Southeast Asia’s banking sector is poised for significant digital transformation. With projected Net Interest Income reaching USD 148 billion by 2024, the market is ripe for continued growth. While traditional banks still hold a dominant position, digital players are making significant inroads. To thrive in this evolving landscape, financial institutions must adapt to rising customer expectations, stringent regulations, and the imperative for resilience. This will require a seamless collaboration between technology and business teams.
To uncover how banks in Southeast Asia are navigating this complex landscape and what it takes to succeed, Ecosystm engaged in in-depth conversations with senior banking executives and technology leaders as part of our research initiatives. Here are the highlights of the discussions with leaders across the region.
#1 Achieving Hyper-Personalisation Through AI
As banks strive to deliver highly personalised financial services, AI-driven models are becoming increasingly essential. These models analyse customer behaviour to anticipate needs, predict future behaviour, and offer relevant services at the right time. AI-powered tools like chatbots and virtual assistants further enhance real-time customer support.

Hyper-personalisation, while promising, comes with its challenges – particularly around data privacy and security. To deliver deeply tailored services, banks must collect extensive customer information, which raises the question: how can they ensure this sensitive data remains protected?

AI projects require a delicate balance between innovation and regulatory compliance. Regulations often serve as the right set of guardrails within which banks can innovate. However, banks – especially those with cross-border operations – must establish internal guidelines that consider the regulatory landscape of multiple jurisdictions.
#2 Beyond AI: Other Emerging Technologies
AI isn’t the only emerging technology reshaping Southeast Asian banking. Banks are increasingly adopting technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and blockchain to boost efficiency and engagement. RPA is automating repetitive tasks, such as data entry and compliance checks, freeing up staff for higher-value work. CIMB in Malaysia reports seeing a 35-50% productivity increase thanks to RPA. Blockchain is being explored for secure, transparent transactions, especially cross-border payments. The Asian Development Bank successfully trialled blockchain for faster, safer bond settlements. While AR and VR are still emerging in banking, they offer potential for enhanced customer engagement. Banks are experimenting with immersive experiences like virtual branch visits and interactive financial education tools.
The convergence of these emerging technologies will drive innovation and meet the rising demand for seamless, secure, and personalised banking services in the digital age. This is particularly true for banks that have the foresight to future-proof their tech foundation as part of their ongoing modernisation efforts. Emerging technologies offer exciting opportunities to enhance customer engagement, but they shouldn’t be used merely as marketing gimmicks. The focus must be on delivering tangible benefits that improve customer outcomes.

#3 Greater Banking-Fintech Collaboration
The digital payments landscape in Southeast Asia is experiencing rapid growth, with a projected 10% increase between 2024-2028. Digital wallets and contactless payments are becoming the norm, and platforms like GrabPay, GoPay, and ShopeePay are dominating the market. These platforms not only offer convenience but also enhance financial inclusion by reaching underbanked populations in remote areas.
The rise of digital payments has significantly impacted traditional banks. To remain relevant in this increasingly cashless society, banks are collaborating with fintech companies to integrate digital payment solutions into their services. For instance, Indonesia’s Bank Mandiri collaborated with digital credit services provider Kredivo to provide customers with access to affordable and convenient credit options.
Partnerships between traditional banks and fintechs are essential for staying competitive in the digital age, especially in areas like digital payments, data analytics, and customer experience.

While these collaborations offer opportunities, they also pose challenges. Banks must invest in advanced fraud detection, AI monitoring, and robust authentication to secure digital payments. Once banks adopt a mindset of collaboration with innovators, they can leverage numerous innovations in the cybersecurity space to address these challenges.
#4 Agile Infrastructure for an Agile Business
While the banking industry is considered a pioneer in implementing digital technologies, its approach to cloud has been more cautious. While interest remained high, balancing security and regulatory concerns with cloud agility impacted the pace. Hybrid multi-cloud environments has accelerated banking cloud adoption.

Leveraging public and private clouds optimises IT costs, offering flexibility and scalability for changing business needs. Hybrid cloud allows resource adjustments for peak demand or cost reductions off-peak. Access to cloud-native services accelerates innovation, enabling rapid application development and improved competitiveness. As the industry adopts GenAI, it requires infrastructure capable of handling vast data, massive computing power, advanced security, and rapid scalability – all strengths of hybrid cloud.
Replicating critical applications and data across multiple locations ensures disaster recovery and business continuity. A multi-cloud strategy also helps avoid vendor lock-in, diversifies cloud providers, and reduces exposure to outages.

Hybrid cloud adoption offers benefits but also presents challenges for banks. Managing the environment is complex, needing coordination across platforms and skilled personnel. Ensuring data security and compliance across on-prem and public cloud infrastructure is demanding, requiring robust measures. Network latency and performance issues can arise, making careful design and optimisation crucial. Integrating on-prem systems with public cloud services is time-consuming and needs investment in tools and expertise.
#5 Cyber Measures to Promote Customer & Stakeholder Trust
The banking sector is undergoing rapid AI-driven digital transformation, focusing on areas like digital customer experiences, fraud detection, and risk assessment. However, this shift also increases cybersecurity risks, with the majority of banking technology leaders anticipate inevitable data breaches and outages.

Key challenges include expanding technology use, such as cloud adoption and AI integration, and employee-related vulnerabilities like phishing. Banks in Southeast Asia are investing heavily in modernising infrastructure, software, and cybersecurity.
Banks must update cybersecurity strategies to detect threats early, minimise damage, and prevent lateral movement within networks.

Employee training, clear security policies, and a culture of security consciousness are critical in preventing breaches.
Regulatory compliance remains a significant concern, but banks are encouraged to move beyond compliance checklists and adopt risk-based, intelligence-led strategies. AI will play a key role in automating compliance and enhancing Security Operations Centres (SOCs), allowing for faster threat detection and response. Ultimately, the BFSI sector must prioritise cybersecurity continuously based on risk, rather than solely on regulatory demands.
Breaking Down Barriers: The Role of Collaboration in Banking Transformation
Successful banking transformation hinges on a seamless collaboration between technology and business teams. By aligning strategies, fostering open communication, and encouraging cross-functional cooperation, banks can effectively leverage emerging technologies to drive innovation, enhance customer experience, and improve efficiency.
A prime example of the power of collaboration is the success of AI initiatives in addressing specific business challenges.

This user-centric approach ensures that technology addresses real business needs.
By fostering a culture of collaboration, banks can promote continuous learning, idea sharing, and innovation, ultimately driving successful transformation and long-term growth in the competitive digital landscape.

Innovation is a driving force behind new approaches, often occurring at the point of adoption rather than technology development. As public sector organisations increasingly focus on improving citizen services through technology, it is important to adopt a strategic approach that considers innovation as a complex journey of systemic and cultural transformation. This strategic approach should guide the integration of technology into citizen services.
Here is a comprehensive look at what public sector organisations should consider when integrating technology into citizen services.
Download ‘Future-Proofing Citizen Services: Technology Strategies for the Public Sector‘ as a PDF
1. Immediate View: Foundational Technologies
The immediate view focuses on deploying technologies that are widely adopted and essential for current digital service provision. These foundational technologies serve as the backbone for enhancing citizen services.
Foundational Technologies
Web 2.0. Establishing a solid online presence is usually the first step, as it is the broadest channel for reaching customers. Web 2.0 refers to the current state of the internet, encompassing dynamic content and interactive websites.
Mobile Applications. Given that mobile usage has surpassed desktop, a mobile-responsive platform or a dedicated mobile app is crucial. Mobile apps provide a more specialised and immersive user experience by utilising device-specific features like GPS, document scanning, and push notifications.
2. Second-Generation Enablers: Emerging Technologies
As organisations establish foundational technologies, they should look towards second-generation enablers. Although less mature, these technologies offer emerging digital opportunities, and can significantly enhance service differentiation.
Emerging Technologies
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems improve the efficiency and effectiveness of digital services by routing callers to self-service options and providing relevant information without human intervention. These systems operate outside typical government agency working hours, ensuring continuous accessibility. Additionally, IVRs generate valuable data for future Voice of the Customer programs, improving overall service quality and responsiveness.
Digital Wallets facilitate transactions by expediting fund transfers and enhancing transparency through meticulous transaction records. They streamline administrative tasks, simplify transactions, and encourage service usage and adoption.
AI-driven Virtual Agents or chatbots revolutionise customer interactions by providing 24/7 support. They offer prompt, efficient, and personalised services, enhancing customer satisfaction and trust. In resource-limited public sectors, virtual agents are cost-effective, optimising resource allocation and meeting growing service demands. Specialised virtual agents for specific sectors can further differentiate service providers.
3. Futuristic View: Ambitious Innovations
The futuristic view focuses on forward-looking technologies that address long-term roadblocks and offer transformative potential. These technologies are currently speculative but hold the promise of significantly reshaping the market.
Innovations
Subscription Management models enable public sector information services to be accessed in highly personalised ways, thereby enhancing citizen engagement. This model supports regulatory oversight by providing common data insights and improves the management of services, ultimately benefiting the public by ensuring more responsive and tailored information delivery.
AI concierge leverages advanced technologies like Natural Language Processing, Computer Vision, and Speech Technologies to provide personalised and proactive customer service. They redefine customer management, ensuring a seamless and tailored experience.
Immersive reality technologies, such as augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) create captivating customer experiences by allowing interactions in virtual environments. These technologies establish a shared virtual environment, helping customers to engage with businesses and each other in new and immersive ways. As an emerging customer management tool, immersive reality can transform the dynamics of customer-business relationships, adding substantial value to the service experience.

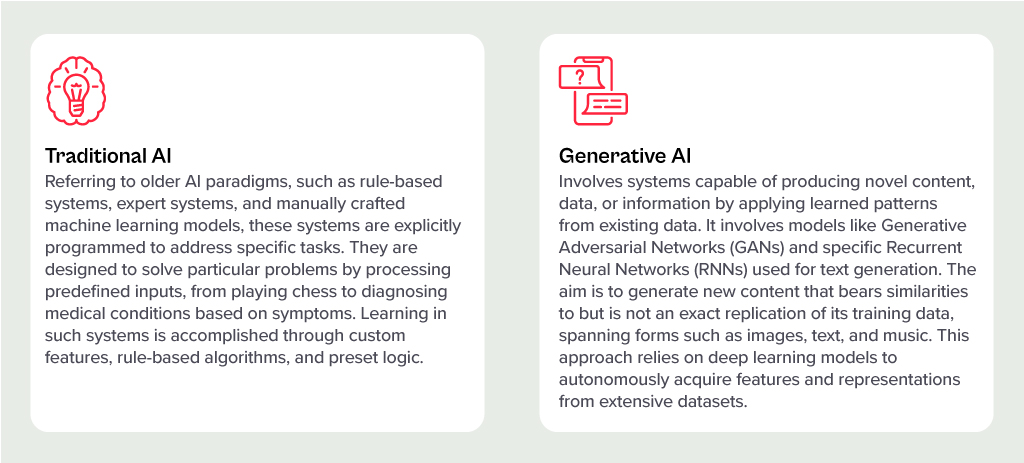
Generative AI has stolen the limelight in 2023 from nearly every other technology – and for good reason. The advances made by Generative AI providers have been incredible, with many human “thinking” processes now in line to be automated.
But before we had Generative AI, there was the run-of-the-mill “traditional AI”. However, despite the traditional tag, these capabilities have a long way to run within your organisation. In fact, they are often easier to implement, have less risk (and more predictability) and are easier to generate business cases for. Traditional AI systems are often already embedded in many applications, systems, and processes, and can easily be purchased as-a-service from many providers.
Unlocking the Potential of AI Across Industries
Many organisations around the world are exploring AI solutions today, and the opportunities for improvement are significant:
- Manufacturers are designing, developing and testing in digital environments, relying on AI to predict product responses to stress and environments. In the future, Generative AI will be called upon to suggest improvements.
- Retailers are using AI to monitor customer behaviours and predict next steps. Algorithms are being used to drive the best outcome for the customer and the retailer, based on previous behaviours and trained outcomes.
- Transport and logistics businesses are using AI to minimise fuel usage and driver expenses while maximising delivery loads. Smart route planning and scheduling is ensuring timely deliveries while reducing costs and saving on vehicle maintenance.
- Warehouses are enhancing the safety of their environments and efficiently moving goods with AI. Through a combination of video analytics, connected IoT devices, and logistical software, they are maximising the potential of their limited space.
- Public infrastructure providers (such as shopping centres, public transport providers etc) are using AI to monitor public safety. Video analytics and sensors is helping safety and security teams take public safety beyond traditional human monitoring.
AI Impacts Multiple Roles
Even within the organisation, different lines of business expect different outcomes for AI implementations.
- IT teams are monitoring infrastructure, applications, and transactions – to better understand root-cause analysis and predict upcoming failures – using AI. In fact, AIOps, one of the fastest-growing areas of AI, yields substantial productivity gains for tech teams and boosts reliability for both customers and employees.
- Finance teams are leveraging AI to understand customer payment patterns and automate the issuance of invoices and reminders, a capability increasingly being integrated into modern finance systems.
- Sales teams are using AI to discover the best prospects to target and what offers they are most likely to respond to.
- Contact centres are monitoring calls, automating suggestions, summarising records, and scheduling follow-up actions through conversational AI. This is allowing to get agents up to speed in a shorter period, ensuring greater customer satisfaction and increased brand loyalty.
Transitioning from Low-Risk to AI-Infused Growth
These are just a tiny selection of the opportunities for AI. And few of these need testing or business cases – many of these capabilities are available out-of-the-box or out of the cloud. They don’t need deep analysis by risk, legal, or cybersecurity teams. They just need a champion to make the call and switch them on.
One potential downside of Generative AI is that it is drawing unwarranted attention to well-established, low-risk AI applications. Many of these do not require much time from data scientists – and if they do, the challenge is often finding the data and creating the algorithm. Humans can typically understand the logic and rules that the models create – unlike Generative AI, where the outcome cannot be reverse-engineered.
The opportunity today is to take advantage of the attention that LLMs and other Generative AI engines are getting to incorporate AI into every conceivable aspect of a business. When organisations understand the opportunities for productivity improvements, speed enhancement, better customer outcomes and improved business performance, the spend on AI capabilities will skyrocket. Ecosystm estimates that for most organisations, AI spend will be less than 5% of their total tech spend in 2024 – but it is likely to grow to over 20% within the next 4-5 years.

Today, Asia is home to nearly 60% of the world’s population and accounts for 39% of the global GDP. As the region’s importance continues to grow (7 out of the top 10 economies is expected to be from the region, contributing to 47% of the global GDP by 2030), investment in Asia is a key priority for governments and large corporates around the world.
With the region taking centre-stage, there is a growing optimism as opportunities open up for local economies. It remains a unique market – differentiated by a strong spirit of innovation, vibrant startup ecosystem, and propensity to leverage technology to transform.
At the Leaders Dialogue: Asian Sentiment 2023 conversation, Ecosystm Founder and Chairman, Amit Gupta; Ahmed Mazhari, President of Microsoft Asia; Padmashree (Paddy) Santosh, VP & Global Head of Learning, Diversity and Organisation Effectiveness at Olam Agri; and Luca Destefanis, Head of Marketing APAC at Kyndryl discussed where Asia is leading and lagging behind when it comes to tech-led transformation and innovation.
Here are the key highlights:
- Asia demonstrates a “Disrupt or be Disrupted Mindset”
- The need for innovation is encouraging corporate venturing
- There is a growing interest in emerging tech
- Yet organisations might be scratching the surface
- Outcome-led transformation will be the key
Read on for more insights into Asian sentiment.
Download State of Digital Transformation in Asia as a PDF