Organisations are uncertain about how 2023 will shape up for them, amidst concerns about recessions, supply chain uncertainties, continued geopolitical volatility, energy crisis, and labour disruptions. At the same time, they have to continue to evolve their products and services, the customer experiences they deliver, and overall brand image.
If you are a tech leader, your first instinct would be to cut down on technology spend to align with your organisation’s cost optimisation strategy. And that is where you would make the first mistake – this is the time to invest in the right technologies to help your organisation face the uncertainties with agility.
Here are 5 things that you should keep in mind when shaping your organisation’s tech landscape in 2023.
- Focus on the shortest time to value. Choose a few smart digital improvements that are aligned with the strategic goals of the business and deliver value quickly.
- Drive better corporate outcomes through Sustainability programs. The transition to smart and sustainable digital assets and infrastructure should be a top priority for today’s technology leaders.
- Build resilience by improving value chain visibility. Digital technologies will continue to play an important role in providing visibility and insights across the value chains for risk management and resilience.
- Treat location data as a feedstock for AI & Automation. With the increasing importance of automation, especially to contemporary service models like digital twins and metaverse, incorporating spatial and location data into your strategy is essential for staying ahead of the competition and driving meaningful business outcomes.
- Find allies against cyber adversaries. Join the cybersecurity communities that exist in your geography and industry. Participate openly as possible so that lessons are shared quickly and widely. Don’t try to defeat the flood on your own.
Read on to find more.
Download Making the Right Tech Decisions for Better Value as a PDF

With organisations facing an infrastructure, application, and end-point sprawl, the attack surface continues to grow; as do the number of malicious attacks. Cyber breaches are also becoming exceedingly real for consumers, as they see breaches and leaks in brands and services they interact with regularly. 2023 will see CISOs take charge of their cyber environment – going beyond a checklist.
Here are the top 5 trends for Cybersecurity & Compliance for 2023 according to Ecosystm analysts Alan Hesketh, Alea Fairchild, Andrew Milroy, and Sash Mukherjee.
- An Escalating Cybercrime Flood Will Drive Proactive Protection
- Incident Detection and Response Will Be the Main Focus
- Organisations Will Choose Visibility Over More Cyber Tools
- Regulations Will Increase the Risk of Collecting and Storing Data
- Cyber Risk Will Include a Focus on Enterprise Operational Resilience
Read on for more details.
Download Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Trends for Cybersecurity & Compliance in 2023 as a PDF

Southeast Asia has evolved into an innovation hub with Singapore at the centre. The entrepreneurial and startup ecosystem has grown significantly across the region – for example, Indonesia now has the 5th largest number of startups in the world.
Organisations in the region are demonstrating a strong desire for tech-led innovation, innovation in experience delivery, and in evolving their business models to bring innovative products and services to market.
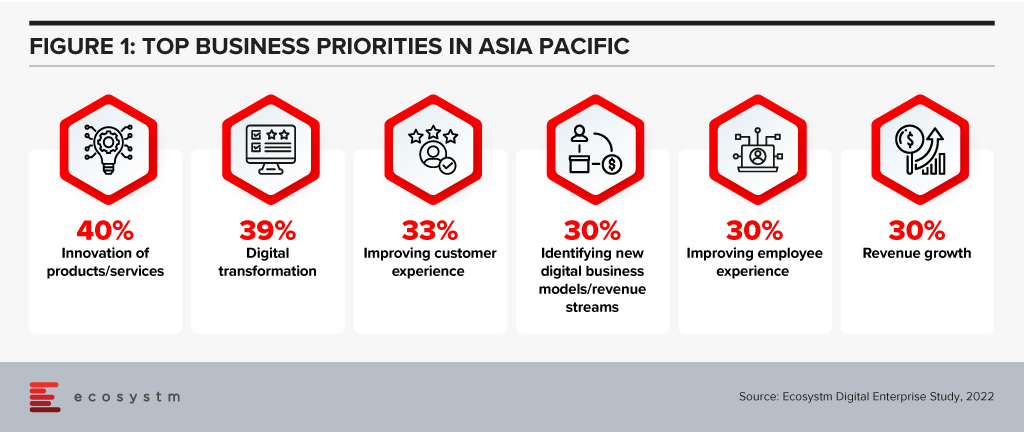
Here are 5 insights on the patterns of technology adoption in Southeast Asia, based on the findings of the Ecosystm Digital Enterprise Study, 2022.
- Data and AI investments are closely linked to business outcomes. There is a clear alignment between technology and business.
- Technology teams want better control of their infrastructure. Technology modernisation also focuses on data centre consolidation and cloud strategy
- Organisations are opting for a hybrid multicloud approach. They are not necessarily doing away with a ‘cloud first’ approach – but they have become more agnostic to where data is hosted.
- Cybersecurity underpins tech investments. Many organisations in the region do not have the maturity to handle the evolving threat landscape – and they are aware of it.
- Sustainability is an emerging focus area. While more effort needs to go in to formalise these initiatives, organisations are responding to market drivers.
More insights into the Southeast Asia tech market below.
Click here to download The Future of the Digital Enterprise – Southeast Asia as a PDF

Life never gets any easier for the digital and information technology teams in organisations. The range and reach of the different technologies continue to open new opportunities for organisations that have the foresight and strategy to chase them. Improving offers for existing customers and reaching new segments depend on the organisation’s ability to innovate.
But the complexity of the digital ecosystem means this ability to innovate will be heavily constrained, causing improvements to take longer and cost more in many cases. Addressing the top business priorities expressed in the Ecosystm Digital Enterprise Study, 2022, will need tech teams to look to simplify as well as add features.
Complexity is Not Just an IT Issue
Many parts of an organisation have been making decisions on implementing new digital capabilities, particularly those involved in remote working. Frequently, the IT organisation has not been involved in the selection, implementation and use of these new facilities.
The number of start-up organisations delivering SaaS has continued to explode. A particular area has been the expansion of co-creation tools used by teams to deliver outcomes. In many cases, these have been introduced by enthusiastic users looking to improve their immediate working environment without the understanding of single-sign-on requirements, security and privacy of information or the importance of backup and business continuity planning.
SaaS tools such as Notion, monday.com and ClickUp (amongst many, many others), are being used to coordinate and manage teams across organisations of all sizes. While these are all cloud services, the support and maintenance of them ultimately will fall to the IT organisation. And they won’t be integrated at all with the tools the IT organisation uses to manage and improve user experience.
Every new component adds to the complexity of the tech environment – but with that complexity comes increased dependencies between components, which slows an organisation’s ability to adapt and evolve. This means each change needs more work to deliver, costs increase, and it takes longer to deliver value.
And this increasing complexity causes further problems with cybersecurity. Without regular attention, legacy systems will increase the attack surface of organisations, making it easier to compromise an organisation’s environment. At a recent executive forum with CISOs, attendees rated the risks caused by their legacy systems as their most significant concern.
An organisation’s leadership needs to both simplify and advance their organisation’s digital capabilities to remain competitive. This balance should not be left to the IT organisation to achieve as they will not be able to deliver both without wider support and recognition of the problems.
Discriminate on Differentiating Skills
One thing we can be sure of is that we won’t be able to employ all the skills we need for our future capabilities. We are not training enough people in the skills that we need now and for the future, and the range of technologies continues to expand, increasing the number of skills that we will need to keep an organisation running.
Most organisations are not removing or replacing ageing systems, preferring to keep them running at an apparently low cost. Often these legacy systems are fully depreciated, have low maintenance costs and have few changes made to them, as other areas of the organisation offer better investment options. But this also means that the old skills remain necessary.
So organisational leaders are adding new skills requirements on top of old, with the older skills being less attractive with so many new languages, frameworks and databases becoming available. Wikipedia has a very long list of languages that have been developed over the years. Some from the 1950s, like FORTRAN and LISP, continue to be used today.
Organisations will not be in a position to employ all the skills it needs to implement, develop and maintain for its digital infrastructure and applications. The choice is going to be which skills are most important to an organisation. This selection needs to be very discriminating and focus on differentiating skills – those that really make a difference within your ecosystem, particularly for your customers and employees.
Organisations will need a great partner who can deliver generic skills and more services. They will have better economies of scale and skill and will free management to attend to those things most important to customers and employees.
Hybrid Cloud has an Edge
Almost every organisation has a hybrid cloud environment. This is not a projection – it has already happened. And most organisations are not well equipped to deal with this situation.
Organisations may not be aware that they are using multiple public clouds. Many of the niche SaaS applications used by an organisation will use Microsoft Azure, AWS or GCP, so it is highly likely organisations are already using multiple public clouds. Not to mention the offerings from vendors such as Oracle, Salesforce, SAP and IBM. IT teams need to be able to monitor, manage and maintain this complex set of environments. But we are only in the early stages of integrating these different services and systems.
But there is a third leg to this digital infrastructure stool that is becoming increasingly important – what we call “the Edge” – where applications are deployed as part of the sensors that collect data in different environments. This includes applications such as pattern recognition systems embedded in cameras so that network and server delays cannot affect the performance of the edge systems. We can see this happening even in our homes. Google supports their Nest domestic products, while Alexa uses AWS. Not to mention Amazon’s Ring home security products.
With the sheer number of these edge devices that already exist, the complexity it adds to the hybrid environment is huge. And we expect IT organisations to be able to support and manage these.
Simplify, Specialise, Scale
The lessons for IT organisations are threefold:
- Simplify as much as possible while you are implementing new features and facilities. Retiring legacy infrastructure elements should be consistently included in the IT Team objectives. This should be done as part of implementing new capabilities in areas that are related to the legacy.
- Specialise in the skills that are the differentiators for your organisation with its customers and employees. Find great partners who can provide the more generic skills and services to take this load off your team.
- Scale your hybrid management environment so that you can automate as much of the running of your infrastructure as possible. You need to make your IT Team as productive as possible, and they will need power tools.
For IT vendors, the lessons are similar.
- Simplify customer offers as much as possible so that integration with your offering is fast and frugal. Work with them to reduce and retire as much of their legacy as possible as you implement your services. Duplication of even part of your offer will complicate your delivery of high-quality services.
- Understand where your customers have chosen to specialise and look to complement their skills. And consistently demonstrate that you are the best in delivering these generic capabilities.
- Scale your integration capabilities so that your customers can operate through that mythical single pane of glass. They will be struggling with the complexities of the hybrid infrastructure that include multiple cloud vendors, on-premises equipment, and edge services.

–
For the last two years organisations have been forced to invest on digital services for their customers and giving their employees access to the right technologies to allow them to work from home – or from anywhere they choose to. Organisations find that they have to continue to evolve – and are now looking to build a ‘Digital Workplace’ that caters to the hybrid workplace.
As organisations in ASEAN define the work model that works for their business operations, work culture and organisational goals, there are a few areas that they must focus on.
Here are 5 insights from the Ecosystm Voice of the Employee Study that will help you shape your Digital Workplace.
- Evolve the physical workplace. 72% of knowledge workers in ASEAN will work both remotely and from the office.
- Build a true hybrid work culture. As organisations form their Digital Workplace strategy, they will have to ensure that the workplace is as comfortable as home offices!
- Focus on employee wellbeing. Only 25% of organisations in ASEAN have made changes to their HR policies in the last two years.
- Invest in the right technologies. To build that resilient hybrid workplace, organisations will first have to conduct a gap analysis and consolidation of their tech investments over the last two years.
- Continue to monitor employee behaviour patterns. As organisations work towards a ‘Return to Work’ policy, they will see significant changes in employee usage behaviour patterns. If the right cyber practices are not in place, this could leave organisations vulnerable again.
Read on for more insights

One of the main questions that I have faced over the past week, since I wrote the Ecosystm Insight – Welcome to the Great Bounce Forward – is “How is this different to the “New Normal”? Many have commented that the concept of the Great Bounce Forward is more descriptive and more positive than the term “New Normal” – but I believe they are different, and require different strategies and mindsets.
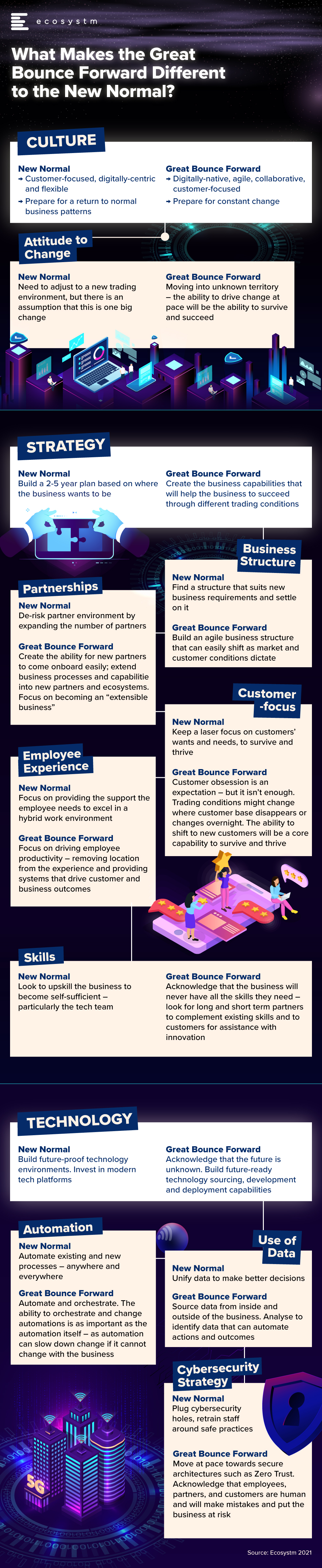
This is a brief summary of some of the major differences between the New Normal and the Great Bounce Forward. I look forward with excitement and some trepidation towards this future. One where business success will be dictated not only by our customer obsession, but also the ability of our business to pivot, shift, change and adapt.
I can’t tell you what will happen in the future – a green revolution? Another pandemic? A major war? A global recession? Market hypergrowth? All the people living life in peace? Imagine that…
What I can tell you is what your organisation needs to do to be able to meet all of these challenges head-on and set yourself up for success. And to me, that won’t look like the new normal. There is nothing normal about these business capabilities at all.

In this edition of Ecosystm RNx – an objective vendor ranking based on in-depth, quantified ratings from technology decision-makers on the Ecosystm platform – we rank the Top 10 Global Cybersecurity Vendors.
If you are an End User, you are having to re-evaluate your Cybersecurity risks and measures as both solution capabilities and the threat landscape become more complex. In a fragmented market, it is difficult to select the right Cybersecurity partner to safeguard your organisation. This vendor ranking will help you evaluate your buying decisions based on key evaluation ratings by your peers across a number of key metrics and benchmarks, including customer experience.
If you are Cybersecurity Vendor, you are aware that end users are looking more for Cybersecurity services than solutions – this is an opportunity to understand how your customers rate you on capabilities and their overall customer experience.

In this Insight, our guest author Anupam Verma talks about how the Global Capability Centres (GCCs) in India are poised to become Global Transformation Centres. “In the post-COVID world, industry boundaries are blurring, and business models are being transformed for the digital age. While traditional functions of GCCs will continue to be providing efficiencies, GCCs will be ‘Digital Transformation Centres’ for global businesses.”

India has a lot to offer to the world of technology and transformation. Attracted by the talent pool, enabling policies, digital infrastructure, and competitive cost structure, MNCs have long embraced India as a preferred destination for Global Capability Centres (GCCs). It has been reported that India has more than 1,700 GCCs with an estimated global market share of over 50%.
GCCs employ around 1 million Indian professionals and has an immense impact on the economy, contributing an estimated USD 30 billion. US MNCs have the largest presence in the market and the dominating industries are BSFI, Engineering & Manufacturing, Tech & Consulting.
GCC capabilities have always been evolving
The journey began with MNCs setting up captives for cost optimisation & operational excellence. GCCs started handling operations (such as back-office and business support functions), IT support (such as app development and maintenance, remote IT infrastructure, and help desk) and customer service contact centres for the parent organisation.
In the second phase, MNCs started leveraging GCCs as centers of excellence (CoE). The focus then was product innovation, Engineering Design & R&D. BFSI and Professional Services firms started expanding the scope to cover research, underwriting, and consulting etc. Some global MNCs that have large GCCs in India are Apple, Microsoft, Google, Nissan, Ford, Qualcomm, Cisco, Wells Fargo, Bank of America, Barclays, Standard Chartered, and KPMG.
In the post-COVID world, industry boundaries are blurring, and business models are being transformed for the digital age. While traditional functions of GCCs will continue to be providing efficiencies, GCCs will be “Digital Transformation Centres” for global businesses.
The New Age GCC in the post-COVID world
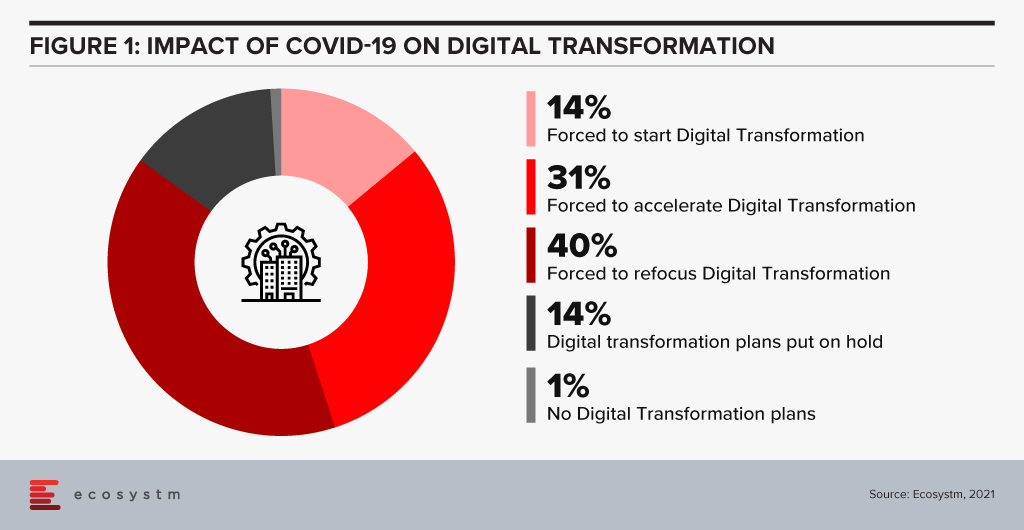
On one hand, the pandemic broke through cultural barriers that had prevented remote operations and work. The world became remote everything! On the other hand, it accelerated digital adoption in organisations. Businesses are re-imagining customer experiences and fast-tracking digital transformation enabled by technology (Figure 1). High digital adoption and rising customer expectations will also be a big catalyst for change.
In last few years, India has seen a surge in talent pool in emerging technologies such as data analytics, experience design, AI/ML, robotic process automation, IoT, cloud, blockchain and cybersecurity. GCCs in India will leverage this talent pool and play a pivotal role in enabling digital transformation at a global scale. GCCs will have direct and significant impacts on global business performance and top line growth creating long-term stakeholder value – and not be only about cost optimisation.
GCCs in India will also play an important role in digitisation and automation of existing processes, risk management and fraud prevention using data analytics and managing new risks like cybersecurity.
More and more MNCs in traditional businesses will add GCCs in India over the next decade and the existing 1,700 plus GCCs will grow in scale and scope focussing on innovation. Shift of supply chains to India will also be supported by Engineering R & D Centres. GCCs passed the pandemic test with flying colours when an exceptionally large workforce transitioned to the Work from Home model. In a matter of weeks, the resilience, continuity, and efficiency of GCCs returned to pre-pandemic levels with a distributed and remote workforce.
A Final Take
Having said that, I believe the growth spurt in GCCs in India will come from new-age businesses. Consumer-facing platforms (eCommerce marketplaces, Healthtechs, Edtechs, and Fintechs) are creating digital native businesses. As of June 2021, there are more than 700 unicorns trying to solve different problems using technology and data. Currently, very few unicorns have GCCs in India (notable names being Uber, Grab, Gojek). However, this segment will be one of the biggest growth drivers.
Currently, only 10% of the GCCs in India are from Asia Pacific organisations. Some of the prominent names being Hitachi, Rakuten, Panasonic, Samsung, LG, and Foxconn. Asian MNCs have an opportunity to move fast and stay relevant. This segment is also expected to grow disproportionately.
New age GCCs in India have the potential to be the crown jewel for global MNCs. For India, this has a huge potential for job creation and development of Smart City ecosystems. In this decade, growth of GCCs will be one of the core pillars of India’s journey to a USD 5 trillion economy.
The views and opinions mentioned in the article are personal.
Anupam Verma is part of the Senior Leadership team at ICICI Bank and his responsibilities have included leading the Bank’s strategy in South East Asia to play a significant role in capturing Investment, NRI remittance, and trade flows between SEA and India.

In March I published an analysis of Samsung DeX – which is a desktop environment which many businesses could benefit from deploying to specific teams, roles or employees. During my research, I found that one of the shortcomings is the lack of native support for dual screens. I know that many information workers in particular use dual-screen setups – and going back to a single screen feels highly unproductive!
Knowing this, a contact at Samsung pointed me to a company that has developed a dual-screen capability for a virtual desktop environment running on DeX – so I jumped at the opportunity to trial the environment in my own dual screen setup.
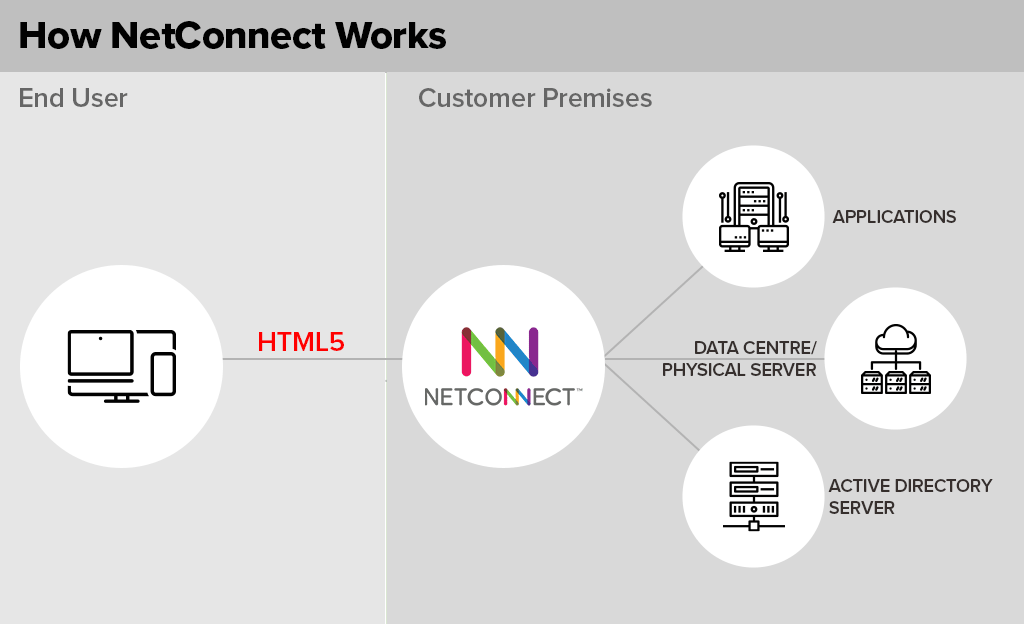
The product is called NetConnect – and is sold by VOIP. It is actually a Branch Of One style solution, which allows employees to access enterprise resources on any device. But one of its unique features is the ability to run a dual screen virtual desktop environment.
NetConnect’s Dual Screen Capabilities – An Analysis
DeX users that run the NetConnect app can extend the desktop to a second, internet connected monitor or screen. The key point here is “internet connected” – the screen is deployed across the internet – not across cables from the phone. This means any tablet, laptop or connected screen can be used as the second screen for the Windows virtual desktop running through NetConnect. In my particular demo environment, the software (both NetConnect and the Windows server) was running in a data centre in Singapore – but the company (VOIP) sells the solution to organisations to run in their own data centre environment.
The overall experience is seamless. The fact that one screen is running on a server in Singapore and being sent across the internet to my Samsung phone, and the other screen is running in Singapore and being sent across the internet to a completely different device is remarkable. The mouse moves across screens as if the desktop is running locally. While my demo environment was limited to web and a few desktop applications, I often found myself astonished that this entire environment was being driven by a smartphone (and a lot of clever technology behind the scenes!). Suddenly the limitations of only having a single screen for DeX disappeared – I now could run one application on my first screen and another on my second screen – and continue working, without the need to endlessly alt-tab between applications and screens.

There are some limitations – video streaming is not very smooth, and connected devices (cameras etc. for Zoom or Teams calls) are not recognised. These features are on the roadmap, but not available today. But the NetConnect solution really does open DeX up to a whole new community of users. Some of the VOIP employees I met at their office don’t have a laptop on their desk or a desktop underneath it – they are running their entire work environment from their Samsung phone!
And being a Branch of One solution, NetConnect also brings with it inherent security benefits – of not ever taking company data out of the data centre, reducing threats from viruses and malware that would normally run on the end-user computing device and others. It also improves the manageability of the desktop environment and makes it simple to deploy to users. Branch of One is about bringing all of the inherent benefits and capabilities that an office or branch would have and enabling a single user to get this power and security.
NetConnect is more than a dual screen solution – so working out which comes first is the interesting challenge. If your business is looking to run a solution like NetConnect, it is worth your while examining the opportunity to use DeX to extend full, dual screen desktop solutions to your employees. And if you are a business running DeX, NetConnect could open opportunities to extend DeX to more employees, roles or teams than originally planned.
Checkout Tim’s previous insight where he provides a detailed analysis on whether Samsung DeX is suitable for your employees. He bases his insights from using Samsung DeX as his primary desktop environment over the past 4 weeks.






















































