of this new, simple language should be familiar to the millions of spreadsheet users. Power Fx provides more advanced citizen developers with a bridge from the drag-and-drop features of the Power Platform to low-code development.
Is 2021 the year RPA finally goes mainstream?
Microsoft’s announcements this week are one of many signs in the last few months that the RPA market is on its way to gaining mainstream acceptance. Also garnering attention was the lofty valuation given to the market leader, UiPath, this year. It recently announced that in its Series F funding round, it closed at $750M, valuing the company at $35B. This is hot on the heels of confirmation that it plans to IPO, probably in the first half of 2021. Last year was also a rapid period of consolidation, with Appian, IBM, and Microsoft all making RPA acquisitions. It seems highly likely that in the next few months we could see acquisitions or RPA launches by some of the cloud and application vendors that have until now been waiting to see the technology mature.
How will RPA be a part of your automation strategy in 2021? The Top 5 AI & Automation Trends for 2021 are available for download from the Ecosystm platform. Signup for Free to download the report.