2020 was a strange year for retail. Businesses witnessed significant disruption to supply chains, significant swings in demand for products (toilet paper, puzzles, bikes etc!) and then sometimes incredible growth – as disposable income increased as many consumers are no longer taking expensive holidays. Overall, it was a mixed year, with many retailers closing down and others reporting record sales. The grocery sector boomed – with many restaurants and fast-food providers closed, sometimes the supermarkets were some of the few remaining open retailers.
For many retailers, technology has become a key enabler to their transformation, survival and success (Figure 1).
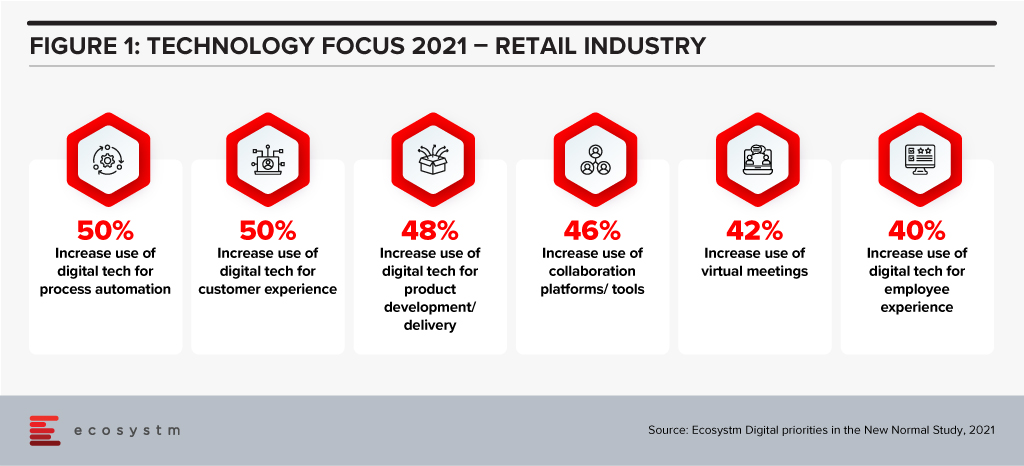
Woolworths, Australia’s largest retailer, operates across the grocery, department store, drinks, and hospitality sectors. They hold a significant market share in most markets that they operate in. The company had a strong 2019/20 (financial year runs from July 2019 to June 2020) with sales up 8% – and in the first half of the 2020/21 financial year, sales were up nearly 11%. But the company is not resting on its laurels – one of its 6 key priorities is to “Accelerate Digital, eCom and convenience for our increasingly connected customers”. This requires more than just a deep technology investment, but a new culture, new skills, and new ways of working.
Woolworths’ Employee Focus
Woolworths has committed to invest AUD 50 million in upskilling and reskilling their employees in areas such as digital, data analytics, machine learning and robotics over the next three years. The move comes as a response to the way the Retail industry has been disrupted and the need to futureproof to stay relevant and successful. The training will be provided through online platforms and through collaborations with key learning institutions.
The supermarket giant is one of Australia’s largest private employers with more than 200,000 employees. Under Woolworths’ ‘Future of Work Fund’ their staff will be trained across supply chain, store operations, and support functions to enhance delivery and decision-making processes. The retailer will also create an online learning platform that will be accessible by Woolworths employees as well as by other retail and service companies to support the ecosystem. Woolworths has plans to upskill their staff in customer service abilities, leadership skills and agile ways of working.
Woolworths’ upskilling program will also support employees who were impacted by Woolworths planned closures of Minchinbury, Yennora, and Mulgrave distribution centres due in 2025.
Woolworths’ Tech Focus
Woolworths has been ramping up their technology investments and having tech-savvy employees will be key to their future success. In October 2020, Woolworths deployed micro automation technology to revamp their eCommerce facility in Melbourne to speed up the fulfilment of online grocery orders, and front and back-end operations. Woolworths also partnered with Dell Technologies in November 2020 to bring together their private and public cloud onto a single platform to improve mission-critical processes, applications and support inventory management operations across its retail stores.
Future of Work
For many years, Ecosystm has been advising our clients to invest more in the skills of the business. Every business will be using more cloud next year than they are this year; they will suffer more cybersecurity incidents; they will use more AI and machine learning; they will automate more processes than are automated today. More of their customer engagements will be digital, and more insight will be required to drive better outcomes for customers and employees. This all needs new skills – or more people trained on skills that some in the business already understand. But too many businesses don’t train in advance – instead waiting for the need and paying external consultants or expensive new hires for their skills. Empowered businesses – ones that are creating a future-ready, agile business – invest in their people, work environment, business processes and technology to create an environment where innovation, transformation and business change are accepted and encouraged (Figure 2).
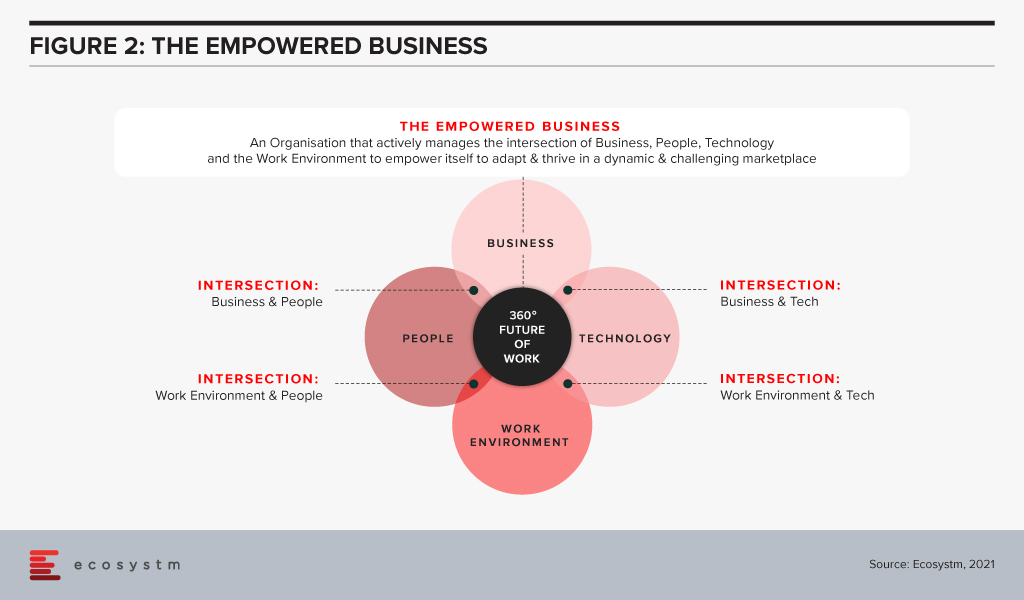
Empowered businesses can adapt to new challenges, new market conditions and respond to new competitive threats. By taking these steps to upskill and empower their employees, Woolworths is building towards empowering their own business for long term success.
Transform and be better prepared for future disruption, and the ever-changing competitive environment and customer, employee or partner demands in 2021. Download Ecosystm Predicts: The top 5 Future of Work Trends For 2021.

Over the next few months, we’re going to be focusing on the five stages of the Digital Value Journey and how an organisation and a leadership team can progress through these stages.
The Journey starts with baselining and then improving your execution capability.
Your Foundation
The quality of your execution needs to be consistently improved as you and your organisation make progress through your Journey. At the start, it is about developing the foundation on which you can build more complex and valuable business capabilities. You need that reliable, performing foundation that delivers what your customers and employees need every day.
For any Digital or IT organisation to succeed, it needs two critical things: a record of consistent success, and the trust from your organisation that past performance is a reliable predictor of the future.
Every day your customers and employees will be evaluating those two things. It’s like sitting a difficult exam every day. Failing one will be remembered – much more so than all the other exams that you successfully passed. To pass that exam you need to clearly understand what people are testing you on every day.
Understanding how the quality of your work will be evaluated is essential to creating and maintaining this firm foundation. Everything you do later in the Journey will depend on the foundation you establish at the start.
Evaluating your Foundation
And you don’t have the freedom to choose how that foundation is going to be evaluated. There is a universe – or perhaps that should be a multiverse – of metrics that you could use. Selecting the small set of metrics that your stakeholders believe demonstrate your performance is essential.
Too many metrics is just as bad as too few – you won’t know which ones to focus on so you will end up spreading yourself too thinly. Your stakeholders are the best people to tell you how to measure your performance. Work with them to determine the one or two indicators that they really care about.
Schools and universities have improved dramatically in explaining how they are going to evaluate a student’s performance since I attended! As part of almost every assignment, educators include an evaluation rubric to guide each student. This sets out what how the educator will assess the students work. So, getting great grades is dependent on understanding this rubric.
What is your rubric? Without one how will you know what outcomes your stakeholders value and how they will evaluate your work? Spending time to talk with your stakeholders about what they value, is a habit that is worth developing early and maintaining throughout the Journey.
Your Next Best Steps
Getting this execution foundation right is the basis for everything that follows.
In the first of a series of webinars on 22 April, we will be introducing the concepts and ideas that we will expand on over the series.
Getting a quality education is a long hard slog – and I can’t promise that starting this Digital Journey will be any different. At each stage of the Journey different levels of capability will be required, but, as with an education, these higher levels of capability will only be possible if the right foundation is in place. So, join us to see how you can use the Digital Value Journey to lift the performance of your organisation and its Digital or IT Team.
How do digital leaders shift from providing a cost-focused to a value-focused service? At the CXO Digital Leaders Dialogue series, together with Best Case Scenario, we will be in discussion with leaders who will share their experiences with navigating these challenges.
To learn more, or to register to attend, visit here

In 2009 one of the foremost Financial Services industry experts was giving my team a deep dive into the Global Financial Crisis (GFS) and its ramifications. According to him, one of the key reasons why it happened was that most people in key positions in both industry and government had probably never seen a full downturn in their careers. There was a bit of a hiccup during the dot com bust but nothing that seriously interrupted the long boom that began somewhere in 1988. They had never experienced anything quite like 2008; so they never imagined that such a crisis could actually happen.
Similarly, 2020 was an unprecedented year – in our lives and certainly for the tech industry. The GFC (as the name suggests) was a financial crisis. A lot of people lost their jobs, but after the bailouts things went largely back to normal. COVID-19 is something different altogether – the impact will be felt for years and we don’t yet know the full implications of the crisis.
While we would like to start 2021 with a clean slate and never talk about the pandemic again, the reality is that COVID-19 will shape what we will see this year. In the first place it looks like the disease will still be around for a substantial part of the year. Secondly, all the changes it has brought in 2020 with entire workforces suddenly moving to operating from home will have profound implications for technology and customer experience this year.
As we ease into 2021, I look at some of the organisational and technology trends that are likely to impact customer experience (CX) in 2021.
#1 All Business is Now eBusiness
COVID-19 has ensured that the few businesses which did not have an online presence became acutely aware that they needed one. It created a need for many businesses to quickly initiate eCommerce. Forbes reported a 77% increase in eCommerce infrastructure spending YoY. This represents about 4 years of growth squeezed into the first 6 months of 2020!
From a CX point of view there is going to be far more interaction with brands and products through online channels. This is not just about eCommerce and buying from a portal. It is also about using tools like Instagram, Facebook and other social media platforms more widely. It is about learning to interact with the customer in multiple ways and touching their journeys at multiple points, all virtually using the web – mostly the mobile web.
Ecosystm research shows that almost three out of four companies have decided on accelerating or modifying the digitalisation they were undergoing (Figure 1). It is fair to expect that this gives a further boost to moving to the cloud. For the customer it will mean being able to access information in many new ways and connect with products, services, brands at multiple points on the web.
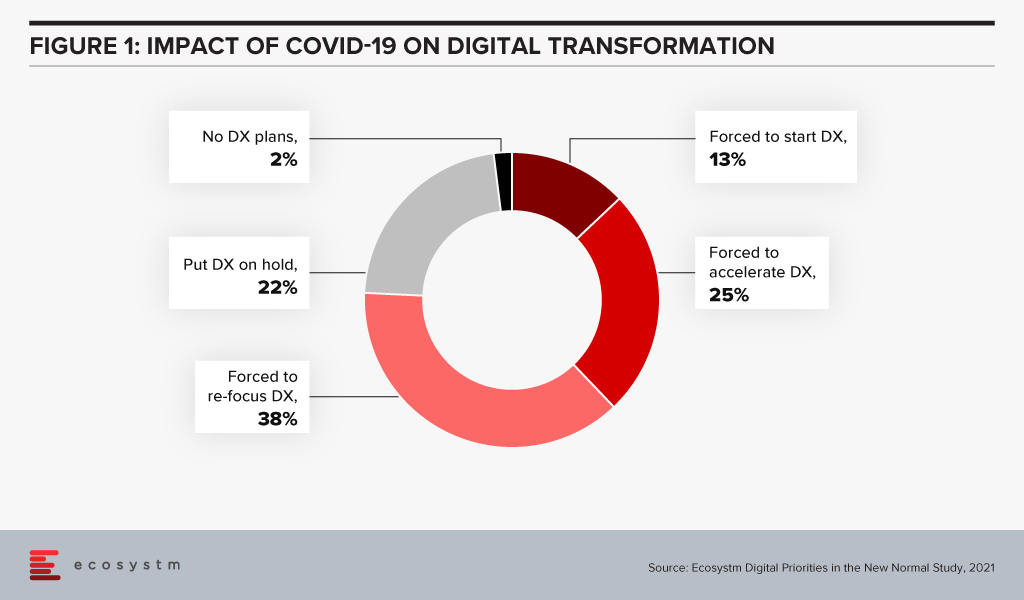
Since interacting with the customer at multiple points is new for most services, I foresee a lot of missed opportunities as companies learn to navigate a completely different landscape. Customers pampered by digitally native organisations often react harshly to even a small mistake. It will become critical for companies to not just become a bigger presence online but also to manage their customers well.
New solutions such as Customer Data Platforms (CDP), as opposed to CRM will become common. Players who are into Customer Experience management are likely to see huge business growth and new players will rapidly enter this space. They will promise to affordably manage CX across the globe, leveraging the cloud.
#2 Virtual Merges with Real
Virtual and Augmented Reality are not new. They have been around for a while. This will now cross the early adoption stage and is likely to proliferate in terms of use cases and importance.
AR/VR has so far been seen mainly in games where one wears an unwieldy – though ever-improving – headset to transport oneself into a 3D virtual world. Or in certain industrial applications e.g., using a mobile device to look at some machinery; the device captures what the eye can see while providing graphical overlays with information. In 2021 I expect to see almost all industrial applications adopting some form of this technology. This will have an impact on how products are serviced and repaired.
For the mainstream, 2020 was the year of videoconferencing – as iconic as the shift to virtual meetings has been, there is much more to come. Meetings, conferences, events, classrooms have all gone virtual. Video interaction with multiple people and sharing information via shared applications is commonplace. Virtual backgrounds which hide where you are actually speaking from are also widely used and getting more creative by the day.
Imagine then a future where you get on one of these calls wearing a headset and are transported into a room where your colleagues who are joining the call also are. You see them as full 3D people, you see the furniture, and the room decor. You speak and everyone sees your 3D avatar speak, gesture (as you gesture from the comfort of your home office) and move around. It will seem like you are really in the conference room together! If this feels futuristic or unreal try this or look at how the virtual office can look in the very near future.
While the solutions may not look very sophisticated, they will rapidly improve. AR/VR will start to really make its presence felt in the lives of consumers. From being able to virtually “try” on clothes from a boutique to product launches going virtual, these technologies will deeply impact customer experience in 2021 and beyond
In the immortal words of Captain Kirk, we will be going where no man has gone before – enabled by AR / VR.
#3 Digital CX will involve Multiple Technologies
AI, IoT and 5G will continue to support wider CX initiatives.
The advances that I have mentioned will gain impetus from 5G networking, which will enable unprecedented bandwidth availability. To deliver an AR experience over the cloud, riding on a 5G network, will literally be a game changer compared to the capabilities of older networks.
Similarly, IoT will lead to massive changes in terms of product availability, customisation and so on. 5G-enabled IoT will allow a lot more data to be carried a lot faster; and more processing at the edge. IoT will have some initial use cases in Retail, Services and other non-manufacturing sectors – but perhaps not as strongly as some commentators seem to indicate.
AI continues to drive change. While AI may not transform CX in 2021, this is a technology which will be a component of most other CX offerings, and so will impact customer experience in the next few years. In fact, thinking of businesses in 2025 I cannot believe that there will be a single business to customer (B2C) interaction which will not feature some form of AI technology.
I’d be interested to hear your thoughts on the technologies which will impact CX in 2021 – Connect with me on the Ecosystm platform.

2020 saw a shutdown in both supply and demand which has effectively put the brakes on many economic activities and forced a complete rethink on how to continue doing business and maintain social interactions. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated digitalisation of consumers and enterprises, and the telecommunications industry has been the pillar which has kept the world ticking over. The rise in data use coupled with the fervent growth of the digital economy augurs well for the telecom sector in 2021.
Ecosystm Advisors Claus Mortensen, Rahul Gupta, and Shamir Amanullah present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for Telecommunications & Mobility trends for 2021. This is a summary of the predictions – the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform.
The Top 5 Telecommunications & Mobility Trends for 2021
- The 5G Divide – Reality for Some and Hype for Others
Despite the economic challenges in 2020, GSMA reports that the global 5G subscriptions doubled QoQ in Q2 2020 to hit at least 137.7 million subscribers. This accounts for 1.5% of total subscribers – and is expected to rise to 30% by 2025.
The value of 5G will become increasingly mainstream in the next few years. 5G offers a tailored user-centric approach to network services, low latency and significantly higher number of connections which will power a new era of mobile Internet of Everything (IoE).
However, there are many operators who are still sceptical about 5G. In the US, many operators failed to get any tangible positives from 5G. In the near term, many operators will continue to evolve their 5G capabilities – a full grown standalone 5G technology implementation in some verticals might take longer.
The unsuccessful launch of 5G by the US operators does not mean that 5G is a failure, however. It also implies that we need to look at other geographies to lead us into 5G – and Asia Pacific may well emerge as a leader in this space. China, for example, leads the drive in 5G adoption; and 5G smartphones account for more than half of global sales in recent months.
- Telecom Operators Will Accelerate Digital Transformation
Telecom operators are facing increasing demands for cutting-edge services and top-notch customer experience (CX). The global pandemic has caused revenue loss, due to struggling economies and many operators will aim to reduce OpEX to circumvent these financial pressures, raise the quality of CX and retain existing customers. To realise this, there will be much focus on improvement in efficiencies, better operations management as well as improving the IT stack. These digital transformation efforts will enable rapid and flexible services provisioning, which will be better prepared for the tailored services customers now demand.
Many operators are increasingly incorporating cloudification alongside the 5G network deployment. Operators are moving towards transforming their operations and business support systems to a more virtualised and software-defined infrastructure. 5G will operate across a range of frequencies and bands – with significantly more devices and connections becoming software-defined with computing power at the Edge. Operators will also harness the power of AI to analyse massive volumes of data from the networks accessed by millions of devices in order to improve CX, ramp up operational efficiencies as well as introduce new services tailored to customer needs to increase revenue.
- Remote Working Will Transform Telecommunications Networks
The changing patterns in peak network traffic and the substantial movement of traffic from central business districts to residential areas require a fundamental rethink in network traffic management. In addition, many businesses continue to ramp up digital transformation efforts to conduct business online as physical channels will remain limited. Consumer onboarding will also be fervent, as organisations look at business recovery – resulting in increase in bandwidth requirements.
The increasing remote working trend is amplifying the need for greater cybersecurity. Cybersecurity has catapulted in importance as the pandemic has seen a worrying increase in attacks on banks, cloud servers and mobile devices, among others. Cyber-attack incidents specifically due to remote working, has seen a rise. A telecom operator’s compromised security can have country-wide, and even global consequences.
- SASE Will Grow – and Sprawl
Although it was perhaps originally seen as an Over-The-Top (OTT) provisioned competitive service to operators’ MPLS services, many telecom service providers have been embracing SD-WAN over the years as part of their managed services portfolio. “Traditional” SD-WAN offers some of the flexibility needed to address the change towards a more distributed access and the workload requirements that the pandemic has accelerated – the technology does not address all of the issues related to this transformed workspace.
Employees are now working from a variety of locations and workloads are becoming increasingly distributed. To address this change, organisations are challenged to move workloads and applications between platforms, potentially compromising security. Despite all the challenges that the pandemic brought with it – both human and technical – it has also provided organisations with an opportunity to rethink their IT and WAN architectures and to adopt an approach that has security at its core.
We believe that secure access service edge (SASE), which is a model for combining SD-WAN and security in a cloud-based environment, will see a drastic rise in adoption in 2021 and beyond.
- OTT Players Will Continue their Expansion in the Telecommunications Space
Facebook, Google, Amazon are no longer considered as web companies as they moved from standalone ‘web’ companies to become OTT providers and are now significant players in telecom space. With the Facebook-Jio deal in India earlier this year, and with Google and Amazon actively eyeing the telecom space, these players will continue to explore this space especially in the emerging markets of Asia and Africa. There are telecom providers in these countries which will be prime targets for partnerships. These operators could be those that have a large customer base, are struggling with their bottom lines or are already looking at exit routes. OTT players were already offering services like voice, messaging, video calling and so on which have been the domain expertise of mobile operators for a long time. The market will see instances where telecom providers will sell small stakes to OTT players at a premium and get access to the vast array of services that these OTT providers offer.

The Retail industry has had to do a sharp re-think of its digital roadmap and transformation journey – Ecosystm research shows that about 75% of retail organisations had to start, accelerate, or re-focus their digital transformation initiatives. However, that will not be enough as organisations move beyond survival to recovery – and future successes. While retailers will focus on the shift in customer expectations, a mere focus on customer experience will not be enough in 2021. Ecosystm Principal Advisors, Alan Hesketh and Alea Fairchild present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for Retail & eCommerce in 2021.
This is a summary of the predictions, the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform here.
The Top 5 Retail & eCommerce Trends for 2021
- There Will Only be Omnichannel Retailers
The value of an omnichannel offer in Retail has become much clearer during the COVID-19 pandemic. Retailers that do not have the ability to deliver using the channel customers prefer will find it hard to compete. As the physical channel becomes less important new revenue opportunities will open up for businesses operating in adjacent market sectors – companies such as food and grocery wholesalers will increasingly sell direct to consumers, leveraging their existing online and distribution capabilities.
Most customers transact on mobile device – either a mobile phone or tablet. New capabilities will remove some of the barriers to using these mobile devices. For one, technologies such as Progressive Web Apps (PWA) and Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) will provide a better customer experience on mobile platforms than existing websites, while delivering a user experience at par or better than mobile apps. Also, as retailers become AI-enabled, machine learning engines will provide purchase recommendations through smartwatches or in-home, voice-enabled, smart devices.
- COVID-19 Will Continue to be an Influence Forcing Radical Shifts
In driving the economic recovery in 2021, we will see ‘glocal’ consumption – emphasis on local retailers and global players taking local actions to win the hearts and minds of local consumers. There will be significant actions within local communities to drive consumers to support local retailers. Location-based services (LBS) will be used extensively as consumers on the high street carry more LBS-enabled devices than ever before. Bluetooth beacon technology and proximity marketing will drive these efforts. Consumers will have to opt-in for this to work, so privacy and relationship management are also important to consider.
But people still want to “physically” browse, and design aesthetics of a store are still part of the attraction. In the next 18 months, the concept of virtual stores that are digital twins will take off, particularly in the holiday and Spring clearance sales. Innovators like Matterport can help local retailers gain a more global audience with a digital twin with a limited technological investment. At a minimum, Shopify or other intermediaries will be necessary for a digital shop window.
- The Industry will See Artificial Intelligence in Everything
AI will increase its impact on Retail with an uptake in two key areas.
- Customer interactions. Retail AI will use customer data to deliver much richer and targeted experiences. This may include the ability to get to a ‘segment of one’. Tools will include chatbots that are more functional and support for voice-based commerce using mobile and in-home edge devices. Also, in-store recognition of customers will become easier through enhanced device or facial recognition. Markets where privacy is less respected will lead in this area – other markets will also innovate to achieve the same outcomes without compromising privacy but will lag in their delivery. This mismatch of capability may allow early adopters to enter other geographic markets with competitive offers while meeting the privacy requirements of these markets.
- Supply chain and pricing capabilities. AI-based machine learning engines using both internal and increased sources of external data will replace traditional math-based forecasting and replenishment models. These engines will enable the identification of unexpected and unusual demand influencing factors, particularly from new sources of external data. Modelling of price elasticity using machine learning will be able to handle more complex models. Retailers using this capability will be in a better position to optimise their customer offers based on their pricing strategies. Supply chains will be re-engineered so products with high demand volatility are manufactured close to markets, and the procurement of products with stable demands will be cost-based.
- Distribution Woes Will Continue
Third party delivery platforms such as Wish and RoseGal are recruiting additional international non-Asian suppliers to expand their portfolios. Amazon and AliExpress are leaders here, but there are many niche eCommerce platforms taking up the slack due to the uneven distribution patterns from the ongoing economic situation. Expect to see a number of new entrants taking up niche spaces in the second half of 2021, sponsored by major retail product brands, to give Amazon a run for their money on a more local basis.
As the USPS continues to be under strain, delivery companies like FedEx in the US who partner with the USPS are already suffering from the USPS’s operational slowdown, in both their customer reputation and delivery speed. In 2021, COVID-19 – and workers’ unions – will continue to impact distribution activities. Increased spending in warehouse automation and new retail footprints such as dark stores will be seen to make up for worker shortfalls.
- China’s Retail Models Will Expand into Other Markets
China’s online businesses operate in a large domestic market that is comparatively free of international competitors. Given the scale of the domestic market, these online companies have been able to grow to become substantial businesses using advanced technologies. All the Chinese tech giants – among them Alibaba, ByteDance, DiDi Chuxing, and Tencent – are expanding internationally.
China’s rapidly recovering economy puts those businesses in a strong position to fund a competitive expansion into international markets using their domestic base, particularly with their Government’s promotion of the country’s tech sector. It is harder to impose restrictions on software-based businesses, unlike the approach that we have witnessed the US Government take for hardware companies such as Huawei – placing constraints on mobile phone components and operating systems.
These tech giants also have significant experience in a Big Data environment that provides little privacy protection, as well as leading-edge AI capabilities. While they will not be able to operate with the same freedom in global markets, and there will be other large challenges in translating Chinese experience to other markets – these tech players will be able to compete very effectively with incumbent global companies. Chinese companies also continue to raise capital from US stock exchanges with The Economist reporting Chinese listings have raised close to USD 17 billion since January 2020.

The Education sector is currently facing immense challenges with enabling a remote learning environment and ensuring the safety of staff, employees, and students. This is on top of the usual challenges of resource optimisation, student retention, student recruitment, and so on. Moreover, today’s students are millennials and post-millennials, who are digital natives – pushing educational institutions to adopt technology to attract the right cohort and provide an education that equips the students for the workplace of the future. The industry is being driven to transform, to keep up with student expectations on delivery, access to the resource, and how they choose to communicate with their educators and peers.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Dr Alea Fairchild says, “Education administration budgets are not increasing, but the pressure for quick response and more personalised interaction for students, means that administrators need to focus on interaction as the core competency. This requires institutions to automate as much of the volume back-office activity as feasible. The challenge is that individualised course structures mean more complex billing configurations.”
Dr Fairchild, who is active in international education in Belgium, says, “Individual study paths, including Erasmus exchanges, create a need for an audit trail on transfers, exemptions and completions.”
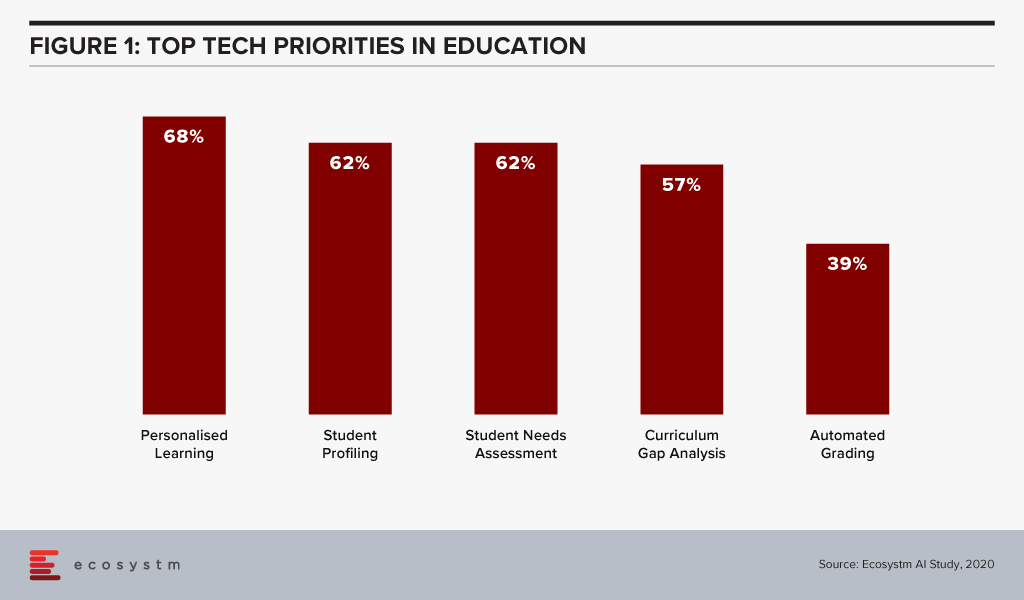
Ecosystm research finds that educational institutions are focused on adopting emerging technologies mainly to improve student services (Figure 1). The processes are being automated to reduce risks, errors and turnaround times for results and application processing, while also removing repetitive tasks so administration can focus on more value-add student-facing activities.
University of Staffordshire Embraces Digital Transformation
The University of Staffordshire is a “connected university” with an emphasis on industry connections and graduate employability. At the heart of Stoke-on-Trent and a regional hub for healthcare education, the university has six schools as well as a well-known degree in computer games design.
The UK-based University has over the years built a reputation for being keen on embracing digital as a way of better management, offering better student services, and serving the larger community. In 2018, Staffordshire University announced plans to build a multi-million-pound apprenticeship hub at its Stoke-on-Trent campus supported by tech giants including Microsoft to equip students with digital skills and to deliver more than 6,500 new apprenticeships over the next decade.
Last year, the University implemented a digital assistant, called Beacon, hosted on Microsoft Azure Cloud that provides support to their students on their learning and on-campus activities, including monitoring their emotional well-being and providing recommendations on groups and societies that they might be interested in. Beacon aims to ease the life of a university student, acting as a digital coach, and to minimise drop-outs due to stress and uncertainty.
Like its peer organisations, in the wake of the pandemic, the university was able to implement a blended learning program – offering courses through digital and remote learning systems from this semester for the entire 2020-21 session.
Focusing on Transformation through Automation
The University of Staffordshire, recently implemented robotic process automation (RPA) as part of its digital transformation plan. Talking about the role of RPA in Education, Dr Fairchild says, “This is a recent trend in higher education, with other new initiatives seen at the University of Auckland and University of Melbourne. RPA as a tool is used in Education to achieve the service levels required to meet both students’ and potential students’ expectations. This includes downloading student applications, processing language waiver requests, and entering academic results. These are all rule-based, high volume applications where automation increases speed and reduces errors.”
The University is using Blue Prism Cloud to access the RPA software and has plans for a automation-led digital transformation roadmap. Dr Fairchild says, “Blue Prism is based on Java and uses a Top-Down approach. It offers a visual designer with no recorders, scripts, or any intervention. Blue Prism is based on process diagrams that utilise core programming concepts and create the operational process flows to analyse, modify and scale business capability.”
The Staffordshire Digital team initially implemented RPA in the Finance department, as it involves a lot of administrative and back-office operations such as management of finance, records, tuition fees details and more. The University’s emphasis is to free up personnel and make them focus on more productive areas. This is beneficial for both the administrative staff’s feeling of personal contribution as well as student service satisfaction levels. “Using RPA gives the opportunity to universities to revisit, redesign, and improve their existing processes in line with expectations from digital native students. For prospective students, the next wave of RPA integration is intelligent machine learning algorithms to help route emails and integrate chatbots to address questions on course selection,” says Dr Fairchild.

Your CEO and Board are asking you to cut costs and do more with the IT budget.
This is the usual refrain you get used to as a Chief Digital or Information Officer. COVID-19 has increased the need for cost savings, without compromising your organisation’s mission. In Ecosystm’s on-going research, Digital Priorities in the New Normal – a COVID-19 Study, there are several common themes that emerge for retailers.

The impact of the cost-cutting measures that organisations are implementing, on CDOs and CIOs has been discussed in my report Managing Costs in the New Normal, where I provide guidance on how to address the necessary cuts.
Super Retail Group (SRG) recently presented at SalesForce Live on their success in using AI to improve their customer engagement – linking digital customer engagement and re-calibration of AI models. I want to highlight a couple of aspects of SRG’s experience for those retailers addressing these themes.
Increasing Customer Engagement
In a well-run online presence, retailers acquire a significant amount of data about their customers’ online behaviour. Data such as customer’s purchase history as well as how they traverse the site, how long they remain on the site and how they leave – often without purchasing. The challenge is how you can collect and use this data to improve the customer experience (CX) and increase sales in our new normal.
SRG, trading under banners such as Super Cheap Auto, BCF and Rebel across Australasia, has adopted a Salesforce tool called Einstein to address this challenge. SRG is using this AI engine to present product recommendations in several contexts across a customer’s online journey.
The impact of COVID-19 means overall sales across the group has declined. At the same time, online sales have grown to be generating almost 20% of the overall sales. Within these online sales, the AI recommendation engine has directly influenced 1 in 5 customer purchases.
SRG has developed a significant base of customer data since they introduced omnichannel and club offers; and are now seeing the return from this investment. Recommendation engines operate best when they have quality data in volume – and the proportion of and growth in, online customers using these recommendations is a guide to the quality of the platform.
Coping with Increasing Online Demands
Ecosystm research finds that over 56% of retailers are increasing their use of digital technologies for CX and will continue to invest after the immediate crisis. As always, getting the right value from this increased expenditure will be critical to a retailer’s price competitiveness and profitability.
With online sales growing dramatically, SRG’s online share of sales has more than doubled over April and May, the potential return from an engaging online CX has increased significantly. In turn, this has increased the importance of the online CX to a retailer’s competitive positioning and market share.
Tech leaders will be expected to provide direction on how to achieve this improvement, with AI engines offering an increasingly important tool in increasing the speed of response to changing customer behaviours.
With their mapping of customer journeys, SRG has been able to target specific stages in the journey for the use of the AI recommendation engine. Their focus on increasing the size and value of a customer’s basket provides the explicit measure of success. And SRG’s customers are showing their enthusiasm for these recommendations. The share of online sales influenced by the AI engine grew by over 600% in the past 12 months.
Customer expectations are continually being redefined by their experiences across the online environment, not just by retailers. In our new normal, with online becoming significantly important, retailers need to be consistently improving their offer to remain competitive.
Our study results shows that retailers are taking this step and will need to pay careful attention to their cost base and profitability while making these changes. SRG’s success with the AI engine shows that this is possible.
Lessons to Learn
COVID-19 has changed customer behaviour significantly, and tech leaders are identifying new tools and processes to improve their CX in line with these changes. SRG has continued its customer-focused omnichannel approach by adopting the Salesforce Einstein AI engine. By using one of their key sales metrics – size and value of basket – they have been able to assess the contribution of this tool.
There are some clear lessons for other retailers from their experience:
- Be very clear on why you are introducing the new tool – how you are going to achieve value.
- Understand the foundation that you need, to introduce new technology. You will find being successful using AI without quality data in volume will be difficult.
- Experiment and learn quickly from experience gained. In this cost-constrained world, don’t over-commit to a new approach without evidence.
- Use products and services that have a low cost of entry and a variable cost model. Cloud services generally provide this cost model.
Our research, along with press release such as SRG’s, show that retail leaders are continuously improving their customer engagement. As a tech leader, you need to be aware that customers will vote with their clicks, for retailers that are delivering.
And getting those non-essential costs out has never been more critical.

We continue to receive responses from the tech buyer community on the impact of COVID-19 on Digital Transformation initiatives, and the early business and technology measures that were implemented to combat the crisis. As the months go by, it is becoming apparent that organisations have implemented the early measures and are now looking ahead to their journey to recovery.
IT Teams realised that even if they had the right technology solutions, they were unprepared for the scale or capacity to extend these technology offerings to handle the sudden and enormous changes required to manage the crisis. Their cloud business applications, cybersecurity and collaboration solutions were simply not sufficient to meet the needs of the remote workforce. As organisations become more conscious of business continuity planning (BCP) for future eventualities, they will boost their technology capabilities, over the next 12 months.
Another area the study aims to explore is how optimistic is the business outlook, when it comes to expecting a return to normalcy. Only 3% of organisations are expecting a New Normal that is very different from where things were at the beginning of the year. About a third of organisations are expecting a return to normalcy by the end of the year, while the majority expect to recover by the middle of 2021. Also, some industries are more optimistic of a recovery than others. As an example, 35% of healthcare organisations expect a return to normalcy by the end of the year. This is a positive indicator, given that the industry has been in the forefront of the crisis, for nearly 6 months now.
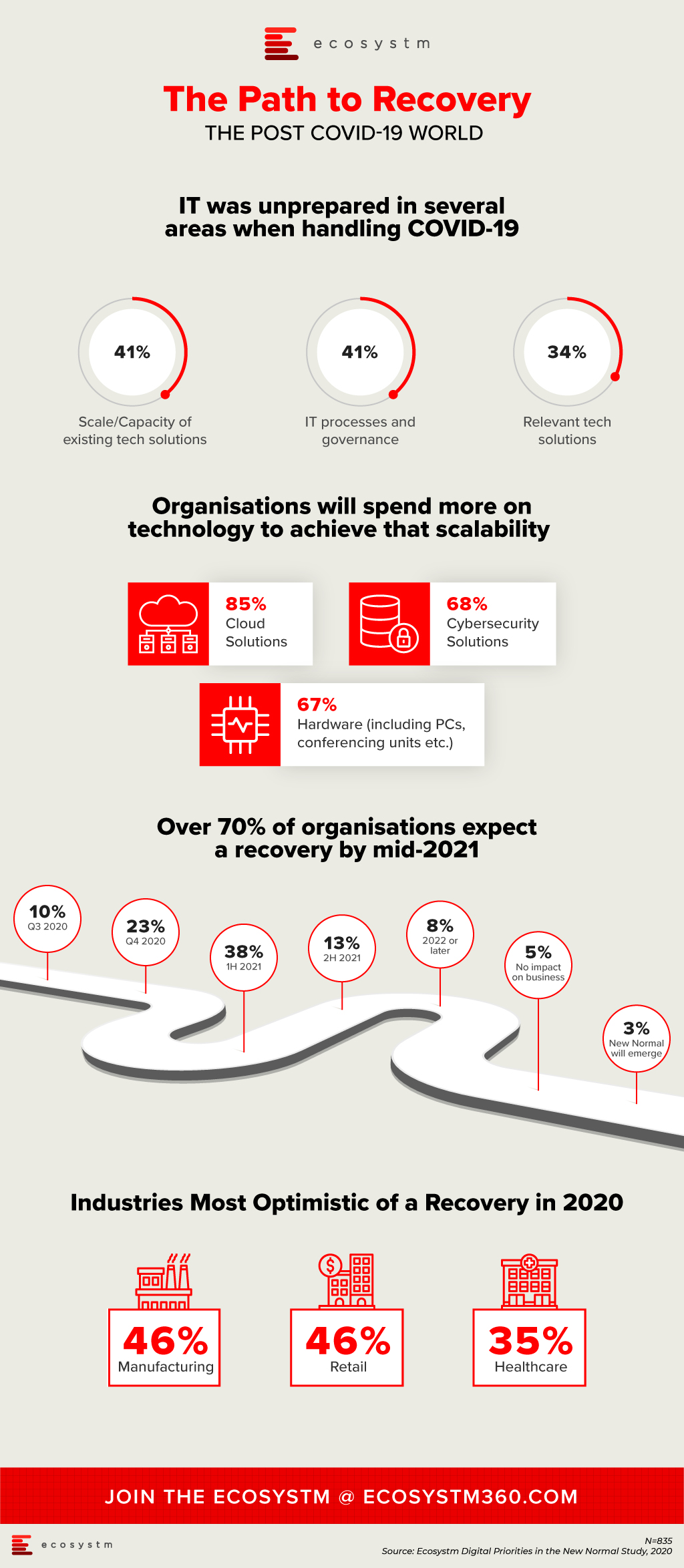
More insights on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and technology areas that will see continued investments, as organisations get into the recovery phase, can be found in the Digital Priorities in the New Normal Study.
Global supply chains were impacted early and badly by the COVID-19 pandemic. The fact that the pandemic started in China – the leader in the Manufacturing industry – meant that many enterprises globally had to re-evaluate their supply chain and logistics. This was compounded by the impact on demand – for some sectors the demand went down significantly, while in others, especially for items required to fight the crisis, there was an unexpected spike in demand. There was also the need for many manufacturers and retailers to shift to eCommerce, to directly access the market and sustain their businesses. These sudden shifts that were required of the industry, opened up the need for a global supply chain that is more integrated, agile and responsive.
Last week, global heavyweights with a stake in the global supply chain, joined a consortium to work on creating that agility. This includes PepsiCo, BMW, Shopify, DHL, and the United States Postal Service and some emerging tech companies. The alliance will actively work on solutions to embed automation and digitalisation in the logistics and supply chain systems. While this consortium was formed last year, recent events have accelerated the need to fix a global problem.
Co-Creation and Innovation
LINK is a collaborative ecosystem, co-founded by Innovation Endeavors and Sidewalk Infrastructure Partners (SIP) to bring together emerging tech start-ups, institutions and global organisations to innovate and make supply chains resilient. The tech start-ups involved include the likes of Fabric, that has large automated micro-fulfillment centres for faster deliveries, and Third Wave Automation, that has developed automated forklifts with enhanced safety measures.
LINK aims to transform global supply chains, with the use of technologies such as automation, IoT, AI, and Robotics. The solutions developed by the start-ups will be tested in real-life situations, often in large organisations with complex operations. On the other hand, the start-ups will have access to the internal systems of these large organisations to understand the data and their organisational needs.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Kaushik Ghatak says, “COVID-19 has brought the need for supply chain agility and resilience to a completely new level of criticality. Companies in the ‘New Normal’ will need higher levels of nimbleness and flexibility to be able to recover from this crisis quickly and sustain in an increasing disruptive world. Increased ability to sense and respond to disruptions will be key to success. It will require better visibility of their entire supply chain, increasing efficiencies, building necessary redundancies (in form of inventory and capacity) where they are required the most – redundancy comes at a cost – and being flexible and innovative to cater to the rapid market and supply-side changes. Rapid digitalisation to build such capabilities will be a key to success.”
“Managing such rapid changes is usually a struggle for organisations with large and complex supply chains, because of the years of past practices, systems and culture. For them Innovation is a must, but the path to innovation is difficult. The LINK collaboration model is the right step towards addressing that challenge. Collaborating with start-ups can infuse new ideas, more innovative ways of solving a problem and rapid testing of use cases in the areas of IoT, AI and automation.”
Involving Start-ups for Innovation
This initiative is a great example of how larger enterprises are looking to leverage innovations by the start-up community. The Financial Services industry has been an early beneficiary, when it stopped competing with Fintech organisations, partnering with them instead. Other industries have started to recognise the benefits of fast pivots and the role start-ups can play.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Ravi Bhogaraju says, “Bringing together companies that have complementary and unique capabilities to solve industry issues is a great way to speed up experimentation and innovation.”
However, he recognises that forming alliances such as this, comes with its own set of challenges. “One of the key things to recognise in such a construct is that the team members from different possessions bring with them their unique belief systems, organisational and country cultural constructs. Expectations on how things should work, can become quite tricky to navigate. The talent and expertise in such an environment need to be facilitated be able to deliver high quality outcomes.”
Talking about how these constructs can work successfully, delivering what started out to deliver, Bhogaraju says, “An agile team setup can help tremendously as it uses two key principles – People and Interactions over processes; as well as Working models over documentation.”
“A clear expectation setting through contracting at the beginning of the project cycle can help establish the ways of working and rules of engagement. Increased regular feedback and problem solving should continuously fine tune the ways of working. This way teams can get through the norming process at pace and scale and eventually focus on outcomes, rather than fumble over each other and/or have ego flareups.”
“The key is to get to creative problem-solving working cohesively – the intent being to challenge the status quo – stepping outside the box and using all capabilities within the team. Blending the subcultures together using agile way of working and principles, can be a fantastic way to make that happen – failing which you have the challenge of trying to somehow bring together different work products, people and preferences.”











