The COVID-19 pandemic has presented us with a set of circumstances that we have never seen before – health, safety, and economic livelihoods are being affected. Companies are being asked to take on roles that they are not familiar with. The global situation continues to evolve rapidly, and we are all having to adapt as we go. During this time, the expectations of customers and employees are evolving in tandem. Companies should look at understanding this evolution and take fuller advantage of the opportunity this evolution will present.
CX at the Centre Stage
Customers have always been the top priority for businesses. In the last few years, we have seen the transition that organisations are making from selling to creating; evolving from selling products to solutions to experiences. This has led to reframing of the selling methodology and, consequently, the technology and people skills needed to make that happen.
While companies have been able to understand the need to make this shift intellectually, it needs to be backed by the right investments in their people and customers. However, industry estimates find that only about 10% of organisations put money where their mouth is. Those that have been able to do so, have been consistently able to meet and exceed their goals.
As such, investments in customer experience (CX) technology is taking centre stage. Ecosystm research finds that improving CX has been the top business priority for organisations, before COVID-19 (Figure 1).
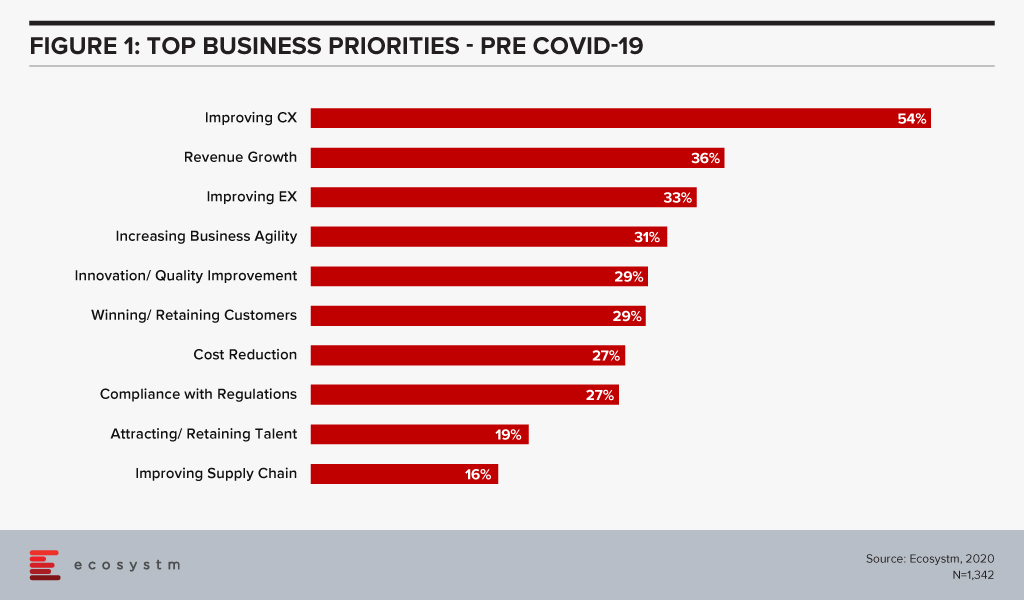
If we take a deeper dive into CX, it becomes clear that CX is not just about good sales skills or customer service. It is about the overall experience of the customer from start to post-purchase. Customers are focussed on not just what they are buying but also on how they are treated along their entire journey. Good CX has consistently shown to help increase price premium, impulse buying and loyalty. Consequently, one bad experience can drive a customer away forever.
So, what does improving CX look like? A vast majority would think technology. That is only part of the story; the key component of making your CX strategy come to life is your people. Customers pay for your products or services, but it is your people who can really deliver the experience. Glassdoor research shows that there is a clear link between employee and customer satisfaction. On an average, a 1-point increase in company rating on Glassdoor is associated with a 1.3-point increase in customer satisfaction, measured by the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI).
So, the fact that only 33% prioritise employee experience (EX) (Figure 1) shows a gap in understanding how to achieve excellent CX. In this gap lies the true opportunity of gaining sustainable competitive advantage.
Reset During COVID-19
Due to COVID-19 all of us have had to re look at who we are and how we operate. It has really changed the world of work and business, almost overnight. Companies have invested a significant amount of time on just enabling their employees to stay safe and work from home. Overnight, access to physical offices was gone and everyone was transitioned to digital workspaces.
The Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal study, that was initiated to gauge the immediate and longer term impact of the pandemic finds that during the crisis, the focus on employees increased drastically, with 75% of organisations introducing measures to manage their employees, while 30% focused more on their customers.
This is a complete reversal in the focus of the organisations. Employees have come into sharper focus. This should be good news. Yes, it is – but partly so.
Initial focus has been rightly on safety and on employees being able to work from home. This was an “adapt” mode, focussed on services like payroll, handling employee queries and onboarding without disruption. After the initial crisis-handling, organisations have been able to focus on digital learning and skills enhancement, while others have been trying to increase productivity (predominantly through giving access to collaboration tools).
The Journey Ahead
As we continue to work in the new normal, one thing comes out even stronger: the new experience needs to be seamlessly connected between all channels – and be agile and more human. It is now even more evident that organisations and people – that are its lifeblood – need to constantly adapt and pivot to meet these changing landscapes.
Customer expectations have evolved in the last few months from a cost and product view, to being loyal to companies that show more empathy and are able to solve their problems. Employee expectations have also evolved, simultaneously – and it now goes beyond a good pantry and an engaging, fun-loving environment. Employees today value connectedness, and expect the organisation to show more care (so they can do their work effectively), and create opportunities for them to grow (job security) as they continue to grapple with the situation.
Thus, the more relevant the EX product and the faster it can adapt to the evolving situation, the better it translates into better engagement and loyalty. But what will definitely be required of organisations, is a continued focus on their employees. If we compare the business priorities before and after COVID-19, we get an indication that EX might once again be left behind in organisations’ obsession about their customers (Figure 2).
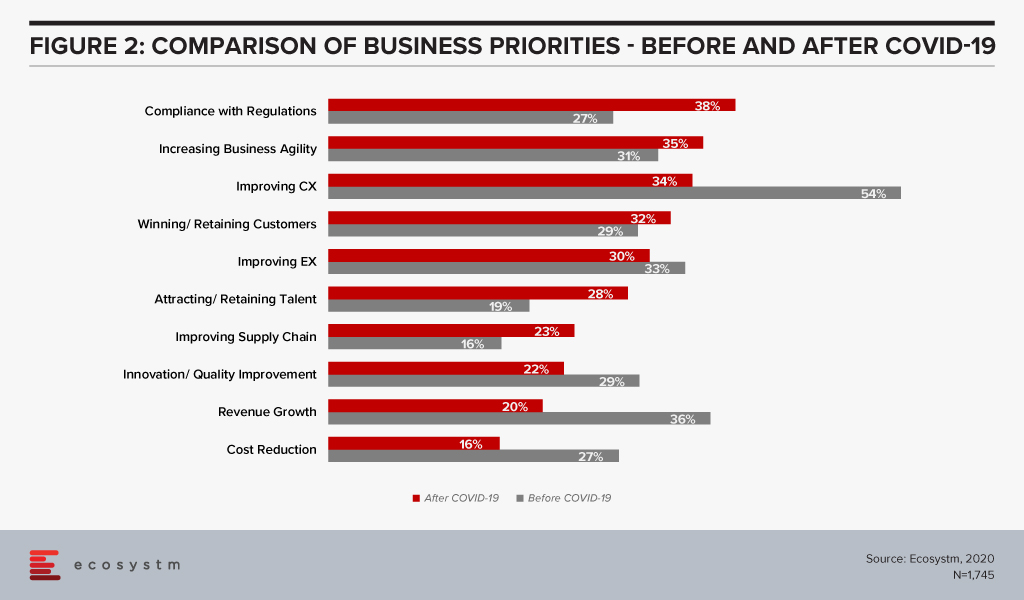
The gap is not as wide as before COVID-19 hit us – but there appears to be a shift towards a customer focus. This is evolving differently from our expectations and can potentially cause a misalignment.
Opportunity to Reshape
The reset has pushed EX and CX expectations closer to each other when it comes to designing experience with the company. The opportunity lies in taking a more holistic view of the company business – bringing HR, IT, Customer Success and Marketing teams together into agile tribes and guilds – to design a consistent CX by improving EX.
This would help to increase the speed of prototyping new experiences, and consequently drive greater visibility of what is needed – from skills to IT systems. Overall, it will drive a greater degree of connectedness between the employee and customer worlds; resulting in better engagement and loyalty.

Organisations are on a fast track to digitalisation. The Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal study finds that 60% of organisations anticipate increased use of digital technologies for process automation, even after the COVID-19 restrictions are lifted. One of the key challenges that these organisations will face is the lack of internal digital skills – especially in emerging technologies. One of the success metrics of any technology adoption is employee uptake. Without the necessary skills or understanding of the benefits of emerging technology, employees will largely shy away from digital offerings, even the ones that will make their work more efficient and their lives easier.
Organisations are realising the value of making their workforce future ready.
DBS Instilling Company-Wide Digital Culture
Far-sighted companies are collaborating with technology vendors and professional training providers to promote tech awareness and education to futureproof their workforce. DBS Bank in Singapore has collaborated with AWS to train and upskill 3,000 employees – including the leadership team – with AI and machine learning skills through gamification in a DBS x AWS DeepRacer League.
The AWS DeepRacer Leagues have been previously organised in several parts of the world, but the DBS x AWS DeepRacer will be the first to be organised at this scale. The league will enable DBS employees to get their hands-on AI and machine learning tutorials online. They will then have the opportunity to test out their new skills in programming a 3D racing simulator and iteratively fine-tune their models and compete with each other. The learning program is entirely cloud-based and aims to ingrain digital skills in the workforce.
DBS has won several accolades for their digital transformation and innovation initiatives, and they continue to experiment with emerging technologies. In 2019, DBS digitalised and simplified end-to-end credit processing, setting the foundation for advanced credit risk management using data analytics and machine learning. They have also deployed an AI-powered engine for self-service digital options to its retail banking customers. Taking their employees along with them on this journey is a wise move.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Ravi Bhogaraju says, “With the increasing use of automation, AI and machine learning, the nature of work and businesses is transforming rapidly. This is creating opportunities for processes to be automated and increasing the use of AI and Deep Learning into the business processes of the organisation. Industry value chains are transforming – AI and machine learning is adding automation, analytics and predictive intelligence to the portfolio. The recent news of DBS and AWS partnering to upskill the bank’s workforce underscores the value of creating a future ready workforce.”
“Such upskilling efforts add industry-specific context to make them more effective. BCG refers to this as ‘Human + AI’. A recent study from BCG and MIT shows that 18% of companies in the world that are pioneering AI are making money with it. Those companies focus 80% of their AI initiatives on effectiveness and growth, taking better decisions – not replacing humans with AI to save costs.”
Government Focus on Digital Skills Upgrade
This week, Singapore also saw another initiative to bridge digital skills gaps – this time from the public sector. In 2018, the Government launched its Smart Nation Scholarship program to attract and nurture talent, and later involve them in various departments to drive Singapore’s Smart Nation initiatives. The most recent Smart Nation Scholarship program 2020 attracted 723 applicants (17% more than the previous year). This is a slightly different approach, aimed at attracting digital native employees and mentoring them for digital leadership. After completing their studies, the 15 scholarship recipients are set to join public sector agencies such as Cyber Security Agency of Singapore (CSA), Government Technology Agency (GovTech), and Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA), to give the younger generation an opportunity to co-create the country’s Smart Nation vision.
Bhagaraju says, “Both private and government institutions are working to enhance workforce skills, improve marketability and making the workforce future ready. Industry 4.0 and the digital revolution have created the need to address the skill gaps that have arisen. Government programs such as the Skills Future program in Singapore, Malaysia’s HRD upskilling program, and the EU-28 European Digital initiative are all making a sustained effort to promote lifelong learning and acquisition/upgrading of skills for their respective citizens with quite successful results, that will have long-term impacts.”

The past 3-4 months have seen technology leaders move mountains to support their newly remote employees and 100% digital customers. Over 40% of businesses in the Asia Pacific didn’t formally support remote working – so these companies have made massive changes in support of their employees. You have rolled out new hardware, new data protection and compliance policies, new security measures, collaboration software and VPNs. You have also strengthened the IT Helpdesk to better support remote employees and digital customer processes. And you are embracing the public cloud to offer new services and capabilities to customers and staff. The pace of change has been breathtaking – and things are not slowing down.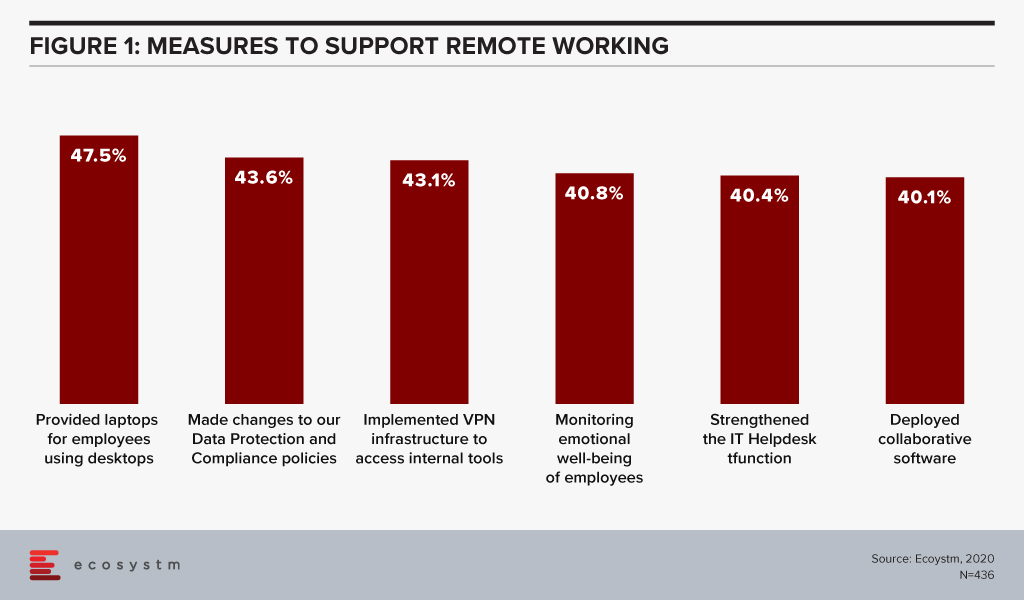
Many countries or economies are now moving to a hybrid working arrangement. This ISN’T about “going back to the way things were”. Hybrid working is really an important step on the road to the Digital Workplace – which enables access to the tools, data and processes that employees need to get their job done regardless of location or device.
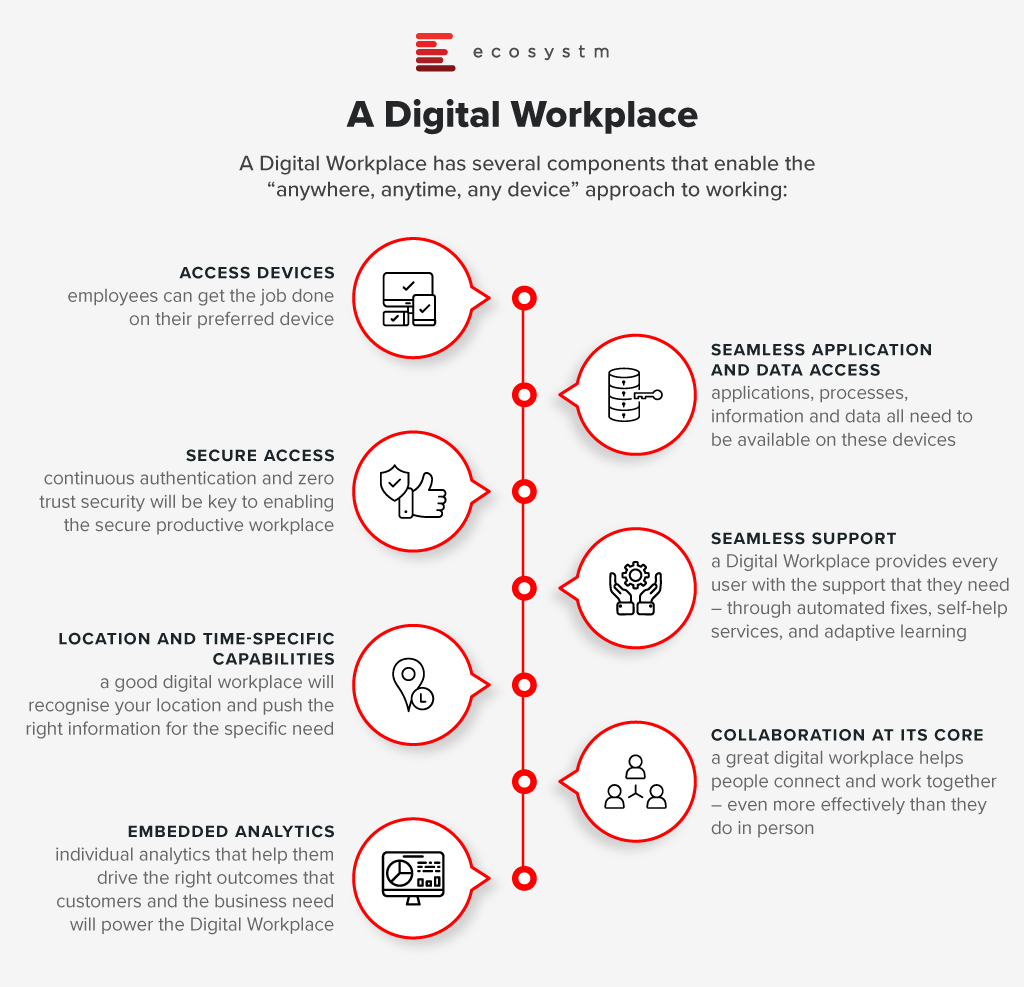
Many businesses claim that productivity has improved now that employees are working from home – some have even measured it and can prove it. We have to ensure that the move back to the office doesn’t negatively impact productivity. To drive continued productivity with hybrid working arrangements, consider:
- How will video calls work with employees in the office and at home? If employees in the office are docking their laptops, they immediately lose access to the camera. If they have monitors on their desk, they might not even be able to work with the laptop open. If they are in an open-plan office, the regular video calls might be distracting.
- What is the role of meeting rooms in the hybrid workplace? With social distancing an expectation in many countries today, the role of meeting rooms has changed. They will cater for fewer employees, and there is a growing need for them to be video-enabled.
- How do you manage hybrid meetings – where maybe 3-5 employees are on a single camera? How do you ensure every voice has equal weight – and that the right employees have their fair share of voice on the calls.
- How do you support employees who are moving between locations? You must focus on self-help services and automating as much of your Service Desk capabilities as possible.
- How can IT support social distancing in the office? Many companies are scaling back their hot desk environments to ensure there are fewer shared working environments.
- How will the changing location of employees impact business processes? Many of your processes were designed assuming employees were on site. You then redesigned many of them to assume they were not. Do you need to rethink them again?
- Does the application strategy work for all employees? There has been an increase in employees accessing applications from mobile devices – sometimes that was because it was a better experience, but too often it was because it was the only option. Is it time to rethink access and interfaces to make them relevant for all users?
- How do you keep employees and their data secure? Employees might move between secure and unsecured networks, work and home devices, on-premise and cloud applications. How do you keep them secure, backed up and synchronised – regardless of their device or location?
The move to hybrid working might not be a smooth one. The last thing you want to deliver is a poorer experience at one location versus the other, so you have work ahead in keeping your employees productive and secure – and hopefully, you’ll also move further down the path towards a Digital Workplace that can enable and empower all of your employees.

In 2018, DBS Bank came together with AI start-up impress.ai to implement Jim – Job Intelligence Maestro – a chatbot that helps the bank shortlist candidates for positions in their wealth planning team. This is primarily for screening for entry-level positions. Apart from process efficiency, the introduction of AI in the recruitment process is also aimed at eliminating bias and objectively finding the right candidate for the right job. The DBS chatbot uses cognitive and personality tests to assess candidates, as well as providing them with answers to the candidates’ frequently asked questions. The scores are then passed on to actual recruiters who continue with the rest of the recruitment process. DBS claims that they have curtailed the initial assessment time of each applicant by an average of 22 minutes.
While some organisations have started evaluating the use of AI in their HR function, it has not reached a mass-market yet. In the global Ecosystm AI study, we find that nearly 88% of global organisations do not involve HR in their AI projects. However, the use cases of AI in HR are many and the function should be an active stakeholder in AI investments in customer-focused industries.
Telstra employs AI to vet Applicants
Last month, Australia’s biggest telecommunications provider Telstra announced its plans to hire 1,000 temporary contact centre staff in Australia to meet the surge in demand amidst the global pandemic. In response to the openings, Telstra received overwhelming 19,000 applications to go through and filter, with limited workforce. To make the recruitment process more efficient, the company has been using AI to filter the applications – and has been able to make initial offers two weeks from the screening. The AI software takes the candidates’ inputs and processes them to find the right match for the required skills. The candidates are also presented with cognitive games to measure their assessment scores.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Audrey William speaks about the pressure on companies such as Telstra to hire faster for their contact centres. “Several organisations are needing to replace agents in their offshore locations and hire agents onshore. Since this is crucial to the customer experience they deliver, speed is of essence.” However, William warns that the job does not stop with recruiting the right number of agents. “HR teams will need to follow through with a number of processes including setting up home-based employees, training them adequately for the high volume of voice and non-voice interactions and compliance and so on.”
The Future of AI in HR
William sees more companies adopting AI in their HR practices in the Workplace of the Future – and the role of AI will not be restricted to recruitment alone. “A satisfied employee will go the extra mile to deliver better customer experience and it is important to keep evaluating how satisfied your employees are. AI-driven sentiment analysis will replace employee surveys which can be subjective in nature. This will include assessing the spoken words and the emotions of an individual which cannot be captured in a survey.”
In the future, William sees an intelligent conversational AI platform as an HR feedback and engagement platform for staff to engage on what they would like to see, what they are unhappy about, their workplace issues, what they consider their successes and so on. This will be actionable intelligence for HR teams. “But for a conversational AI platform to work well and to encourage users within the organisation to use it, it must be designed well. While it has to be engaging to ensure employee uptake, the design does not stop at user experience. It must include a careful evaluation of the various data sets that should be assessed and how the AI can get easy access to that data.”
AI and Ethics
With the increased use of AI, the elephant in the room is always ethical considerations. While the future may see HR practices using conversational AI platforms, how ethical is it to evaluate your employees constantly and what will be the impact on them? How will the organisation use that data? Will it end up giving employers the right reasons to reduce manpower at will? These and allied issues are areas where stricter government mandates are required.
Going back to AI-assisted recruitment, William warns, “Bias must be assessed from all angles – race, education, gender, voice, accents. Whilst many platforms claim that their solution removes bias, the most important part of getting this right is to make sure that the input data is right from the start. The outcomes desired from the process must be tested – and tested in many different ways – before the organisation can start using AI to eliminate bias. There is also the added angle of the ethical use of the data.”
The current state of the world is alarming. The COVID-19 virus is not only disrupting businesses and economies – it is taking away loved ones, it is separating friends and families, it is disrupting the education of young adults and children and it is seeding fear in communities. But while the media is dominated with doom and gloom at the moment – and we do need these reports – I believe it is worth stopping for a moment to consider the fact that if the pandemic happened ten or fifteen years ago, many businesses – and government agencies – would have closed down. You could argue that the world wasn’t as globally connected then as it is now. And to an extent that is correct – the numbers of air travellers increased up until the end of 2019. But even in 2005, the world was still a very global place – economies relied on cross-border commerce as much then as they do now.
Depending on your business or industry 10-15 years ago:
- Staff couldn’t have effectively worked from home. And if they did, collaboration would have been hard (if not impossible outside of the usual voice services). Teleconference services would have needed to be booked.
- Remote access would have been painful and slow – relying heavily on VPNs over slower internet connections.
- Software would have mainly been running in company datacentres – with very little SaaS-based applications. These applications were often designed for LAN access…
- Those lucky few with a Blackberry or iPhone might have had access to email – everyone else would have needed to go into the office to get work done.
But worse than this would have been our customer engagements. While eCommerce had healthy adoption by 2005, it often relied on very manual processes – and it was mainly focused on consumer products and services – B2B adoption was still a number of years away. And, for many businesses, it represented a tiny proportion of their revenue. Small companies didn’t often have the web presence to compete with the big players. But if I look at the big fast-food giants in Australia (e.g. McDonalds and KFC) – these companies didn’t have a web or mobile ordering until a few years ago, and even more recently for home delivery services. Any company that had to shut down their face-to-face contact would have likely fallen back on their contact centres – but even these would have been impacted as the ability to route calls to remote or home-working call centre agents barely existed then – so they would have been understaffed or closed due to an infection being discovered…
Today’s digital connectivity has the opportunity to save lives. Less physical contact means less people being exposed to – and spreading – the virus.
If this pandemic had happened 10-15 years ago, many small AND large businesses would have had to shut their doors very quickly. Very early in the cycle, businesses would have had to make the decision to shut their doors straight away, or risk accelerating the infection rates by having staff continue to attend the office or contact centre. So if there is one small positive we can take away, it is that our digital investments are paying off very quickly. The ability to continue to trade, continue to sell, continue to do business in such a market as we are facing today and tomorrow is priceless. I can purchase goods and services online, register my car without leaving my desk, upgrade or change my health insurance without speaking to a single human being. Most businesses have the ability to have their employees access many of their critical applications wherever they are located. Our accountants can still pay and send bills, HR can hire for open positions, product teams can continue to innovate on the products and services they offer.
Don’t get me wrong – business survival is not guaranteed. This is why I implored governments to aim their stimulus spending towards small and medium businesses digital initiatives – as cafes, retailers, bars and restaurants close down across cities, states and countries, many are now lamenting their immature online presence, their lack of delivery and their lack of pre-ordering. If you have any doubt about this, check your local Facebook group – it is full of small businesses putting up images of menus in the hope that customers will reach out directly to keep their businesses running. If these businesses are given incentives to build digital services quickly, they might see less of a slowdown in business.
COVID-19 will definitely stress test our digital assets and strategies. Just recently, the Australian government’s citizen-facing portal crashed as too many citizens logged on to register for welfare. This forced many people out into government shop-fronts – putting themselves, the staff and all connected families and friends at risk of catching the virus. I also heard today of a bank that called many of its staff back to the office as the VPN could not cope with the number of users and volume of traffic! If you have not already, you will quickly find out how your digital capabilities are performing – where you need extra capacity, where services are running smoothly, where you need to rethink process design or where you need to consider re-crafting this approach for the fully digital era.
But stay safe – listen to the advice of medical experts and act on that advice. A senior medical officer recently stated that social distancing is the only way that we will overcome this virus – so stay safe and stay home (if you can!). But also take the time to review your digital capabilities – start making moves now to ensure they help your business stay afloat – or your government agency to keep serving citizens in times of restricted trading or shutdowns.
For most companies, End-User Computing (EUC) is considered an expense to the business. EUC strategies are typically exercises in cutting costs – with often not much more than lip service given to the needs of employees (or employee personas). I know – I help companies write these strategies, and the costing component is always the piece that gets the strategy over the line.
But the winds are changing. Employee Experience (EX) is taking off as a serious business initiative. For example:
- Edmunds.com wrapped the traditional Facilities and Human Resources functions into a combined WEE Team which represents Workplace and Employment Experience. They engaged in a campaign to rid the company of the term “Human Resources”
- Airbnb has a dedicated team to “drive the company’s health and happiness”
- Nitro has “turned old-school HR on its head and instead created Employee Experience (EX)
In our upcoming CX research, the early data is showing that EX is the number two initiative for businesses across the globe in 2019. And for information workers, the technology that sits in front of them is a HUGE component of their experience – and their ability to get and stay productive.
Productivity Should Be The Focus Of Our EUC Strategies
Smart businesses understand that. They allow employees to choose (or bring) the devices that they need to remain productive. While desktop PCs might not be making a comeback, they are increasingly being adopted as an alternative to the “laptop as one device” strategy that many businesses embrace. Sometimes a powerful computer with a big screen (or multiple screens) is what people need to get the job done. Other times a small form factor desktop is perfect. Employees may need tablets or smartphones. And other times they need regular laptops, convertibles, or 4G connected laptops. Smart businesses also focus on seamless security – knowing that security is a key enabler of productivity. We are seeing that “The best, most secure device for the job” is taking off as a EUC hardware strategy in businesses that are striving to build a productive and enjoyable employee experience. This helps them to keep employees productive and will help them attract and retain the best talent.

And EUC goes beyond the device to the entire user experience
Collaboration initiatives often disappoint. Limited adoption, and limited interoperability between applications limits effectiveness. There is often a disconnection between the collaboration system and how it helps employees hit their goals. Microsoft is currently rebooting its collaboration strategy – and has created a more modern system that more closely mimics the processes of a typical information worker (Teams). Slack is also taking the world by storm – as it is a collaboration tool that helps people the way they work today – it doesn’t require any training.

IT Operations professionals need to take a fresh look at EUC – but this time within the context of the other initiatives in your business. Do you already have a team focusing on EX? Are there initiatives you can help with – or piggyback on? There is real academic research proving the link between happiness and productivity – or the “state of flow”. IT holds the key to productivity – and therefore happiness – for information workers in particular – it’s time to step up and put employee experience and productivity – not costs – at the centre of our IT end-user computing strategies.







